Sampling Techniques
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Random Sampling
Non-Random Sampling
Sampling Techniques
Random Sampling
A process whose members had an equal chance of being selected from the population.
Simple Random Sampling
Systematic Random Sampling
Stratified Random Sampling
Cluster Random Sampling
Random Sampling
Simple Random Sampling
Usually uses the table of random numbers or through lottery.
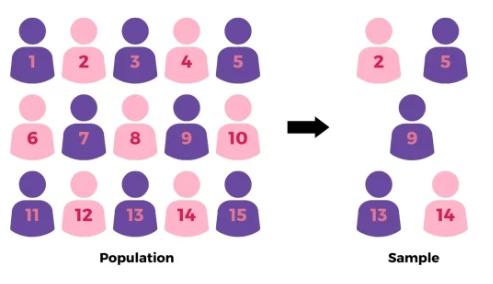
Example of Simple Random Sampling
Systematic Random Sampling
To draw members or elements, we have to select a random starting point (kth), then draw successive elements from the population.
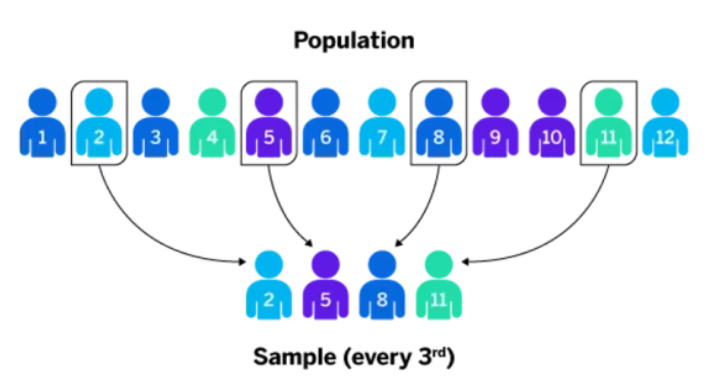
Example of Systematic Random Sampling
Stratified Random Sampling
Used when the members of the population do not belong to the same category; we are dividing the elements of a population into different categories or groups and then the members of the sample are drawn or selected proportionally from each subpopulation.
Strata
Dividing the elements of a population into different categories or groups
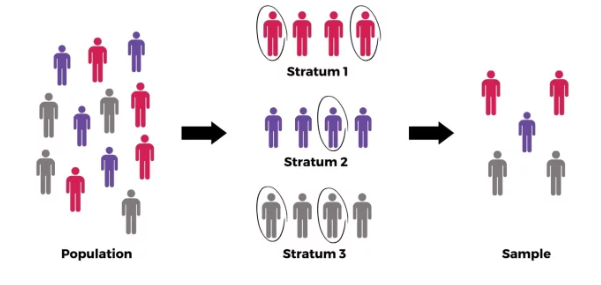
Example of Stratified Random Sampling
Cluster Random Sampling
Sampling wherein groups or clusters instead of individuals are randomly chosen.
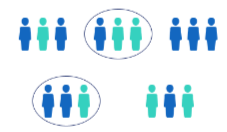
Example of Cluster Random Sampling
Non-Random Sampling
Sampling procedure where samples selected in a deliberate manner.
Convenience Sampling
Purposive Sampling
Quota Sampling
Snowball Sampling
Non-Random Sampling
Convenience Sampling
Offers convenience to the researcher.
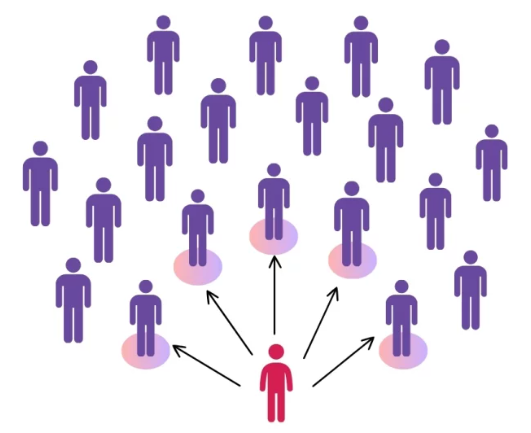
Example of Convenience Sampling
Purposive Sampling
Selecting based on judgment by the researcher or based on prior information.
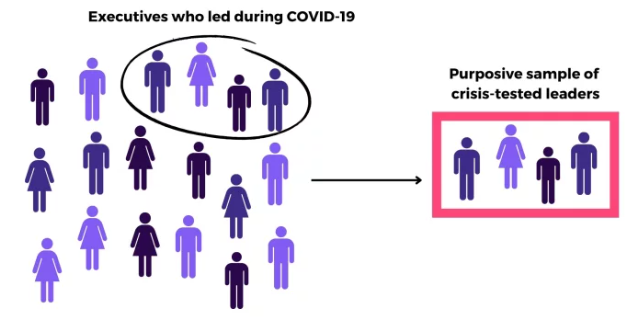
Example of Purposive Sampling
Quota Sampling
Applied when an investigator survey collects information from an assigned number.
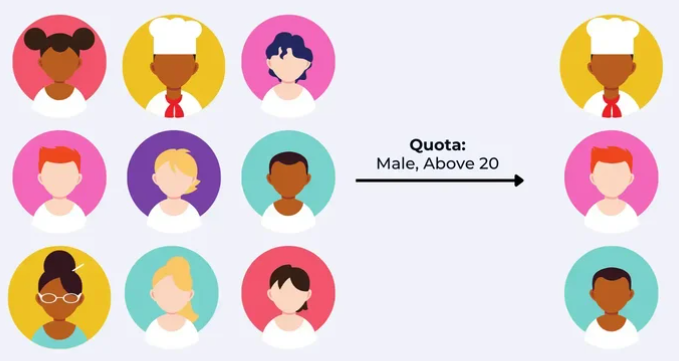
Example of Quota Sampling
Snowball Sampling
One or more members of a population are located and used to lead the researchers to other members of the population
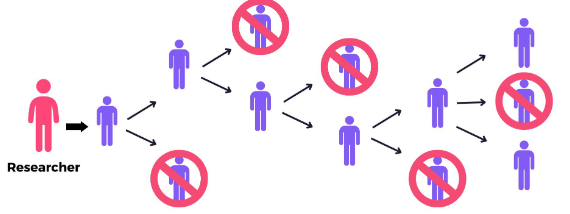
Example of Snowball Sampling