microbio Listeria, Erysipelothrix, Clostridium, Bacillus
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
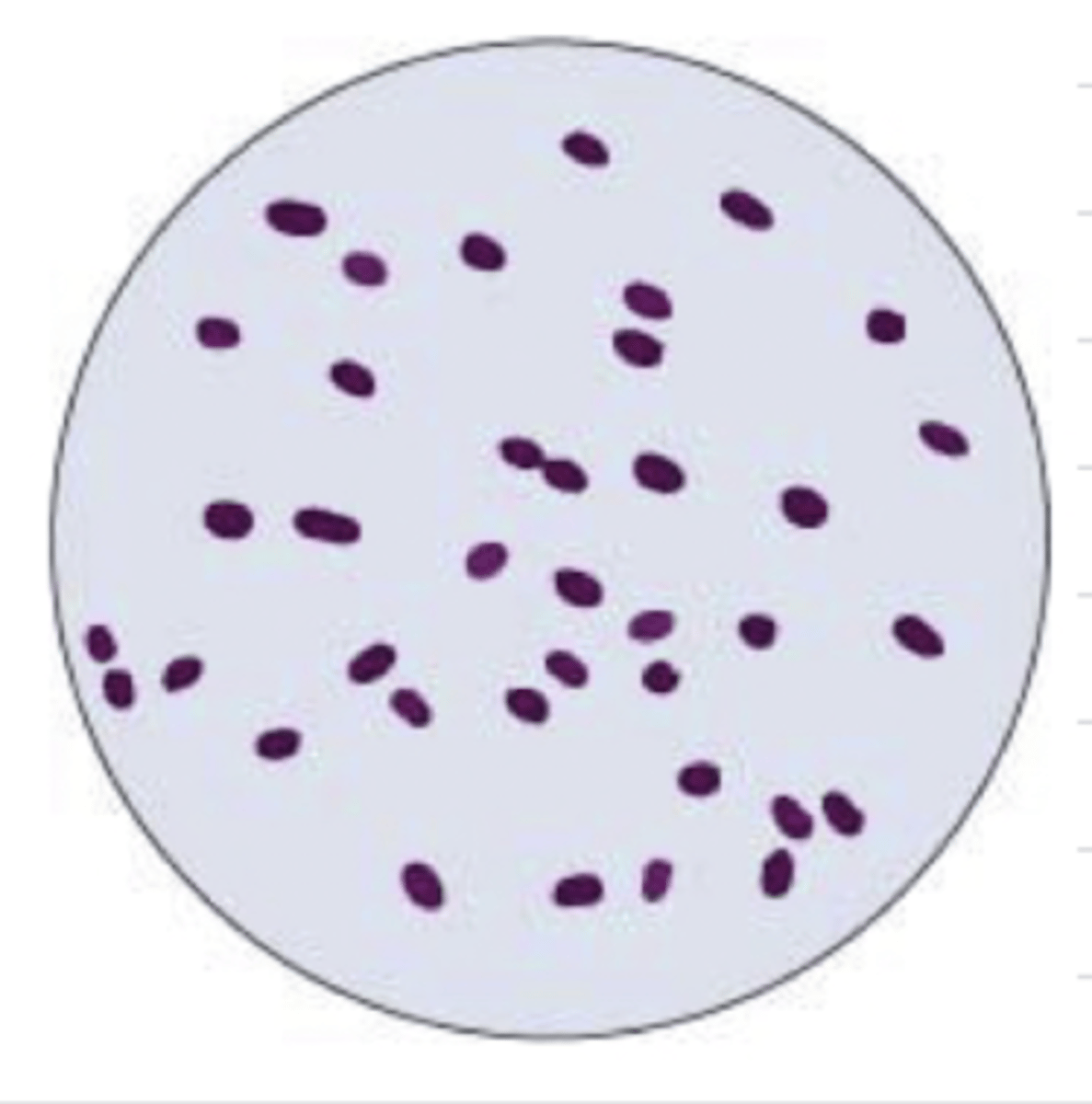
purple rods
how does Listeria appear with the gram stain?
Listeria
which bacteria appears like this with the gram stain?
non enriched media, rapid L-mono, blood agar
in what media can we isolate Listeria?
no
can Listeria be isolated in Macconkey?
yes
can Listeria be isolated in non enriched media?
yes
is Listeria hemolytic in blood agar?
it can be, but it is not necessary- it is facultatively anaerobic
does Listeria need to be isolated with oxygen?
catalase +
oxidase -
what is the result of Listeria's catalase and oxidase test?
environment- it is saprophytic in herbage, fresh water, and feces
where does Listeria normally live?
Listeria, ingestion of contaminated food and sometimes by direct contact
listeriosis is caused by the bacteria ________, and infects the animal via this route:
neurological-
circling- "circling disease"
headache
stiff neck
confusion
loss of balance
convulsions
fever
muscle aches
sometimes abortions
what are the signs of an animal with listeriosis?
penetrates the intestine, where it is absorbed into the blood and disseminates throughout the body. it targets the liver and spleen and can also cross the blood brain barrier to cause neurological signs
how does Listeria affect the animal's body?
Listeria
which bacteria can cross the placenta in a pregnant animal?
Listeria monocytogenes
an animal with "circling disease" and other neurological signs is mos likely infected with what bacteria?
CSF or spinal cord tissue if there are neuro. signs
cotyledons, fetal abomasal content or uterine discharge if there was an abortion
liver, spleen and blood
feces from a carrier (asymptomatic) animal
what specimens are acceptable to take from an animal with an Listeria monocytogenes infection?
Listeria monocytogenes
this animal has been circling around, cant move its neck, and is acting very confused. it also just had an abortion. what bacteria can we add to our list of differential diagnosis?
Listeria monocytogenes
with the rapid L-mono media, we see these results. what bacteria is this?

Listeria monocytogenes
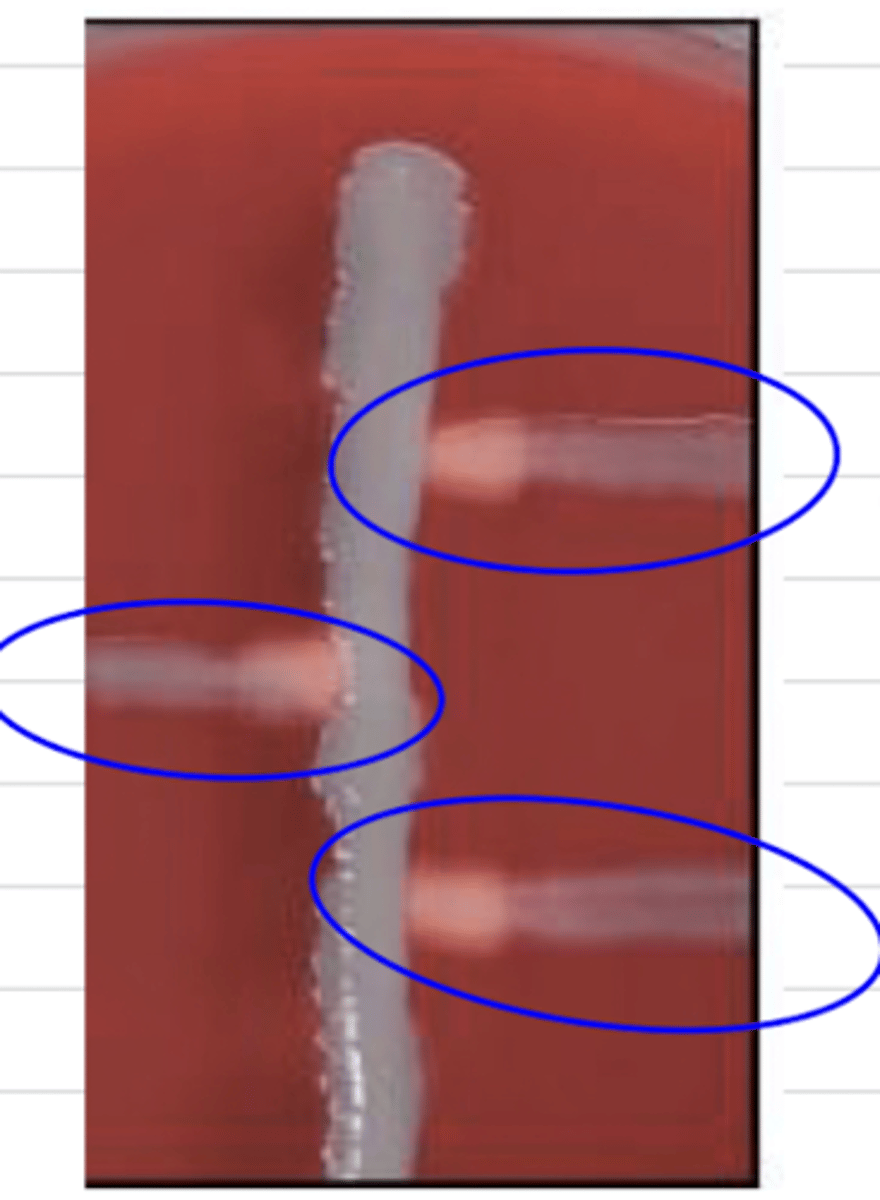
when performing the CAMP test, the bacteria forms these shapes. what species is it?

Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
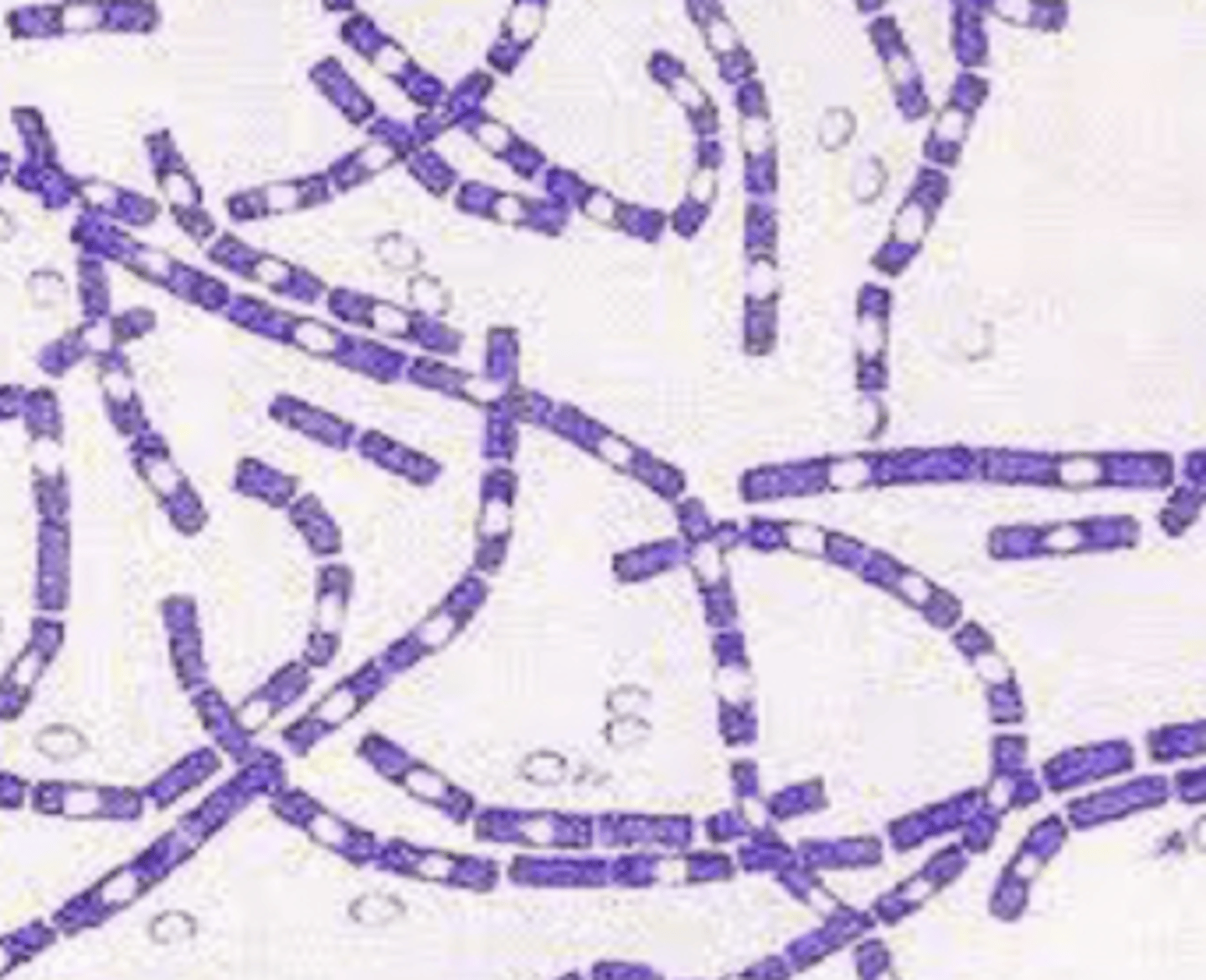
what bacteria is this?
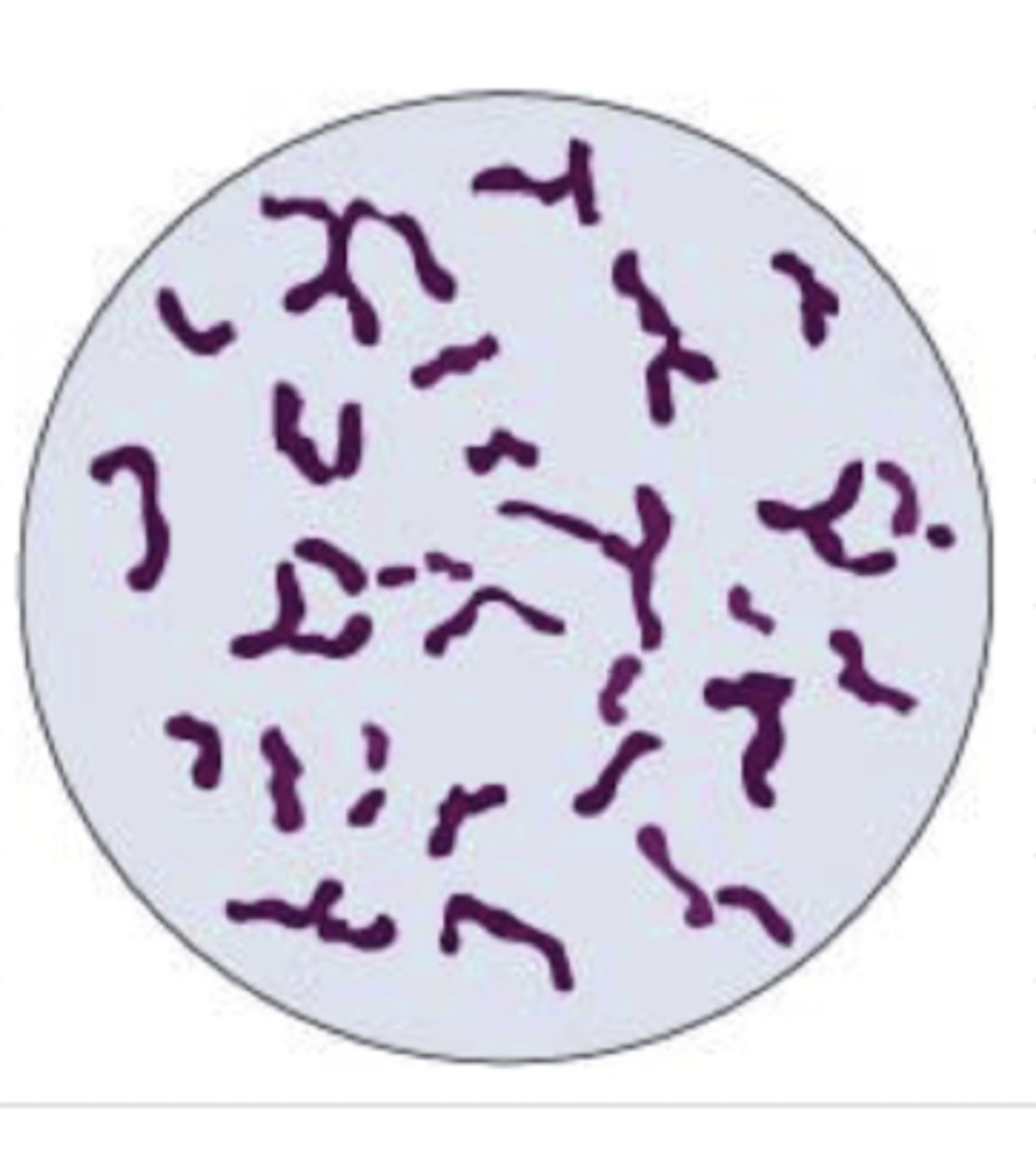
purple rods/filaments
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae appears as _______ with the gram stain
in the tonsils of 50% of healthy pigs
what is the natural habitat of
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
-ingestion of contaminated water or food
-direct contact with pig feces
-arthropod transmission
-iatrogenic- contaminated needle
how is Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae transmitted?
pigs
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is most important in what species?
catalase-
oxidase-
what are the results of the catalase and oxidase tests of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
which of these bacteria are coagulase +?
