Dynamic Planet Freshwater - Science Olympiad 2021-2022
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
1
New cards
fresh water
water that contains very low amounts of salts, such as rivers and lakes

2
New cards
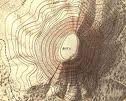
topographic maps
show elevation of land with shape and spacing of contour lines; closer lines mean steeper slopes; flat places have widely spaced lines; series of increasingly smaller closed loops indicates hill or mountain
3
New cards
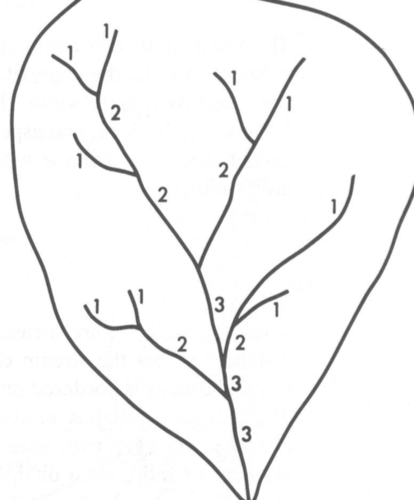
stream order
a measure of the relative size of streams
4
New cards
drainage patterns
The pattern a drainage network takes when viewed from the air.

5
New cards
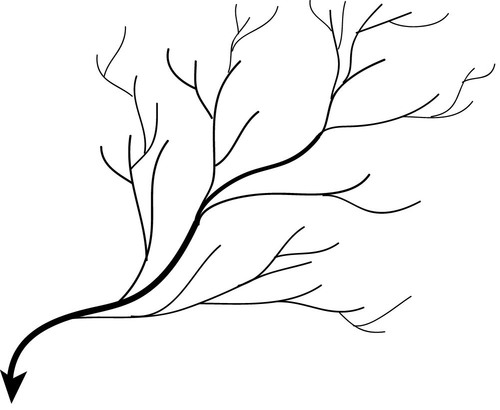
dendritic drainage pattern
a stream system that resembles the pattern of a branching tree
6
New cards
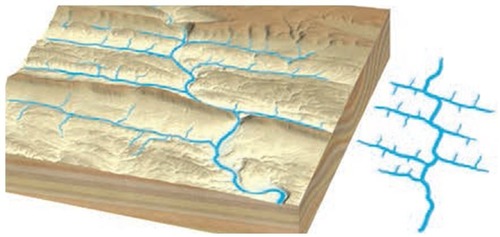
trellis drainage pattern
a pattern in which the tributaries join the main stream at right angles
7
New cards
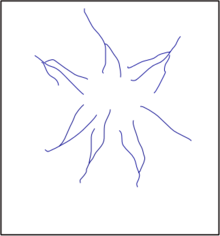
radial drainage pattern
develops where streams flow away from a common high point on cone- or dome-shaped geologic structures, such as volcanoes (opposite is centripetal).
8
New cards
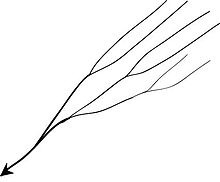
parallel drainage pattern
direction of water flow is where two rivers come together
9
New cards
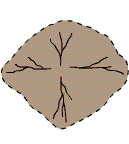
centripetal drainage pattern
A basin structure in which the streams converge toward the center.
10
New cards
Deranged drainage pattern
no clear pattern, areas covered by continental galcial ice sheet
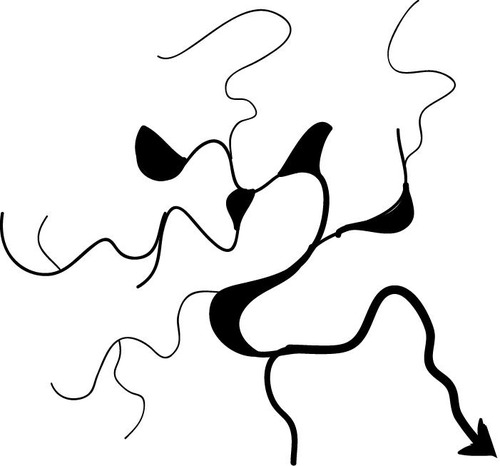

11
New cards
angular drainage pattern
A drainage pattern in which streams follow a roughly circular or concentric path along a belt of weak rock, resembling in plan a ringlike pattern.

