L4// Biology: Carbohydrates and Lipids - Structure, Function, and Diversity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Organic Compound
A compound containing carbon
Carbon Valence
Carbon (valence = 4) can form four covalent bonds with other atoms
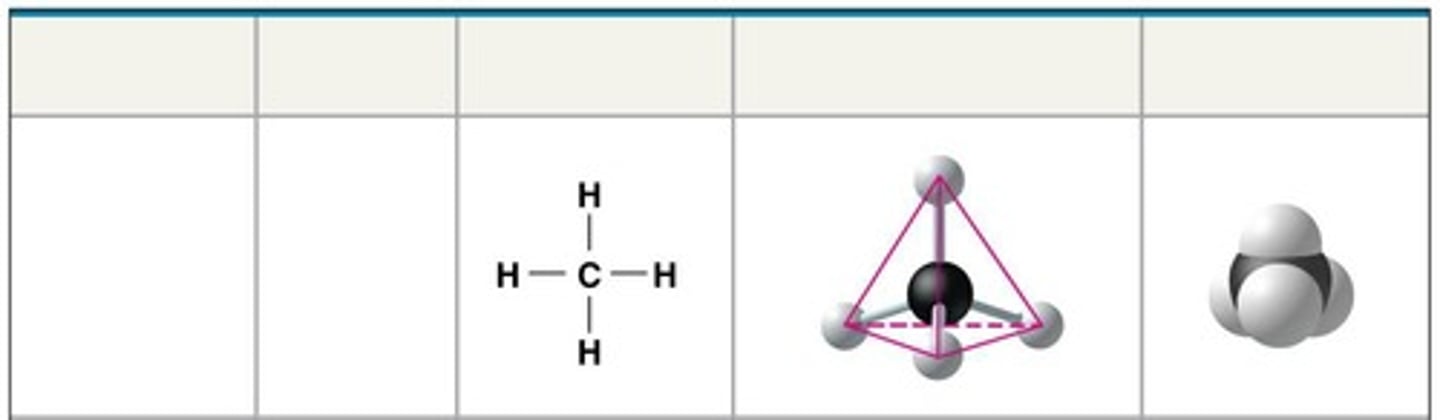
Methane
Molecular formula: CH4
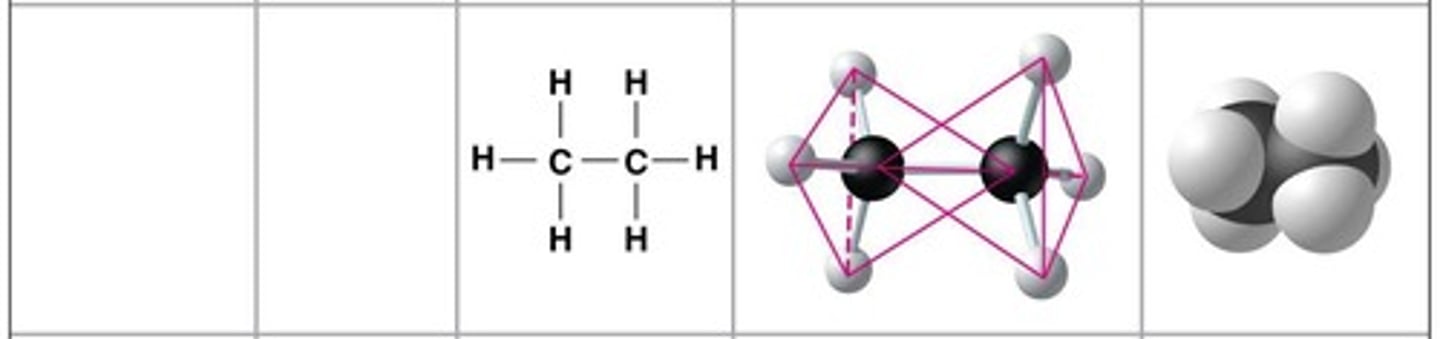
Ethane
Molecular formula: C2H6
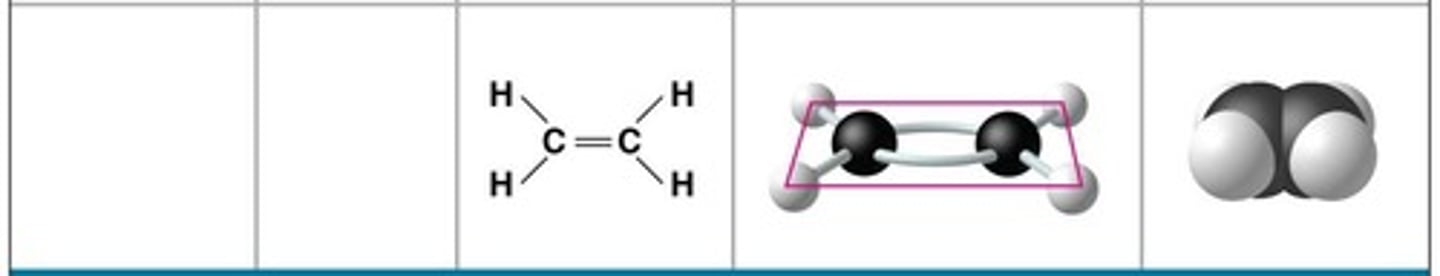
Ethene (ethylene)
Molecular formula: C2H4
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
Polymers
Macromolecules built from monomers
Monomers
The small building-blocks of molecules
Dehydration Reaction
Occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
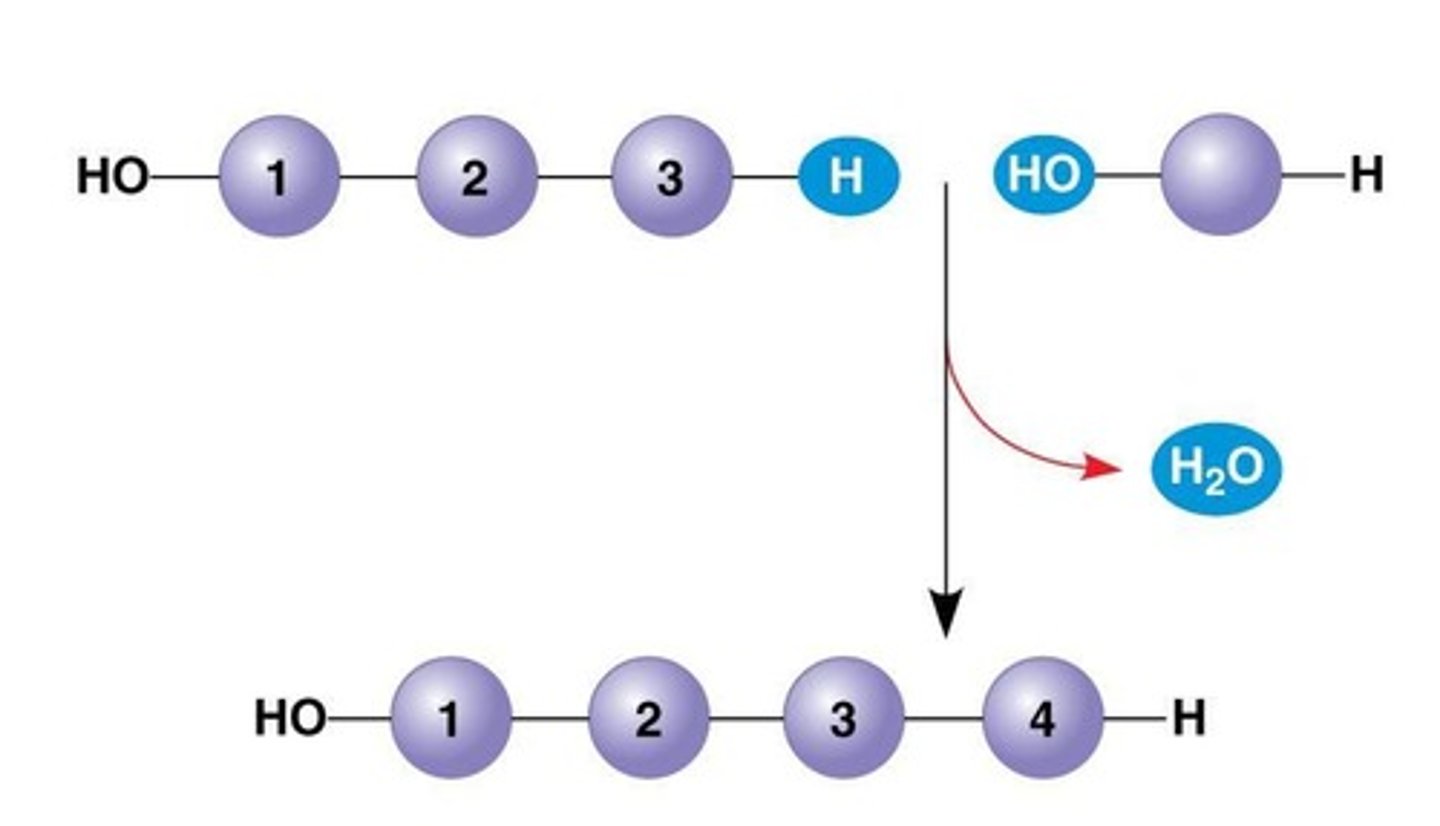
Hydrolysis
The reverse of dehydration reaction, breaking down a polymer into monomers
Monosaccharides
The simplest carbohydrates, or simple sugars
Glucose
The most common monosaccharide, molecular formula: C6H12O6
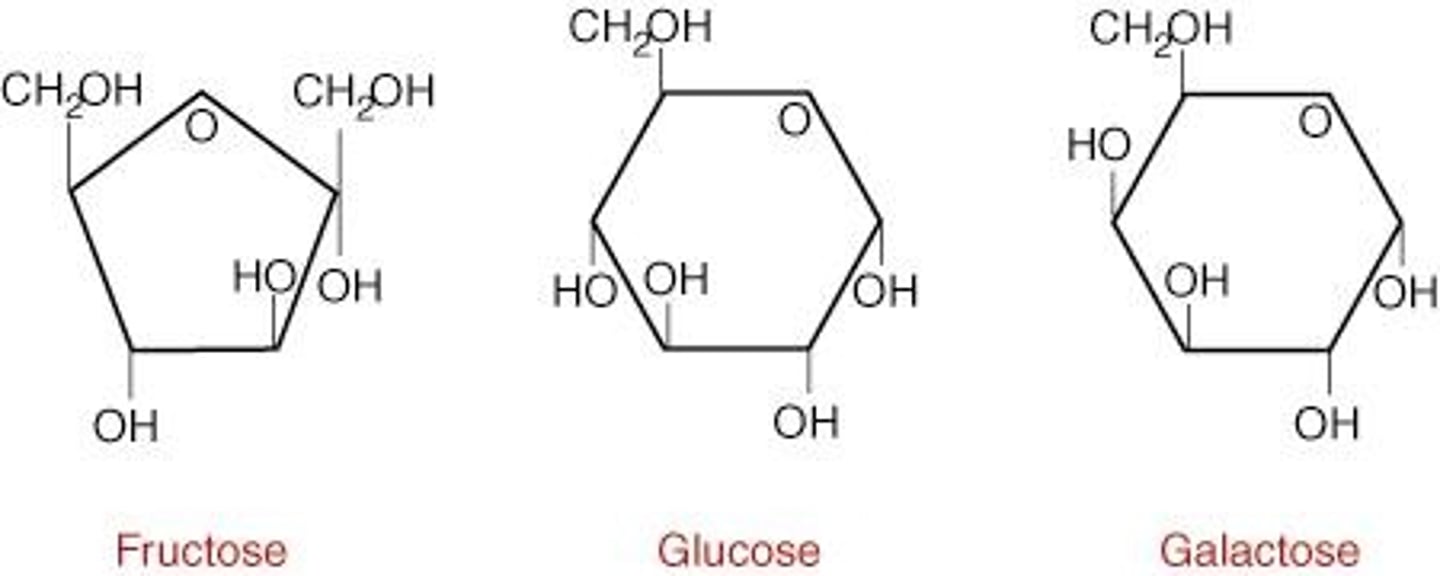
Hexoses
6-carbon sugars
Triose
3-carbon sugars
Pentose
5-carbon sugars
Disaccharide
Formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides
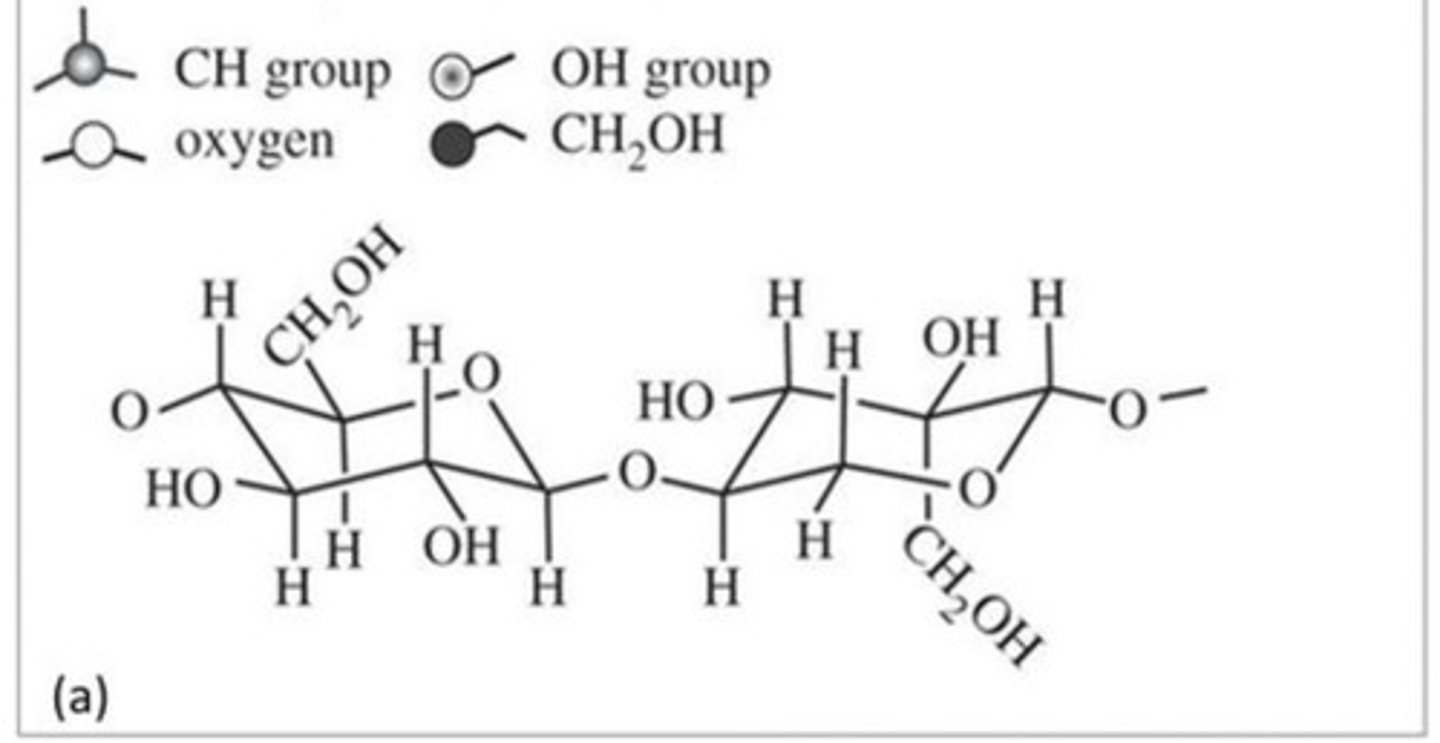
