Topic 2 - Innate Immunity 1 (Inflammation + Phagocytosis)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
True or False: Both Innate and Adaptive immunity Only exist in higher organisms?
False
Innate immunity exists in most/all organisms
Adaptive only exists in bony fish+ higher organisms
Innate vs. Adaptive immunity
What type of defense is each
What makes up the defense for each?
1st, 2nd + 3rd line
INNATE: Non-specific defense
1st line of defense = skin, mucous membranes + chemicals eg. enzymes, pH AMPs from lecture 1)
2nd line = Innate immune cells (Phagocytosis, complement, interferon, inflammation + fever)
ADAPTIVE = Specific defense
3rd line = Lymphocytes + Antibodies
***Fundamentals of INNATE immunity: 4 differences with Adaptive
Non-specific recognizes general patterns present on most pathogens using PRR (pattern recognizing receptors - physl) Adaptive recognizes specific markers on specific pathogens
Exists before infection, already in pace + ready to act (Adaptive immunity is developed after infection)
Rapid response encoded (adaptive immunity takes days)
Identical response with repeat infection (adaptive response typically gets stronger with repeat infection)
Where is the rapid response of Innate immunity encoded?
In the germ line DNA in sperm + egg cells
About how long does it take for Adaptive immunity to develop vs. innate
Adaptive ~ 6 days
Innate = hours
What were the innate immune cells listed throughout the slides?
Define/describe each if needed
(don’t know if need to know the details at this stage)
Phagocytes - eg. Neutrophils(have unique nucleus shape)
Dendritic cells - Good at presenting pathogens to the lymph nodes for recognition
Complement - similar to AMPs (OIL, opsonization, inflammation + Lysis)
NK cells (natural killer cells) - ONLY INNATE LYMPHOCYTE. A type of WBC that are rapid + innate
Mast cells - Located in TISSUE near skin surface for easy release upon infection. Release things that trigger Inflammation + recruit immune cells
What are the 2 main Innate immunity responses covered in these slides?
Inflammation
Phagocytosis
What is one Function/ purpose of inflammation?
MOBILIZING bodily defenses at site of infection
What are 2 aspects of Inflammation, what is the purpose of each aspect + What is the result?
Vasodilation of CAPILLARIES = Increase volume = slow down blood flow in the area to allow for WBC to have time to interact with capillary walls = allow for leukocyte rolling
Increase in capillary permeability = allow for more cells into tissue eg. WBC
Result = Influx of immune cells to affected tissues
What are the 4 signs of inflammation + what are the causes of each?
Redness: Vasodilation = increase blood volume
Heat: Increase blood volume
Edema: swelling due to accumulation of fluid from blood in affected tissue
Pain: Some inflammatory mediators trigger pain response
What was the Experiment that was Evidence for Inflammation
Who
What was the method
What was observed
Elie Metchnikoff 1800s
Experiment:
Insult starfish larvae with thorn (contained Bacteria)
Observations:
Rapid localization of cells to site of insult
Break down of thorn by cells
Inflammatory response steps + cells involved
Detection of infection by MAST cells in tissue
Release of inflammatory mediators by MAST cells
Causes Vascular change: The 2 aspects of inflammation - Vasodilation + increased permeability
Mediators act on Endothelial cells to express adhesion molecules
NEUTROPHILS arrive first to site + aggregate at site of infection (margination) + other innate WBC follow
Chemotaxis to infection + Phagocytosis
****What are the 4 steps to make WBC move past the endothelial cells (barrier) from blood to tissue?
describe what occurs at each step
Margination - WBC move to vessel wall near site of infection
Diapedesis - Mediators change WBC shape to allow them to squeeze between endothelial cells into the tissue
Chemotaxis
Phagocytosis
Where was PHAGOCYTOSIS first observed?
