Abeka 7th Grade Science Test 3
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine
Trachea
The scientific name for the windpipe.
Spleen
The largest lymphatic organ.
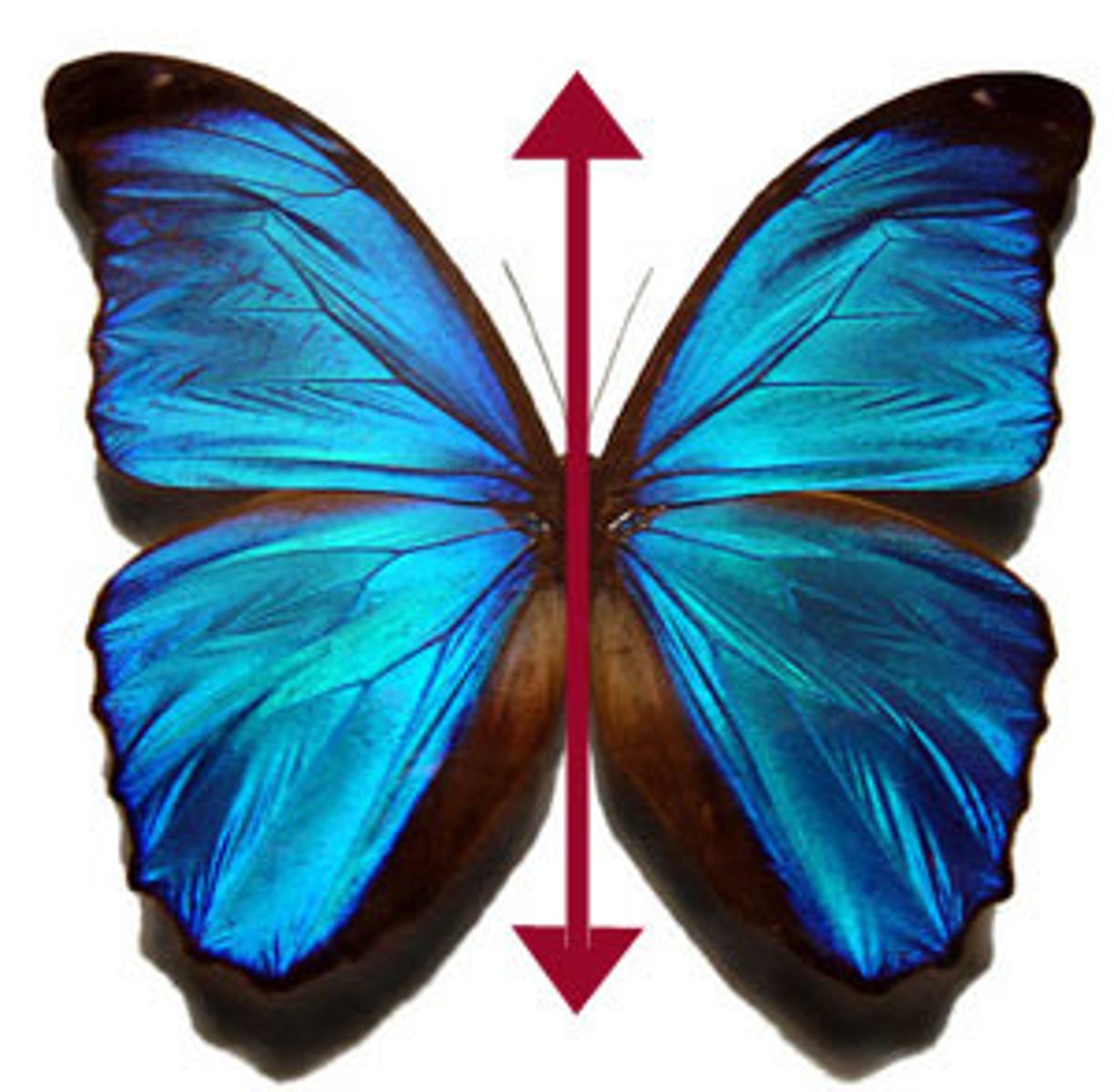
Bilateral symmetry
The type of symmetry that an organism has, that can be cut into equal halves in only ONE direction.

Placenta
The structure that exchanges oxygen and nutrients between the blood of an unborn child and his/her mother.
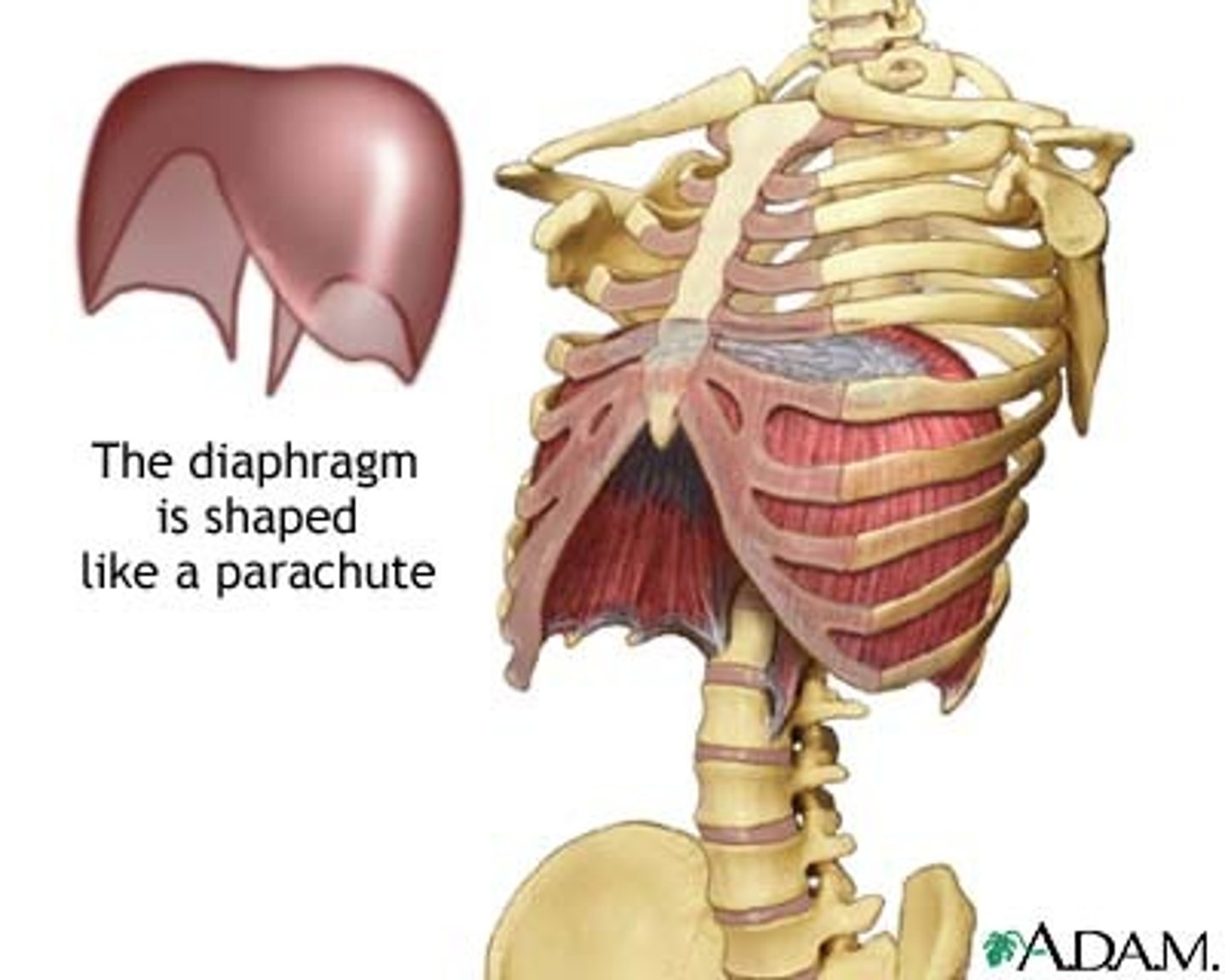
Diaphragm
Dome-shaped muscle that aids in breathing.
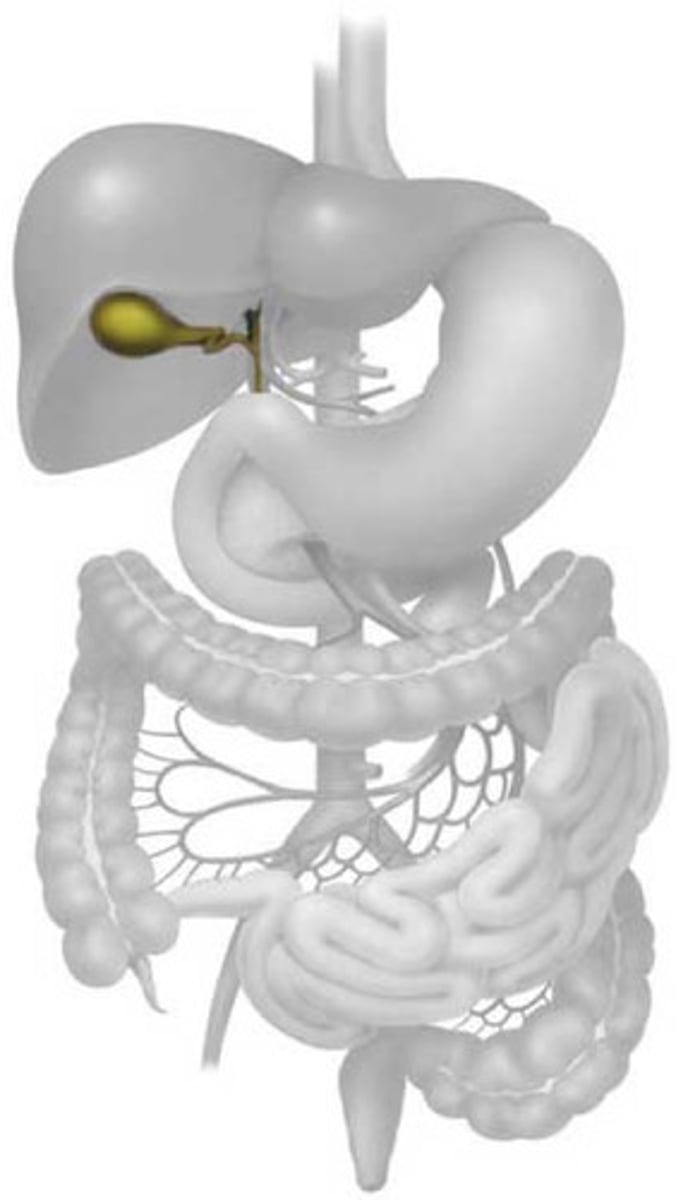
Gallbladder
The organ that stores bile.
Melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color

B cells
A type of white blood cell that matures in the thymus.
Spinal cord
The structure that controls simple reflexes.
Trunk
The portion of body that contains most of the vital organs.
Pea family
the plant family that restores nitrogen to the soil

Phloem
The plant tissues that carry food downward to the stems and roots.
Law
The scientific idea that has survived many experiments and observations without ever being proven false.
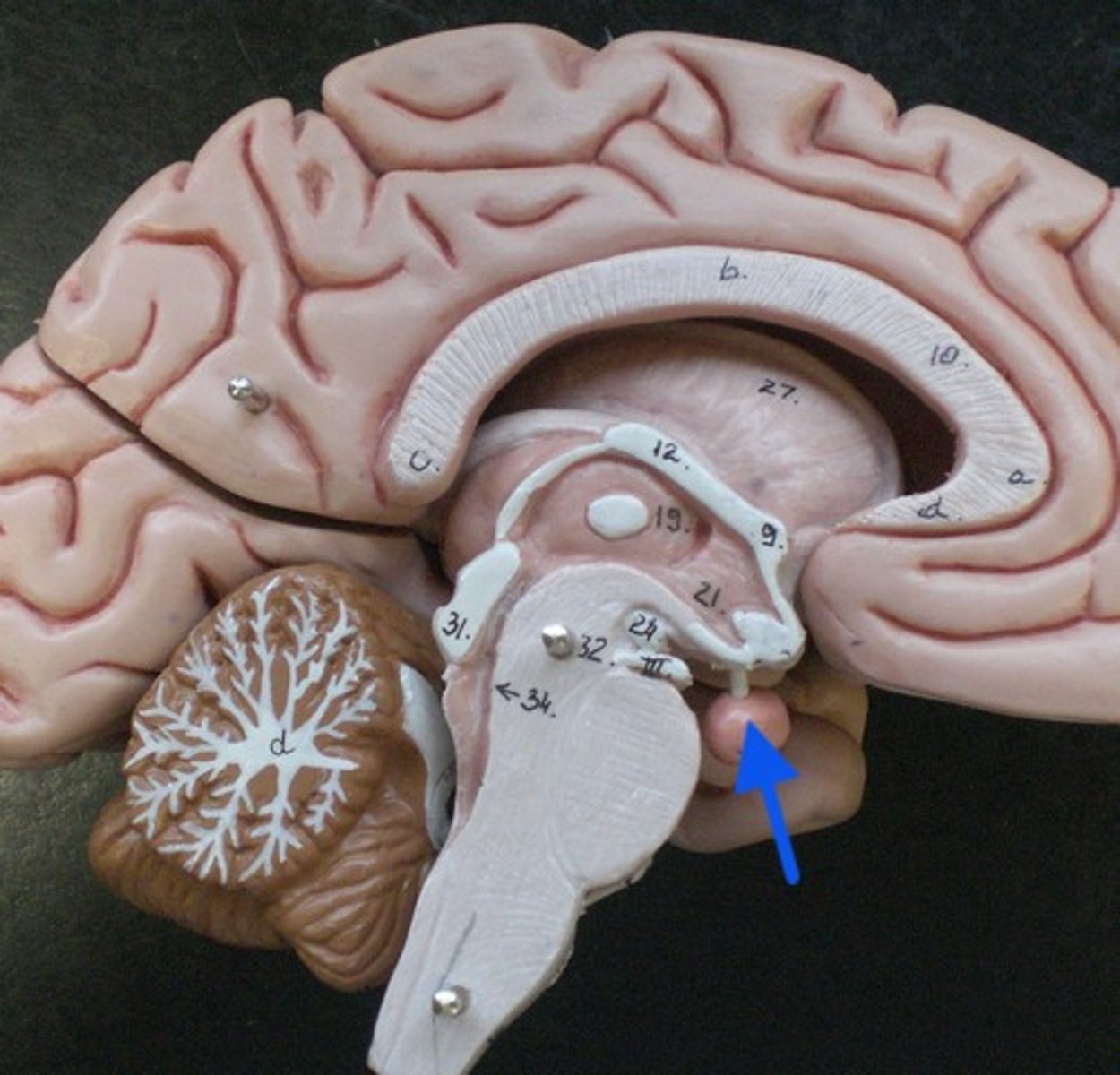
Pituitary gland
The gland that is considered the "master gland".
