Chapter 7 - Specific Defenses
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
differences between viruses and bacteria
viruses non living, req host cell to multiply, genetic material is DNA or RNA, NO cell wall and NO organelles
bacteria living cell, dont req host cell, MAIN genetic material is DNA(altho still contain RNA), cell wall made of peptidoglycan, have organelles
gram staining
gram positive bacteria(THICKER peptidoglycan layer) retain crystal violet stain
gram negative lose crystal violet stain, stained by safranin
transmissable diseases
infectious disease that can be passed from one person to another by infection with microorganisms
direct VS indirect transmission
contact
body fluids
droplet
airborne
ingestion
vectors
contact
direct: infected individual pustules burst and non infected individual touch pustule and touch own face
indirect: infected individual sneeze on hand, transfer virus to doorknob and non infected individual touch doorknob and touch face
body fluids
direct: exchange of fluids during sex
indirect: sharing of needles
droplet
direct: individual sneeze and pathogens remain SUSPECTED IN AIR ON DROPLETS OF SALIVA and is inhaled by uninfected individual
indirect: individual sneeze and pathogens remain on INANIMATE OBJECTS and uninfected touch object and touch face
airborne
indirect: individual sneeze and pathogens remain SUSPENDED IN AIR ON DUST PARTICLES and is inhaled by uninfected
ingestion
indirect: food products contaminated with pathogen during preparation by an infected individual and is consumed by uninfected individual
vectors
indirect: insect not affected by pathogen transfers pathogen from infected to uninfected individual
body defense mechanisms
non specific
specific
non specific response
dont target specific pathogens, first line of defense
external defenses, protective reflexes, internal non specific defenses
external defenses
skin
mucous membrane
hair
cilia
skin
physical barrier to prevent entry of pathogens
sweat have flushing action and is acidic to inhibit growth
prescence of harmless bacteria as part of normal bacterial flora
hair
traps dust particles and prevent entry into body
cilia
move like waves to sweep away mucus and pathogens trapped in mucus
mucous membranes
trap bacteria and dust particles in mucus secreted by cells
protective reflexes
forceful expulsion of large quantities of pathogen or fluid containing those pathogens
