Bootcamp.com - Microscopy and Lab Techniques
1/117
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
_____ adheres cells to microscope slides in their most lifelike state, and it makes it easier for those cells to be _____
fixation; stained
describe the process of heat fixation
living cells are placed on a slide --> the slide is passed over a flame to kill/"glue" the cells to the slide --> stain is applied
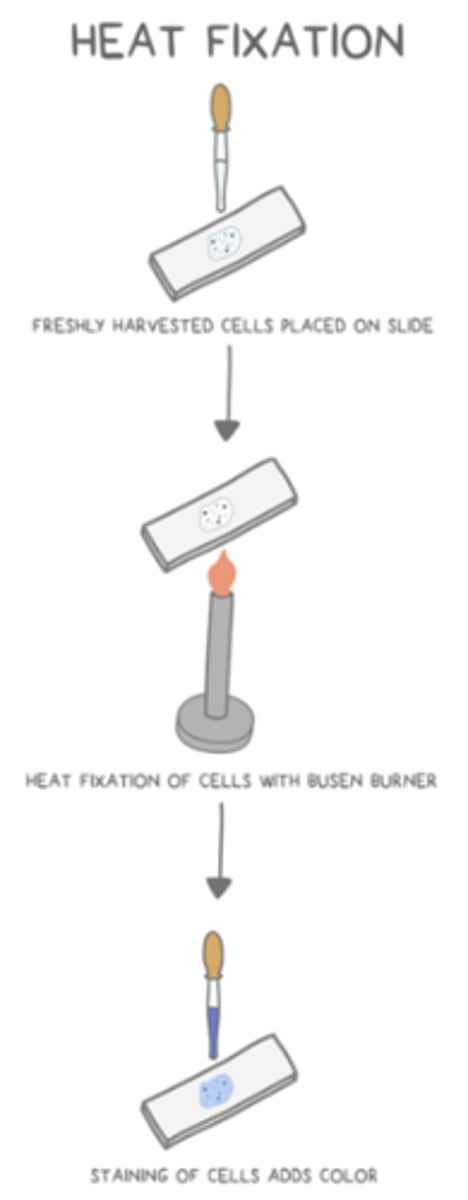
_____ is the process of adding color to cells, which allows them to be viewed more easily under microscope
staining
most optical microscopy techniques can be used to view _____ samples of cells
living
how does optical microscopy work?
it involves shining light on a sample that reflects off of it and passes through lenses that magnify the object
_____ microscopy allows for higher magnification than _____ microscopy
electron, optical
can electron microscopy be used to look at living specimens? why or why not?
no, due to fixation and staining
most viruses are so small that they must be viewed using _____ microscopy.
electron
how does electron microscopy work?
it bombards a sample with electrons that bounce off the sample and pass through magnetic fields onto a screen. The image produced is viewed indirectly on a computer.
_____ are light microscopes that focus visible light to produce a 2D image of a sample's surface
stereo-microscopes (dissection microscopes)
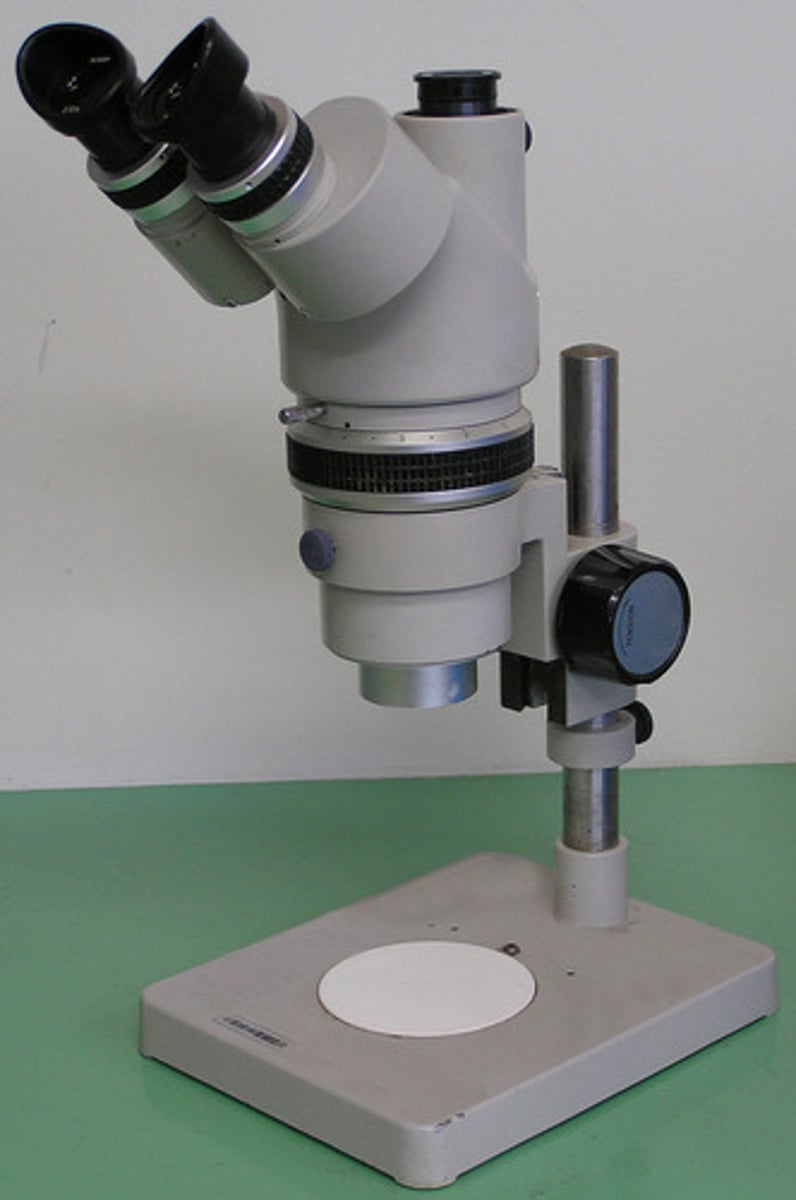

what is an advantage of stereo-microscopes (dissection microscopes)?
they are light microscopes that can be used to view living samples
electron microscopy offers _____ (higher/lower) resolution than optical microscopy because the wavelength of an electron is _____ (larger/smaller) than that of light
higher; smaller
what is a disadvantage of stereo-microscopes (dissection microscopes)?
they are light microscopes that have a low resolution
_____ are light microscopes that focus visible light to produce a 2D image of thin samples (single cell layers)
compound microscopes
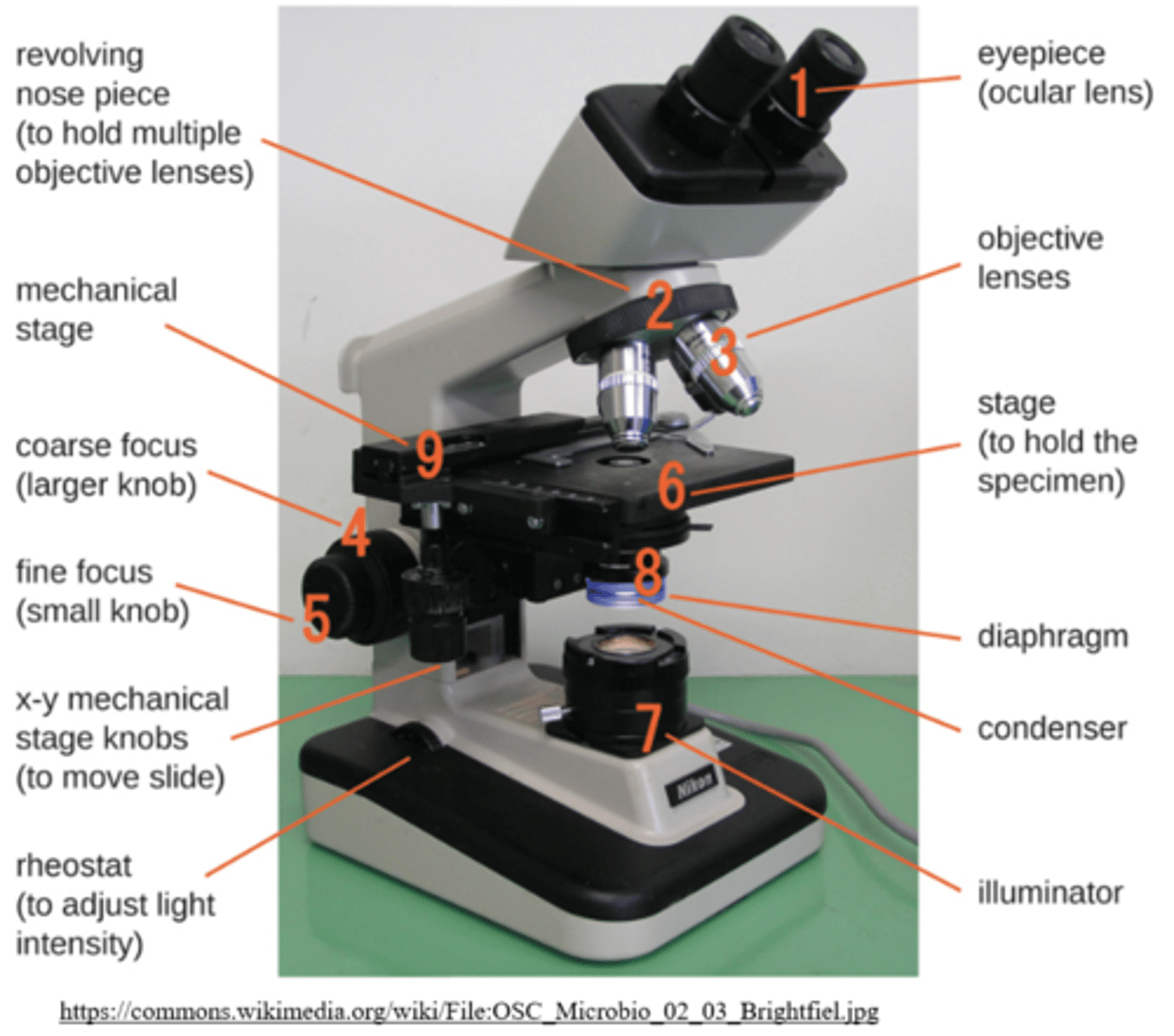
compound light microscopes usually have different _____, which gives them the ability to make more resolute images than a stereo-microscope (dissection light microscope)
lens magnifications
what is an advantage of compound light microscopes?
they can be used to view 2D images of living samples (1 cell thick)
what are some disadvantages of compound light microscopes?
they only view samples that are 1 cell thick and they have a poor contrast, which means some samples may need to be fixed & stained (killed)
_____ are optical microscopes that use light phase changes and contrast to produce 2D image of thin samples
phase-contrast microscopes
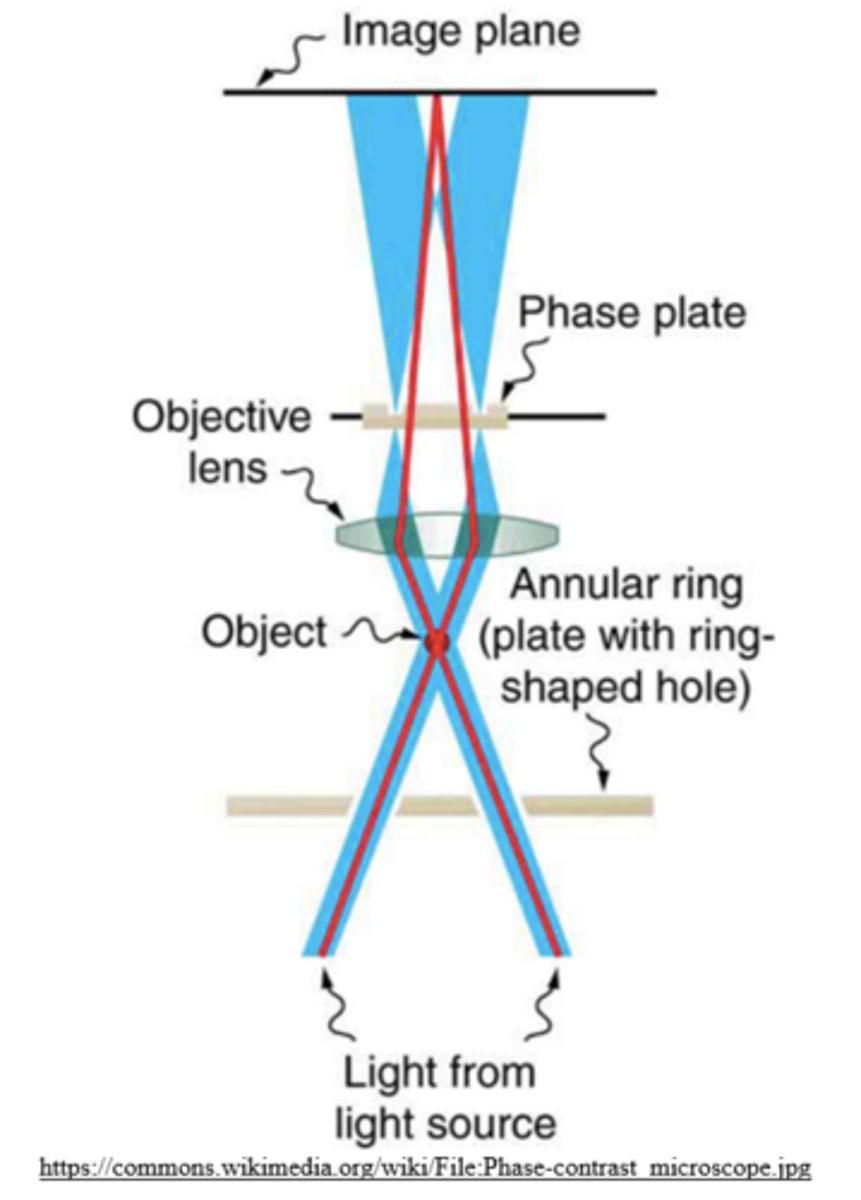
what are some advantages of phase-contrast optical microscopes?
good resolution and contrast; can be used to observe thin samples of living cells - including their internal structures
what are some disadvantages of phase-contrast optical microscopes?
ineffective on thick samples; halo effect around sample edges
what are some strategies to reduce the halo effect of phase-contrast optical microscopy?
using phase plates to reduce the phase shift; use thinner samples
_____ are fluorescent chemicals that will re-emit light upon being excited by another light source
fluorophores

_____ is the emission of photons (light) from a particle that has absorbed light
fluorescence
_____ and _____ are optical microscopy techniques that use laser light to produce 2D images of samples that have been tagged with fluorophores
fluorescence; confocal laser scanning
what are some advantages of fluorescence optical microscopy?
