5- pigmented lesions
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
2 categories of pigmented lesions
non-melanin associated
melanin-associated
2 types of non-melanin associated pigmented lesions
exogenous:
amalgam tattoo (focal argyrosis)
graphite + other foreign body tattoos
med-induced pigmentation
endogenous
hemosiderin
bilirubin
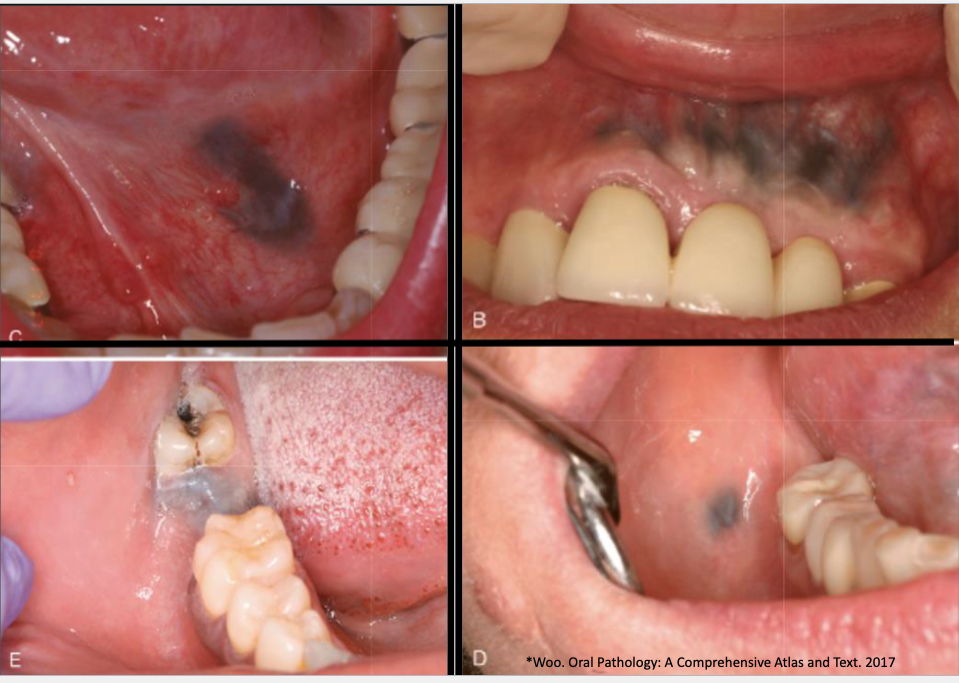
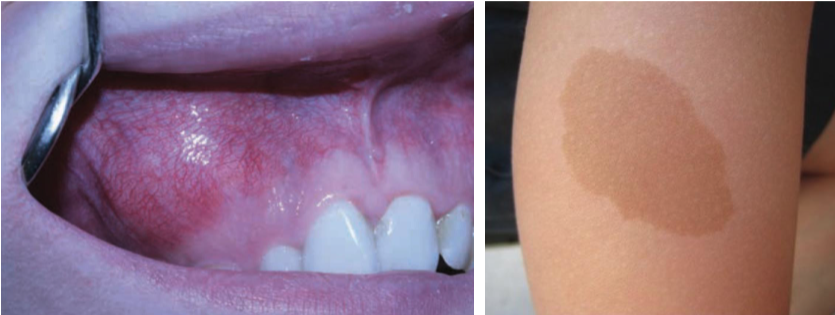
2 clinical features of amalgam tattoo (focal argyrosis)
blue-gray macule
asymptomatic, localized
3 regions commonly affected by amalgam tattoo (focal argyrosis)
gingiva/alveolar ridge mucosa (50%)
buccal mucosa
floor of mouth
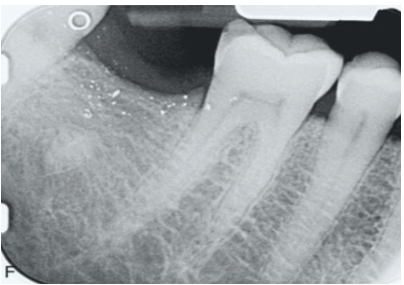
T/F: you can see amalgam tattoo (focal argyrosis) radiographically
true

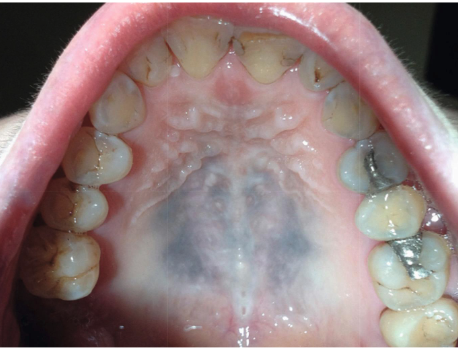
what is this
graphite tattoo
4 causes of med-induced pigmentation
accumulation of melanin via increase in melanin production or decrease in melanin clearance
