Chapter 1 and 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
Psychology
Scientific study of mind and behavior
* scientific method
* scientific method
2
New cards
Empirical method
acquiring knowledge through observation, includes experimentation, rather than a method based only on forms of logical argument or previous authorities
3
New cards
Willhelm Wundt
* 1st person to be referred to as psychologist
* Psychology is scientific study of conscious experience
* goal was to identify components of consciousness and how those components combined to result in our conscious experience
* Introspection (internal perception): process by which one examines their own conscious experience in an attempt to break it into its component parts
* Voluntarism: people have free will and should know intention of psychological experiment they are participanting in
* Psychology is scientific study of conscious experience
* goal was to identify components of consciousness and how those components combined to result in our conscious experience
* Introspection (internal perception): process by which one examines their own conscious experience in an attempt to break it into its component parts
* Voluntarism: people have free will and should know intention of psychological experiment they are participanting in
4
New cards
Introspection
* (internal perception); the process by which one examines their own conscious experience in an attempt to break it into its components
* a process by which someone examines their own conscious experience as objectively as possible, making the human mind like any other aspect of nature that a scientist observed.
* learning about one's own currently ongoing, or very recently past, mental states or processes
* a process by which someone examines their own conscious experience as objectively as possible, making the human mind like any other aspect of nature that a scientist observed.
* learning about one's own currently ongoing, or very recently past, mental states or processes
5
New cards
Voluntarism
people have free will and should know intentions of psychological experiment they are participating in
6
New cards
Edward Tichener
* Willhelm’s student
* created structuralism
* created structuralism
7
New cards
Structuralism
understanding conscious experience through introspection
* focus on content of mental process rather than its function
* studying the contents of the mind through the use of lab experiments and introspection
* Analyzes the basic elements of the conscious mind by considering sensations, images, and feelings in a very basic way
* focus on content of mental process rather than its function
* studying the contents of the mind through the use of lab experiments and introspection
* Analyzes the basic elements of the conscious mind by considering sensations, images, and feelings in a very basic way
8
New cards
Functionalism
* Defined: focused on how mental activities helped an organism adapt to its environment
* created by WIlliam James, John Dewey, Charles Sanders Peirce
* Accepted Darwin’s theory of natural selection, explanation of organism’s characteristics
* Natural selection leads to adaptation to environment and behavior
* survival and reproduction
* purpose of psychology was to study the function of behavior in the world
* James believed that introspection could serve to study mental activities but relied on more objective measures
* created by WIlliam James, John Dewey, Charles Sanders Peirce
* Accepted Darwin’s theory of natural selection, explanation of organism’s characteristics
* Natural selection leads to adaptation to environment and behavior
* survival and reproduction
* purpose of psychology was to study the function of behavior in the world
* James believed that introspection could serve to study mental activities but relied on more objective measures
9
New cards
Sigmund Freud
* studied patients with hysteria and neurosis
* introduced psychoanalytic theory, psychoanalysis, and psychotherapy
* theorized problems came from unconscious mind (dream analysis, 1st word that come up to mind)
* introduced psychoanalytic theory, psychoanalysis, and psychotherapy
* theorized problems came from unconscious mind (dream analysis, 1st word that come up to mind)
10
New cards
Neurosis
a disorder involving obsessive thoughts through anxiety. It is described as mental, emotional, or phyical reactions that are drastic and irrational.
