Economics Test 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Macroeconomics
study of whole part of economy and how each economy (country’s, city, etc) interact with others
Minimum wage, unemployment rate, inflation, GDP
Who is considered the founder of modern macroeconomics?
John Maynard Kaynes
Believe government do big things (policy, funding, etc) and change country state
Microeconomics
study of individuals, households, firms in decision making and allocation of resources
Business making decisions, how narrow policies affect single entities, individual markets
Opportunity cost
most desirable alternative that was given up as result of final decision being made/chosen
Can only be one
Most important option picked, next important option given up (opportunity cost)
Trade-offs
other things you give up beside most desirable outcome/alternative
Individual trade-offs
personal choices made
ex: personal spending or time allocation
Business trade-offs
how to use land, labor, capital
Society trade-offs (relate to gov)
chose where to what to spend money on -> ex: fund social security or reduce payments and use government money for something else
“guns or butter”
Factors of production
land, labor, capital -> all resources sacre, must make decision on how to use/allocate them
Land
all natural resources
clean air and water, renewable and nonrenewable
Labor
the work you do
Capital
physical and human capital
Physical Capital:
tools used to do work/labor
Human Capital
your skills, ability, knowledge (soft and hard skills) -> you’re in control of the things you bring to table
Entrepreneurship is human capital (“skill”)
What is money?
Money serves as transaction
Use money to buy resource, physical capital, human capital, labor, natural resources
not a resource or factor of production
Scarcity
refers to state when resource is available in finite quantities at particular point of time (limited)
Usually created by nature and involve nature resources
Shortage
situation in which quantity of a good or service demand by consumers exceeds the quantity supplied at the current price
Usually created by ppl/market
What results from scarcity or shortages? (what is outcome?)
Both usually lead to limited availability of products and higher prices
Who is Adam Smith?
father of modern economics who outlined capitalism
What is Adam Smith’s theory of markets?
Invisible hand theory
What is the Invisible hand theory?
ppl are rational, make rational decisions for their best interests, leave them alone and economy sort itself out (reach equilibrium)
Gov don’t need to intervene in economy
Market sort itself out but take a long time
What book did Adam Smith write and when?
He wrote the Wealth of Nations in 1776
Free (capitalistic) economy
the government is less involved in the economy, doesn’t own factors of production, doesn’t plan the economy out (ex: doesn’t plan how much goods produced, production, etc), lets businesses/individuals run freely
Command economy (planned)
the government is heavily involved in economy, owns factors of production, plan the economy out (ex: how much wheat needs to produced, etc) in best interests of the people
How are economies mixed? (Mixed economy)
Economies combine elements of capitalism and command/planned economies together, usually get socialism
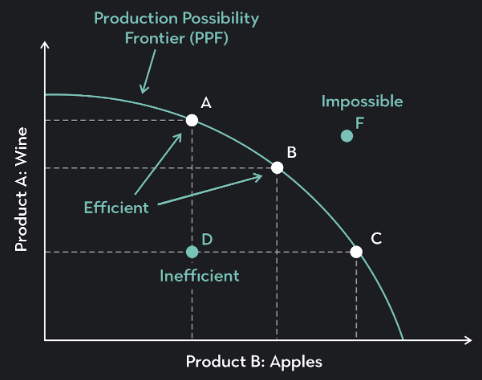
Explain the points on the Production Possibility Curve
points on the curve indicate production is at full capacity (efficient)
Points A, B, C
production is inefficient and not running at full capacity when point inside the curve → point D
economy cannot produce that amount of goods given current factors of production when point above/beyond the curve → point F
Efficient (PPF)
economy is running at full capacity
Inefficient (PPF)
economy is not running at full capacity
Have resources but not using them effectively
No demand for products
Layoffs, slowed production
Indicate recession
Impossible (PPF)
given current factors of production economy cannot product that amount of goods unless if factor of production are expanded
What can move a PPC to the impossible?
Increase of land, labor, capital, and technology to expand production
What does increasing and decreasing opportunity costs have in common?
a person/company must give up something when producing more of one good or another
Increasing Opportunity costs
production of a good increases, the opportunity cost of producing another good rises because resources cannot efficiently produce all goods equally
What is an example of increasing opportunity costs?
Ex: Starbucks only make coffee, and begin making sandwiches, overtime to maximize production, produce more sandwiches and less coffee
Decreasing Opportunity costs
cost of sacrificing production of main good diminishes as more resources are allocated to another good, often resulting from specialization or efficiency gains
What is an example of decreasing opportunity costs?
Ex: Apple initially face high cost for producing laptops and give up producing iphones, but overtime workers more specialized and give up less to produce iphone and laptops
Constant Opportunity costs
trade-offs between producing 2 goods remain unchanged/constant as production shifts
What is an example of constant opportunity costs?
Give up 5 tacos to produce 5 burgers
Comparative advantage
have comparative advantage in producing good or service if opportunity cost of producing good is lower for that individual than others
China make 10 cars a day and 5 shoes while America make 5 cars a day and 10 shoes—who has the comparative advantage in cars?
China have comparative advantage in cars
Absolute advantage
in an activity if individual do it better than others -> use less input and get more output, etc
China make 20 cars a day, while America make 10 cars a day—who has the absolute advantage?
China has the absolute advantage
What do countries do in trade? (involve comparative and absolute advantages)
In trade, 2 countries specialize in good where they have comparative advantage and trade for other product leading to better production and economic advantage
Productivity
amount of output per hour
Produce more output with less input or produce more output with same input
How does labor productivity increase?
increase when get more output with same input or same output with less input
How does productivity (overall) increase?
Increase through tech advance, improve worker skills, improve management practices