rapid removal of pathogens
EG: sneezing, coughing, vomiting
non specific internal defenses
phagocytosis
fever
inflammation
self antigen
antigen that is recognised by immune sytem as belonging to host body and wont stimulate further immune response
non self antigen
antigen that is not recognised by immune system as belonging to host body and will stimulate a further immune response
phagocytosis
macrophages migrate to site of infection due to release of histamine by Mast cells
macrophages recognize non self antigens and extend their cytoplasm to engulf pathogen
forms a phagosome
phagosome fuses with lysosome to form phagolysosome
lysozymes in the phagolysosome breakdown the pathogen
inflammatory responses(swelling, redness, heat)
histamine released by Mast cells promotes vasodilation, hence more blood flow to site of injury, lead to redness
more warm blood at site of injury lead to heat
increased permeability of capillaries, thus more plasma enters tissue, thus swelling restricts movement of damaged areas
heparin released by Mast cells acts as anticoagulant to prevent blood at site of injury, blood clots form surrounding the site of injury instead
role of inflammatory responses
prevent damage from spreading
begin tissue repair mechanisms
remove damaged tissue and cell debris
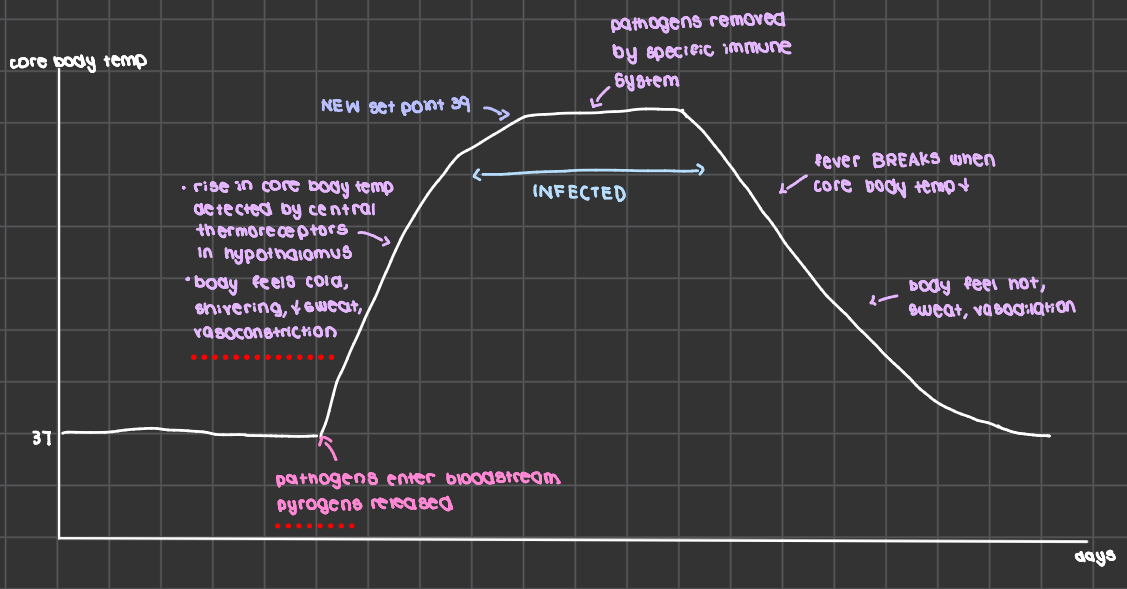
fever cause
caused by cytokine induced upward displacement of set point
pyrogens
substances which cause a fever
exogenous pyrogens: microbes of their products, release endogenous pyrogens like interleukin-1
benefits of fever
inhibit bacterial growth
increase rate of tissue repair by increasing rate of reactiona
increase blood flow so lymphocytes reach infection site fast
development and process of fever
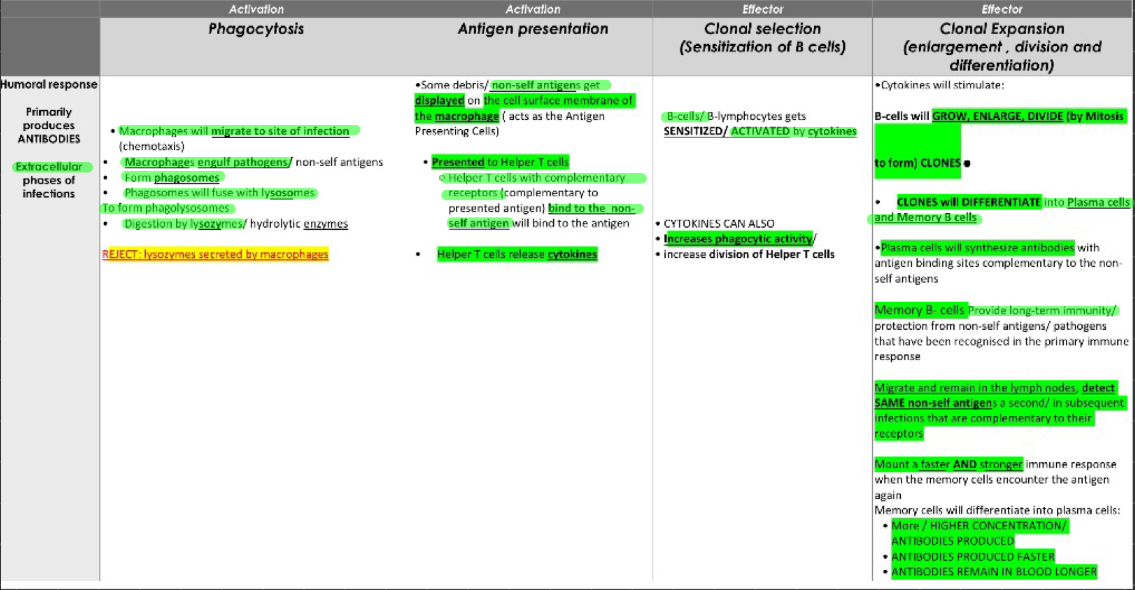
antibody mediated immunity
provide resistence to virus, bacteria and bacterial toxins BEFORE they enter our cells
process of antibody mediated immunity
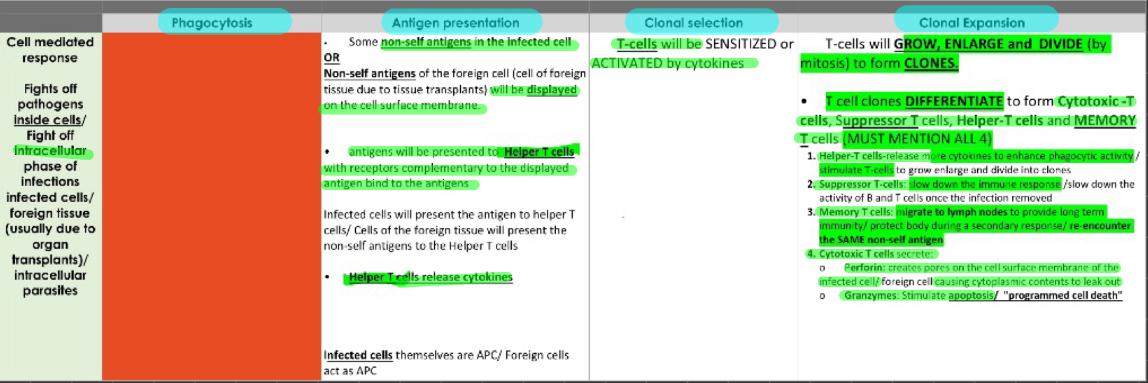
cell mediated immunity
provide resistence once pathogens already invaded cells, INTRACELLULAR PHASE
process of cell mediated immunity
types of response
primary response
secondary response
primary response
immune response to FIRST exposure to an antigen
takses time for B cells to multiply and differenciate into plasma cells(makes antibodies)
secondary response
