Lab 4: Roots, Primary Growth, and Modification
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
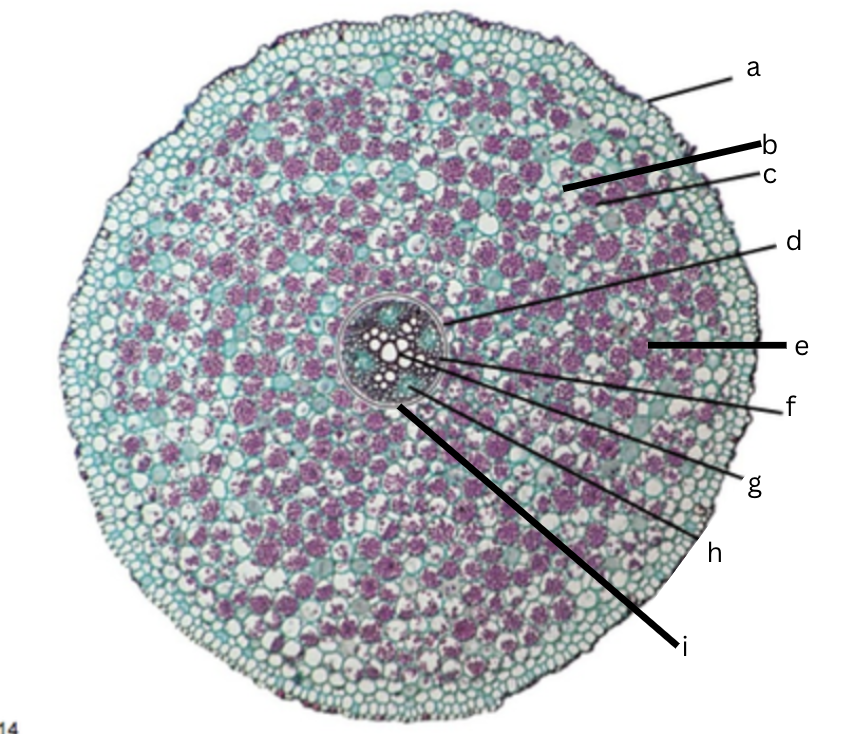
Is this a dicot or monocot? Why? What plant is it?
Dicot, the x in the middle in the xylem and indicator, Ranunculus
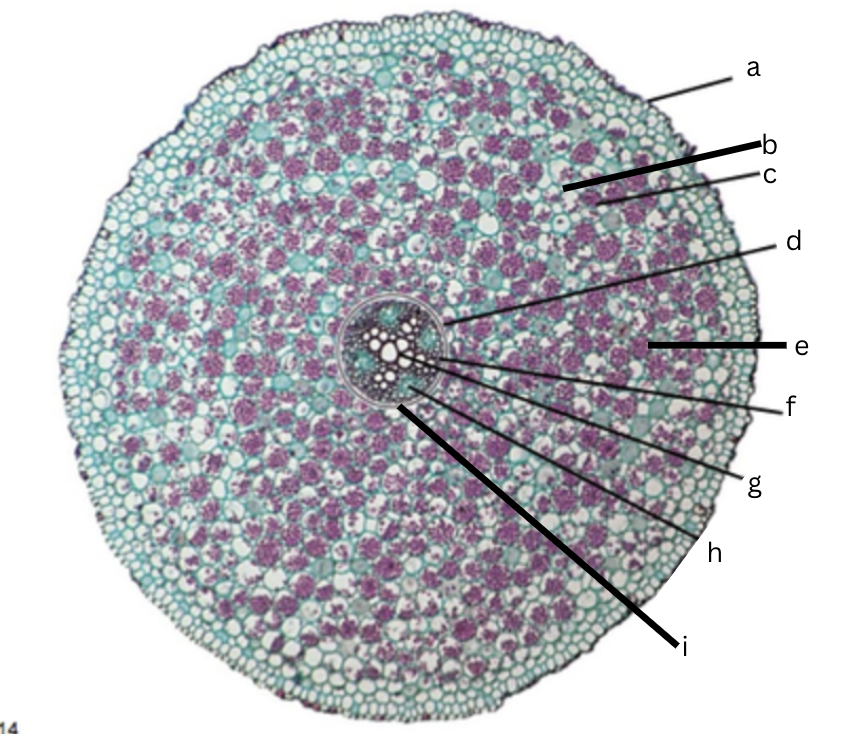

