chemistry year 1
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
First ionisation energy definition
The energy required to remove 1 electron from 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of gaseous ions in their gaseous state.
Factors affecting first ionisation energy
Shielding, nuclear charge, atomic radius
What happens with successive ionisation energies
Successive ionisation energies increase due to greater number of protons per electron and decreased electron shielding as electrons are removed.
Where is the large jump in successive ionisation energies
When the electron being removed is from a new inner shell.
Trend in first ionisation energy down a group
First ionisation energy decreases due to increased atomic radius and greater electron shielding, making it easier to remove an outer electron.
Trend of first ionisation energy across a period
First ionisation energy increases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, which attracts electrons more strongly and decreases atomic radius.
Why is removing an electron from a group 3 element easier than group 2
Group 3 elements’ outer electron is on the p-orbital as opposed to s-orbital, which is higher in energy and further from the nucleus, making it easier to remove.
Why is removing an electron from a group 6 element easier than group 5
Group 6 has 2 electrons in the p orbital where the electron is being removed, and due to the electrostatic repulsion between them this makes an electron easier to removecompared to group 5, where there is only one electron in the p orbital.
Word to use instead of “charge carrier”
Mobile electrons/ions
Elements that form giant covalent lattices
Silicon, carbon and boron
Why does sulfur have a higher melting point than phosphorus
Because sulfur forms S8 and phophorus forms P4, so S8 has more electrons so larger london forces
Why do giant covalent structures have higher melting points than metallic structures
Giant covalent structures have 4 covalent bonds per atom, requiring more energy to break compared to the metallic bonds in metallic structures.
Electronegativity definition
The ability for atoms to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bonds
What is the Pauling scale
The measure of electronegativity
What does electronegativity difference dictate
Bond type
How do simple molecular substances interact in polar solvents
Does not dissolves in water
How to represent a hydrogen bond on a diagram
Dashed line between H nucleus and lone pair
What can increase london forces?
The number of electrons in the molecule
If all of the atoms are in a longer and thin structure
Order of intermolecular forces in strength
London forces < permanent dipole dipole < hydrogen bonding
Are non polar substances soluble in polar solvents
No
Is a non polar substance soluble in a non polar solvent
Yes (e.g. hexane)
Why is the solubility of polar molecules are hard to predict?
Depends on the strength of the dipole
How do london forces come about?
Random movement of electrons produces a changing dipole which will induce a dipole on the neighbouring molecules. London forces are the attraction due to these instantaneous dipole.
How do permanent dipole dipole forces arise?
In a polar molecule, the permanent dipoles attract each other so the molecules form an arrangement with positive and negative charges adjacent
What are the anomalous properties of water due to hydrogen bonds
Higher B.P./M.P, high viscosity and surface tension, liquid water is more dense than ice
Why is water less dense than ice
The hydrogen bonds form a open lattice structure which is less dense than liquid structure
What elements form hydrogen bonds
H/N/O/F
Hydrogen bond definition
A strong dipole dipole interaction between a positive hydrogen nucleus and a lone pair of electrons
Symbol for dipoles

What is a polar molecule
A non symmetrical molecule with polar bonds so there is an overall dipole
Factors that affect electronegativity
Nuclear charge, atomic radius and shielding
How many hydrogen bonds does a water molecules form
2 hydrogen bonds
Why are non polar substances insoluble in polar solvents
The intermolecular forces are weaker in the substance so there will not be enough interaction between solvent and solute to dissolve
Why is a non polar substance soluble in a non polar solvent
Because the intermolecular forces interact and weaken in the simple molecular lattice, causing the solvent to move apart and allow the substance to dissolve
How does nuclear charge affect electronegativity
The more protons the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and the bonding pair
How does atomic radius affect electronegativity
Closer to the nucleus means stronger attraction between the nucleus and bonding pair
How does shielding affect electronegativity
Less shells of electrons between the nexulus and shared pair causes stronger attraction
How can you find atomic mass from mass spectrometry
The furthest right significant peak at mass spectrometry is the M+ peak, which represents the atomic mass as m/z when z = 1 is equal to m
What is the M+1 peak
A tiny peak 1 above the M+ peak, representing the fragment ions with an extra neutron on the carbon atom
How does a mass spectrometer work
An electron beam knocks 1 electron off each molecule, accelerated through an electromagnetic field, then the amount that the ion was deflected and where it is detected indicates the m/z ratio
What are fragment ion peaks used for
we can use fragments to figure out the overall structure of the molecule like where alkyl branches are
How does an infrared spectrometer work
We fire infrared radiation at the molecules and different bonds absorb the radiation and we can detect which wavenumbers of waves are absorbed which tells us the functional groups present in the moleucle
What ways can bonds vibrate
A bond can stretch or bend
How do greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect
The radiation emitted by earth is absorbed by the bonds in greenhouse gases causes the earth to warm by reabsorbing the reemitted radiation
What is the fingerprint region
A section of an infrared spectrum which, using computer analysis, can identify the specific molecule
What is infrared spectroscopy used for
We can analyse air samples to see which pollutants are present
In breathalysers, so it can be detected if there is a certain concentration of alcohol in the breath
What does a receiver look like