11
New cards
Hysteria
ancient diagnosis for disorder, women who had wide variety of symptom (physical and emotional disturbances), no physical cause
12
New cards
Psychoanalysis
patient talks about experiences and selves
13
New cards
Psychotherapy
examine unconscious aspects of self and relationships between therapist and client
14
New cards
Psychoanalystic theory
focuses on the role of person’s unconscious, early childhood experiences
15
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
* Max Wethemier, Kurt Koffka, Wolfgang Kohler
* Gestalt “whole” principles: sensory experiences can be breaken down or relate to each other as a whole
* Today: humanistic theory, influenced research on sensation and perception
* Gestalt “whole” principles: sensory experiences can be breaken down or relate to each other as a whole
* Today: humanistic theory, influenced research on sensation and perception
16
New cards
behaviorism
focus on observing and controlling behavior
1. learned behavior and its interaction with inborn qualities of organism
2. established psychology as scientific discipline through objective methods and experimentation
3. used in behavioral/cognitive-behavioral therapy
* Ivan Pavlov
* John B. Watson
* B.F. Skinner
1. learned behavior and its interaction with inborn qualities of organism
2. established psychology as scientific discipline through objective methods and experimentation
3. used in behavioral/cognitive-behavioral therapy
* Ivan Pavlov
* John B. Watson
* B.F. Skinner
17
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
* conditioned reflex to stimulus which overtime conditioned response to different stimulus
* classical conditioning
* classical conditioning
18
New cards
John B. Watson
study of conciousness flawed, objective analysis of mind impossible, preferred to focus on observable behavior and try to bring it under control
19
New cards
B.F. Skinner
* behavior and drive affected by conequences
* skinner box
* skinner box
20
New cards
Humanism
perspective within psychology that emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans
* Abraham Maslow: hierarchy of needs
* Carl Roger: client-centered therapy; must have unconditional positive regard, genuineness, empathy
* Abraham Maslow: hierarchy of needs
* Carl Roger: client-centered therapy; must have unconditional positive regard, genuineness, empathy
21
New cards
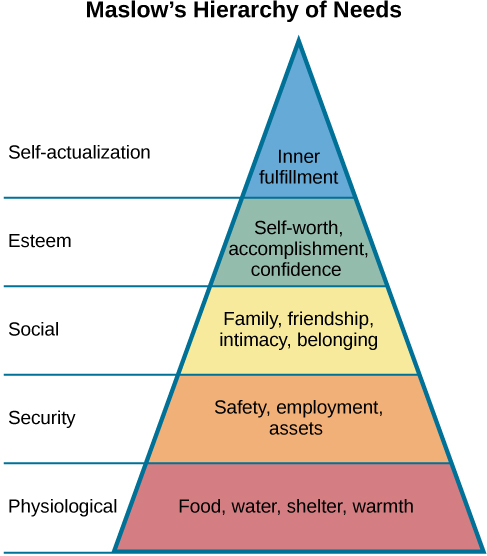
Hierarchy of Needs
created by Abraham Maslow
22
New cards
Client-centered therapy
a therapy where the therapist must show unconditional positive regard, genuineness, empathy
* created by Carl Rogers
* created by Carl Rogers
23
New cards