What is a?
epidermis
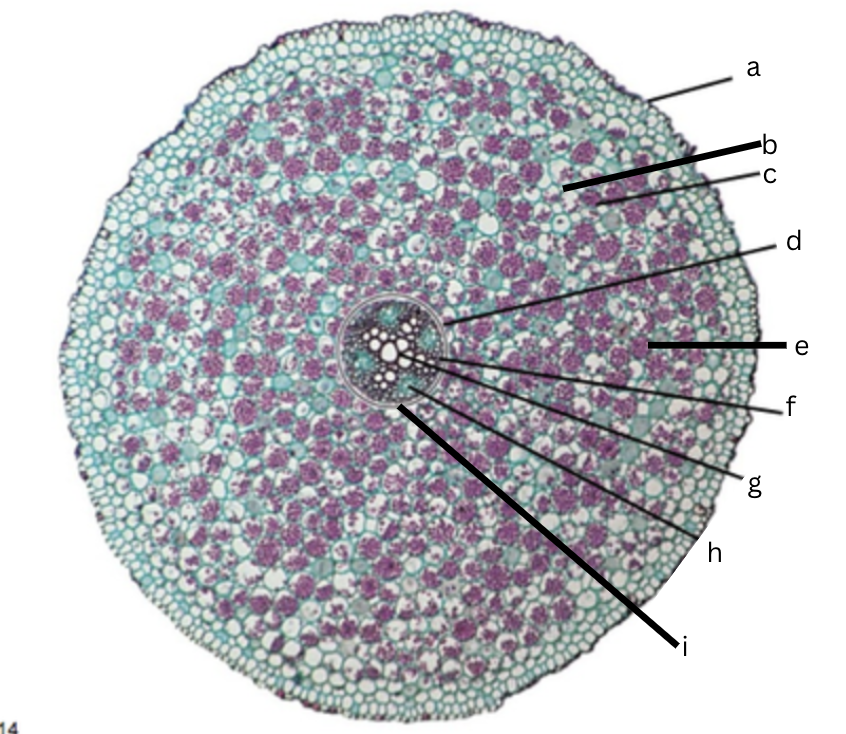

What is b?
intercellular space
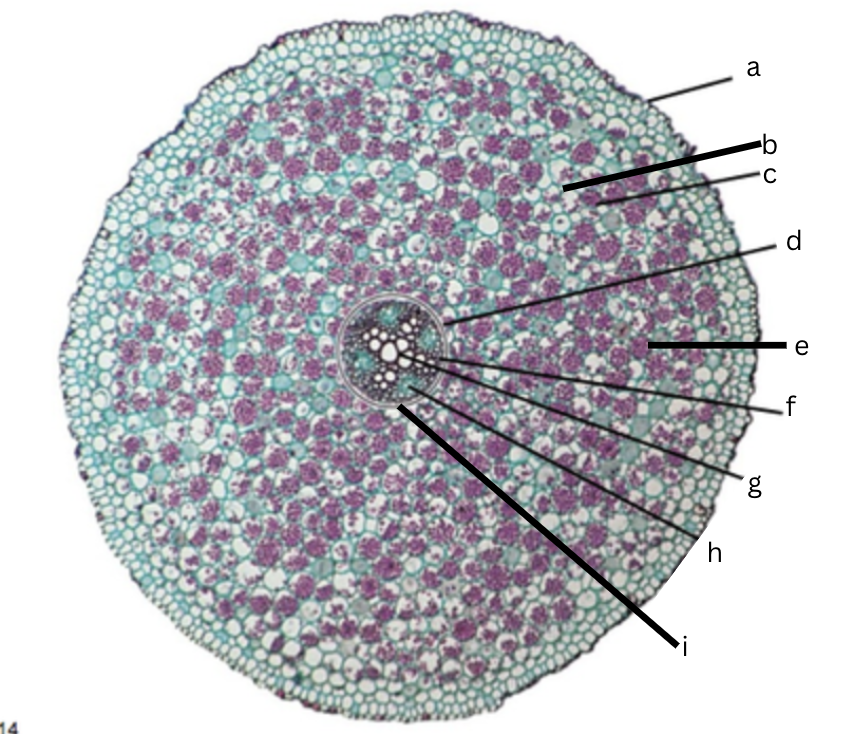

What is c?
cortex
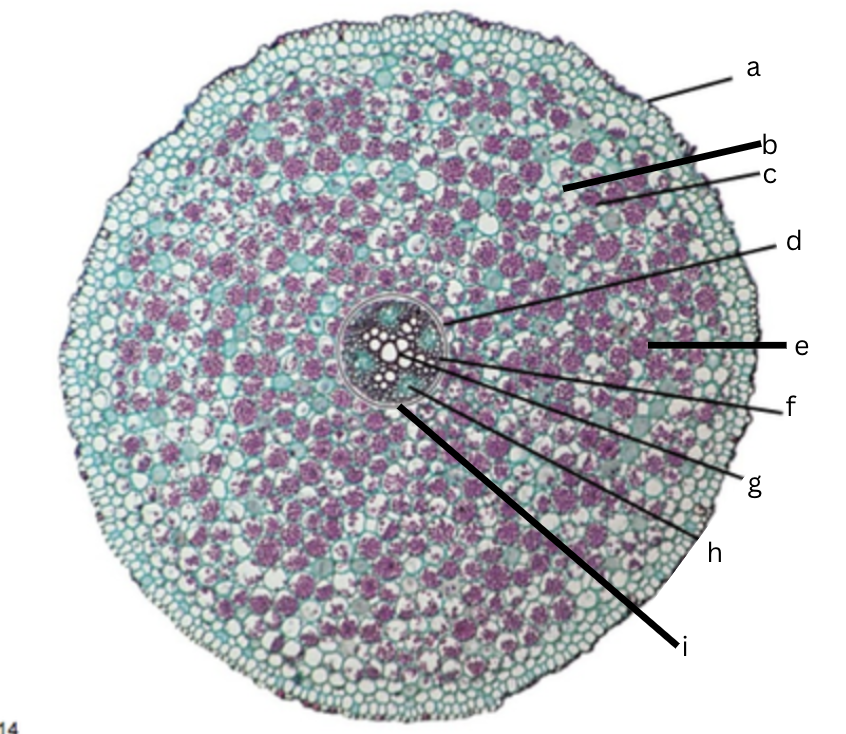

What is d?
endodermis
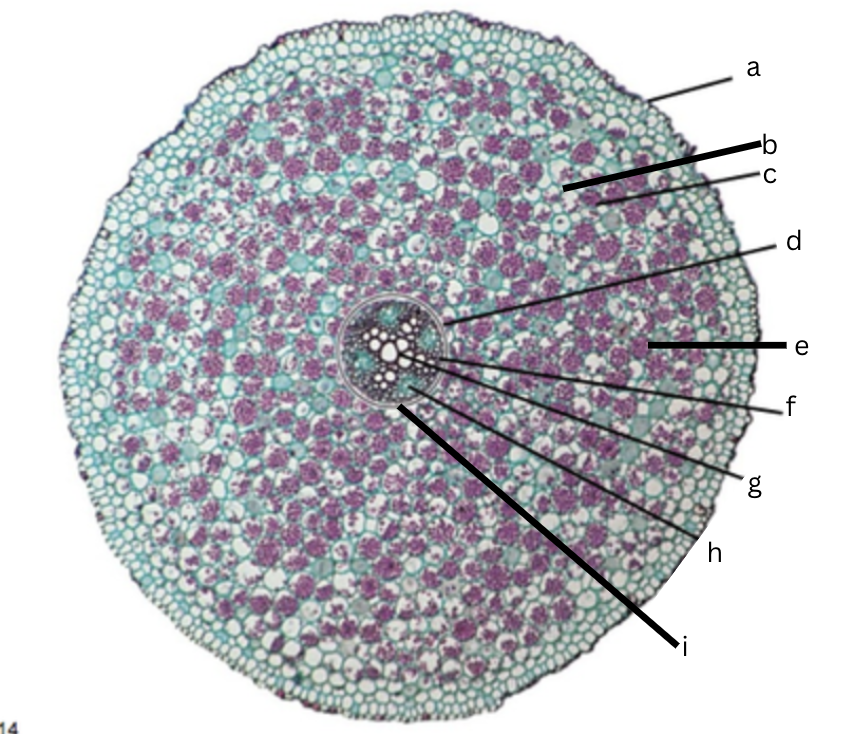

What is e?
starch grains
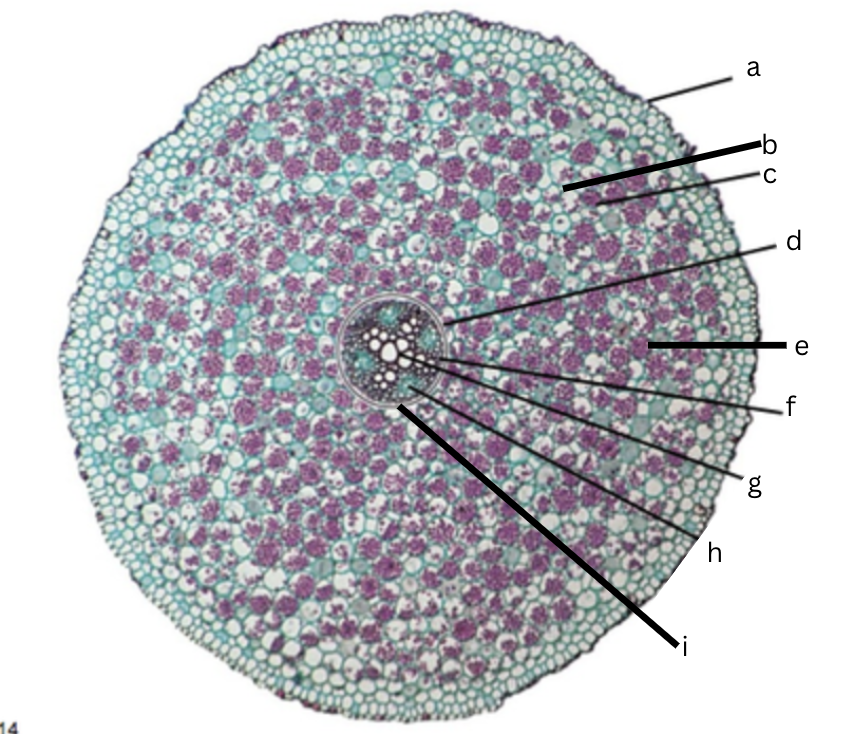

What is f?
pericycle
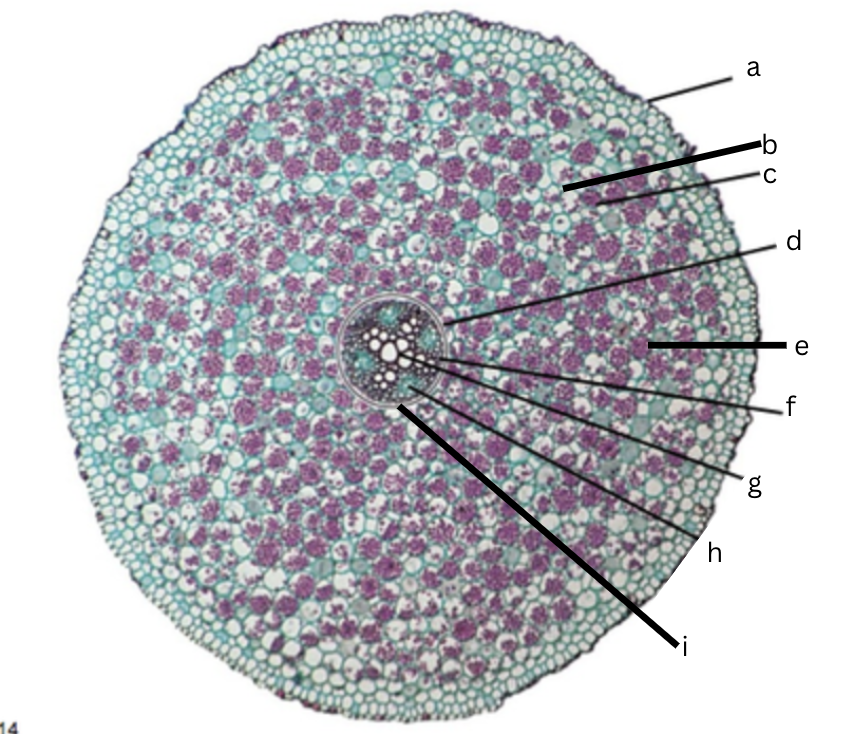

What is g?
xylem
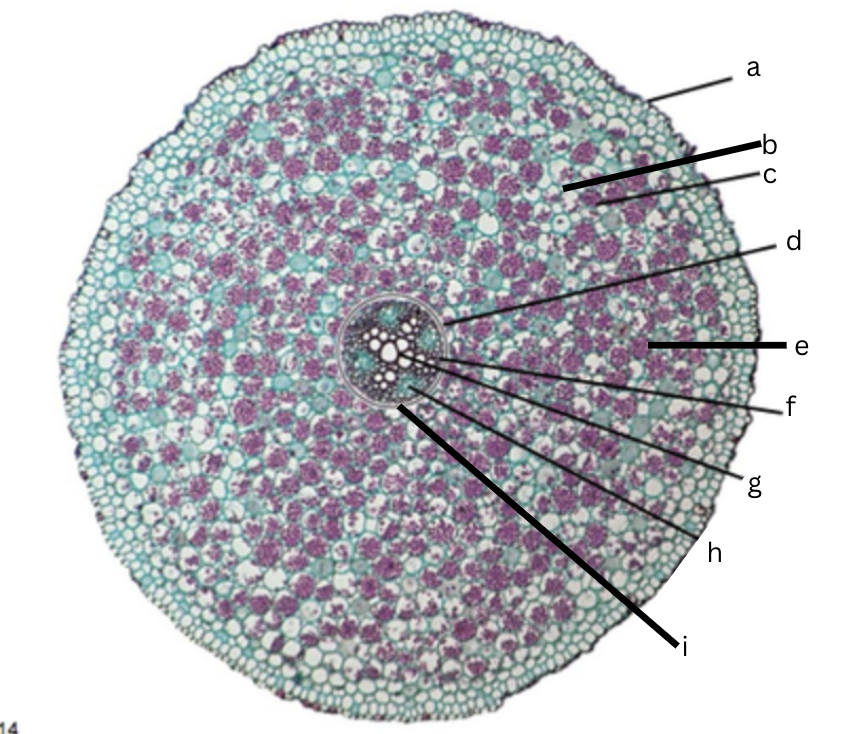

What is h?
phloem
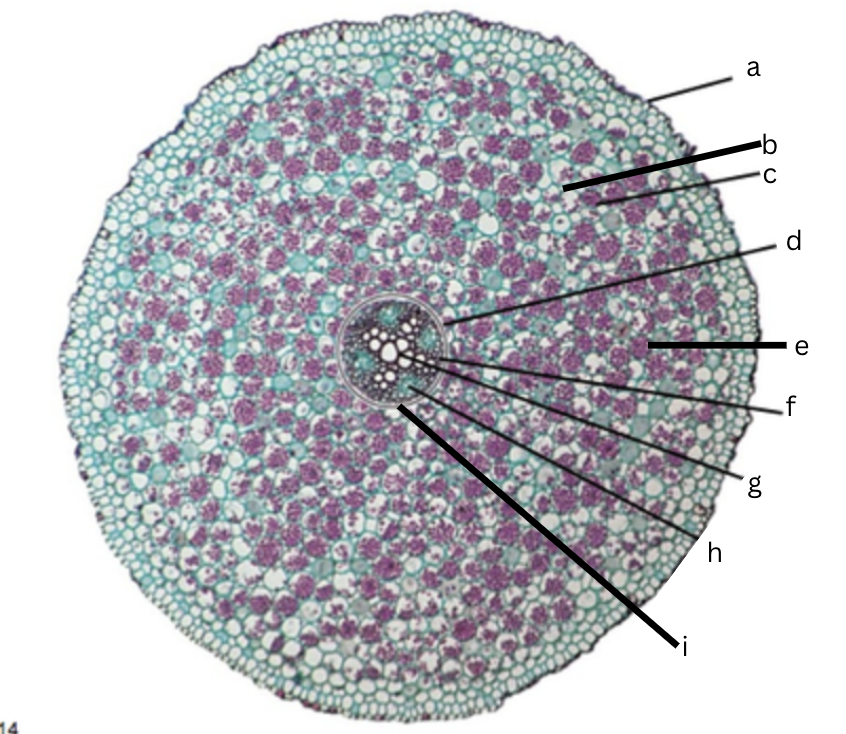

What is i?
Casparian strip (thick wall on cells)
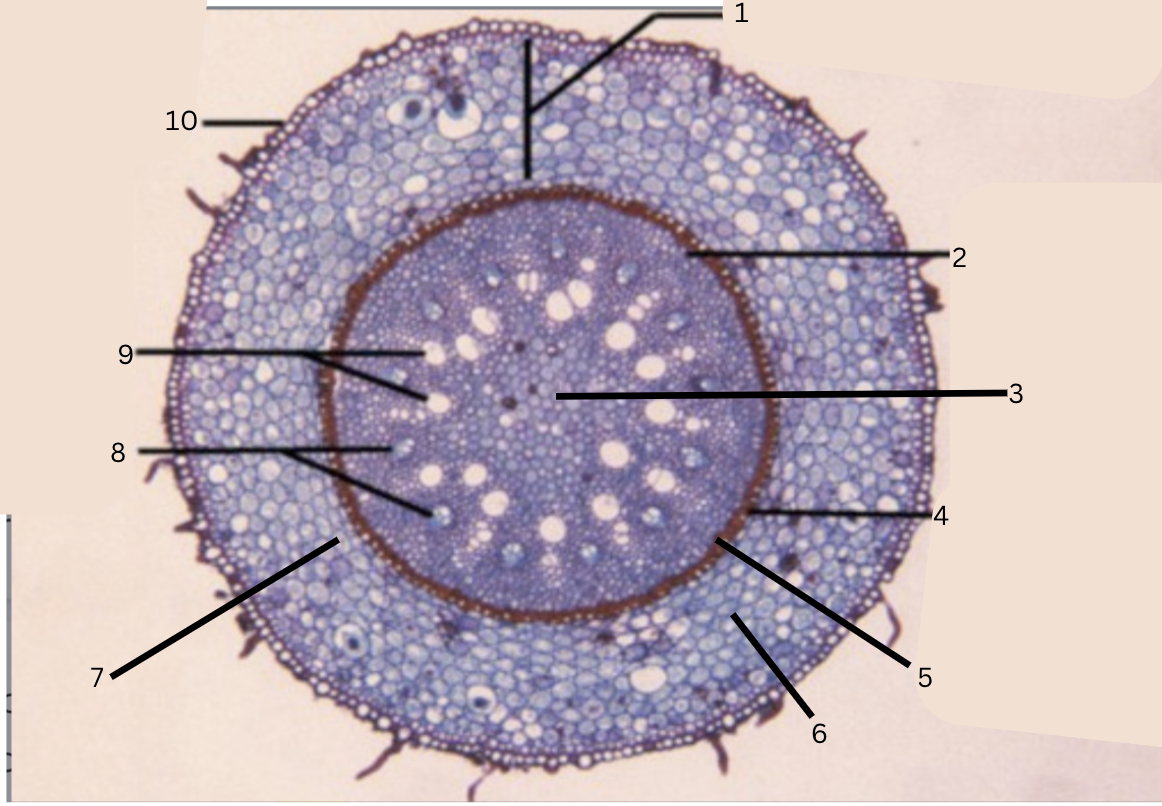

Is this a monocot or dicot? Why? What plant is this?
Monocot, no x in the middle(xylem is not a x), Smilax
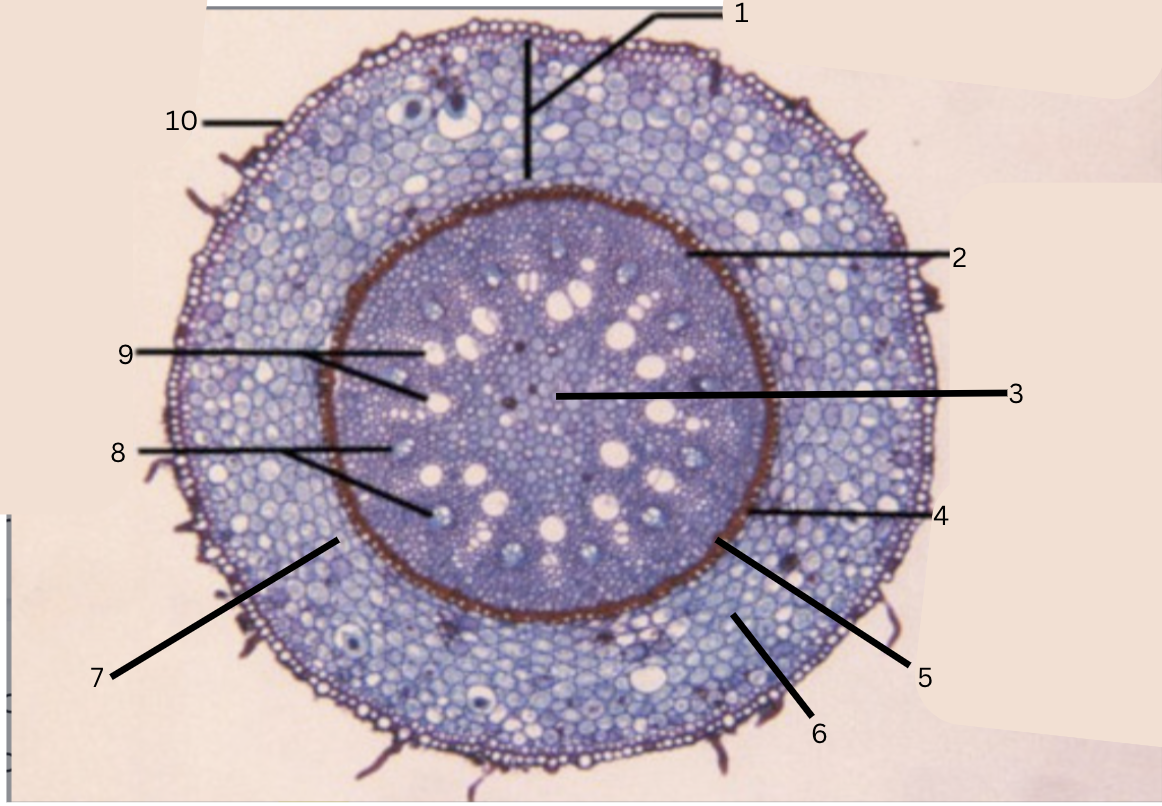