colorful, 2D images of thin samples of living cells; increased brightness
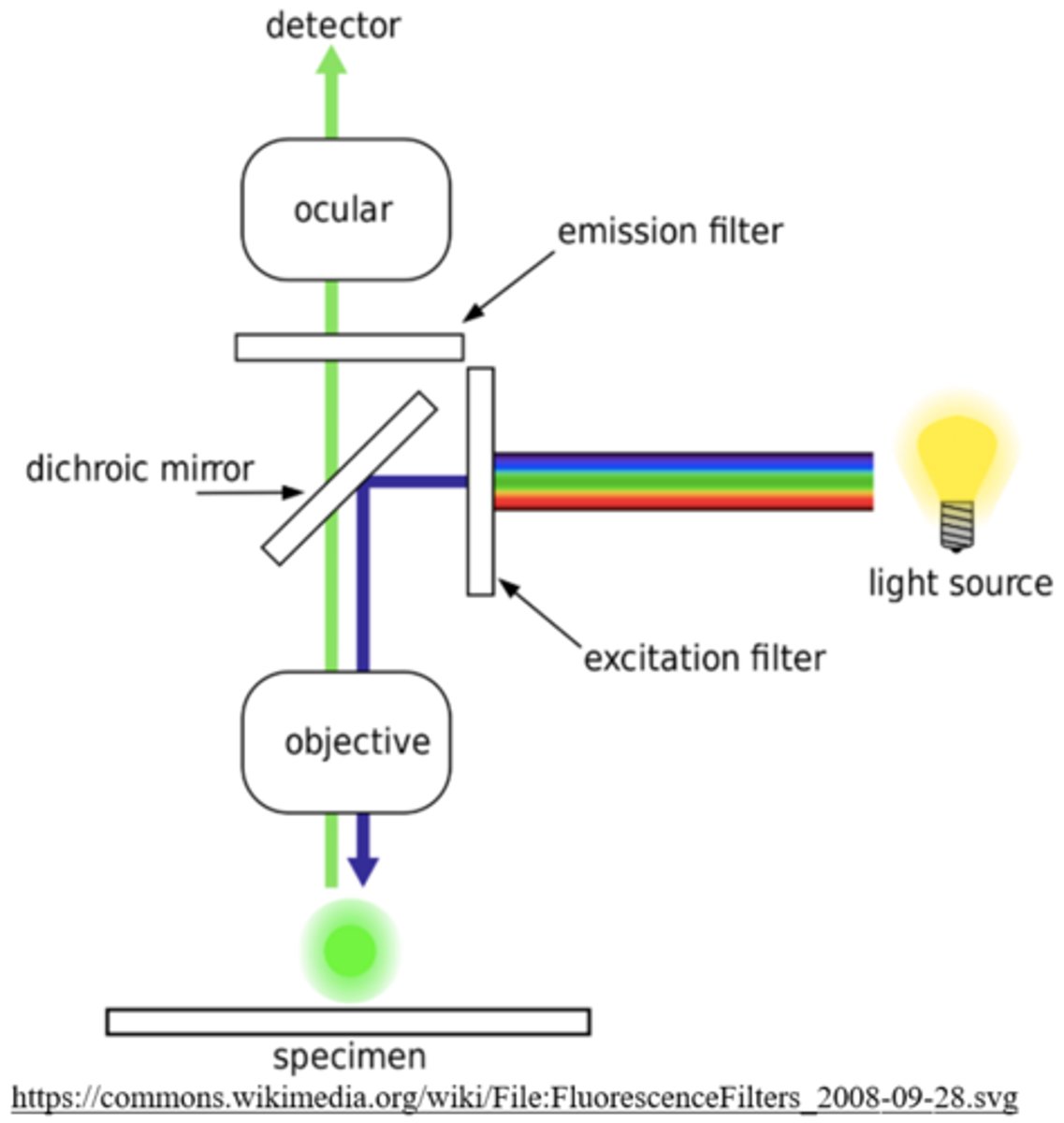
what are some disadvantages of fluorescence optical microscopy?
fluorescence sometimes creates distortions (artifacts) that reduce the resolution
what are some advantages of confocal laser scanning optical microscopy?
colorful, 2D images of thin samples of living cells; view chromosomes during mitosis; overcomes fluorescence artifacts (higher resolution)
what are some disadvantages of confocal laser scanning optical microscopy?
reduced light intensity and longer illumination times than fluorescence optical microscopy
in _____, only scattered light from the sample is transmitted to produce 2D images of unstained, living cells
dark field optical microscopy
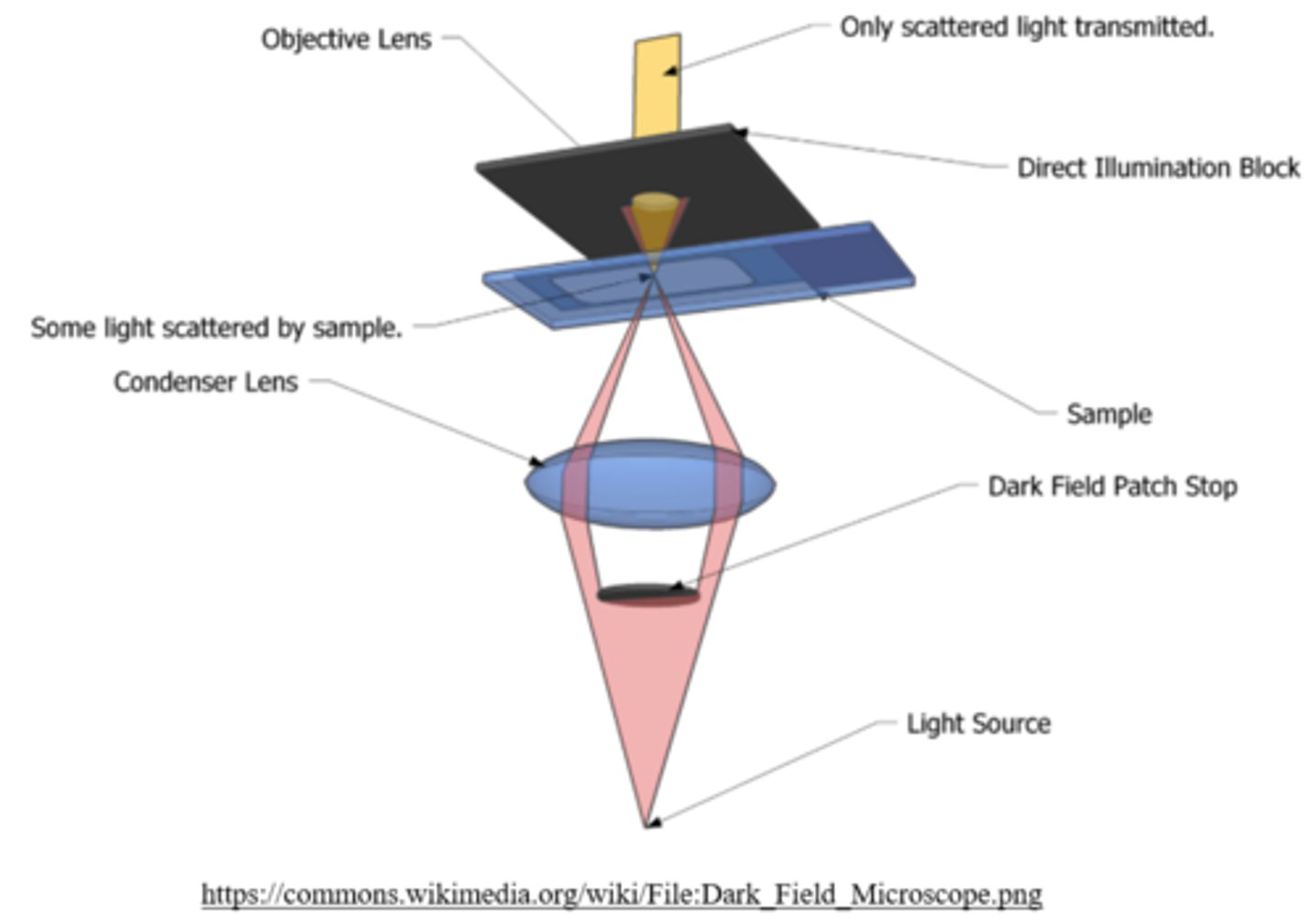
what is an advantage of dark field optical microscopy?
excellent contrast on living samples of unstained cells (black background)
what is a disadvantage of dark field optical microscopy?
low light intensity
in electron microscopy, electrons are shot through a _____ at a sample which has been fixed and
metal coated (cells are dead)
vacuum
(the vacuum prevents electrons from deviating in path)
_____ captures electrons that are scattered by atoms found on the surface of dehydrated samples
scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
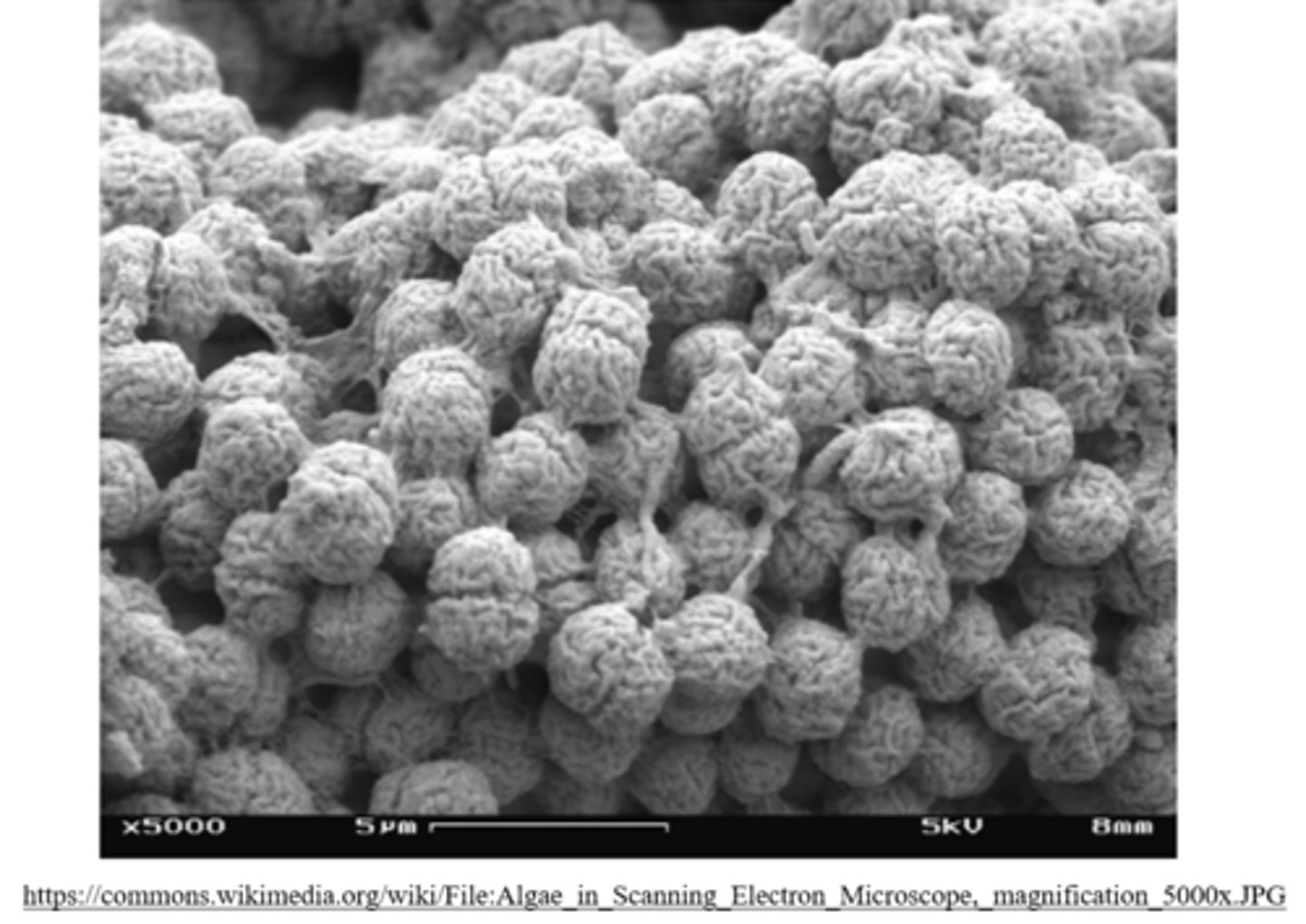

what is an advantage of SEM?
high resolution, 3D images of sample surfaces
what are some disadvantages of SEM?
it is costly, and the fixation/staining/dehydration kills the sample
_____ is like SEM, but the sample is frozen instead of dehydrated
cryo-scanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM)
what are some advantages of cryo-SEM?
high resolution, 3D images of sample surfaces, which are presented in a more natural form than SEM (due to freezing)
what are some disadvantages of cryo-SEM?
it is costly, and the fixation/staining/freezing kills the sample
_____ captures electrons that are transmitted through a thin slice of a sample
transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
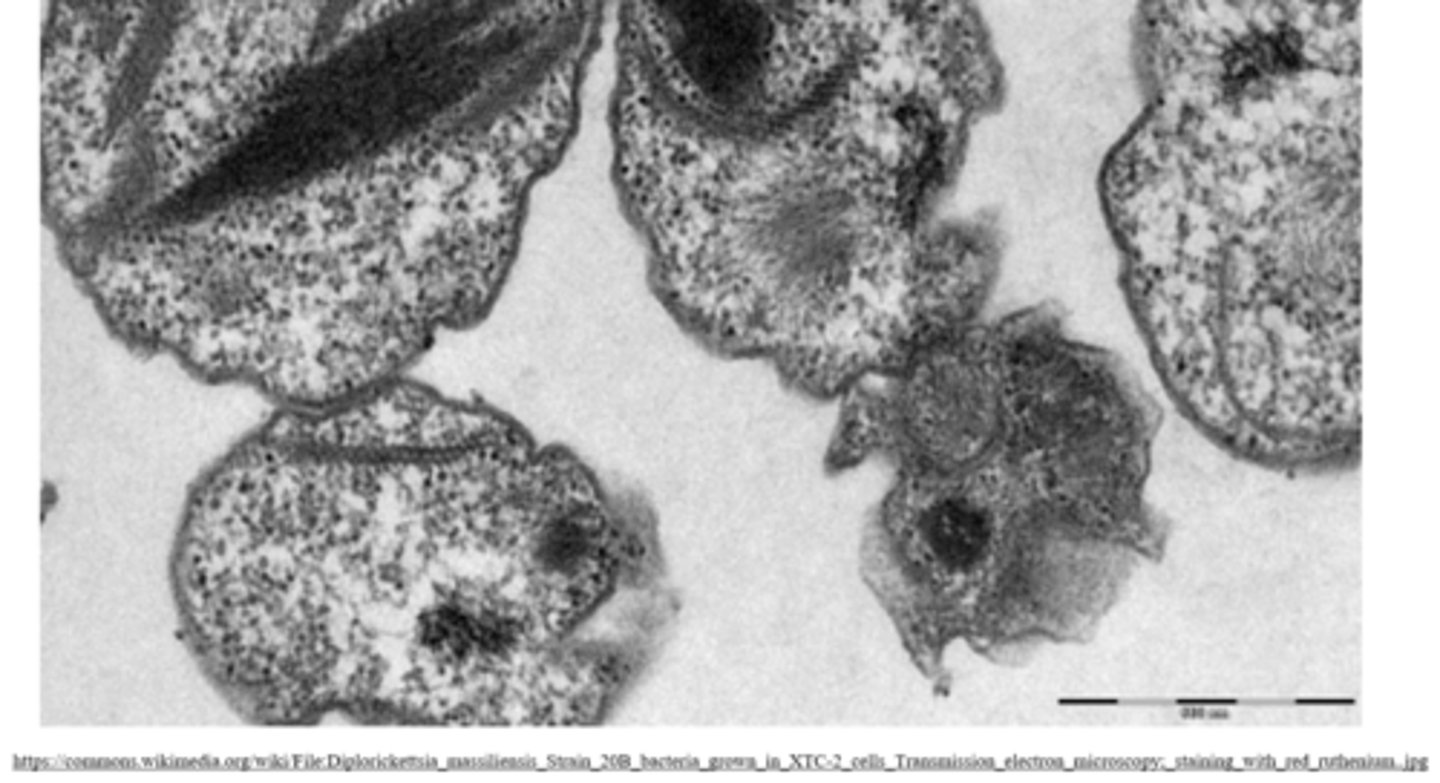
what are some advantages of TEM?
high resolution 2D images of internal sample structures
what are some disadvantages of TEM?
it is costly, and the extensive sample preparation kills all living cells
_____ integrates multiple TEM 2D images into a 3D model
electron tomography
(not a form of microscopy)
what are some advantages of electron tomography?
can look at objects and their relative positions in 3D
what are some disadvantages of electron tomography?
it is costly, and the extensive sample preparation kills all living cells
(because it is based on TEM)
is SEM or TEM used to look at surfaces?
