Chapter 18 Electric Forces + Electric Fields
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Electric Charge
positive/negative, like charges repel and unlike charges attract one another, always conserved and only exchanged
Unit=Coulomb
Symbolized by e
e=1.6×10-19 C
Conductors
materials in which the electric charges move freely, when charged in small region, charge readily distributes itself over entire surface of material
Example: copper/aluminum/silver
Insulators
materials in which electric charges do not move freely, when charged by rubbing, only rubbed area becomes charged
Example: glass/rubber/plastic
Semiconductors
characteristics of it are between those of insulators and conductors
Example: silicon/germanium
Proton
charge e+
positive charge
doesn’t move from one material to another because held firmly in nucleus
Electron
charge of e-
negative charge
gaining/losing electrons is how an object becomes charged, negative charge move from one object to another
Coulomb’s Law
the attraction of a particle is inversely proportional to the square of the separation between 2 particles and is along the joining line
Equation: F = k * (q1 * q2) / r2
K=9×109 Nm2/C2
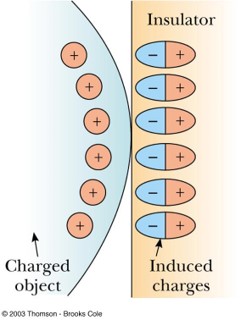
Polarization
the realignment of charge on the surface of an insulator, where the center of positive charge in neutral atoms or molecules may separate slightly in the presence of a charged object
Example: charged comb attracts bits of paper due to polarization of the paper
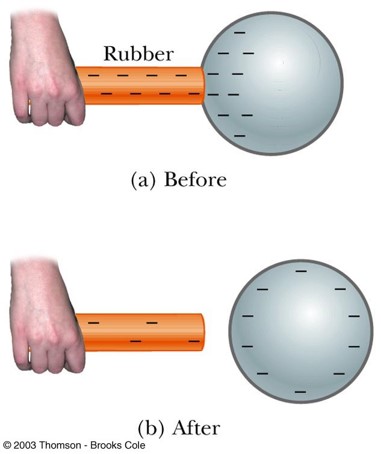
Charging by Conduction
when a charged object, like a rod, contacts a charged sphere, electrons move to the sphere, leaving the sphere with same charge as the charging object
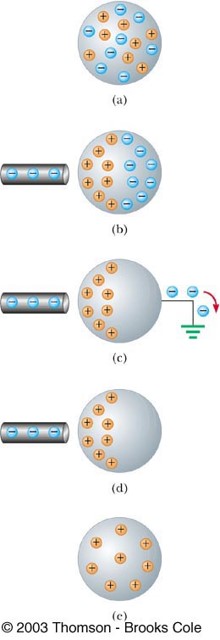
Charging By Induction
requires no contact with the object inducing the charge, when a charged object attracts a neutral object, causing electrons to temporarily redistribute charges within the neutral object
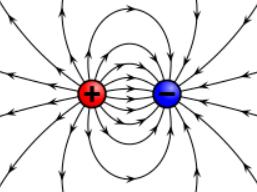
Electric Field Pattern
a pattern of lines around a charged object; the lines indicate the direction a positively charged particle will move in the field
Electric Field of a Charge
the space around the charge in which an electric force due to that charge is experienced
3x^4+18=21x^2