Starfish larvae + thorn experiment (Elie Metchnikoff 1800s)
***What are the steps of Phagocytosis?
Receptors on surface of phagocyte recognize pathogens (primitive way)
Reach out + Engulf the pathogen intracellularly into a Vesicle
A lysosome fuses with the vesicle
Break down + digestion of contents
The fused vesicles fuses with the PM + exocytosis the Garbage (inert/non-infectious) into extracellular space
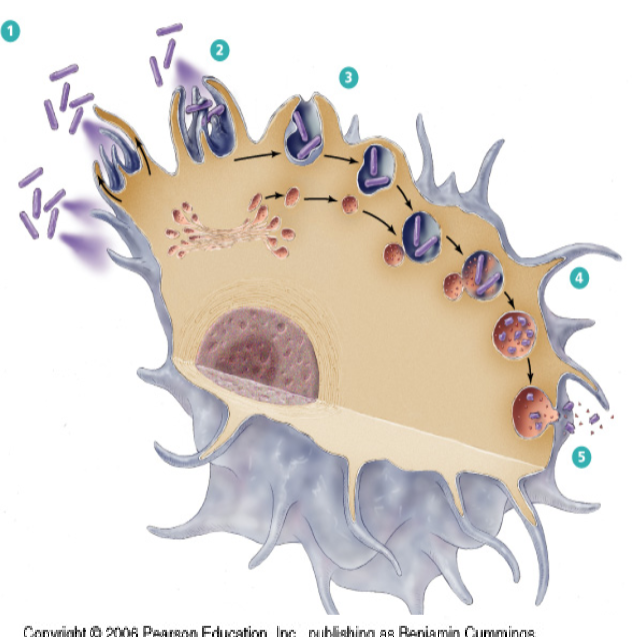
Expand upon the “primitive way” That phagocytes recognize pathogens
Recognize entire classes of pathogens, non-specific
What is the Initial Intracellular vesicle containing the pathogen called?
Where do they lysosomes come from?
What is the Lysosome fused vesicle now called?
Phagosome = Initial vesicle containing only pathogen
Lysosomes originate from the GOLGI
Phagolysosome = The Lysosome + Phagosome fused
True or False: Phagocytosis is highly CONSERVED throughout evolution
TRUE
****What are the 3 examples of Phagocytes mentioned in the slides?
Macrophage (differentiated Monocyte)
Monocyte (precursors that circulate in the blood)
Neutrophil
*****Phagocytes perform what 2 processes?
2 step process:
CHEMOTAXIS
PHAGOCYTOSIS

What is the main idea of this image?
General receptors on phagocyte recognize microbe
Recognition results in activation of signal transduction pathways
Convergent intracellular signaling - all the different pathways CONVERGE INTO ONE SIGNALING PATHWAYS
The converged signaling activates pathways involved in cytoskeletal changes for engulfment
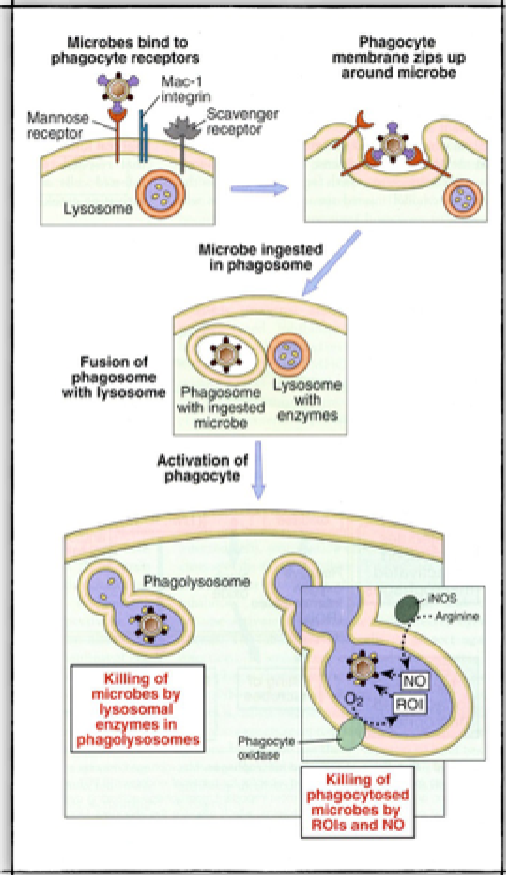
****What are the 5/6 steps of Phagocytosis listed on the slides
Phagocyte detects + engages microbe
Detection of microbe initiates cytoskeletal rearrangements that drive phagocytosis
Microbe is internalized into a specialized phagosome
Phagosome fuses with lysosome = phagolysosome
ROI (reactive oxygen + Nitrogen intermediates) NO killing
Lysosomal enzymes killing
Are Lysosomal enzymes and NO + ROI the same thing?