SEM
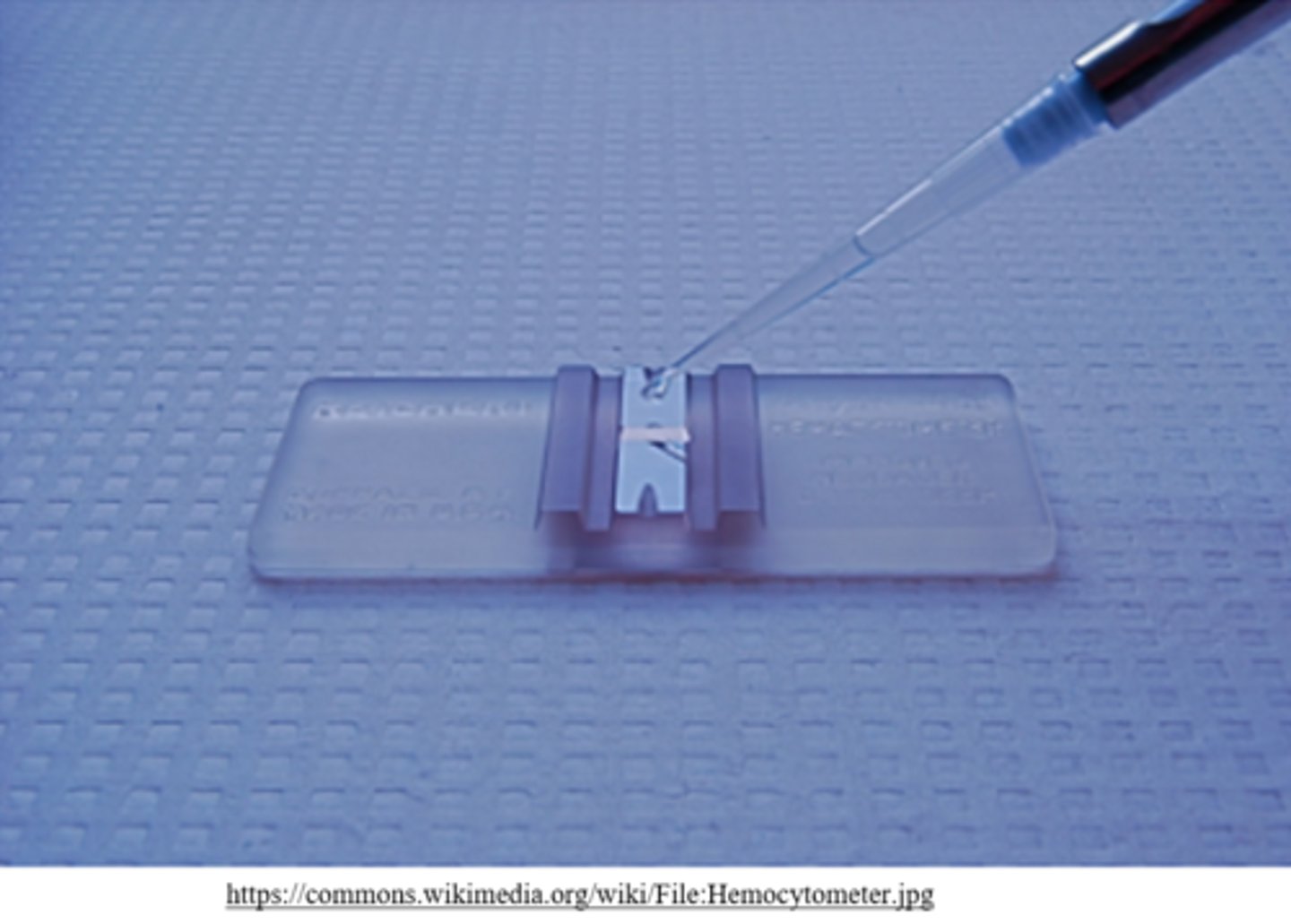
what are hemocytometers?
cell counting chambers
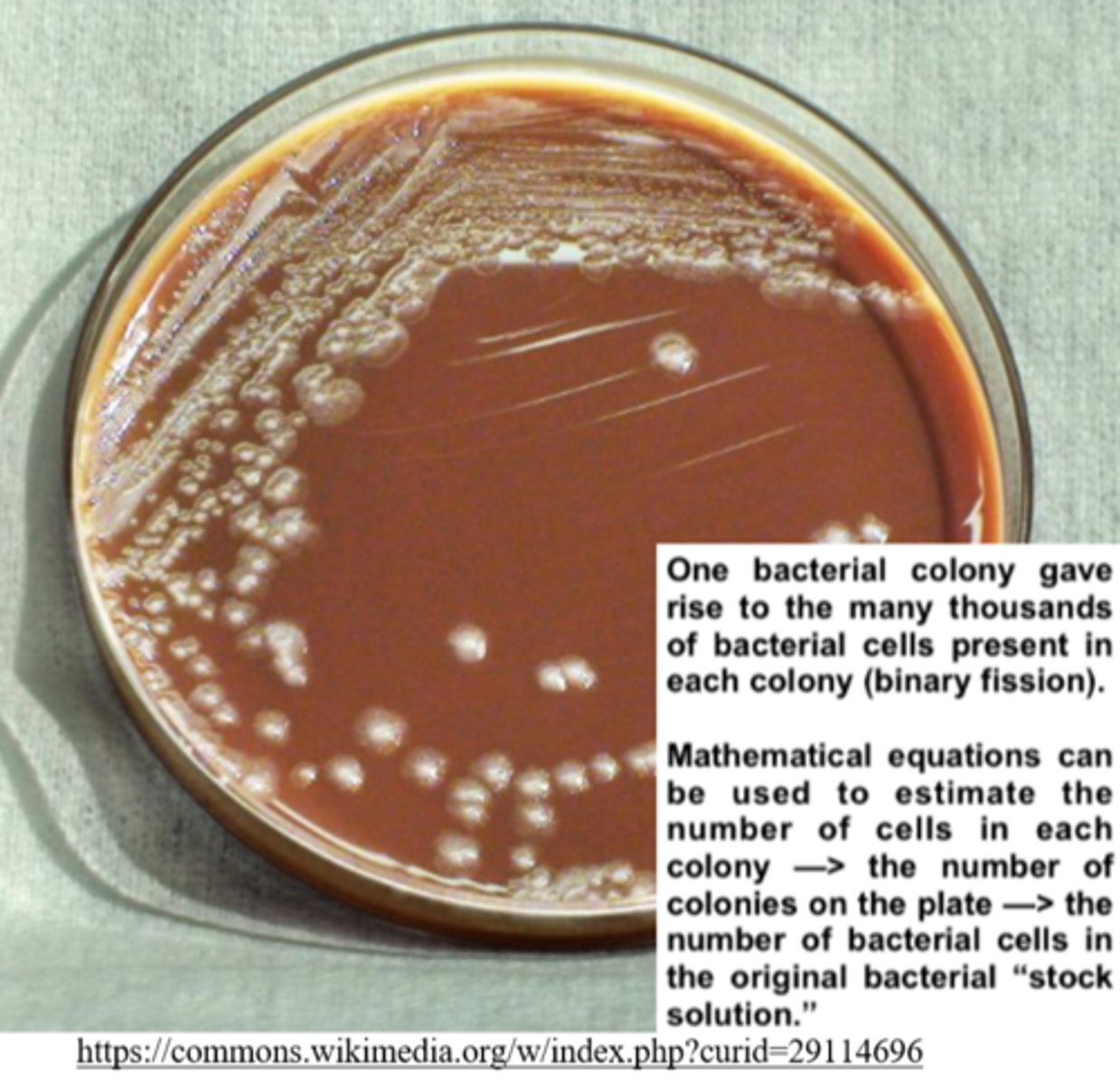
_____ are used to estimate the number of cells plated on a growth medium
colony forming units (CFUs)
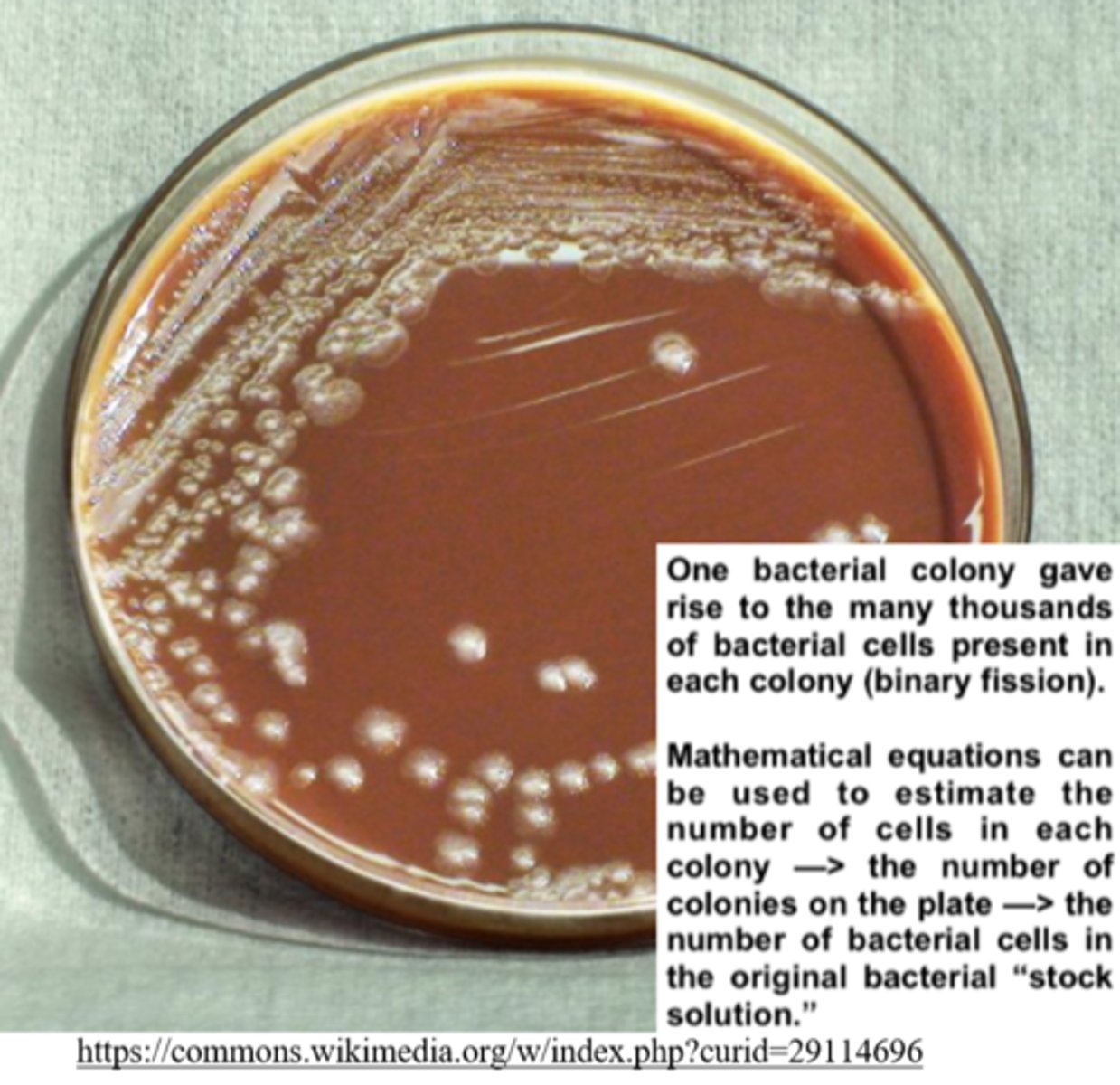
colony forming units (CFUs) are based on the assumption that each viable cell initially plated gave rise to a _____
colony
what are 2 methods for automated cell counting?
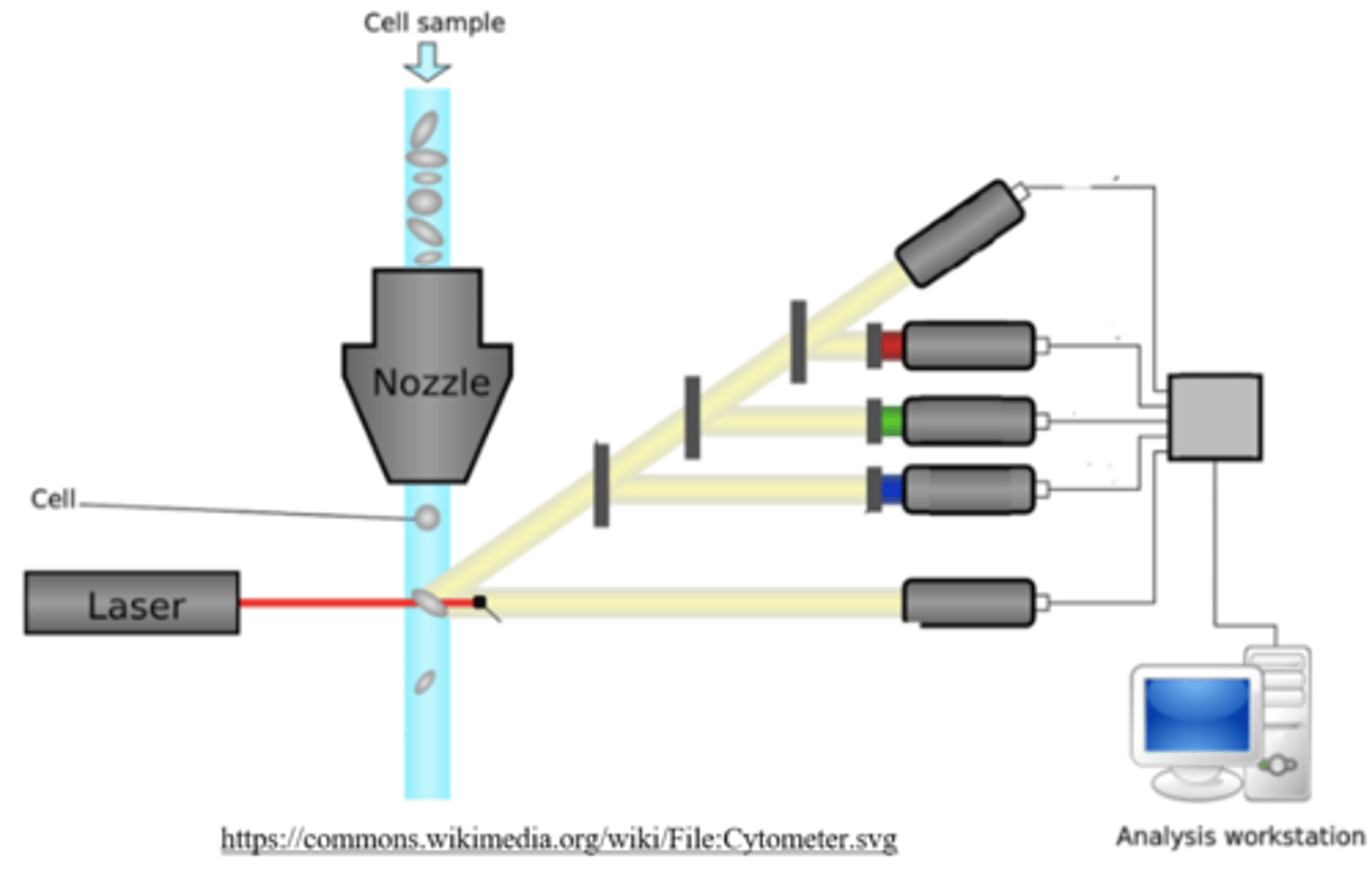
electrical resistance and flow cytometry
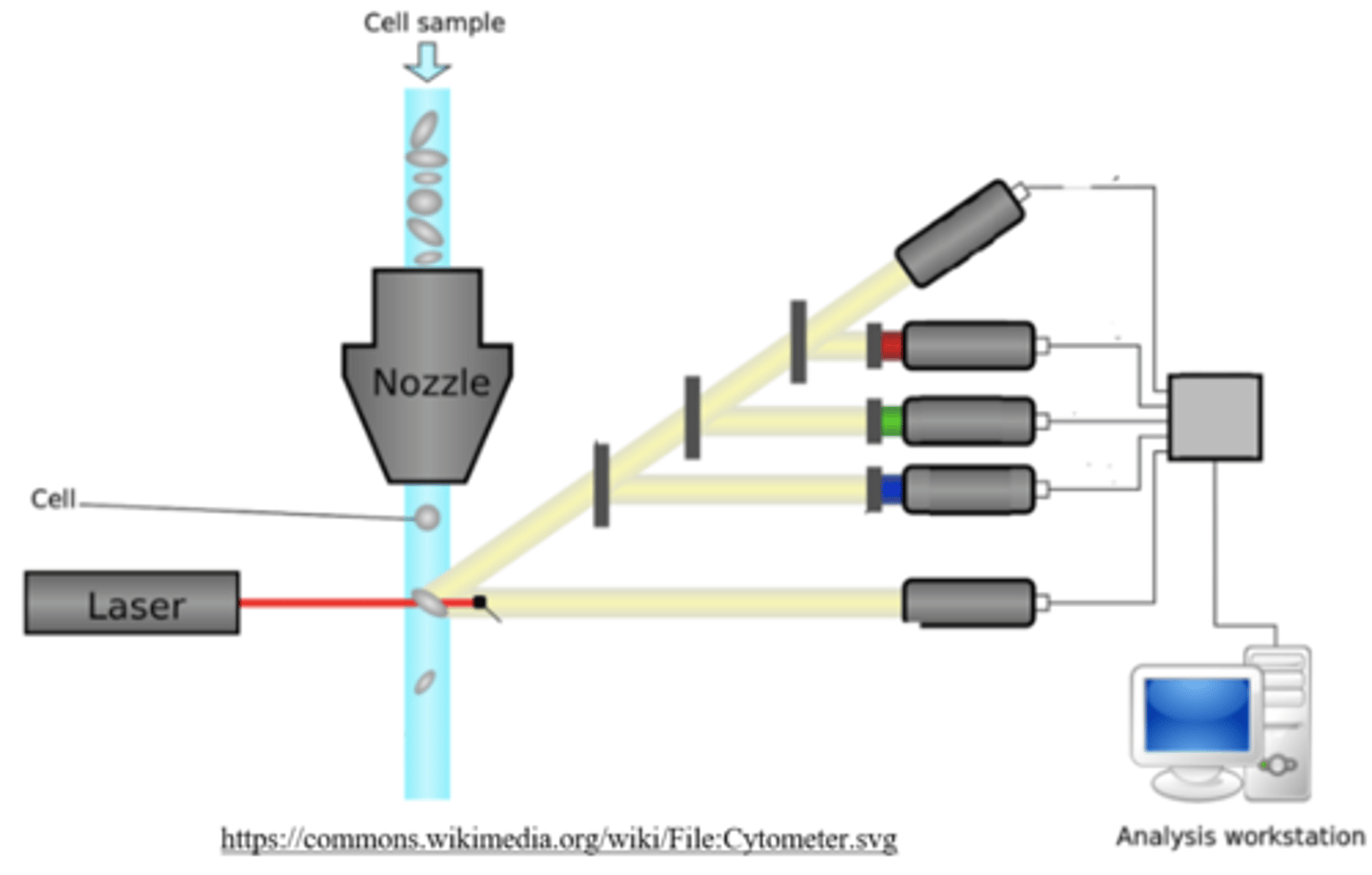
as cells show electrical resistance and impede conductance, the _____ in a solution can be estimated by observing the flow of electricity
number of cells
in _____, cells pass through a very narrow tube and can be counted via detection by a laser beam.