Glycosidic Linkage
The covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides
Starch
A storage polysaccharide of plants, consisting entirely of glucose monomers
Glycogen
A storage polysaccharide in animals, mainly stored in liver and muscle cells
Cellulose
A major component of the tough wall of plant cells, a polymer of glucose
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of arthropods and cell walls of fungi
Energy Storage in Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have more free energy than CO2
Fatty Acids
Components of fat molecules with a higher ratio of C-H and C-C bonds to C-O bonds
Lipid
What is a Lipid?
Lipid Characteristics
Largely nonpolar and hydrophobic
Lipids
Do not dissolve in water due to their hydrocarbon components.
Saturated Fatty Acid
Fatty acid chains that consist of only single bonds between the carbons.
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Fatty acid chains that contain one or more double bonds, causing kinks in the chains.
Highly Saturated Fats
Solid at room temperature and more common in animals than in plants.
Highly Unsaturated Fats
Liquid at room temperature.
Triacylglycerols
Fats composed of three fatty acids linked to glycerol.
Ester Linkage
The bond formed between the hydroxyl group of glycerol and the carboxyl group of a fatty acid.
Steroids
A family of lipids distinguished by a bulky, four-ring structure.
Cholesterol
A steroid that is an important component of plasma membranes in many organisms.
Phospholipids
Membrane-forming lipids that contain a polar, hydrophilic region and a nonpolar, hydrophobic region.
Lipid Micelles
Structures formed when phospholipid heads face the water and tails face each other.
Phospholipid Bilayers
Two sheets of phospholipid molecules that align with hydrophilic heads facing a surrounding solution.
Selective Permeability
The ability of membranes to allow some substances to pass while excluding others.
Permeability Scale
A measure of how easily different substances can cross phospholipid bilayers.
Fluidity of the Membrane
Refers to how individual phospholipids can move laterally within the lipid bilayer.
Fluid-Mosaic Model
Describes the structure of membranes as a dynamic mosaic of phospholipids and proteins.
Integral Proteins
Proteins that span the membrane and can affect membrane permeability.
Transmembrane Proteins
Integral proteins that span the membrane and are involved in the transport of selected ions and molecules.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins found only on one side of the membrane, often attached to integral proteins.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Interactions that reduce the permeability of membranes by preventing close packing of hydrocarbon tails.
Cis Double Bonds
Double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids that introduce kinks into hydrocarbon chains.
Hydrophilic Region
The part of phospholipids that contains highly polar covalent bonds.
Hydrophobic Region
The part of phospholipids that consists of nonpolar fatty acid or isoprene chains.
Biological Role of Lipids
Lipids serve various functions including energy storage, membrane structure, and signaling.
Physical State of Lipids
Affected by bond saturation; saturated fats are solid, while unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature.
Membrane Function
To keep damaging materials out of the cell and allow entry of materials needed by the cell.
Hydrophobic Tails
The nonpolar parts of phospholipids that face each other inside the bilayer.