Safety and PE, Body Positions 2023, Range of Motion 2023
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Moving and positioning the body in ways that prevent injury to oneself and to others is called ____ .
body mechanic
What is the most common type of injury experienced by health care workers?
back injuries
Always bend at your ____ when lifting heavy objects.
knees
Which muscles are the strongest in your body?
Leg muscles
When carrying a heavy object, hold the object _____ your body to prevent injury.
close to
What should you do if a patient is too heavy for you to move alone?
ask a co-worker for help
Which of the following equipment may help a patient or healthcare worker lift correctly?
Walkers, Canes, Hydraulic lifts, and Wheelchairs
Which position is used for back treatments?
Prone
Which position is used for patients with cardiovascular or respiratory problems?
Fowler's
During a patient transfer from bed to wheelchair, where should the wheelchair be placed?
Beside the bed and against the wall or something stable to prevent movement
What piece of equipment is used to help lift a patient during a transfer?
Transfer/gait belt
What is one of the most important guidelines to providing a safe environment in a health care facility?
Know the surroundings, such as exits.
Health care workers should know ____.
The location of stairways, elevators, and exits, location of fire alarms and fire extinguishers and the meaning of emergency codes.
The study of promoting the safety of a person by adapting the environment and preventing injury is called _____.
ergonomic
The key to ergonomics is to create an environment that cares for a person's _____________________.
physical, mental, and emotional well-being
All health care workers are responsible for maintaining a _________ facility.
clean
How often should high traffic areas in a health care facility be cleaned?
Daily
Why should you knock and ask for permission before entering a patient's room?
It makes the patient feel comfortable and secure.
Always identify a patient by using the patient's name and ____.
Birth date
When should you explain a procedure to a patient?
Before you begin the procedure
When you observe a safety violation, you should report it to _______________.
your supervisor immediately
When should an event report be filed?
When an accident involves a patient, employee, or visitor
What type of attitude should a health care worker have when interviewing a victim of an accident?
Concerned and non-threatening
In what type of setting should a health care worker interview a victim of an accident?
In a private, confidential setting
A sickness that results from eating a food that is infected with bacteria called a ____ illness.
foodborne
In order to survive, bacteria need moisture, oxygen, and _____________ .
a warm temperature
Symptoms of foodborne illness resemble ____
flu
Foodborne illness can almost always be prevented by ____.
Handling, preparing, and storing foods properly
Perishable foods should not be left at room temperature for more than ____ hours.
2
Why should surfaces that touch food be sanitized?
to destroy microorganisms
Raw hamburger and cooked hamburgers cannot be _______________.
stored together
Patients should be placed in a _________________ position during mealtime.
Full fowler's or sitting
What should be offered to a patient between each bite of food?
A drink
Health care workers should encourage patients to _____________.
chew properly
How can you confine a fire to an area?
Close doors and windows
Which of the following acronyms can help you remember what steps to take if a fire should occur in your facility?
RACE
If a fire is blocking your escape path to the stairway, you should evacuate through the closest elevator.
False
During a fire emergency, health care workers must remember to
stay calm
A(n) _____________________ for fires should be posted in plain sight on every floor and in every wing of a facility.
evacuation plan
In an emergency situation, when should the secondary exit be used?
When the primary exit is blocked
Which is the most common type of fire extinguisher?
ABC
Where should you point the nozzle of a fire extinguisher when you are putting out a fire?
The base of the fire
Which of the following acronyms can help you remember how to operate a fire extinguisher?
PASS
What does MSDS stand for?
Material Safety Data Sheet
Why is it important to read the information on an MSDS before cleaning up a chemical spill?
To avoid injury to oneself and others, to learn proper precautions for handling the chemical and to prevent causing damage to the facility
How many times should you read a label before using a chemical solution?
3 times
What should you do if a chemical does not have a label?
do not use it
What is RACE?
Rescue>Alarm>Contain>Extinguish or Evacuate.
What is PASS?
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) does what?
enforces safety standards in the workplace to protect employees from injury and illness.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) does what?
The goal is to protect human health and the environment.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does what?
is responsible for protecting and advancing public health through medicine and food regulation.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) does what?
compile all health information from Health Departments in the city and states and make health decisions and fund research.
The National Institute of Health (NIH) does what?
conducts health research
What are the proper body mechanics tips for healthcare workers?
Bend knees, Push, not pull, Resist the twist, Get close to Pt, Stability for ability and Exhale during movement of the patient
Whom should an event/ incident reported for?
An accident involves a patient, employee, or visitor
What should a health care worker do immediately after a safety violation occurs?
Report it to the supervisor.
To evacuate patients who cannot walk during fires, you must ____________.
place the patient in a fire tower or equally fire-safe area.
Types of events/incidents that must be reported are ____________.
Accidents, thefts from a person on hospital property, errors of omission of patient treatment or errors in administration of patient treatment, including medication and exposure to blood and body fluids, as may be caused by a needle stick.
Electrical Safety includes?
Avoid using damaged power chords, avoid using any extension chords, avoid any electrical equipment while collecting blood and when available, try and use three-pronged plugs
Radiation Safety includes?
Time: exposed to the source, shielding: if anything is between you and the source of radiation and distance: how far person of the object is away from the source
What position is best for patients getting rectal medication?
Sim's
What position is best for patients getting an abdominal exam?
Supine
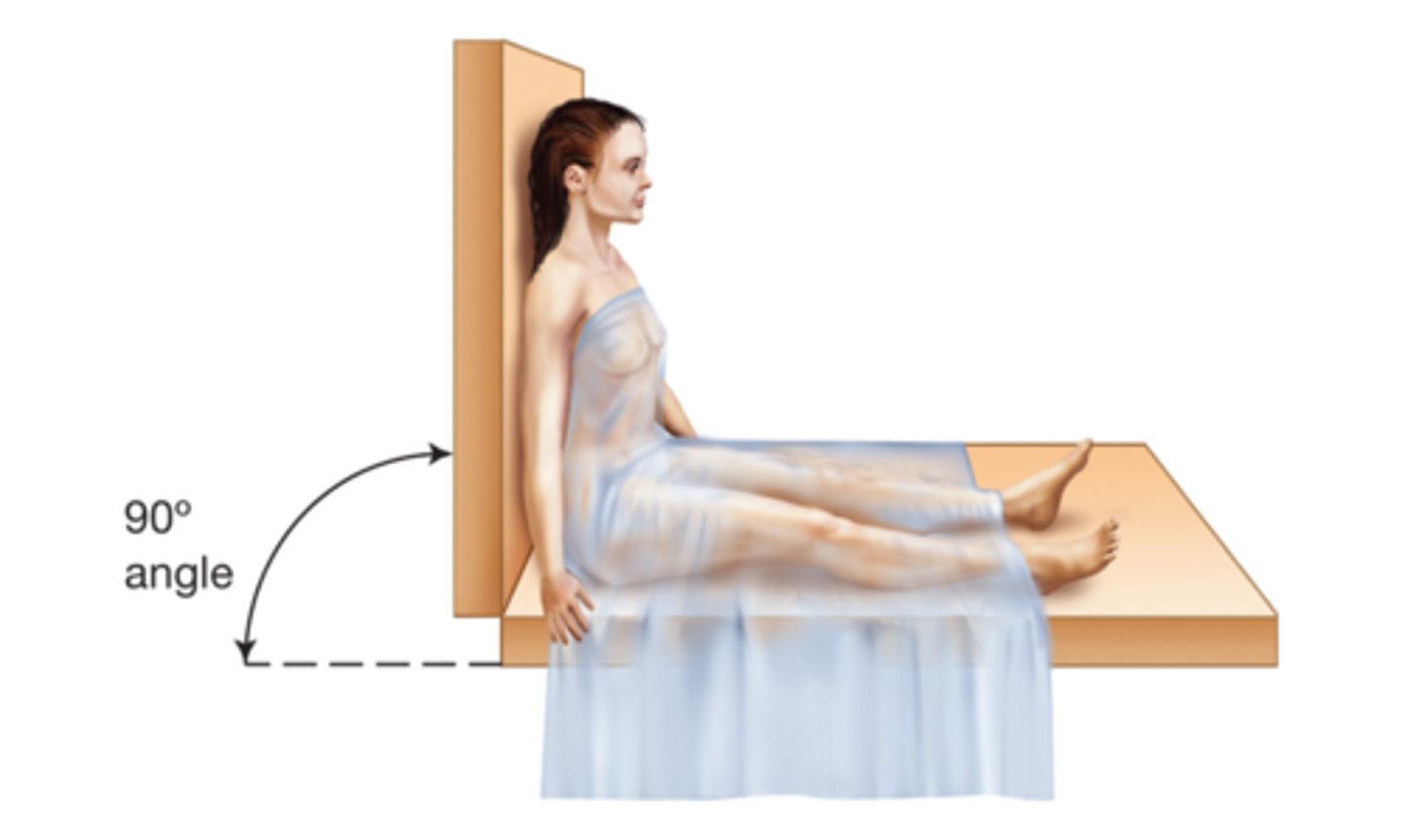
Fowler's Position
Raise the head of the bed to a 90-degree angle, the patient sitting up.
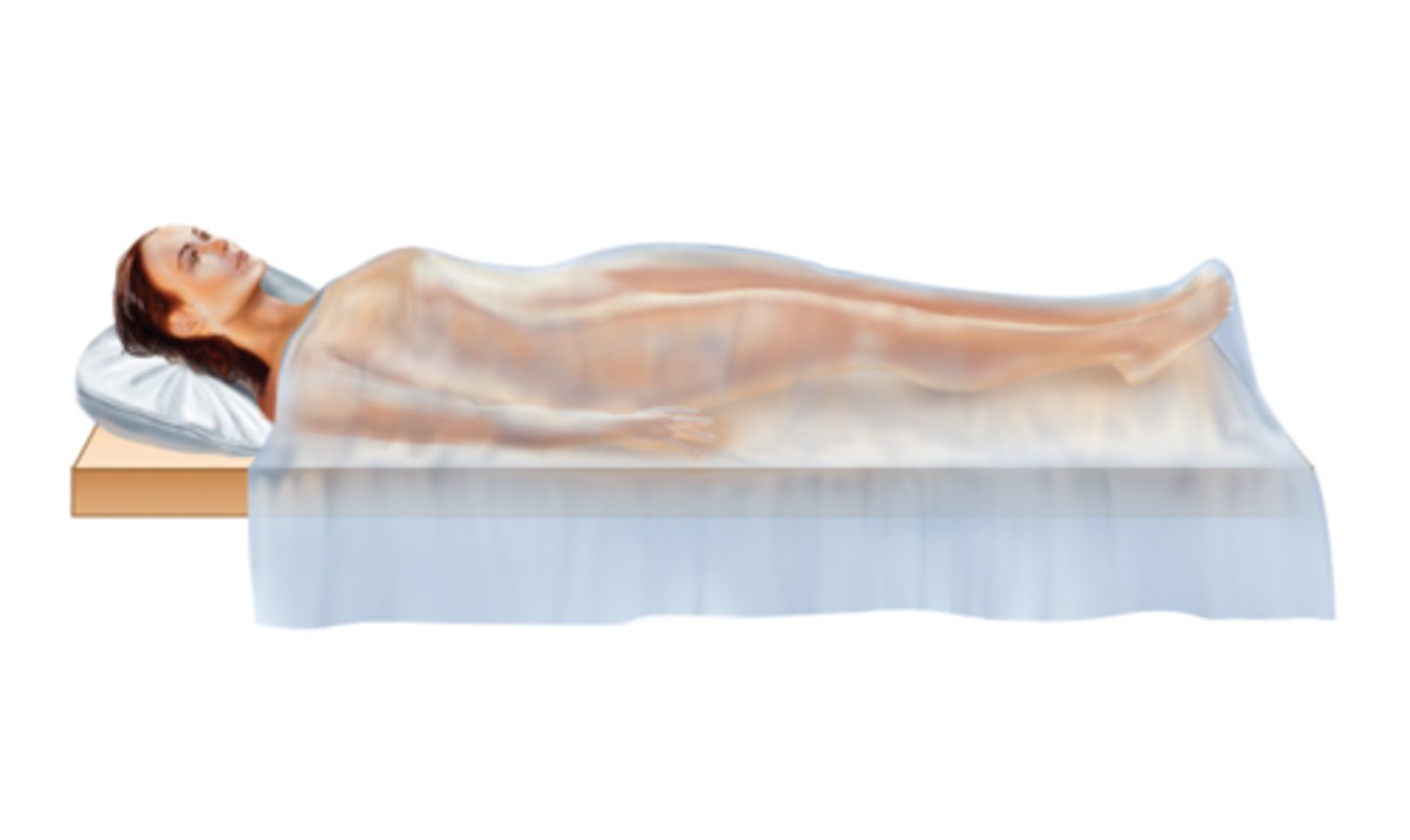
Supine or Horitzontal dorsal recumbent position
Lying flat on back with face upward and arms at the side
Sims' Position
Lying on the left side, right knee and thigh flexed well above the left leg, placing the body weight on the chest.