American Psychological Association
professional organization representing psychologists in the US
* advance and disseminate pychological knowledge for betterment of people
* diversity, 54 branches
* advance and disseminate pychological knowledge for betterment of people
* diversity, 54 branches
24
New cards
Association for Pychological Science
an association seeking to advance scientific orientation of psychology
25
New cards
Biopsychology
study of how biology influences behavior
* how structure and function of nervous system is related to behavior
* how structure and function of nervous system is related to behavior
26
New cards
Evolutionary psychology
seeks to study the ultimate biological causes of behavior
* Charles Darwin evolution by natural selection
* Charles Darwin evolution by natural selection
27
New cards
Neuroscience
interdisciplinary approach with biological psychology as component
28
New cards
Cognitive psychology
study of cognitions, or thoughts, and their relationship to experiences and actions
29
New cards
Developmental pychology
scientific study of development across a lifespan
* Jean Piaget
* Jean Piaget
30
New cards
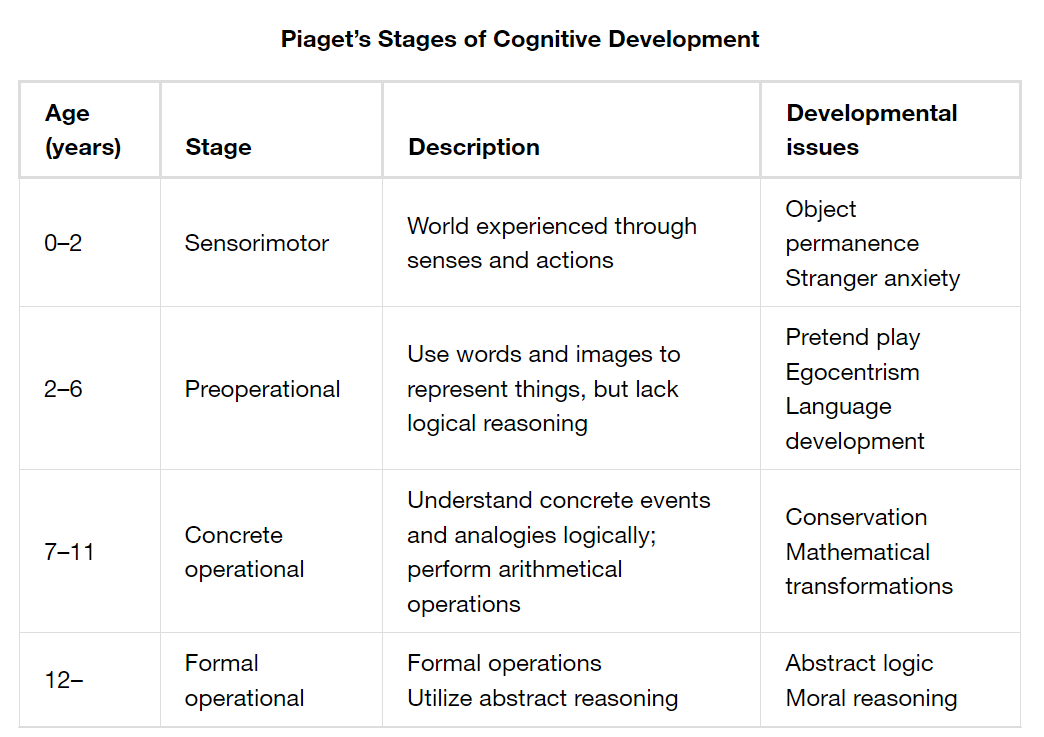
Jean Piaget
* Young children have no object permanence
* focused on cognitive change during infancy, childhood, as we move to adulthood
* However, there are changes that occur much later in life
* focused on cognitive change during infancy, childhood, as we move to adulthood
* However, there are changes that occur much later in life
31
New cards
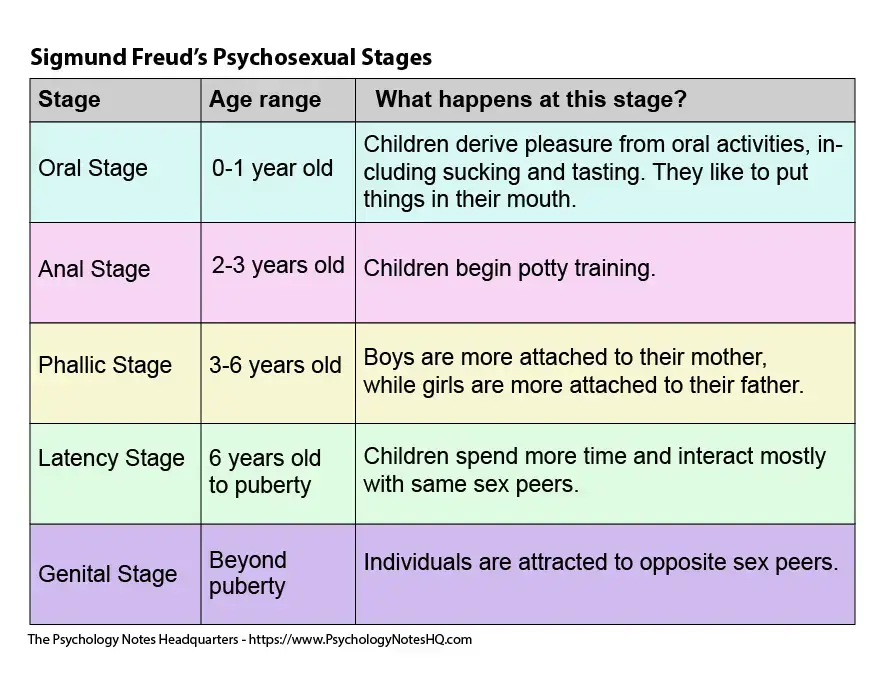
Freud
personality arose as conflicts between unconscious and conscious part of the mind
* part of personality psychology
* psychosexual stage of development
* part of personality psychology
* psychosexual stage of development
32
New cards
Personality trait
consistent pattern of thought and behavior, stable over lifespan, influenced by genetics
* part of personality psychology
* Big Five: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extroversion, Agreeable, Neuroticism (OCEAN)
* part of personality psychology
* Big Five: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extroversion, Agreeable, Neuroticism (OCEAN)
33
New cards
social psychology
how people interact and relate with others
* Stanley Milgram study on obedience
* Stanley Milgram study on obedience
34
New cards
Health Psychology
Focuses on how health is affected by interaction of biological, psychological, sociocultural factors
35
New cards
Biopsychological model
a health psychological perspective that asserts that biology, psychology, social factors interact to determine an individual’s health