What does a screw tap adaptor look like

What does a still head look like
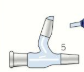
What are anti bumping granules for
To prevent large bubbles from forming and shaking the apparatus
How to find out which layer in a solution is organic and aqueous
If you add water the aqueous layer will increase in size
What will cause impurities in organic layers
Reactions with acids
How to remove acid impurities from the organic layer
Add sodium carbonate to a separating funnel, invert and open the tap to let the carbon dioxide out
Drying agents
Anhydrous salts
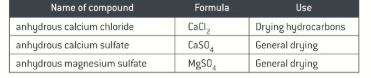
How to dry a solution
Add a drying agent and swirl the flask then leave a stopper on. The liquid will be clear if it is dry
Alkane to haloalkane conditions/reagants
halogen and UV light
Alkene to haloalkane conditions/reagants
hydrogen halide (or halogen)
Alkene to alkane conditions/reagants
Hydrogen with nickel catalyst at 423K
Alkene to alcohol conditions/reagants
Steam with a phosphoric acid catalyst
Alcohol to alkene conditions/reagents
Concentrated phosphoric acid to undergo elimination
Alcohol to haloalkane conditions/reagents
Concentrated sulfuric acid and sodium halide
Haloalkane to alcohol conditions/reagents
Sodium hydroxide under reflux
Alcohol to ketone
Heating under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate with a secondary alcohol
Alcohol to carboxylic acid
Heating under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate with a primary alcohol
Alcohol to aldehyde
Distillation with acidified potassium dichromate of a primary alcohol
What is the prefix for OH
hydroxyl
Why do alcohols have higher melting points than alkanes
Because there is a dipole on the OH causing hydrogen bonds between the alcohol, which are stronger than the london forces
Alcohols solubility in water
Very soluble because the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with the water, solubility decreases as chain length increases
How is a primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol defined
How many carbons are attached to the carbon with the OH
What does the oxidation of primary alcohols form
Aldehydes and carboxylic acids
Conditions for alcohol forming aldehyde
Gentle heating under distillation with acidified potassium dichromate with an oxidising agent
Conditions for alcohol to carboxylic acid
Heated under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate and oxidising agent
Conditions for alcohol to ketone
Heated under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate and oxidisng agent
What is a dehydration reaction
When water is removed from an alcohol to make an alkene
Conditions for dehydration
Acid catalyst and heated under reflux
What reactants are required to make a haloalkane from an alcohol
Sulfuric acid, alcohol, and sodium halide (hydrogen halide is formed with sufuric acid and sodium halide)
What mechanism do haloalkanes to alcohols undergo
Nucleophilic substitution
What is hydrolysis
The breaking of a bond in a molecule in a solution with hydroxide or water
Name 3 main nucleophiles
Water, ammonia and OH- ion
What reagents and conditions are there for the hydrolysis of a haloalkane
NaOH and heated under reflux
How does carbon-halogen bond strength vary down the group
The average bond enthalpy decreases
How does bond enthalpy of carbon-halogen bond affect the rate of hydrolysis
The larger the bond enthalpy of the carbon-halogen bond, the slower the reaction rate
How to measure rate of hydrolysis
Add aqueous silver nitrate, so precipitate is formed as halide is released into solution. This has to be done with ethanol and water so the haloalkane doesn’t form a separate layer
What is a cfc
Chlorofluorocarbon
Why is depletion of the ozone layer dangerous
Because more UVB radiation will hit humans which can cause genetic damage and skin cancer
Is hydrolysis quicker in tertiary or primary haloalkanes and why
Tertiary because it uses a two step mechanism instead of a one step mechanism like primary
Where does the nucleophile attack in hydrolysis
The opposite side of the carbon atom to the functional group
How does a nitrogen oxide radical react in the ozone layer (equations)
Acts as a catalyst

How does a chlorine radical (as a catalyst) react in the atmosphere
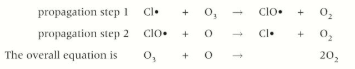
How do OH radicals react in the ozone layer

What is needed for a collision to be successful
Correct orientation and particles must have activation energy
Activation energy definition
The minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
How does rate of reaction change during a reaction
Starts at its quickest, and the rate gradually slows down
What factors can alter rate of reaction
Concentration/pressure
Temperate
Catalyst
Surface area
How does conc/pressure effect ror
Particles are closer together so particle collisions are more frequent collisions so more effective collisions
How to measure ror experimentally (2 ways)
Measuring the decrease in mass using a balance during a reaction or measuring the volume of gas produced
Catalyst definition
When a substance isn’t used up in a reaction and decreases the activation energy
Homogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats in the same physical state as the reactants
Heterogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats a different physical state as the reactants (usually solids with gaseous reactants)