Simple leaf
The type of leaf that has only one blade attached to the petiole.

Ecology
The branch of biology that studies the relationships between organisms in their environment.
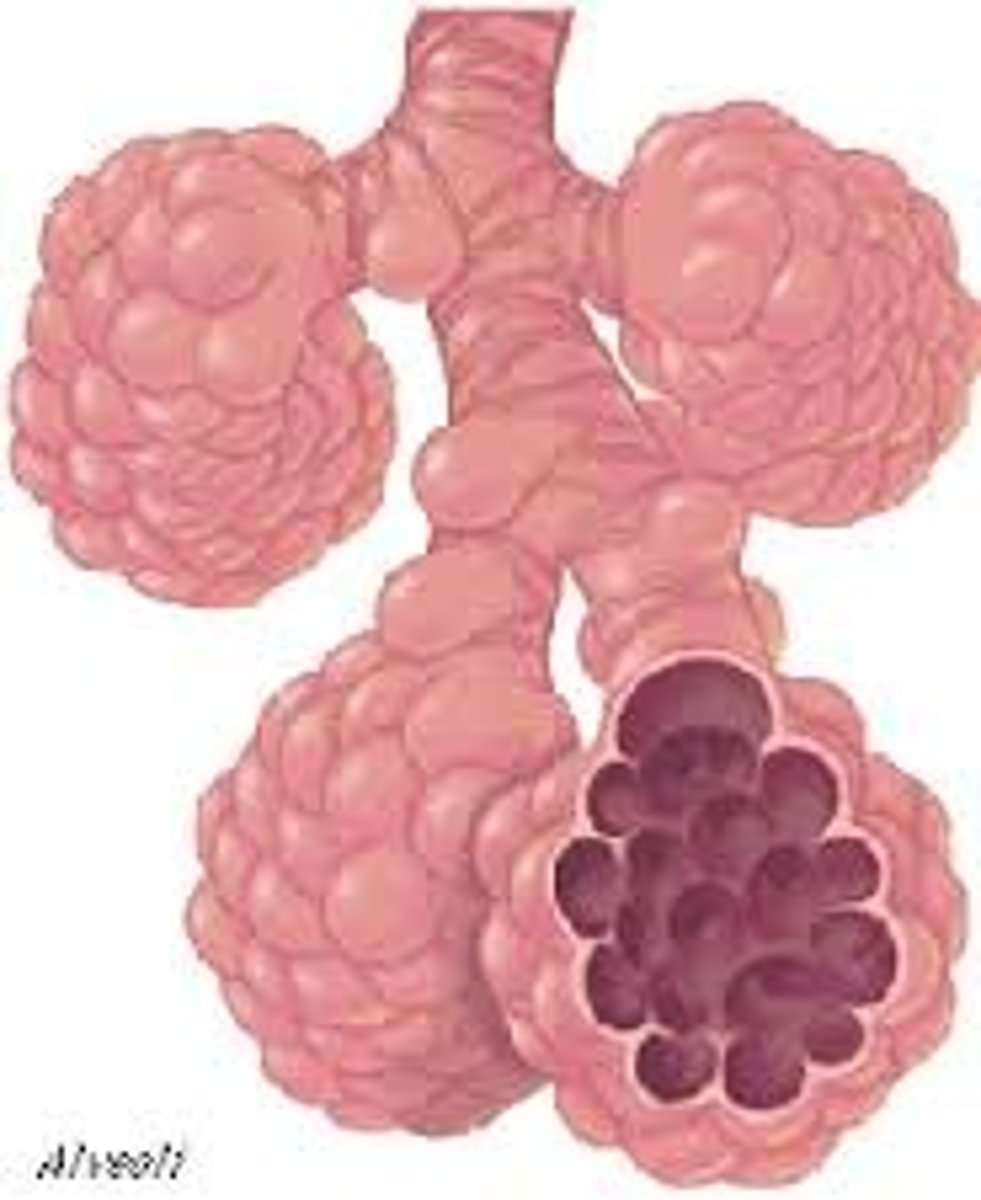
Alveoli
The air sacs in the lungs
Hypothesis
The sensible explanation to a scientific problem.
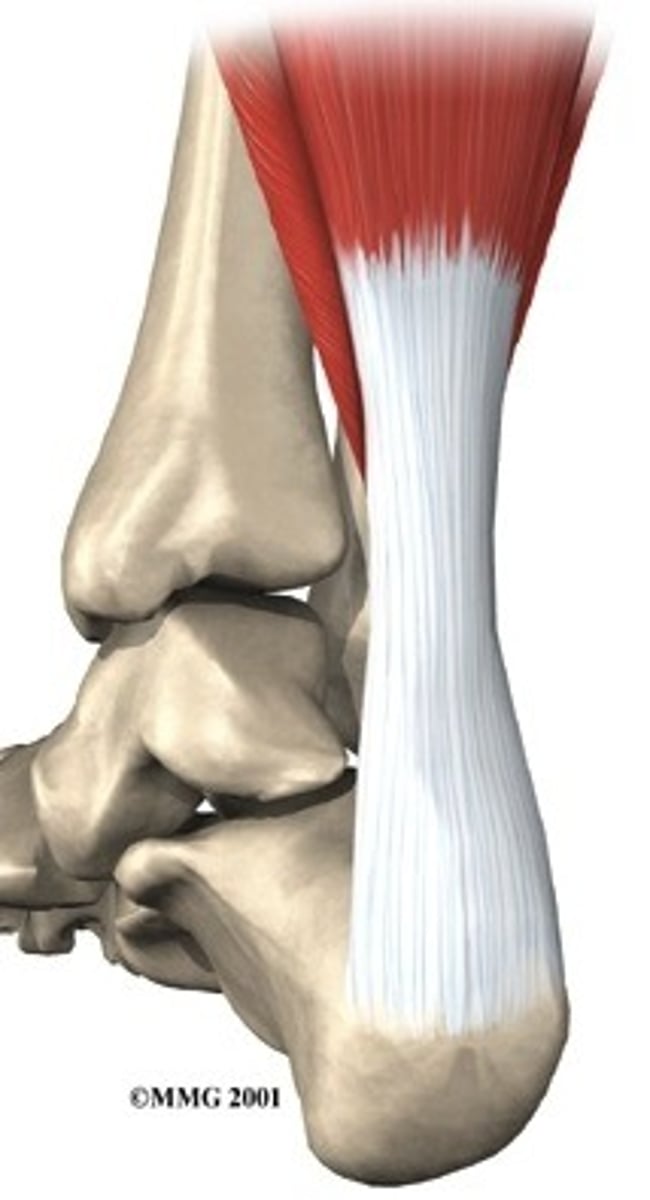
Tendon
The structure that connects bones to muscles.
Experimentation
The term that refers to the methodical testing of scientific ideas.
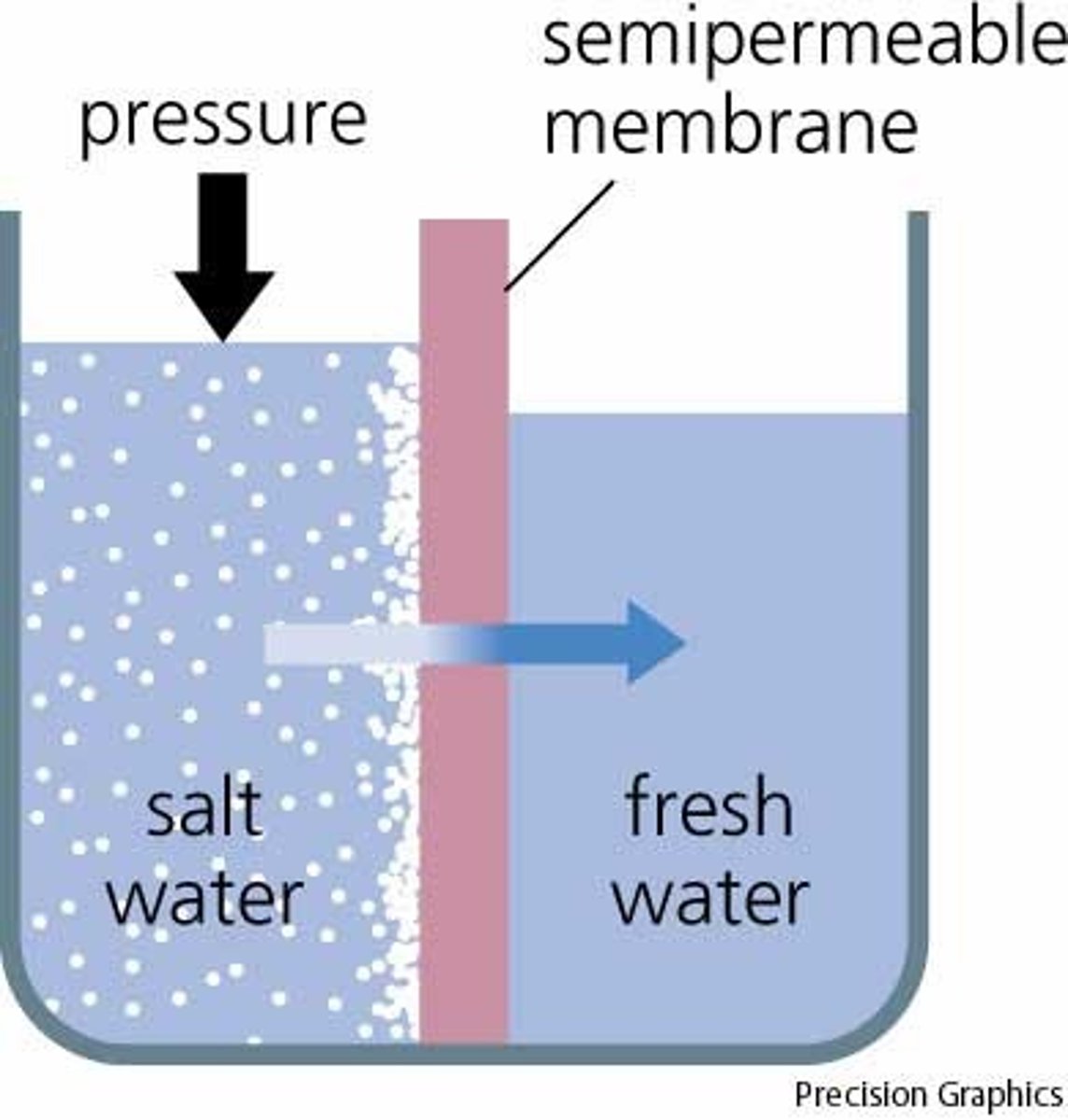
Osmosis
The process through which water in the soil enters a root's root hairs.
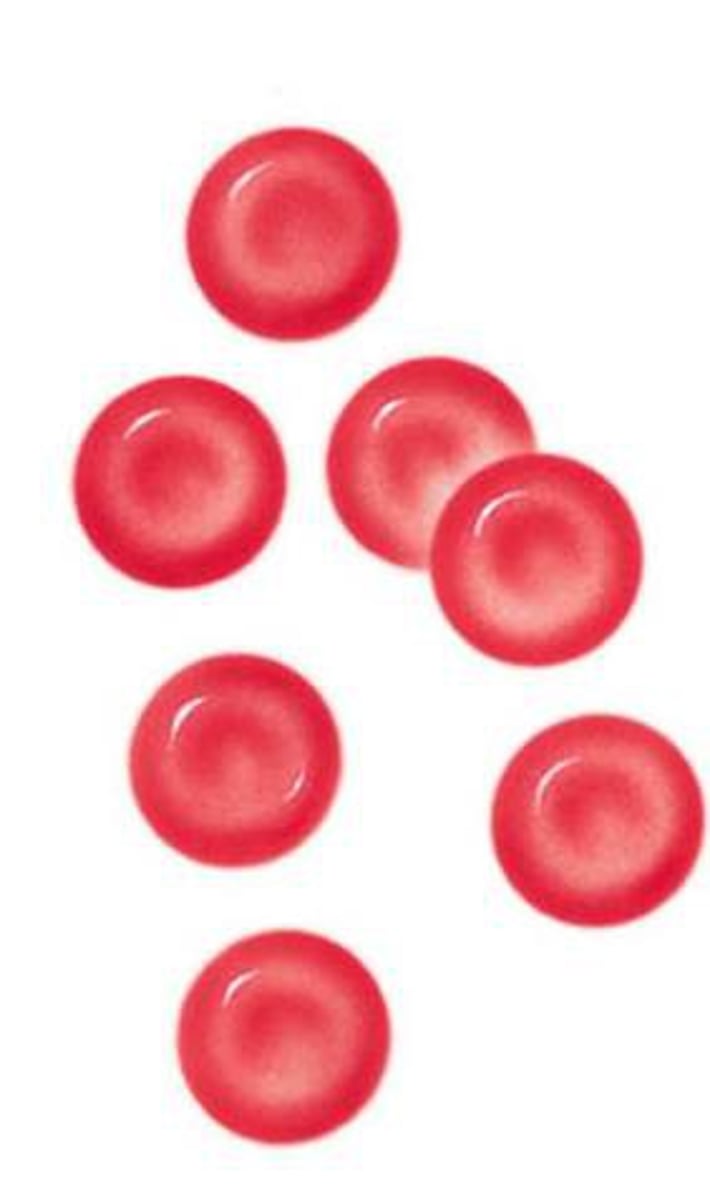
Red blood cells
Cells that carry oxygen through the blood.