accumulation of med
synthesis of special pigments
iron deposition
2 clinical features of med-induced pigmentation
diffuse, painless, symmetric bluish-gray macule
melanonychia + skin lesions
7 common meds that can cause med-induced pigmentation
minocycline
antimalarials
clofazamine
tranquillizers
hormones
heavy metals
amiodorone
M A C T H H A
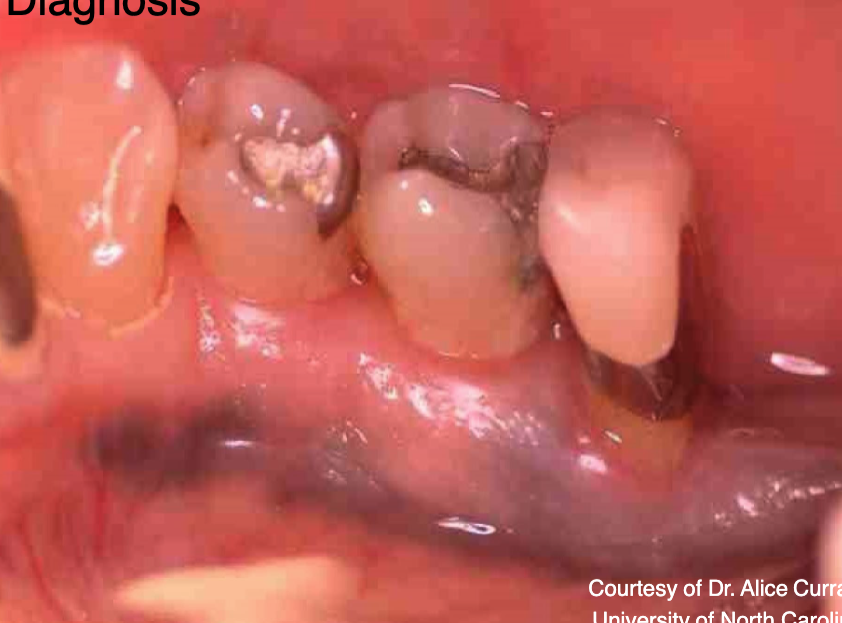
what is this
amalgam tattoo

what is this
Burton line: indicating heavy metal toxicity
7 types of melanin-associated pigmented lesions
developmental
reactive/inflammatory
infectious
autoimmune + immune mediated
metabolic/systemic
neoplastic
premalignant/malignant
melanocytes are developed from which cells
neural crest cells
2 types of developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesions
physiological (racial) pigmentation
ephelides (freckles)
ephelides (freckles) affects men or women more
women
3 types of reactive/inflammatory melanin pigmented lesions
oral melanotic macule
