1.4.1 Government intervention in markets
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Indirect taxation
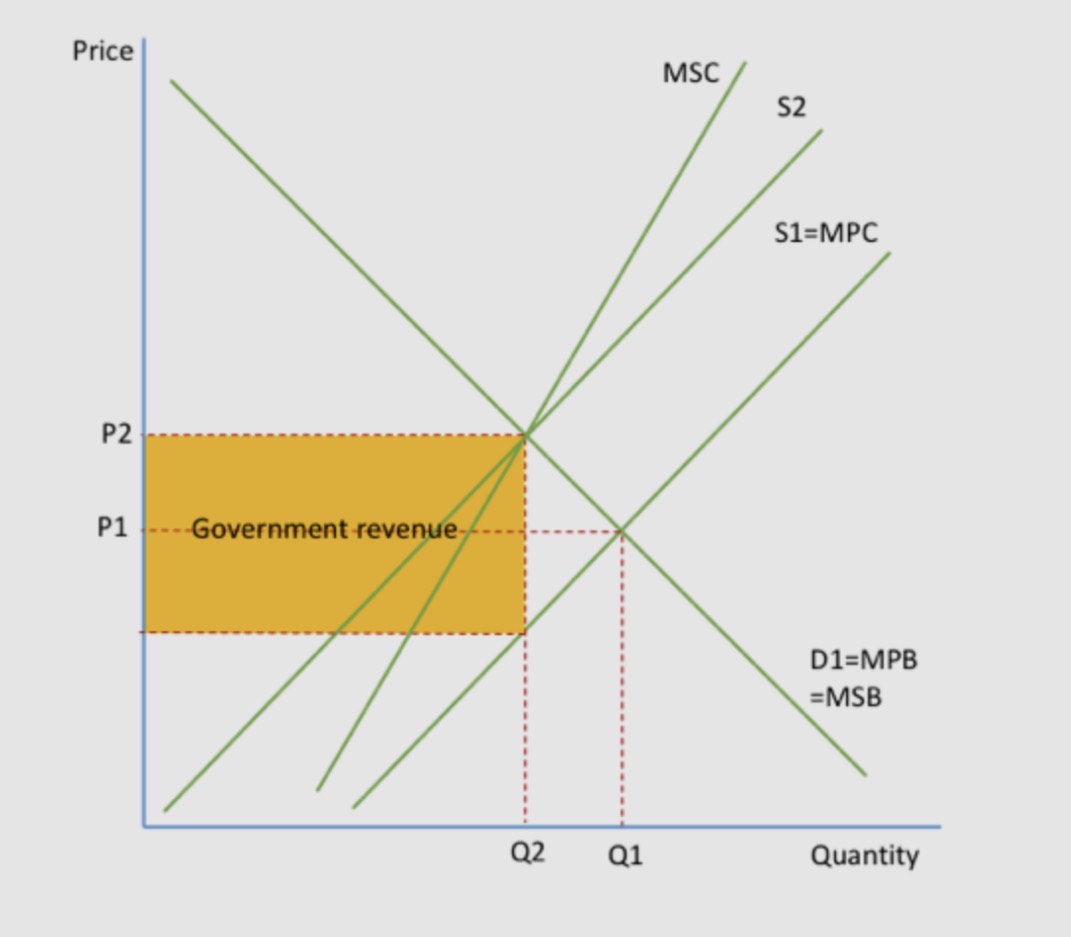
When the good has a negative externality, the government can introduce indirect taxation to prevent market failure.
This will cause a fall in supply and increase the costs to the individual, so the supply curve/MPC curve will shift from S1 to S2.
The free market would produce at P1Q1, where MPC=MPB, but the social optimum position is P2Q2, where MSB=MSC.
Following the introduction of the tax, the equilibrium position is S2=MPB=MSB, at P2Q2.
The tax internalises the externality and social welfare is now maximised.
This diagram shows a specific tax but an ad valorem tax could also be introduced, which would have the same effect, but the shift of the curve would look slightly different.
Advantages of indirect tax
● It internalises the externality- the market now produces at the social equilibrium position and social welfare is maximised.
● It raises government revenue , which could be used to solve the externality in other ways such as through education. This may help goods to become more elastic in the long run. The effect will depend on what the government does with the revenue they raise.
Disadvantages of indirect tax
● It is difficult to know the size of the externality and so it is difficult to target the tax ; the effect depends on where the tax is set. The government suffers from imperfect information when setting the tax.
● There could be conflict between the government goal of raising revenue and solving the externality, which makes setting the tax difficult.
● It could lead to the creation of a black market
● If demand for the good is inelastic, then the tax will be ineffective at reducing output.
● Taxes are politically unpopular and so governments may be reluctant to introduce them.
● They are regressive , meaning they the poor spend a larger proportion of their income on indirect taxes than the rich do.
Some examples of indirect taxes used for externalities in the UK are: landfill taxes, fuel duties, alcohol duties, tobacco duties, air passenger duties and sugar taxes.
Subsidies