Fauna
The term referring to animals in an environment.

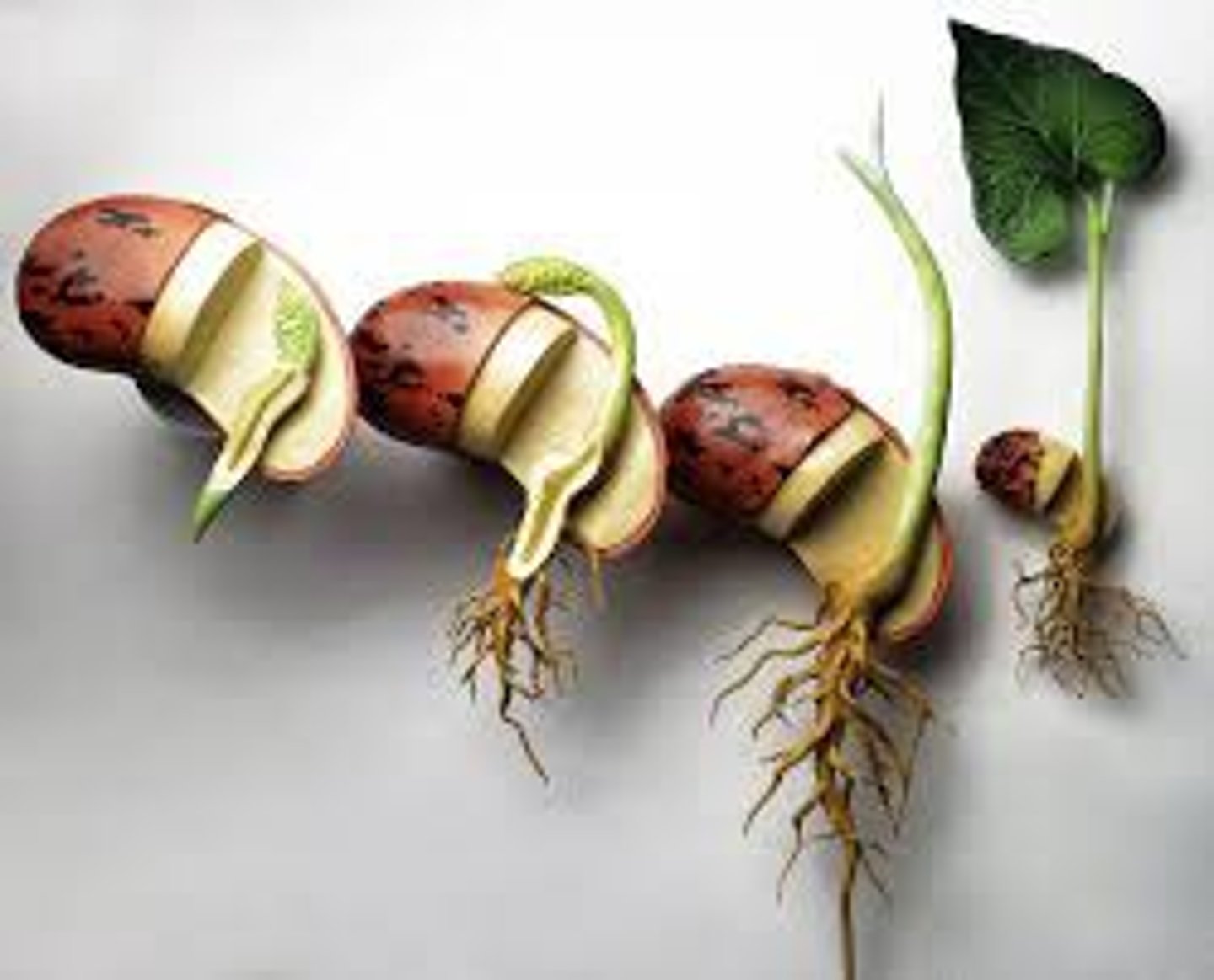
Germination
The early growth of a seed.

Reproduction
The process by which life continues through a new generation of organisms.
Fertilization
The uniting of a sperm cell and an egg cell.
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical processes of life.
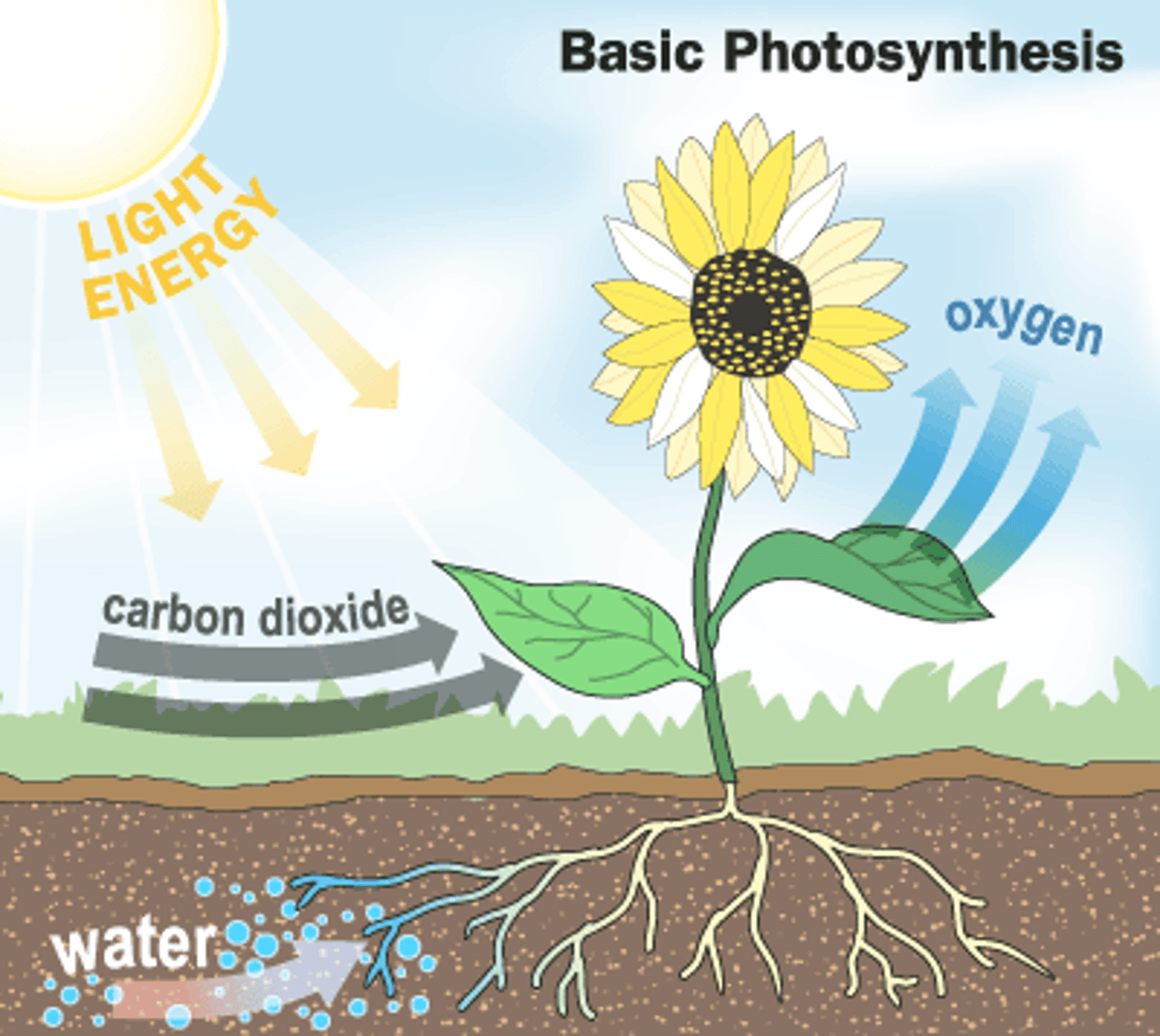
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants manufacture their food.
Seedling
a young plant that is no longer dependent on its cotyledons

Species
a distinct type of organism
Involuntary
Muscles that work without conscious thought.
Habitat
An organism's home within the environment.
Logic
The study of reasoning .
