units 1-6 econ final review
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
economics
- science of scarcity
- study of choices
- social science concerned with the efficient use of limited resources to achieve maximum satisfaction of economic wants
scarcity
the condition in which our wants are greater than our limited resources
positive statements
- facts
- avoids value judgements (what is)
normative statements
- opinions
- value judgements (what ought to be)
marginal
- additional
- additional benefit ≥ additional cost
economic assumptions
- society wants are unlimited but resources are limited (scarcity)
- every choice has a cost/trade-off
- maximizers
- MC = MB
trade offs
alternatives that we give up whenever we choose something else (opportunity cost)
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision (second best option)
product market
- firms sell
- households buy
factor/resource market
- firms buy
- households sell
factors of production
capital, land, labor, entrepreneurs
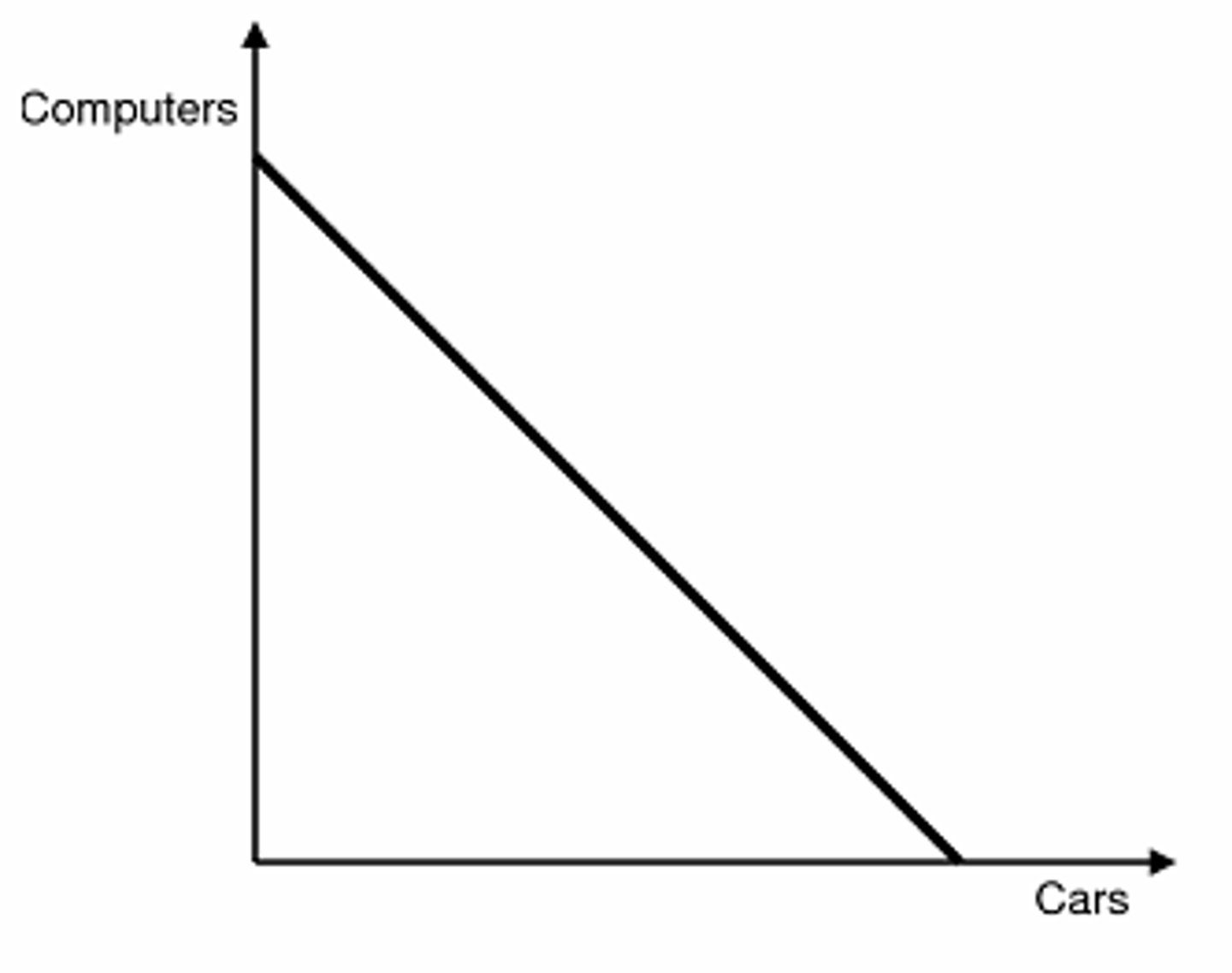
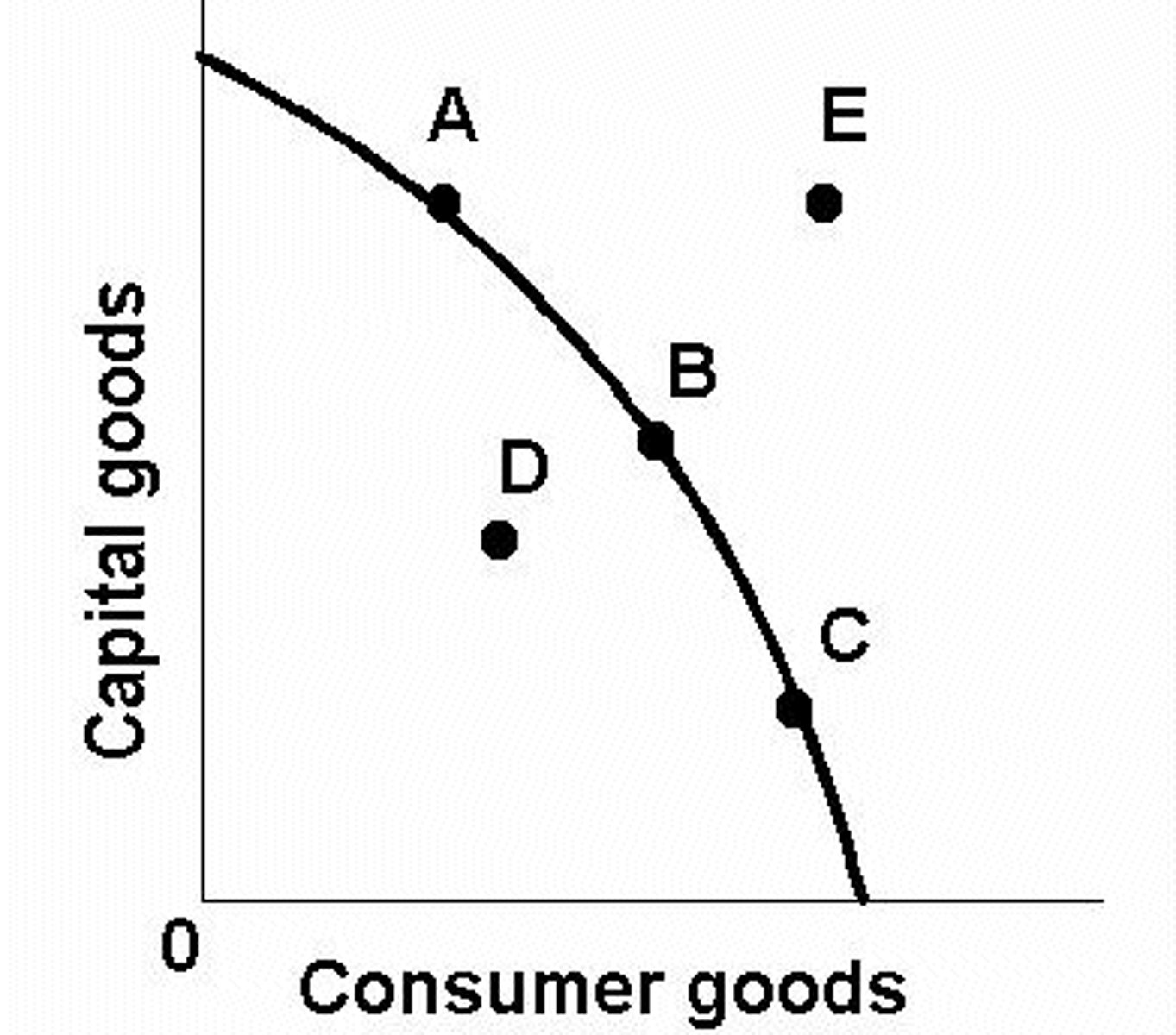
production possibilities curve/frontier
- shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scare resources
- demonstrates scarcity, tradeoffs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
production possibilities curve/frontier assumptions
- only two goods can be produced
- full employment of resources
- fixed resources (ceteris paribus)
- fixed technology
constant opportunity cost
resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
increasing opportunity cost
- resources are not easily adaptable to producing both goods
- as you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase
shifters of production possibilities curve/frontier
- resource quantity or quality
- technology
- trade
productive efficiency
- products are being produced in the least costly way
- point on PPC
allocative efficiency
- products being produced are the ones most desired by society
- optimal point on PPC
per unit opportunity cost
opportunity cost/ units gained
absolute advantage
- producer that can produce the most output or requires the least amount of inputs/resources
- input: smallest #
- output: largest #
comparative advantage
- producer with the lowest (per unit) opportunity cost
- input: cross-add -> smallest #/ other goes under
- output: cross-add -> largest #/ other goes over
economic questions
- WHAT goods and services should be produced?