post-inflammatory hypermelanosis (Smoker’s melanosis)
melanoacanthosis
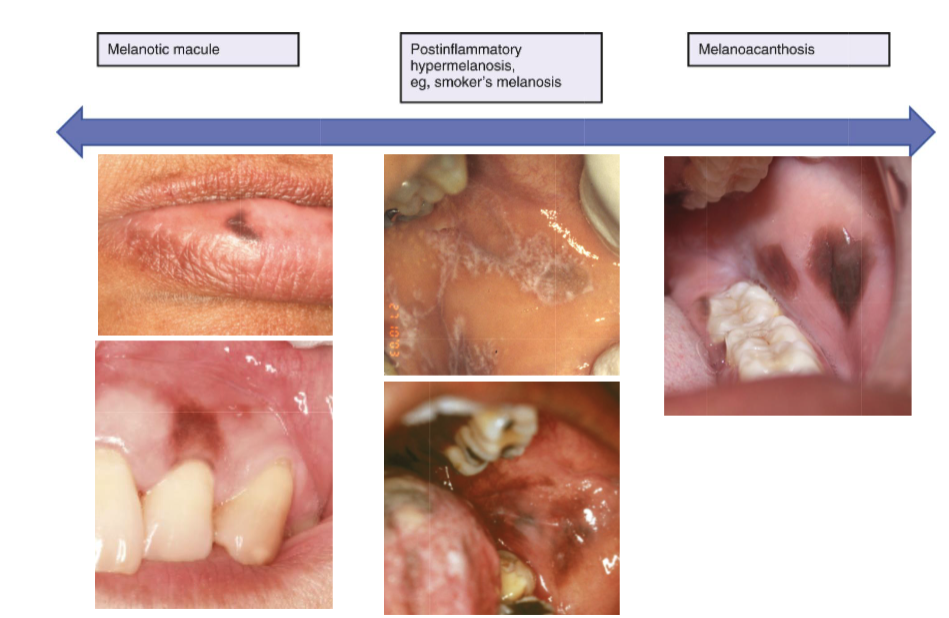
oral melanotic macule affects men or women more
women
oral melanotic macule is usually on which areas
lip mucosa
gingival mucosa
palatal mucosa
buccal mucosa
L G P B

which of the 3 reactive/inflammatory melanin pigmented lesions progress
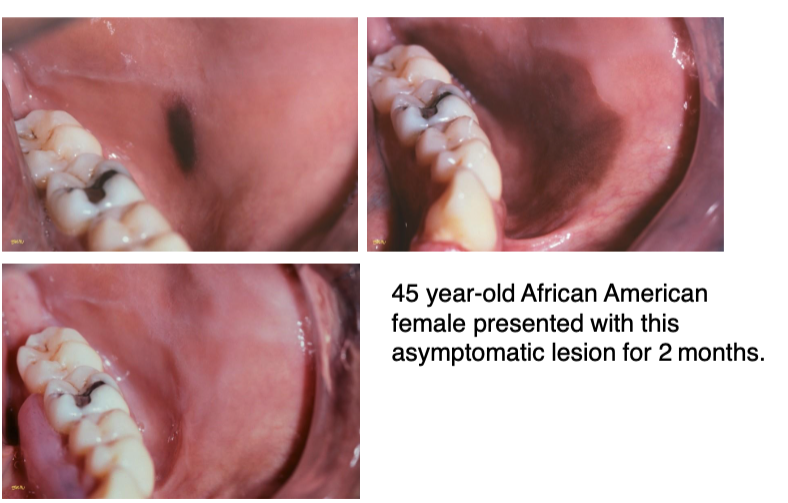
melanoacanthosis, must be biopsied to rule out melanoma
post-inflammatory hypermelanosis (Smoker’s melanosis) usually affects which area
facial gingiva
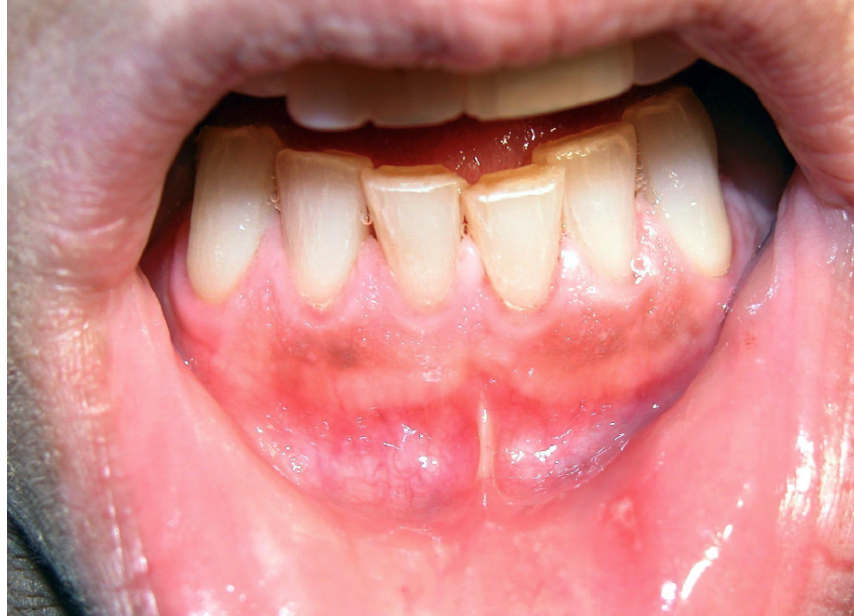
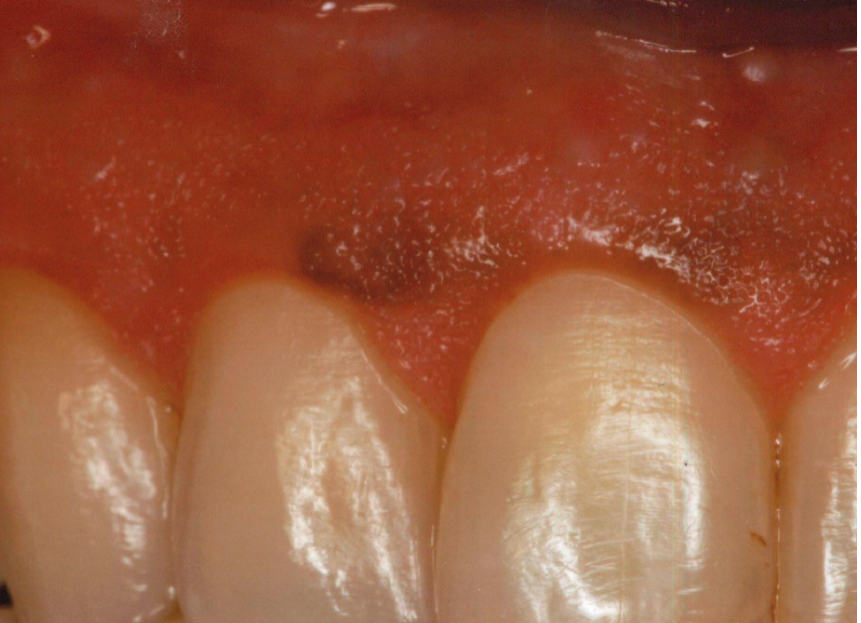
differentiate between melanotic macule vs. post-inflammatory hypermelanosis (Smoker’s melanosis)
post-inflammatory hypermelanosis (Smoker’s melanosis) lesions are more diffused
melanoacanthosis affects men or women more
women, specifically African-American
7 types of developmental melanin pigmented lesions
McCune Albright Syndrome