Appendicular
One of the main divisions of the skeleton.
Fruit
A ripened flower ovary.

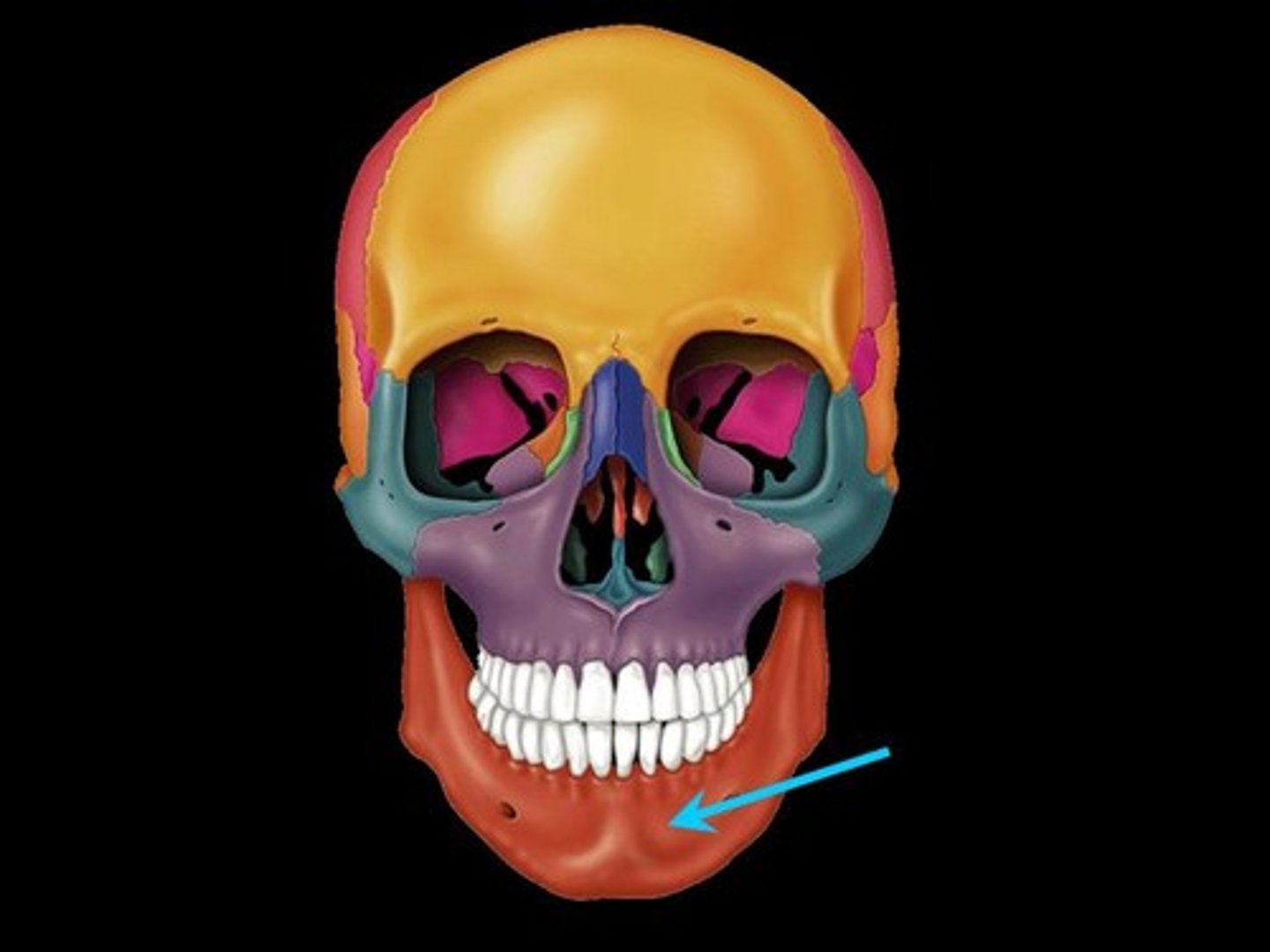
Mandible
lower jaw bone
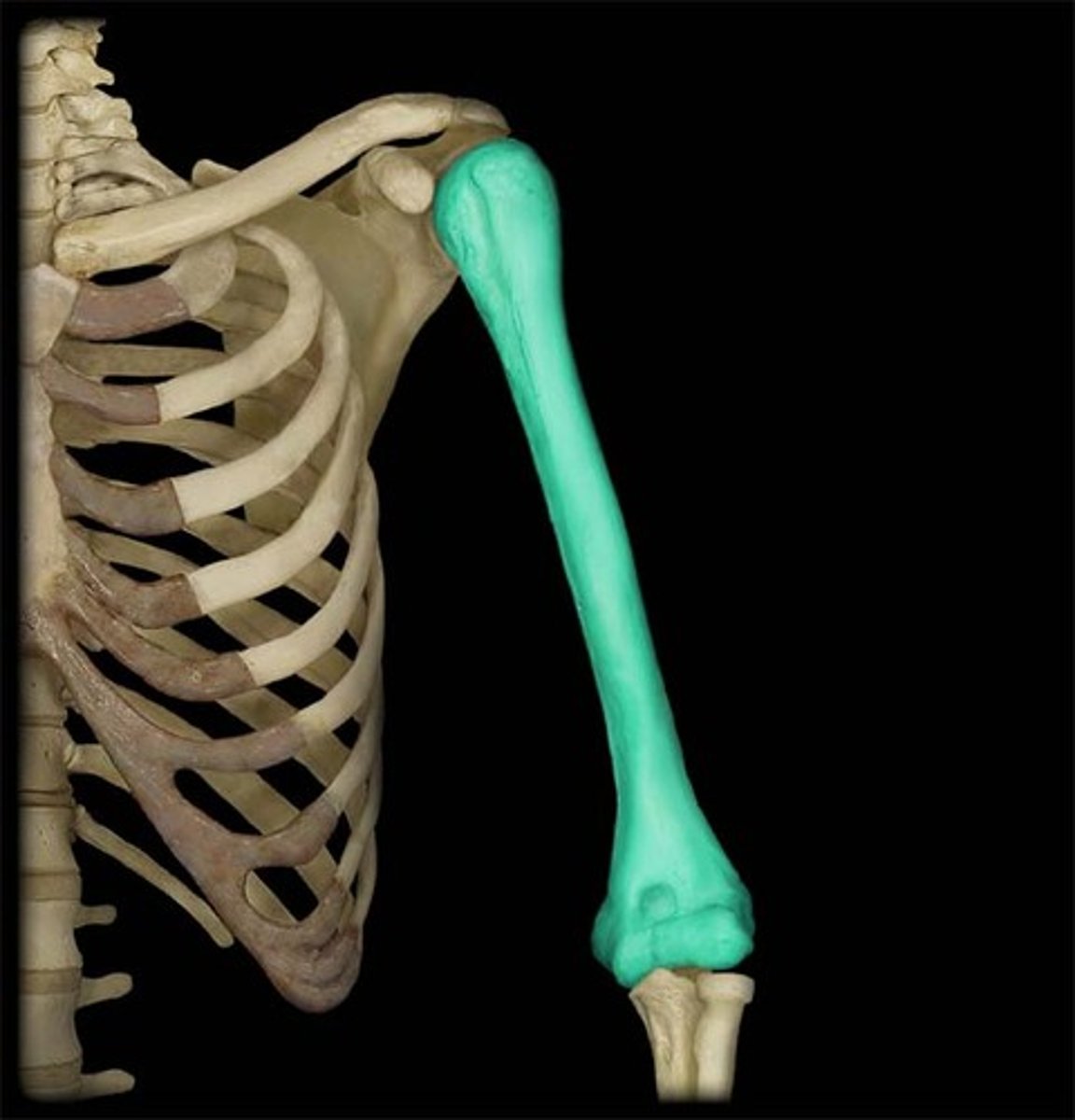
Humerus
upper arm bone
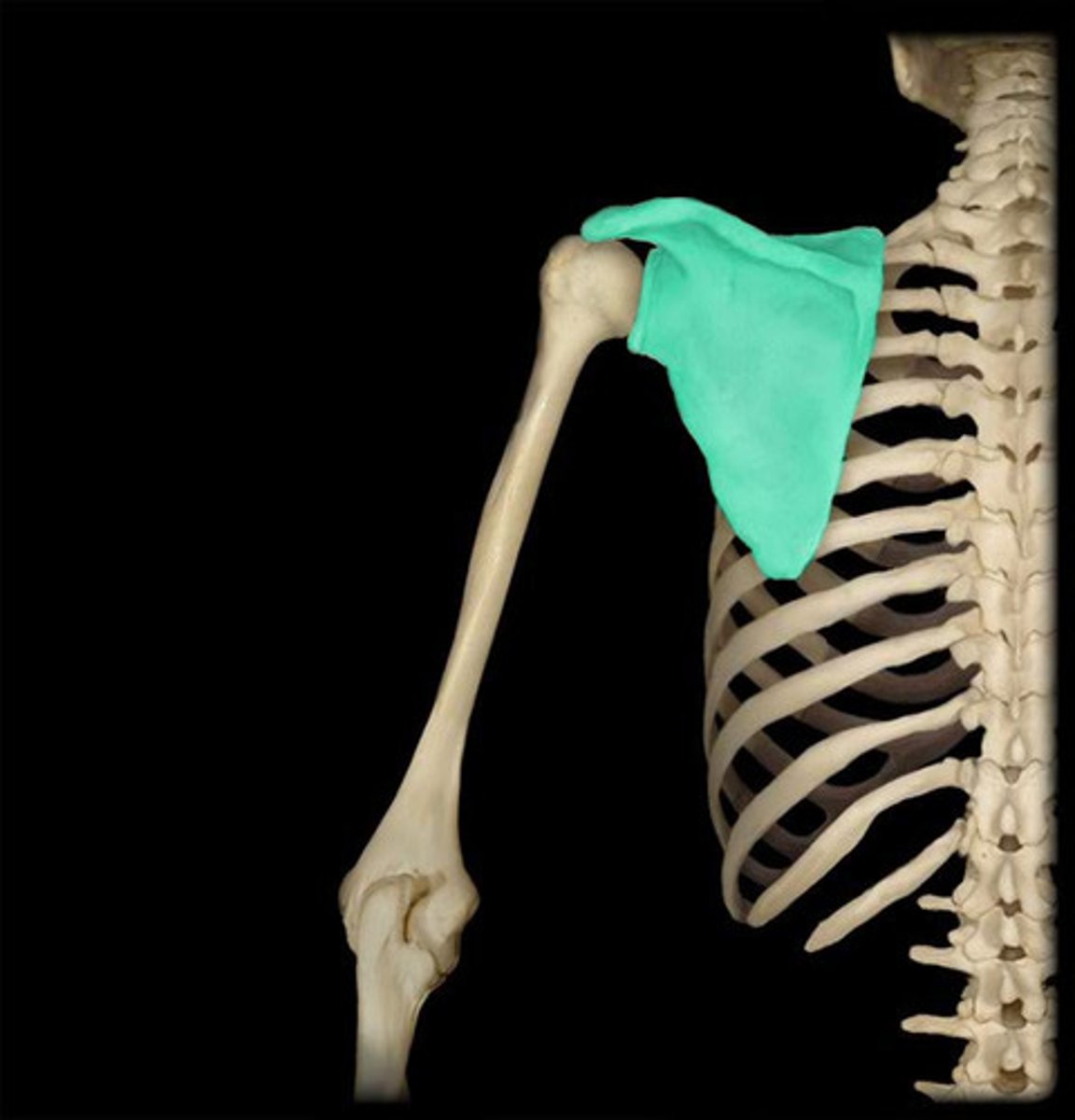
Scapula
shoulder bone
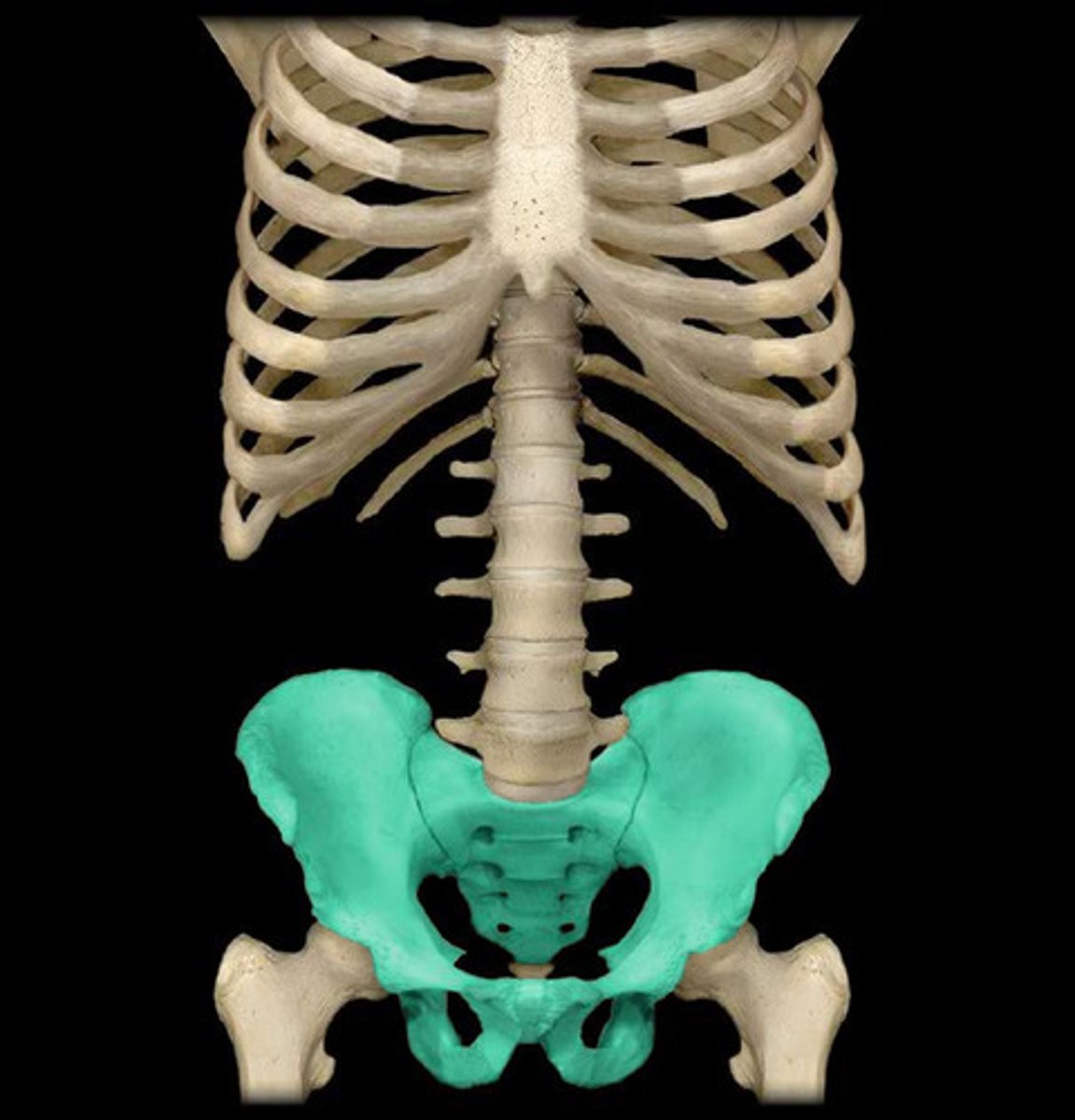
Pelvis
hip bone
Insulin
The hormones released by the islets of Langerhans to regulate sugar levels in the body, along with glucagon.
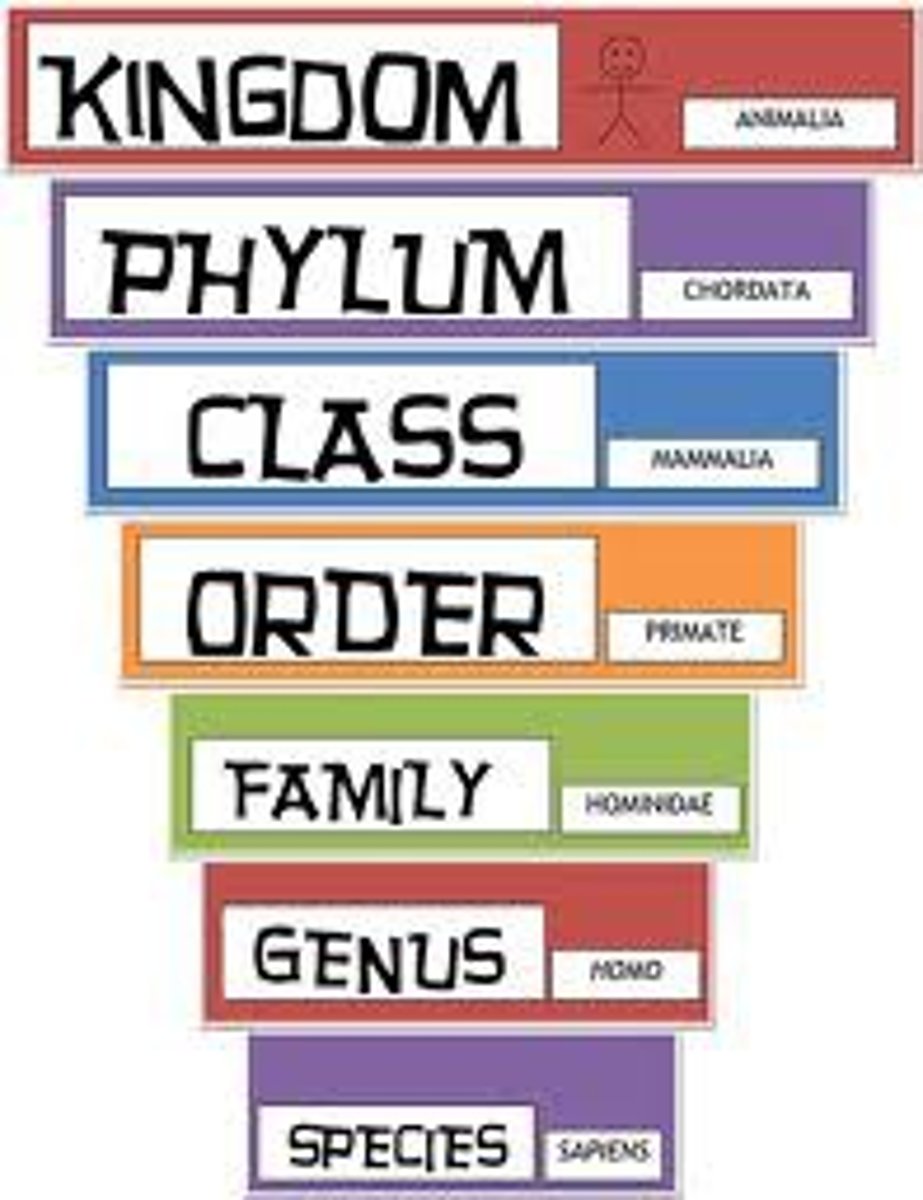
Taxonomy
science of classification
Stolon
A creeping stem that runs along the soil surface.

Angiosperms
The scientific term for a flowering plant.

Tissue
A group of cells that are designed to work together as a unit.
