Disorders of haemostasis - embolism, DIC, shock
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Shit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Non thrombus causes of embolism
Bacterial, parasites, fat droplets (fractures), bubbles, bone marrow, cartilage, foreign bodies, tumour fragments (metastases)
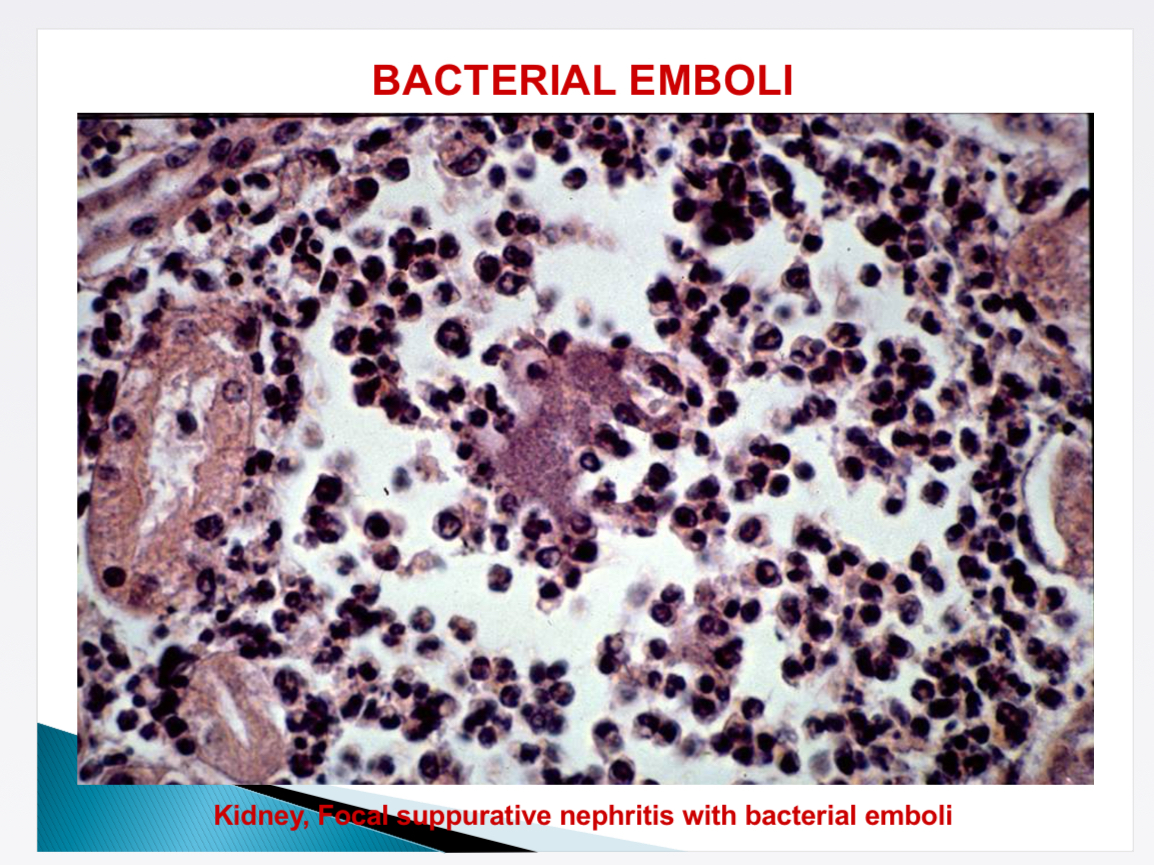