What is 1?
cortex
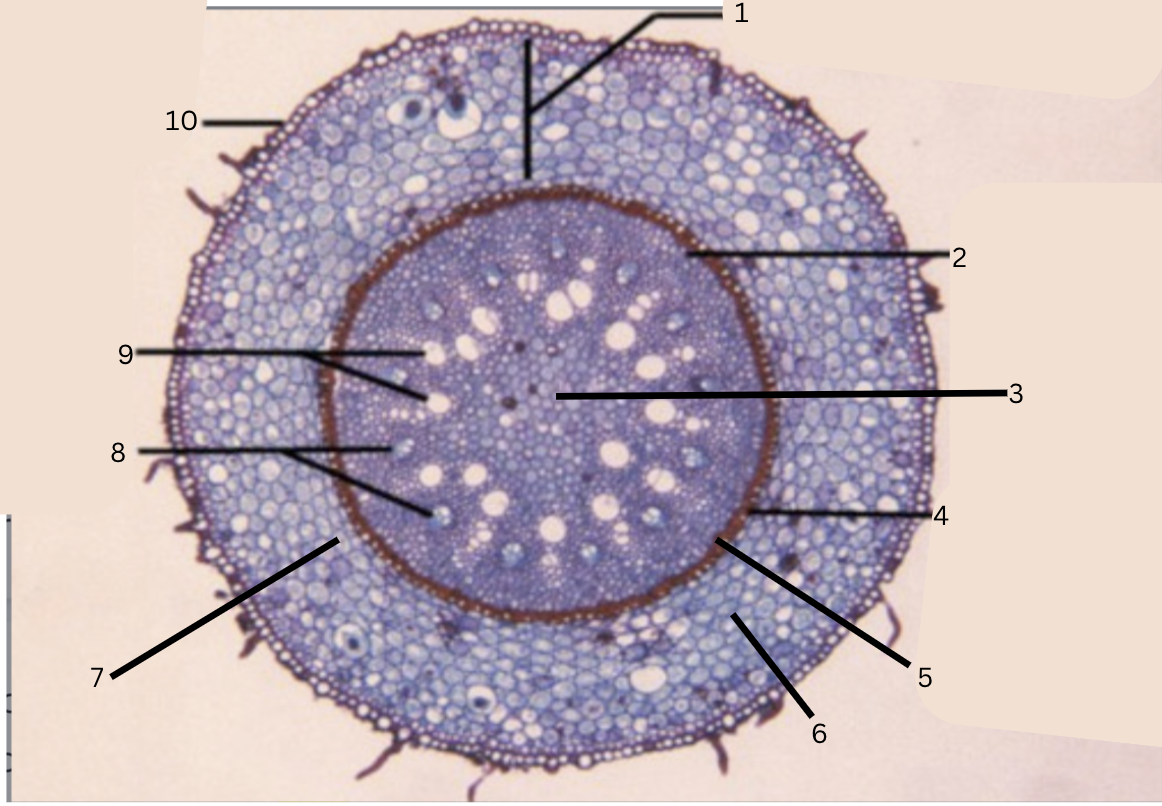

What is 2?
pericycle
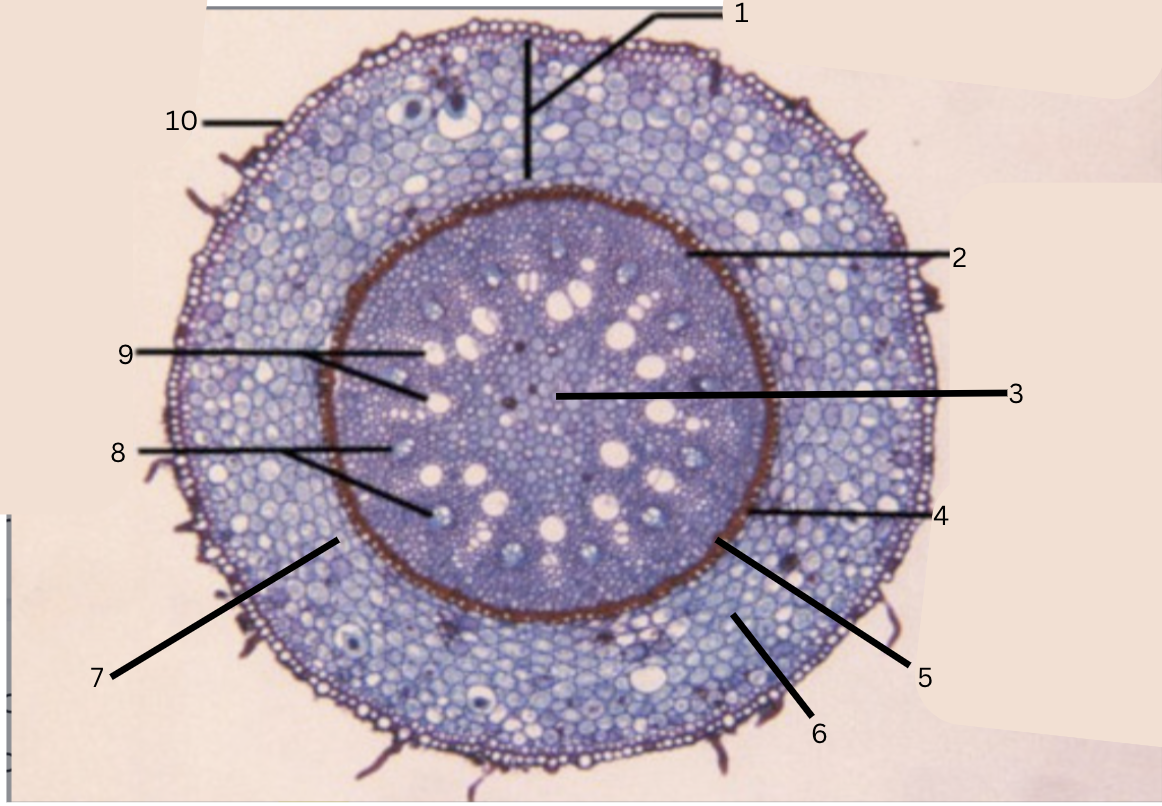

What is 3?
pith
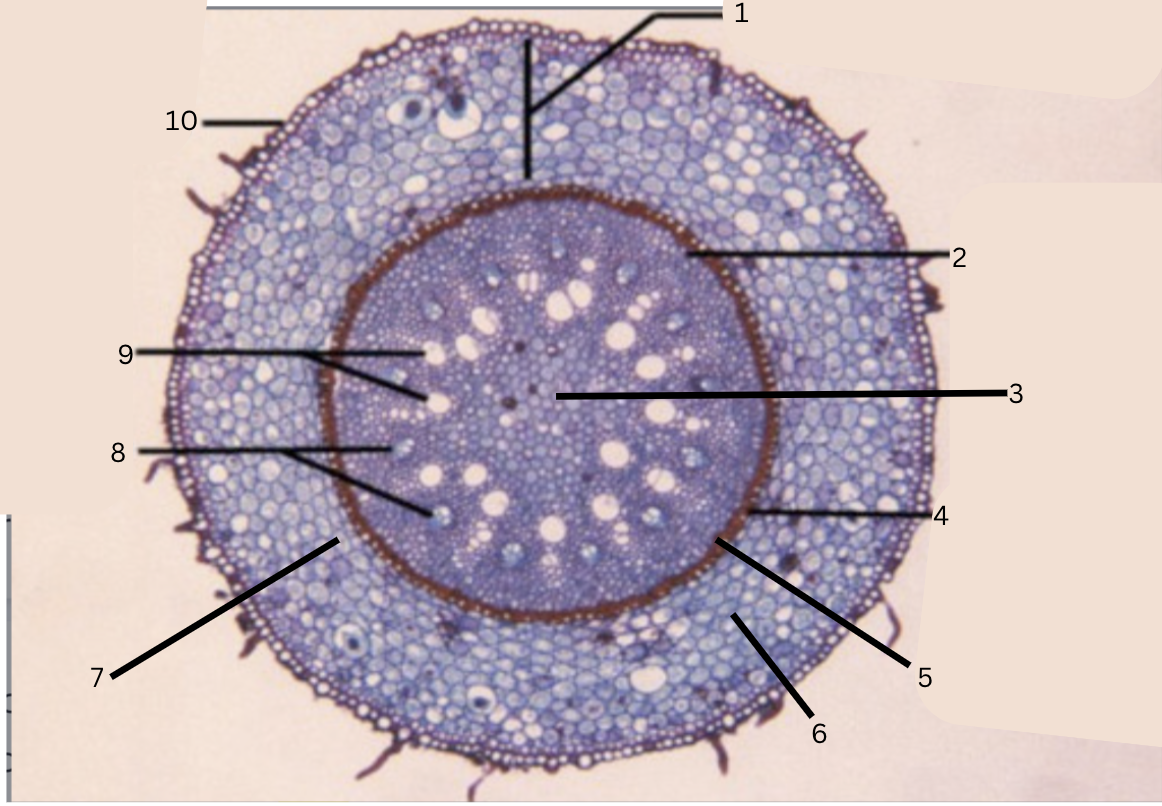

What is 4?
casparian strip (thick wall on cells)
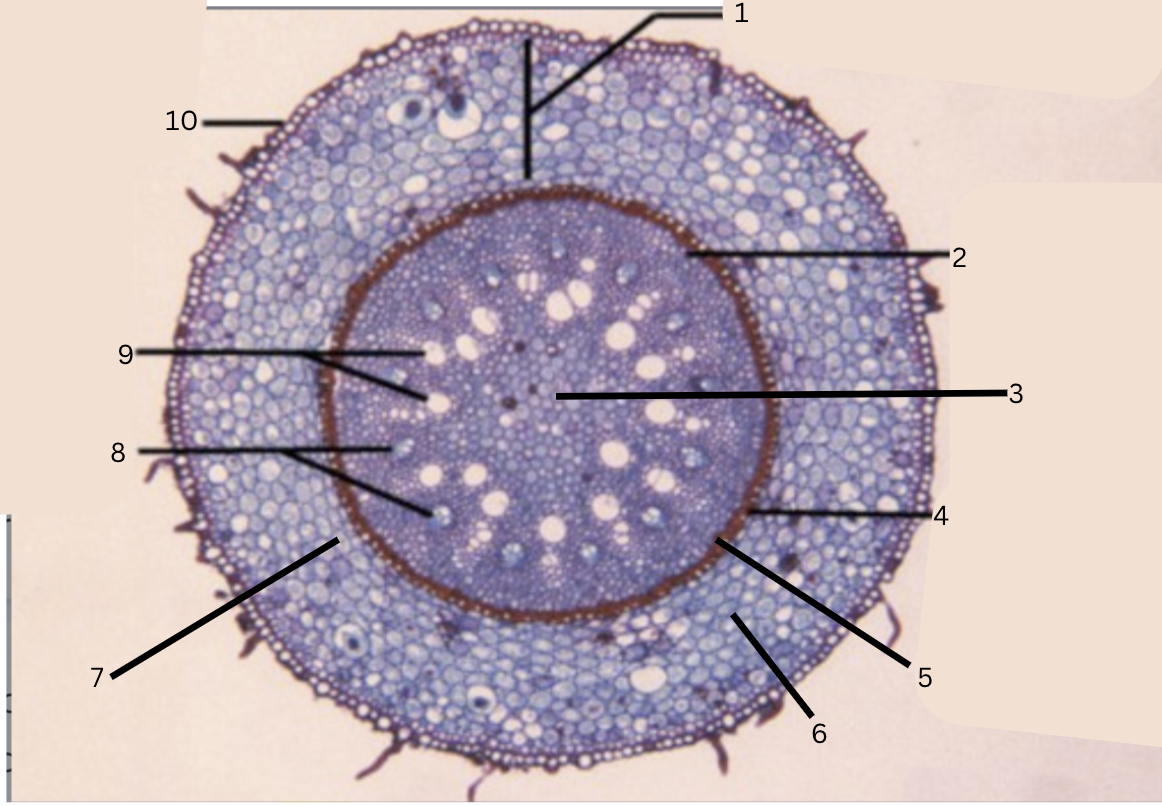