36
New cards
Clinical psychology
focuses on diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic pattern of behavior
37
New cards
Counseling psychology
focus on improving emotional, social, vocational, other aspect of lives of psychologically healthy individuals
* part of clinical psychology
* part of clinical psychology
38
New cards
Sports and exercise psychology
interactions between mental and emotional factors with physical performance in sports, exercise, and other activities
39
New cards
forensic psychology
applies science and practice of psychology to issues within and related to justice system
40
New cards
PhD
doctoral degree conferred in many disciplinary perspective house in a traditional college of liberal arts and sciences
41
New cards
dissertation
long research paper/bundled published articles describing research that was conducted as part of the candidate’s doctoral training
42
New cards
postdoctoral training programs
allows young scientists to further develop their research programs and broaden their research skills under the supervision of other professionals in field
43
New cards
PsyD
places less emphasis on research-oriented skills and focus more on application of psychological principles in clinical context
44
New cards
Fact
objective and verifiable observation, established using evidence collected through empirical research
45
New cards
opinion
personal judgements, conclusions, attitudes that may or may not be accurate
46
New cards
empirical
grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless who is observing
47
New cards
deductive reasoning
* results are predicted based on general premise (**broad → specific**)
* Generalization/hypothesis → logical conclusions about real world
* Hypotheses correct=conclusion correct, incorrect=logical, yet incorrect conclusion
* Used to empirically test hypotheses
* Experimental research
* Generalization/hypothesis → logical conclusions about real world
* Hypotheses correct=conclusion correct, incorrect=logical, yet incorrect conclusion
* Used to empirically test hypotheses
* Experimental research
48
New cards
Inductive reasoning
conclusions drawn from observations (**specific → broad**)
* Conclusions may/not be correct, regardless of observations which they’re based
* Formulate theories to generate hypotheses tested with deductive
* Case studies
* Conclusions may/not be correct, regardless of observations which they’re based
* Formulate theories to generate hypotheses tested with deductive
* Case studies
49
New cards
theory
well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for oberved phenomena
50
New cards
hypothesis