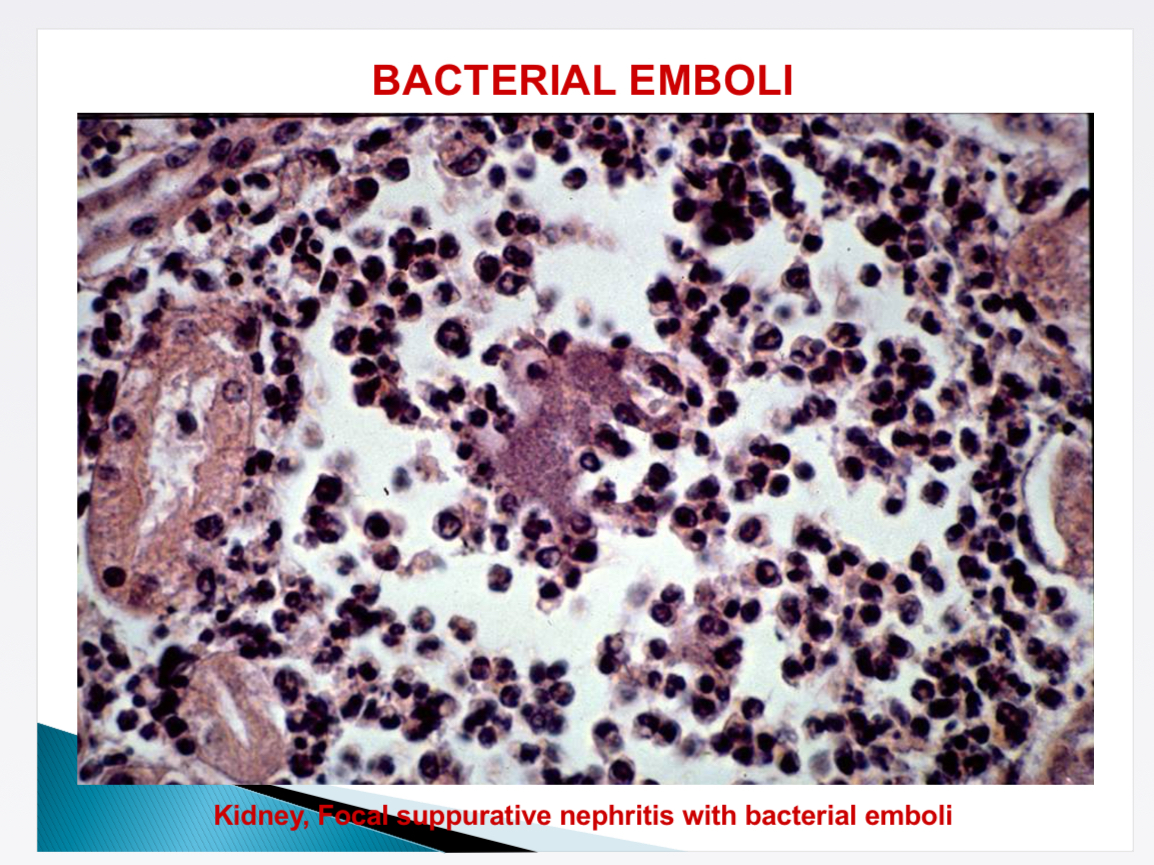
What happens in bacterial emboli (bacterial endocarditis)
Bacterial embolus in pulmonary + systemic circulation → embolic metastatic diseases (glomerulonephritis, pneumonia, hepatitis)
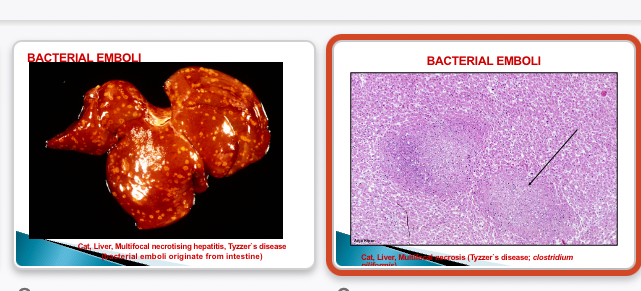
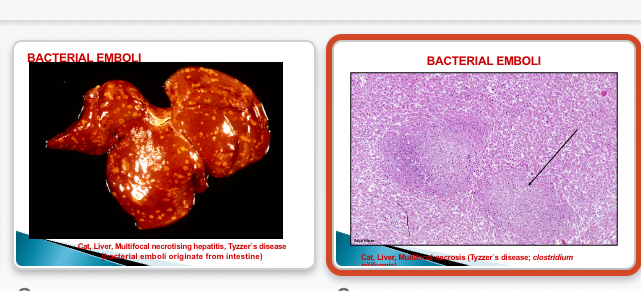
Tyzzers disease
Enterocolitis → organisms enter hepatic portal vein