Listeria monocytogenes
which of these bacteria are CAMP +?
no
is Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae motile?
yes
is Listeria motile?
we can, but it is not necessary- it is facultatively anaerobic
do we need to use oxygen for Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolation?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
which bacteria has hyaluronidase and neuraminidase for invasion into epithelial cells and CT?
hyaluronidase and neuraminidase
what important enzymes does Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae have to aid in cell invasion?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
which bacteria can adhere to epithelial cells?
acute- septicemia, abortion, skin lesions
chronic- endocarditis, polyarthritis, skin lesions
describe the acute and chronic effects of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
this pig is likely infected by...
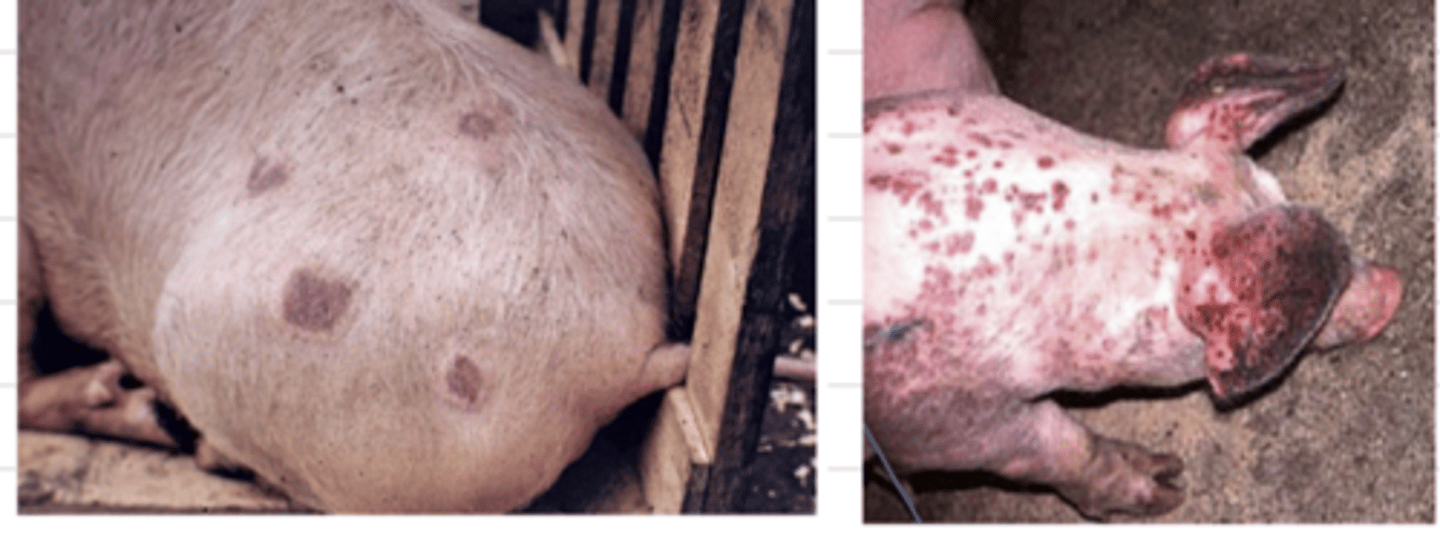
diamond shaped skin lesions
what is the most common lesion of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
yes
can Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infect humans?
tonsil scrapings, blood
how do we collect samples from an alive pig infected with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
liver, spleen, heart valves, synovial tissues, joints, tonsils
what samples can we take from a dead pig that was infected with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
no
is Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae hemolytic?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
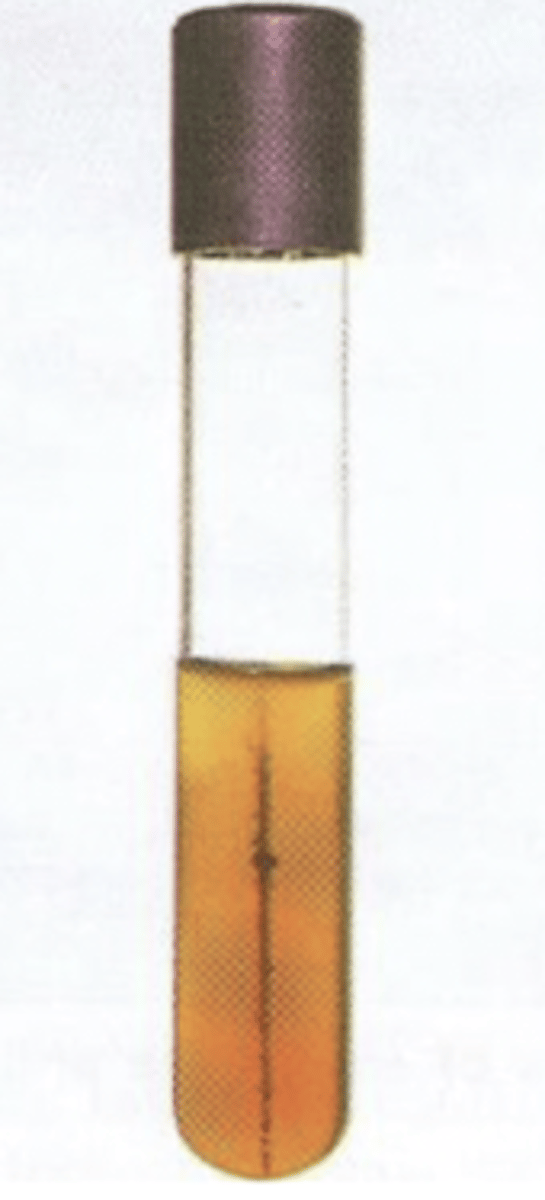
which bacteria produces H2S when performing the Triple sugar iron (TSI) test?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae- TSI test
which bacteria produces this result?

Bacillus anthracis
what bacteria is this?
Bacillus and Clostridium
which bacteria produces endospores?
yes
can Bacillus anthracis grow on non enriched media?
catalase +
oxidase -
what are the results of the catalase and oxidase test of Bacillus anthracis?
yes
is Bacillus anthracis motile?
Bacillus anthracis
what bacteria causes anthrax?
50 years- they tolerate dessication, high temperatures, and chemical disinfectants
the endospores of Bacillus anthracis last how long in the environment?
cattle, sheep, carnivores, horses, pigs, humans
what species can be affected by Bacillus anthracis?
inhalation
ingestion of infected meat
wounds
injected
vectors
what are the routes of ingection of Bacillus anthracis?
inhalation
how is respiratory anthrax transmitted?
contact with wounds
how is cutaneous anthrax transmitted?
Ingestion of contaminated water
how is GI anthrax transmitted?
anthrax toxins
what toxin does Bacillus anthracis produce?
cause cells to release H20, causing pulmonary edema
what do anthrax toxins do?