flow cytometry
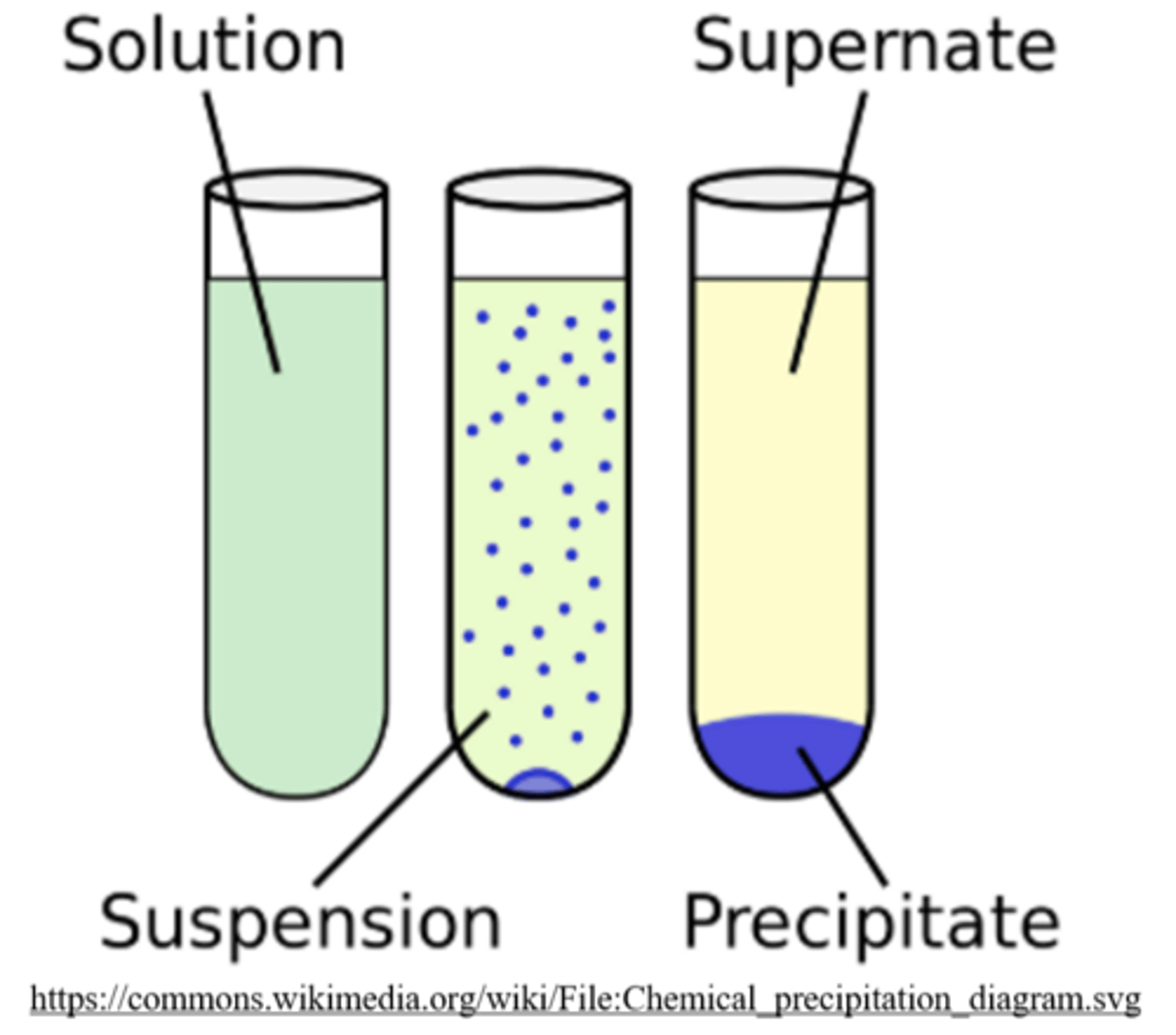
_____ is the process where cell contents are separated into their fractions (one part of a whole) by centrifugation
cell fractionation
a _____ is a laboratory apparatus that spins in a circular path at very high speeds.
centrifuge
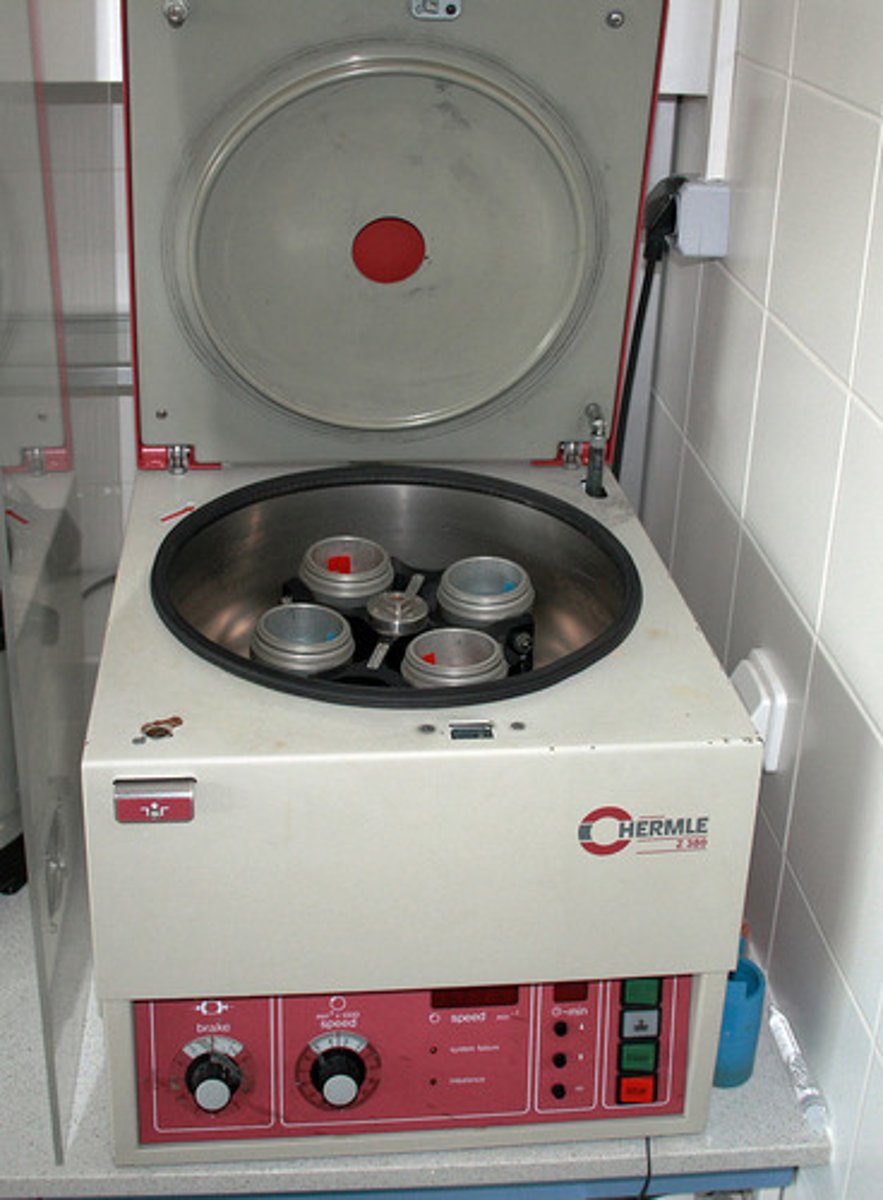

centrifugation separates cell components through _____
mass, density, and/or shape
in centrifugation, the densest and most compact particles will _____ to the bottom of the tube first, becoming pressed together as a _____ (precipitate)
sediment; pellet
(top liquid is the supernatant)
centrifugation can be used to separate _____ based on solubility
proteins
(insoluble proteins pellet out, while the soluble proteins remain in the supernatant)
in _____, cells are split open with a blender and the resulting homogenate is separated based on mass, density, and/or shape
differential centrifugation
(the homogenate is centrifuged/fractionated)
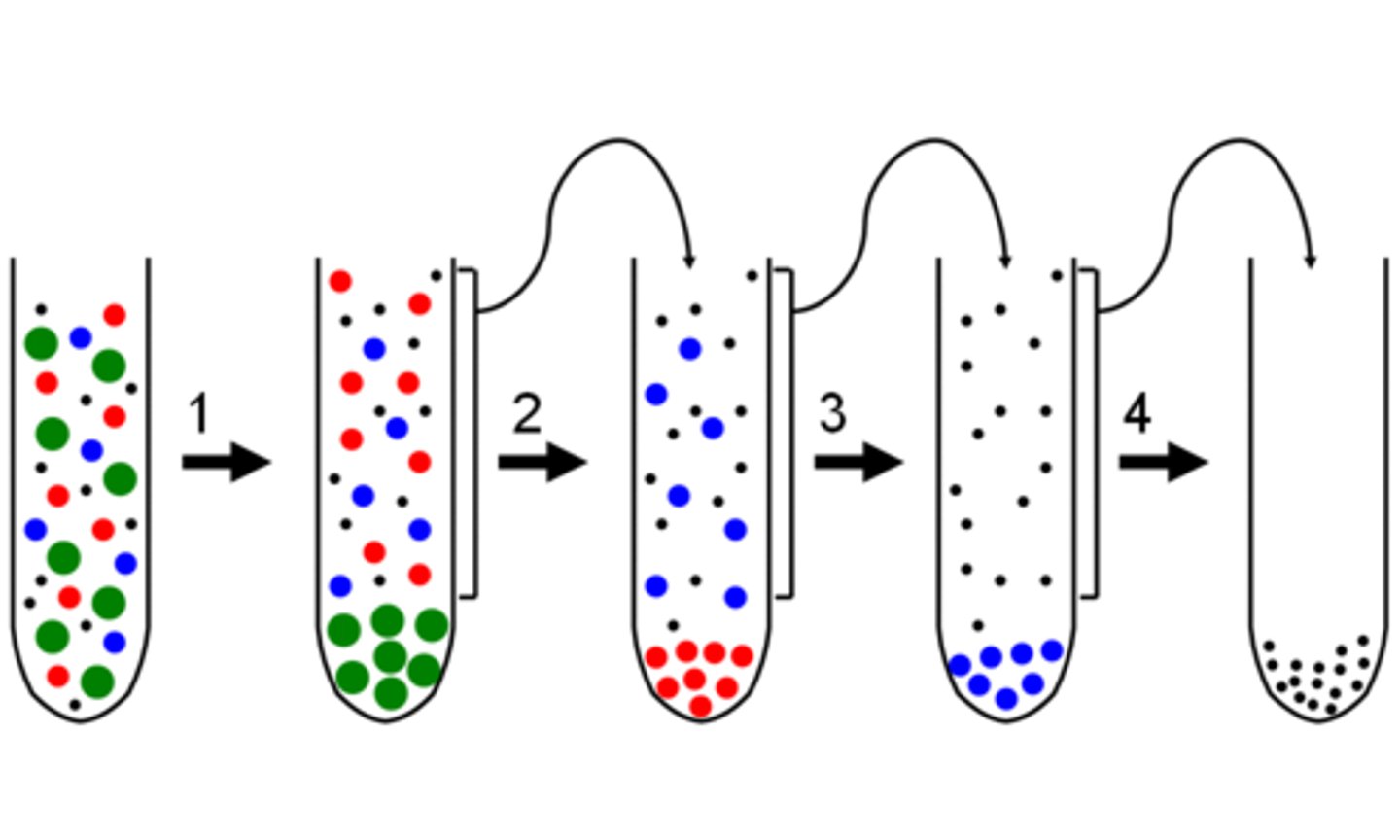
_____ centrifugation separates cell contents in just 1 spin step, creating multiple layers separated by density
density