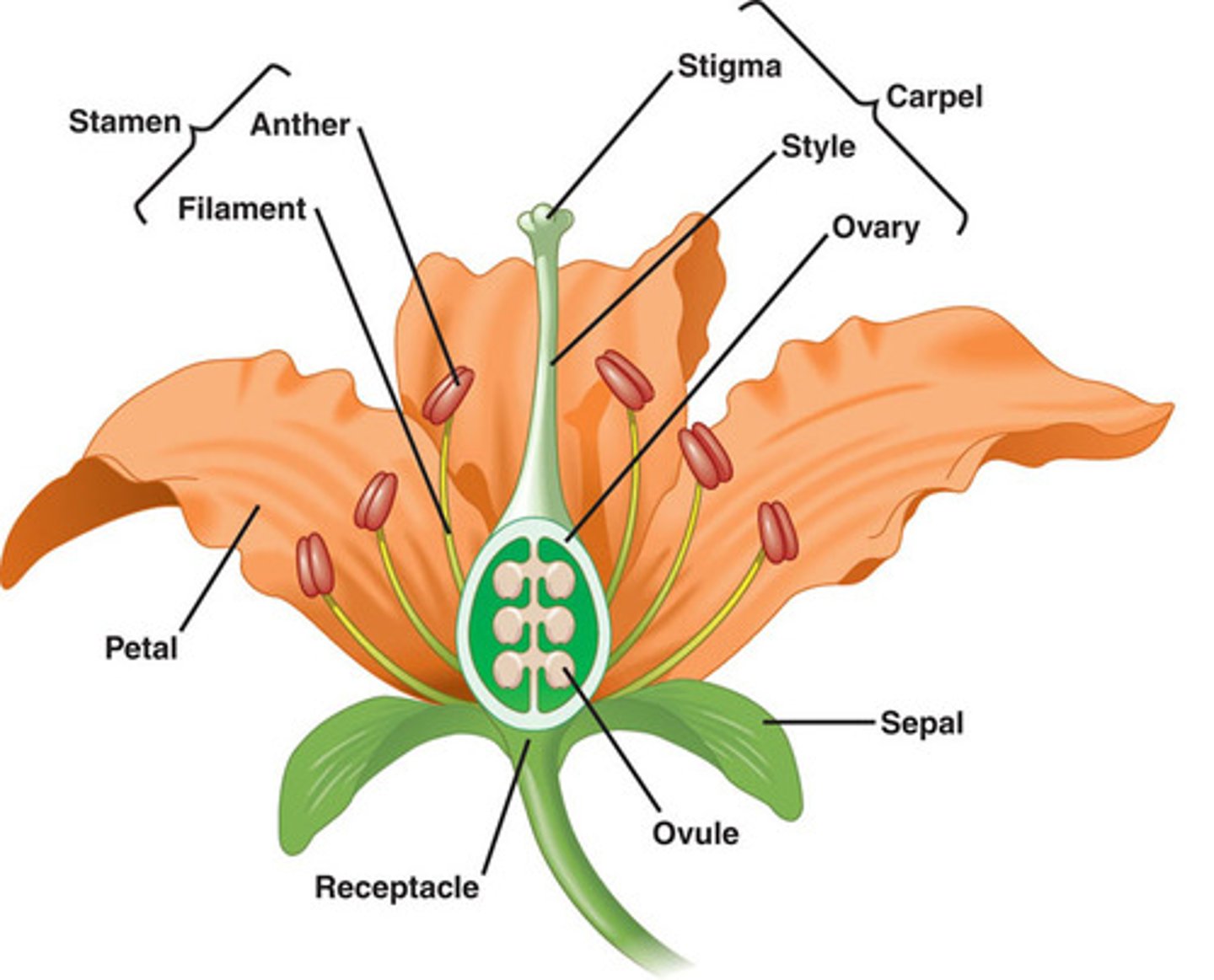
Anther to stigma
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the _________?
Agent
The scattering of seeds by wind, water, or animals, or people.
Grass
Grains are the fruits of this plant family.

One
A properly designed experiment should have _____ independent variable.
Composite
A plant with flower heads consisting of disk and ray flowers is from this family.
Central
The brain and spinal cord are part of this nervous system.
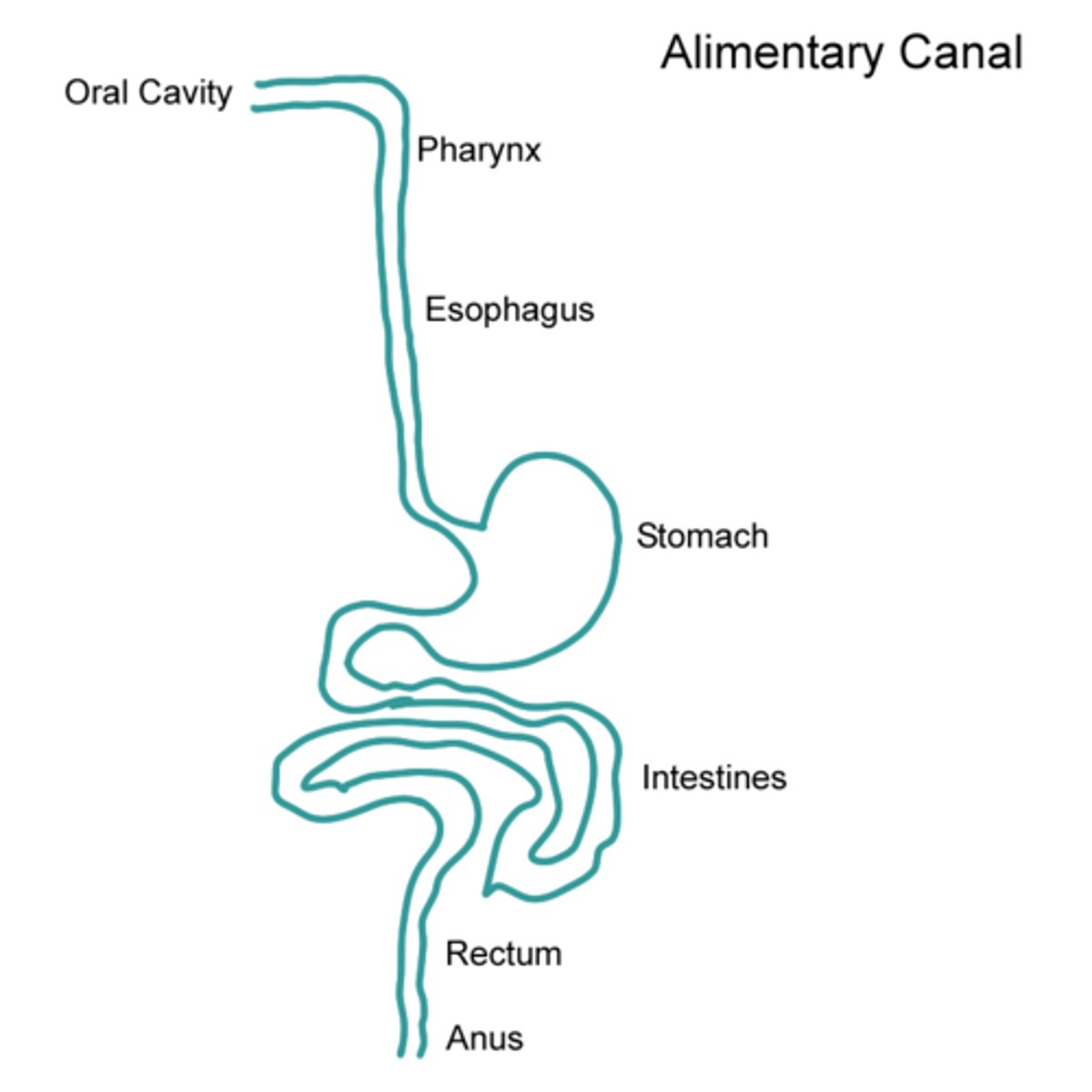
Alimentary
The canal that food follows through the digestive system from when it is eaten until the indigestible wastes leave the body.
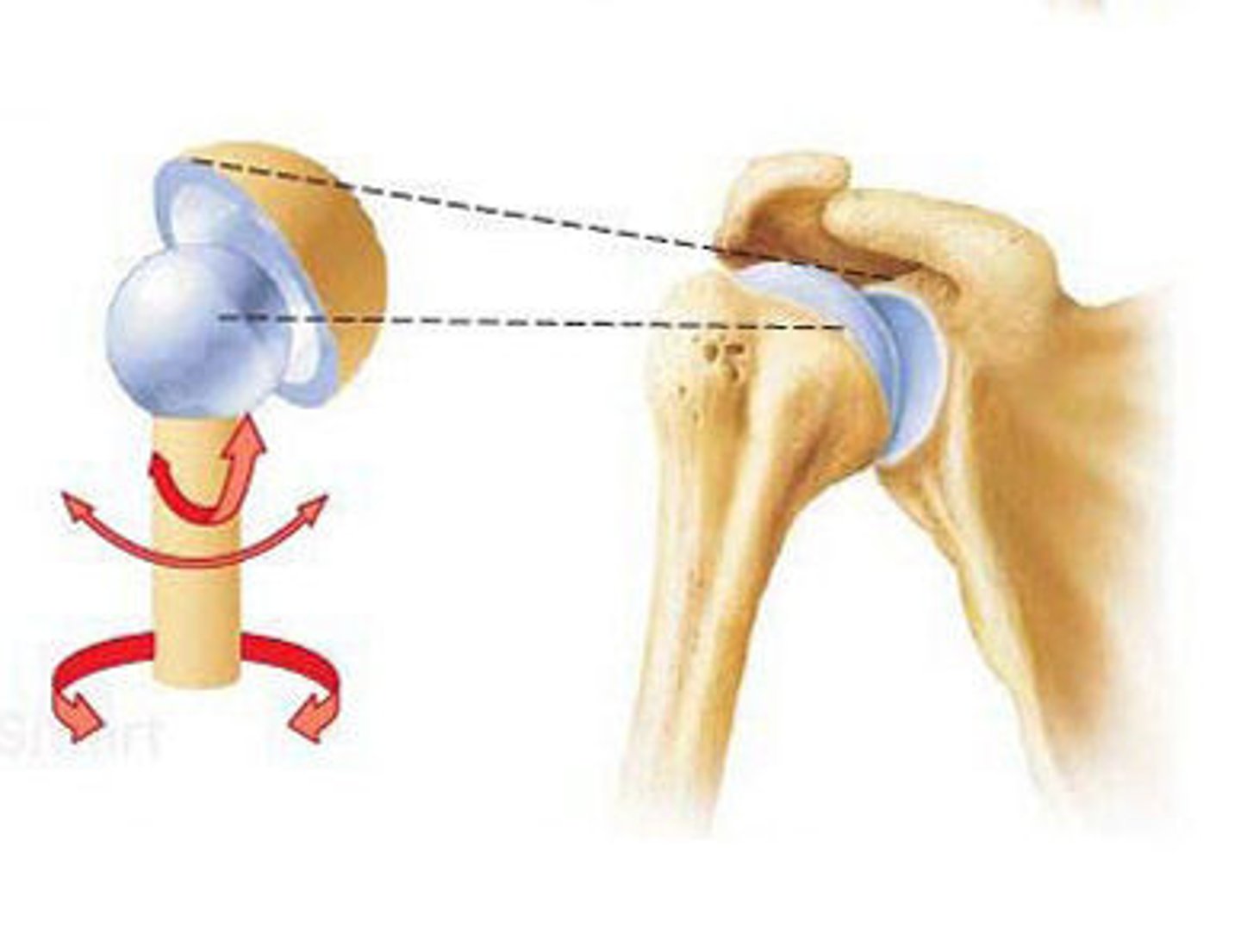
Ball-and-socket
The joints that give the shoulders and hips their wide range of motion.
Nerve
The tissue used by the body to conduct impulses.