tentative and testable statement about relationship between 2+ variables
51
New cards
Falsifiable
able to be disproven by experimental results
52
New cards
Clinical/Case study
observational research that focus on 1 or few people
* **Pros**: gain deep insight of individual(s)’s phenomenon, unmatched by other single research method
* **Cons**: used when individuals are interested b/c of rare characteristics, applying to average people may be limited, __hard to generalize__
* Ex: Krita and Tatiana Hogan who are conjoined twins
* connected at the head, thalamus; insight of mind and brain
* **Pros**: gain deep insight of individual(s)’s phenomenon, unmatched by other single research method
* **Cons**: used when individuals are interested b/c of rare characteristics, applying to average people may be limited, __hard to generalize__
* Ex: Krita and Tatiana Hogan who are conjoined twins
* connected at the head, thalamus; insight of mind and brain
53
New cards
Generalize
inferring that results for sample apply to large population
54
New cards
Naturalistic observation
observation of behavior based in its natural setting
* **Pros**: higher degree of ecological validity, __generalize findings of research to real-world__
* **Cons**: difficult to et up and control, require investment of time, money, luck
* **Pros**: higher degree of ecological validity, __generalize findings of research to real-world__
* **Cons**: difficult to et up and control, require investment of time, money, luck
55
New cards
observational bias
when observations may be skewed to align with observer expectations
56
New cards
inter-rater reliability
measure of agreement among observers on how they record and classify a particular event
57
New cards
Survey
list of question to be answered by research participants--paper and pencil--administered electronically--conducted verbally allowing researchers to collect data from large number of people
* **Pros**: collect info from large sample allows __better generalizations__
* **Cons**: not able to collect same depth of info on ea person, people don’t always give accurate responses (lie, misremember, anwers what makes them look good)
* **Pros**: collect info from large sample allows __better generalizations__
* **Cons**: not able to collect same depth of info on ea person, people don’t always give accurate responses (lie, misremember, anwers what makes them look good)
58
New cards
sample
subset of individuals selected from large population
59
New cards
population
overall group of individuals that researchers are interested in
60
New cards
Measures of center
mode, median, mean, range, standard deviation
61
New cards
mode
frequently occurring response