7 days
-fever
-cough
-chills
-shortness of breath
-shock
locally- darkening, edema, necrosis
systemically- septicemia, vascular perm., hemorrhage
symptoms of anthrax occur ______ after infection. they include....
respiratory anthrax
which type of anthrax- respiratory, cutaneous, or GI, is more severe?
endospores go to the alveoli, where they trigger an immune response. macrophages engulf spores, but cannot destroy them. so, endospores germinate inside of the macrophage and then are released into the lymph glands and can travel throughout the body and infect the blood stream
explain what Bacillus anthracis does once it enters the animal's body via inhalation
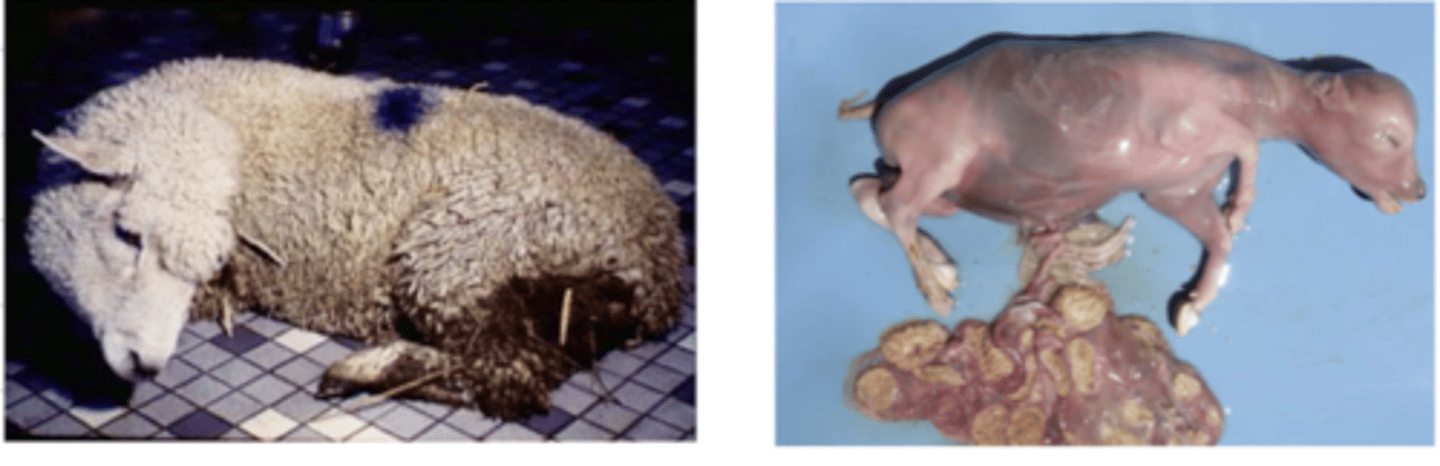
Bacillus anthracis
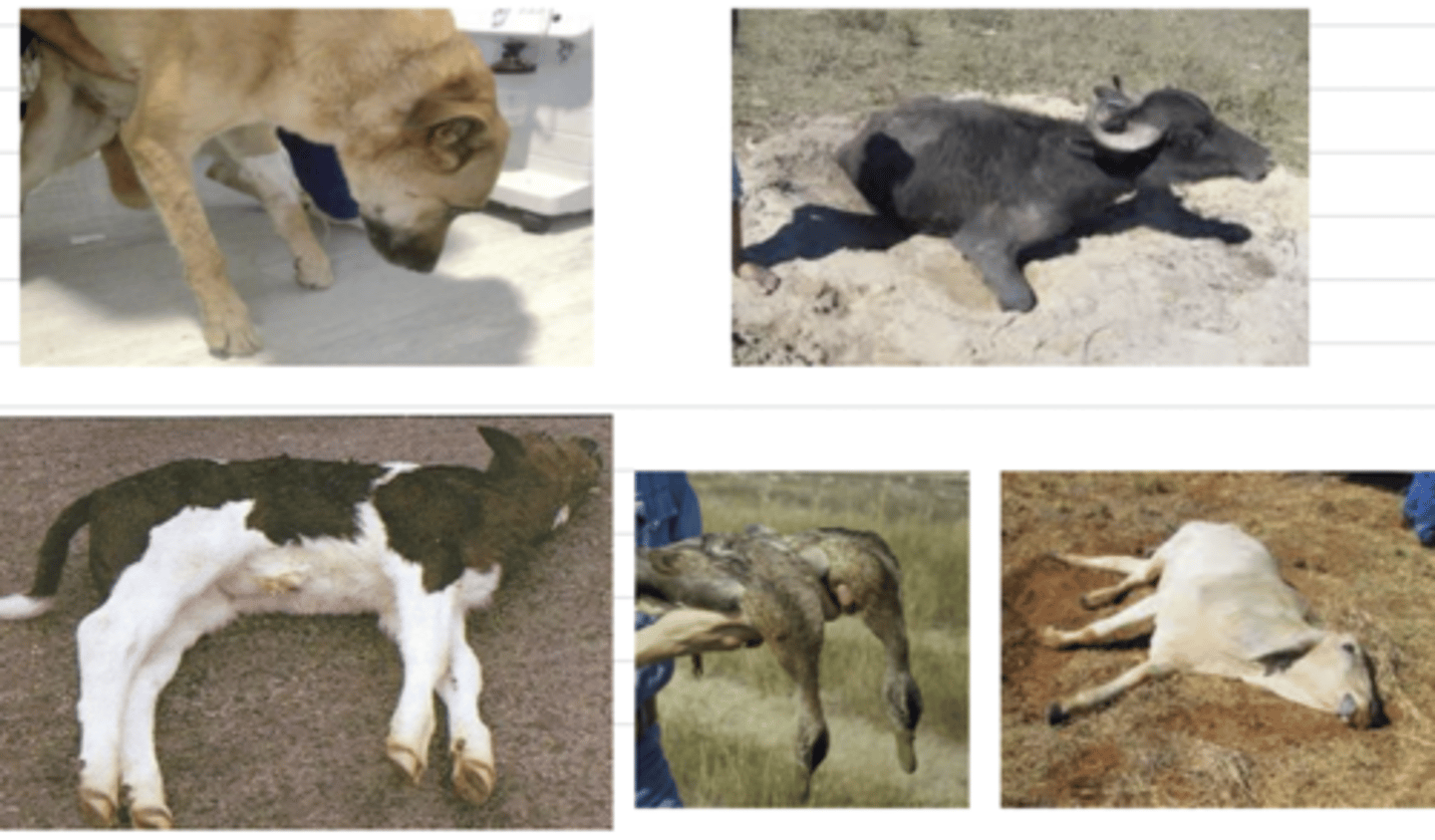
what bacterial infection do these animals have?
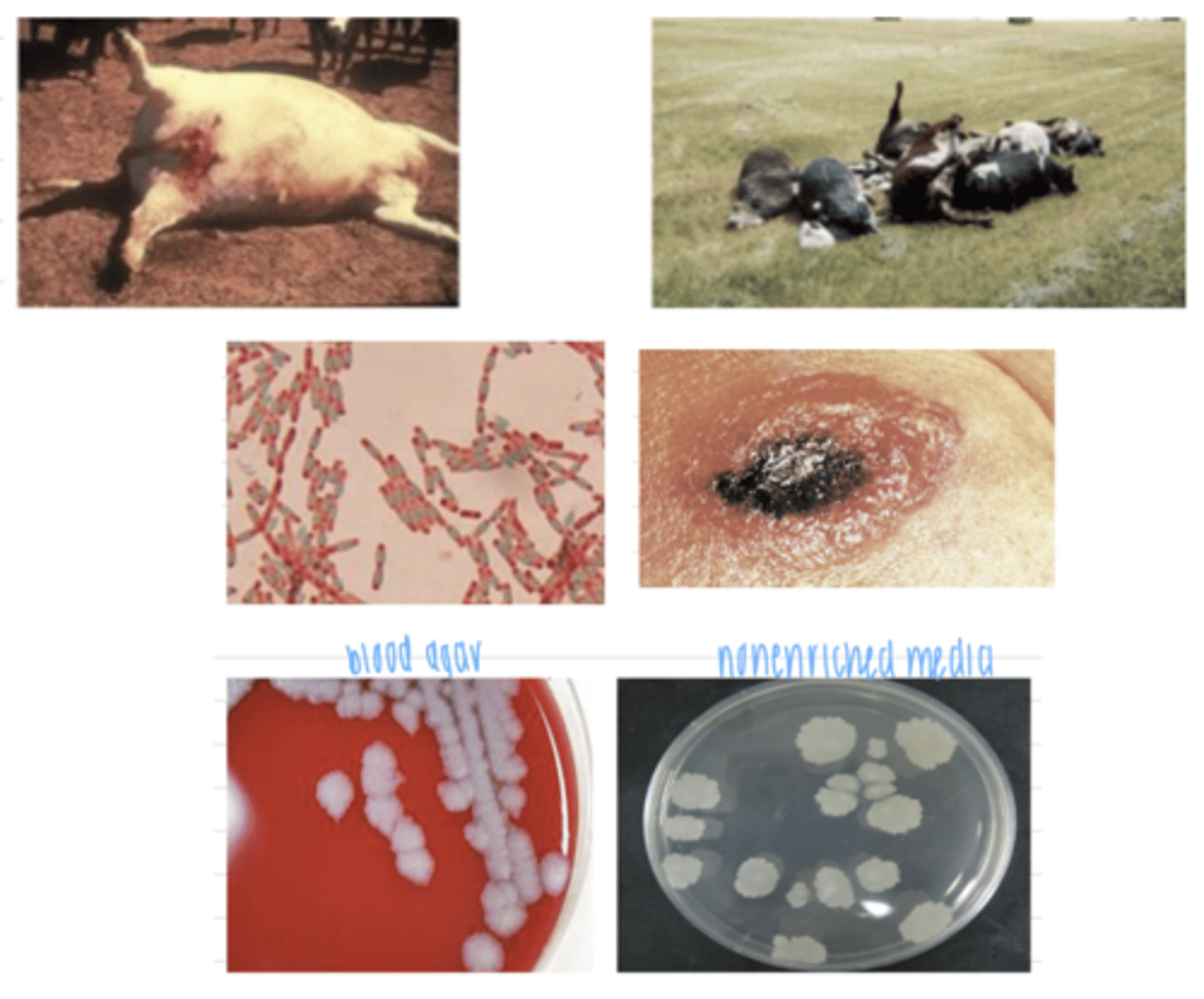
Bacillus anthracis
which bacteria appears like this with the ZN stain?