12
New cards
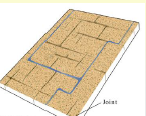
rectangular drainage patterns
Some rocks are fractured in a rectangular fashion and streams develop on the fractures. The drainage pattern developed in this case is called _______ drainage.
13
New cards
tributaries
smaller streams and rivers that flow into a main river

14
New cards
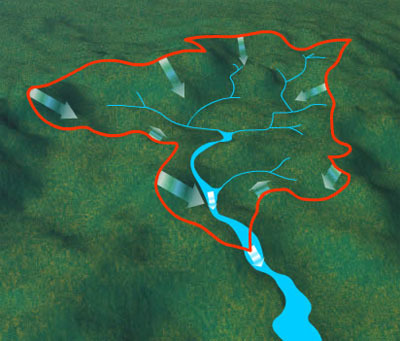
watersheds
river basins drained by a river and flowing into the same large body of water
15
New cards
river channels
a type of landform consisting of the outline of a path of relatively shallow and narrow body of fluid

16
New cards
river mouth
the point where a river enters a lake or sea

17
New cards
river head
a stream's point of origin

18
New cards
bedrock channels
channels in which the streams are actively cutting into solid rock

19
New cards
alluvial channels
a river flows down a steep slope into a flat valley

20
New cards
braided channels
a stream consisting of numerous intertwining channels

21
New cards
meandering stream
A river or small stream that curves back and forth across its valley

22
New cards
straight channels
Rare; short; deepest part typically wanders back and forth

23
New cards
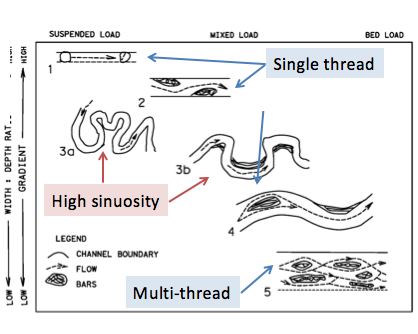
channel sinuosity
is the ratio between the length of the channel and the straight-line path length along the valley floor.
24
New cards
weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.

25
New cards
erosion
the process of eroding or being eroded by wind, water, or other natural agents.

26
New cards
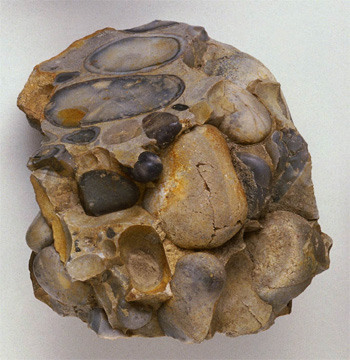
clastic sediments
physically deposited particles derived from weathered rocks
27
New cards
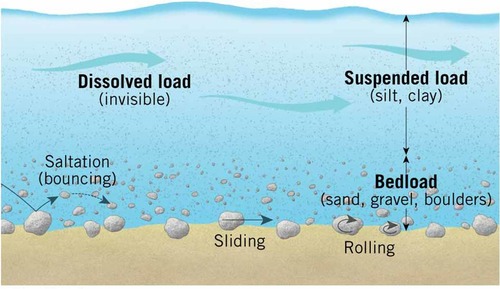
sediment transportation
streams move sediments acquired from mass wasting, overland flow, and groundwater
28
New cards
dissolved load
The load contains dissolved materials such as sodium and calcium.

29
New cards
suspended load
the fine sediment carried within the body of flowing water

30
New cards
bedload
the sediment carried along the bed (bottom) of the river

31
New cards
river capacity
total amount of sediments a river is capable of transporting

32
New cards
river competence
maximum particle size that a river is capable of transporting at a given point
33
New cards
deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.

34
New cards
alluvium
the sorted material deposited by a stream

35
New cards
Aeolian landforms
Are formed by the chemical and mechanical action of the wind

36
New cards
Dust storms
strong winds that pick up large quantities of dust
37
New cards
fluvial deposits
sediment deposited in a stream channel, along a stream bank, or on a floodplain
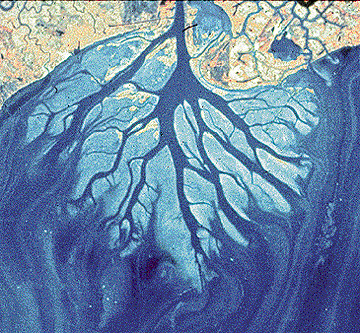
38
New cards
Fluvial landforms
landforms shaped by running water

39
New cards
River valley
areas of land that have been eroded by water and are always U or V shaped

40
New cards
Stream flow
water flow in streams.

41
New cards
Stream gaging
measure the stream channel shape, monitor the velocity and the water level
42
New cards
Ground water
underground water that is held in the soil and in previous rocks