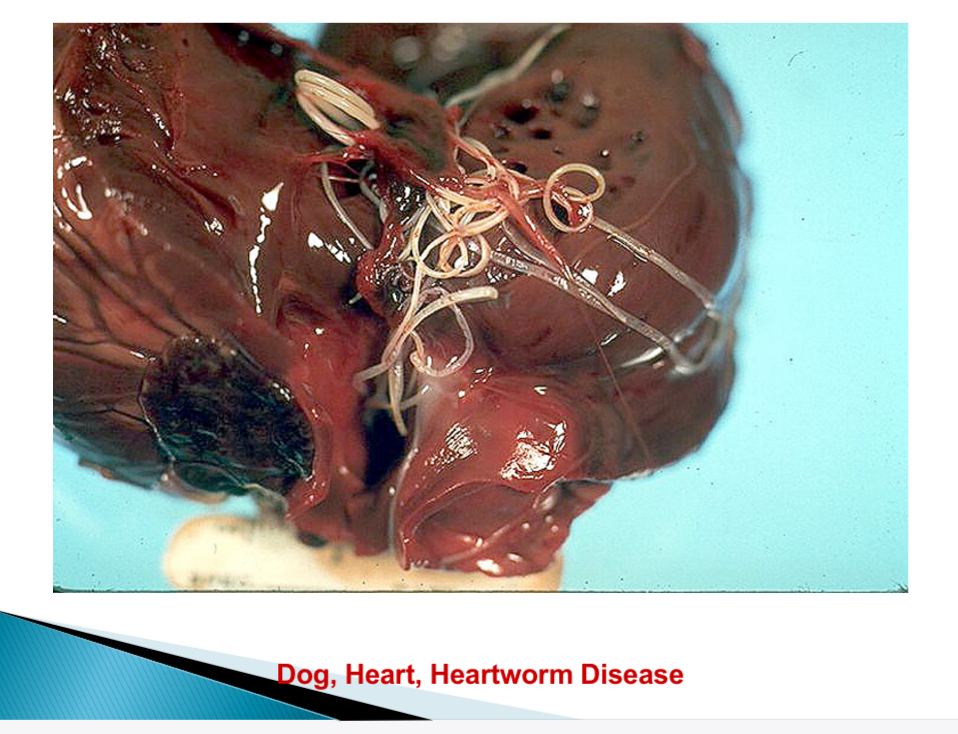
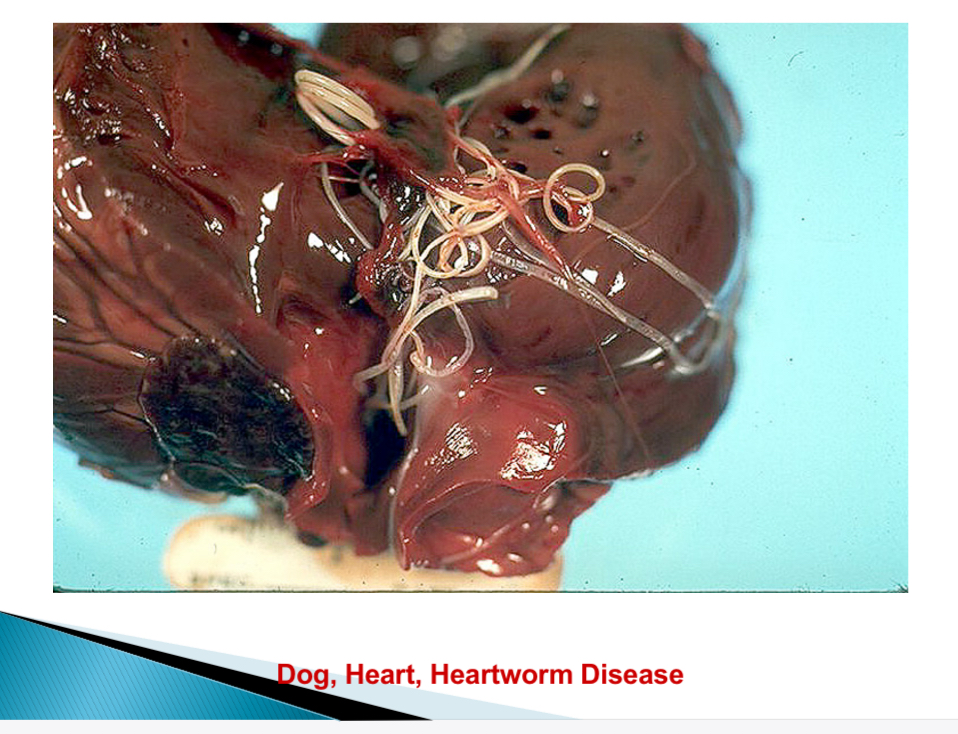
Dirofilaria immitis
Heart worm in RV + pulmonary artery → systemic circulation
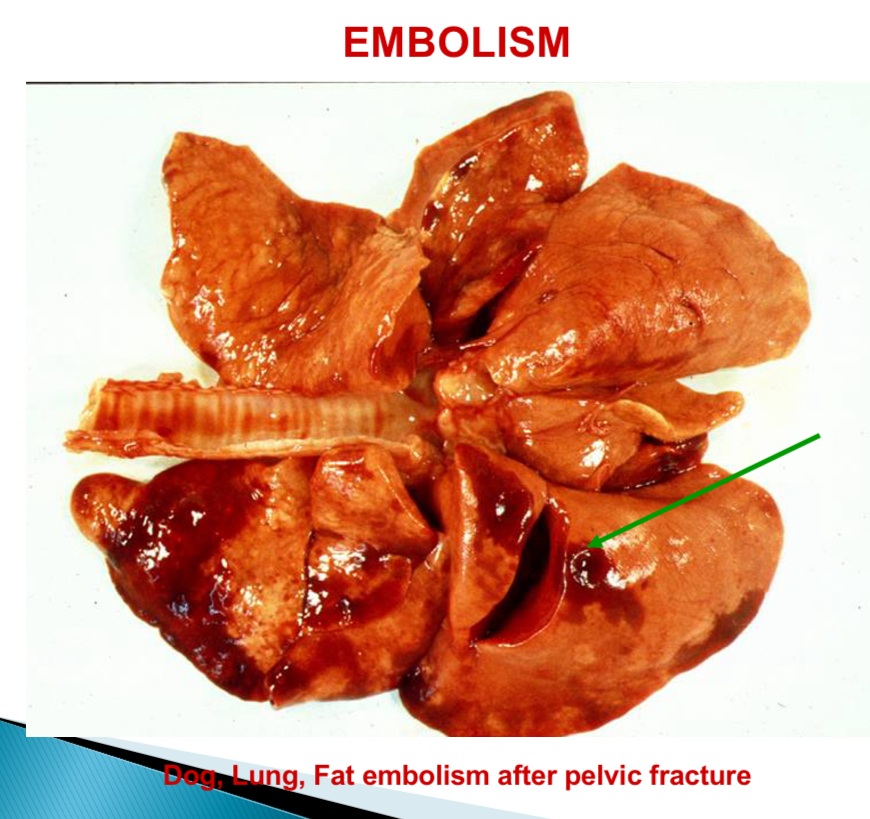
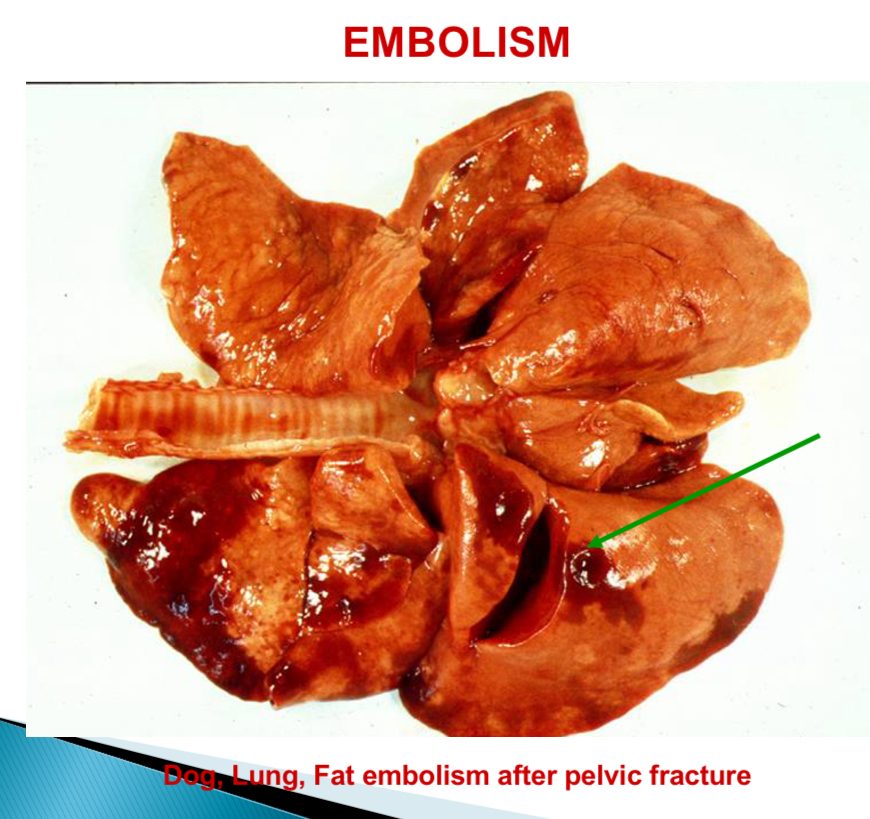
What can happen after fractures
Fat embolism
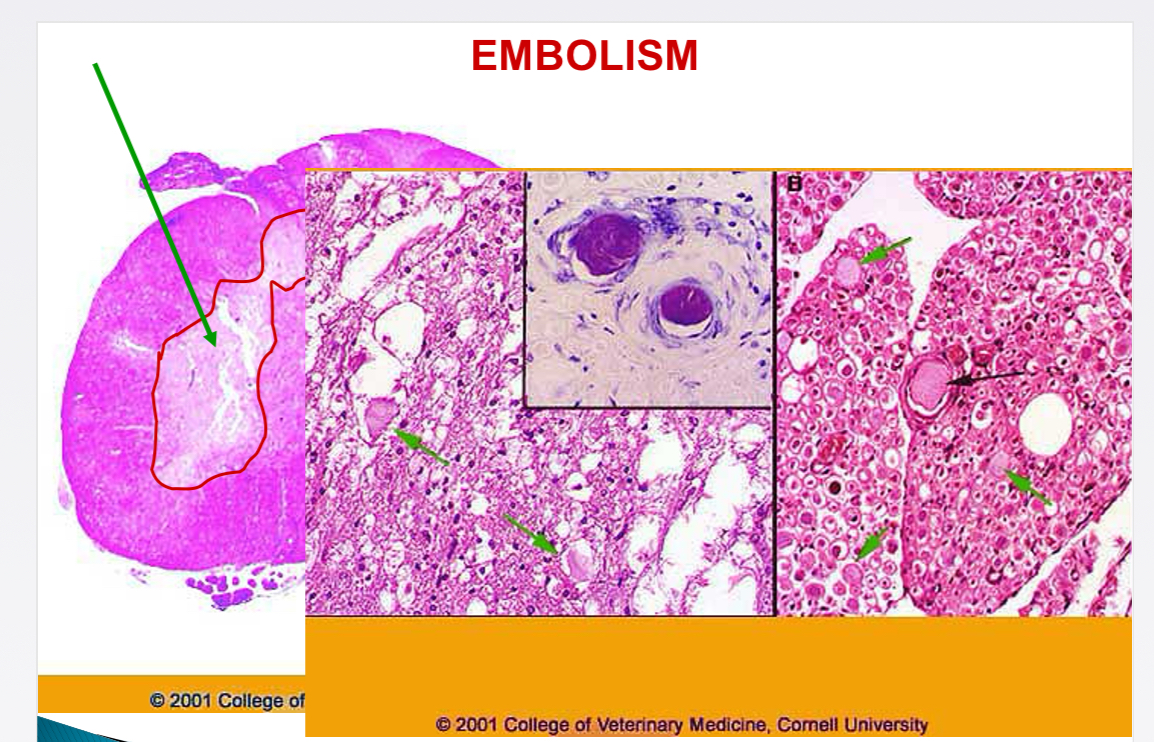
Common site of fibro-cartilaginous embolism
Spinal cord