What is 5?
endodermis
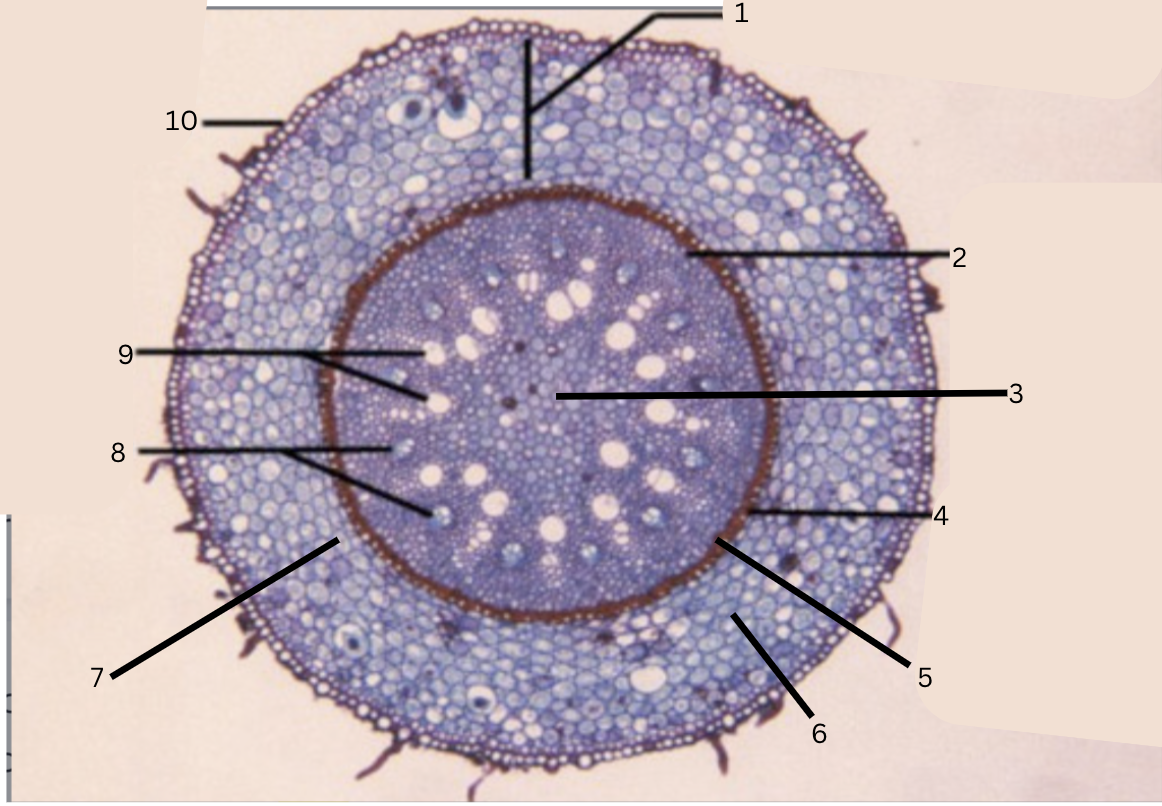

What is 6?
intercellular space
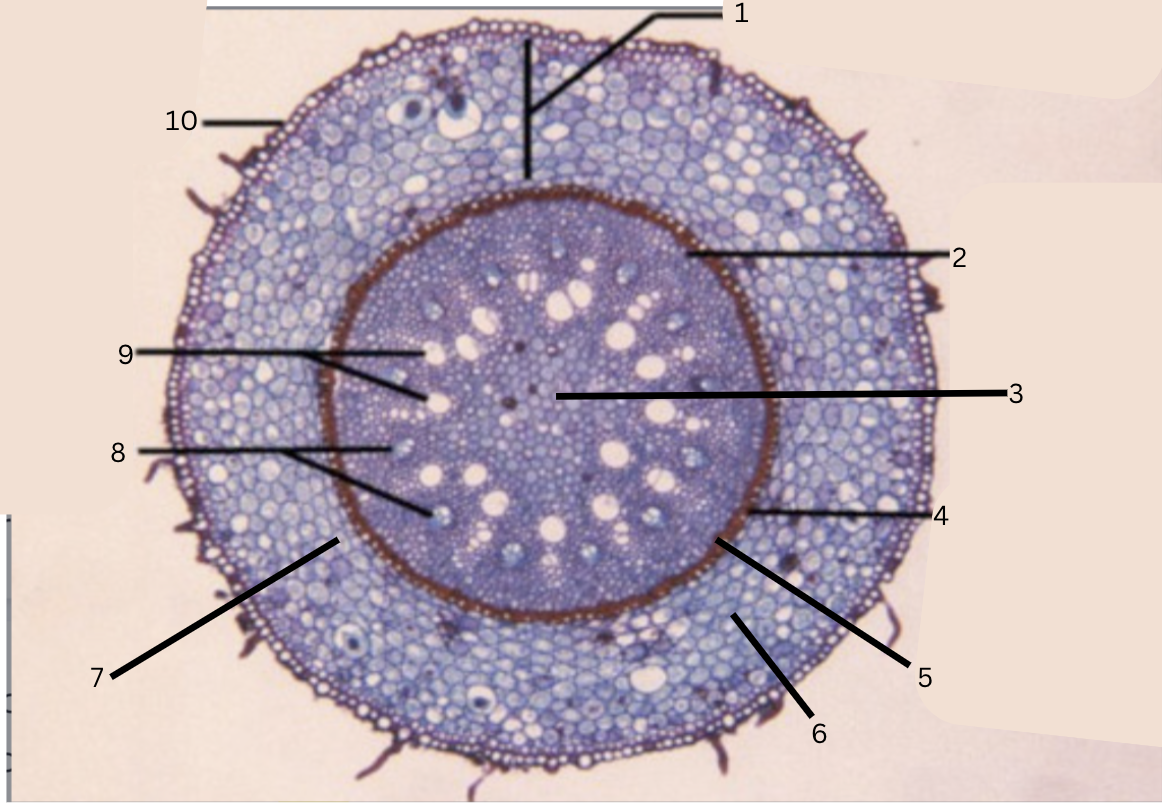

What is 7?
starch grains
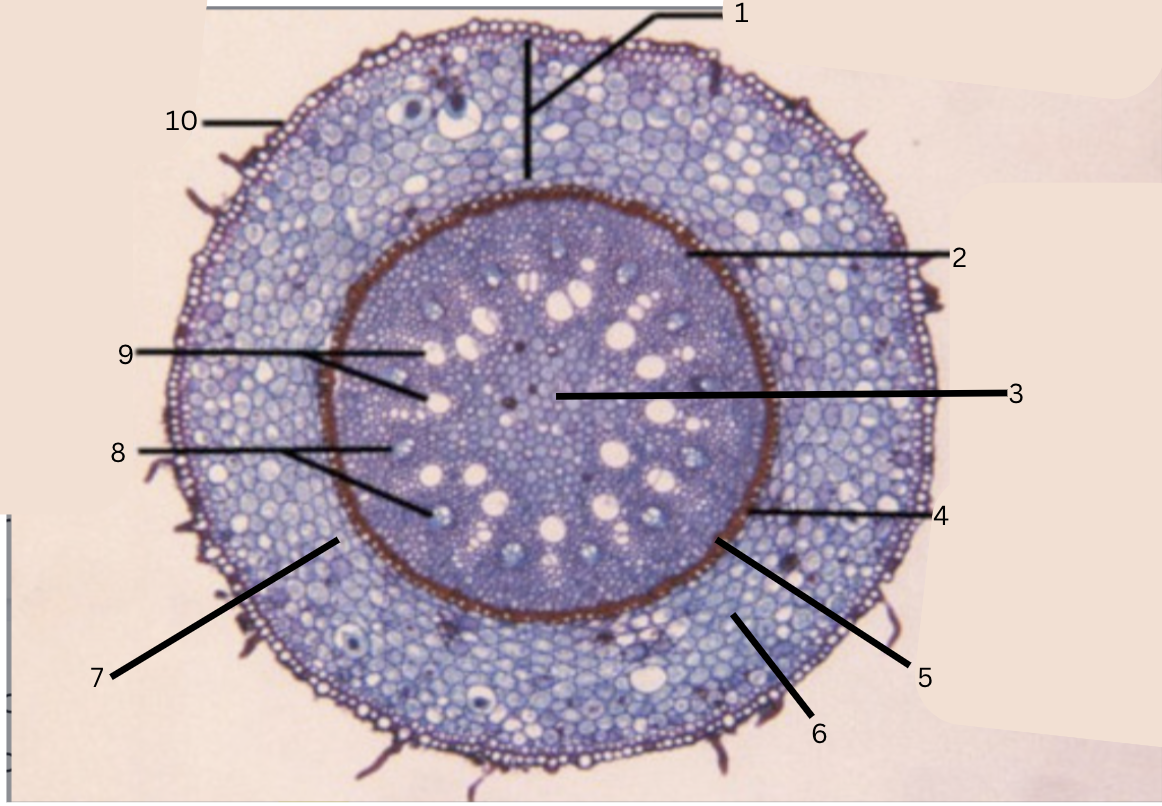

What is 8?
phloem
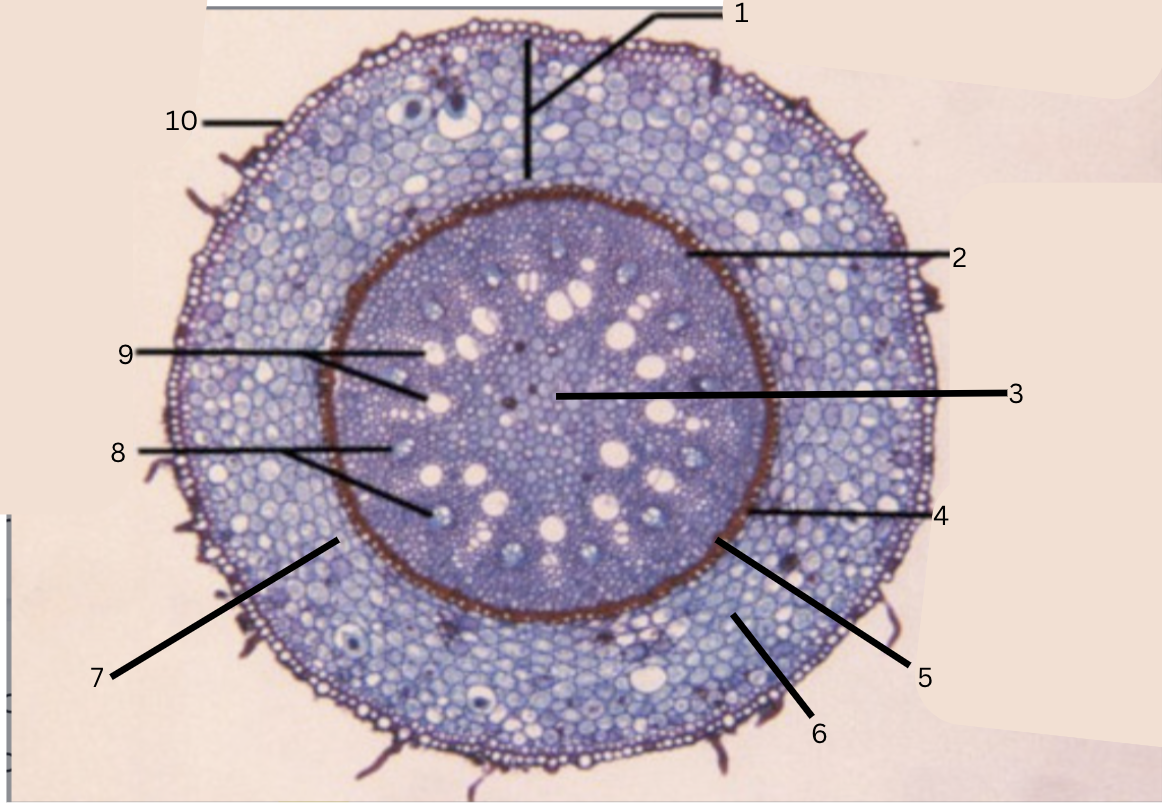

What is 9?
xylem
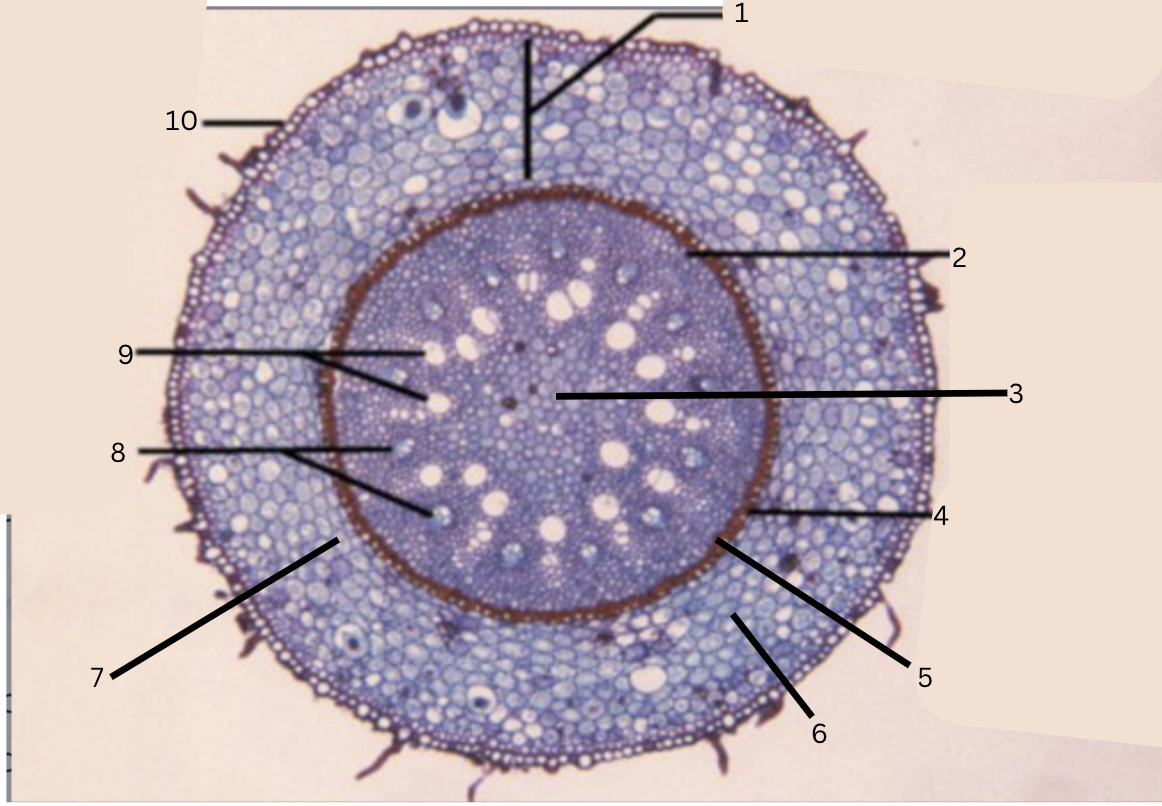

What is 10?
epidermis


What is this a cross section of?
Lateral root origin/growing out.
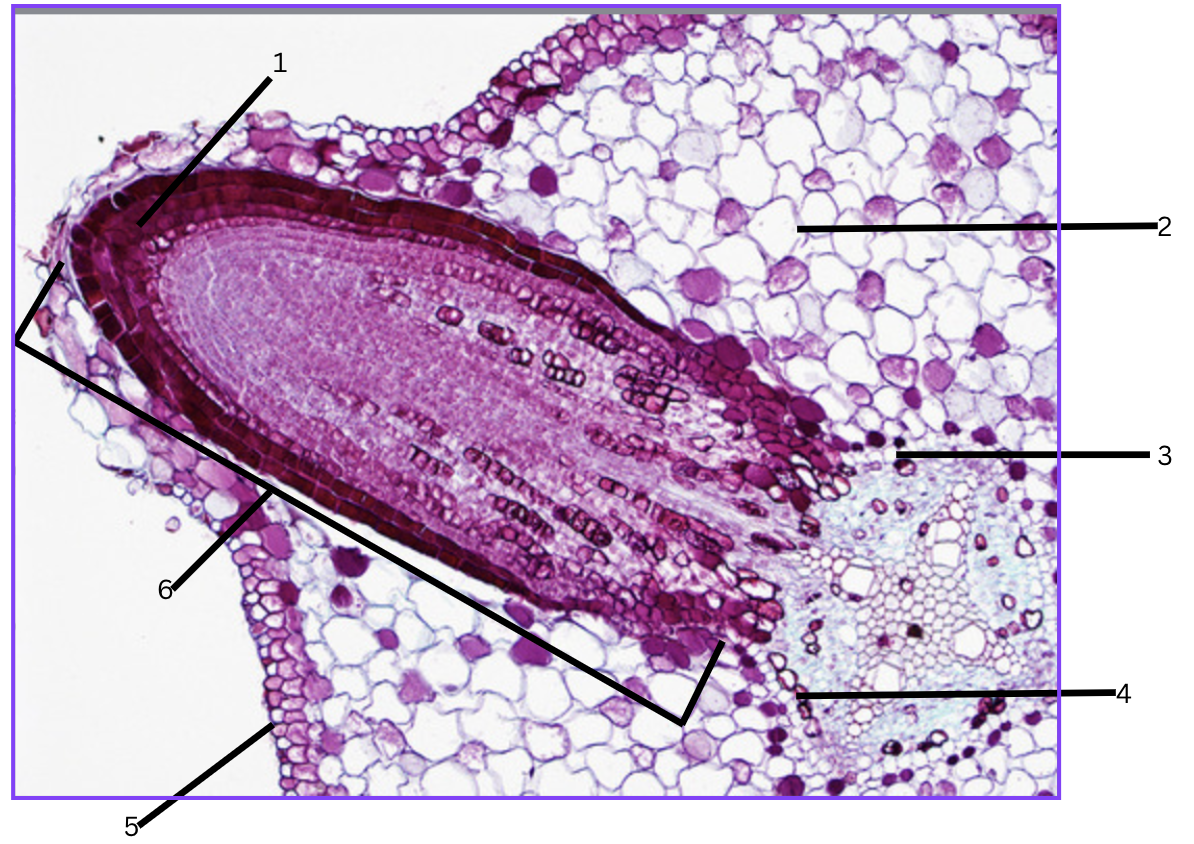