response to SUBSEQUENT exposure to an antigen
faster stronger response, involves memory cells
plasma cells form quickly, antibody levels rise quickly
immunity
resistence to infection by invading microoganisms
natural immunity
occurs without human intervention
artificial immunity
results from giving people an antibody or antigen
active immunity
long lasting immunity when body manufactures antibodies against foreign antigen
presence of memory cells
can be naturally acquired(actual attack)or artificially acquired(vaccine)
during subsequent infection, antibody production faster, and at higher conc
passive immunity
short term immunity produced by introduction of antibodies from another person
naturally acquired(from mother through placenta or breast milk) or artificially acquired(injection of antibodies)
vaccines
antigen preparation
antigen strong enough to provoke immune response but not product symptoms
types of vaccines

how do vaccines work?
biological standpoint: stimulate immune system to produce memory cells
social standpoint: provide herd immunity, protect those that cant be vaccinated
factors considered with vaccines
social - use of animals to make vaccine
health issues - allergic
cultural - religious objections
economic - cost
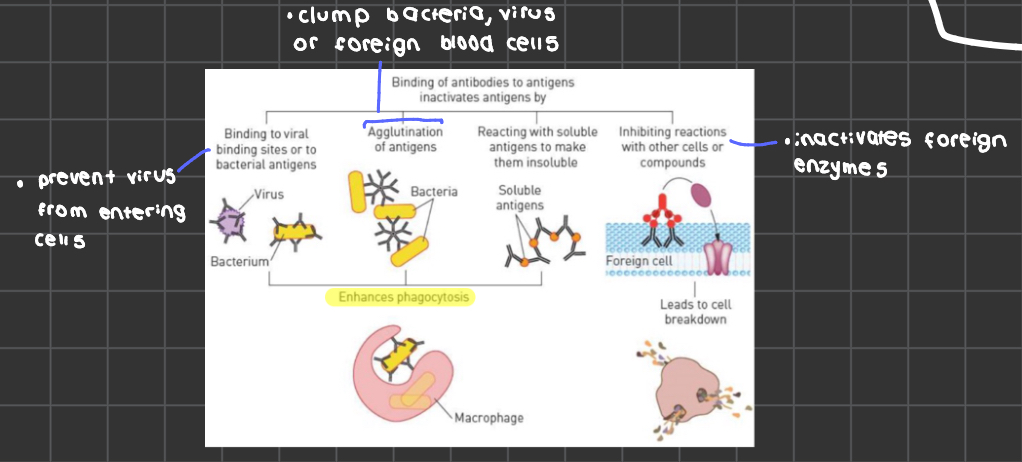
antibodies
antibodies combine with specific antigen to form antigen antibody complex
coats bacterian so bacteria can be easily consumed by phagocytes and enhance phagocytosis
antibiotics
drugs used to fight infection of microorganisms
cant treat virus
types of antibiotics
bactericidal
bacteriostatic
broad spectrum
narrow spectrum
bactericidal
cause death of bacteria by disrupting cell membrane
cause cells to lyse
bacteriostatic
slow down population growth by disrupting protein synthesis
broad spectrum
affects wide eange of different bacteria
narrow spectrum
effective only against specific bacteria
examples of antibiotics
penicillin - prevent synthesis of bacterial cell wall
streptomycin - interfere with protein synthesis
cephalosporin - interfere with synthesis of bacterial cell wall
over/under prescription of antibiotics
some bacteria have natural resistsnce to antibiotics due to genetic mutation
some bacteria will survive and pass resistent allele to offspring
increase population of resistant strains
antivirals
treat viral infections
drug interferes with virus replication insids host cells