62
New cards
median
lies at the middle of a given data set
63
New cards
mean
average, conducts additional analyzes, sensitive to outliers
64
New cards
range
highest minus lowest
65
New cards
standard deviation
variance of the whole
* square root variance
* high: spread out; low: close
* square root variance
* high: spread out; low: close
66
New cards
archival research
method of research using past records/data sets to answer various research questions, or to search for interesting patterns/relationships
\*no direct interaction with research participants, no control over info collected, no guarantee of consistency
\*no direct interaction with research participants, no control over info collected, no guarantee of consistency
67
New cards
longitudinal research
studies in which the same group of individuals is surveyed/measured repeatedly over an extended period of time
* **pros**: same individuals (less concerned with different cohorts)
* **cons**: require time/financial investment, participants willing to continue over extended period of time
* **pros**: same individuals (less concerned with different cohorts)
* **cons**: require time/financial investment, participants willing to continue over extended period of time
68
New cards
cohorts
people with similar characteristics or experiences
69
New cards
attrition
reduction in the number of research participants as some drop out of the study over time
70
New cards
cross-sectional research
compares multiple segments of a population at single time
* **Pros**: requires shorter-term investment
* **Cons**: limited by difference that exit between different generations b/c of social and cultural experiences
* **Pros**: requires shorter-term investment
* **Cons**: limited by difference that exit between different generations b/c of social and cultural experiences
71
New cards
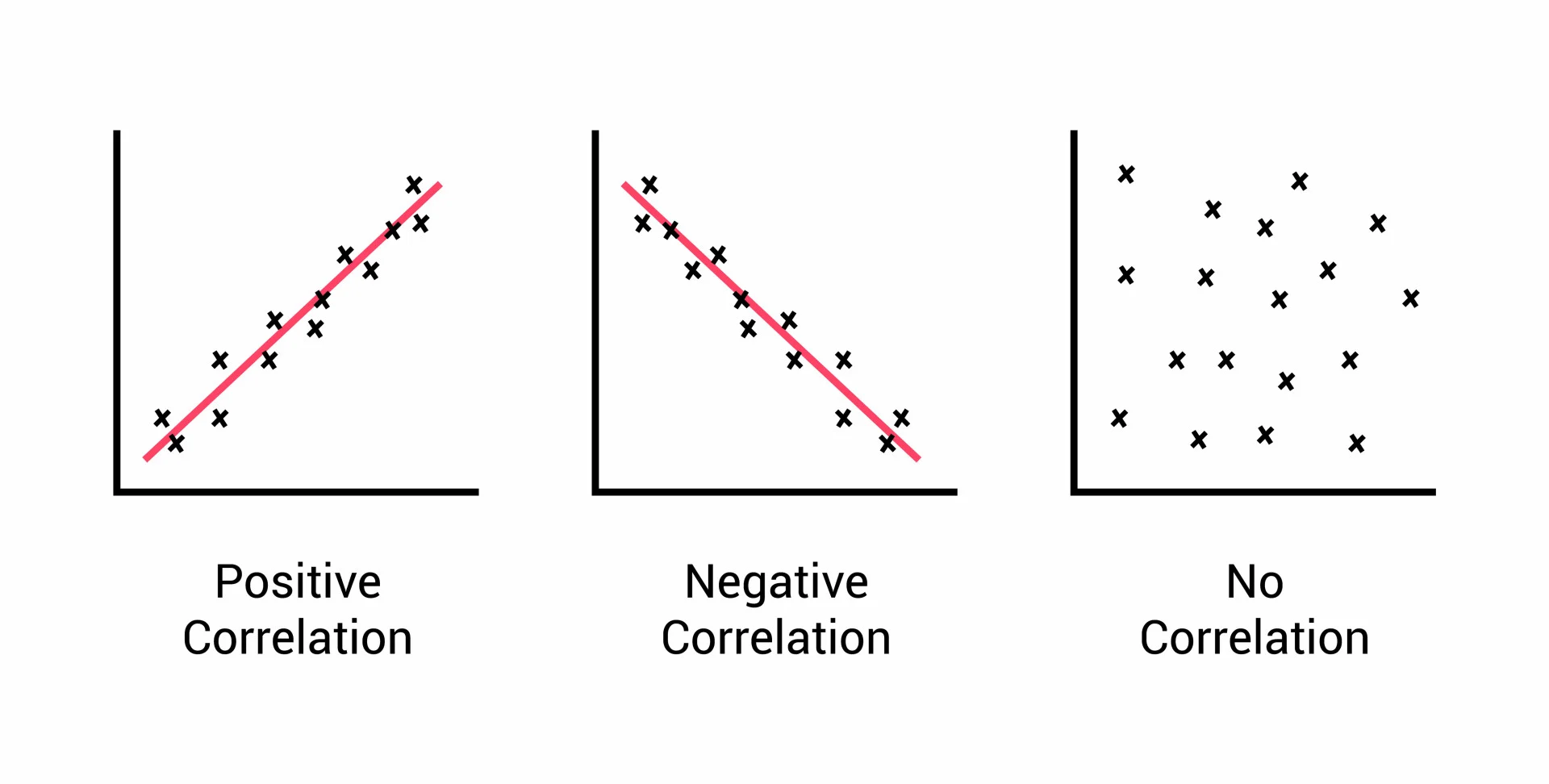
correlation
relationship between 2+ variables; when 2 variables are correlated, one variable change a the other does
* positive correlation
* negative correlation
* positive correlation
* negative correlation
72
New cards
positive correlation
2 variables change in the **same** direction, both becoming either smaller/larger
73
New cards
negative correlation
2 variables change in **different** directions, 1 becoming larger as other becomes smaller; not the same as no correlation
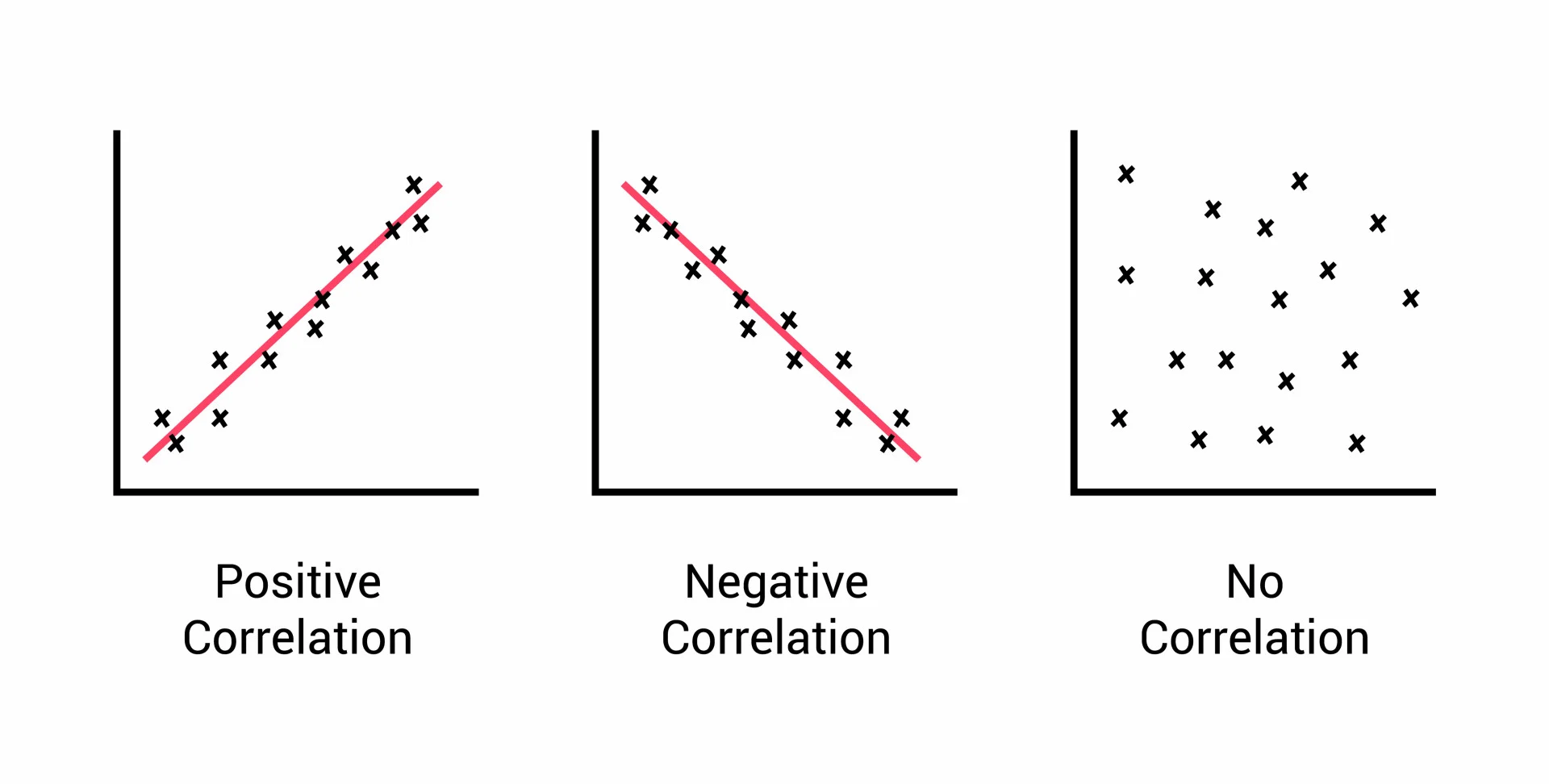
74
New cards
Correlation coefficient
number from -1 to +1, indicating strength and direction of relationship between variables \[r\]
* closer to -/+1 means strongly related and predictable variables are; 0 then weaker relationship and less predictable
