Caring & Communication
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Caring
Universal phenomenon influencing the ways in which people think, feel, and behave in relation to one another
Comforting
Actions that serve to alleviate a person’s feelings of grief or distress
listening, touch, being there for someone
Compassion
A feelig of deep concern, sorrow, or pity for another’s suffering, accompanied by a strong desire to alleviate it
Ethic of Care
Is concerned with relationships between people and with a nurse’s character and attitude toward others. Nurses who function from an ehtic of care sensitive to unequal relationships that lead to an abuse of one person’s power over another — intentional or otherwise
Places the nurse as the patient’s advocate, influences the nurse’s lcinical judgment, and helps guide clinical decision making regarding ehtical dilemmas by attending to relationships and giving priority to each patient’s unique personhood
Presence
A person-to=person encounter conveying a closeness and a sense of caring. Presences invovles “being there” and “being with”. Not only in the physical sense it includes communication and understaning, you are available and responsive to a patient's expressed needs
Transcultural
Nurses need to understand and apply cultural caring behaviors. Human caring is a universal phenomenon, the expressions, processes, and patterns of caring vary among people of different cultures
Caring is very personal and its expression differs for each patient
Nurses need to learn culturall specific behaviors and words that rflect human caring in different ultures to identify and effectivley meet the needs of all patients
Transformative
The relationship influences both the nurse and patient for better or worse.
Active listening
Means begin attentive to what a patients is saying both verbally and nonverbally
It facilitates patient communication
SURETY Model:
S: sit at an angle facing the patient
U: uncross your legs and arms
R: relax
E: eye contact
T: touch
Y: Your intuition
Assertiveness
Allows you to express feelings and ideas without judging or hurtin others. Assertive behavior includes appropriate eye contact; nonverbal communication that reflects interest, honesty, and active listening; spontaneous verbal responses with a confident boice; and culturally sensitive use of touch and space
Autonomy
Is being self-directed and independent in accomplishing outcomes and advocating for others. Professional nurses make choices and accept responsibility for the outcomes of their actions. Take initiative in porblem solving and communicate in a way that reflects the importance an purpose of a therapuetic conversation
Channel
A way to send an receive messages through visual, auditory, and tactice senses
Facial expressions send visual messages
Spoken words travel through auditory channels
Touch uses tactile senses
Circular Transactional Communication Process
Each person is both a speaker and a listener and can simultaneously send and receive messages
Both parties view the perceptions, attitudes, and potential reactions to a sent message
Communication is continuous and interactive
Feedback from the receiver or environment enables the communicators to correct or validate the communication
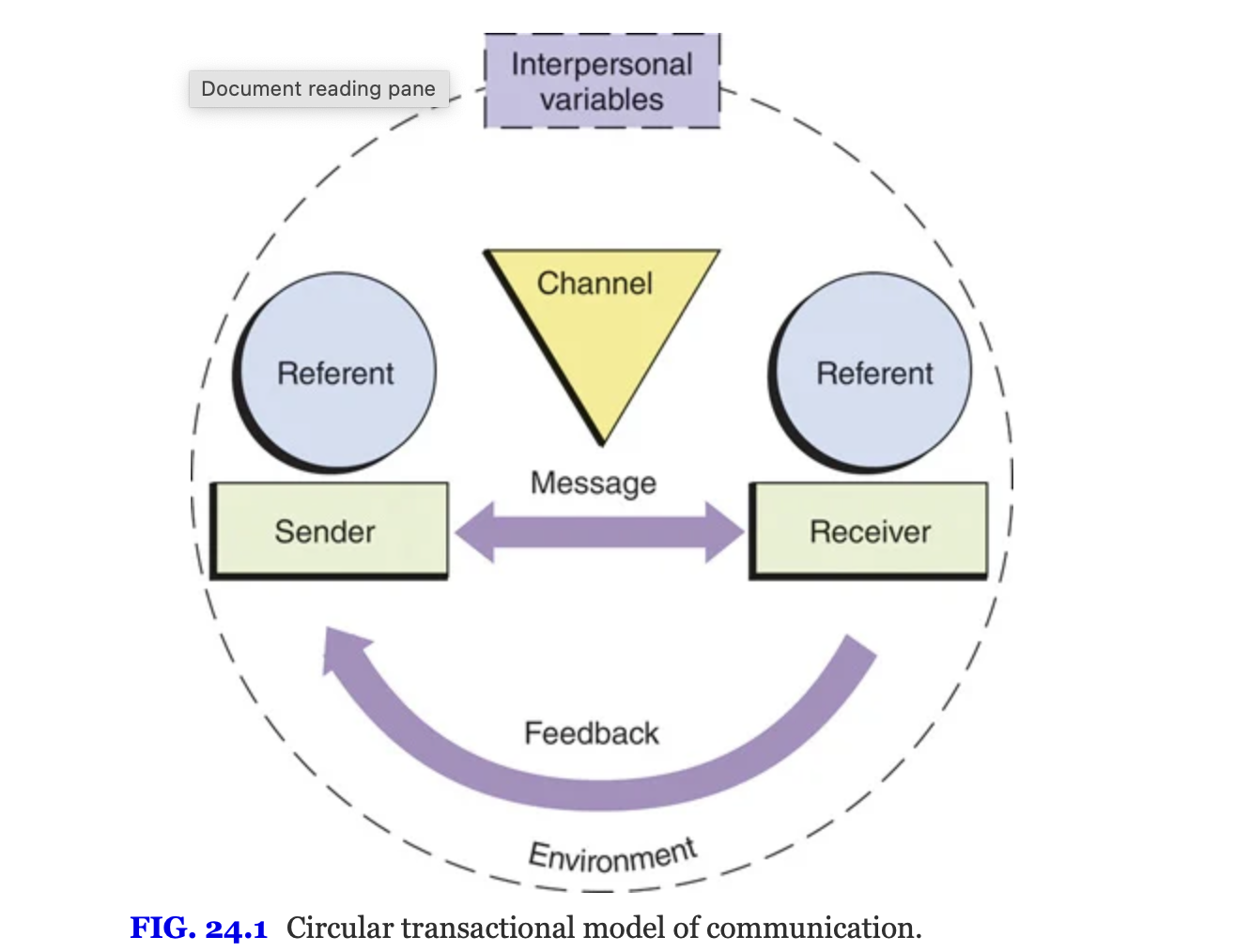
Circular Transactional Model
Includes several elements: the reerent, sender, and receiver, message, channels, context or environment in which the communication process occurs, feedback, and interpsonal variables
Communication
A lifelong learning process