- HOW should these goods and services be produced?
- WHO consumes these goods and services
economic system
method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services
command (centrally-planned) economy
gov owns resources and decides what to produce, how much, and who will receive it
capitalism/ free market system
- laissez faire: little gov involvement
- individuals own resources and determine the economic questions
- ppl can make profit = incentive to produce quality items efficiency
- wide variety of goods
- competition and self-interest regulate economy
invisible hand
society's goals will be met as individuals seek their own self-interest
demand
different quantities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
law of demand
- inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
- occurs bc of substitution effect, income effect, and law of diminishing marginal utility
substitution effect
product price increases = consumer buys more of substitute product and less of that product (and vice versa)
income effect
produce price decreases = consumers buy more
law of diminishing marginal utility
consuming more units = additional satisfaction from each additional unit eventually decreases
utility
satisfaction
market demand
summation of the consumers' demand
shifters of demand
anything but price
substitutes
Px↑ = Dy↑ (direct relationship)
complements
Px↑ = Dy↓ (inverse relationship)
normal
income↑ = D↑ (direct relationship)
- goods you buy when you have money
inferior
income↑ = D↓ (inverse relationship)
- goods you buy when your poor
substitutes
- goods used in place of another
- ex: pepsi and coke
complements
- two goods that are bought and used together
- ex: skis and ski boots
supply
different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices
law of supply
direct/positive relationship between price and quantity supplied
shifters of supply
anything but price
subsidies
- gov payment that supports market
- supply of a good increases
consumer surplus
- difference between what you are willing to pay and what you actually pay
- CS = buyer's maximum - price
producer's surplus