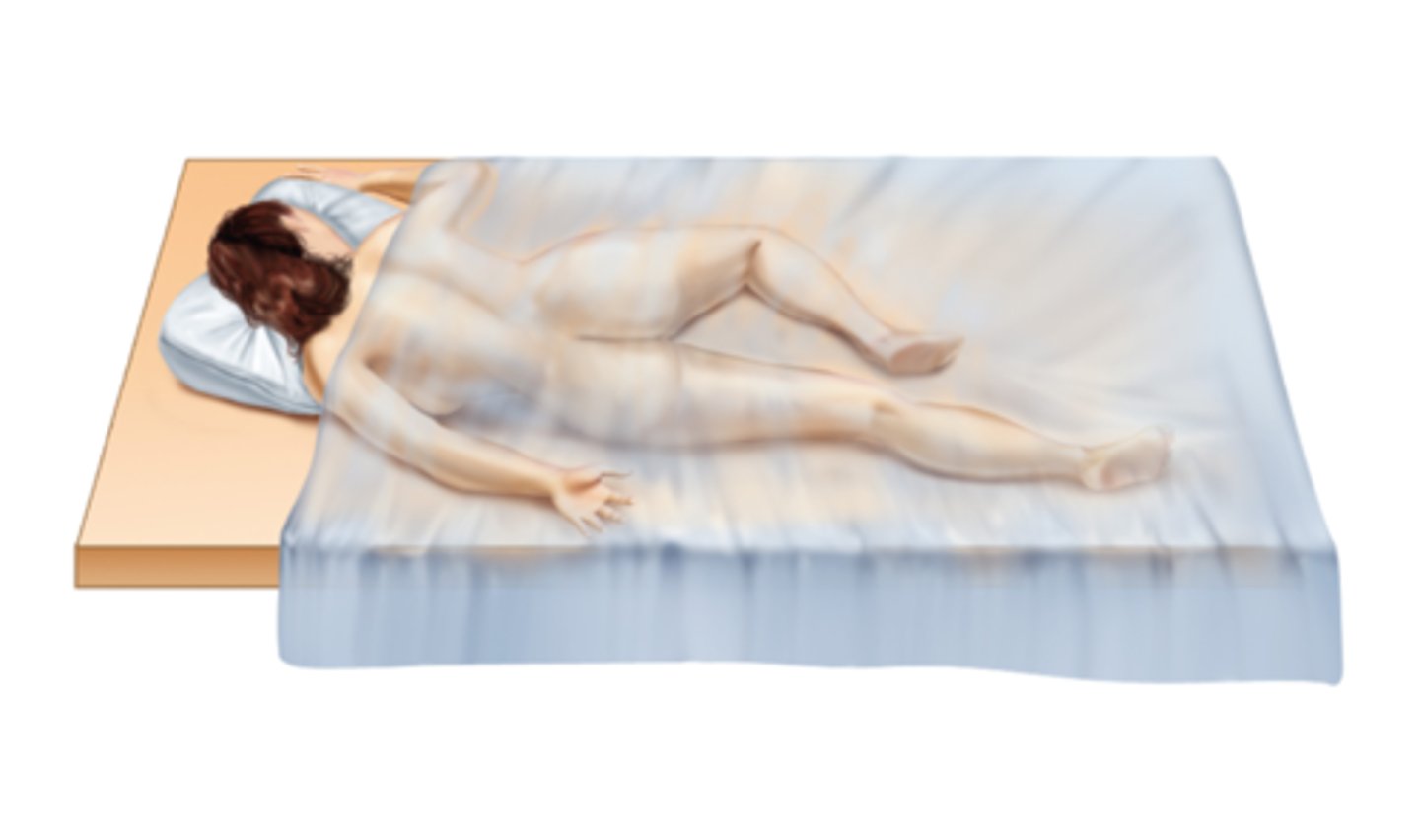

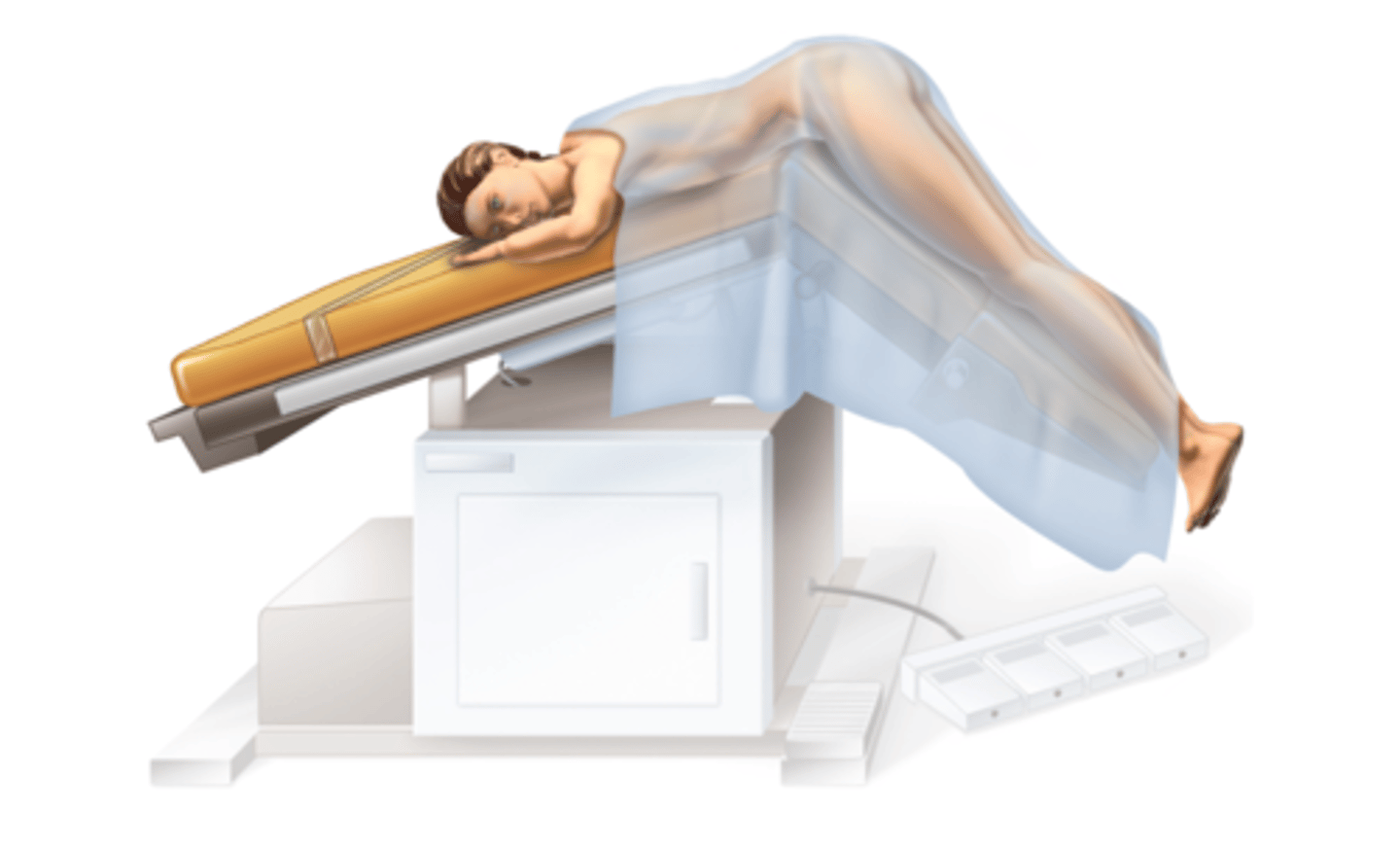
Proctologic Position
Similar to knee-chest but with a greater bend at the hips. Referred to as Jack-knife position.