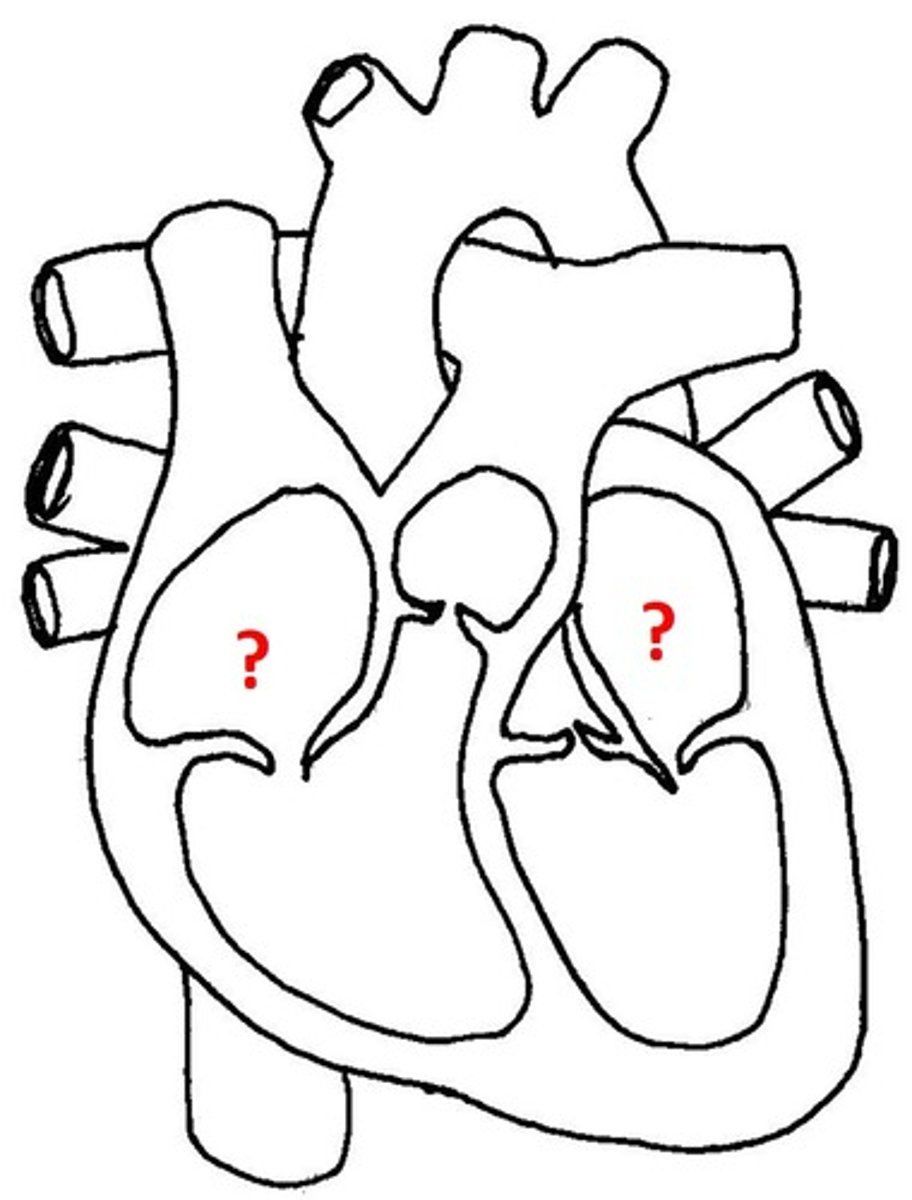
Atria
Upper chambers of the heart that receive blood
Sir Francis Bacon
He developed the scientific method

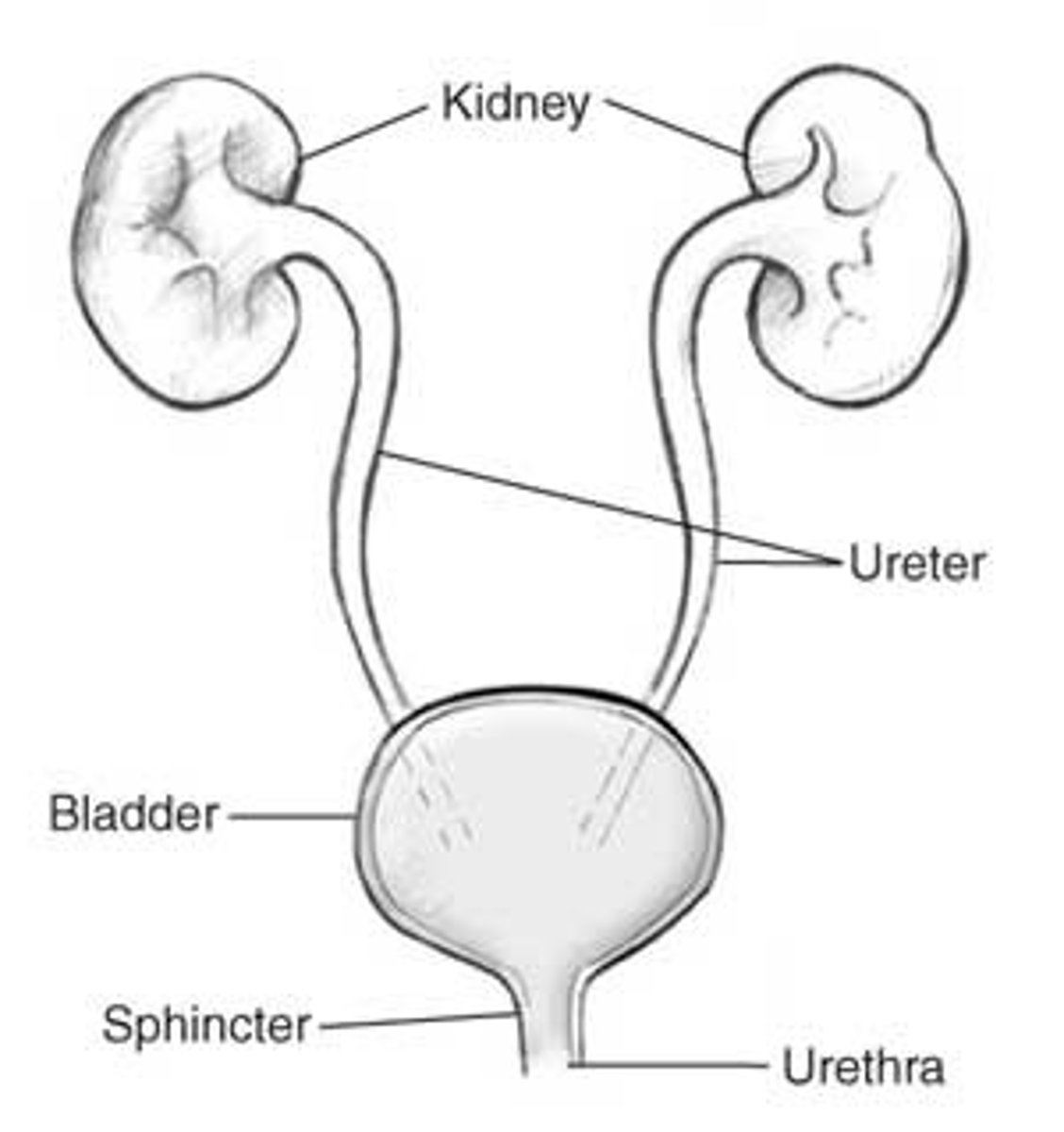
urinary system
Concentrates and removes liquid waste
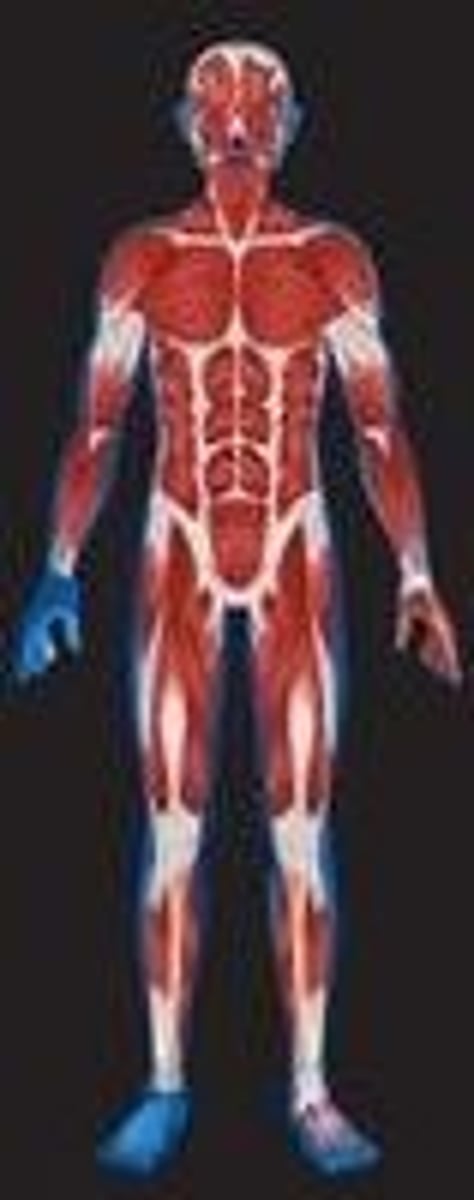
Muscular System
provides movement for the body
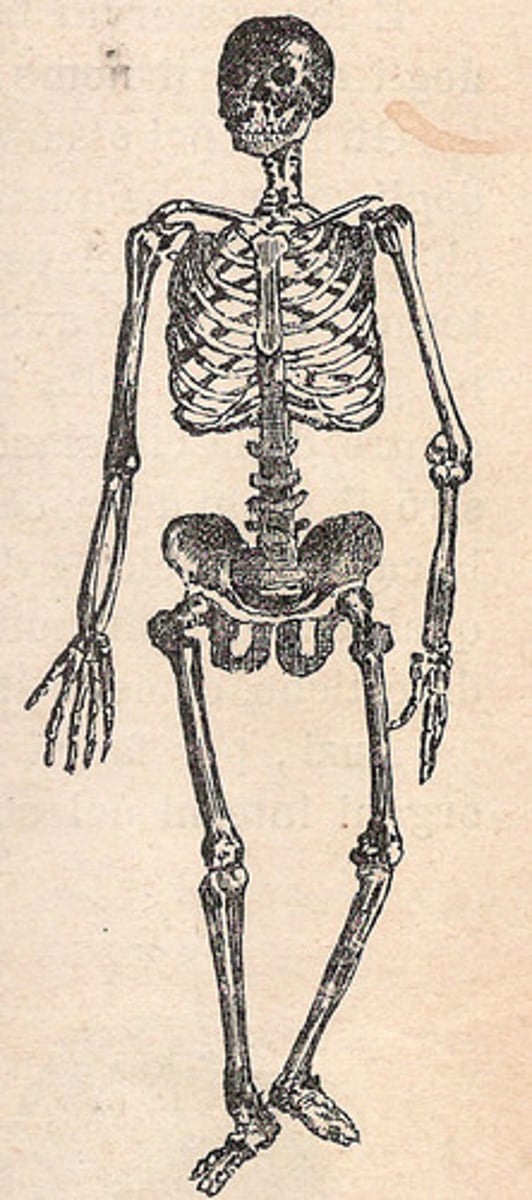
skeletal system
supports the body and protects vital organs
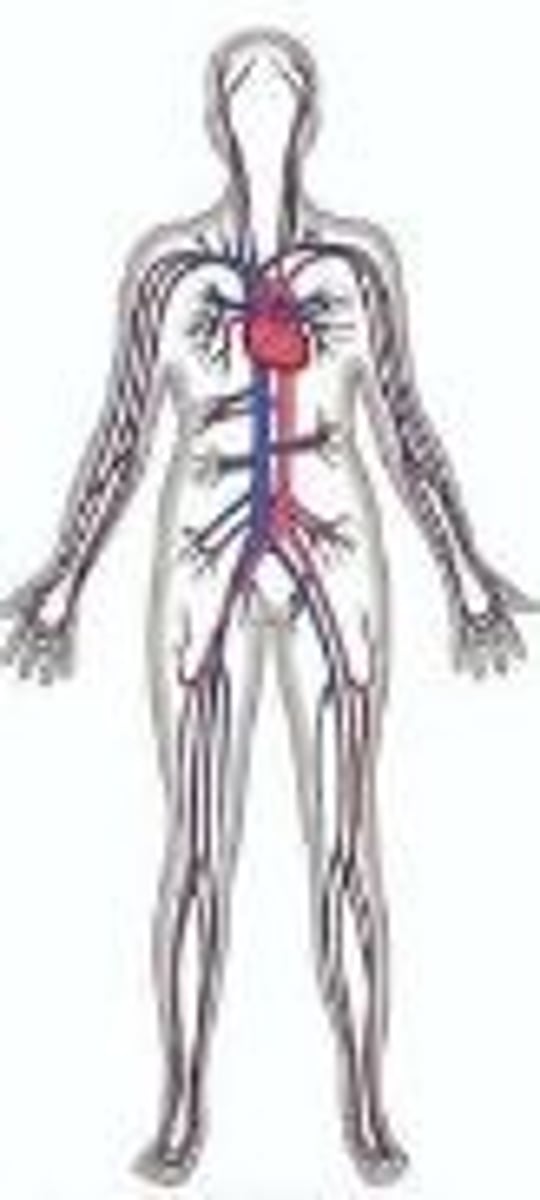
cardiovascular system
Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and carries wastes from cells.
integumentary system
Covers and protects the body.

nervous system
Controls other body systems.
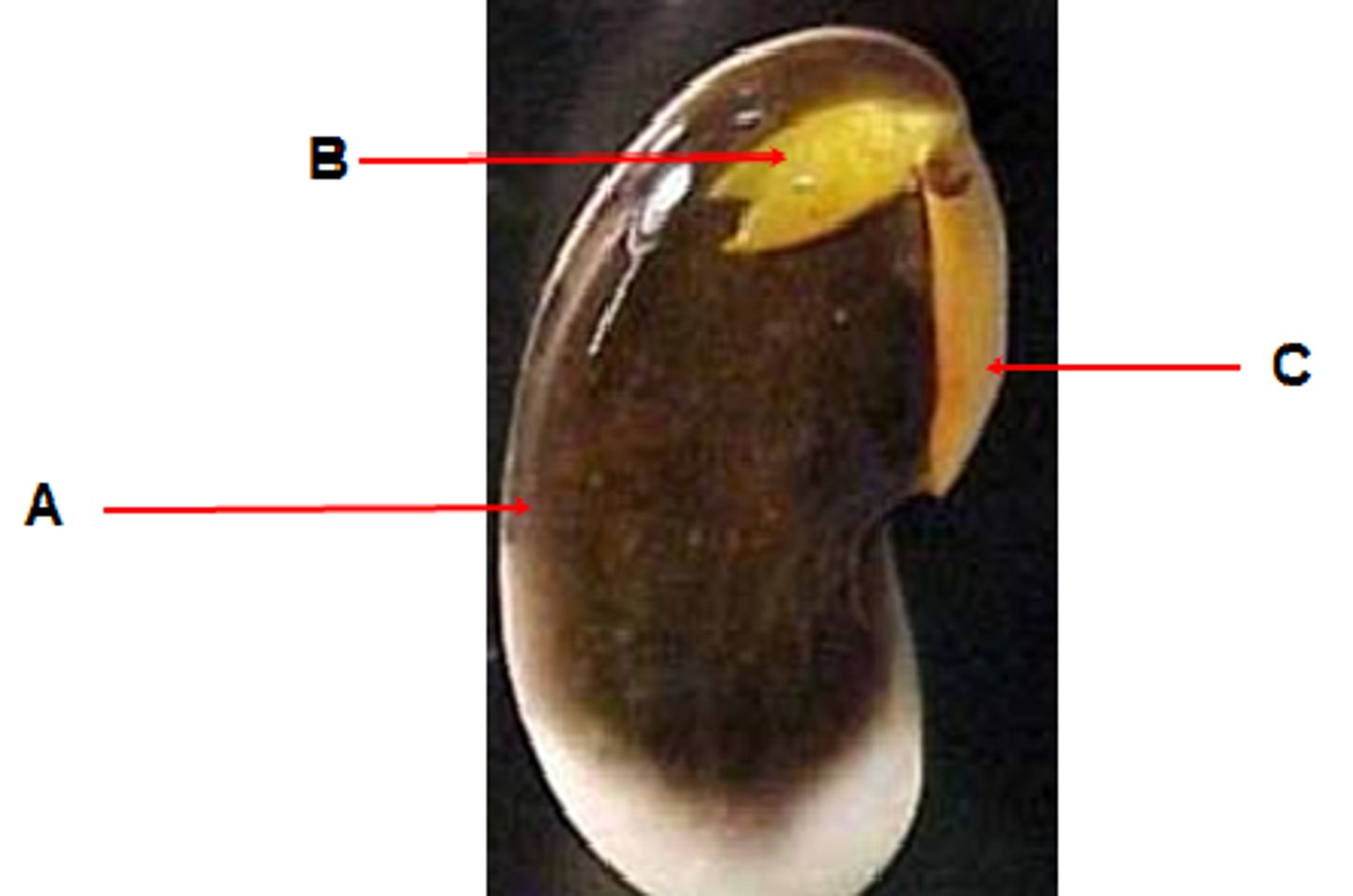
Radicle
The root system of a plant develops from this part of the seed. "C" on picture.