* closer to -/+1 means strongly related and predictable variables are; 0 then weaker relationship and less predictable
75
New cards
Cause-and-effect relationship
changes in one variable causes the changes in other variables; can be determined only through an experimental research design
76
New cards
confounding variable
unanticipated outside factor that affect both variables of interest, often giving the false impression that changes in 1 variable change in other variable(s), when, in actuality, the outside factor causes changes in both variables
77
New cards
illusory correlation
seeing relationships between two thing when in reality no such relationship exists
78
New cards
experimental group
designed to answer research question
is given the manipulated independent variable
is given the manipulated independent variable
79
New cards
control group
serves as basis for comparison, controls for chance factors that might influence study’s results
not given the manipulated independent variable
not given the manipulated independent variable
80
New cards
operational definition
description of what actions and operations will be used to meaure the dependent variables and manipulate independent
81
New cards
experimenter bias
researcher expectation skews studies’ results
82
New cards
double-blind study
experiment in which both researchers and participants are blind to group
83
New cards
single-blind study
experiment in which researcher knows which participant are in the experiment vs control group
84
New cards
placebo effect
people’s expectations/beliefs influence/determine their experience in given situation
85
New cards
independent variable
influenced/controlled by experimenter; in well-designed experimental study, the variable is the only important difference between experimental and control groups
86
New cards
dependent variable
measured by researcher to see how much effect independent variable had
87
New cards
participants
subjects of psychological research
88
New cards
random sample/selection
subset of larger population in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
89
New cards
random assignment
method of experimental group assignment in which all participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either groups
90
New cards
peer-reviewed journal articles
read by several other scientist with expertise in subject matter, providing feedback regarding quality of manuscript before publication
91
New cards
replicate
repeating an experiment using different samples to determine research reliability
* reliability
* validity
* reliability
* validity
92
New cards
reliability