43
New cards
zone of aeration
upper soil layers that hold both air and water
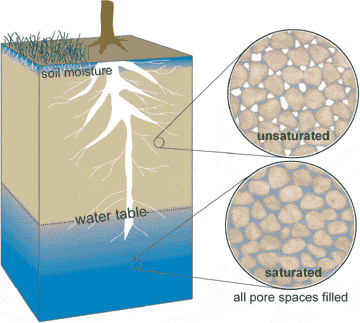
44
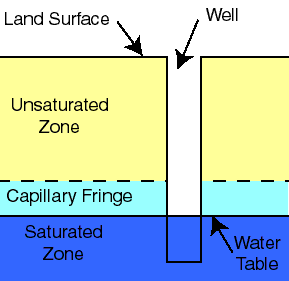
New cards
zone of saturation (phreatic zone)
zone where all open spaces in sediment and rock are completely filled with water
45
New cards
water table
the top of the saturated zone and is completely filled with water
46
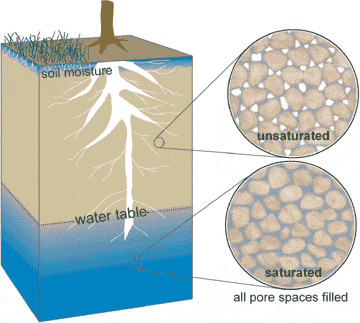
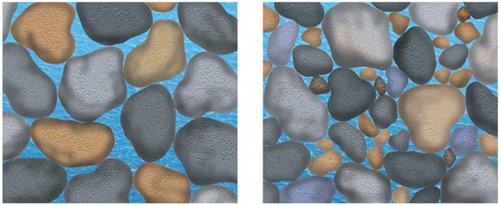
New cards
porosity
the volume of open spaces in rock or soil
47
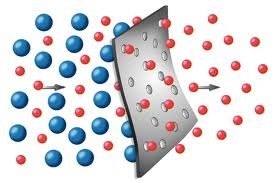
New cards
Permeability
Ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it
48
New cards
aquifers
An underground water reservoir.
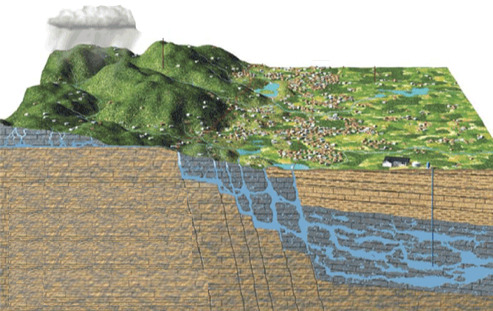
49
New cards
karst features
caves, speleothems (stalactites and stalagmites), sinkholes, springs

50
New cards
caverns
a naturally formed underground chamber or series of chambers most commonly produced by solution activity in limestone

51
New cards
sinkholes
a large surface crater caused by the collapse of an underground channel or cavern; often triggered by groundwater withdrawal

52
New cards
springs
A natural source of water formed when water from an aquifer percolates up to the ground surface.

53
New cards
lakes
A body of water that is surrounded by land it can be fresh water or salt water.

54
New cards
speleothems
Collective term for the dripstone features found in caverns (Cave formations)
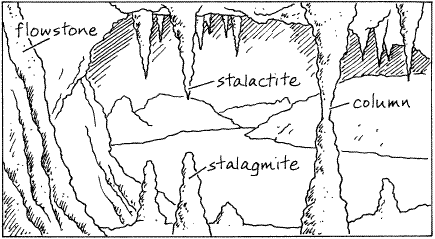
55
New cards
Fluvial lakes
lakes formed by rivers (oxbow lakes)
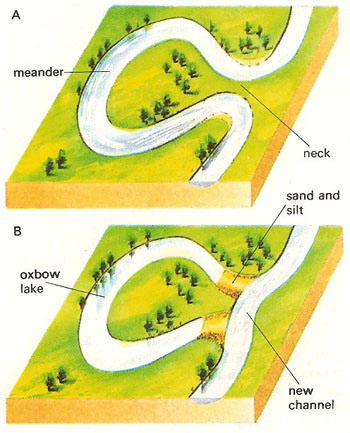
56
New cards
Solution lakes
formed by the dissolution of limestone deposits