Arteries
The largest vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
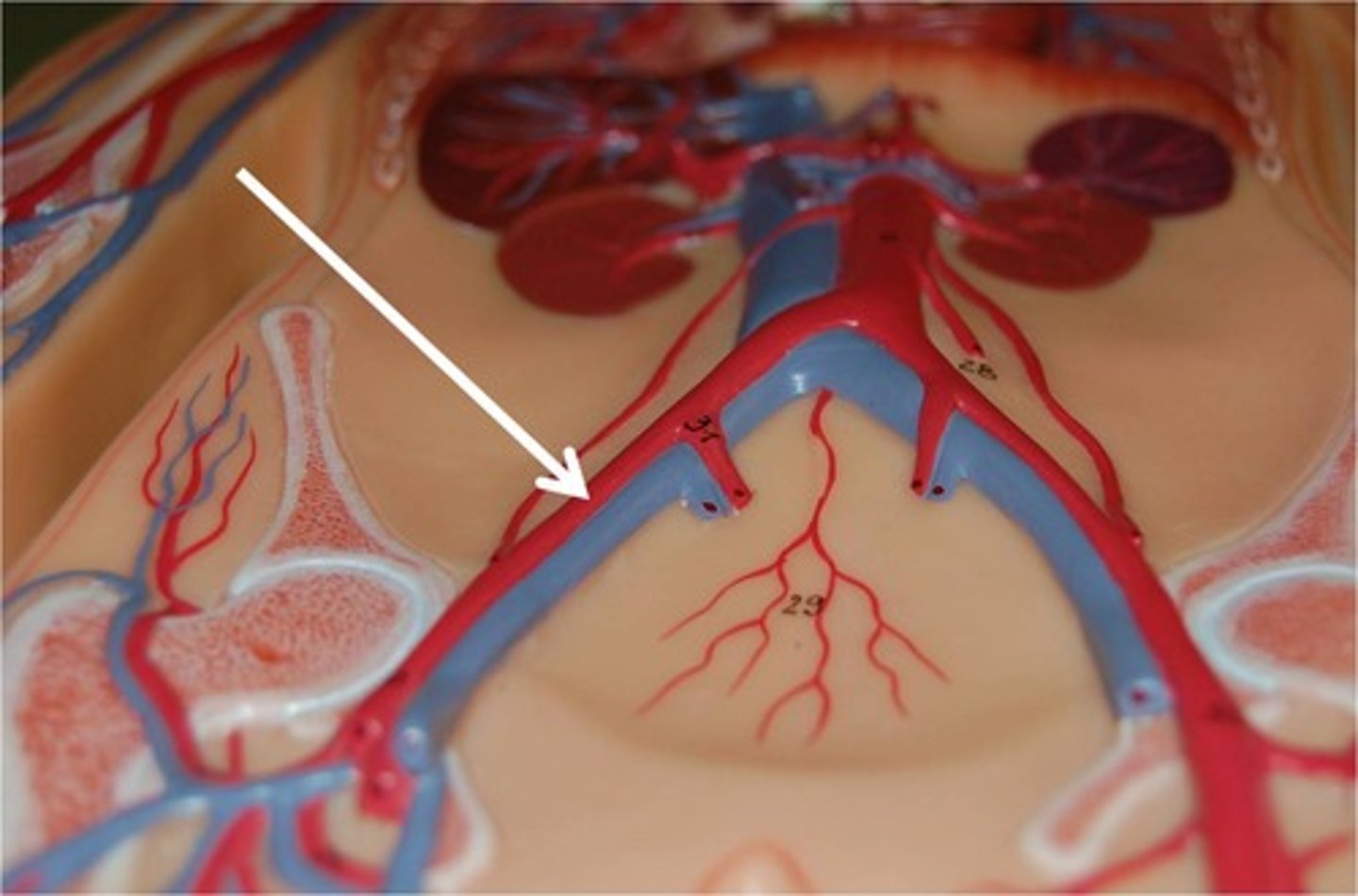
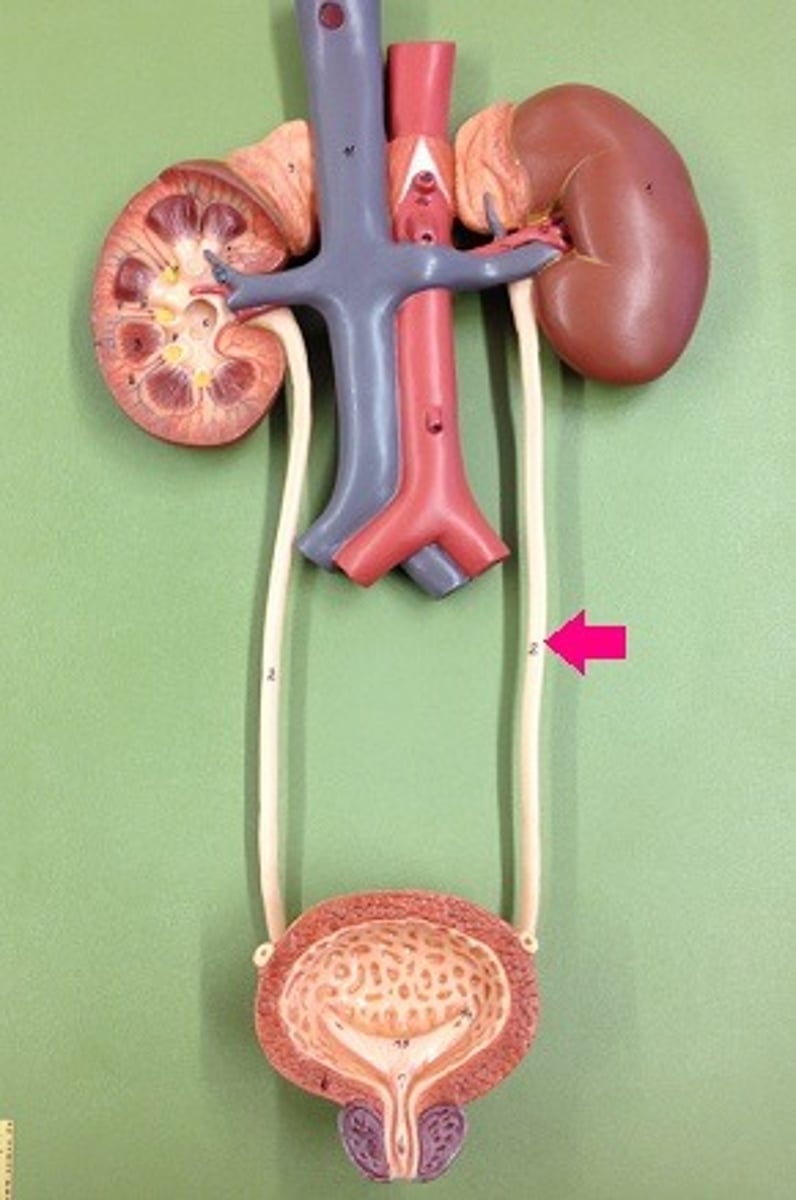
Ureters
They connect the kidneys to the bladder.
Perennials
Plants that live through more than one growing season

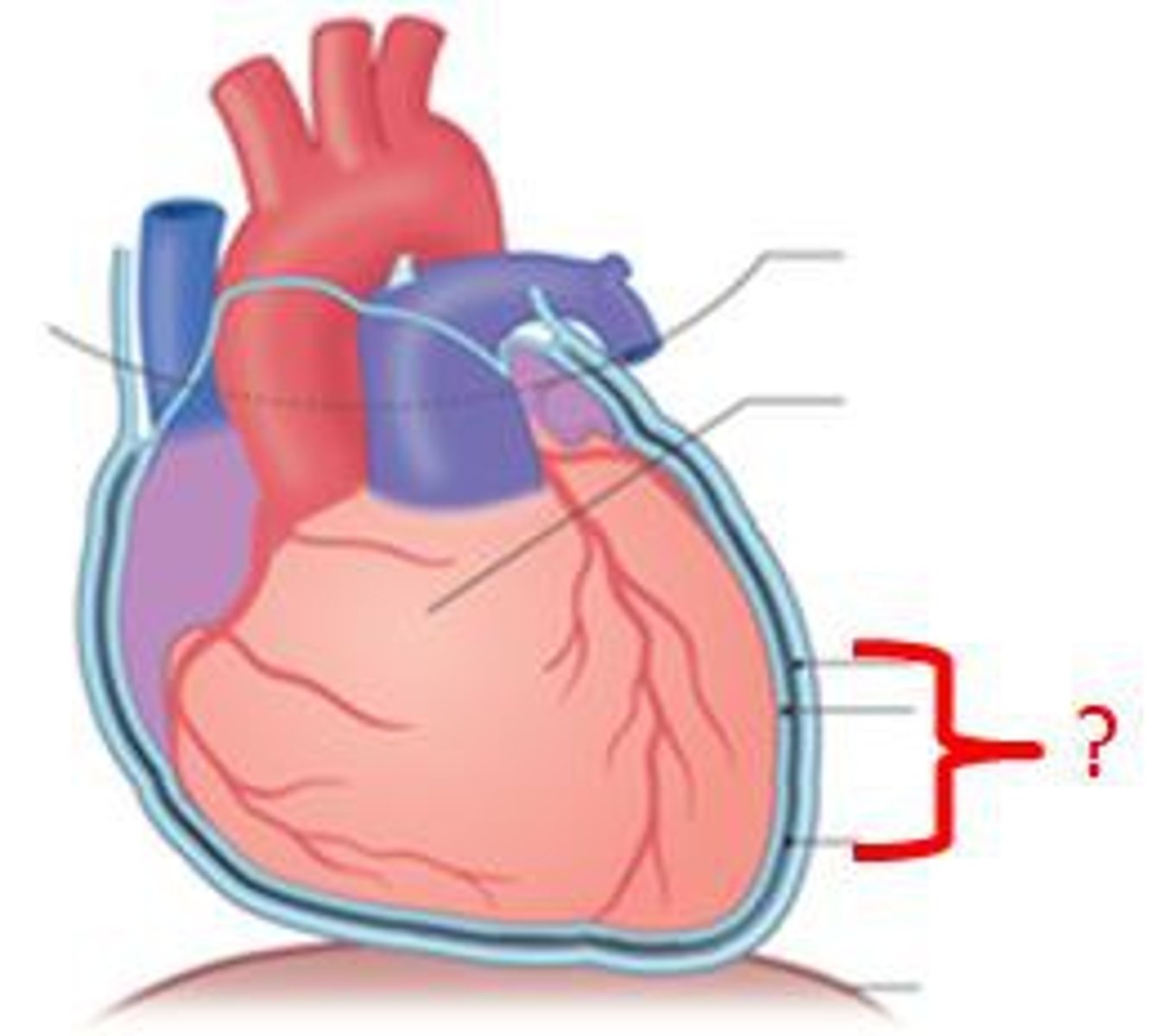
Pericardium
Tough membrane that encloses the heart.