Dorsal recumbent position
On back with lower extremities flexed and rotated outward
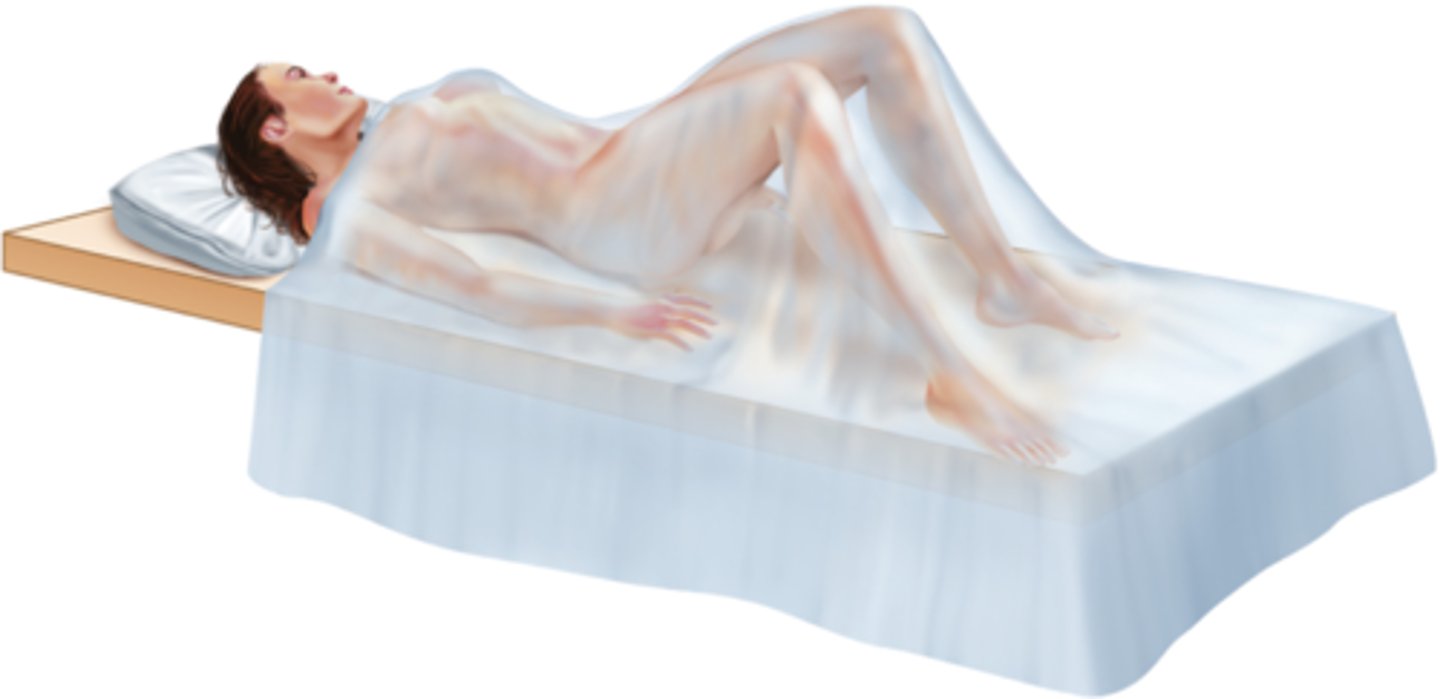

Semi-Fowler's Position
Same as Fowler's only head of the bed is partially elevated
Knee- Chest Position
On knees with hips bent, keeping the chest on the table
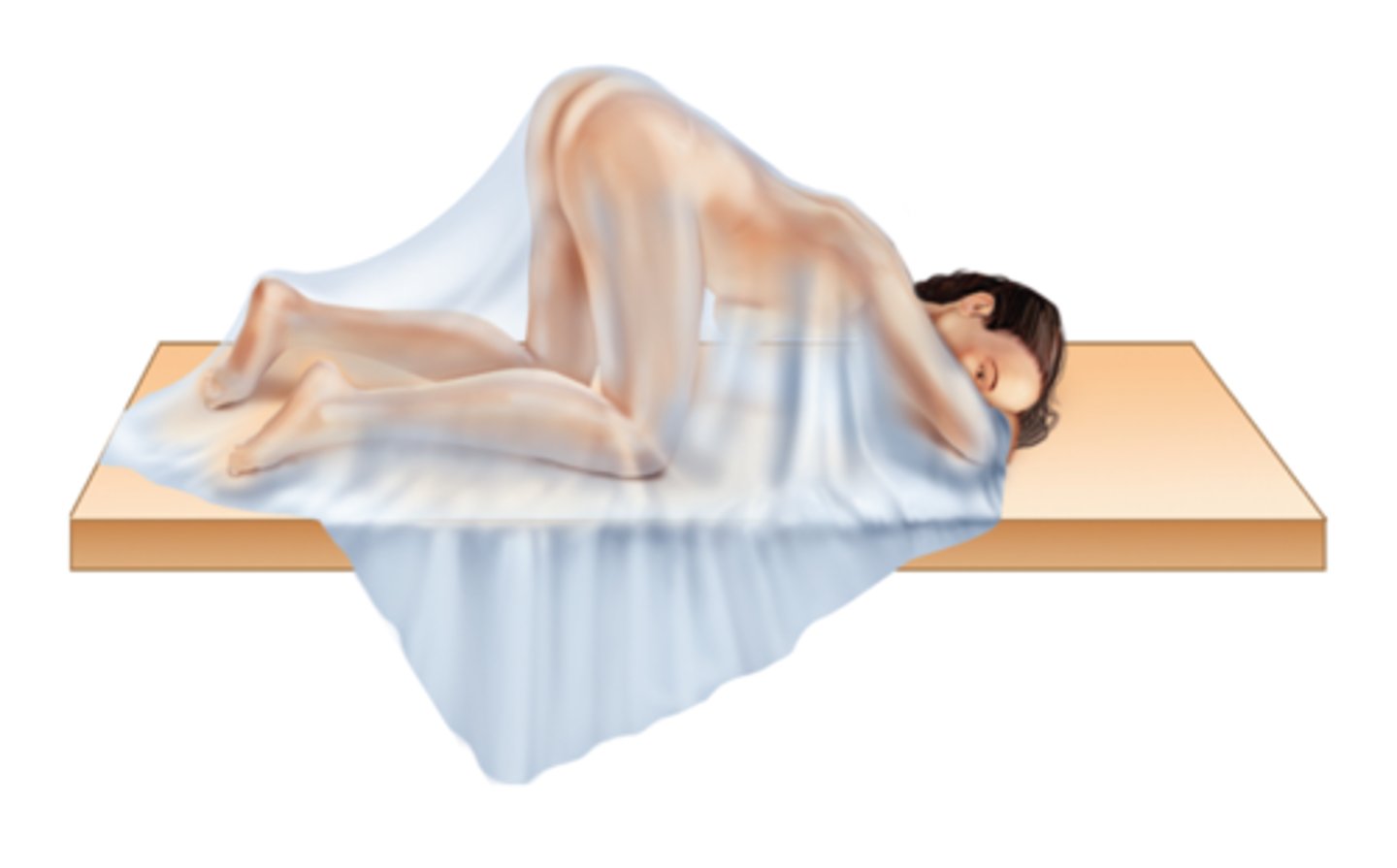
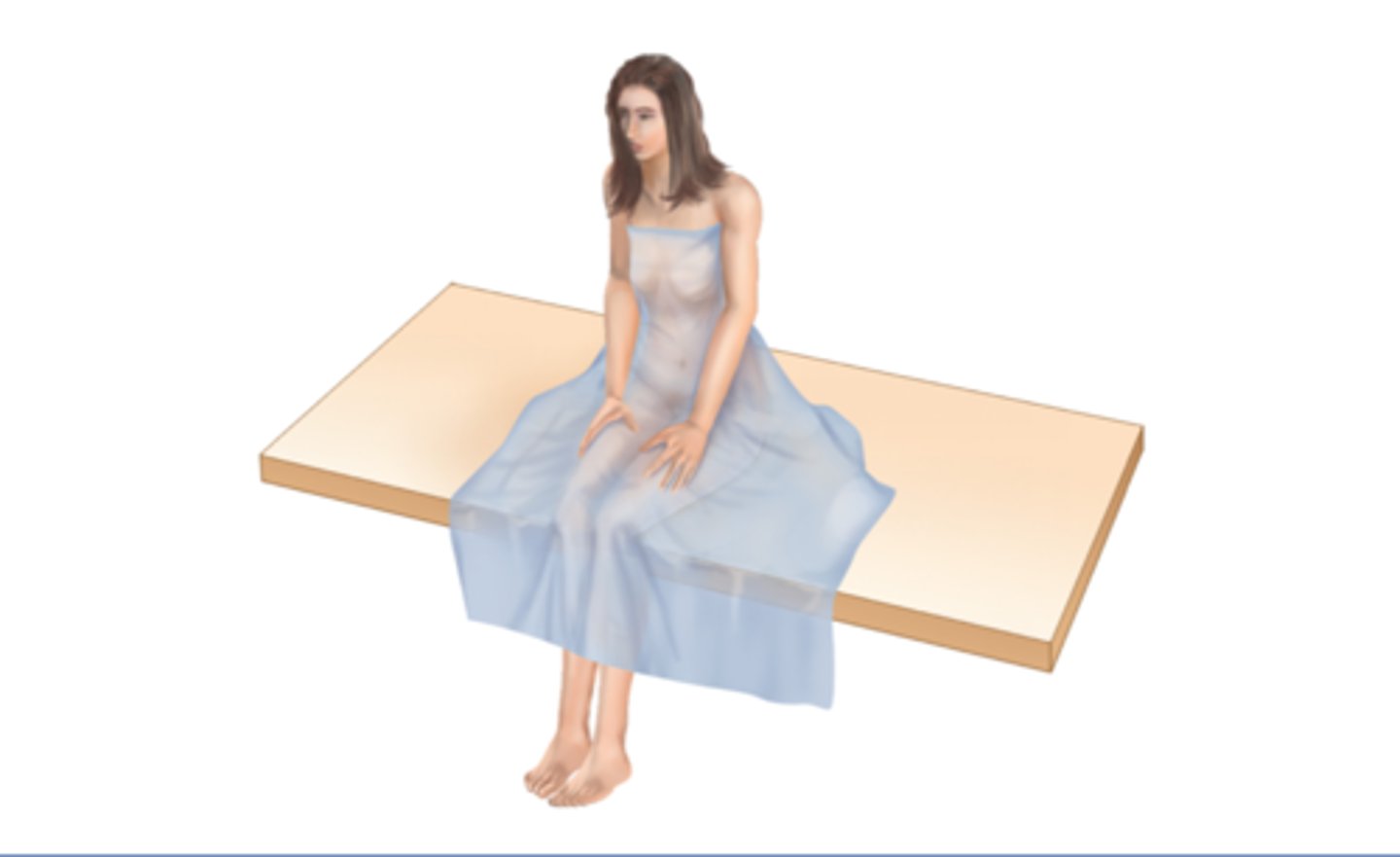
Sitting Position