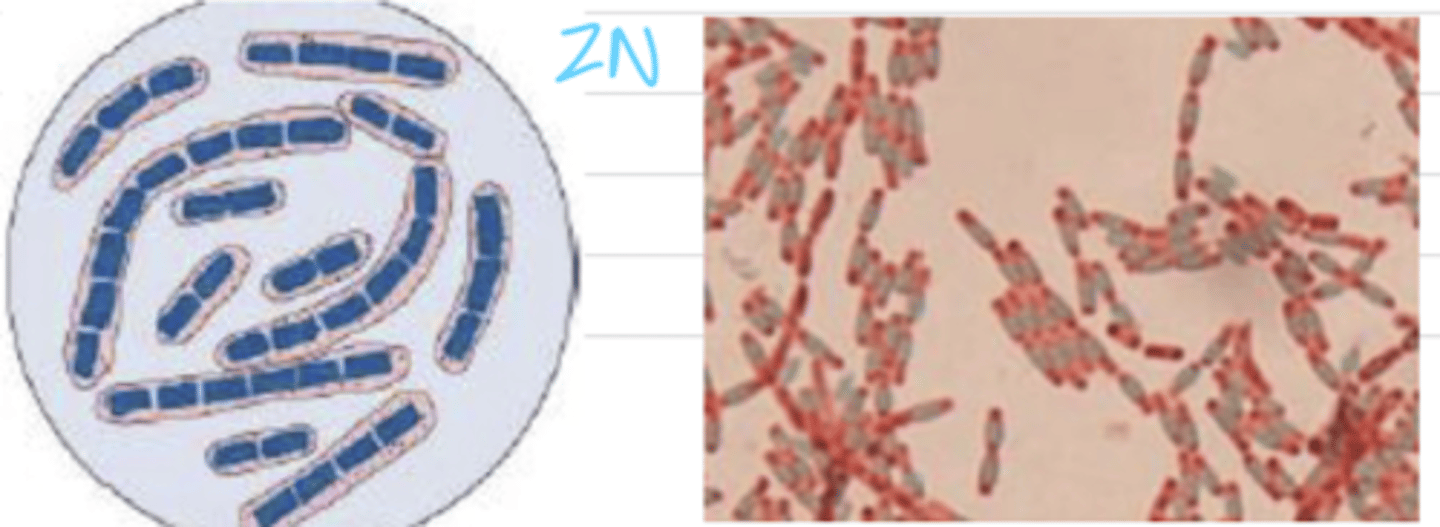
negative- cells are blue, but endospores are red
is Bacillus anthracis ZN positive or negative?
Bacillus anthracis
which disease is very fatal and the animals that it kills are bloated, have dark, unclotted blood, hemorrhage in their anus, mouth, and nostrils, and have no rigor mortis?
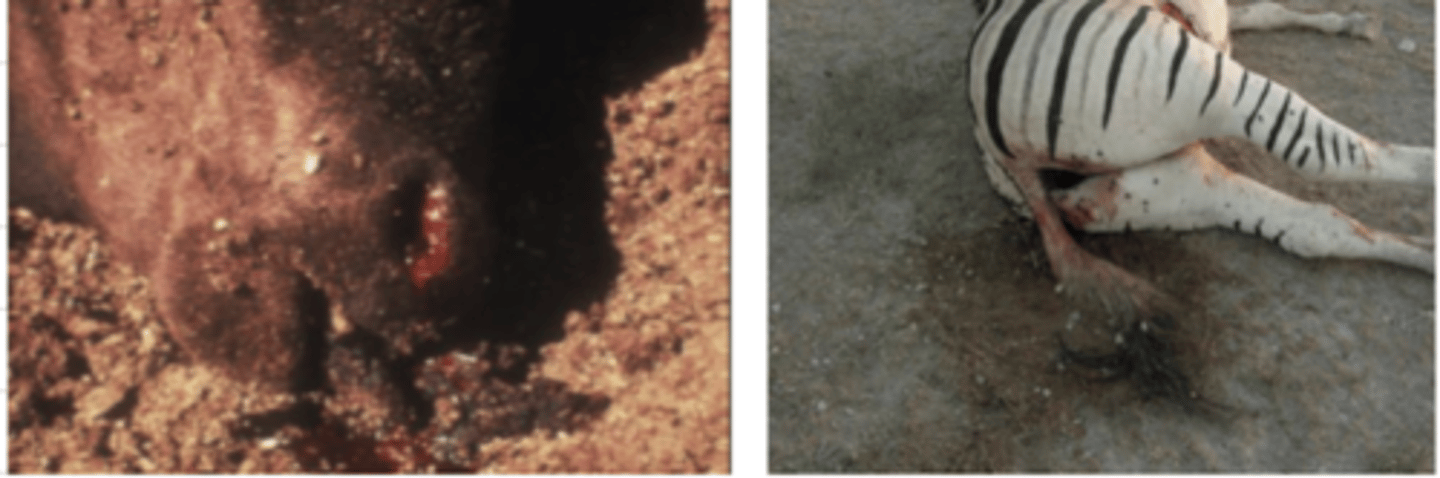
Bacillus anthracis
which bacteria looks like this with the methylene blue stain?