Neurofibromatosis I
Carney Complex
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
Leopard Syndrome
Dyskeratosis Congenita
Laugier Hunziker Syndrome
McCune Albright Syndrome is a result of what mutation
GNAS1 mutation
3 clinical features of McCune Albright Syndrome
cutaneous hyperpigmentation: café au lait macules
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
endocrine dysfunction: hyperthyroidism, sexual precocity
neurofibromatosis I is caused by which mutation
NF1 mutation, autosomal dominant
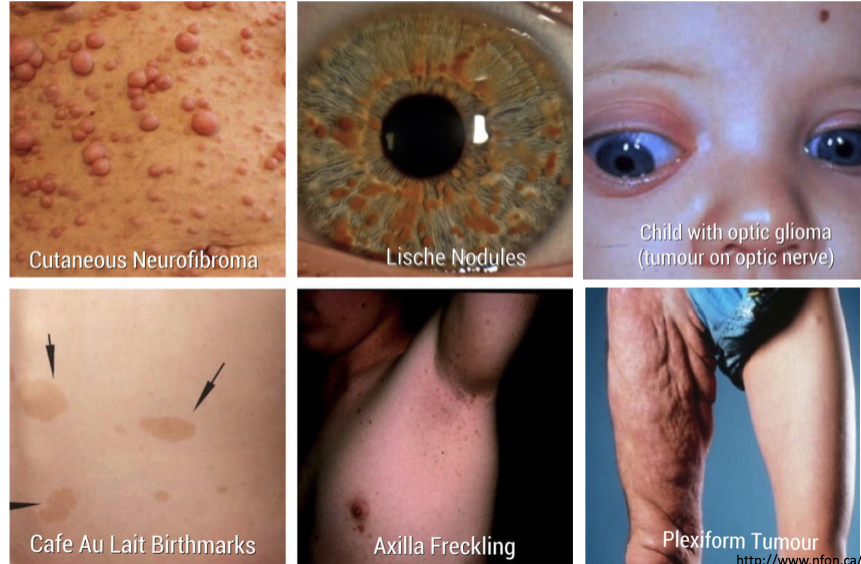
6 clinical features of neurofibromatosis I
café au lait macules
axilla freckling
cutaneous neurofibroma
lische nodules
optic glioma
plexiform tumor
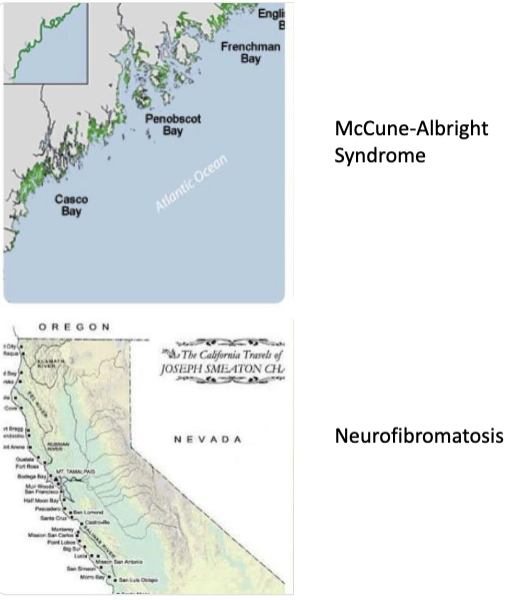
differentiate between the café au lait macules of McCune-Albright syndrome vs. neurofibromatosis
McCune-Albright syndrome: irregular margins
neurofibromatosis: smooth margins
Carney complex is caused by which mutation