Sitting upright with legs over the side of the examination table

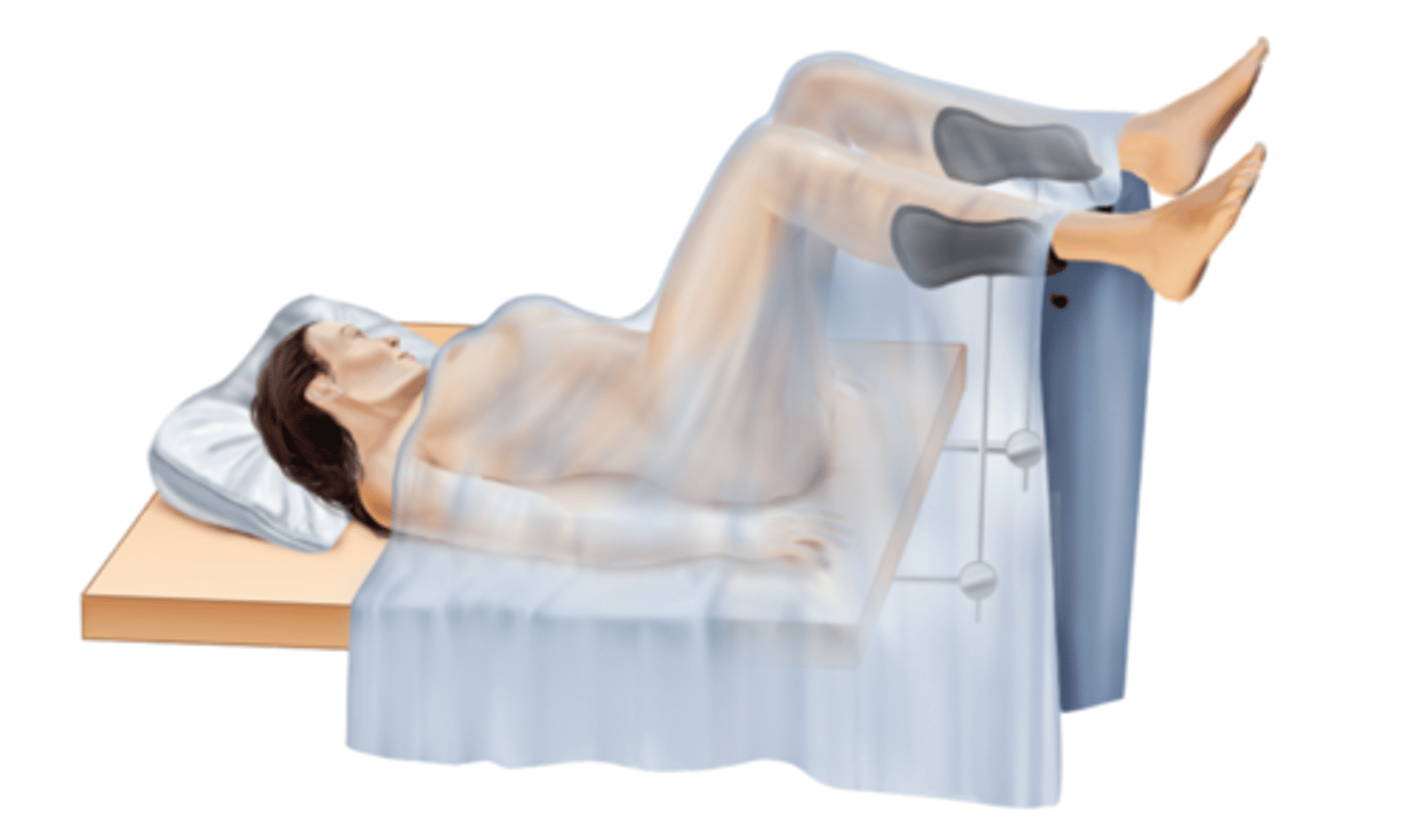
Lithotomy position
On back with lower extremities flexed and feet placed in stirrups
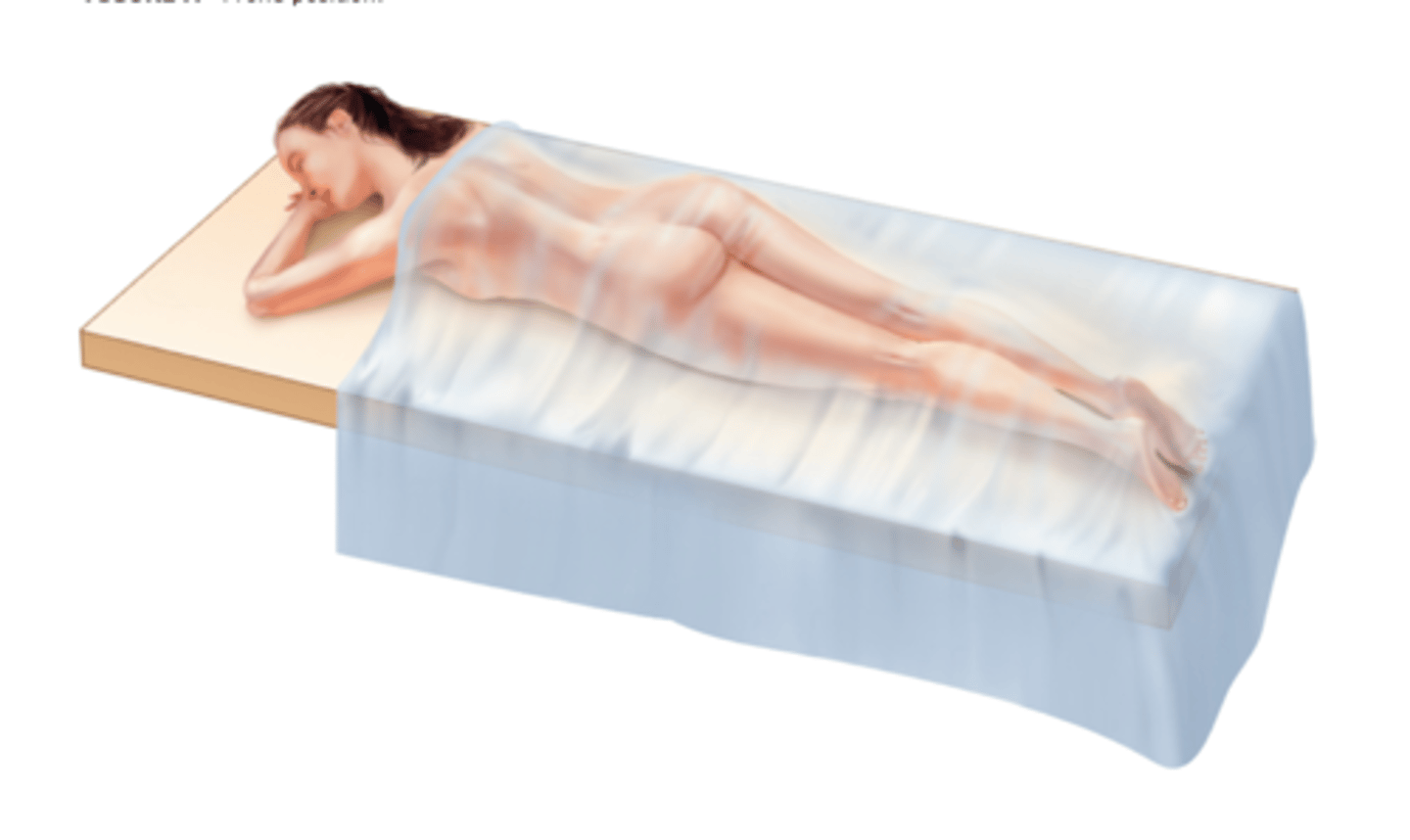
Prone Position
Lying on abdomen, face down or to one side.
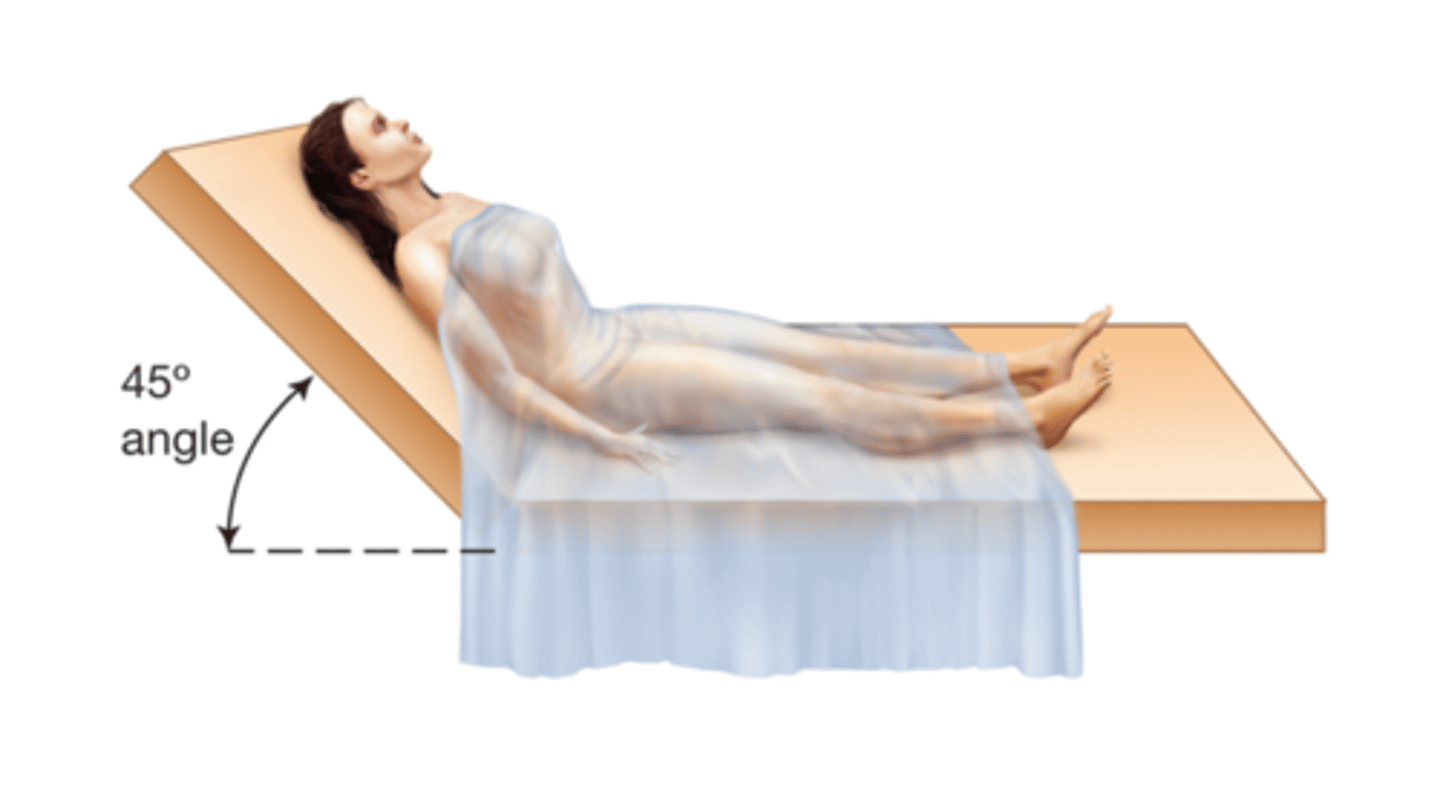
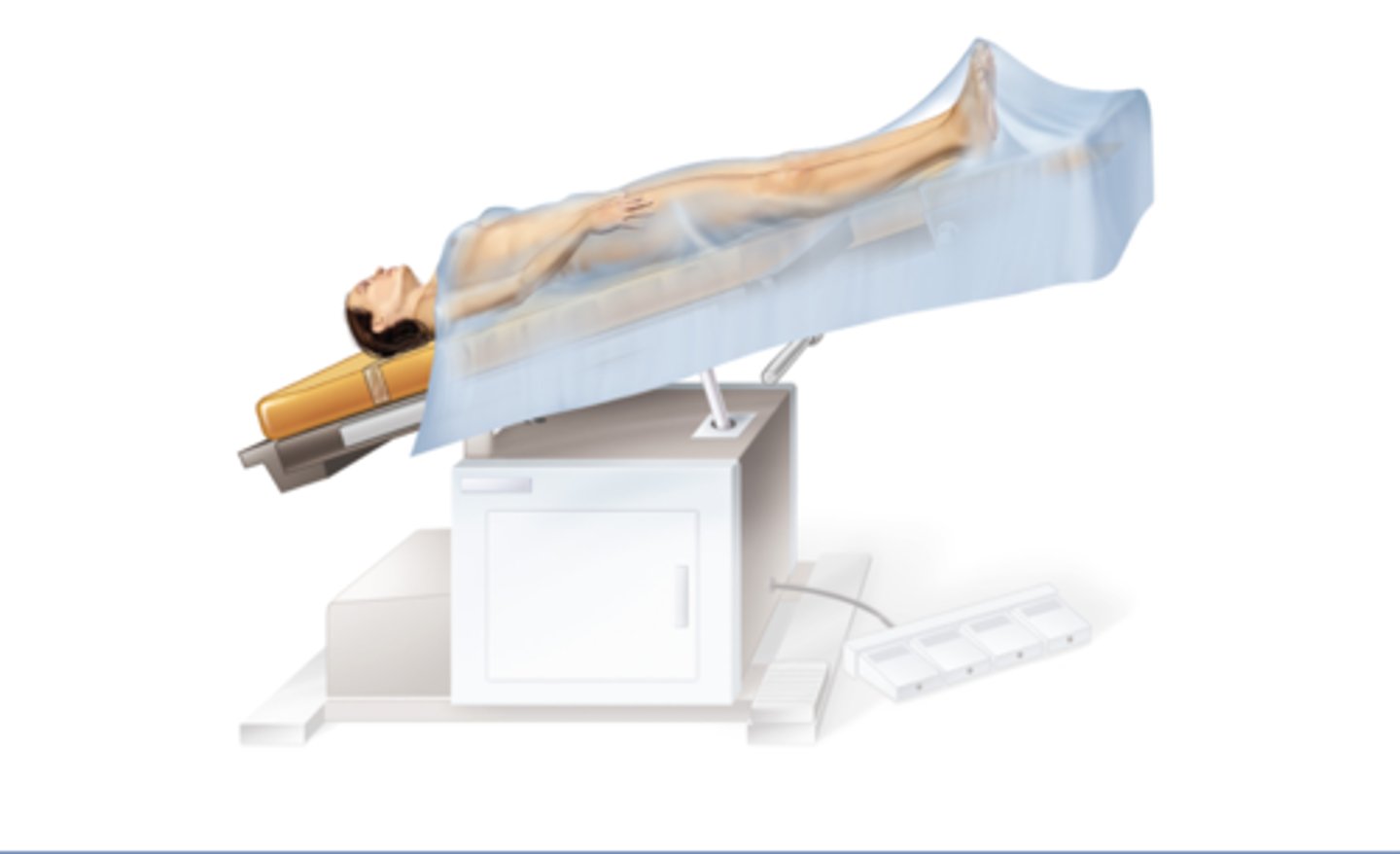
Trendelenburg Position