What is 1?
root cap (tip of lateral root)

What is 2?
cortex

What is 3?
endodermis
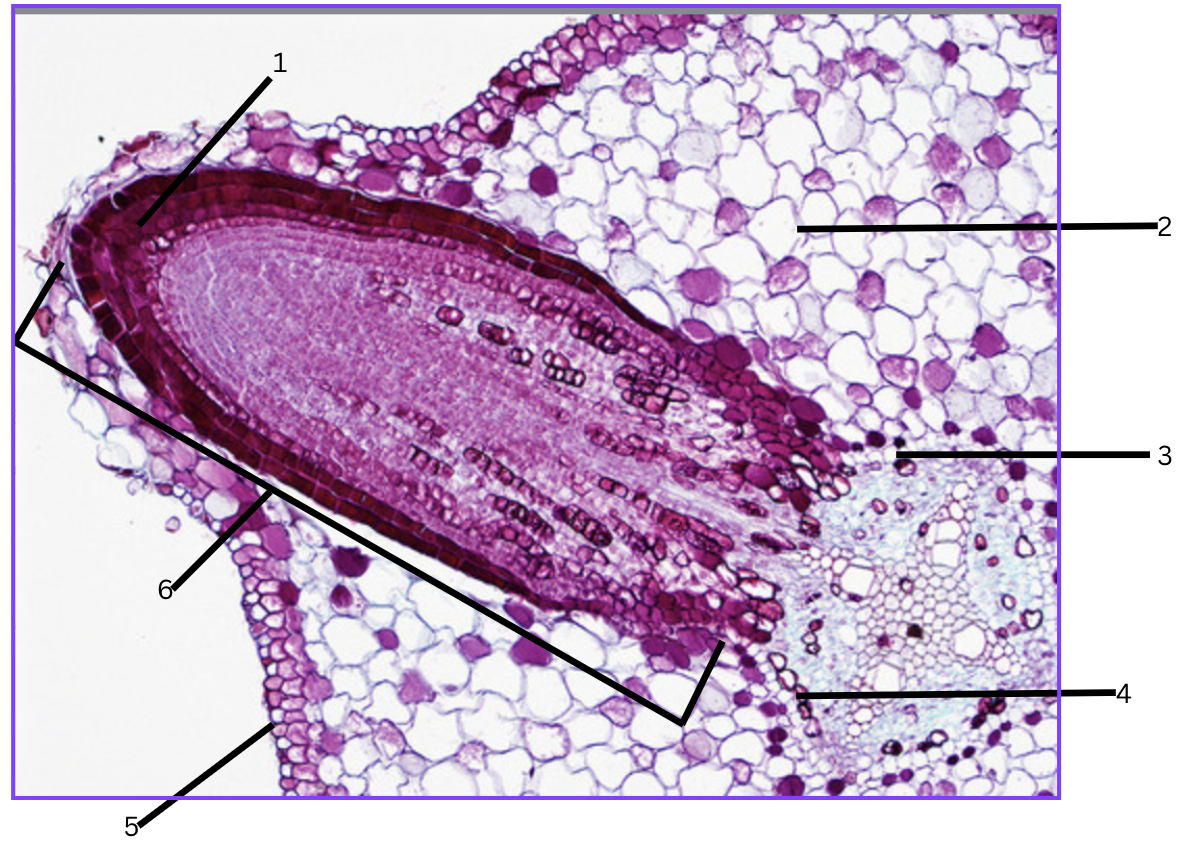

What is 4?
pericycle
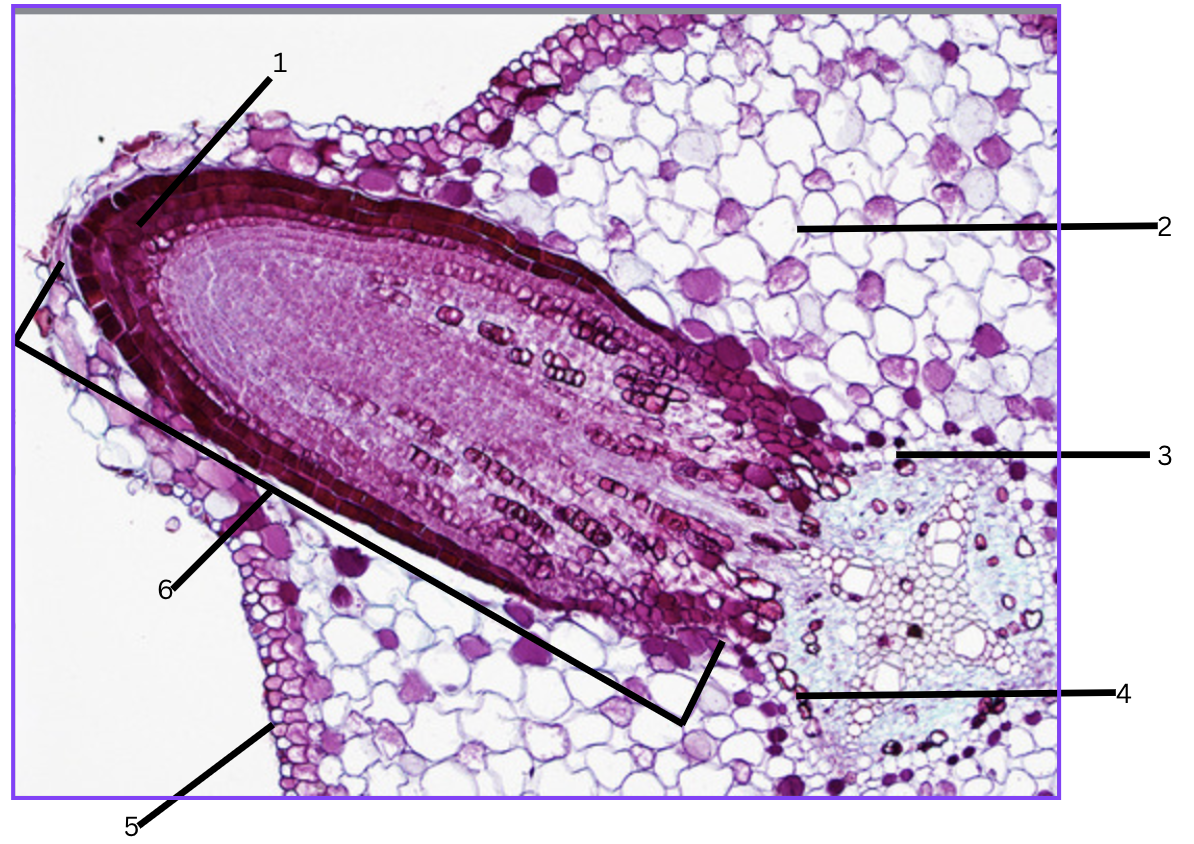

What is 5?
epidermis
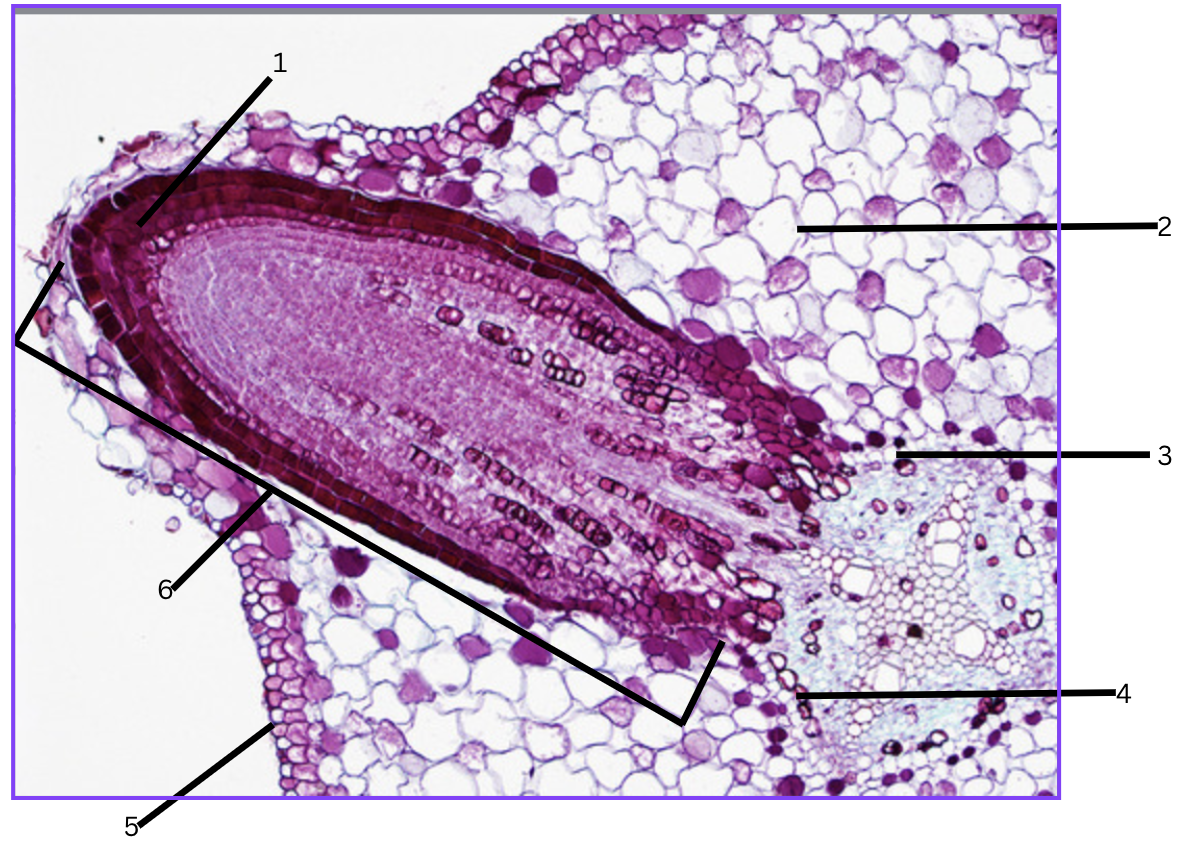

What is 6?
lateral root(penis)
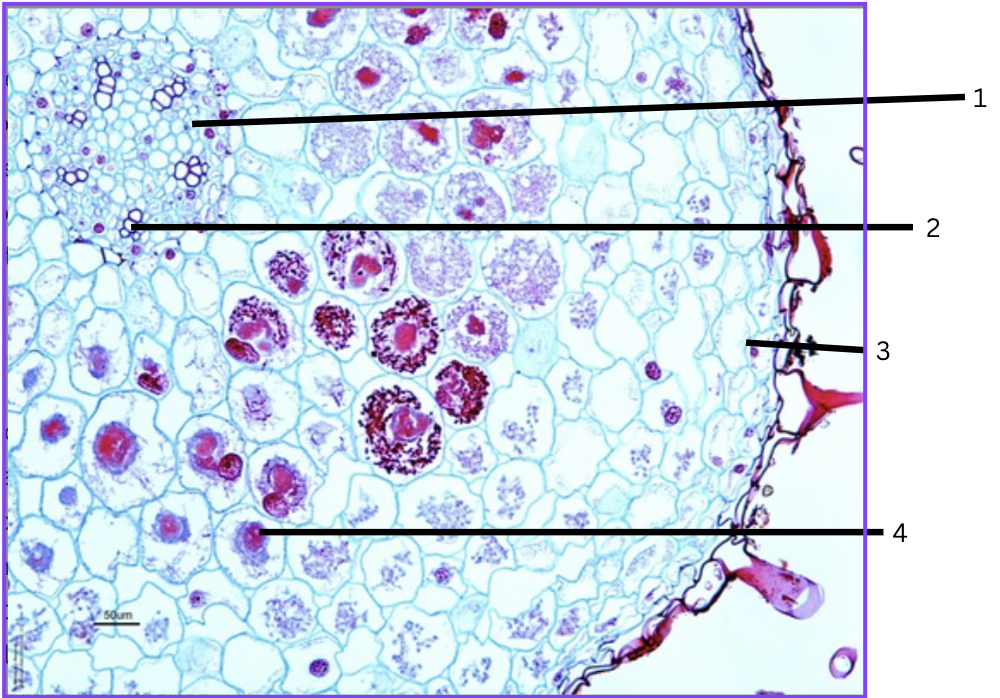

What is this a cross section of?
Orchid root with mycorrhizal association
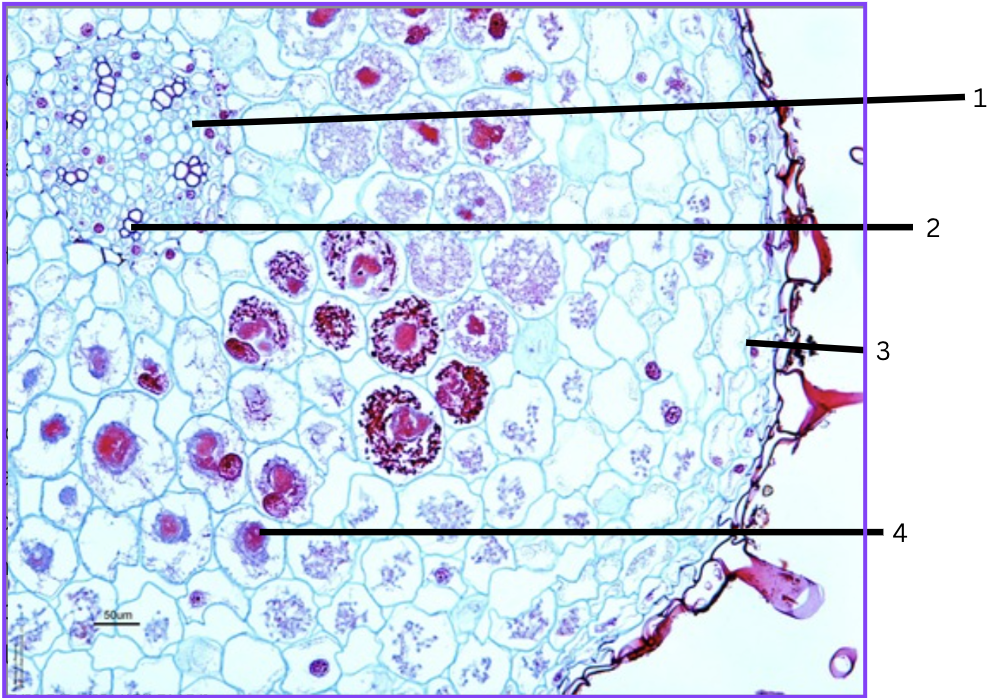

