Biochem Exam 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
covalent bonds
strong sharing of electrons
hold atoms together so molecules are formed
noncovalent bonds
weaker bond; do not share electrons
macromolecules
have a sense or directionary
biomolecules
3 dimensional architecture, weak forces
macromolecule examples
proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, polysacharides
monomer examples
amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, monosacharides
linkage examples
peptide(amide), glycoside, phosophpodiester, ester
____ forces influence structure and behavior; create interactions that are constantly forming and breaking, restrict organisms to a narrow range of environmental conditions
weak
examples of weak forces
vander Waals interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, hydrophobic interactions
prokaryotic cells
single membrane, no nucleus(has a nucleoid) or organelles
eukaryotic cells
much larger, nucleus + many organelles
high BP, heat of vaporization, surface tension, polar
unique properties of water
hydrophilic
water loving, polar/charged, ions, alcohols, proteins, nucleic acids
hydrophobic
water fearing, no polar, oils & cholesterol
amphipathic
both hydrophobic and hydrophilic, polar and non polar ends, fatty acids and detergents
dipeptide
2 residues
each amino acid unit is called a
residue
tripeptide
3 residues
12-20 residues
oligopeptide
many residues
polypeptide
monomeric
only 1 polypeptide chain
multimeric
more than 1 polypeptide chain
homomultimer
one kind of chain
heteromultimer
two or more different chains
isolated system
exchange neither matter or energy with their surroundings
closed system
may exchange energy ; not matter
open system
may exchange matter and/or energy
enthalpy
heat content of a system
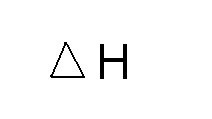
heat absorbed in a constant pressure process
endothermic
when heat is absorbed by a system
exothermic
when a system loses heat to the surroundings
entropy
a measure disorder of randomness/disorder in a system
an organized or ordered state is:
low etnropy
a disordered state is:
a high entropy state
1st law of thermodynamics
the total energy of the universe must be constant
cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
the entropy of an isolated system will tend to increase maximum volume
entropy is unchanged by ____ processes
reversible
entropy increases for _____ processes
irreversible
all naturally occurring processes proceed toward _____, that is, to a state of minimum potential energy
forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate
No net change in reactant or product concentrations
ΔG = 0
equilibrium
homeostasis
organisms maintain homeostasis by keeping the concentrations of most metabolites at steady state
in a steady state, the rate of synthesis of a metabolite equals the rate of breakdown of this metabolite
Reduced coenzymes
NADH and FADH
nucleotide functions
energy for metabolism, enzyme cofactors, signal transduction
nucleic acid functions
storage, processing and transmission of genetic info, protein synthesis
nucleotide components
nitrogenous base, pentose, phosphate
nucleoside components
nitrogenous base, pentose, no phsphate
nitrogenous bases are
planar
nitrogenous bases absorb uv light around
250-270nm
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil
purines
adenine and guanine
Nutrigenetics
embodies the science of intensifying and characterizing gene variants associated differential responses to nutrients and relating this variation to disease status
focuses on differences at SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) level
Nutrigenonics
studies of constituents of the diet interact with genes and their products and how
focuses on the effects of nutrients on the genome, protons, and metabolism
↑ Reactants
→ shift toward products
↑ Products
→ shift toward reactants
↑ Temperature
→ favors endothermic reaction
↓ Temperature
→ favors exothermic reaction
↑ Pressure (gases)
→ shift toward fewer gas molecules
↓ Pressure (gases)
→ shift toward more gas molecules
Negative ΔG
exergonic
Positive ΔG
endergonic
Endergonic reaction
Requires energy; nonspontaneous
Exergonic reaction
Releases energy; spontaneous
Negative ΔH (energy released)
favors spontaneity
Positive ΔS (increased disorder)
favors spontaneity
ΔG
change in free energy
ΔH
change in enthalpy (energy in bonds)
ΔS
change in entropy (disorder)
Free Energy (G)
second law in open systems, energy available to do work at constant temperature and pressure
G=0 is equilibrium/ G>0 is non-spontaneous or endergonic/ G<0 is spontaneous or exogonic
Phospholipids
polar head + nonpolar fatty acid tails
Fatty acids
charged carboxyl group + hydrocarbon chain
Detergents & bile salts
help mix fats with water
Nucleus
Stores DNA; controls gene expression; nucleolus makes ribosomes
Mitochondria
Produces ATP; cellular respiration; regulates apoptosis
Rough ER
Synthesizes proteins for secretion and membranes
Smooth ER
Lipid synthesis; detoxification; calcium storage
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis (free → cytosolic proteins; bound → secreted/membrane proteins)
Lysosomes
Intracellular digestion; breakdown of macromolecules and old organelles
Peroxisomes
Fatty acid oxidation; detoxifies hydrogen peroxide
Cytoskeleton
Cell shape, movement, and intracellular transport
Plasma Membrane
Selective barrier; regulates transport and cell signaling
Chloroplasts (plants)
Photosynthesis
Vacuole
Storage; maintains turgor pressure in plant cells
Cell Wall
Structural support and protection
Centrosome/Centrioles
Microtubule organization; spindle formation during cell division
System
portion of the universe w/which we are concerned
SNP
occurs within a gene, having more than one allele
may lead to variations in amino acid sequence
not just genes
Genome Wide Association Study (GWAS)
working towards detection, treatment, and prevention to find SNP associated with a trait or disease
Genotyping
Laboratory method to identify specific genetic variants
Tells which alleles an individual has
Does not analyze traits or inheritance
Linkage Analysis
Family-based method
Tracks inheritance patterns of traits
Identifies genes near each other on chromosomes
Focuses on co-inheritance, not population association
omics
large-scale study of an entire set of biological molecules in a system
Genomics
entire genome (DNA)
Transcriptomics
all RNA transcripts
Proteomics
all proteins
Metabolomics:
all metabolites
Epigenomics
gene-regulating chemical modifications
Lipidomics
all lipids
Microbiomics
microbial communities
Single gene disorder
PKU and lactose intolerance
Complex disorder
nutritional modifies the expression of genes and metabolism of nutrients varies by genotype
Thrifty gene hypothesis
obesity used to be beneficial for energy storage, might explain the increase in obesity