Supine position but the end of the table is raised 30-45 degree angle
Abduction
Moving a body part away from the midline
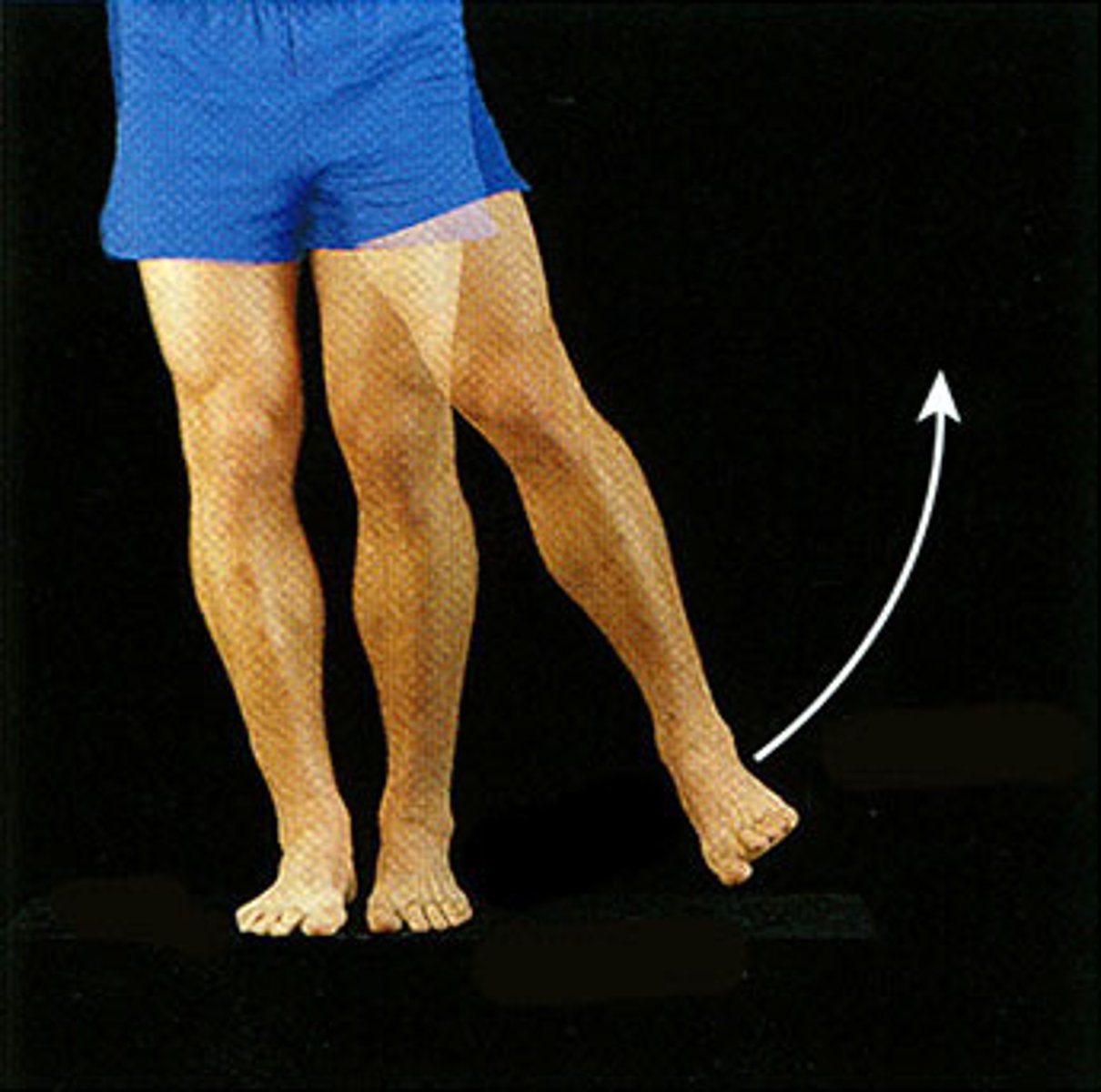
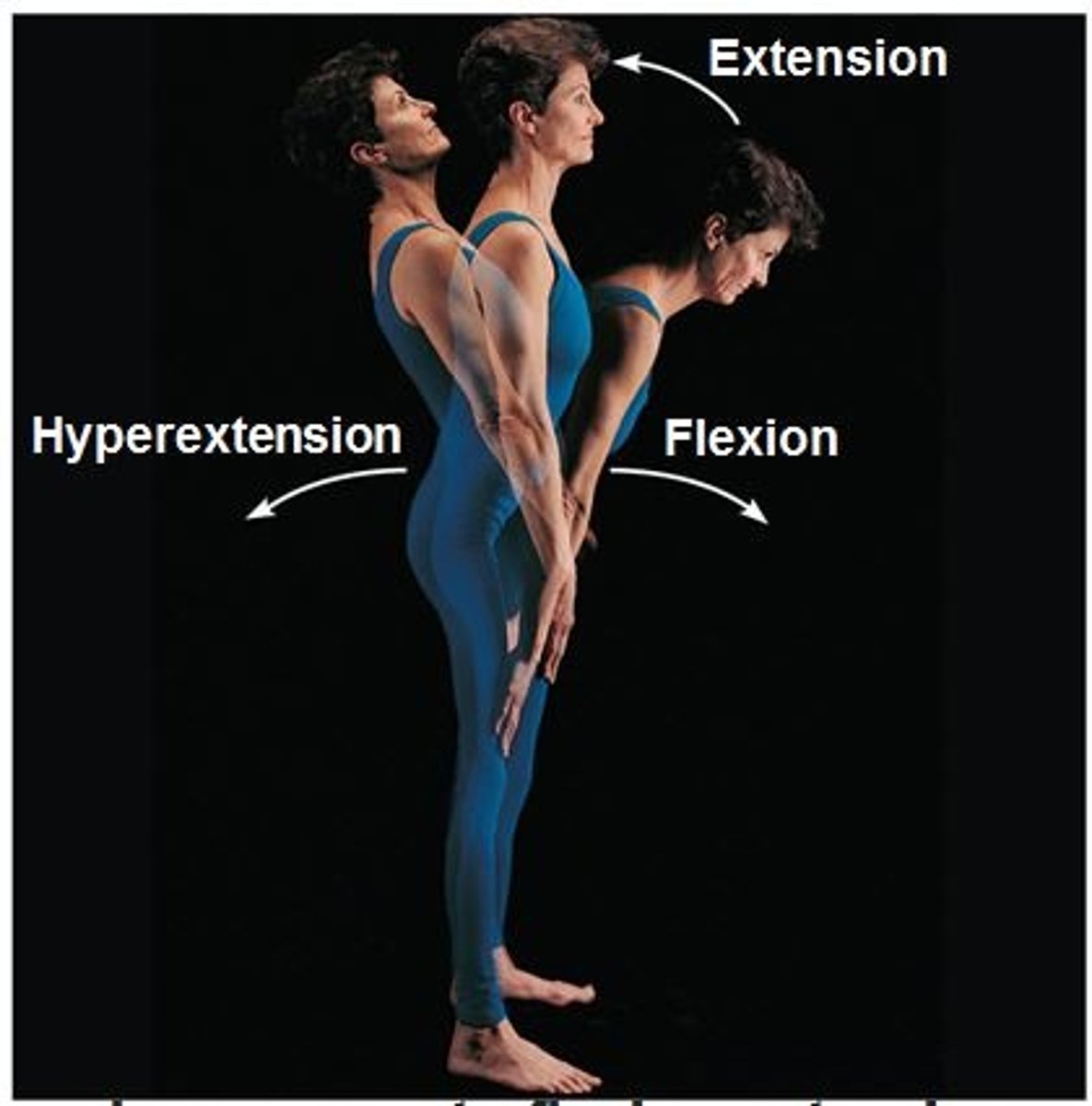
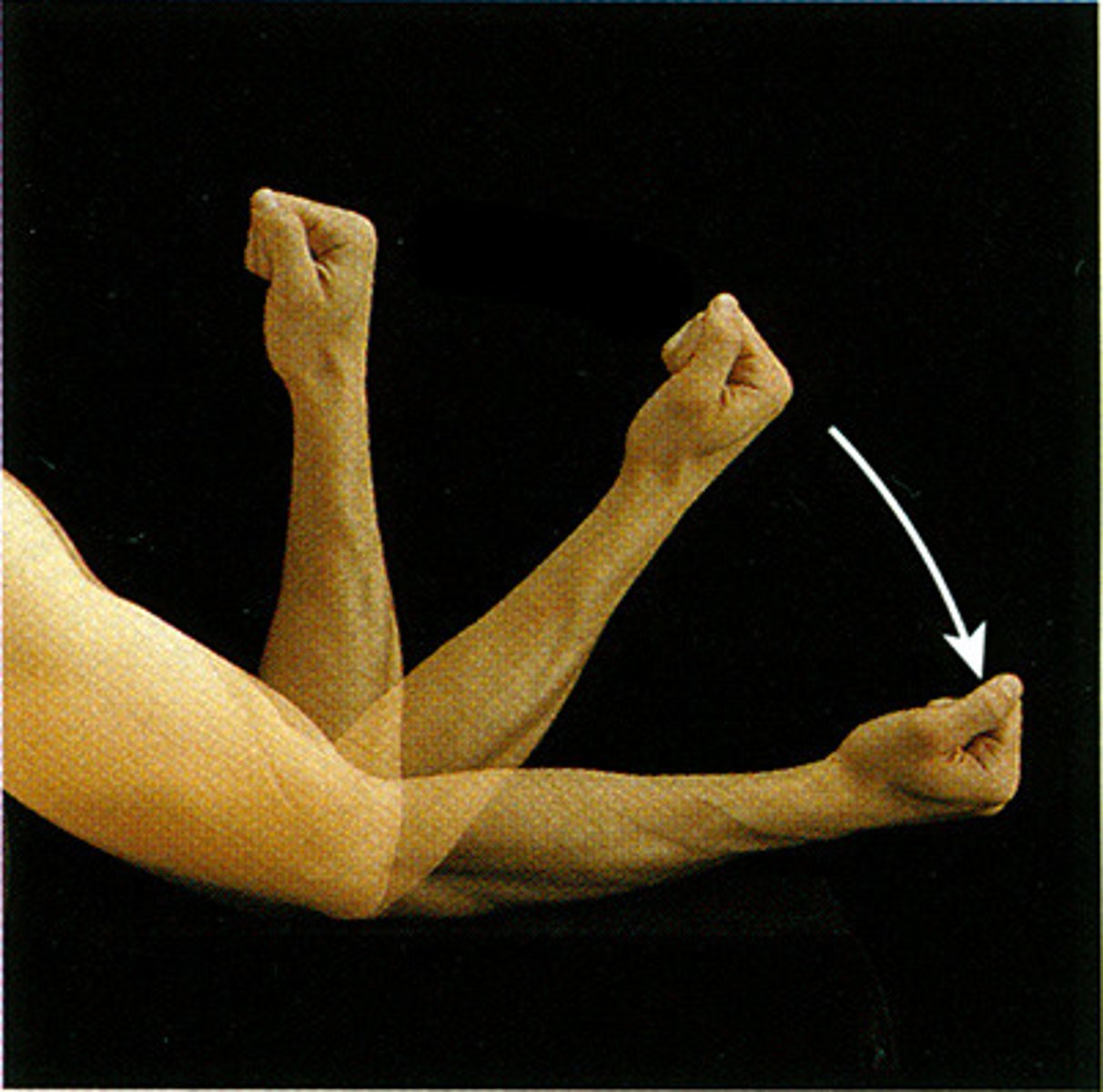
Flexion
decreasing the angle of a joint, shortening the muscle
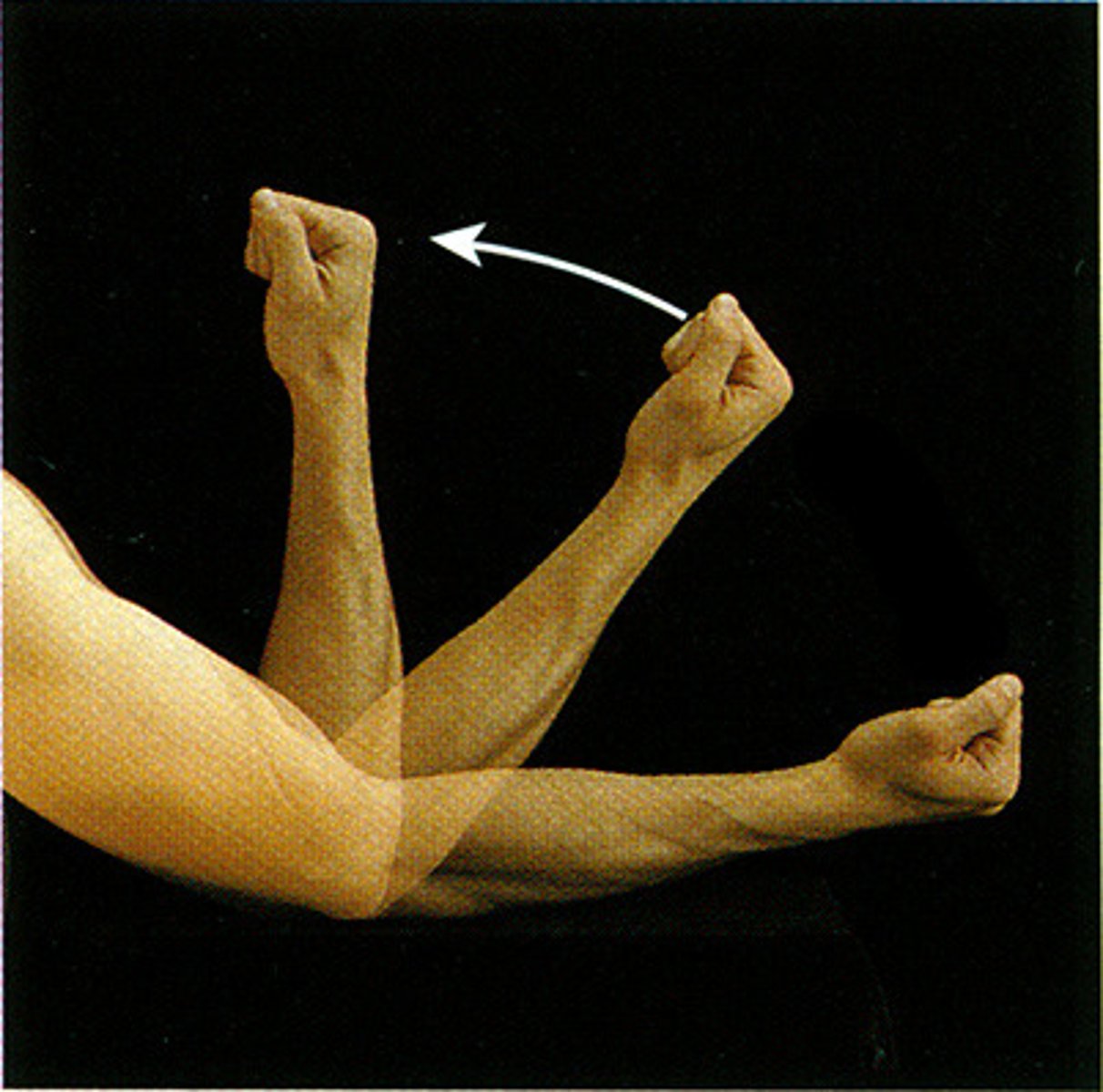
Dorsiflexion
pulling toes towards shin