PRKAR1A gene, autosomal dominant
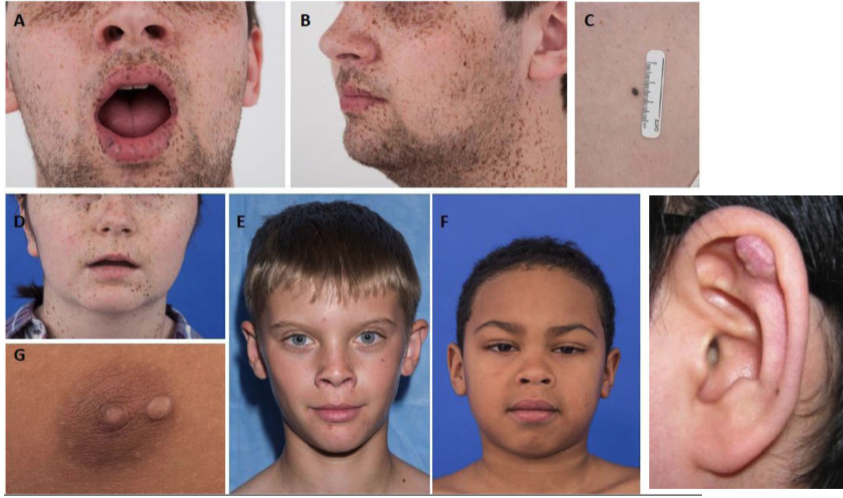
4 clinical features of the Carney complex
cardiac myxomas
cutaneous myxomas
spotty pigmentation: lentigines on face + lip vermillion border, blue nevi
endocrine disease/tumor
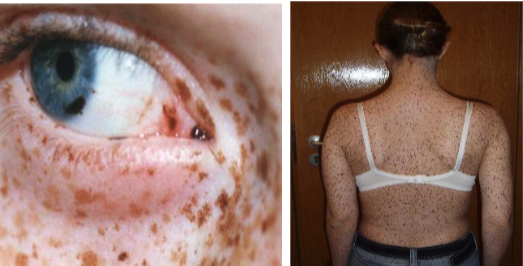
Peuts-Jegher syndrome is caused by what mutation
STK11/LKB1 gene, autosomal dominant
2 clinical features of Peuts-Jegher syndrome
Freckle-like lesions of the hands, peri-oral region, and/or oral mucosa
Intestinal polyposis w/ predisposition to adenocarcinoma

LEOPARD syndrome is caused by which mutation
PTPN11 gene
7 clinical features of LEOPARD syndrome
Lentigines
ECG conduction abnormalities
Ocular hypertelorism
Pulmonic stenosis
Abnormal genitalia
Retardation of growth
Deafness
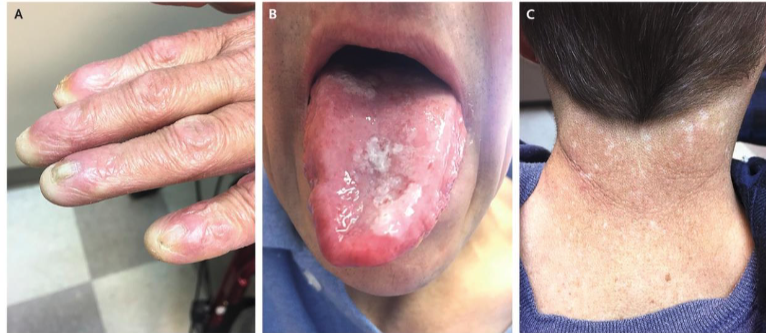
dyskeratosis congenita is caused by which mutation
DKC1 gene
3 clinical features of dyskeratosis congenita
nail dystrophy
mucosal leukoplakia
hyperpigmentation