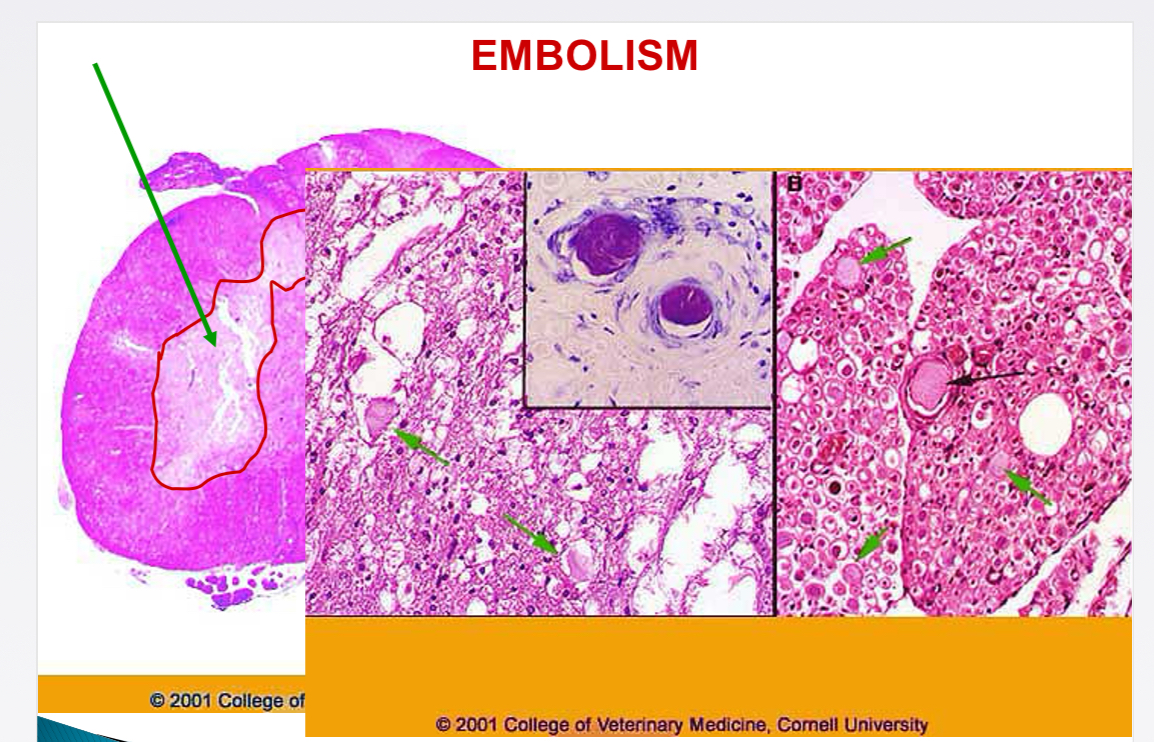
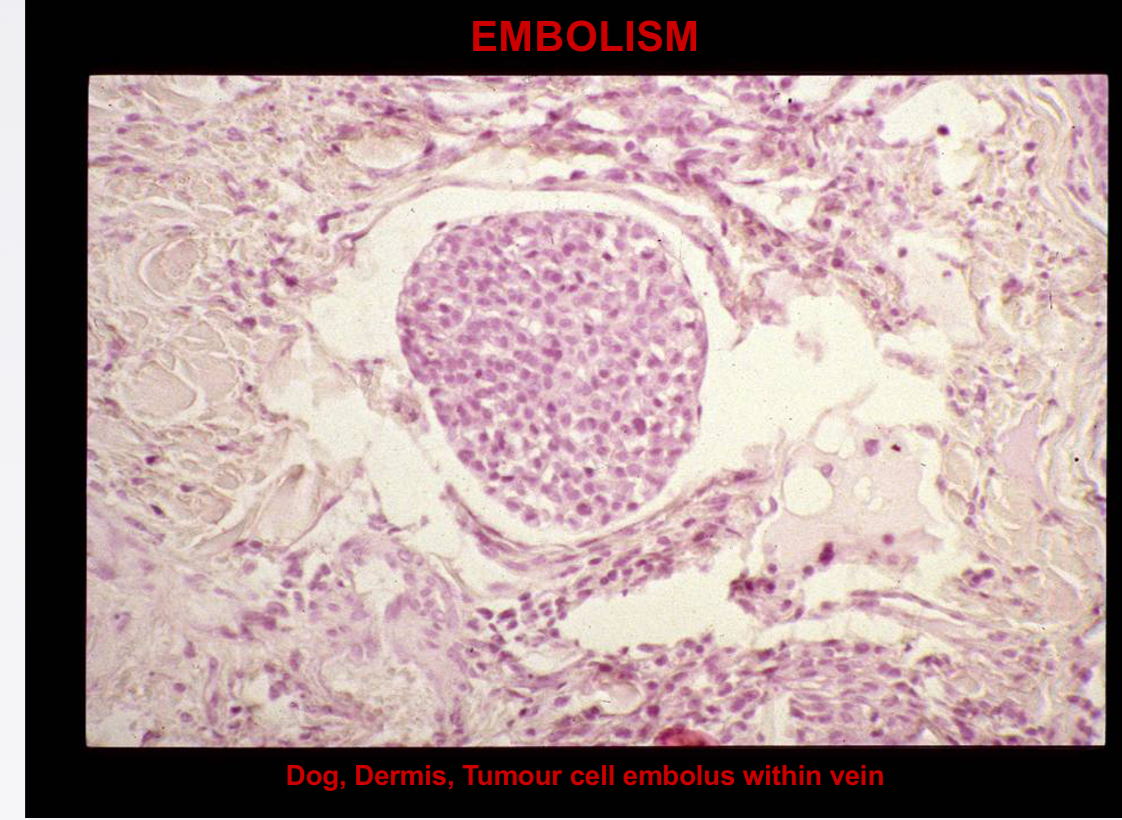
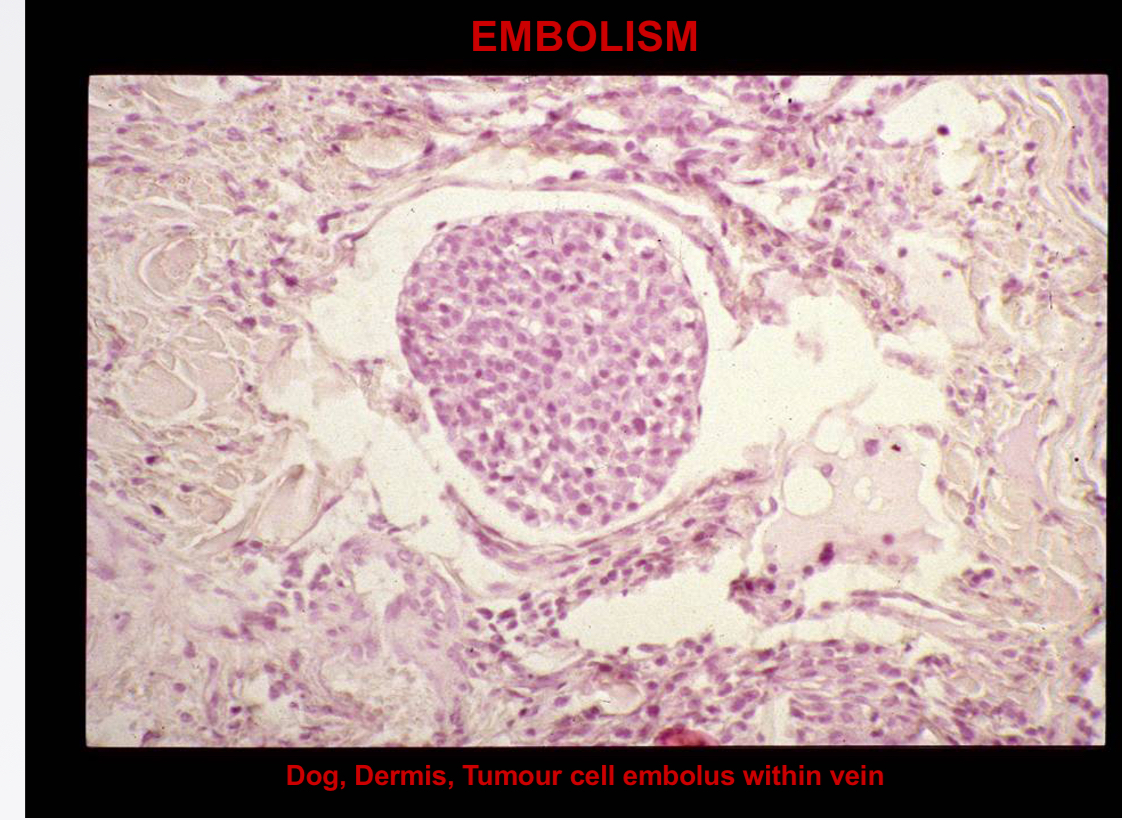
Term for tumour cell embolus production
Metastasis
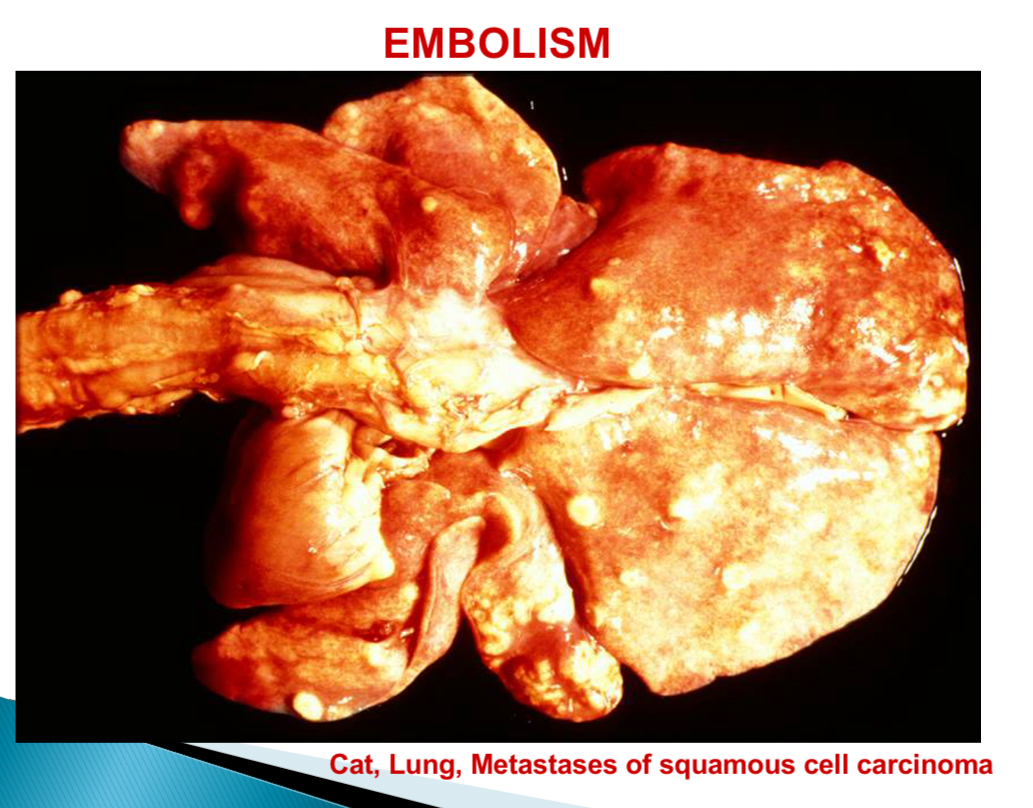
Squamous cell carcinoma is what (common in white cats)
Neoplasm of keratinocytes
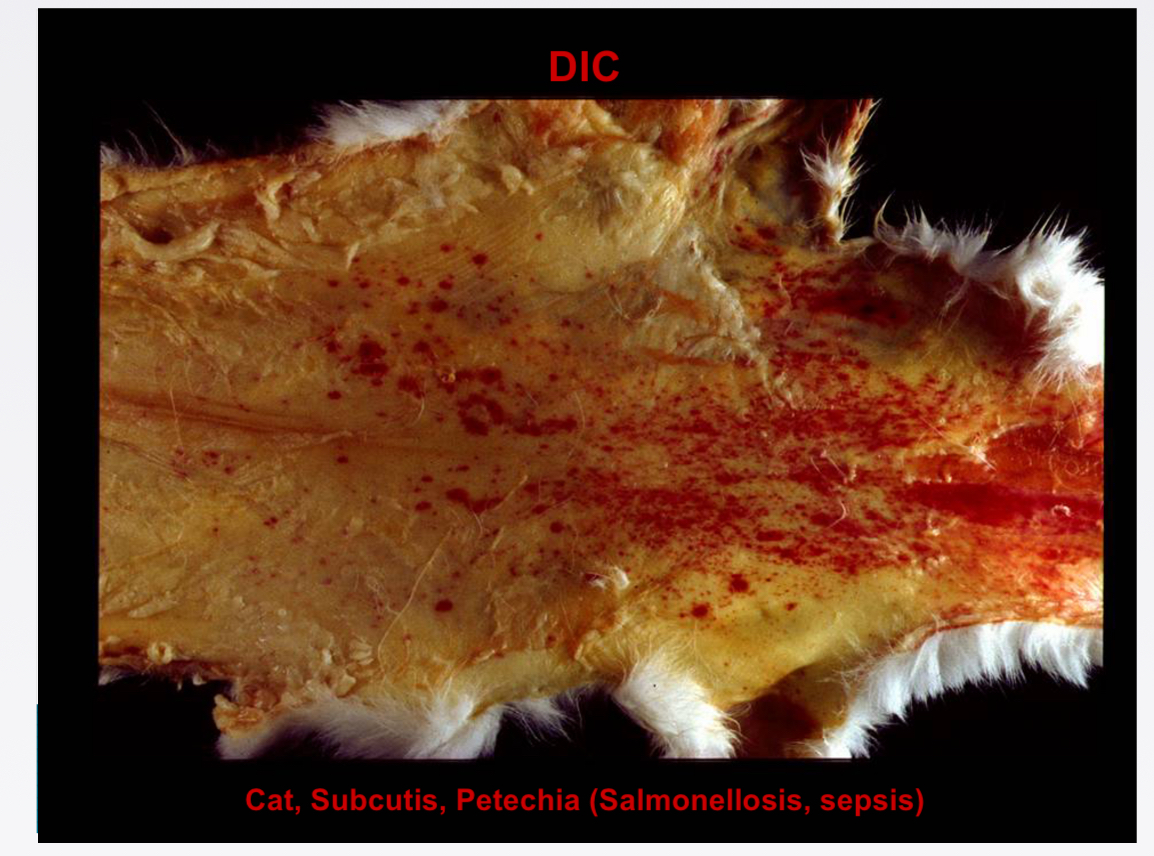
DIC stands for
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