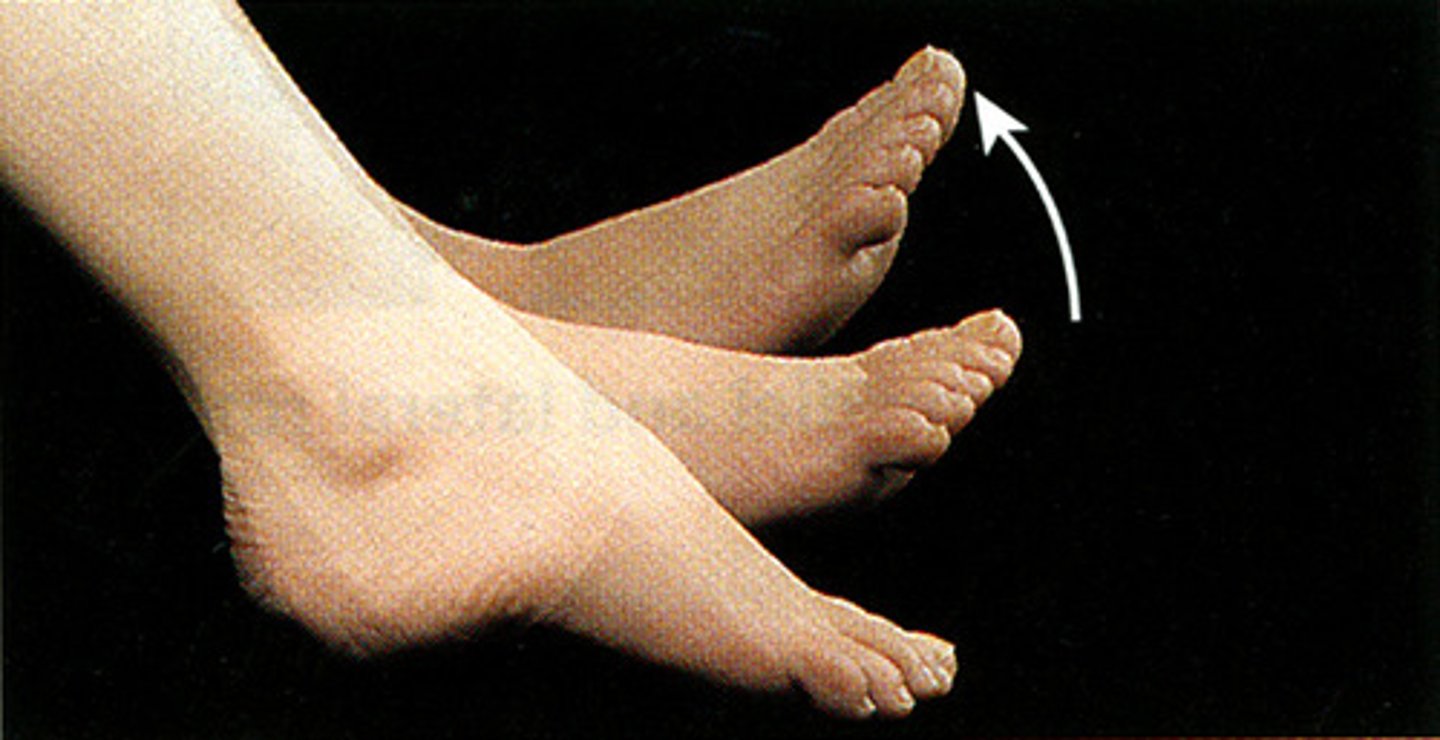
Hyperextension
Excessive extension of a body part
Adduction
Moving a body part toward the midline of the body
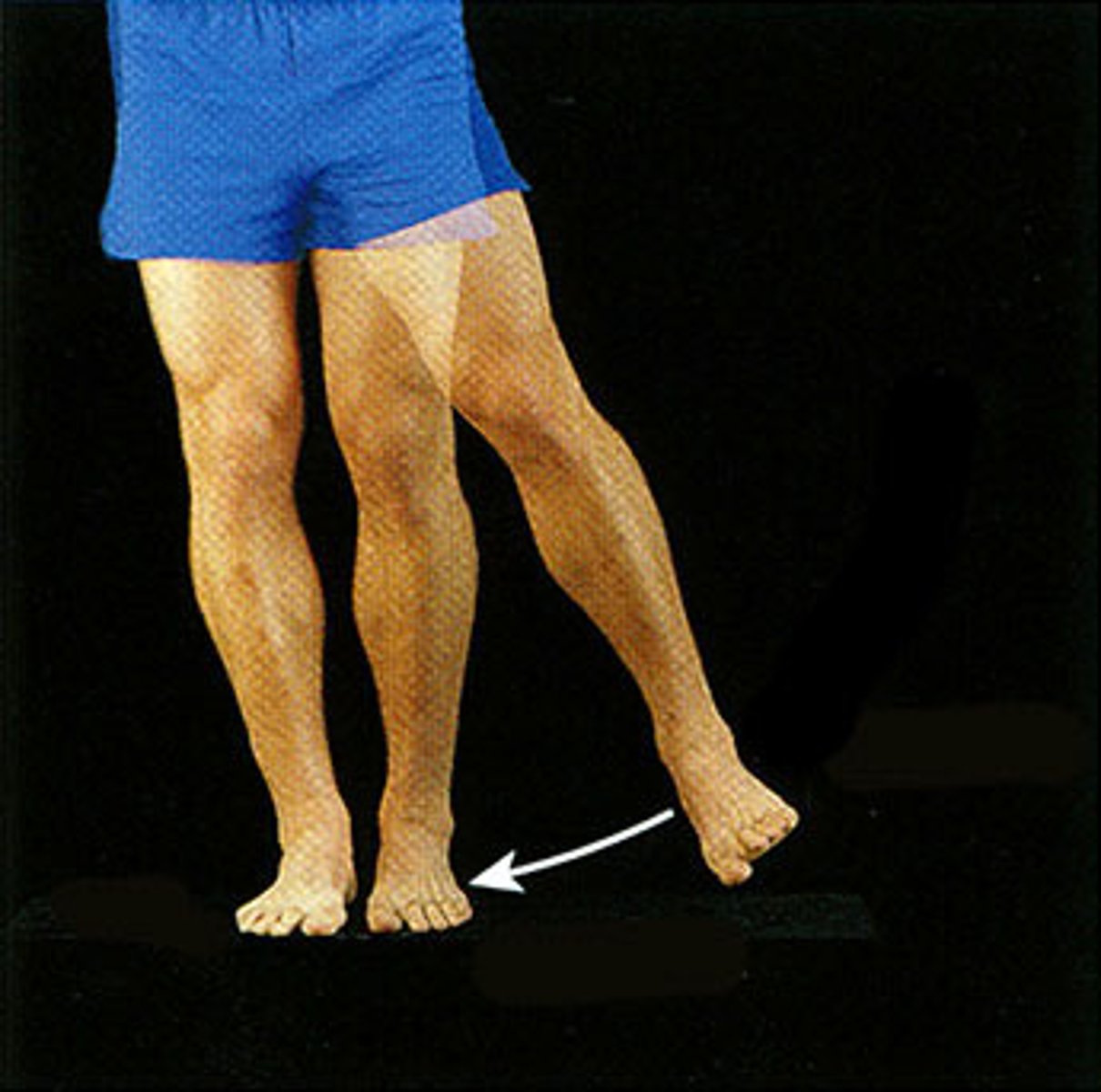
Extension
increases the angle of a joint, lengthening the muscle
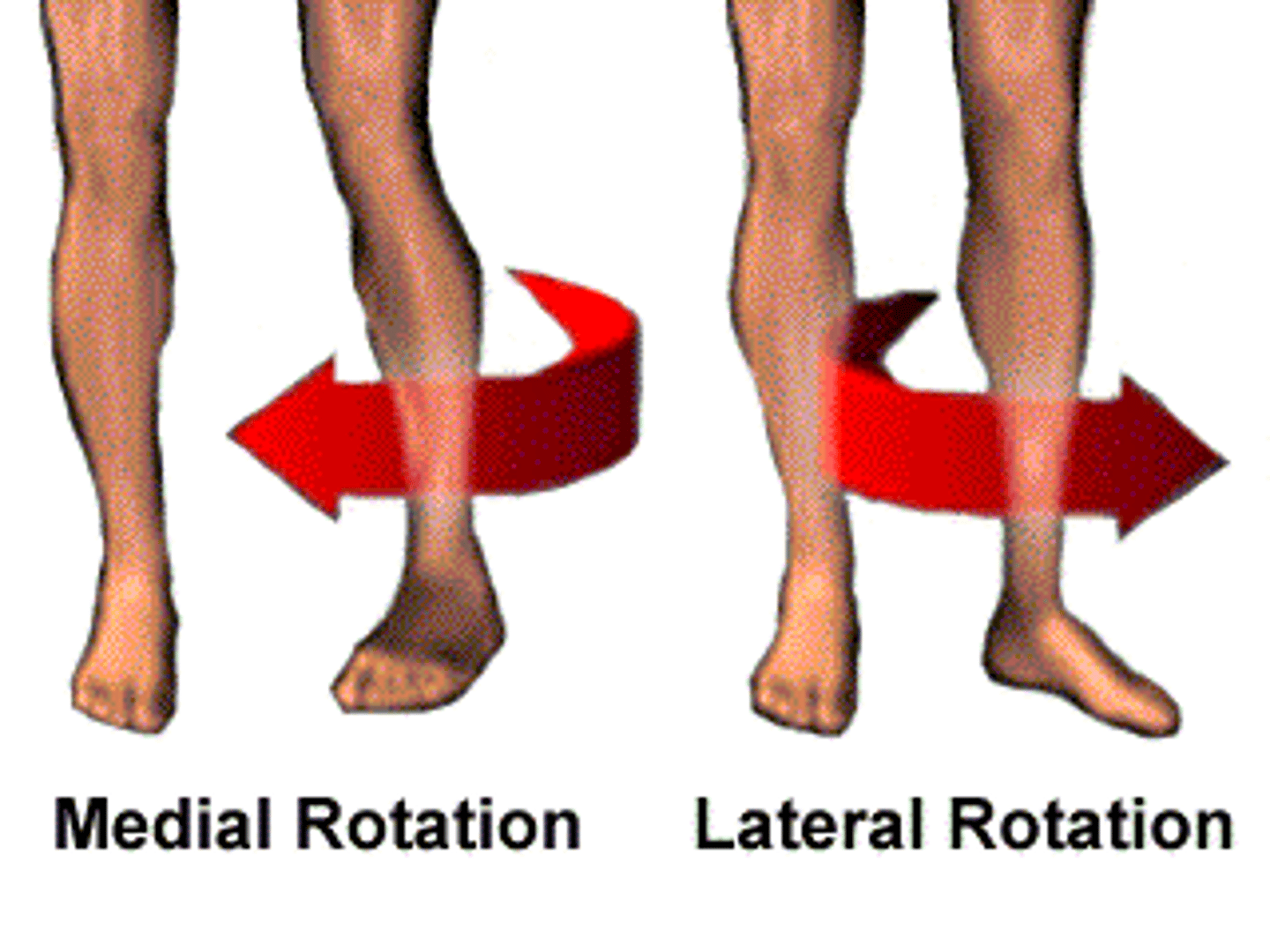
internal rotation
Rotation of a joint toward the middle of the body.