What is 1?
phloem
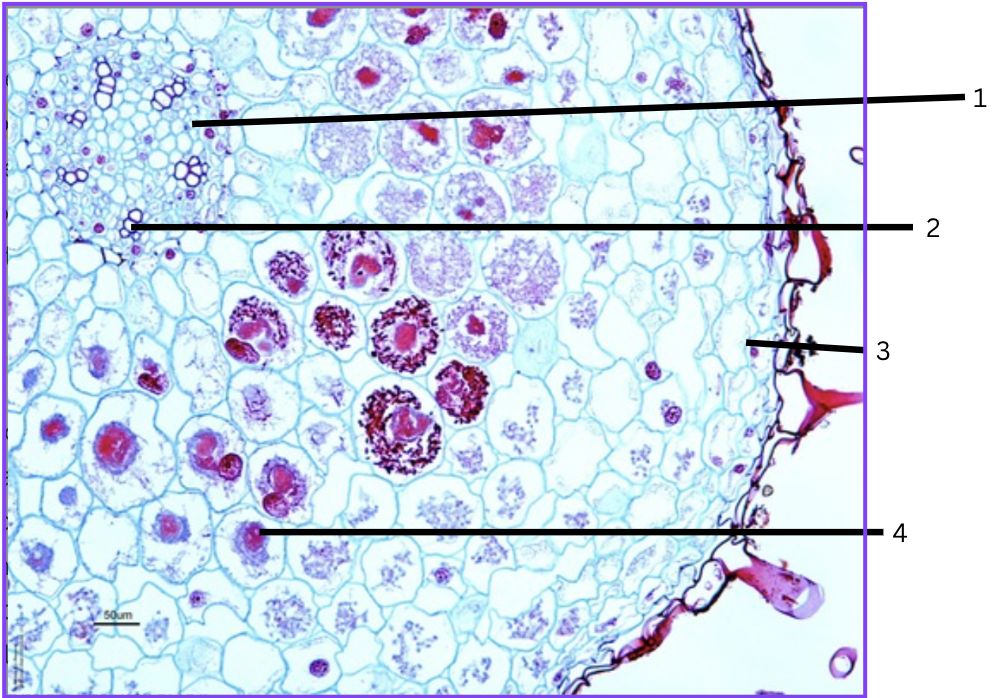

What is 2?
xylem
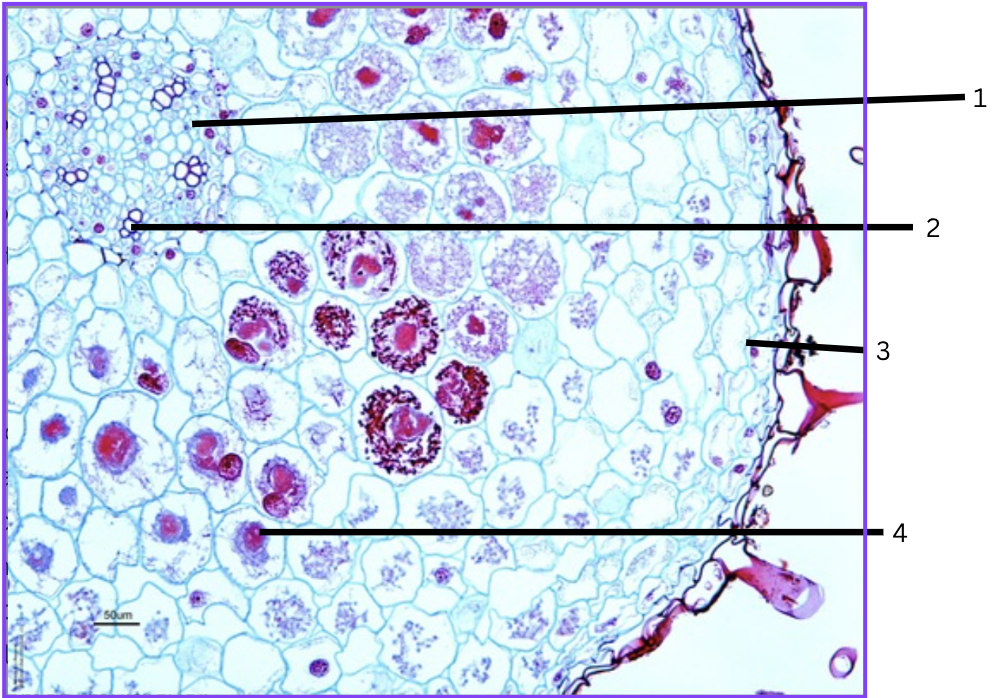

What is 3?
velamen (multilayer epidermal zone)
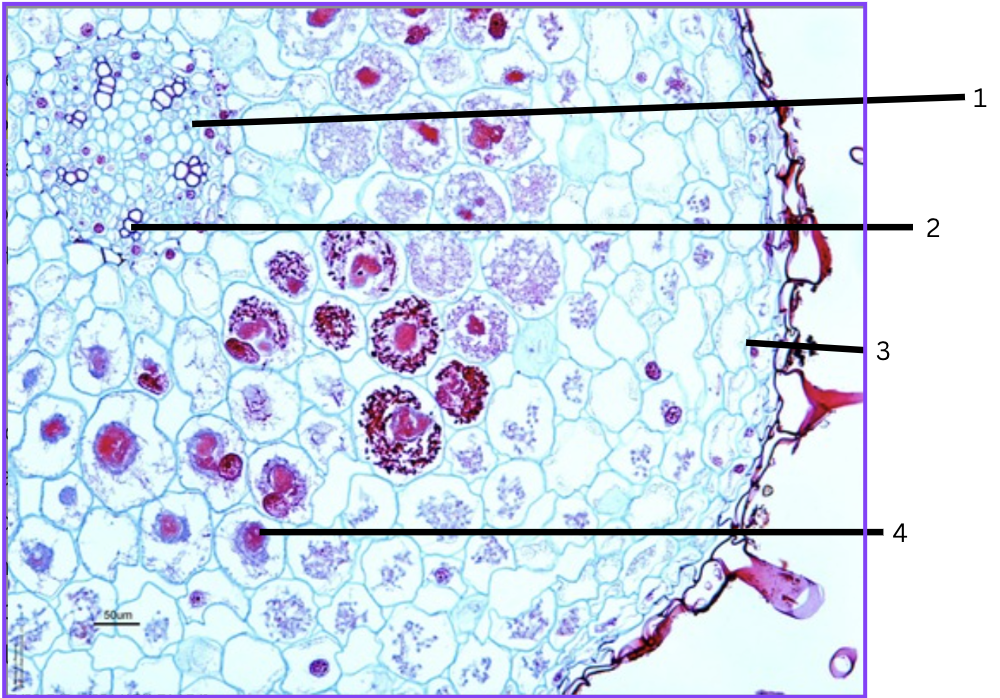

What is 4?
parenchyma cell containing symbiotic fungus
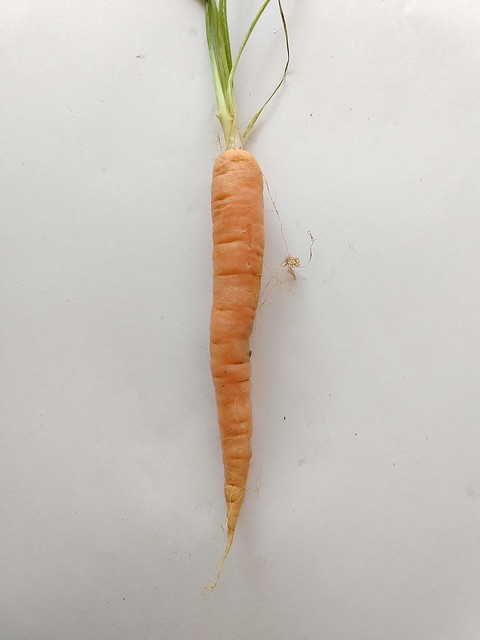


What type of root is this?
What is the name of the plant?
Is this a monocot or dicot?
Taproot
Carrot
Dicots
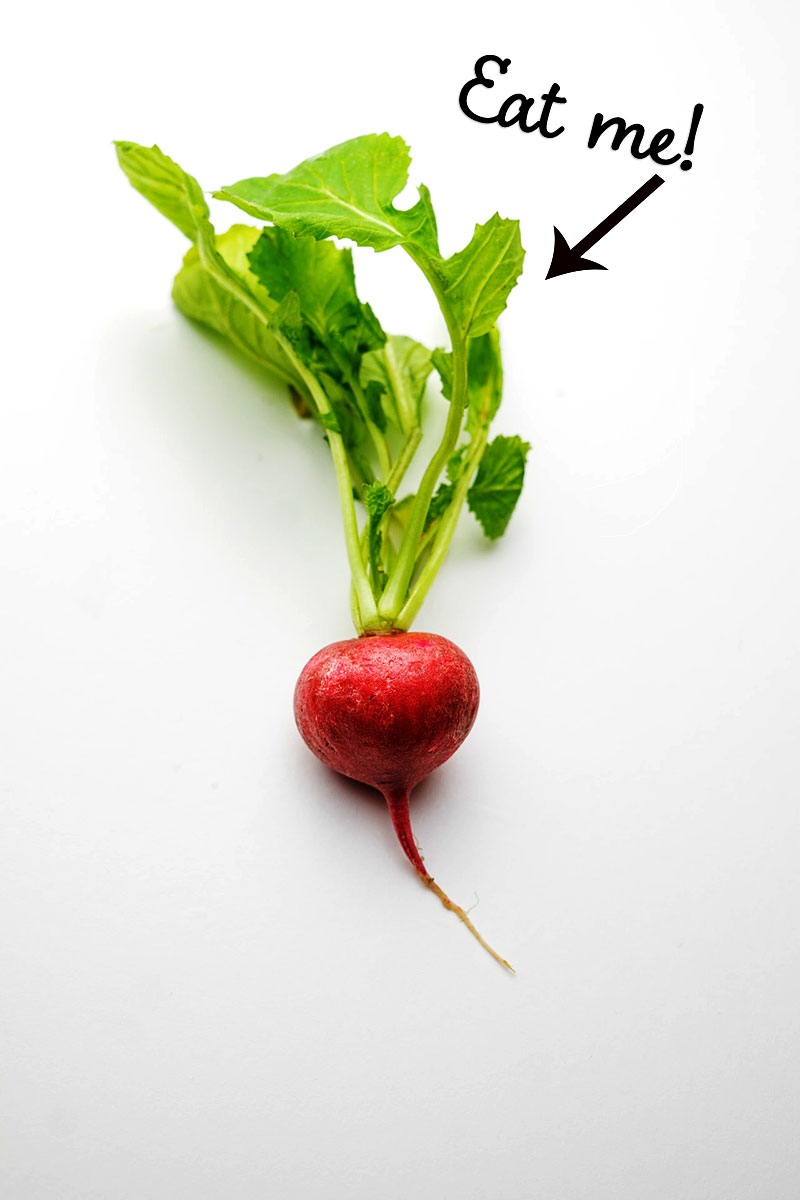