e.g. blood centrifugation
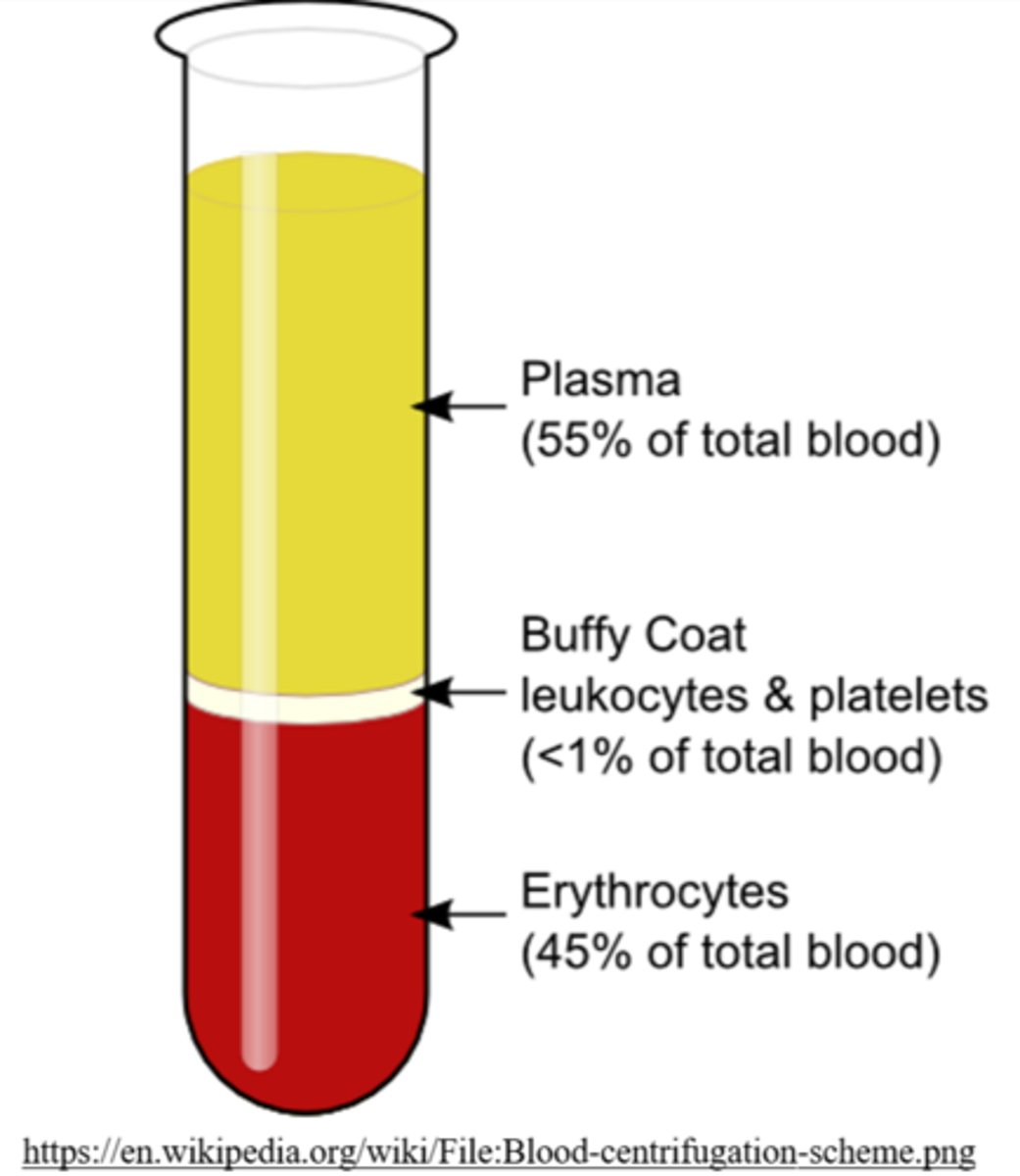
arrange the following organelles from most to least dense: endoplasmic reticulum (ER), ribosomes, mitochondria, nuclei, chloroplasts
nuclei > mitochondria/chloroplast > ER fragments >
ribosomes
_____ is the observation of chromosomes under a light microscope using staining
karyotyping
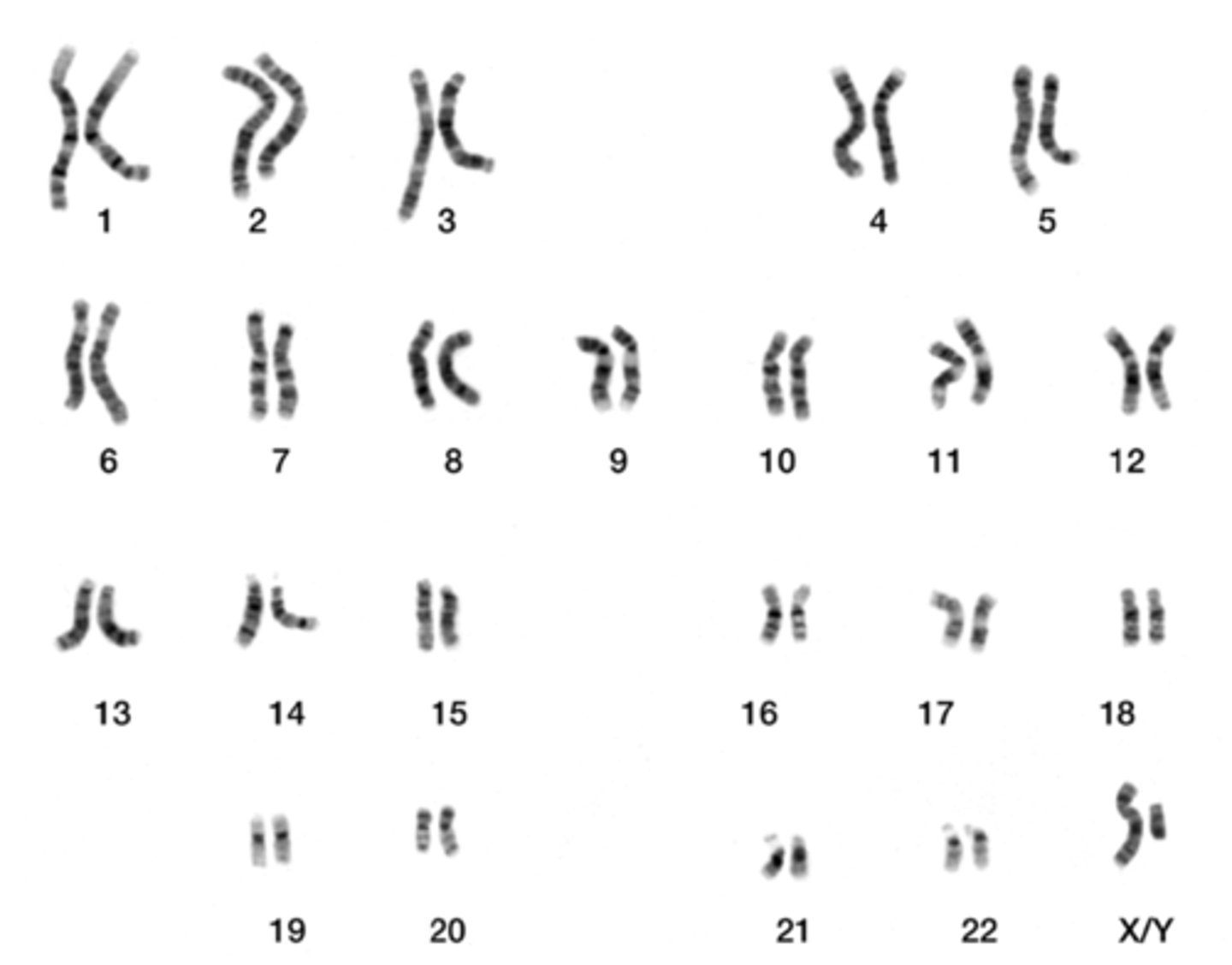
a karyotype shows both the _____ of chromosomes and their _____
number; physical appearance
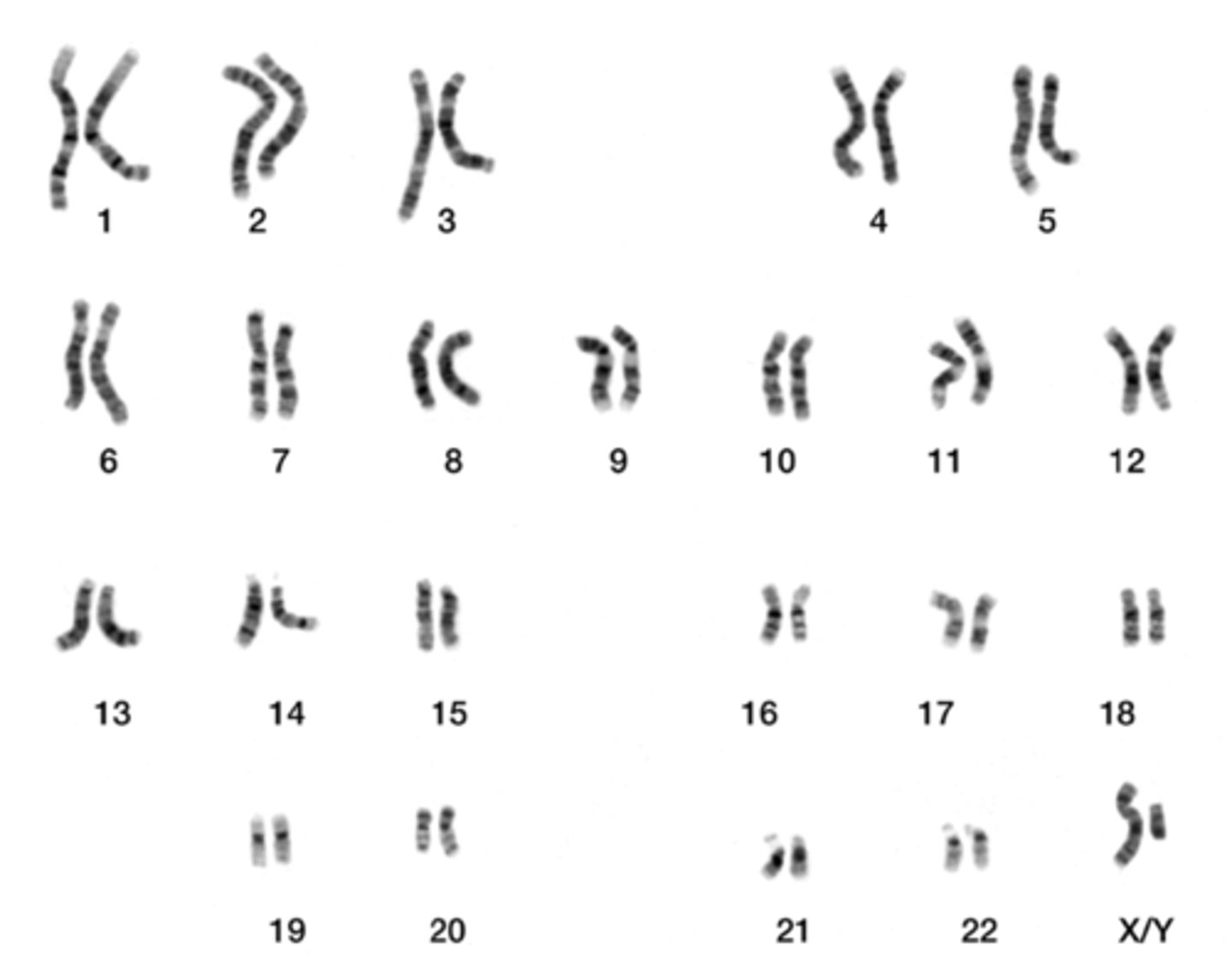
karyotyping is preformed during _____
metaphase
_____ is a condition that results in a third copy of chromosome 21, and _____ allows for substantiation of its diagnosis
Down syndrome (or trisomy 21); karyotyping
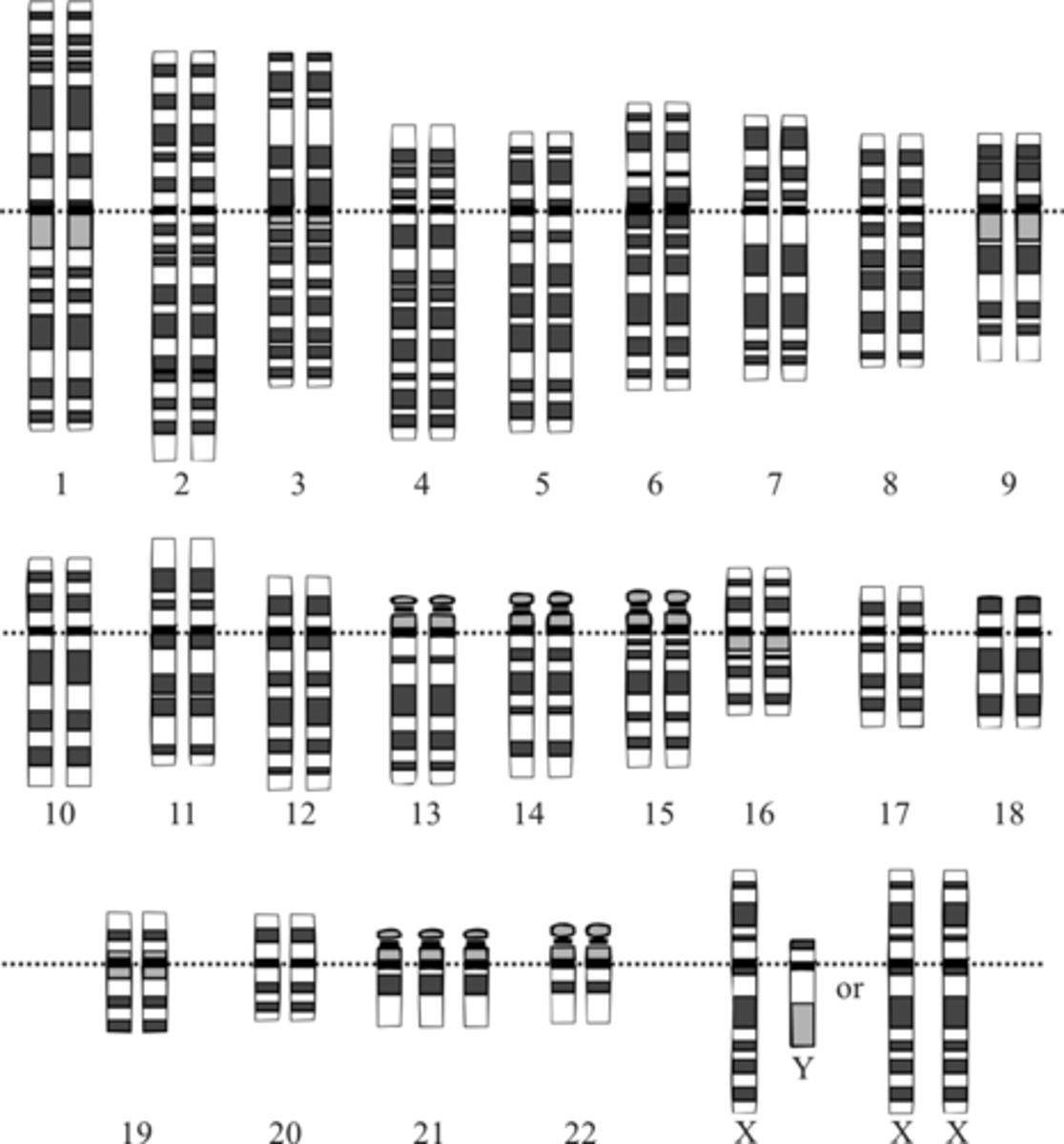
for the most part, the human genome is the same, with slight differences in the sequence every ~ 1000 nucleotides (called _____), which serve as markers for genes that cause disease
single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
what are the 2 most common methods for DNA sequencing?