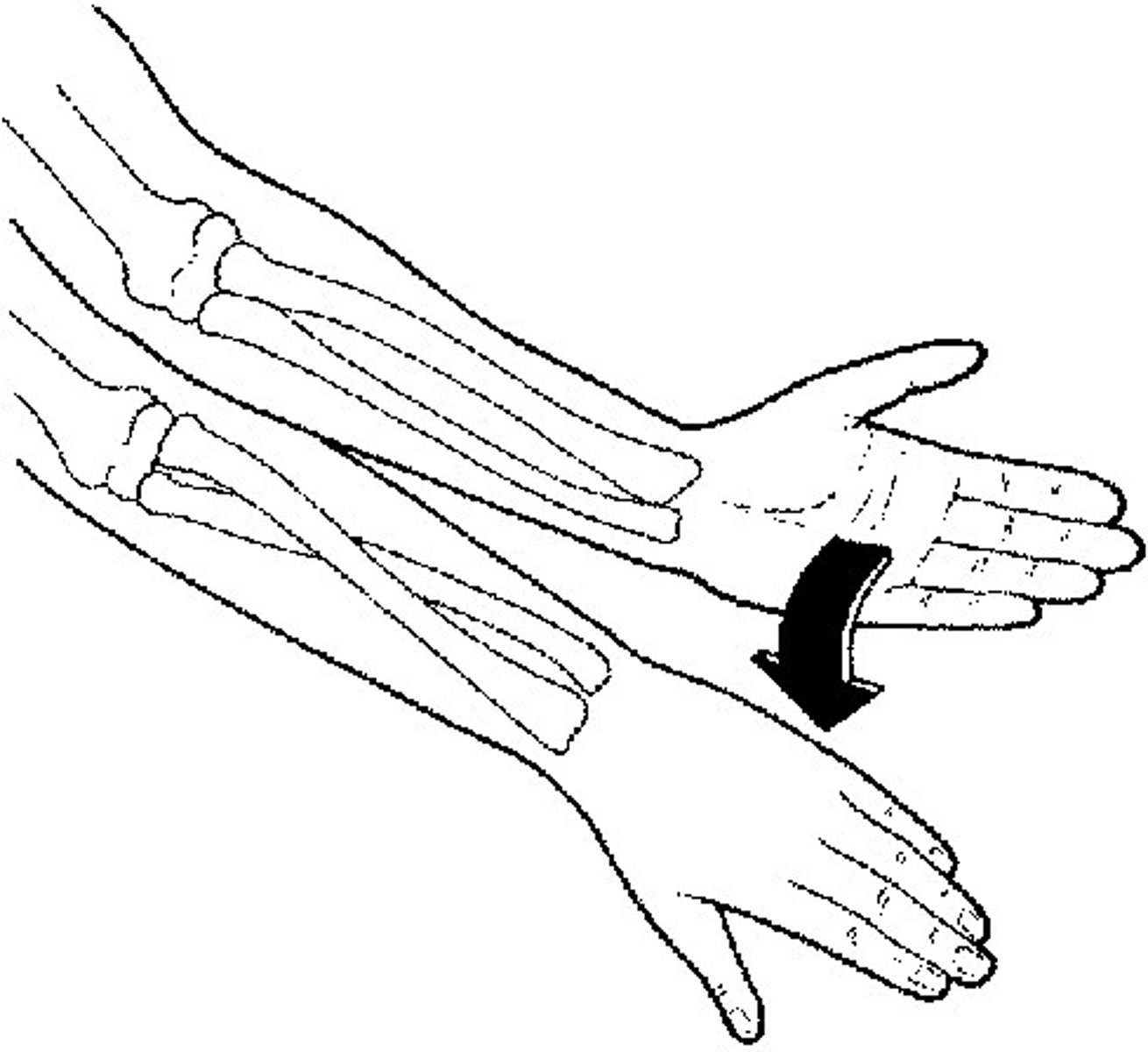
Pronation
rotation of the hands and forearms so that the palms face downward
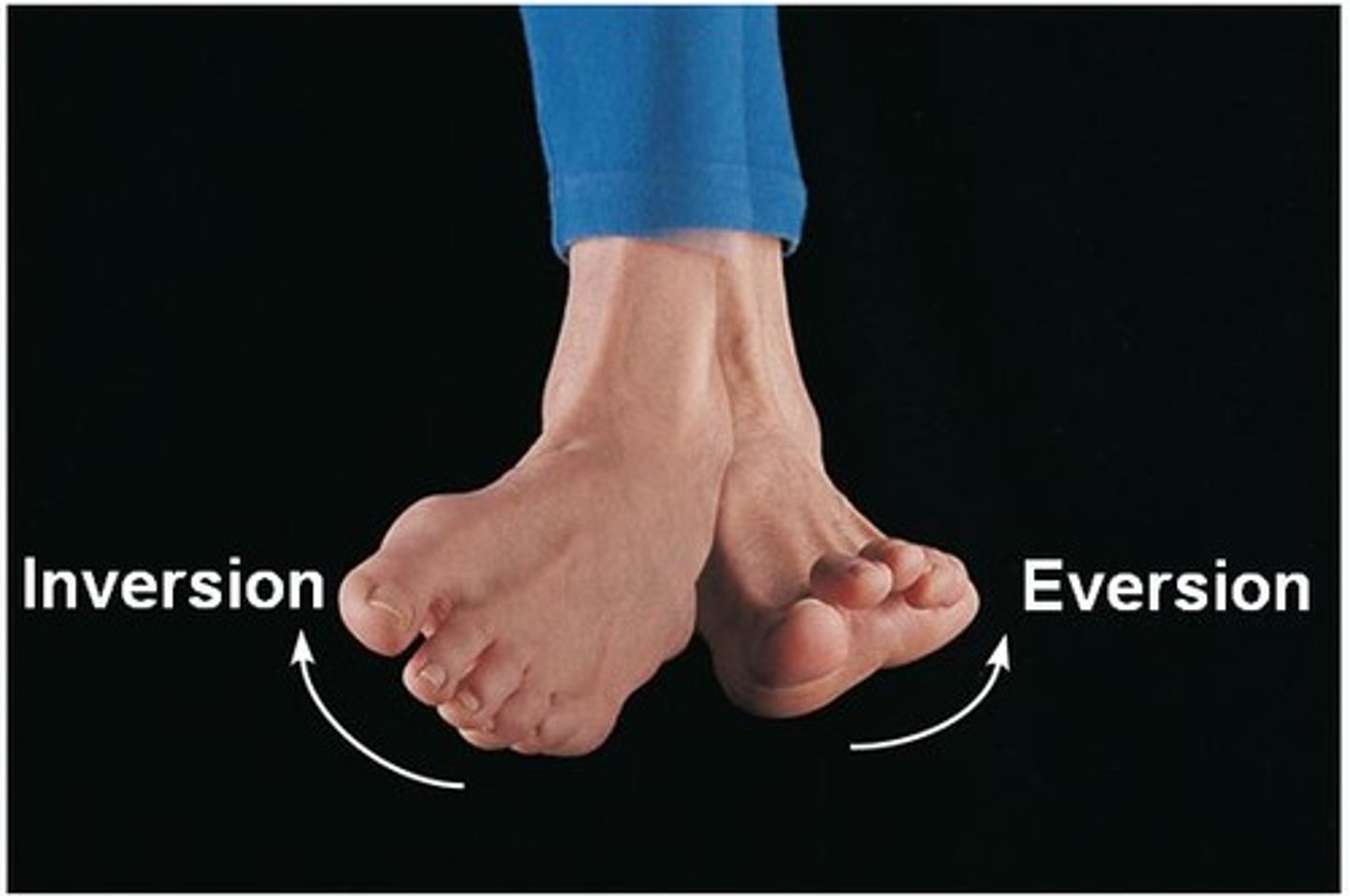
Eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
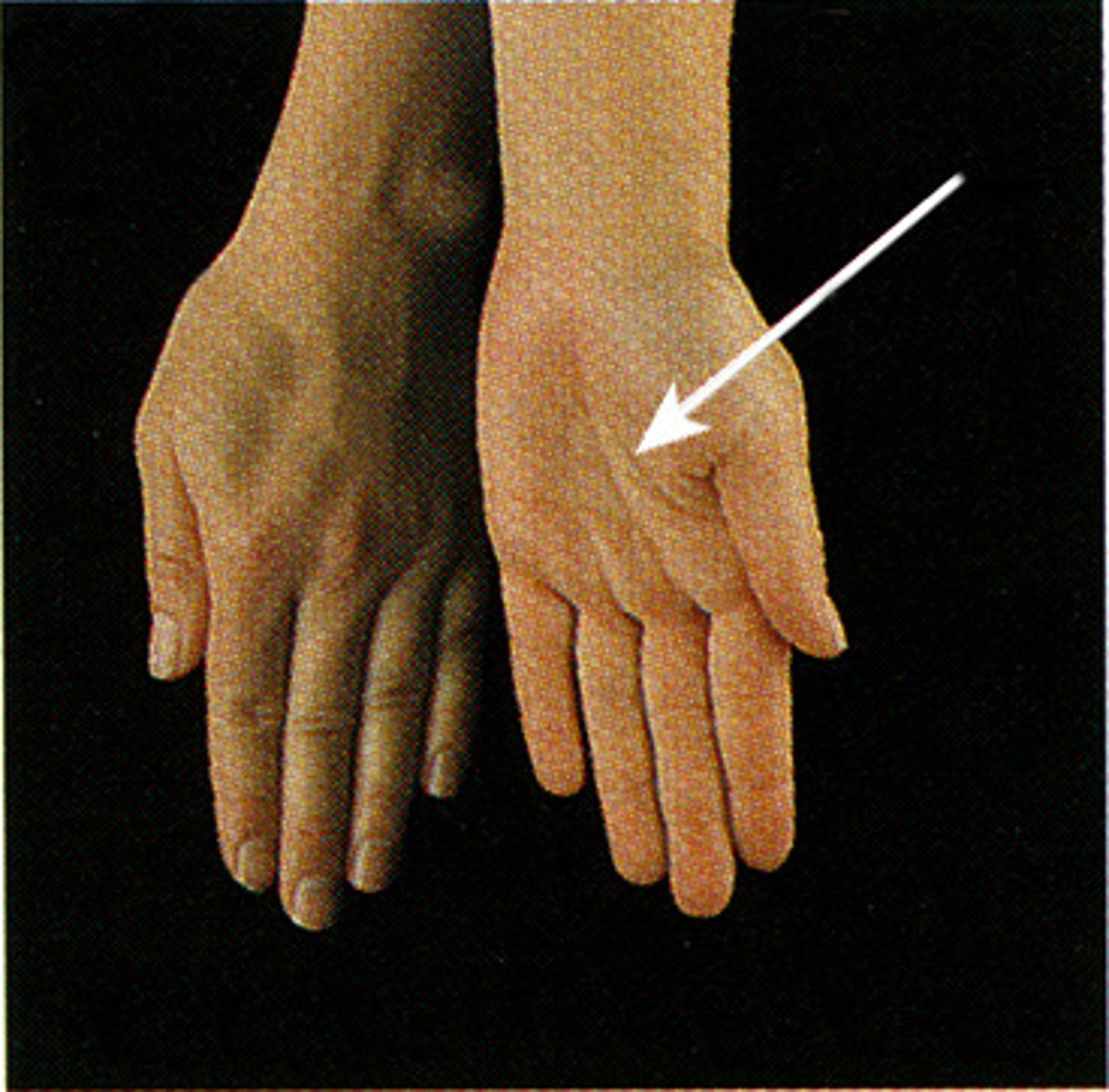
Supination
rotation of the hands and forearms so that the palms face upward
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
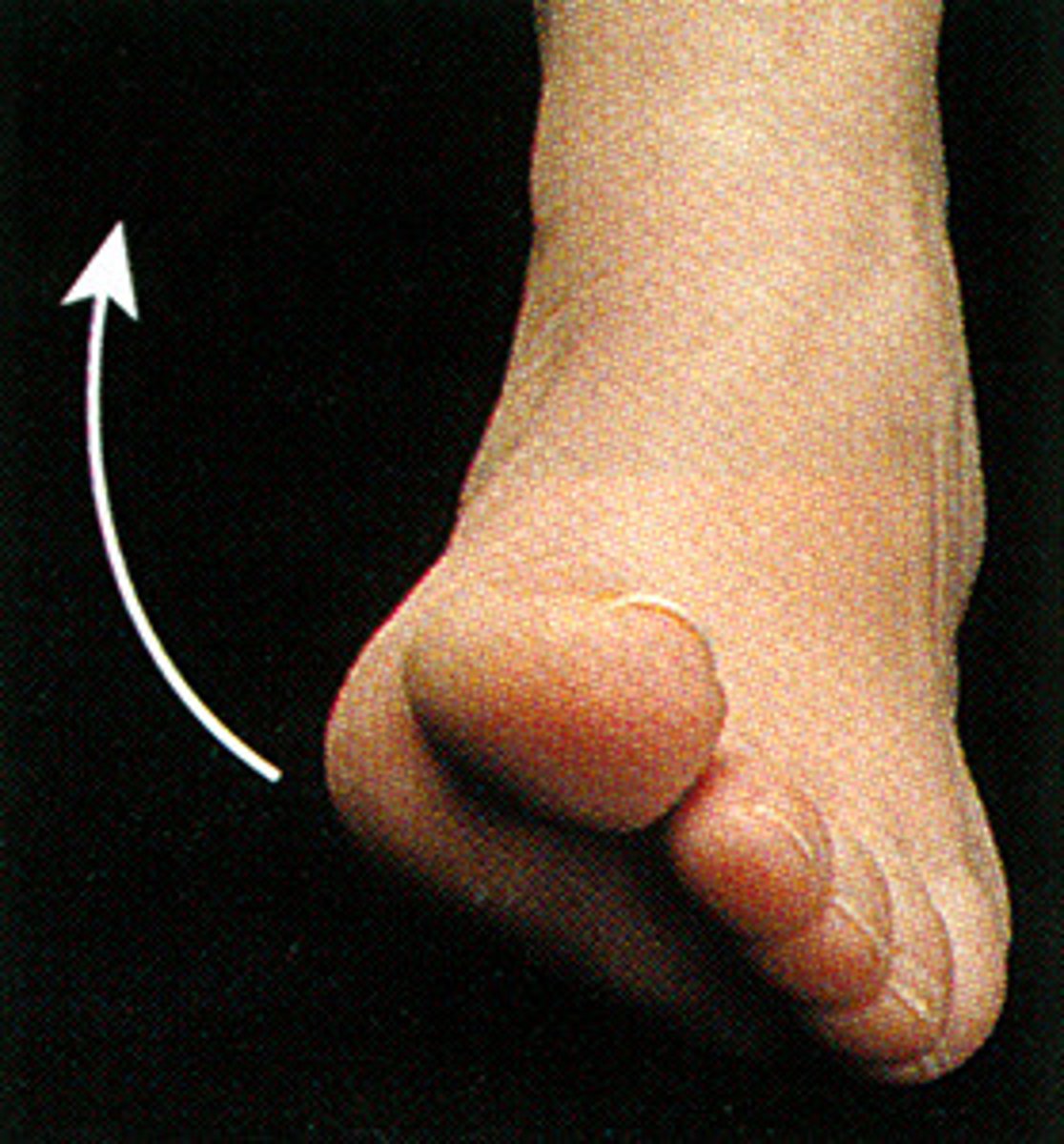