- difference between the price the seller received and how much they were willing to sell it for
- PS = price - seller's minimum
unit elastic
consumer surplus and producer surplus is balanced
surplus
producers lower prices
shortage
producers raise prices
double shifts
either price or quantity will be indeterminate
elasticity of demand
- measurement of consumers responsiveness to a change in price
- helps firms determine prices and sales
- helps gov decide how to tax
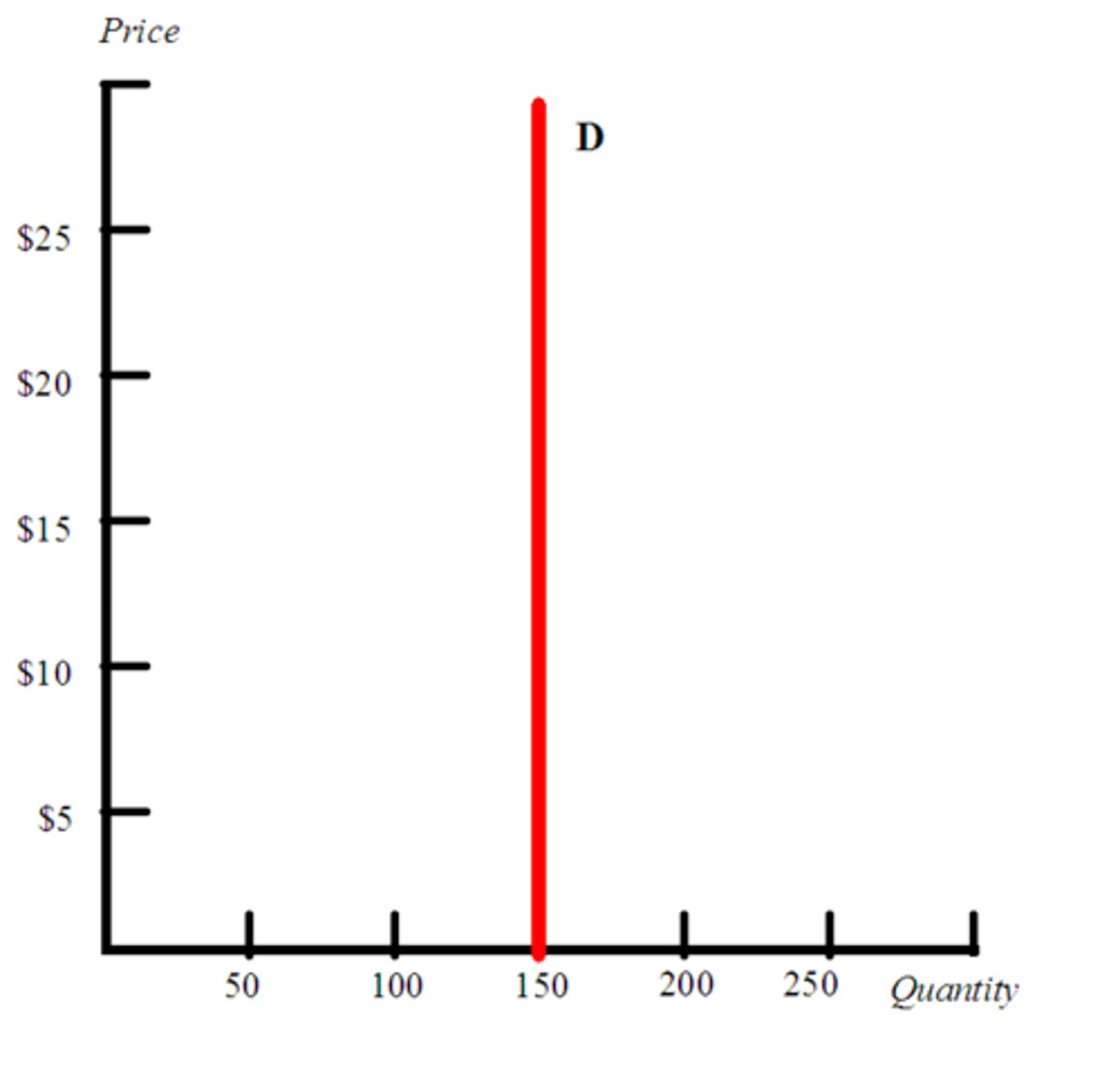
inelastic demand
- not sensitive to price change
- ppl will continue to buy it regardless of price
- elasticity coefficient <1
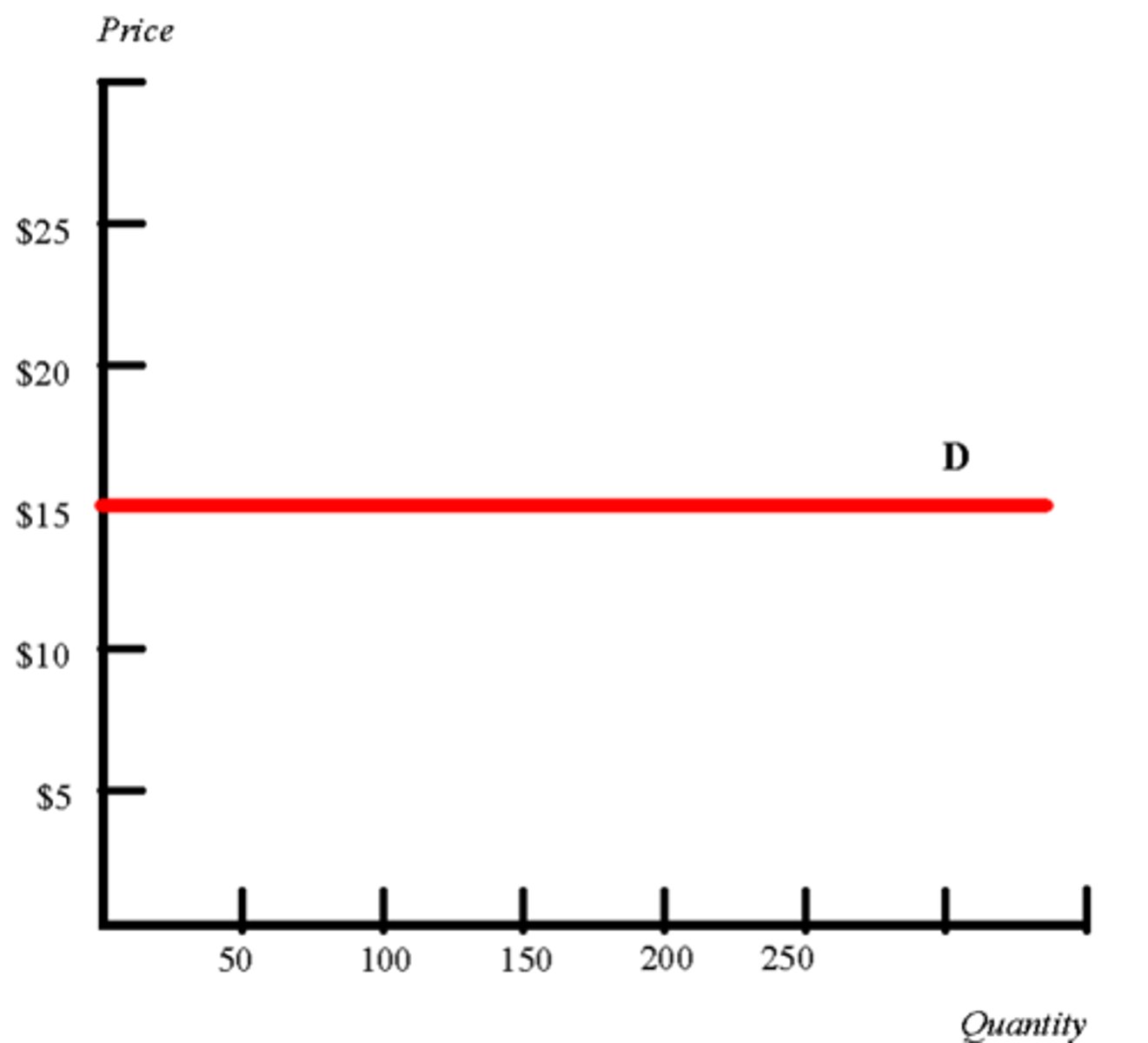
elastic demand
- sensitive to price change
- price change = quantity demanded changes a lot
elastic demand
P↑ = TR↓ (inverse relationship)
inelastic demand
P↑ = TR↑ (direct relationship)
unit elastic
P↑ = TR—
elastic
positive marginal revenue
total revenue
price x quantity
elastic demand
P↑ = TR↓ (inverse relationship)
- total revenue test
inelastic demand
P↑ = TR↑ (direct relationship)
- total revenue test
price elasticity of supply