functions
NO they are 2 different methods of killing
Lysosomal enzymes (O2 independent - physl)= destroy ingested microbes
stored in lysosomes
ROI + NO (O2 dependent - Physl) = destroy microbial proteins, genomes + walls
produced
Describe the Macrophage Development Process
3 steps
Arise from undifferentiated stem cells in the bone marrow (Like all blood cells)
Monocytes = differentiated from stem sites. Leave the bone marrow to circulate in the blood
Inflammation recruits monocytes to sites of infection where they differentiate in resident macrophages
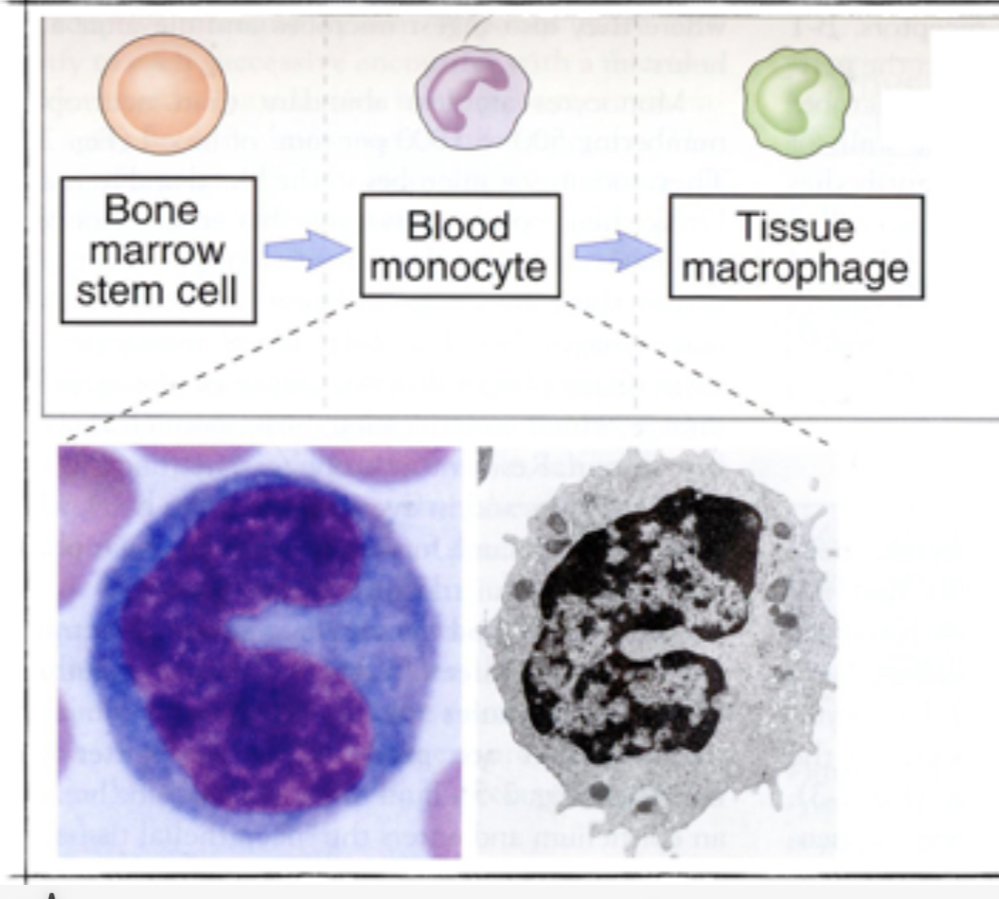
*What are resident macrophages?
LONG LIVED “professional” Phagocytes that ingest large amounts of extra cellular material
Macrophages differentiate to best fit the tissue that they are in
Since macrophages differentiate to best suit their tissue, they also have different names corresponding to their tissue. What are the 4 different macrophages mentioned in the slides + What tissue do they specialize in?
Microglia = CNS
Kupfter cells = liver
Alveolar macrophage = lungs
Osteoclasts = bone
***Is the only function of Phagocytes to eliminate microbes?
No
they also ACTIVATE NEIGHBOURING CELLS
How do phagocytes activate neighbouring cells?
By releasing cytokines + Chemokines
***Are CYTOKINES + CHEMOKINE the same thing?
define each if applicable + differentiate
Functions?