DIC def
Acute/subacute/chronic thrombo-haemorrhagic disorder occurring as secondary complication in variety of diseases
steps of DIC
Activation of coagulation cascade in whole body → formation of micro thrombi throughout microcirculation → consumption of platelets, fibrin, coagulation factors, activation of fibrinolysis
CS of DIC
Tissue hypoxia, infarction, haemorrhagic disorder (consumption coagulopathy)
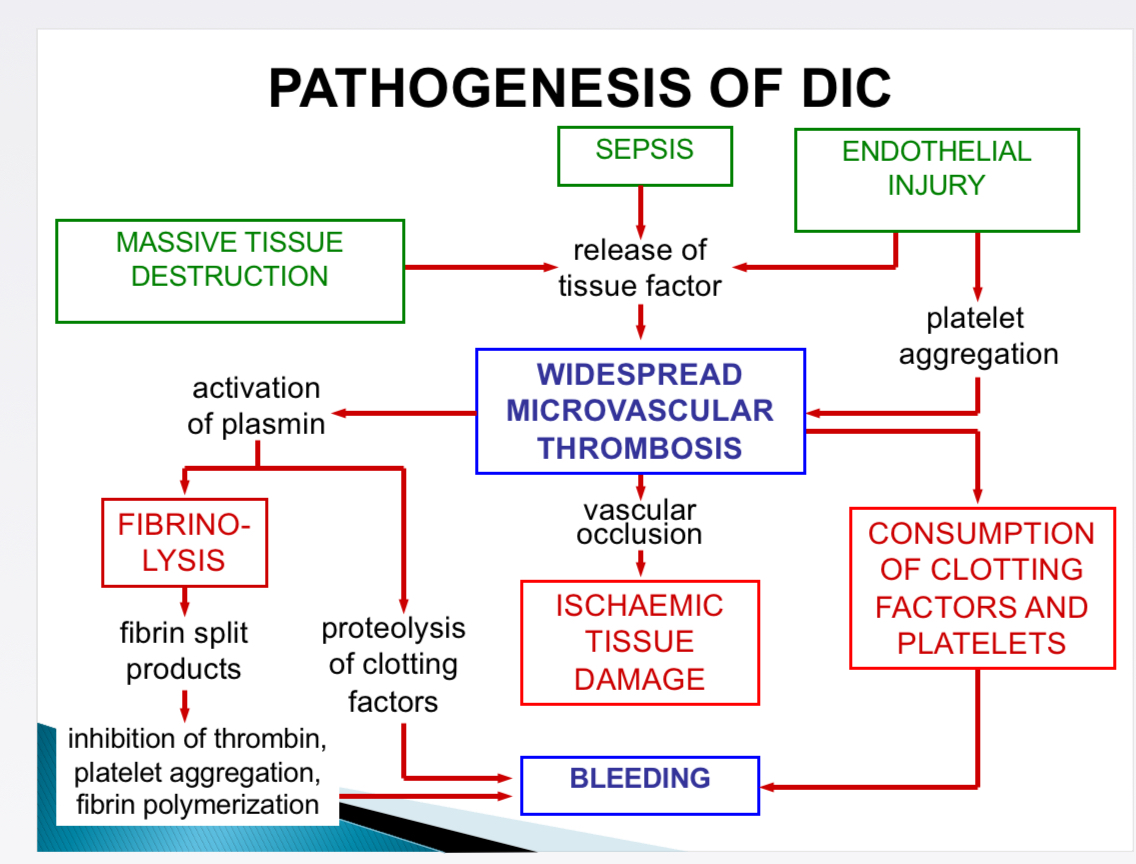
Major underlying mechanisms of DIC (causes)
Release of tissue factor, thromboplastic substances into circulation
Widespread injury to endothelial cells → coagulation cascade
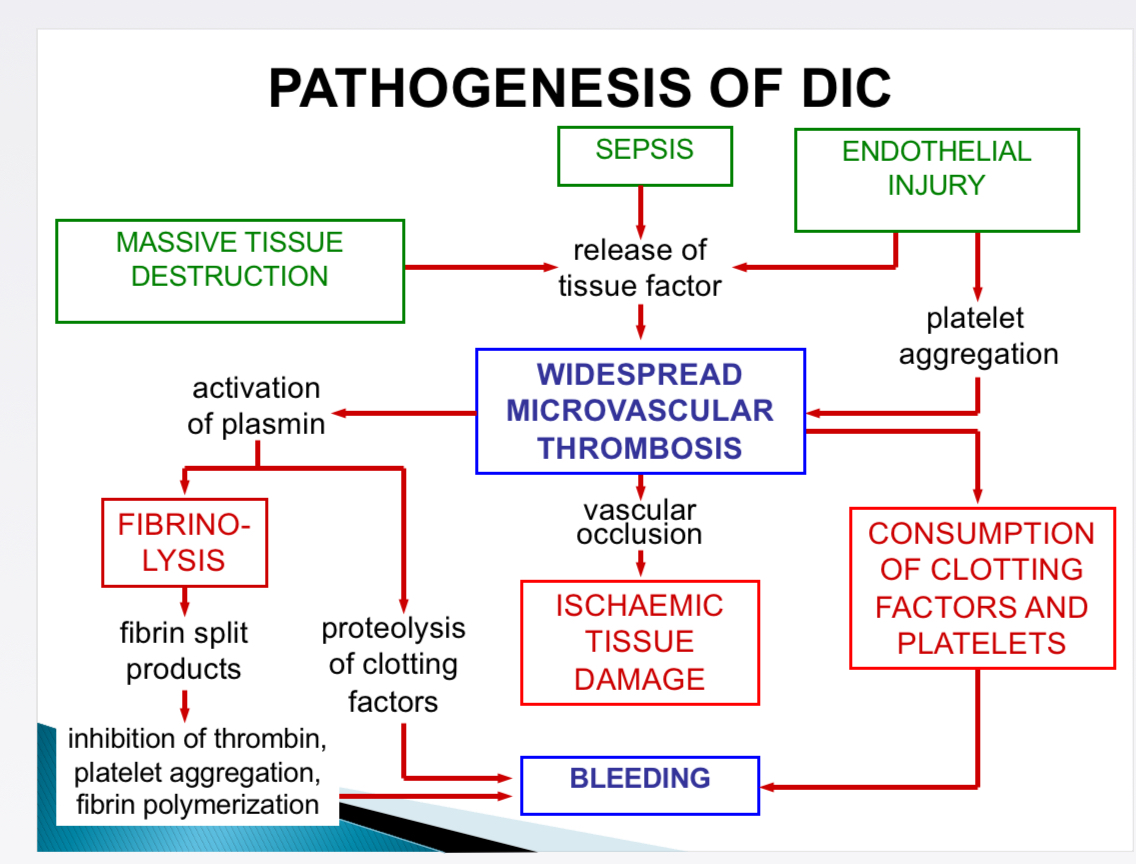
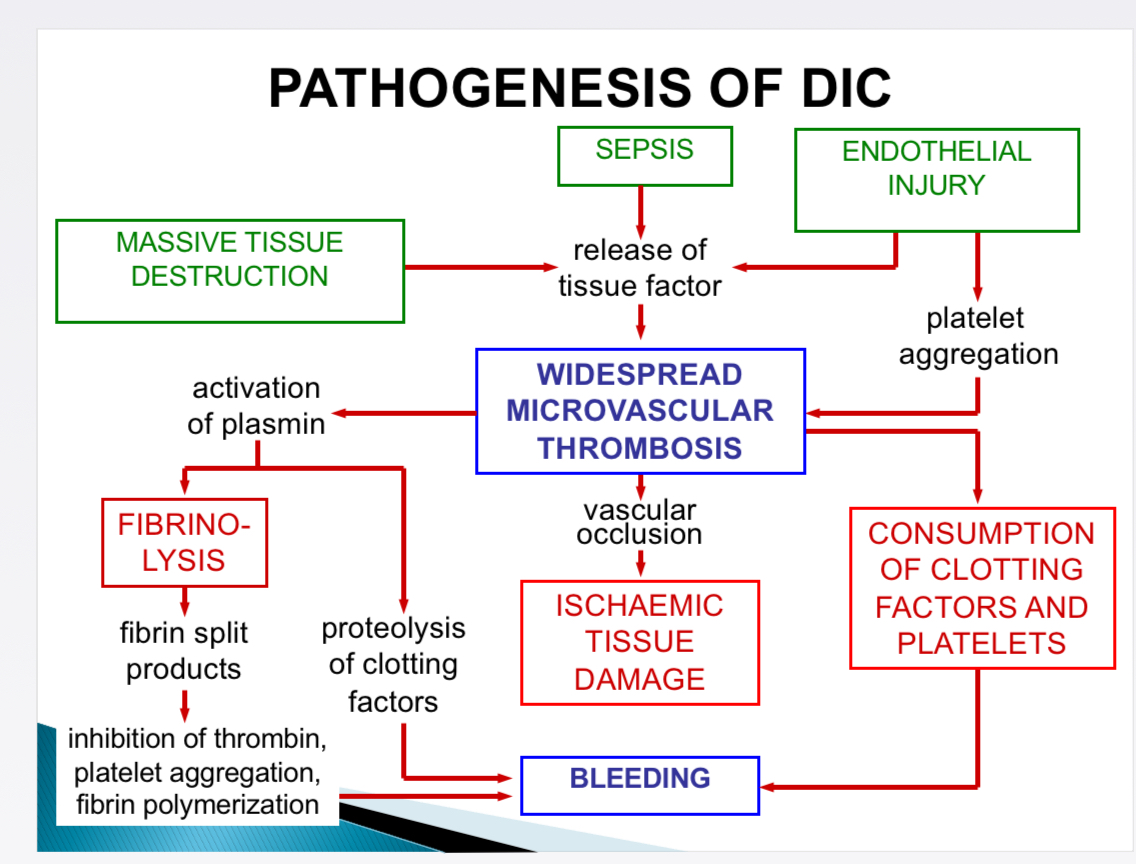
Pathogenesis of DIC- causes