how sensitive producers are to a change in price
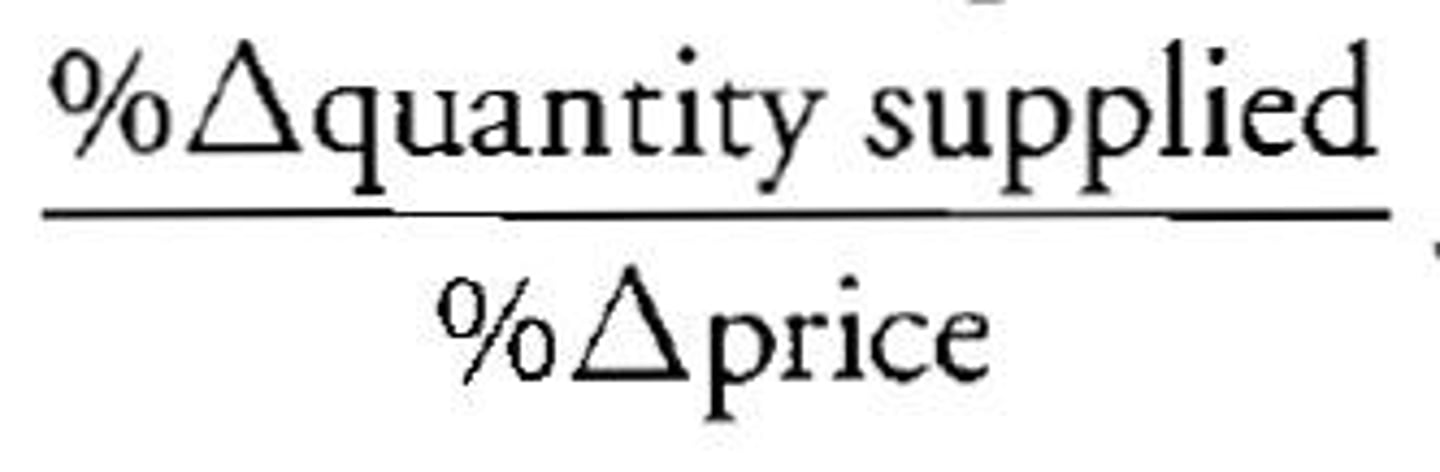
cross price elasticity of demand
- how sensitive a product is to a change in price of another good
- shows if goods are substitutes or complements
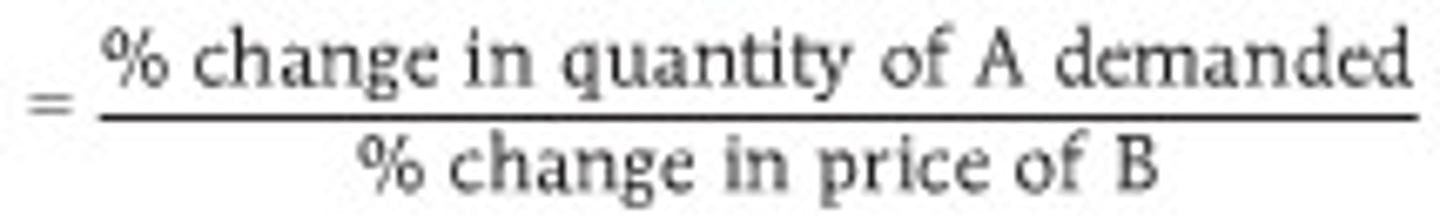
complements
coefficient = negative (shows inverse relationship)
- cross price elasticity
substitutes
coefficient = positive (shows direct relationship)
- cross price elasticity
income elasticity of demand
- how sensitive a product is to a change in income
- shows if goods are normal or inferior
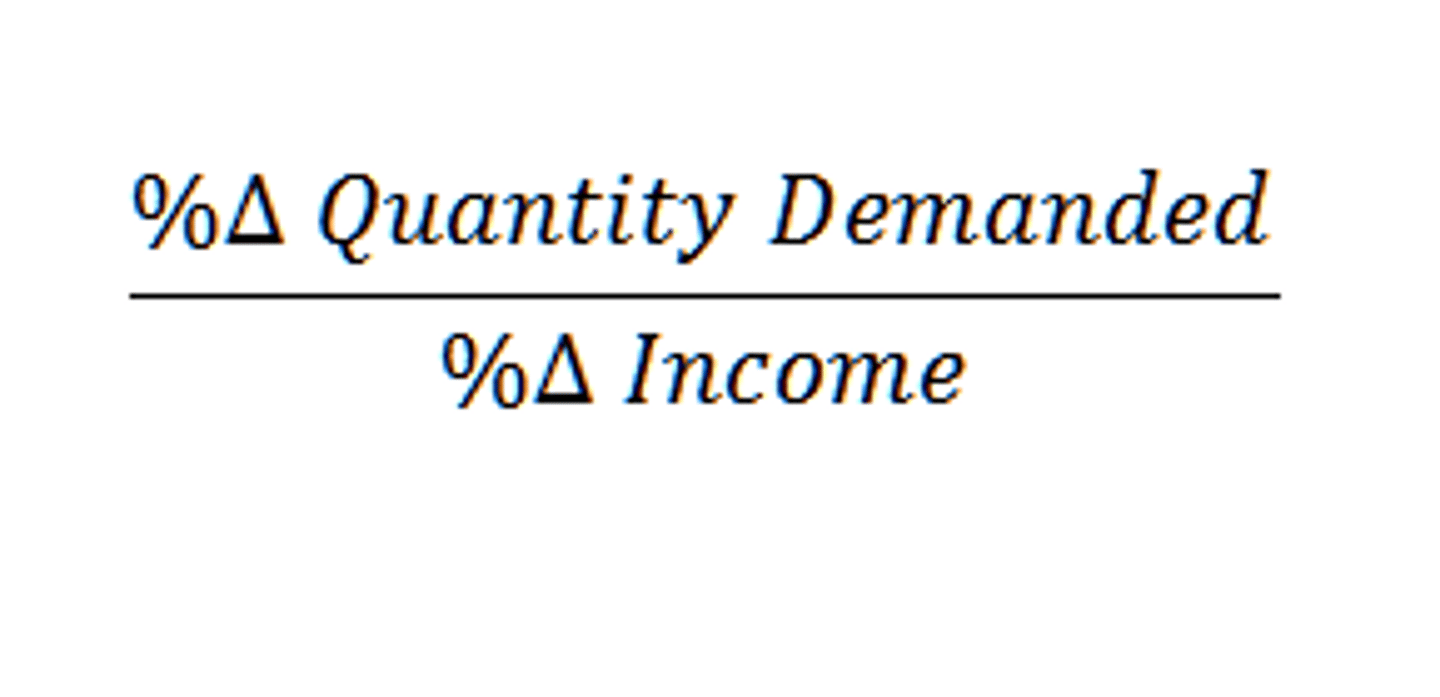
inferior
coefficient = negative (shows inverse relationship)
- income elasticity
normal
coefficient = positive (shows direct relationship)
- income elasticity
price ceiling
maximum legal price a seller can charge
price floor
minimum legal price a seller can sell
excise tax
per unit tax on producers
MB = MC
when to stop consuming
utility maximization
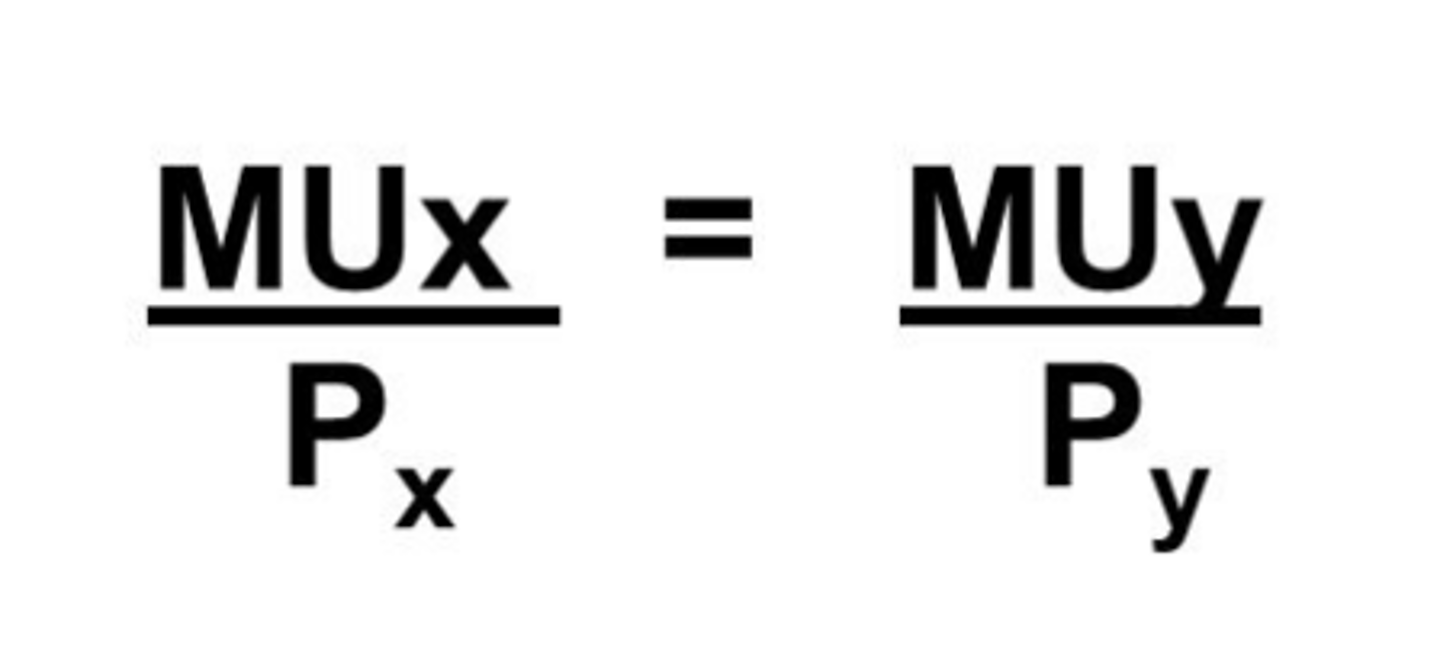
accountants
explicit costs only
economists
explicit costs and implicit costs