Plantar flexion
pointing toes towards the floor
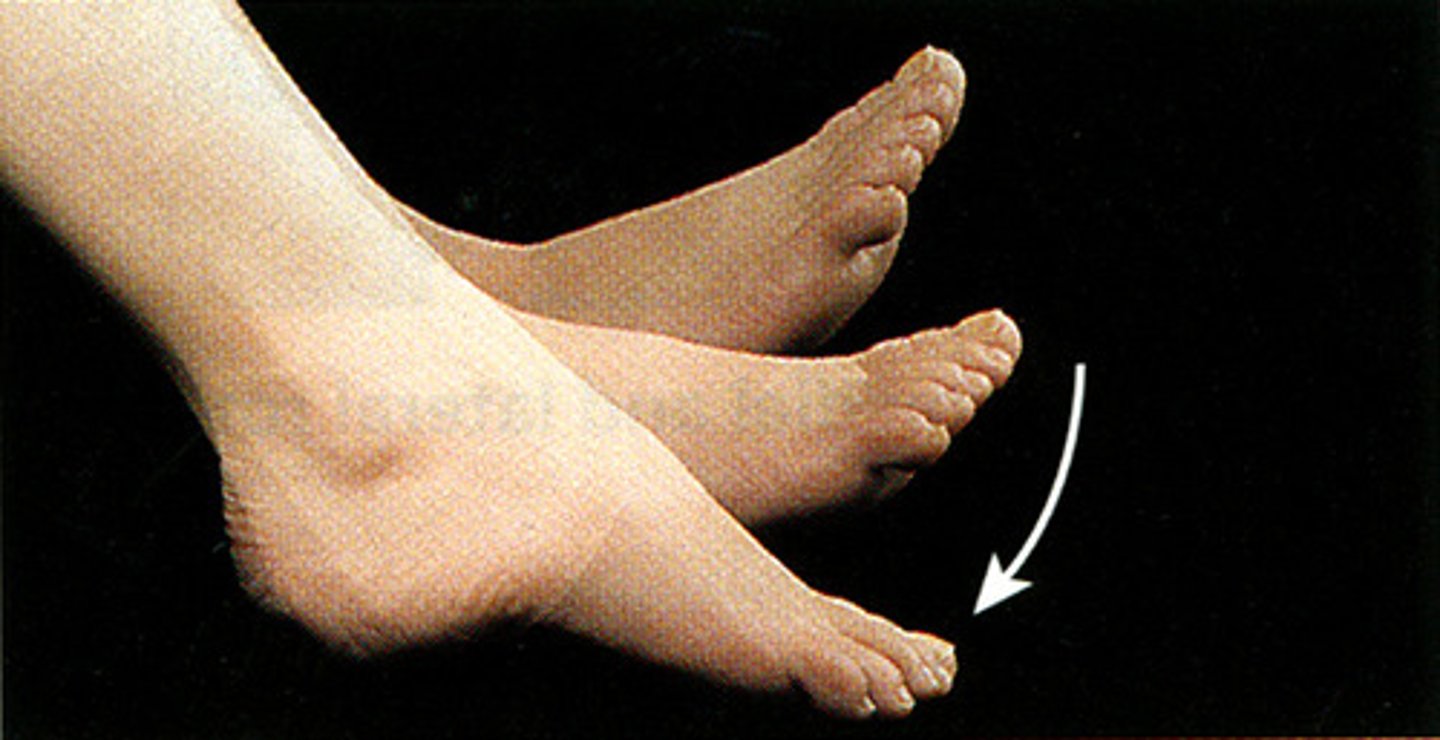
external rotation
Rotation of a joint away from the middle of the body.
opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
Protraction
Moving a part forward
Retraction
moving a part backward
Depression
downward movement of a body part
Elevation
upward movement of a body part