dideoxy chain termination (Sanger sequencing) and next generation sequencing
_____ is an older and more established method of DNA sequencing, while _____ is used more often now because it is quicker and cheaper
dideoxy chain termination (Sanger sequencing); next generation sequencing
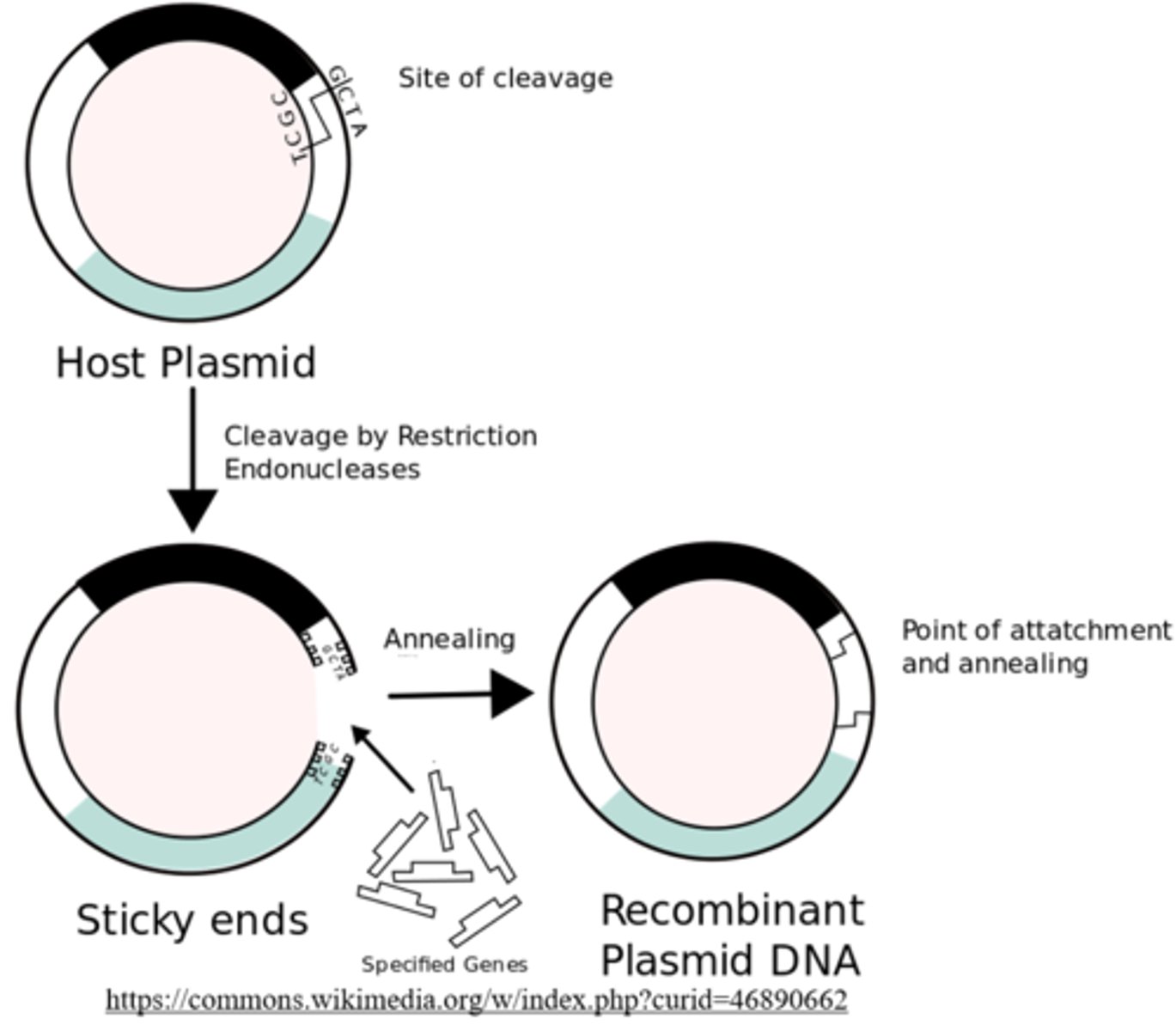
_____ is produced when DNA fragments from different sources are joined together
recombinant DNA
a _____ occurs when there is a block of nucleotides that are inverted mirrors of each other
palindromic sequence

the DNA fragments that get incorporated into recombinant DNA are produced by _____, which tend to cut DNA at palindromic sequences to produce _____ ends
restriction enzymes; sticky or blunt
sticky ends have _____, which makes it easy for complementary sticky ends to hybridize
unpaired nucleotides
(complimentary sticky ends are made by the same restriction enzyme)
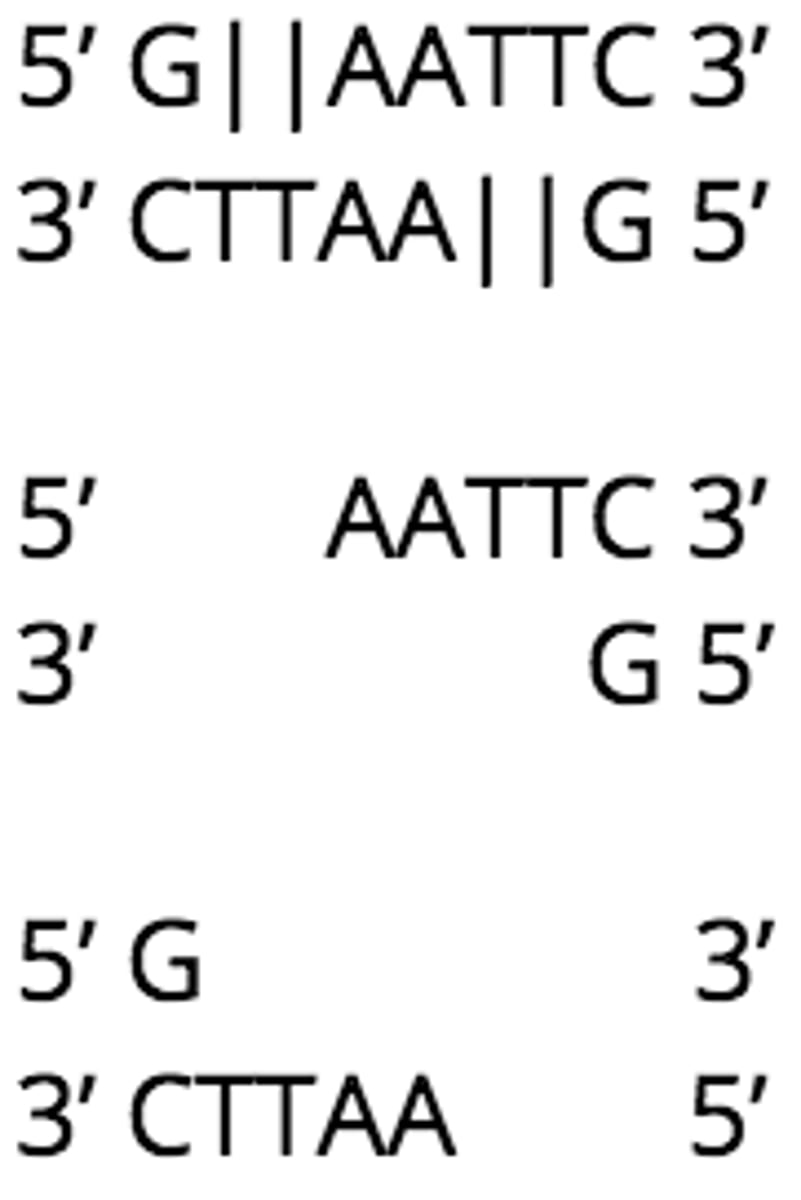
_____ are less common than sticky ends, and they do not have unpaired nucleotides
blunt ends
(blunt ends are harder to hybridize because of the paired nucleotides)

_____ are unique lengths of DNA that result from restriction enzymes, allowing for the comparison between individuals
restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)
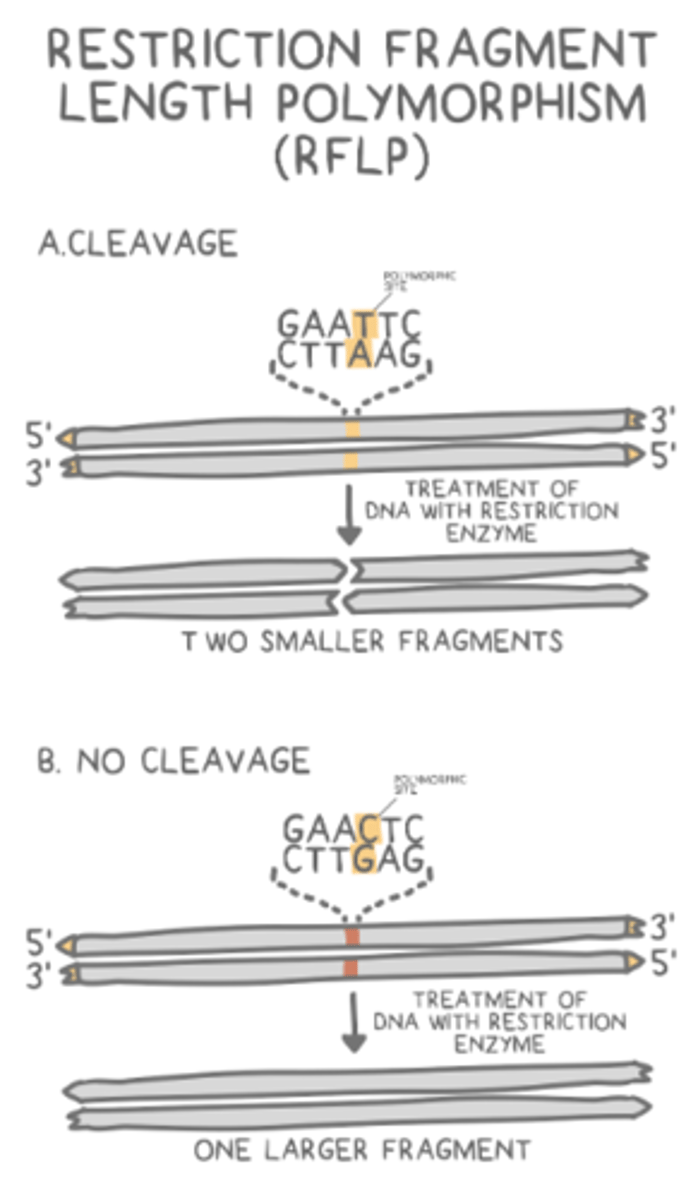
a _____ is a group of nucleotides that repeats multiple times in a stretch of DNA
short tandem repeats (STRs)
in which individuals are RFLPs and STRs not unique?
twins
RFLPs and STRs are used in _____, which is a technique that may be used in paternity and forensic cases
DNA fingerprinting
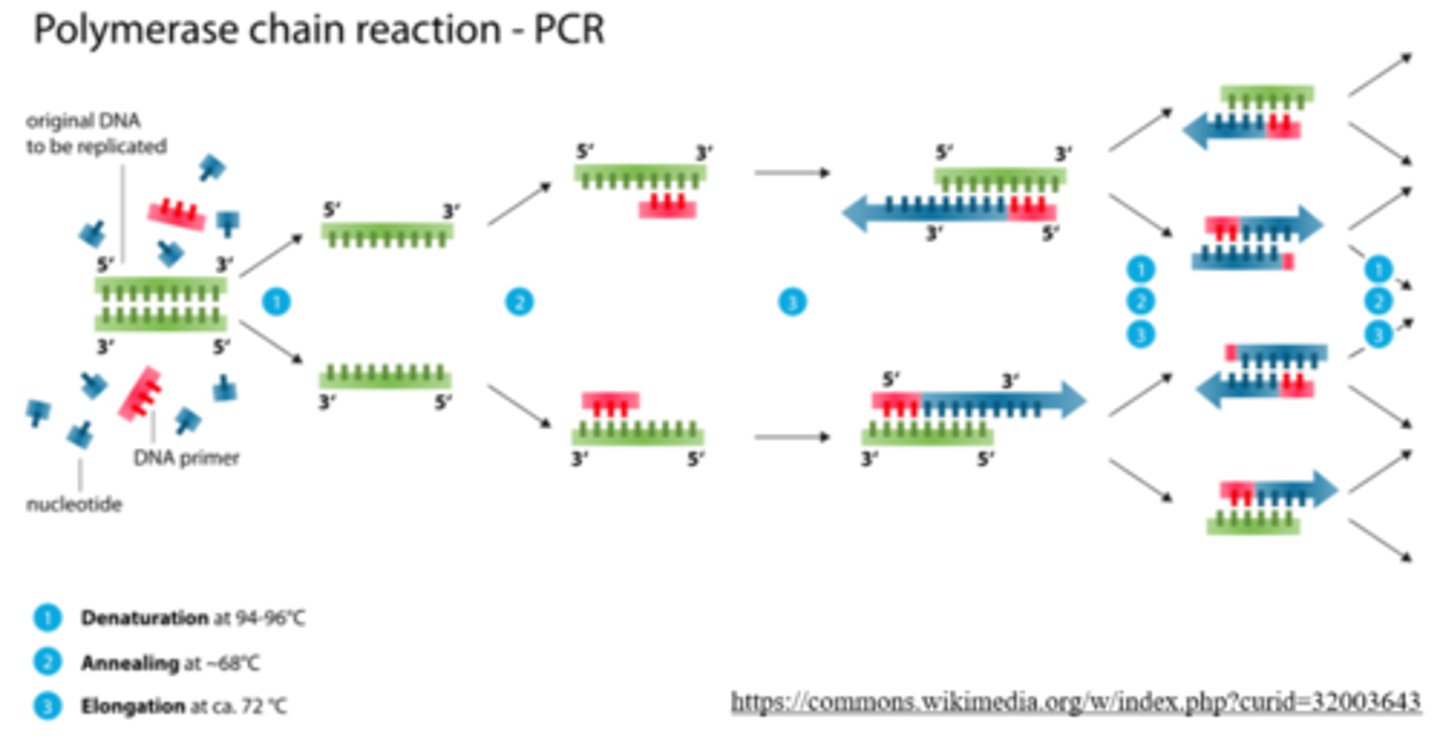
the _____ is an automated biotechnology process that can quickly create millions of
copies of DNA, and it requires no cells
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