Massive tissue destruction, sepsis, endothelial injury

Pathogenesis of DIC- Effects
Fibrinolysis, ischaemic tissue damage, consumption of clotting factors + platelets, bleeding
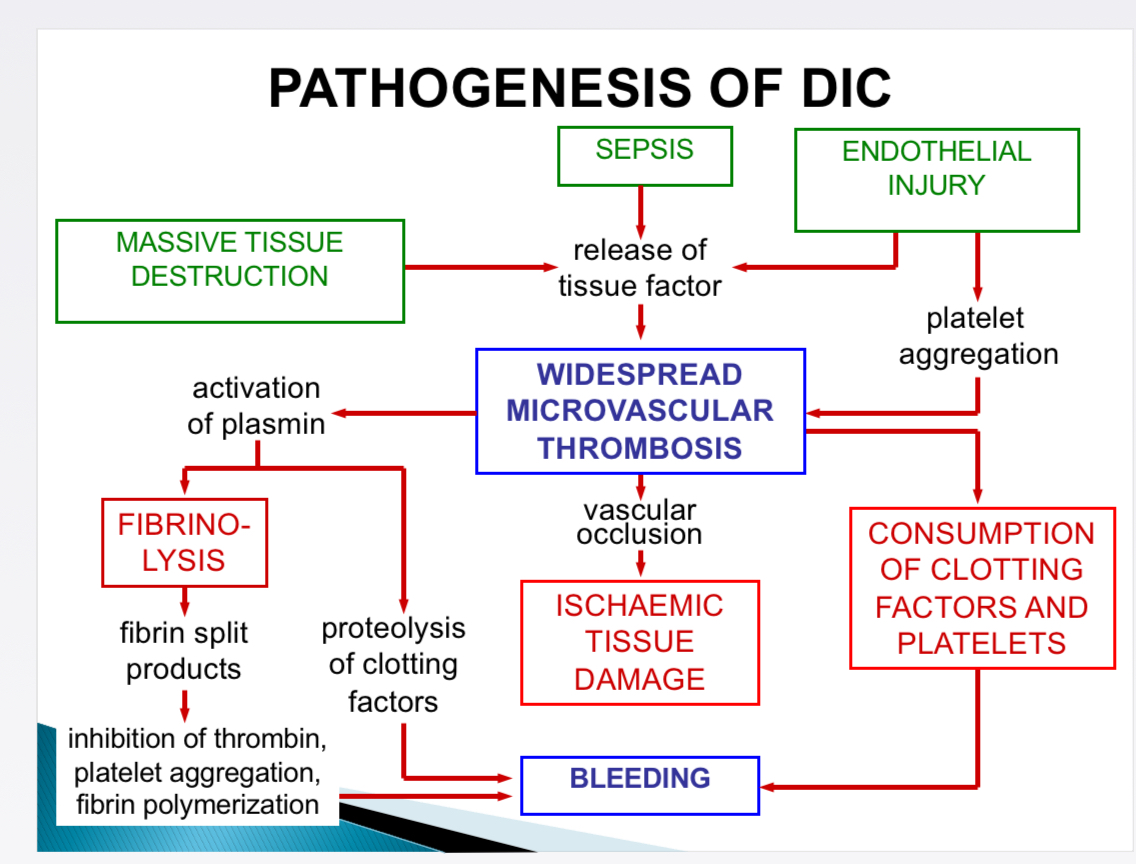
Pathogenesis of DIC- Commonly associated with
Severe systemic infections (from direct endothelium injury, immune complex deposition), septic shock, neoplasm, extensive trauma/burns, extensive surgery