What type of root is this?
What is the name of the plant?
Is this a monocot or dicot?
taproot
Radish
Dicot
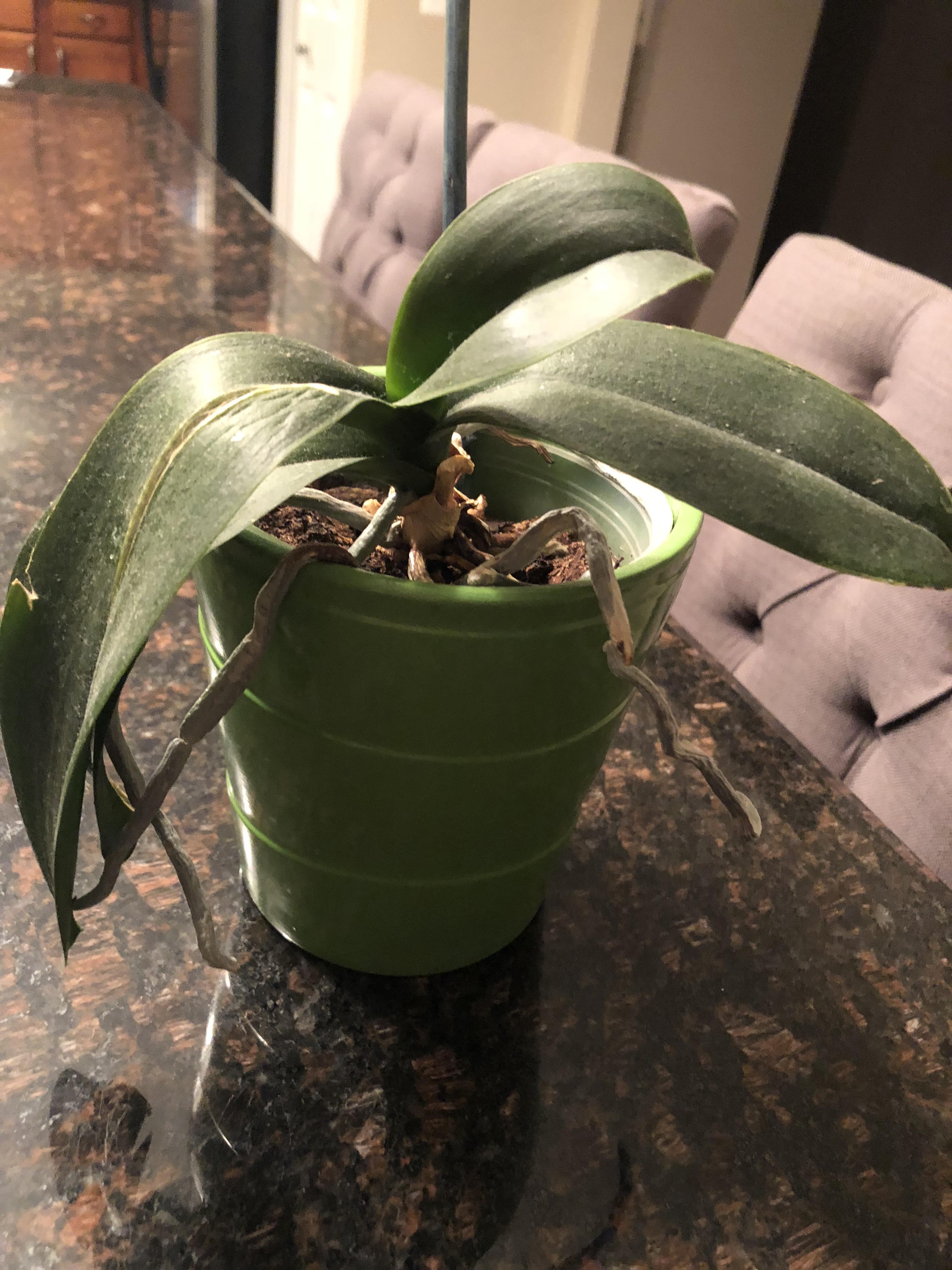


What type of root is this?
What is the name of the plant?
Is this a monocot or dicot?
Fibrous root(aerial roots too)
Orchids
Monocot
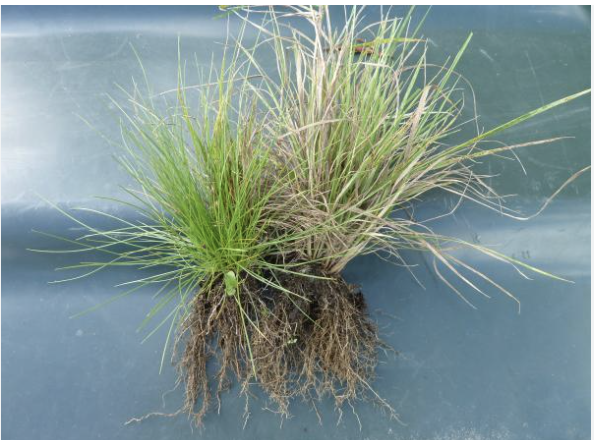


Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Monocot (fibrous root)
Grass


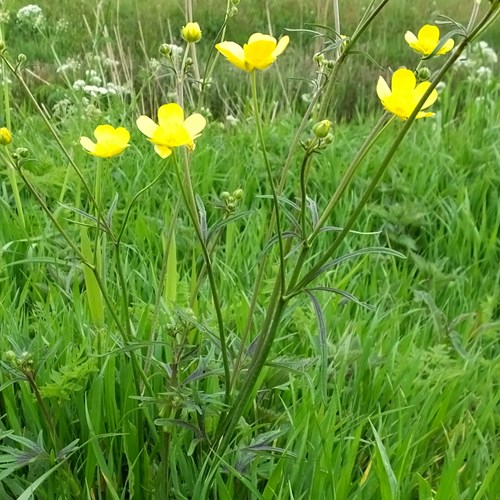
Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Dicot(taproot)
California poppy


Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Dicot(taproot)
California poppy
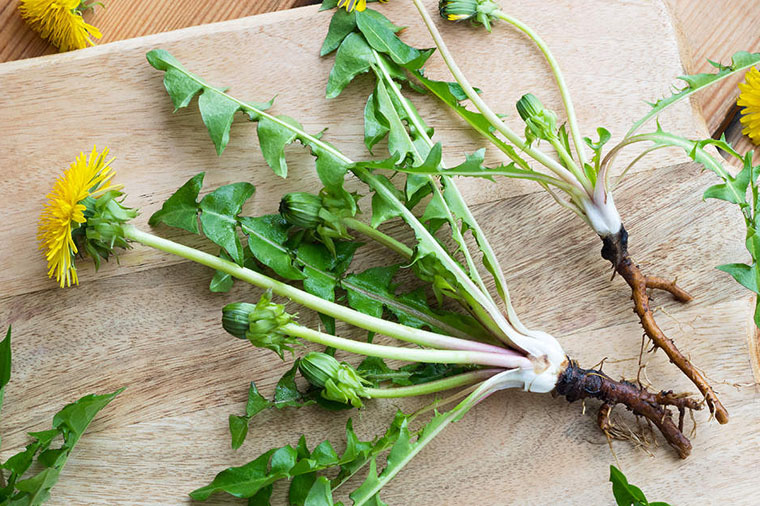


Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Dicot(taproot)
Dandelion
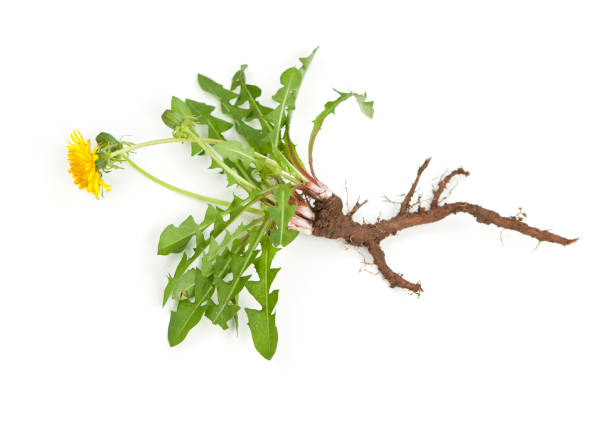


Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Dicot(taproot)
Dandelion


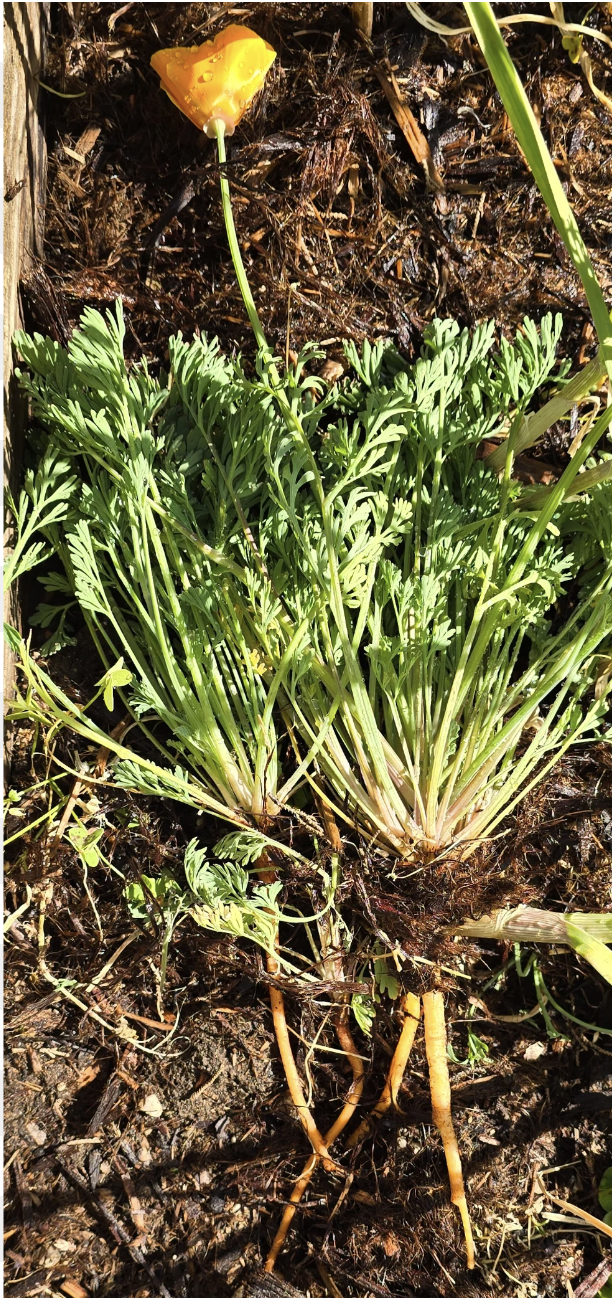
Is this a monocot or dicot?
What plant is this?
Dicot(taproot)
Ranunculus/Buttercup
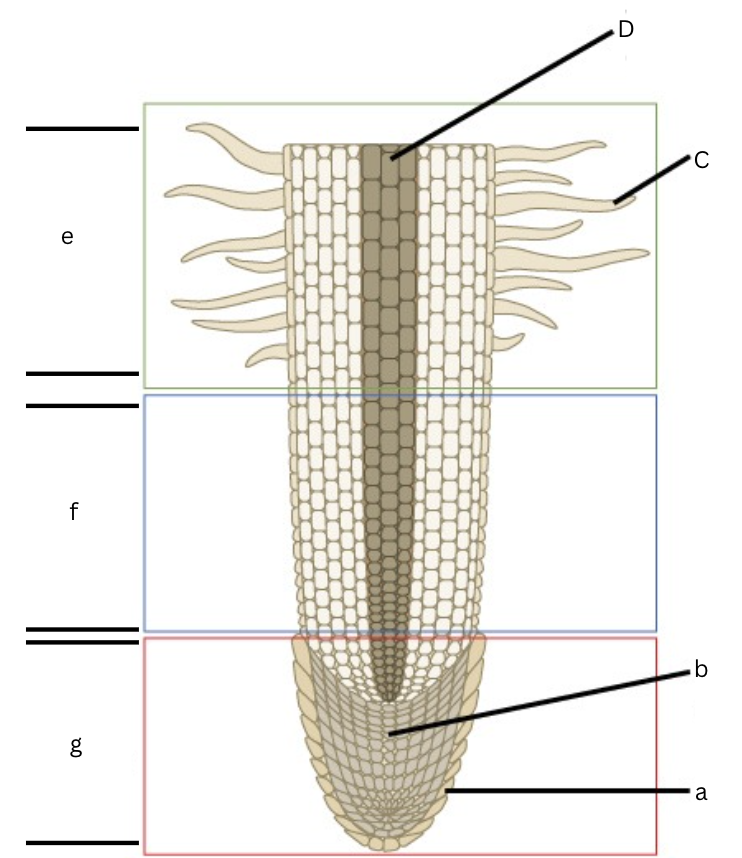

Is this a longitudinal or cross section view?
Longitudinal
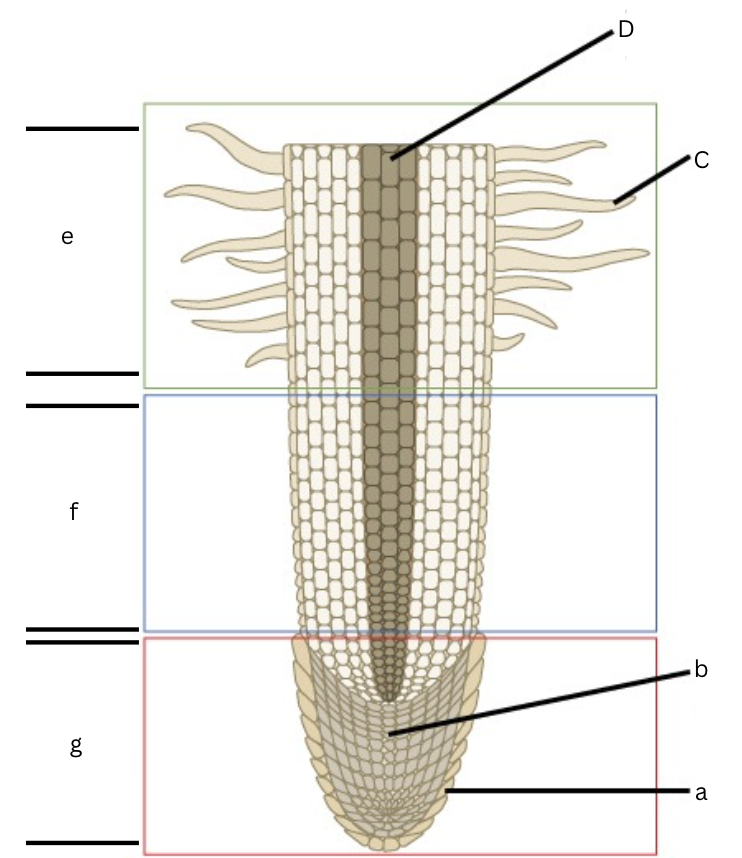

