1 Steroidal anti-inflammatory agents
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Terminology
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Autoimune disease. dysregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α ,IL-1 → inflamation. Treatment NSAID, SAID
DMARD known: synthetic DMARDs , biological DMARDs and JAK-i
Addison's Disease:
Hypercortisolism(Cushing's disease ):
Crohn's disease:
ulcerative colitis:
Cushing's Syndrome:
glucocorticoid therapy:
Cyclooxygenases (COX):
Thromboxane (TXA2):
ALL NSAID are COX inhibitors
Hydrocortisone
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drug,Glucocorticoid receptor agonists, short acting
IND: Acute and chronic cortex adrenal insufficiency (hormonal replacement)

Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone Dexamethasone
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, Glucocorticoid receptor agonists, medium long acting
1 fastmembrane stabilizing effects (lysosomal, mast cell stabilization)
2. Slow, genomic effects, intracellular corticosteroid receptor activation
Anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, anti-allergic, anti-shock, immunosuppressive, antiproliferative effect
IND: Autoimmune diseases (RA), Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn's disease),Transplantology, Allergy (anaphylactic shock, bronchial asthma)
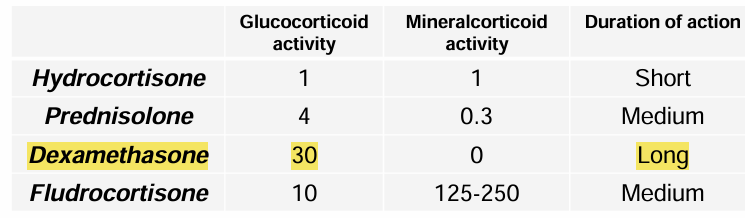
Fludrocortisone
affecting the adrenal cortex, , , Long acting
SAID → Mineralocorticoid receptor agonists → water retention
Fluorinated hydrocortisone derivative, Aldosterone receptor agonist in distal renal tubules and collecting ducts DNA transcription, promotes expression of epithelial Na + channels, increases Na + reabsorption and water retention, → ↑ BP, promotes K + excretion
IND: mineralocotricoid substitution, Replacement therapy for Addison's disease
Side effect: hypertension, oedema, hypokalemia
Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
NSAID, Non-selective inhibition of COX1 / COX2 (dose dependent)
1. Inhibition of COX2: Anti-inflammatory, inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects (medium high dose)
2. Inhibition of COX1 - irreversible ,antiplatelet effect
IND: mild/moderate acute pain
SE: gout, ulcer, bleeding, thrombosis, gastrointestinal bleeding
Contraindication: children under 12 with fever
(170x more potent on COX-1)
Diclofenac Ibuprofen
NSAID, analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory action
IND: Pain, Muscuskeletal disorders
Inhibiti: COX1/COX2, prostaglandin synthesis,
SE: prothrombotic Cardiovascular risk
Diclofenac: most anti-inflammatory
Etoricoxib
NSAID, Selective inhibition of COX2 → inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis,analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory action
IND: Musculoskeletal disorders (rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis), acute pain
Interaction: increased risk of bleeding with systemic GC, anti platelets and anticoagulants; reduces the antihypertensive effect of ACE-I
SE: prothrombotic Cardiovascular risk, but at the same time less risk of bleeding
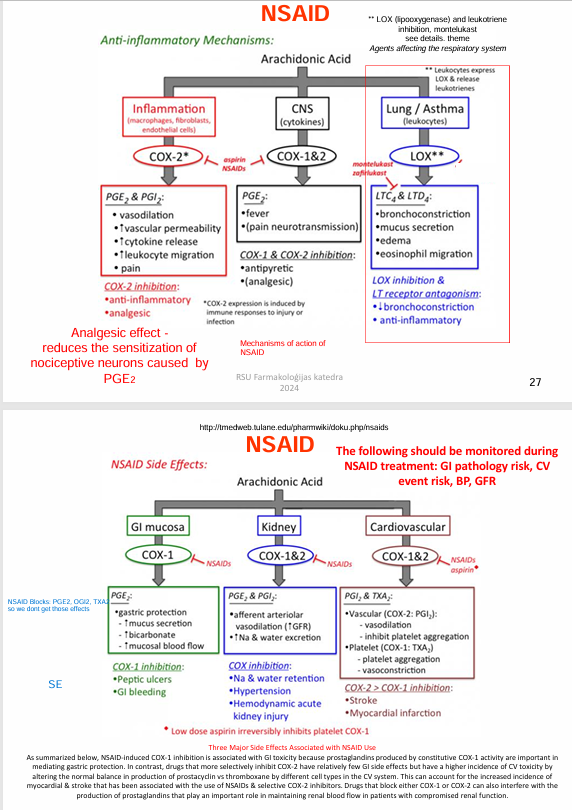
Allopurinol
xanthine oxidase inhibitor, block uric acid production
IND: Gout
Uricostatic effect
prodrug metabolized to alloxanthine →
1. Alloxanthine - irreversible xanthine oxidase inhibitor, inhibition of hypoxanthine / xanthine oxidation → blockade of uric acid synthesis
2. Inhibition of purine synthesis
Febuxostat
metabolism of uric acid, Reversible, Selective, xanthine oxidase inhibitor of non-purine origin, Uricostatic effect
IND: ➢ Chronic hyperuricemia in gout patients, Prevention of complications of chemotherapy