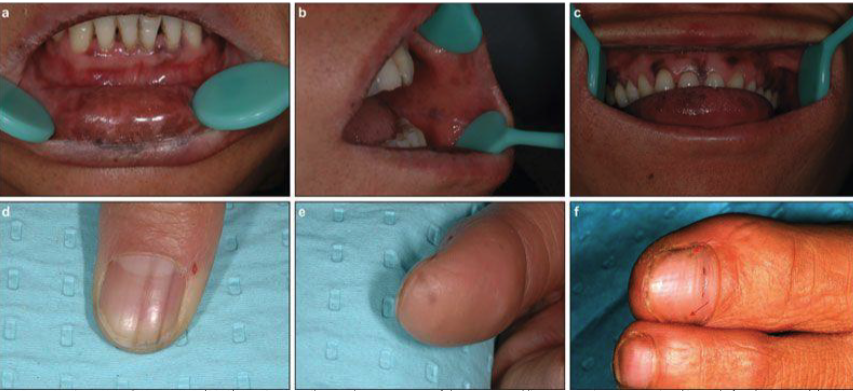
2 clinical features of Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome
macules of the labial and/or buccal mucosa
longitudinal streaks in fingernails (melanonychia)
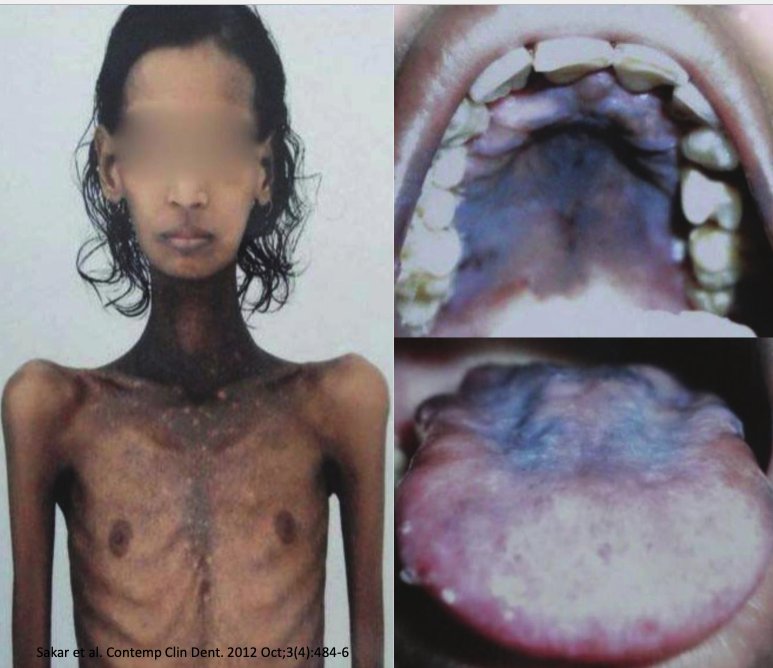
what’s the autoimmune syndrome that produces melanin pigmented lesions
Addison disease: hypoadrenocorticism
4 clinical features of Addison disease
bronze pigmentation of skin
insufficient production of adrenal corticosteroids
weight loss
postural hypotension
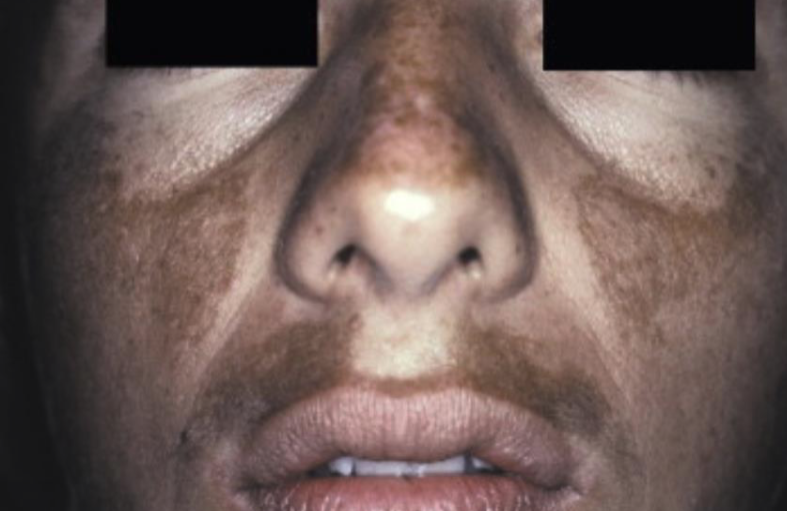
what is this
melasma: mask of pregnancy
2 types of neoplastic melanin pigmented lesions
melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
oral melanocytic nevus
4 clinical signs of melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
90% in the head + neck within the first 6 months
60% on the palatal mucosa
brownish-red mass of alveolar mucosa
high levels of vanillylmandelic acid in urine
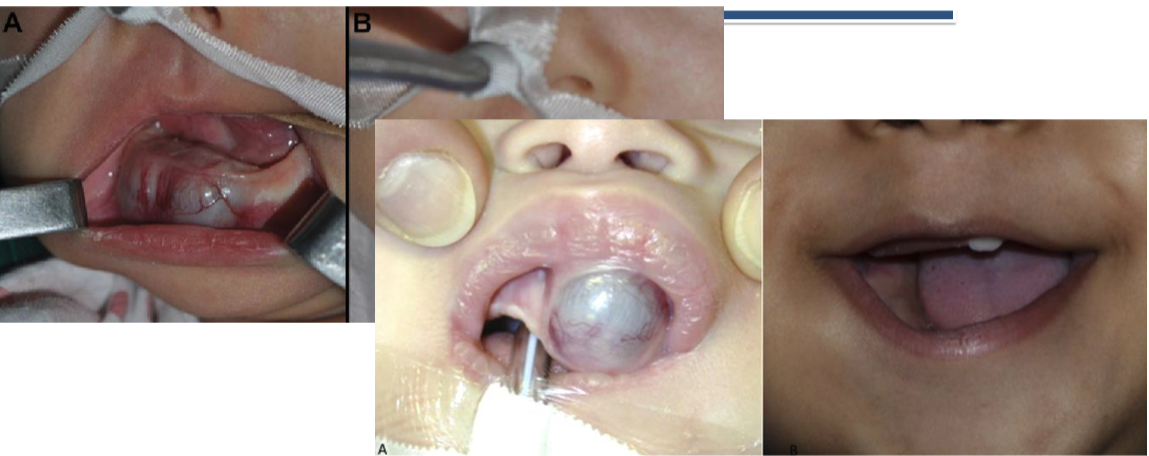
melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy affects men or women more
men
3 tx options for melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
surgical resection
radiation
chemo
what type of nevi is the most common
intramucosal
oral melanocytic nevus is benign or malignant
benign
T/F: oral melanocytic nevus can be acquired or congenital
true
what age of ppl get oral melanocytic nevus
20s-40s
5 areas affected by oral melanocytic nevus
Hard Palatal Mucosa (44%)
Buccal Mucosa (22%)
Vermilion Border (18%)
Gingiva (12%)
Retromolar Pad (4%)
which are more common: macules or nevi
macules
4 types of cutaneous melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma
Nodular melanoma
oral melanomas are most prevalent in which ethnicity
African Americans + Japanese
oral melanomas affect men or women more
men
which 2 areas are most commonly affected by oral melanoma (>70%)
palatal mucosa + max gingiva
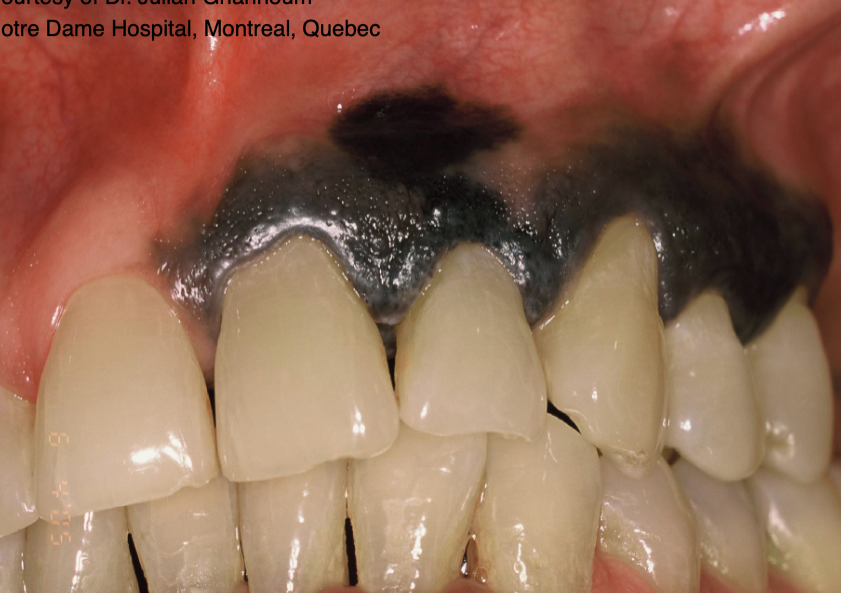