explicit costs
- payments paid by firms for using the resources of others
- out of pocket costs
- ex: rent, wages, materials, electricity bills
implicit costs
- opportunity costs that firms "pay" for using their own resources
- ex: time
production
converting inputs into outputs
inputs
- resources used to make outputs
- also called factors
total physical product (TP)
total output or quantity produced
marginal product (MP)
- additional output generated by additional inputs (workers)
- ΔTP/ Δinput
average product (AP)
- output per unit of input
- TP/ units of labor
law of diminishing marginal returns
- as resources (workers) are added to fixed resources (machinery), the additional output produced from each new worker will eventually fall
- short run concept bc of fixed resources
stages of returns
- increasing marginal returns
- decreasing/diminishing marginal returns
- negative marginal returns
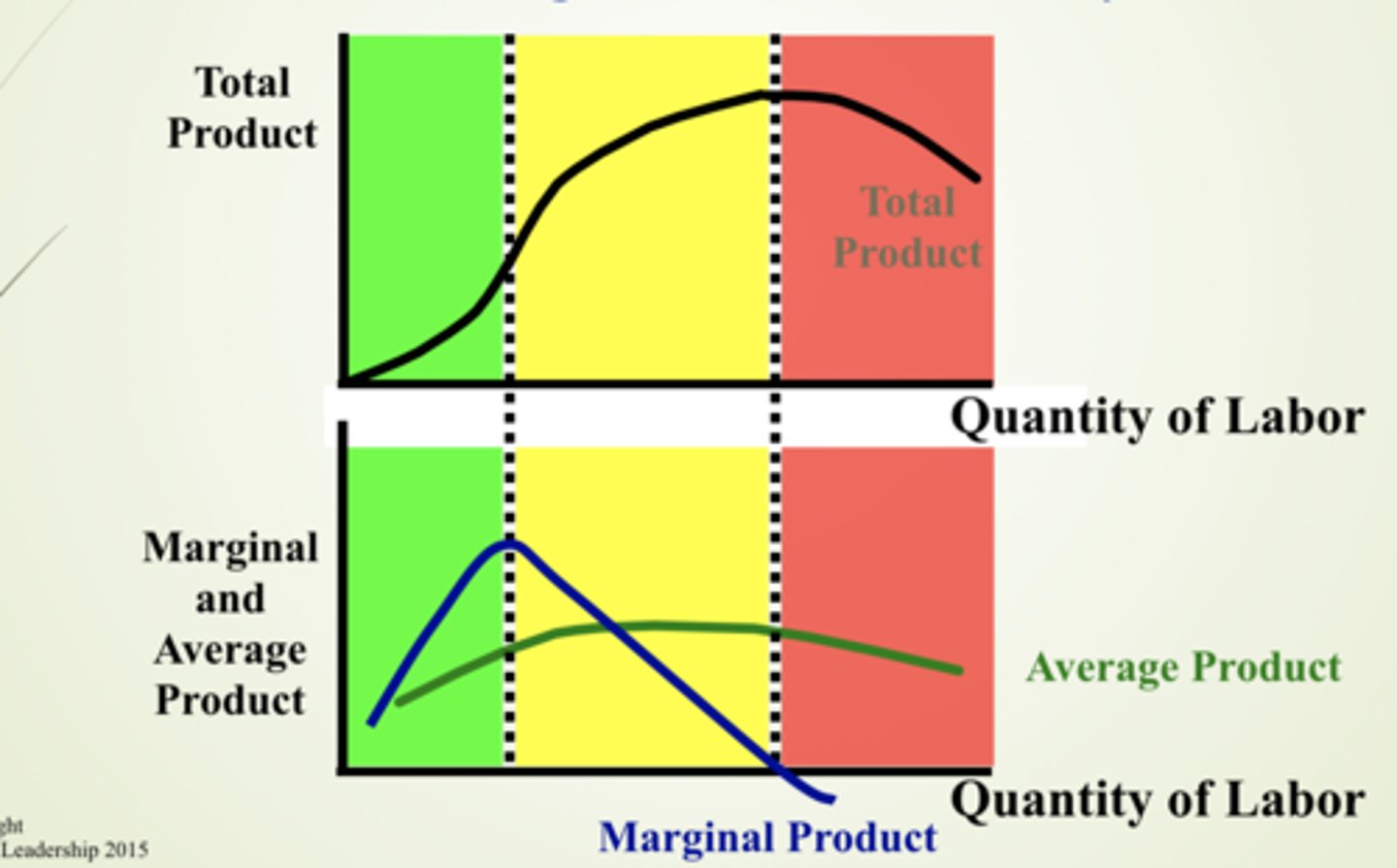
increasing marginal returns
- MP rising
- TP increasing at an increasing rate
decreasing/diminishing marginal returns
- MP falling
- TP increasing at a decreasing rate
negative marginal returns
- MP is negative
- TP decreasing
accounting profit
total revenue - accounting costs
economic profit
total revenue - economic costs
short run
period in which at least one resource is fixed
long run
- all resources are variable
- no fixed resources
total costs
- total fixed costs (FC)
- total variable costs (VC)
- total costs (TC)
per unit costs
- average fixed costs (AFC)
- average variable costs (AVC)
- average total costs (ATC)
- marginal cost (MC)
fixed costs
- costs for fixed resources that don't change with the amount produced
- ex: rent, insurance, managers, salaries
average fixed costs
fixed costs/ quantity
variable costs
- costs for variable resources that do change as more/less is produced
- ex: raw materials, labor, electricity
average variable costs
variable costs/ quantity
total cost
sum of fixed and variable costs
average total cost
total costs/ quantity
marginal cost
- additional costs of an additional output
- U-shaped bc of diminishing marginal returns
marginal cost
Δtotal costs/ Δquantity