PCR can be carried out in a single container - list the components that container needs to contain in order for PCR to take place:
DNA to be cloned; nucleotides; DNA primers; heat-resistant DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase)
what are the 3 cyclical steps of PCR?
denaturation; primer annealing; elongation
bacterial cloning is an important technique to produce medicines because _____ are cloned in _____
eukaryotic gene products; prokaryotic cells
(note that the insulin gene is obtained as cDNA from processed human mRNA)
_____ corresponds to a eukaryotic gene with all introns removed (used in microarrays and bacterial cloning)
processed mRNA
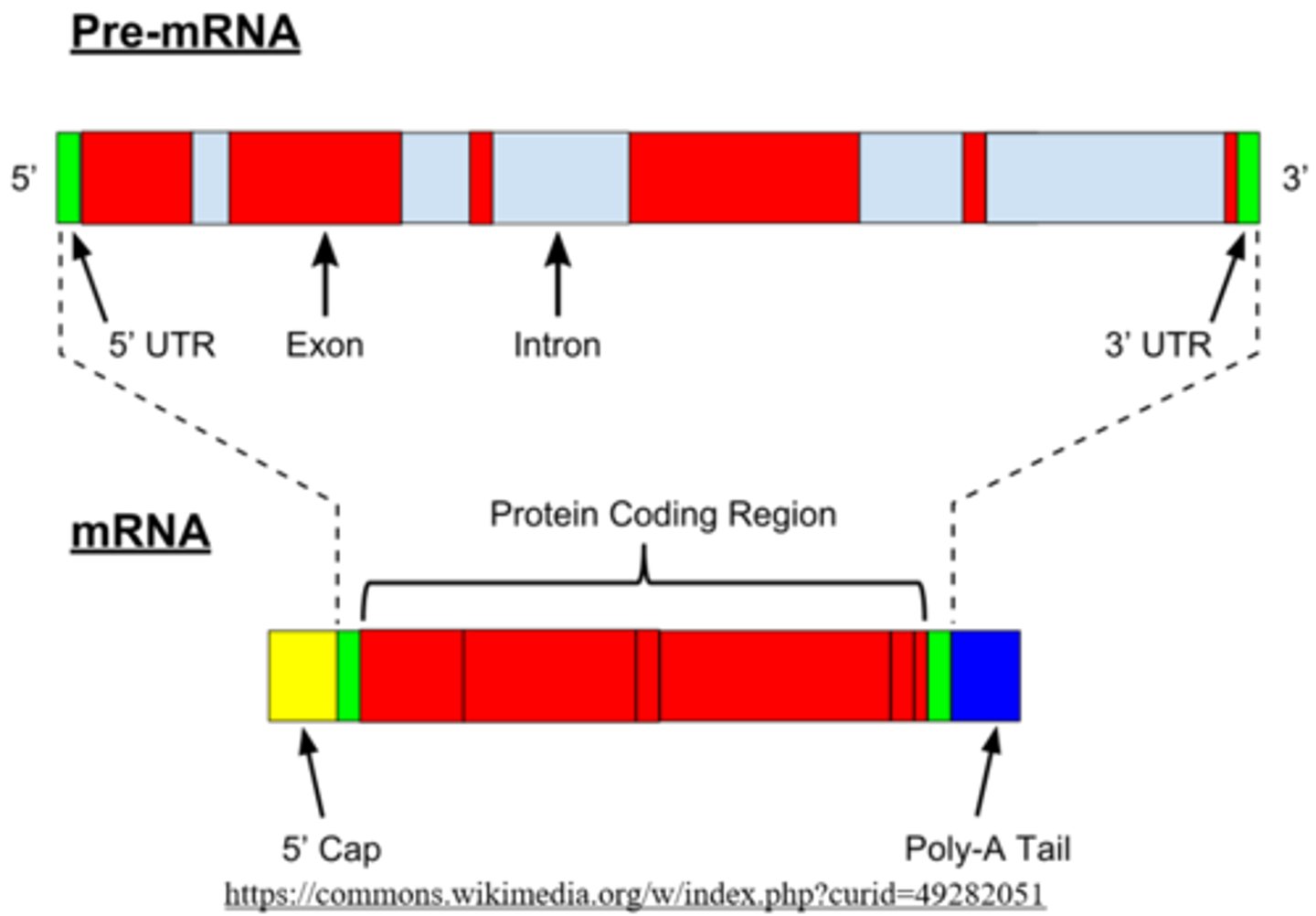
_____ is DNA made from RNA, and it is used in microarrays and bacterial cloning
complementary DNA (cDNA)
_____ produces complementary DNA (cDNA) from mRNA, and it is relied upon for microarrays and bacterial cloning
reverse transcriptase
_____ catalyzes phosphodiester bonds between the ends of DNA restriction fragments (used heavily in genomic libraries and bacterial cloning)
DNA ligase
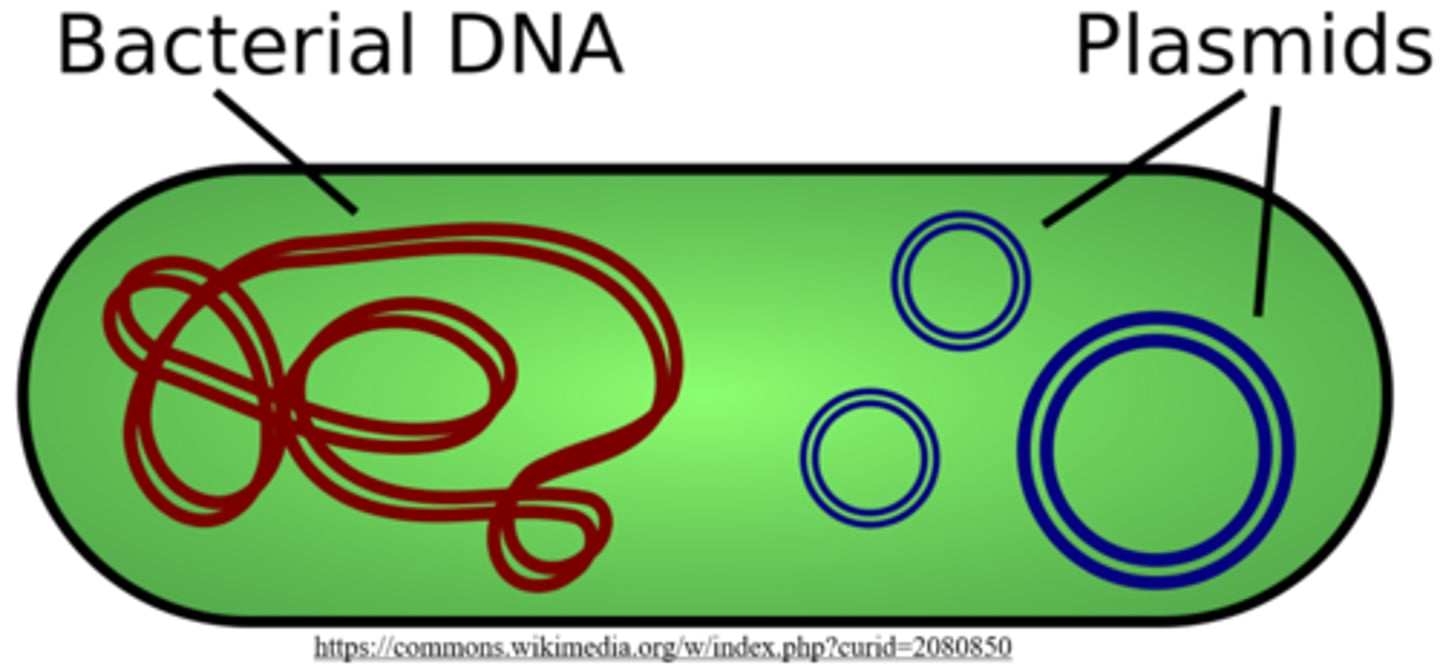
_____ are circular pieces of extrachromosomal DNA in bacteria (used in bacterial cloning and genomic libraries)
plasmids
a _____ is a piece of DNA (such as a plasmid) that can be taken up by competent cells
vector
(used heavily in genomic libraries and bacterial cloning)
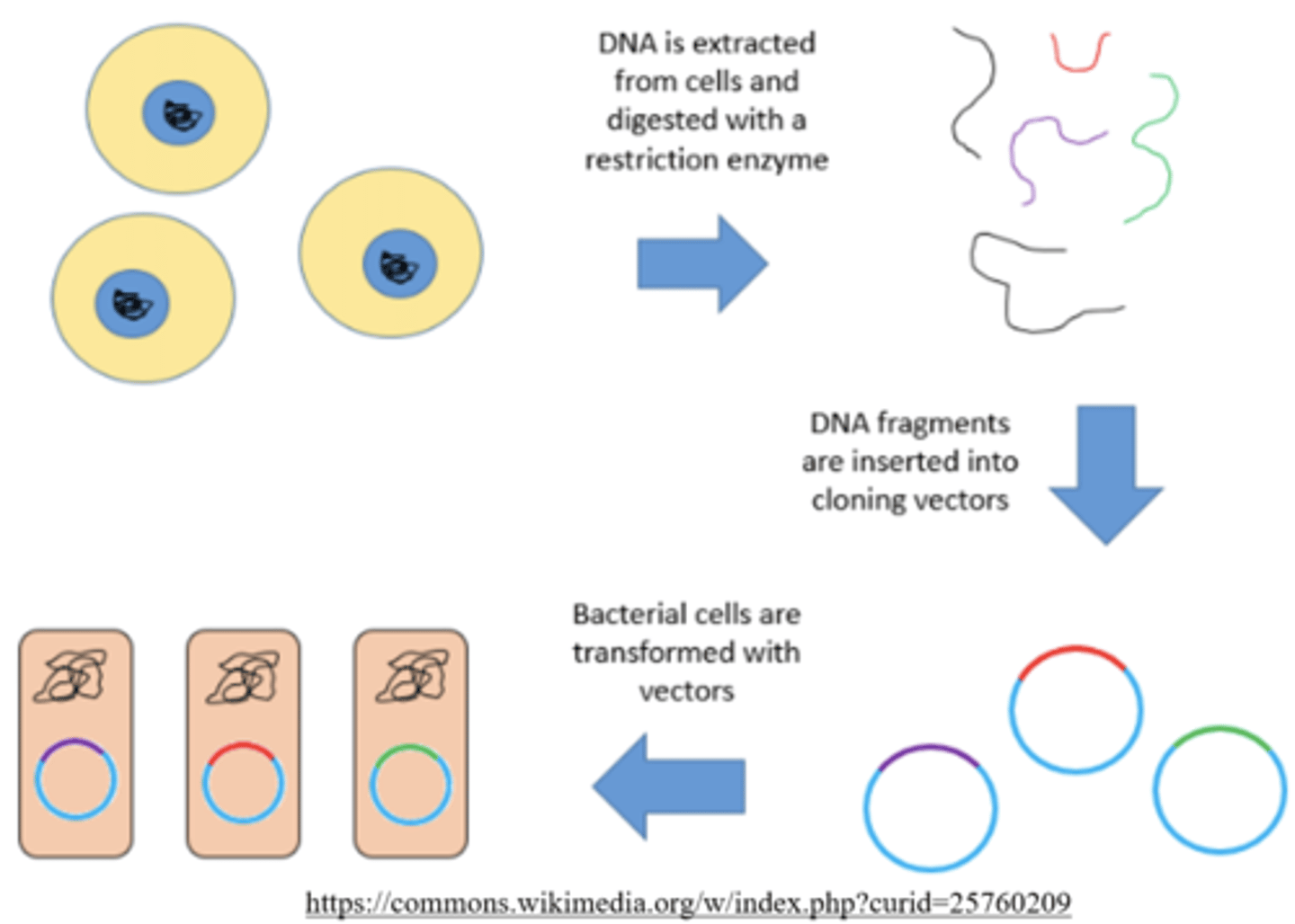
_____ is a process that occurs when a cell's genome is changed by the addition of DNA that was once floating freely in the environment
transformation
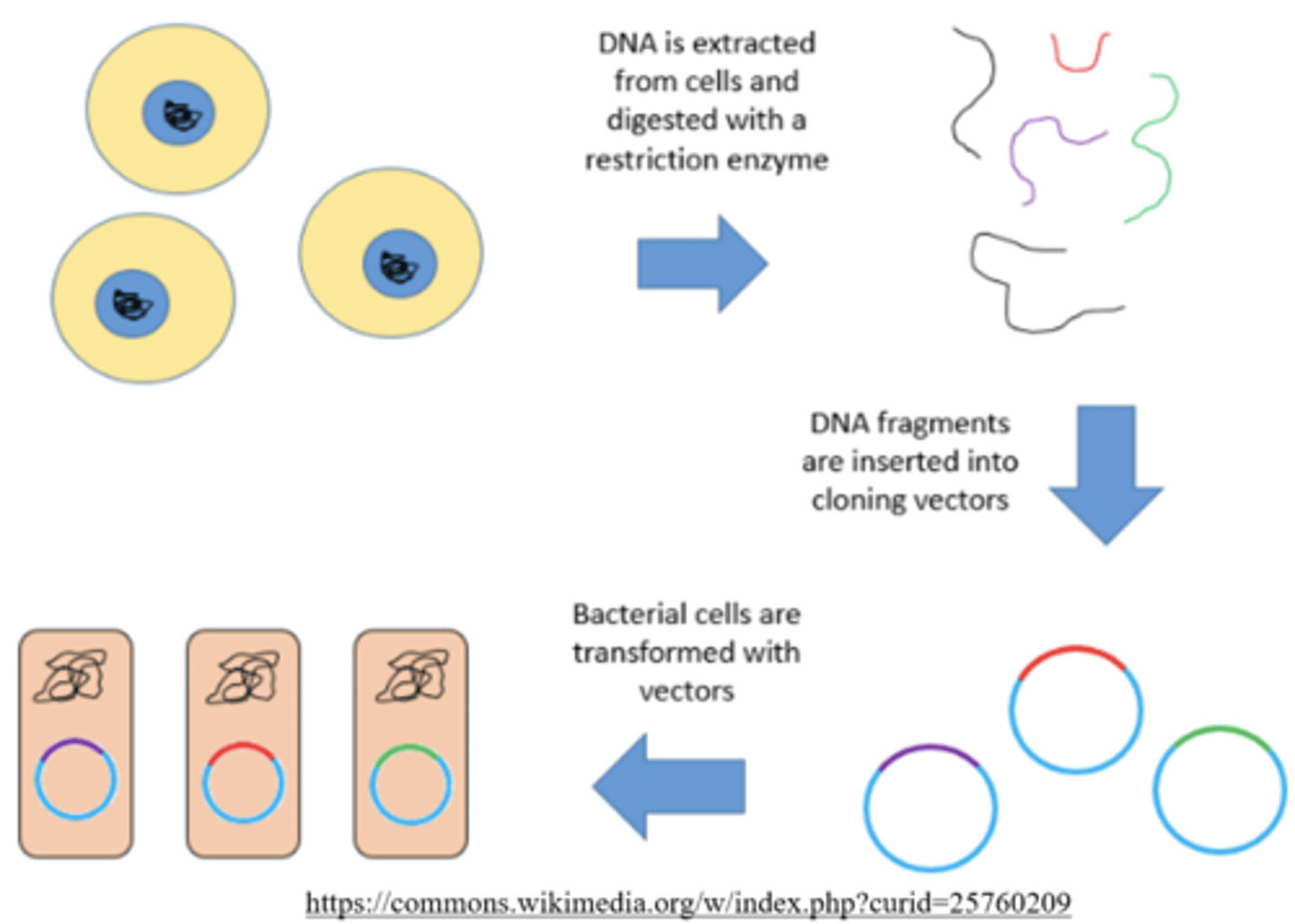
competent bacterial cells can undergo _____, and they can be made competent through _____
transformation; electroporation
_____ is a process where electricity is applied to cells, creating temporary holes in the plasma membrane
electroporation