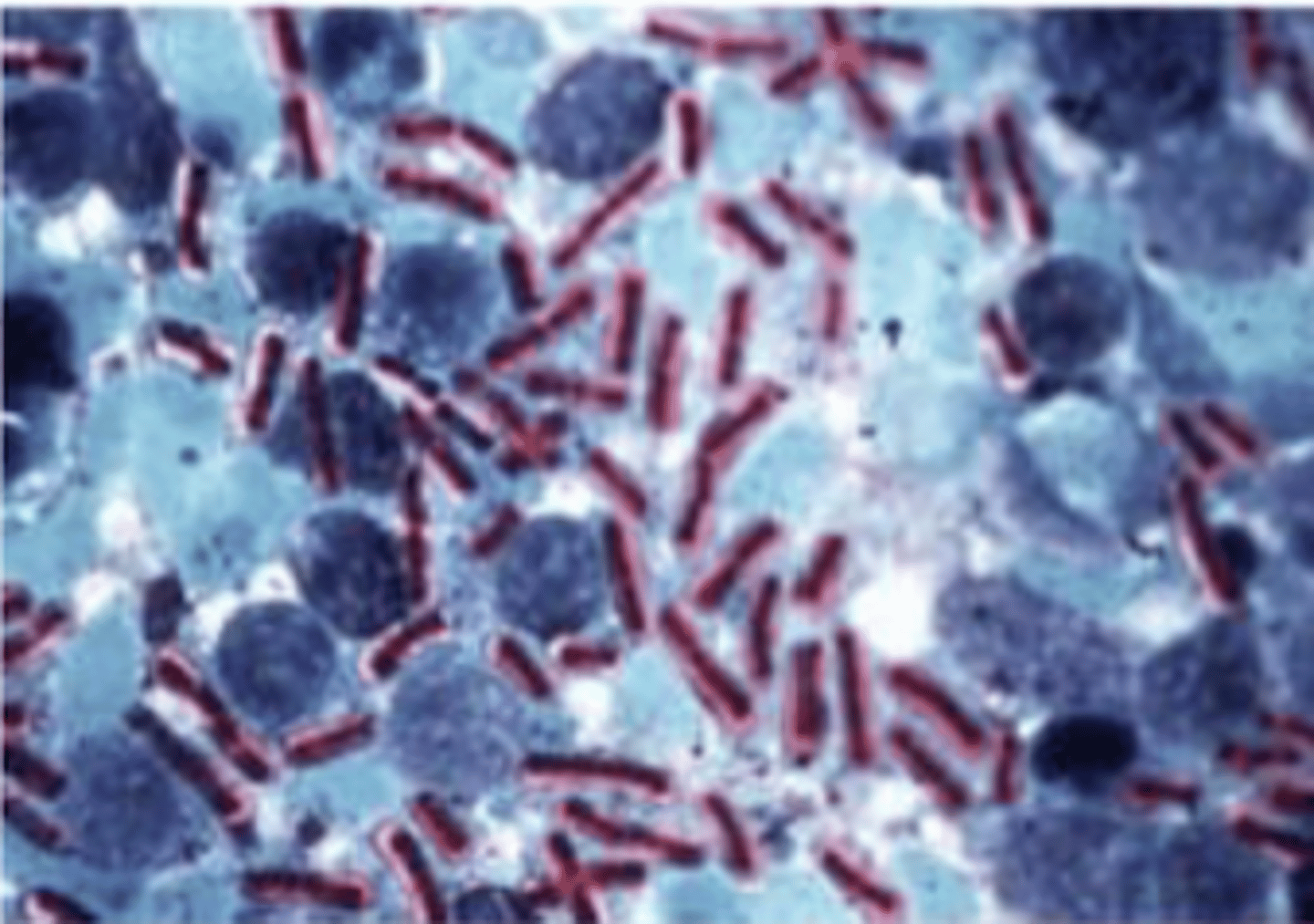
chains of purple rods
how does Bacillus anthracis appear with the gram stain?
no
does Bacillus anthracis grow on macconkey agar?
no
is Bacillus anthracis hemolytic?
Bacillus anthracis
which bacteria is this, on non enriched media?
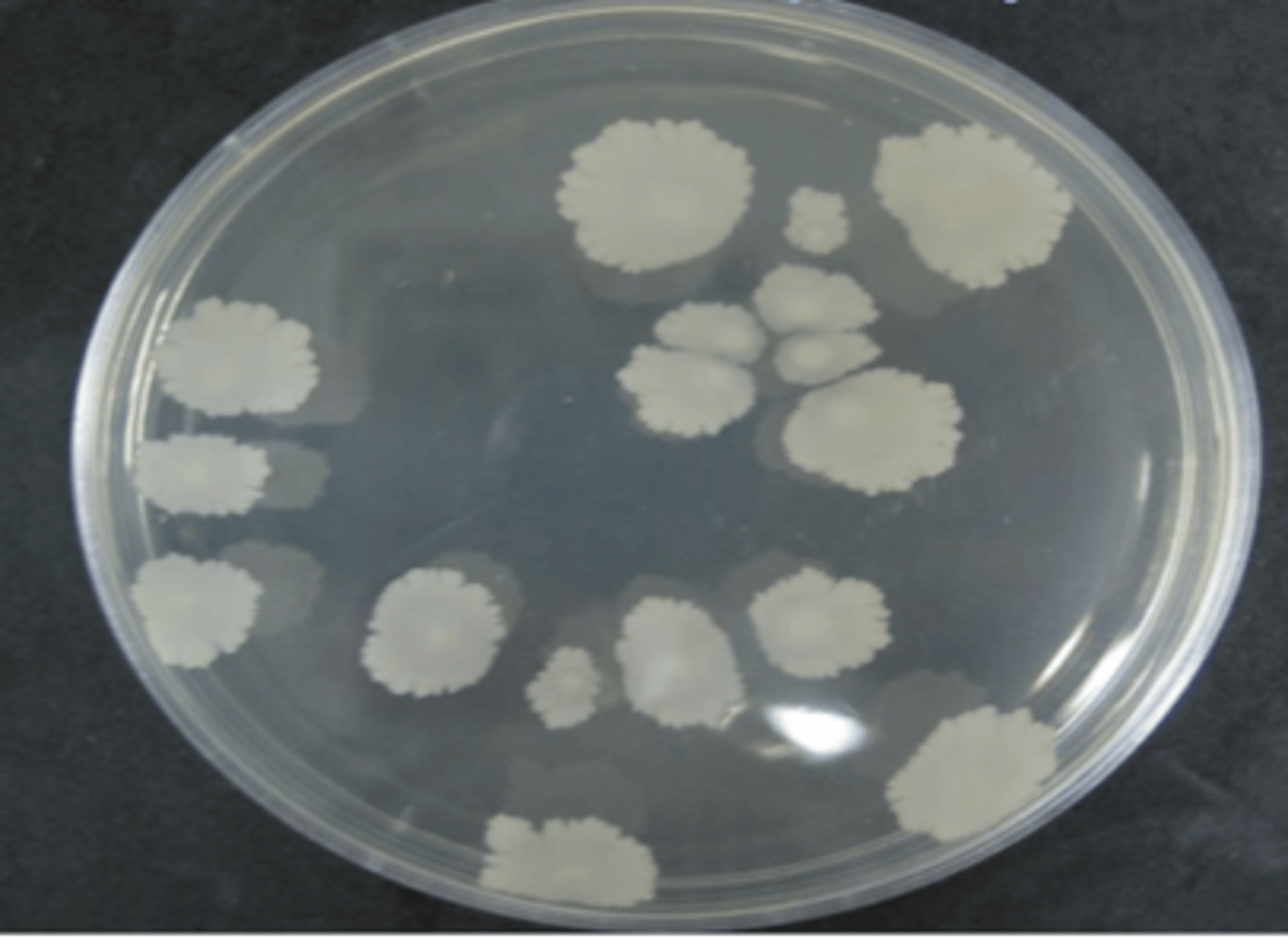
purple rods
how does Clostridium appear with the gram stain?
no- it is anaerobic
can we isolate Clostridium with oxygen?
catalase-
oxidase-
what are the results of Clostridium's catalase and oxidase tests?
yes, except P. perfringens
is Clostridium motile?
soil, GI tract (intestines), muscles, liver, feces
where is the usual habitat of Clostridium?
C. tetani
C. botulinum
what are the neurotoxic species of Clostridium?
C. chavoei
C. septicum
C. perfringens
which are the histotoxic species of Clostridium?
C. perfringens
C. dificile
which are the enteropathogenic species of Clostridium?
