Science Chem Reactions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Metallic Bonding
between 2 metals
Ionic Bonding
between 2 metal and non metal
Covalent
between 2 non metals
Naming covalent bonds
Using number prefixes to say how many of each atom

Naming Ionic
Drop the end and add ide when a non-metal becomes an ion
exothermic reactions
chemical reactions that release energy into the surroundings
endothermic reactions
chemical reactions that absorb energy from their surroundings
Polyatomic ions
an ion composed of two or more atoms
Energy Profile Diagrams
a diagram of different energies involved in a reaction
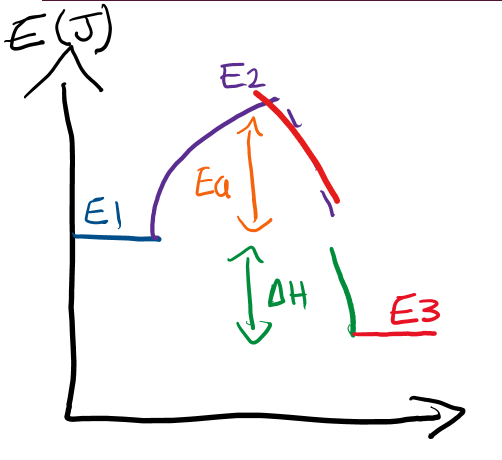
Activation energy
the energy required to break the bonds between the atoms to start a reaction
Activation Energy Formula
E2-E1
Enthalpy
The change of energy between the reactants and products
Enthalpy Formula
E3-E1
4 factors that affect ROR
concentration temperature surface area catalyst
Precipitation
the formation of a solid in a solution during a chemical reaction
Categories of Reactions
Synthesis Decomposition Combustion Neutralisation Precipitation Displacement
Catalysts
a substance that lowers the activation energy required for a reaction to occur
precipitation reaction
Dance partners swap, The non-metal or negative Ion groups swap “partners”
AB + CD -> AD + CB
2 products - AD + CB – need to determine if the products stay in solution or if they form a material that is insoluble – precipitate (solid)
LHS and RHS in displacement
Metals in solution and Metals by itself
Reaction occurs Displacement General Form
A+BC=B+AC
No Reaction Displacement General Form
A+BC= No Reaction
LHS>RHS
reaction will occur
LHS<RHS
no reaction will occur
Displacement reactions
the a possibility that a negative ion will swap with the metal.
Combustion Reactions
a reaction where reaction when a fuel is burned and reacts with oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide
Concentration Formula
= Mass of solute dissolved (grams)/Volume of Solvent Litres
Synthesis
reactants come together to create a single product:
Decomposition
where a single reactant breaks down into 2 (or more) products:
Are cataylsts used up in a reaction
catalysts are not used up in a reaction
How do catalysts help a reaction proceed more quickly
less energy required to break bonds, makes reaction quicker
Explain why the temperature of an endothermic reaction decreases despite having more energy than the reactants
energy from environment is absorbed in the reaction
this energy is then stored in the products making temperature decrease
Method to identifying oxygen or hydrogen gas
Put a glowing splint/match in the test tube, it reignites
How can temperature affect rate of reaction
higher temperature increases ROR due to more kinetic energy which makes particles collide more
How to Identify gases
Limewater test
bubble gas in limewater if it turns milk or cloudy it is insoluble
Which gas pops when tested with a lit match
hydrogen gas
TEMPERATURE Increase in reaction is a
exothermic reaction
TEMPERATURE Increase in reaction is a
endothermic reaction