what are 2 key methods for selecting bacterial cells that have undergone transformation in bacterial cloning?
antibiotic resistance and color change
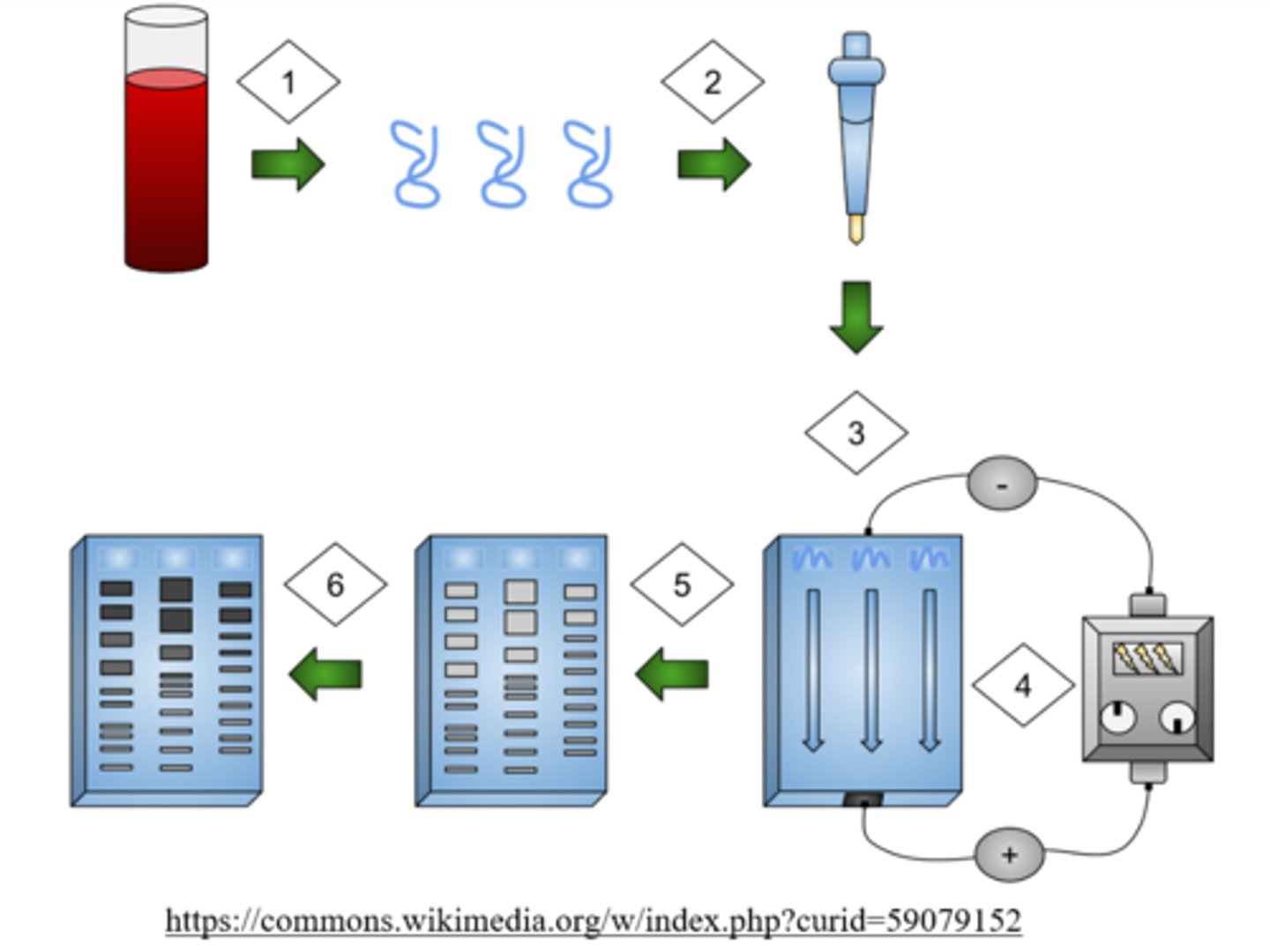
gel electrophoresis separates macromolecular fragments on their _____ and _____
charge; size
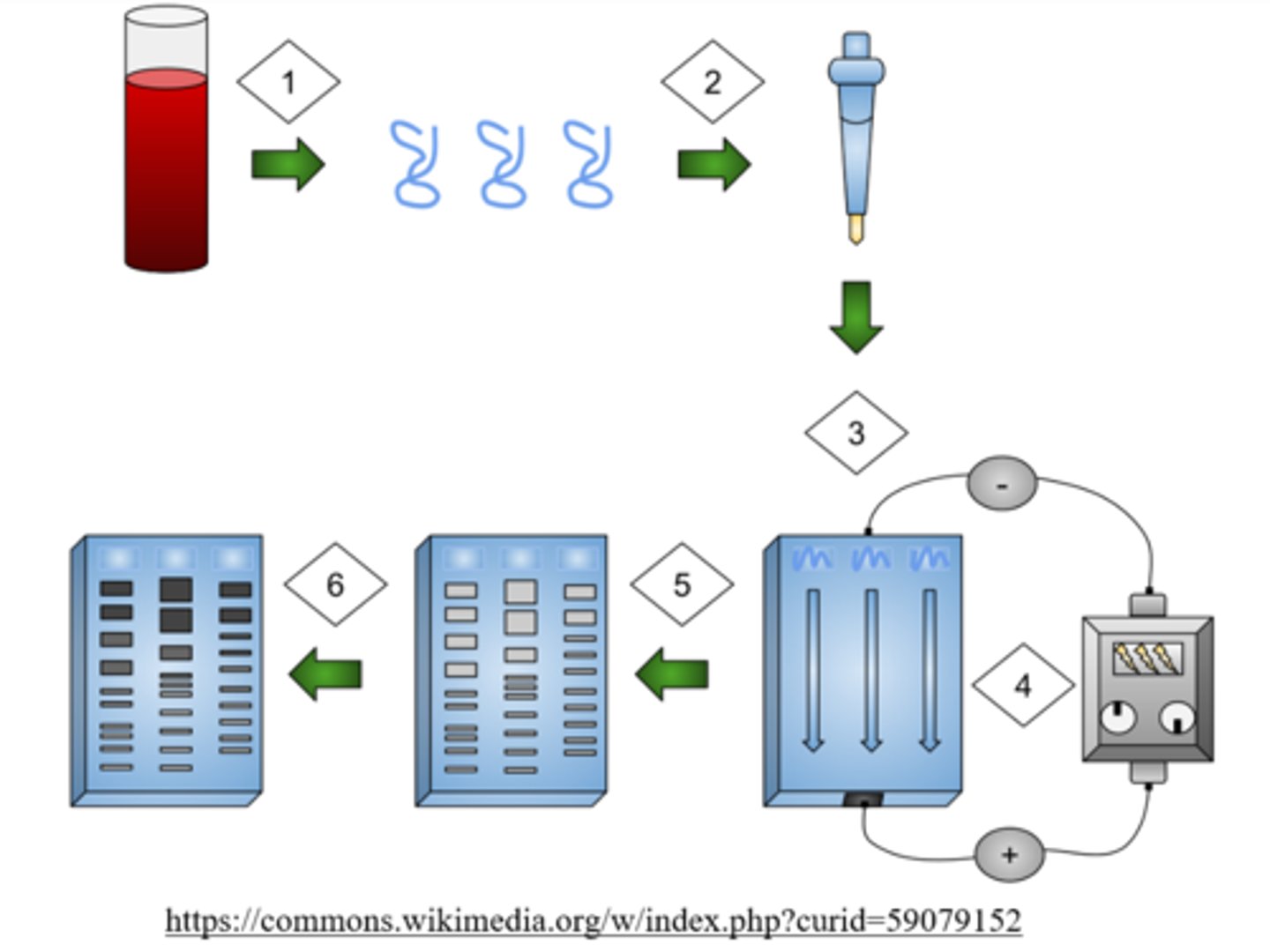
gel electrophoresis has a _____ (positive/negative) _____ (anode/cathode) at the top and a _____ (positive/negative) _____ (anode/cathode) at the bottom
negative cathode at the top; positive anode at the bottom
in gel electrophoresis, the _____ (smallest/largest) fragments travel the furthest
smallest
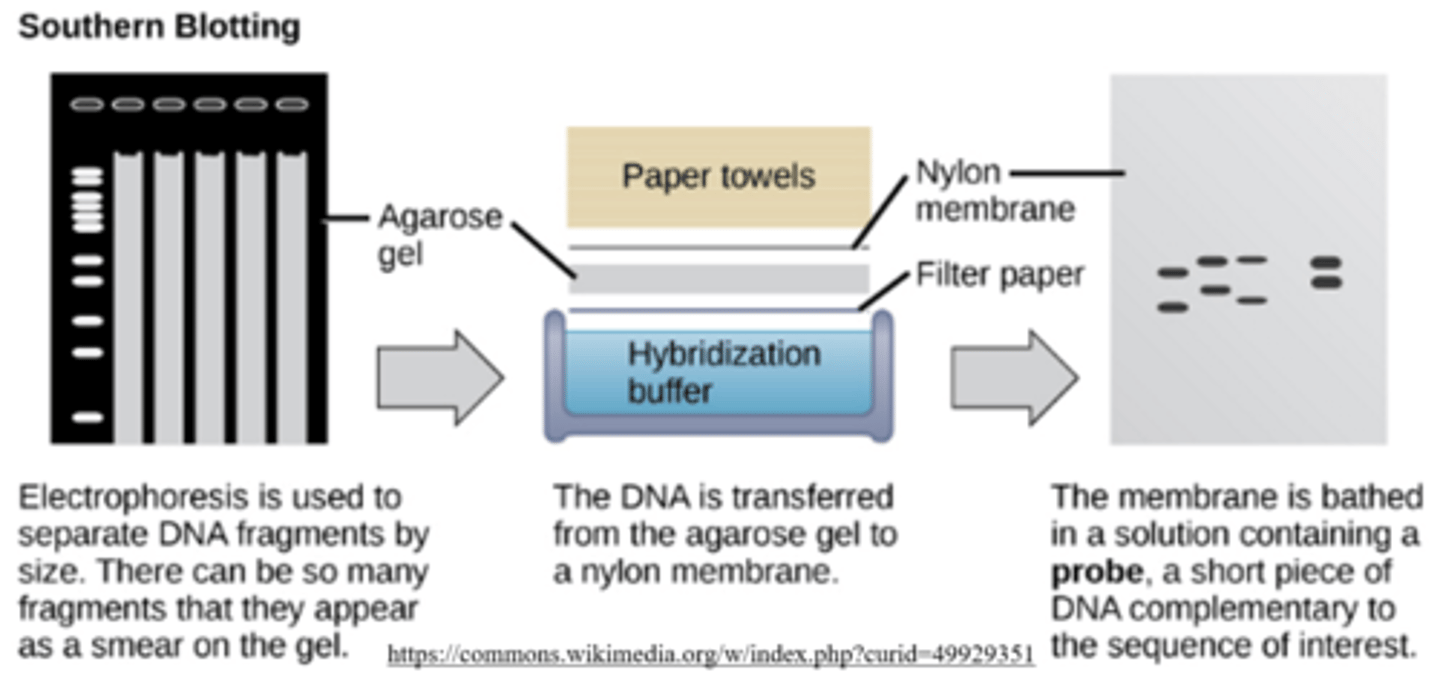
a _____ is a fluorescent or radioactively labeled tool that allows scientists to identify a specific sequence within a large sample
probe
_____ is an electrophoresis technique for separating DNA fragments, and it uses _____ probes
southern blotting; DNA
_____ is an electrophoresis technique for separating RNA fragments, and it uses _____ probes
northern blotting; RNA
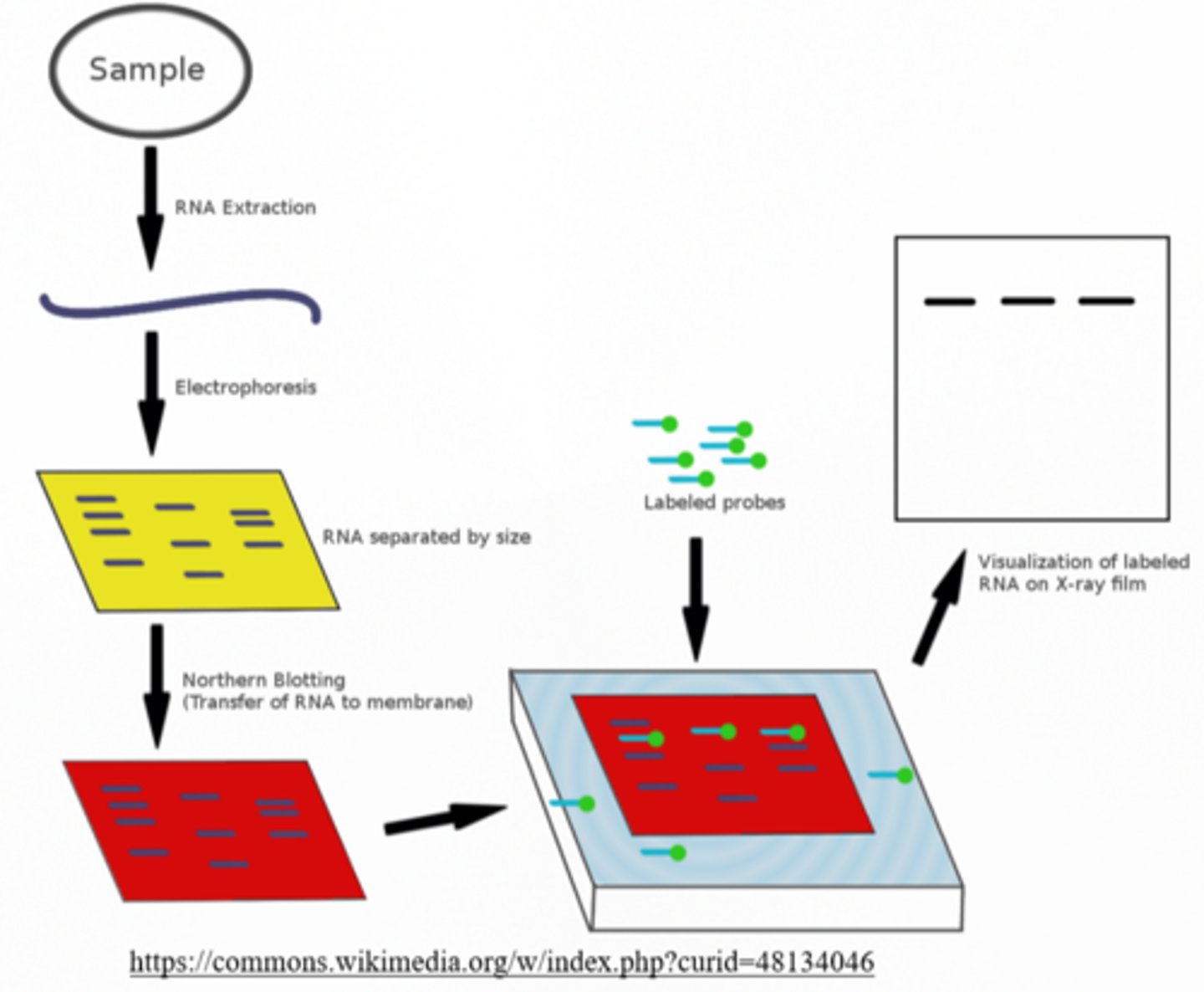
_____ is an electrophoresis technique for separating proteins, and it uses _____ as the probes
western blotting; primary and secondary antibodies
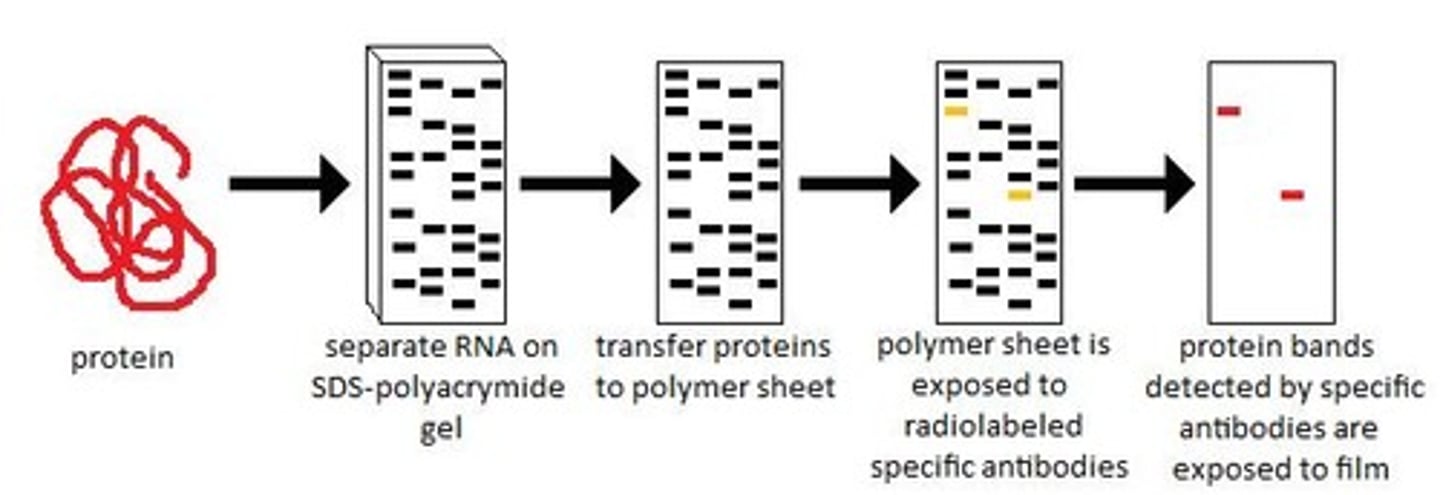
southern and northern blotting tend to use _____ gel, whereas western blotting tends to use _____
agarose; SDS-PAGE
_____ is a technology to determine if a specific antigen exists in a person, aiding in the diagnoses/exposure to certain diseases
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA is based on the idea that a person will have _____ for a given disease's _____ if they have the disease, or have been exposed to it
antibodies; antigens
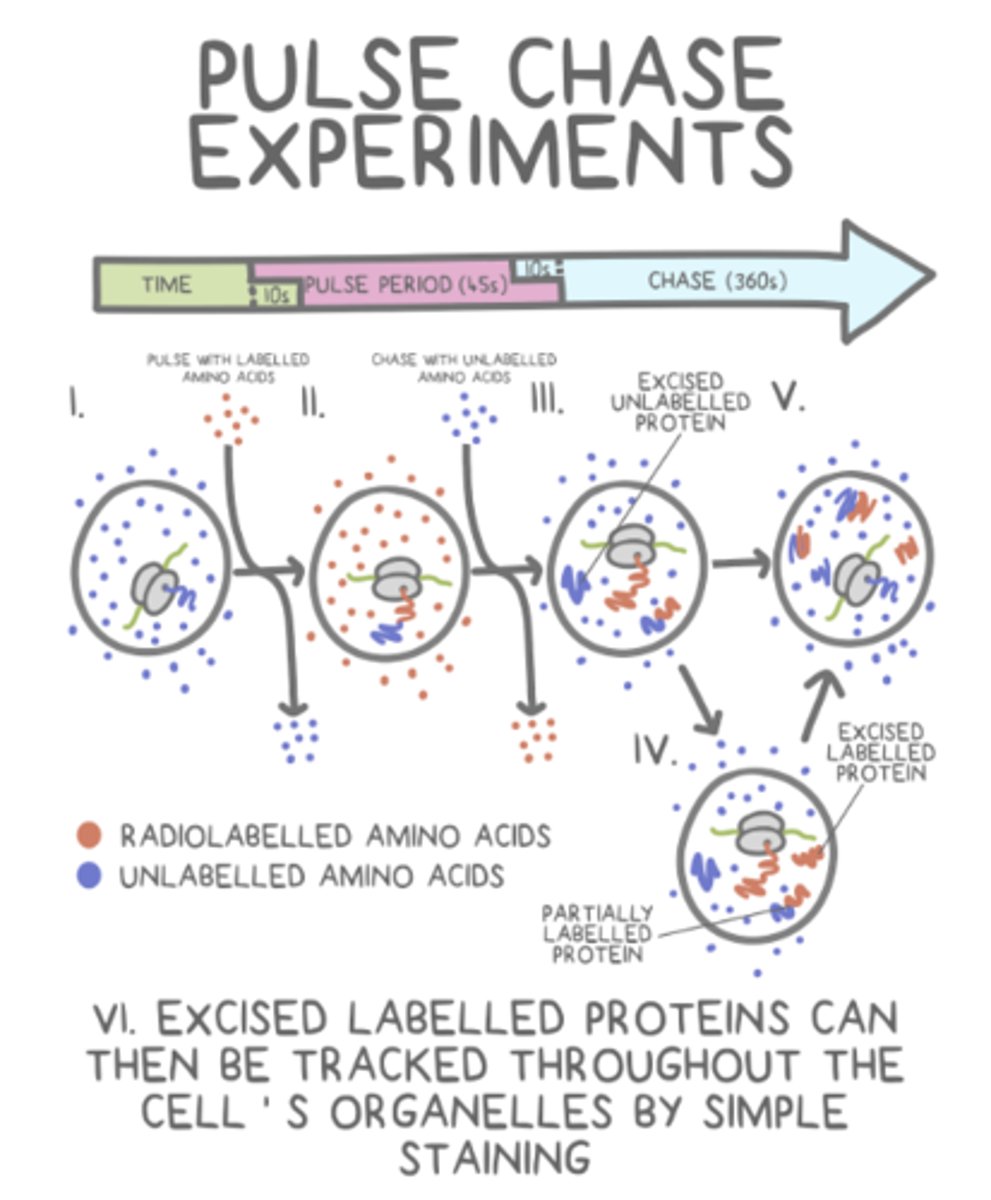
_____ experiments allow for the visualization/tracking of molecules of interest throughout a cell
pulse chase