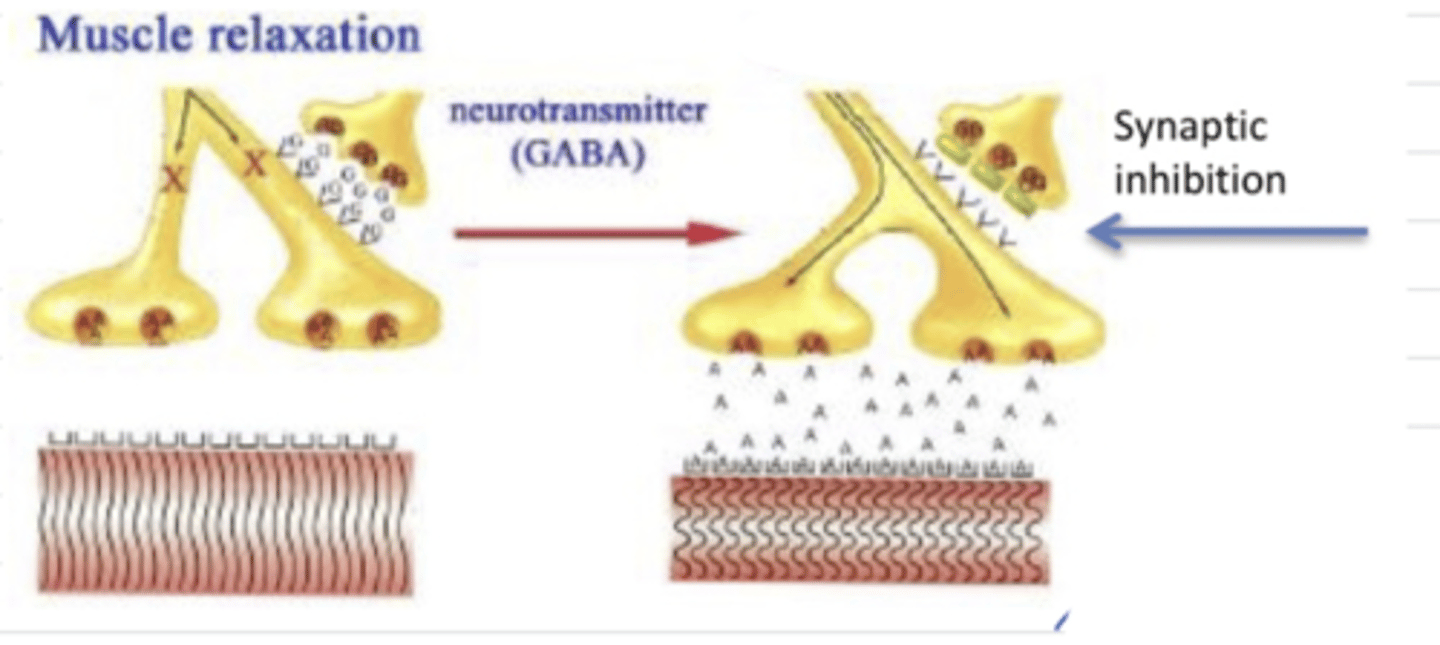
it inhibits the transmission of GABA between neurons. GABA's function is to inhibit AcH transmission to the muscle fibers, stopping contraction. However, because C. tetani inhibits it, AcH continues to be transmitted and muscle spasms occur
what is the mechanism of Clostridium tetani in the body?
Clostridium tetani
this is the mechanism of which bacteria?
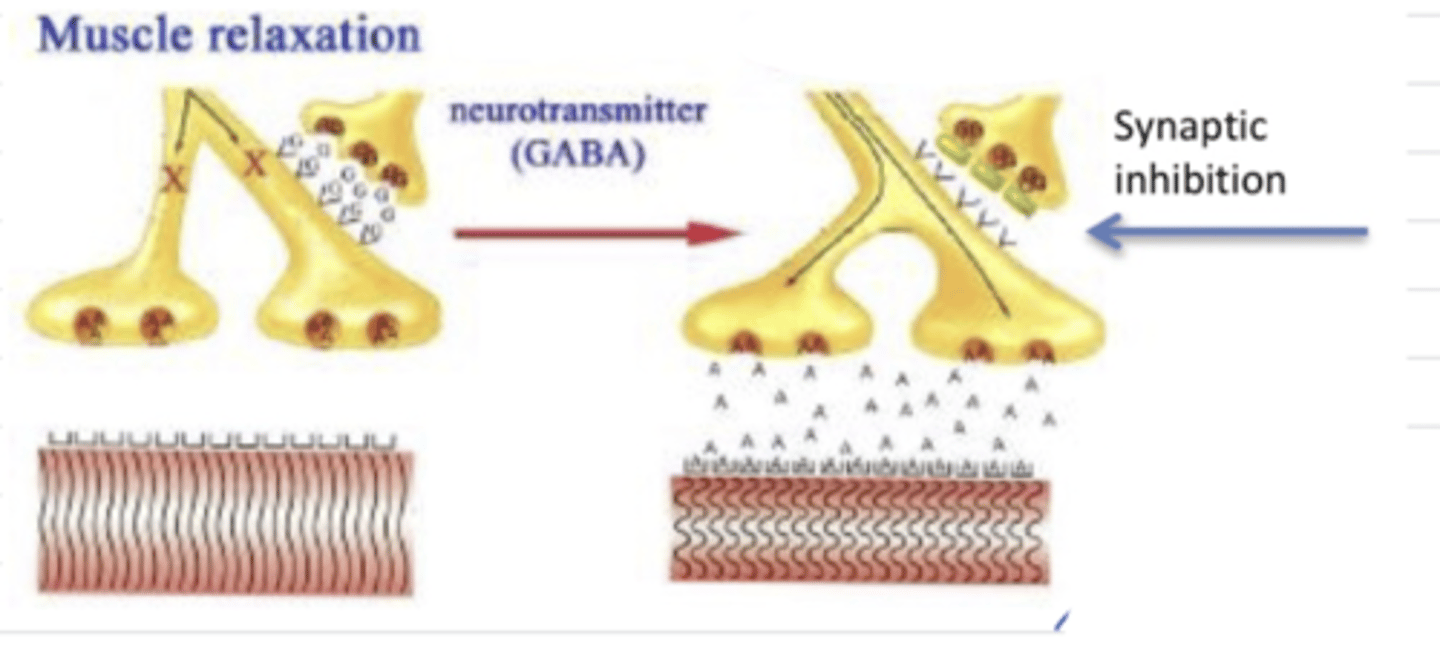
Clostridium tetani
muscle tremors and lock jaw is the affect of what bacteria?
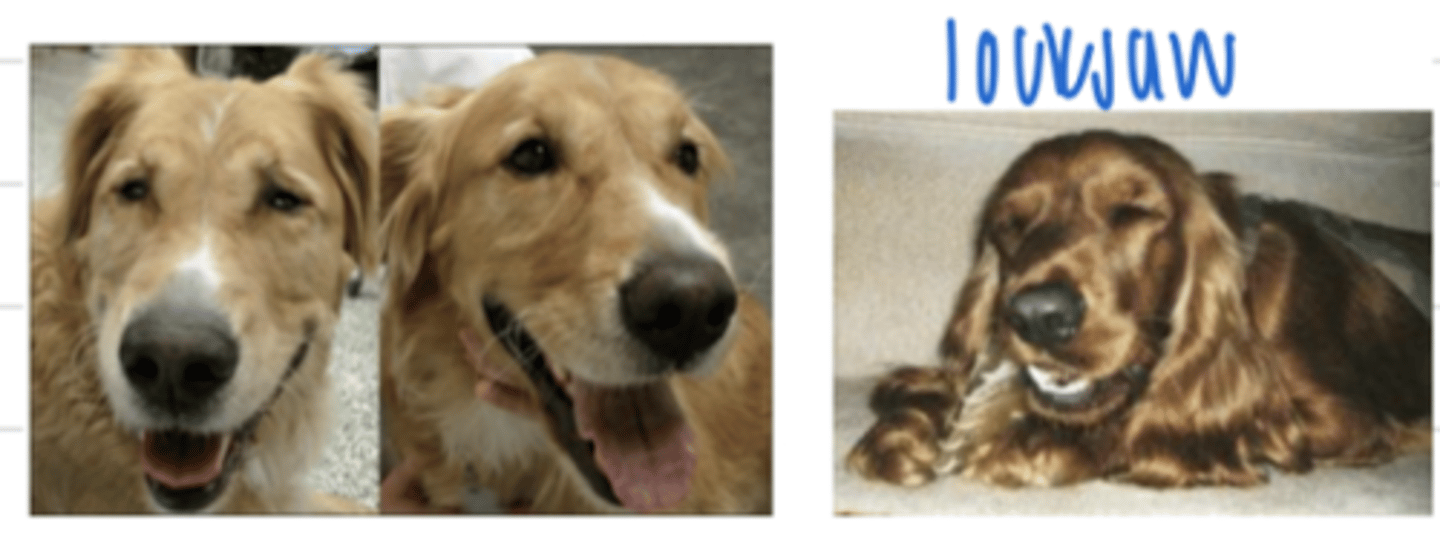

Clostridium tetani
which bacteria has an effect on synaptic junctions between 2 neurons?
it inhibits the release of AcH in the neuromuscular junction, so the muscles cannot contract= flaccid paralysis
what is the mechanism of Clostridium botulinum in the body?
Clostridium botulinum
which bacteria causes flaccid paralysis?
Clostridium botulinum
these are all symptoms of an infection of...

wounds
Clostridium tetani produces its neurotoxins in......
canned food
Clostridium botulinum produces its neurotoxins in...
Clostridium chauvoei
which bacteria causes blackleg disease?
cattle- endogenous (from spores in muscles)
sheep- exogenous
is a Clostridium chauvoei infection endogenous or exogenous?
local necrosis and systemic affects
histotoxins of Clostridium cause what?
Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium septicum
which Clostridium species causes gas gangrene?
-malignant edema
-braxy
-big head in young rams
-gas gangrene
what are the effects of Clostridium septicum?
Clostridium septicum
which bacteria can cause big head, braxy, malignant edema, and gas gangrene?
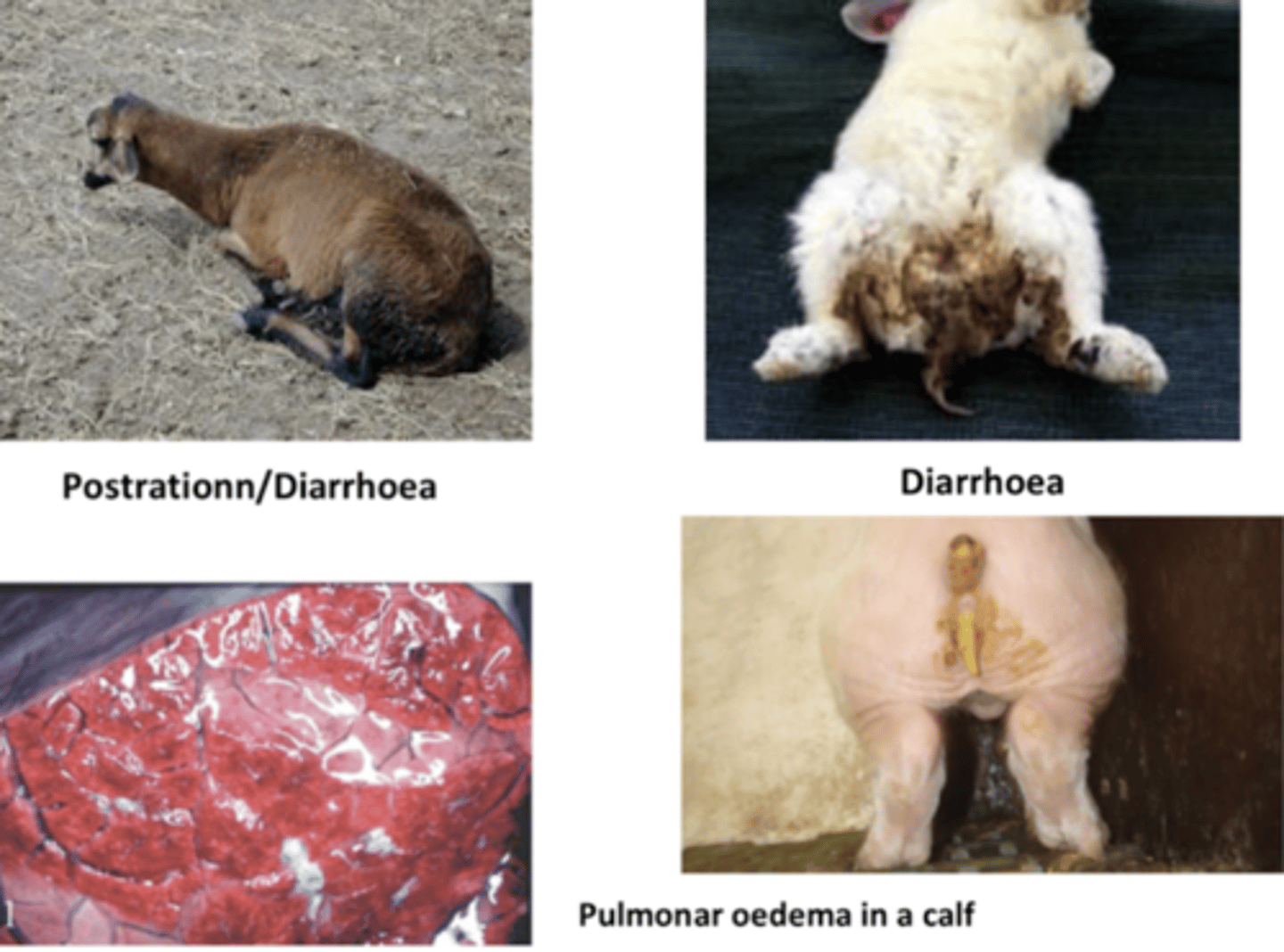
gas gangrene, diarrhea, hemorrhages
chickens- necrotic enteritis, gangrenous dermatitis
pigs- necrotic enterocolitis
what are the effects of Clostridium perfringens?
Clostridium dificile
which species of Clostridium is very difficult to isolate and treat?
Clostridium dificile
which bacteria produces exotoxins that alter the function of enterocytes, ultimately causing diarrhea?
although they are enteropathogenic, sometimes the bacteria is absorbed into the blood stream and goes to the lungs
why can Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium dificile sometimes cause pulmonary edema?
Clostridium dificile and Clostridium perfringens
which bacteria can cause this?
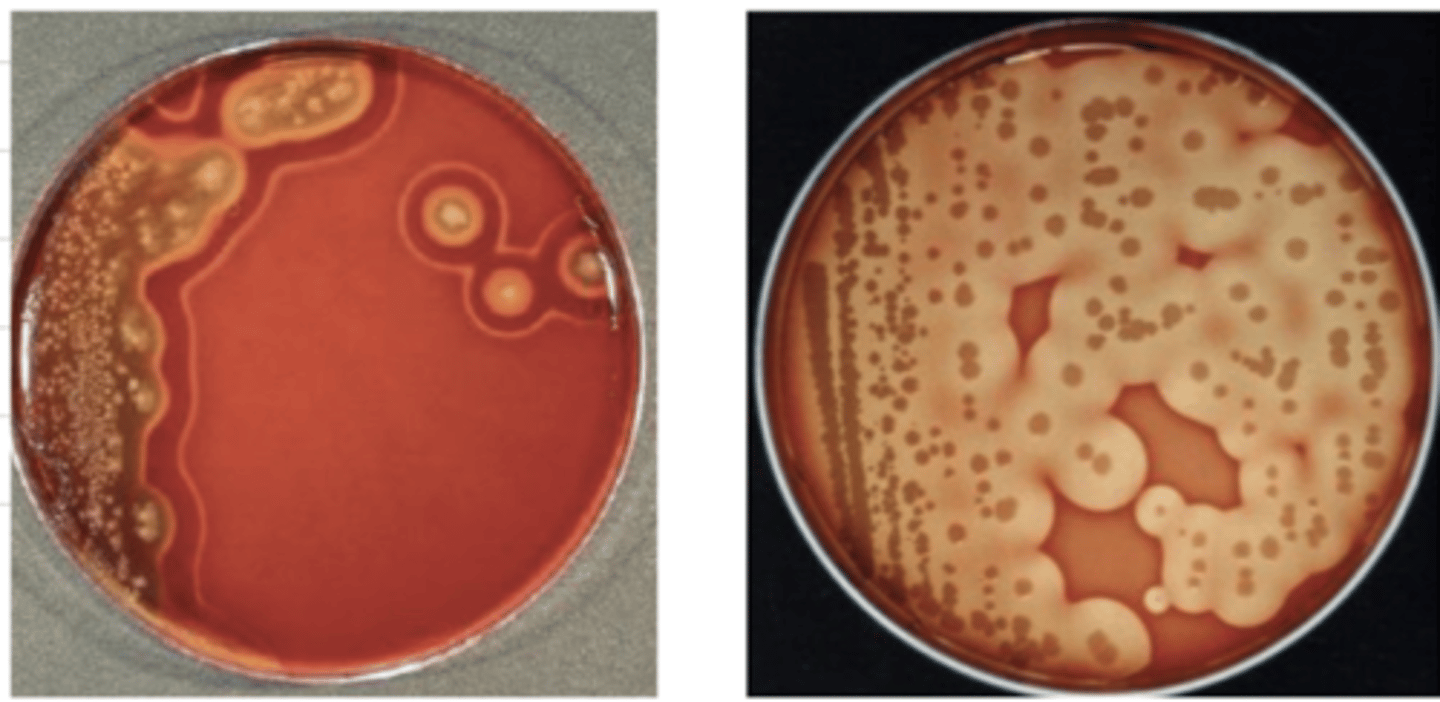
yes- it is double hemolytic
is Clostridium hemolytic?
Clostridium
which bacteria produces this result in blood agar?
Clostridium botulinum
this is the mechanism of what bacteria?