Experiment can be repeated multiple times with same result
* **Inter-rater: degree of 2+ different observers agree on what has been observed**
* **Internal consistency: degree of different items on survey that measure same thing correlate with one another**
* **Test-retest**: degree of outcomes of particular measure remain consistent over multiple administrations
* **Inter-rater: degree of 2+ different observers agree on what has been observed**
* **Internal consistency: degree of different items on survey that measure same thing correlate with one another**
* **Test-retest**: degree of outcomes of particular measure remain consistent over multiple administrations
93
New cards
inter-rate
degree of 2+ different observers agree on what has been observed
* a type of reliability
* a type of reliability
94
New cards
internal consistency
degree of different items on survey that measure same thing correlate with one another
* a type of reliability
* Ex: if the respondent expresses agreement with statements like “i like riding bicycles”, “I used to like riding bicycles”, or disagreement “I hate bicycles.” This is internal consistency because it covers the same subject: bicycles.
* a type of reliability
* Ex: if the respondent expresses agreement with statements like “i like riding bicycles”, “I used to like riding bicycles”, or disagreement “I hate bicycles.” This is internal consistency because it covers the same subject: bicycles.
95
New cards
test-retest
degree of outcomes of particular measure remain consistent over multiple administrations
* a type of reliability
* a type of reliability
96
New cards
Validity
accuracy of given result in measuring what it’s designed to measure
* Çan this test actually measure intelligence?
* **Ecological: degree of research results generalize real-world applications**
* **Construct: degree of given variable actually captures/measures what it’s intended to measure**
* **Face**: degree of given variable seems valid on surface
* Çan this test actually measure intelligence?
* **Ecological: degree of research results generalize real-world applications**
* **Construct: degree of given variable actually captures/measures what it’s intended to measure**
* **Face**: degree of given variable seems valid on surface
97
New cards
ecological
degree of research results generalize real-world applications
98
New cards
construct
degree of given variable actually captures/measures what it’s intended to measure
99
New cards
face
degree of given variable seems valid on surface
100
New cards
Institutional review board (IRB)
committee of administrators, scientists, community members that reviews proposal for research involving humans