57
New cards
Landslide lakes
Large landslides can block rivers and create lakes in the mountains

58
New cards
Aeolian lakes
lakes formed by wind

59
New cards
organic lakes
These lakes are caused by the activities of living organisms

60
New cards
Anthropogenic lakes
man-made lakes

61
New cards
Meteorite lakes
impact lakes

62
New cards
lake stratification
Lack of mixing of a lake due to differences in water temperature (density)
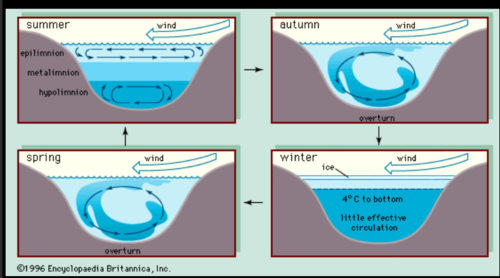
63
New cards
waves
Waves produced by the energy of moving water
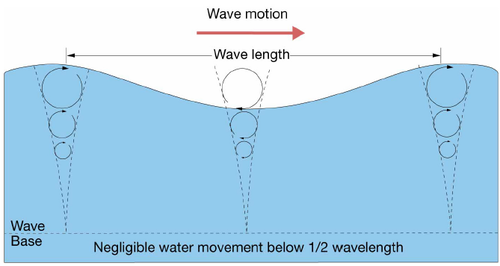
64
New cards
wetlands
water-saturated land area that supports aquatic plants

65
New cards
swamps
wetlands with trees

66
New cards
marshes
a wetland typically covered with grasses

67
New cards
bogs
low swampy lands

68
New cards
fens
An area of waterlogged soil that tends to be peaty; fed mainly by upwelling water; low productivity.

69
New cards
hydrologic cycle
the movement of water through the biosphere
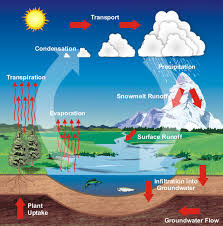
70
New cards
pollution
Release of harmful materials into the environment

71
New cards
air pollution
the contamination of the atmosphere by the introduction of pollutants from human and natural sources

72
New cards
water pollution
the addition of any substance that has a negative effect on water or the living things that depend on the water

73
New cards
land pollution
The contamination of land by both solid and hazardous waste

74
New cards
soil pollution
pollutants being added to soil by agricultural runoffs, unclean technology, waste disposal

75
New cards
noise pollution
Type of pollution characterized by unwanted or potentially damaging sound.

76
New cards
light pollution
brightening of the night sky caused by street lights and other man-made sources, which has a disruptive effect on natural cycles and inhibits the observation of stars and planets.

77
New cards
radioactive pollution
radioactive waste and nuclear accidents

78
New cards
thermal pollution
a temperature increase in a body of water that is caused by human activity and that has a harmful effect on water quality and on the ability of that body of water to support life

79
New cards
critical zone
heterogeneous, near surface environment in which complex interactions involving rock, soil, water, air, and living organisms regulate the natural habitat and determine the availability of life-sustaining resources
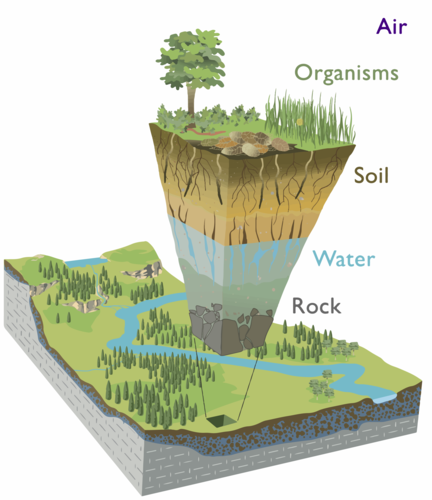
80
New cards
Darcy's Law
A mathematical equation stating that a volume of water, passing through a specified area of material at a given time, depends on the material's permeability and hydraulic gradient.

81
New cards
ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)
is a hydroacoustic current meter similar to a sonar, used to measure water current velocities over a depth range using the Doppler effect of sound waves scattered back from particles within the water column.

82
New cards
ADV (Acoustic Doppler velocimetry)
Is a velocity measurement technique that allows for the measurement of 3D flow velocities by using the Doppler shift principle. _____ operates by emitting short acoustic pulses along a transmitter beam, the central transducer.
83
New cards
Stages of river development
youthful, mature, old