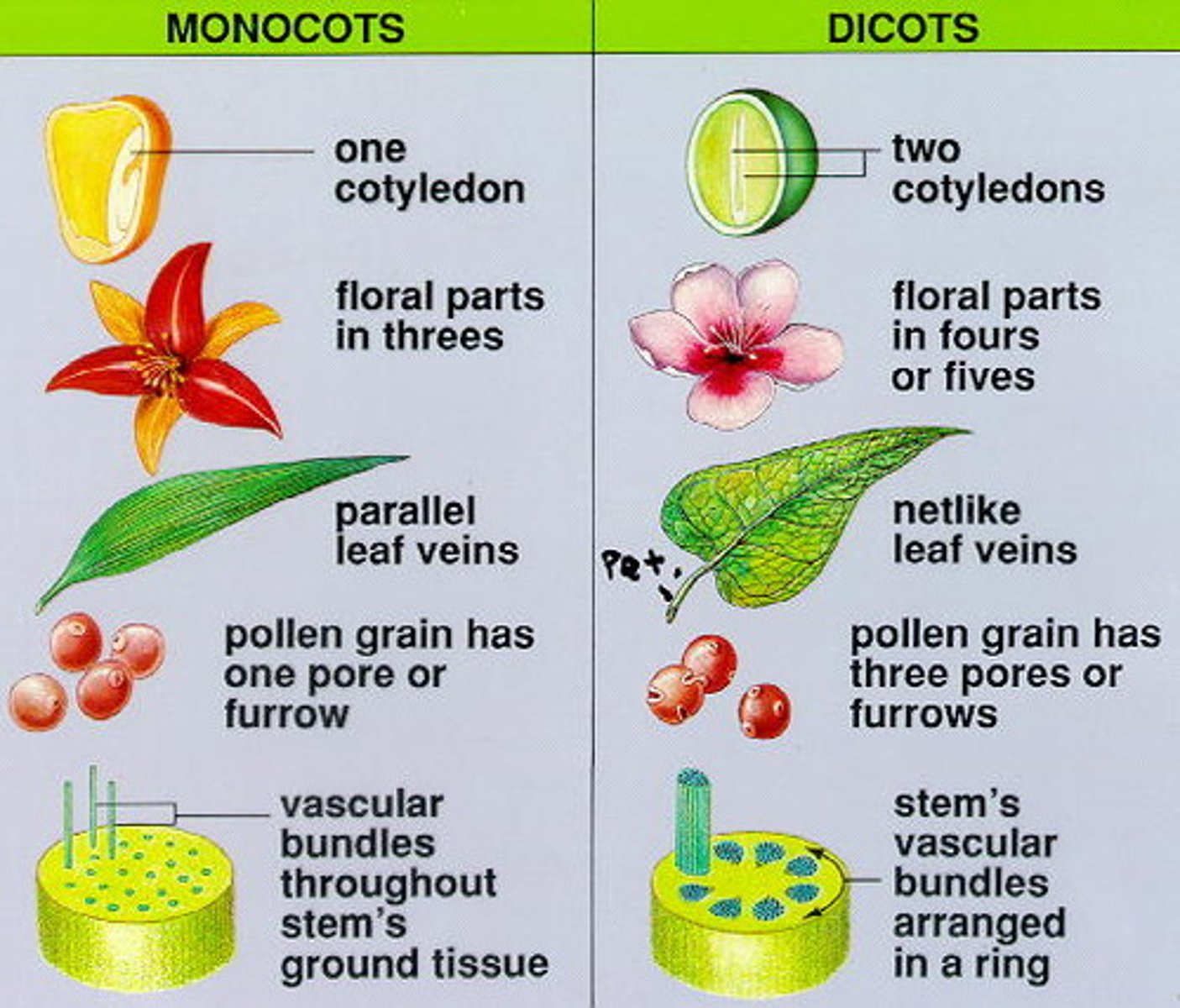
Monocots
Parallel veins, petals in multiples of three, and a fibrous root system are all characteristics of these.
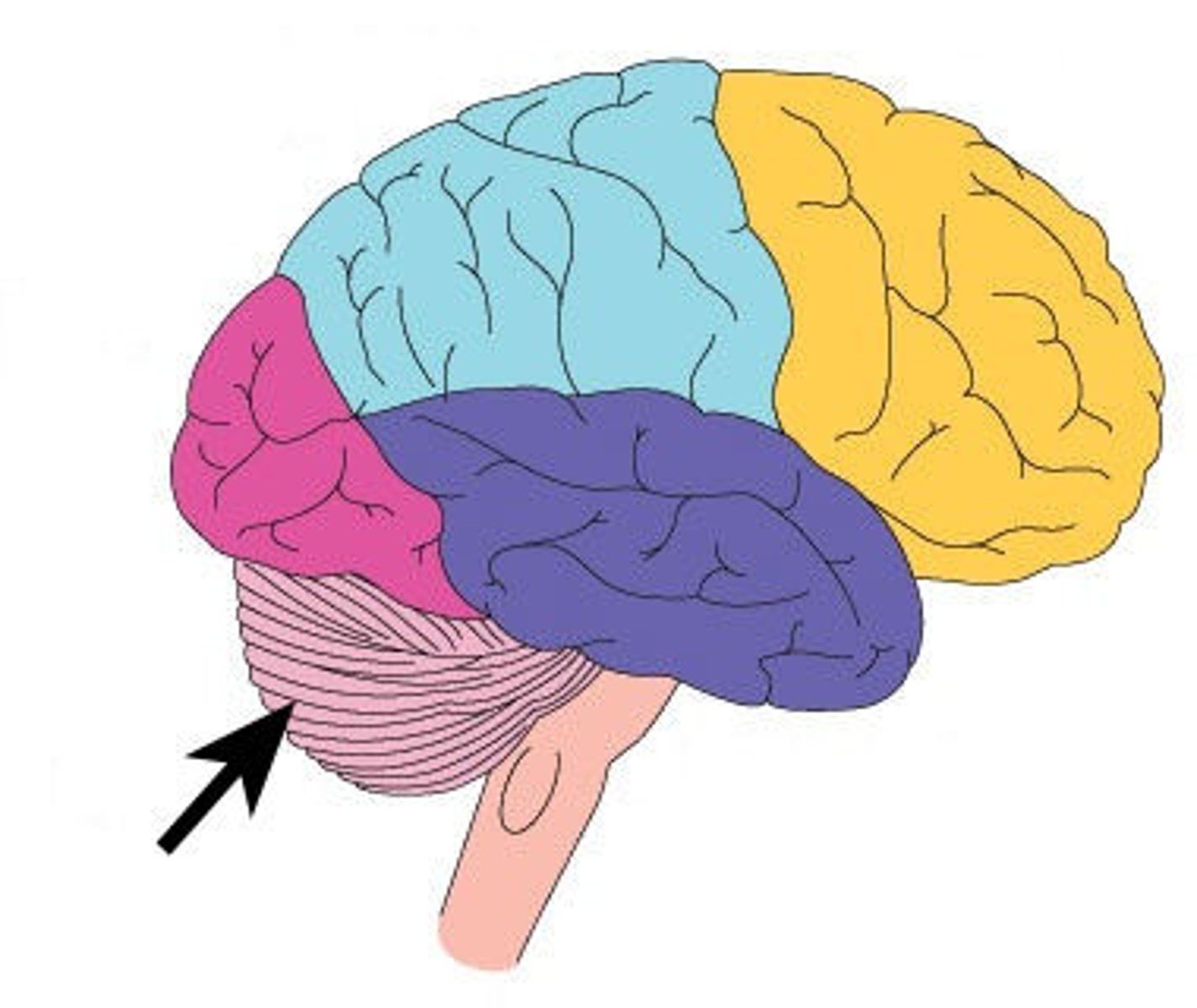
Cerebellum
It controls balance and muscle coordination.
Model
In science, anything that is used as a partial representation of something else is a scientific ______ of that thing.
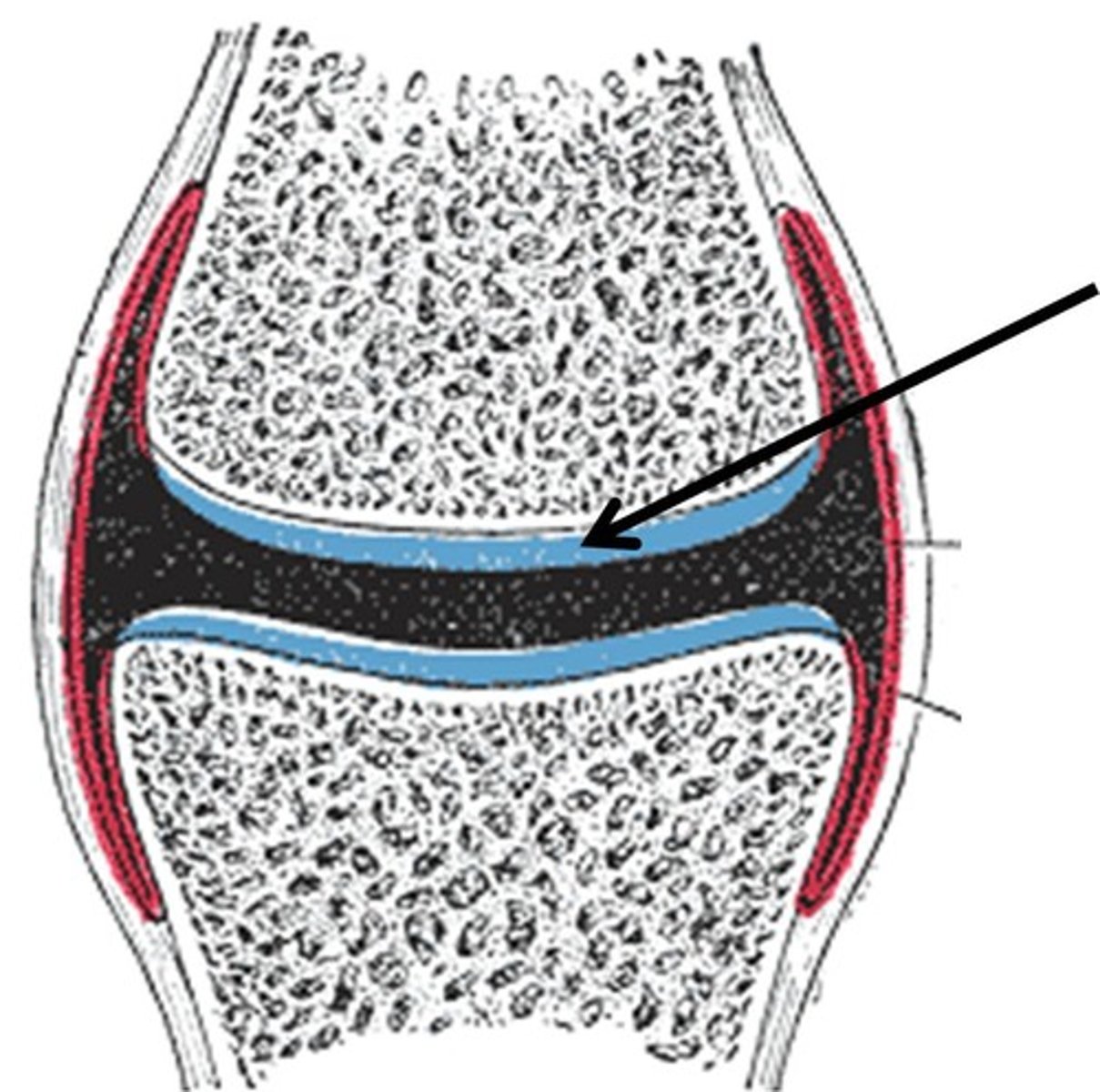
Cartilage
This wears away as a person ages, then his bones can begin rubbing together at their joints.
Hormone
This chemical is released when the calcium level in the blood is too low. Then, the thyroid gland releases this chemical messenger that signals the bones to release calcium into the bloodstream.
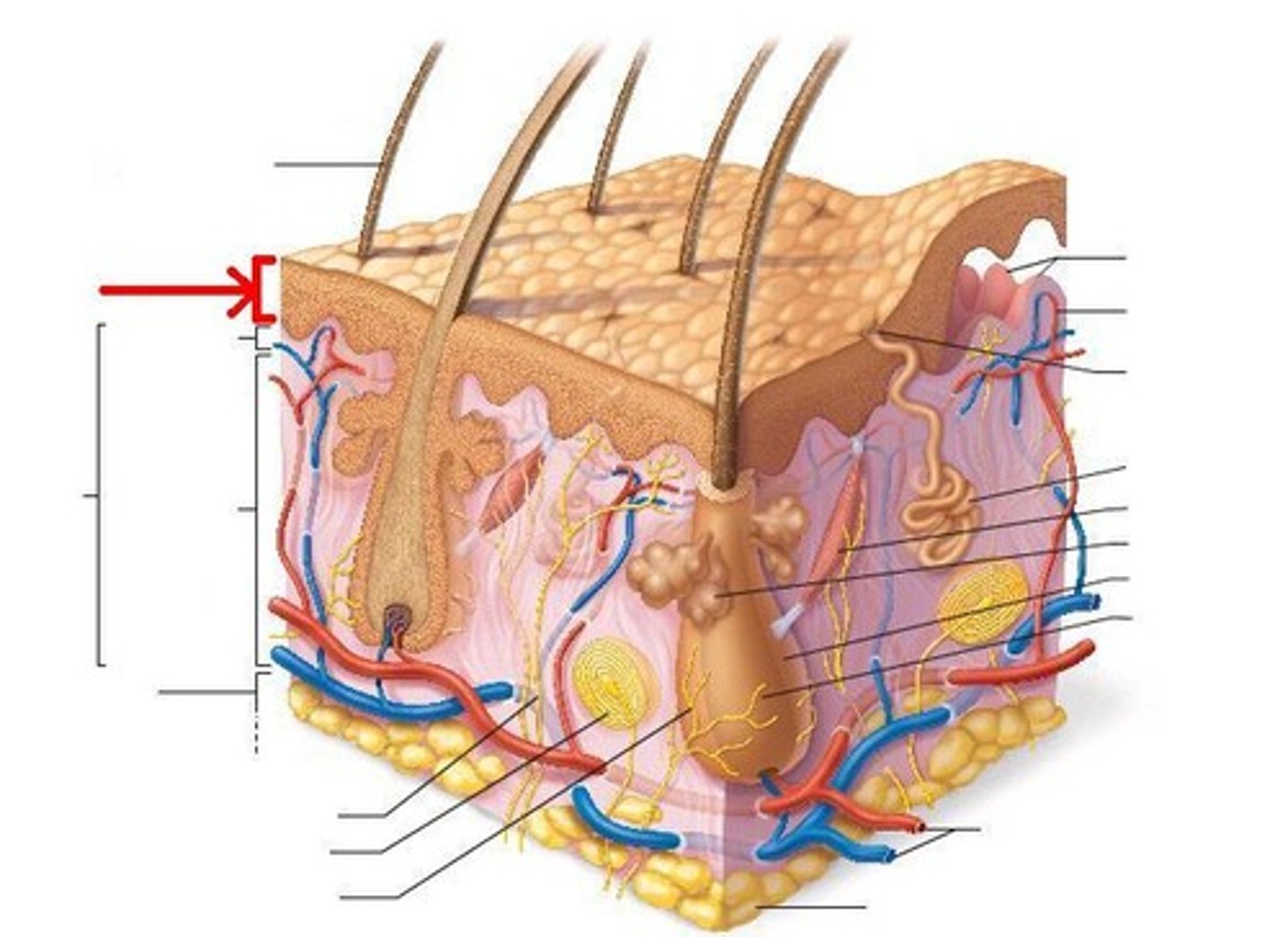
Epidermis
Outer layer of skin that is "exfoliated"
Genus
First part of a scientific name. Such as in the green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas, Chelonia is the genus.