What is a?
root cap
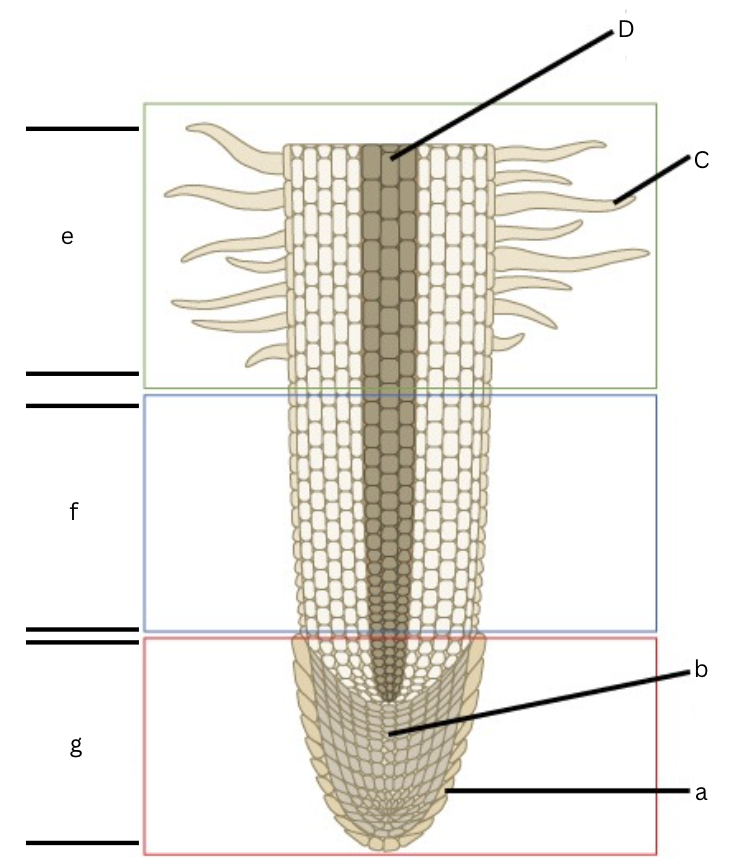

What is b?
apical meristem
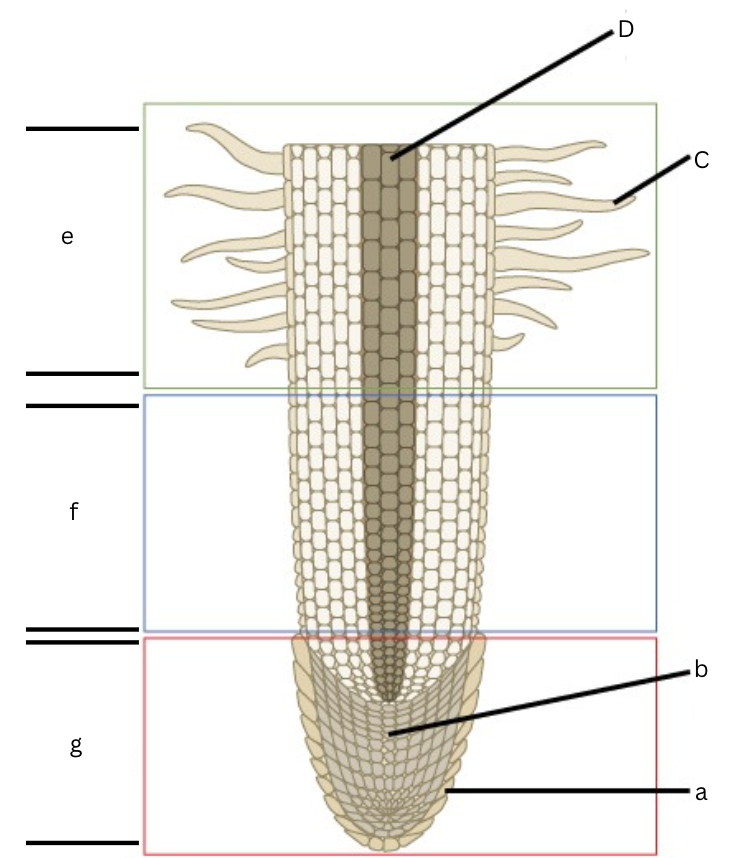

What is c?
root hair
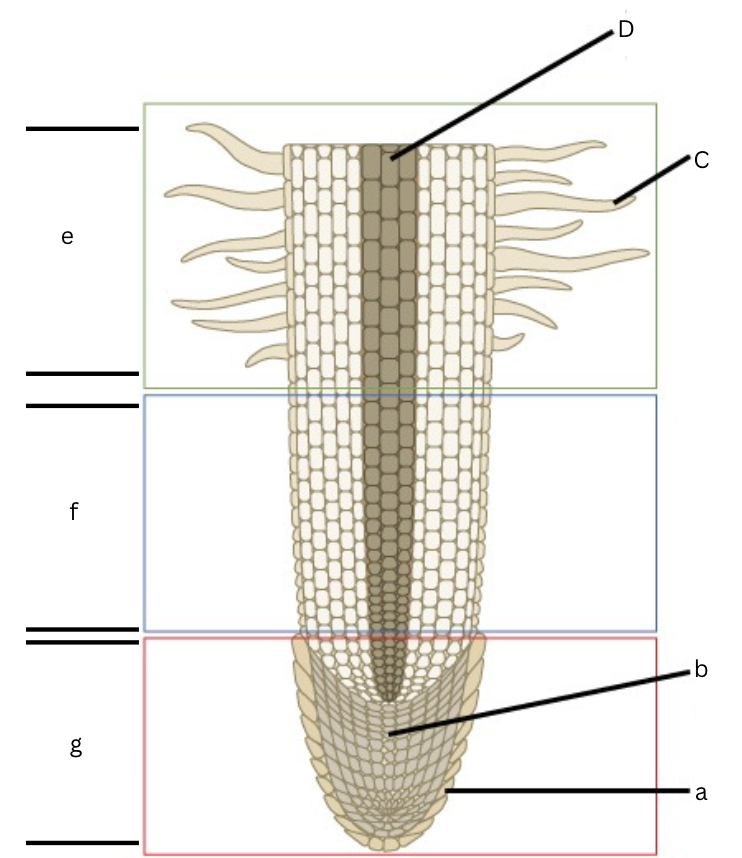

What is d?
vascular cylinder


What is e?
area of maturation
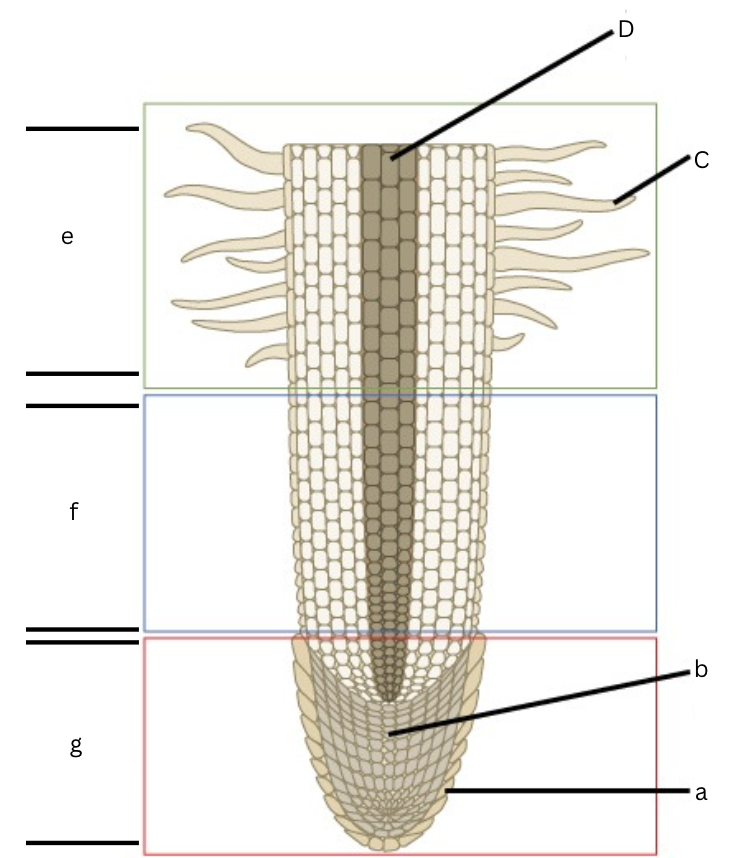

what is f?
area of elongation
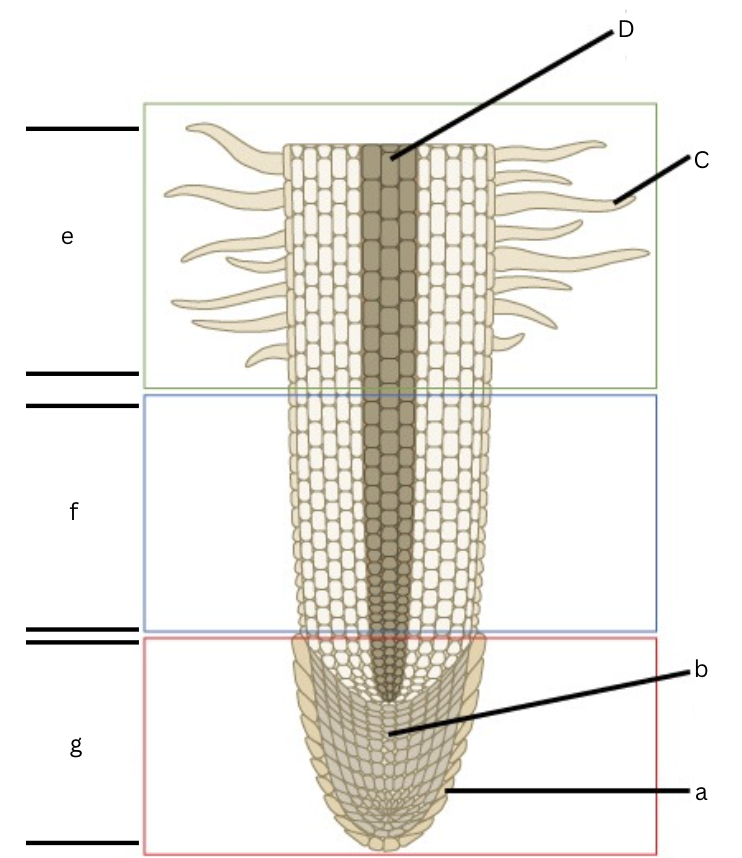

What is g?
area of cell division
what is the primary function of roots?
Anchoring plants
absorbing water with dissolved minerals
store food or water
form a passageway in which substance can move from outside env. to diff places in plant.
What are the parenchyma cells b/t the epidermis and vascular cylinder?
Cortex
What(primary meristem) gives rise to the epidermis?
protoderm
What is the inner boundary of the cortex?
endodermis
Haustoria
parasitic root/portion of parasitic plant that draws sugars from host
What is the name of spongy roots that extend above ground?
pneumatophore
What gives rise to primary xylem and phloem?
Procambium
What is the general term for the primary tissue in roots?
parenchyma (ground tissue/most of the plant)
What is the symbiotic relationship b/t plant roots and fungus?
mycorrhizae
What is a plant with aerial roots?
orchid
What anchors the plant?
roots
What is the symbiotic relationship b/t plant roots and (nitrogen-fixing) bacteria?
root nodule (little ball on roots)
An orchid is a monocot. What are three observations that provide evidence for this claim?
Leaves have a parallel pattern
Roots are fibrous
Flower parts in multiples of 3
As a lateral root grows, it pushes through several tissues or tissue layers. List them, starting from the layer from which the lateral root originates to the outside soil.
Originates from the pericycle, then endodermis, cortex, epidermis, and finally to outside soil.
What does the specific regions of a root in a longitudinal section include?
Root cap, cell division, elongation, and maturation zones.
What does the root cap do?
Protects the cell division zone(apical meristem) and perceives gravity
What do you see in the maturation zone?
Root hairs and differentiated tissues in a cross section.
What do root hairs do?
Increase the area of water absorption and become associated with nitrogen-fixing bacteria to form root nodules.
What are root nodules?
Found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria.[
What are root hairs?
Extensions of epidermal cells.
Where is the elongated region located?
Located b/t the meristematic and the differentiation(maturation) zone
What is the elongation zone?
Cells actively expand as they mature and differentiate into mature cells.
What is the outer most layer of a root?
Epidermis-protects the cell.
What is the cortex?
composed of storage parenchyma and make up the plant body/ground tissue.
Cells may contain starch grains (purple) and have large intercellular spaces.
What is the endodermis?
Boundary between the cortex and the vascular tissue region(vascular cylinder).
Central cylinder starts in this cell layer.
Has thicker cell walls in most cells, except for passage cells. Well defined one is a monocot.
What are passage cells?
Cells in the endodermis w/o a casparian strip.
What is the function of endodermis?
Regulate the movement of water and dissolved minerals into the vascular system by acting as a barrier, filtering what enters the the central vascular tissue and preventing unwanted substances from reaching it
Controlling the uptake of nutrients and protecting the plant from harmful substances in the soil
Forces cells to go symplastically(moves through cytoplasm)
What are the thicker walls with suberin bands known as in the endodermis?
Casparian Strips
What does the xylem look like in a dicot and monocot?
Dicot=X cross like in the center of the root
Monocot= like strips of vessels.
Where does the phloem occur in dicots?
in clusters in the radial arms of the xylem. Greenish in color with companion cells near the sieve tubes.
What do monocot roots have that dicot root dont?
Distinctive pith region composed of parenchyma cells in the center, dicots LACK a pith.
What is the cell layer inside of the endodermis?
Pericycle
What is the pericycle?
Keeps some meristematic qualities as it’s responsible for forming lateral or branch roots and secondary growth in roots.
Have thin cell walls that appear similar to parenchyma cells
Do roots have vascular bundles?
NNOOOO! has a vascular cylinder! Xylem and phloem alternate along the diameter of the root.
May see vasc. cambium b/t xylem and phloem in some roots
What color does lignin pick up when stained?
Cell walls of xylem are lignified, so they pick up a red color! Primary xylem have thicker cell walls than the phloem cells.
Where are the lateral roots close to?
youngest roots are close(proximal) to the apex(tip of a plant root where growth occurs)
The pattern of lateral root production is readily observed in taproot systems(dicots)
In woody roots, where does the cork cambium first develop?
At the pericycle.
What can the taproot also be called? How about its branches?
Primary root, while its branches are called secondary or lateral roots.
In orchids, the root is surrounded by…
symbiotic fungi, thus relationship.
Where can you find fungal filaments(hyphae) growing?
Cortex cells (cortical cells) through the parenchyma.
What is the velamen?
Multilayer epidermal zone
In most mycorrhizae, the fungus…
invade only the cortex region of the root
What type of root are monocot roots? Dicots?
Monocot=fibrous with many branches of about the same thickness.
Dicot=central taproot with smaller side branches
What are adventitious roots?
The mature roots that develop from the stem, not the radicle(in most monocots). They aren’t roots that comes from where they should.