T/F: all oral melanomas are black in color
false
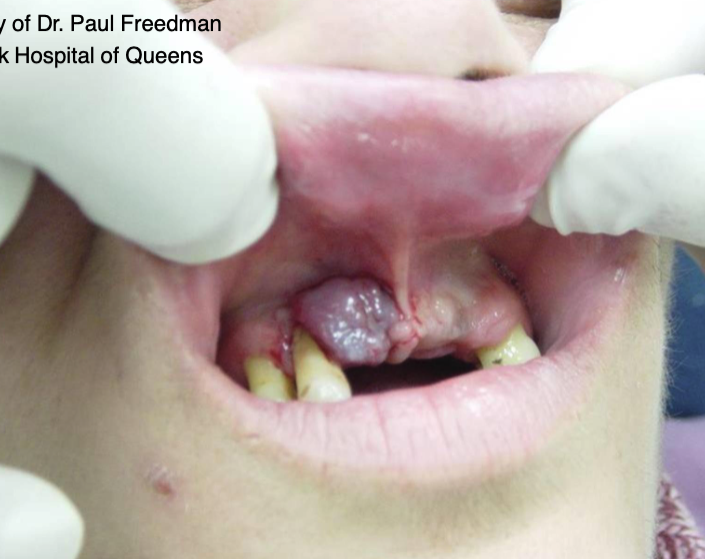
which area is most commonly affected by head + neck melanoma
nasal cavity
2 tx options for oral melanoma
excision
radiation
what’s the survival rate for oral melanoma
5 year survival = 10-20%
T/F: oral melanoma has a 50% recurrence rate
true
Melanomas are a type of cancer that occurs in both the skin and oral mucosa. It however occurs far less commonly intraorally and the palate and gingiva are high risk sites.
• A. Both statements are true
• B. Both statements are false
• C. First true, second false
• D. First false, second true
A. Both statements are true
Which of the following cutaneous melanoma is found more commonly in the oral cavity?
a) Superficial Spreading Melanoma
b) Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
c) Nodular Melanoma
d) Metastatic Melanoma
e) Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
b) Acral Lentiginous Melanoma