No
Cytokine = Secreted Protein that drive immune + inflammatory reactions
larger molecule + BROADER FUNCTION
One function = Induce proteins in the endothelium that make the endothelium more adherent for passing leukocytes → leads to diapedesis
Produced by: Macrophages + NK cells
Chemokine: Large family of structurally related, low molecular weight cytokines that stimulate LEUKOCYTE MOVEMENT (chemotaxis) + regulate migration of leukocytes from the blood to tissues
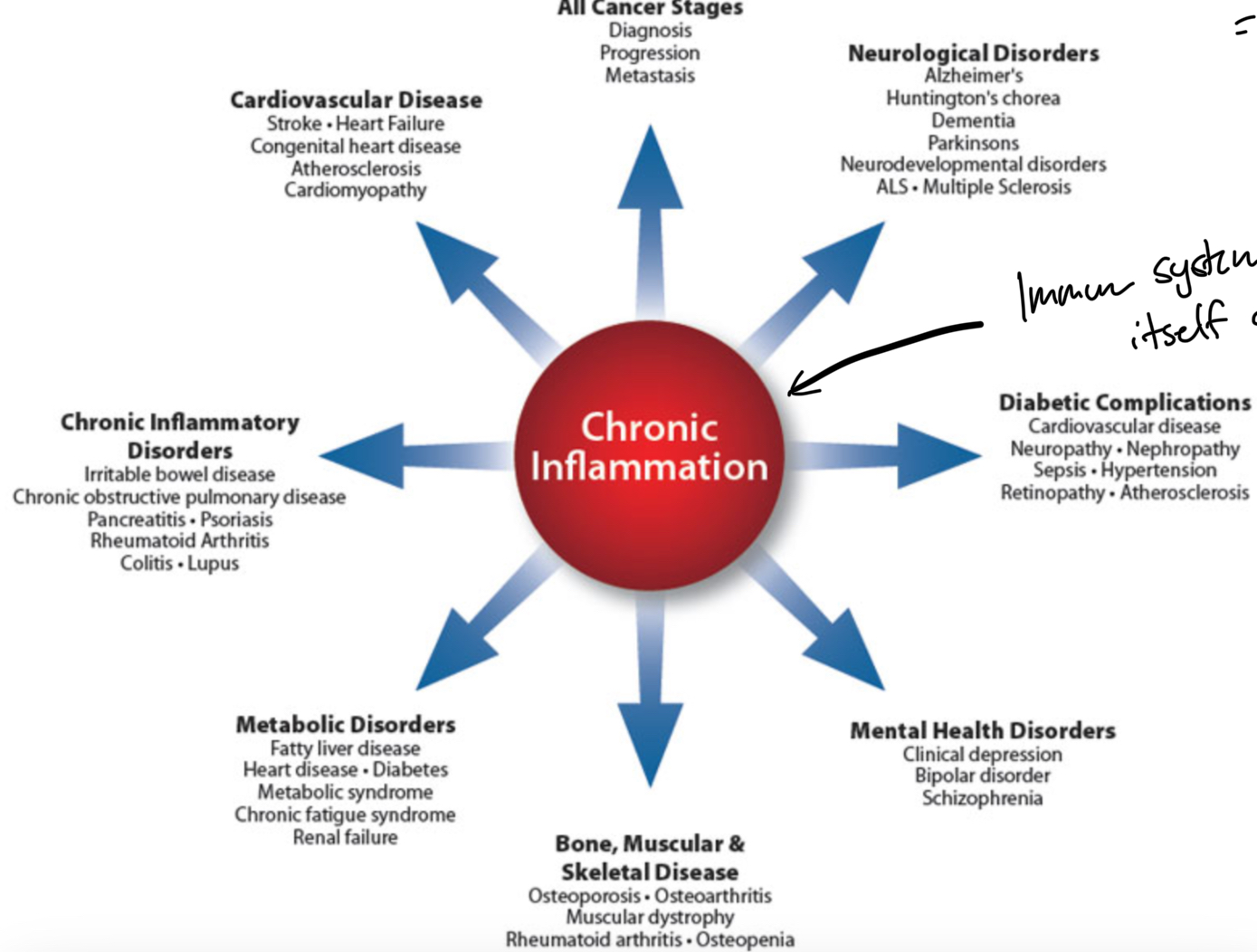
Expand on “Everything comes at a cost”
Immune system is not perfect. If it can’t regulate self, prolonged immune response results in CHRONIC INFLAMMATION