84
New cards
Waterfalls
Occur where a river meets an area of rock that erodes slowly
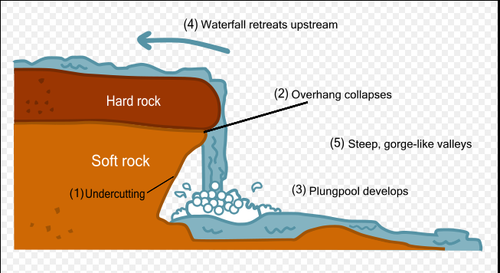
85
New cards
stream capture
process by which a stream in one watershed is captured by a stream in an adjacent watershed
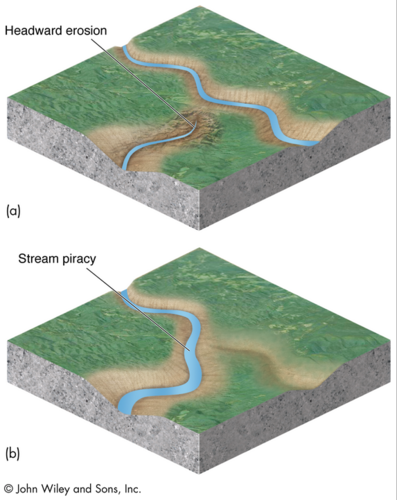
86
New cards
knickpoints
channel irregularities such as rapids and waterfalls

87
New cards
deltas
deposits of sand and soil at the mouth of a river form
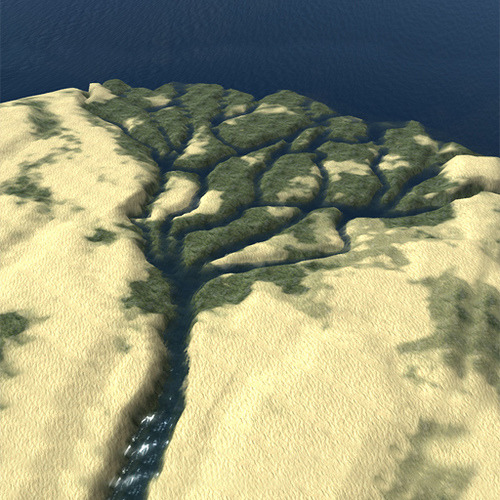

88
New cards
Hjulstrom Diagram
graph used to show if sediments will deposit, transport, or erode sediment
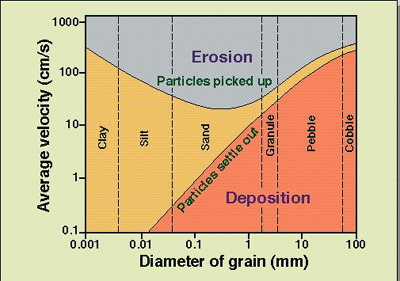
89
New cards
Estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean.

90
New cards
oxbow lake
A meander cut off from a river.
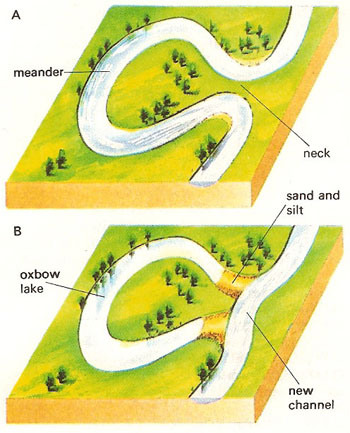
91
New cards
stream load
The materials other than the water that are carried by a stream
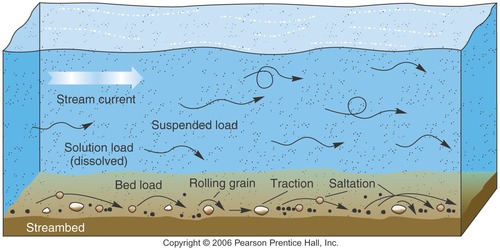
92
New cards
wells
Holes dug or drilled deep into the ground to reach a reservoir of groundwater

93
New cards
artesian well
A well in which water rises because of pressure within the aquifer

94
New cards
water table well
well that extends into the zone of saturation in an unconfined aquifer
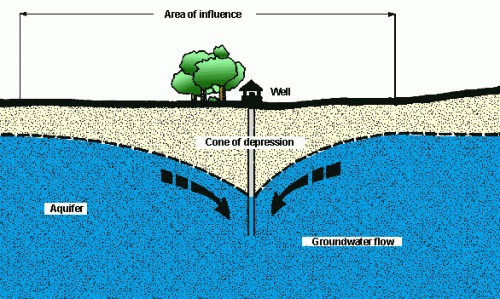
95
New cards
Evapotranspiration
The combined amount of evaporation and transpiration

96
New cards
Permafrost
permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground

97
New cards
Pingo
a dome-shaped mound consisting of a layer of soil over a large core of ice, occurring in permafrost areas.