As a nurse your aim is to communicate with patients and families by developing meaningful and helping relationships
Apply critical thinking and clinical judgment to collect relevant assessment data, analyze the nature of the patient’s health problems, provide education and counseling, and interact puposefully during nursing interventions
Therapeutic communication poromotes personal growth and helps patients reach their desired health-outcomes
Complementary
Complementary role relationships function with one person holding an elevated position over the other perosn. A complementary role occurs when a nurse provides education to a patient about a new medication or therapy
Empathy
The ability to understand and accpet another persons’s reality, accurately perceive feelings, and communicate this understanding to the other
Therapeutic communication technique that enables you to understand a patient’s situation, feelings, and concerns
Environment
The setting for sender-receiver interaction.
An effective communication setting provides participants with physical and emotional comfort and safety
Noise, temperature extremes, distractions, and lack of privacy or space create confusion, tension and discomfort
Environmental distractions are common in health care settings and interfere with messages sent between people
Feedback
The message a sender receives from a receiver. It indicates the extent to which the receiver understood the meaning of the sender’s message. Feedback occurs continuously between a sender and receiver.
Interpersonal Variables
Are factors within both the sender and receiver that influence communication.
Lateral Violence
AKA workplace bullying
Among colleagues
Includes behaviors such as withholding information, being hypocritcal, raising blame or making put-downs, criticizing without solutions, excluding, and using nonverbal expressions of disapproval such as raising eyebrows or making faces
Adversley afects the work enviornment leading to job disatisfaction, a decreased sens of value, poor teamwork, poor retention of qualified nurses, and nurses leaving the profession
Message
The content of the communication
Includes verbal and noverbal expressions of thoughts and feelings
Motivational Interviewing
A collaborative, person-centered, and goal-oriented technique that encourages patients to change their behavior
Based On: understanding the patnership between you and your patient, accepting the patient’s thoughts and feelings, using compassion to promote the patient’s well being and prioritize needs, and drawing out th epatient’s motivation to change
OARS Model:
O: Open-ended question
A: affirmation
R: reflective listening
S: summarizing
Perceptual biases
AKA stereotypes
That interfere with you ability to accurately perceive an interpret messages from others
Receiver
The person who receives and decodes the message
Referent
Motivates one person to communicate with another
sighs, sounds, sensations, perceptions, and ideas are examples of cues that initiate the communication process
knowing a simulus or referent that initiates communication allows you to develop and organize messages more efficiently
Sender
The person who encodes and delivers a message
Symmetrical
A symmetrical relationship is (more) equal. A group of patients dicussing their plans after discharage is an example of a sysmmetrical role relationship. One person does not hold an elevated position over the other person or people.
Therapeutic Communication
Techniques that are specific responses that encourage the expression of feelings and ideas an convey acceptance and respect. These techniques apply in a variety of differnt situations