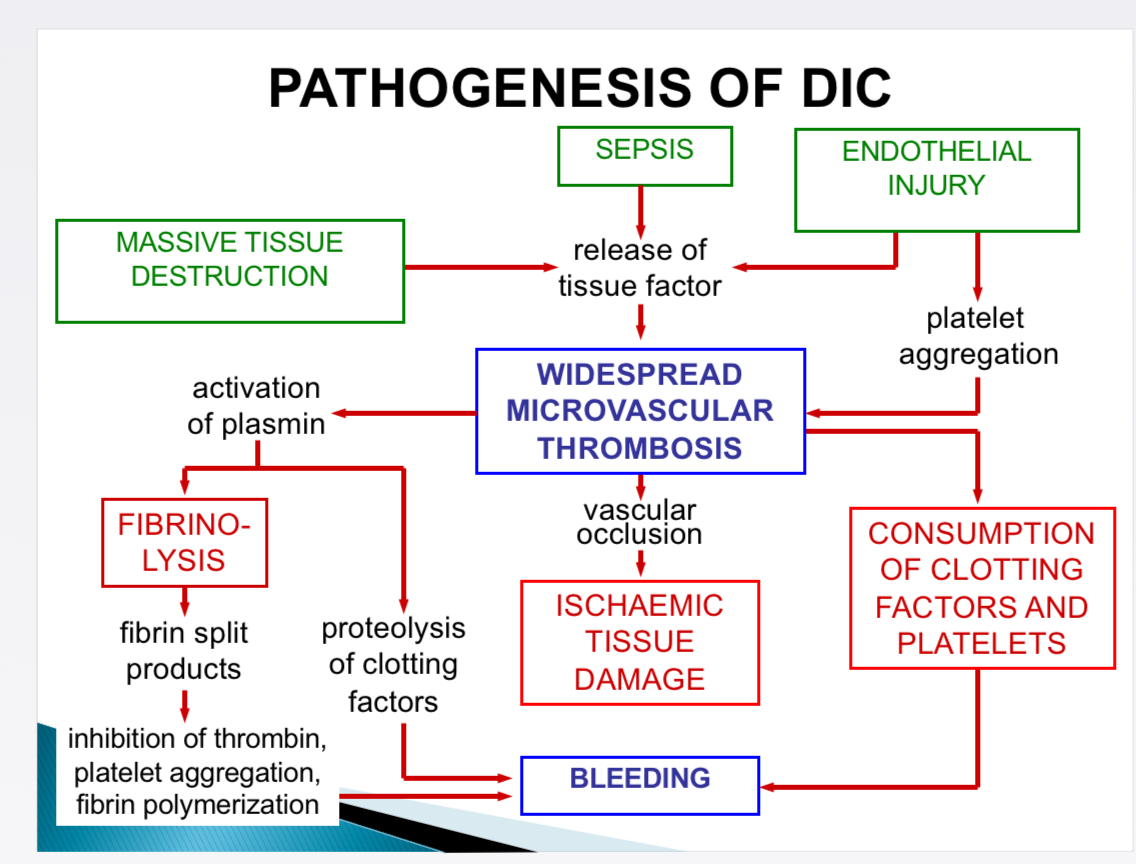
Pathogenesis of DIC- How does sepsis (gram -) leads to DIC
Bacterial endotoxins → monocytes release tissue factor + pro inflammatory cytokines → endothelial cells increase expression of tissue factor, decrease expression of thrombomodulin → activate clotting cascade, inhibit clotting control
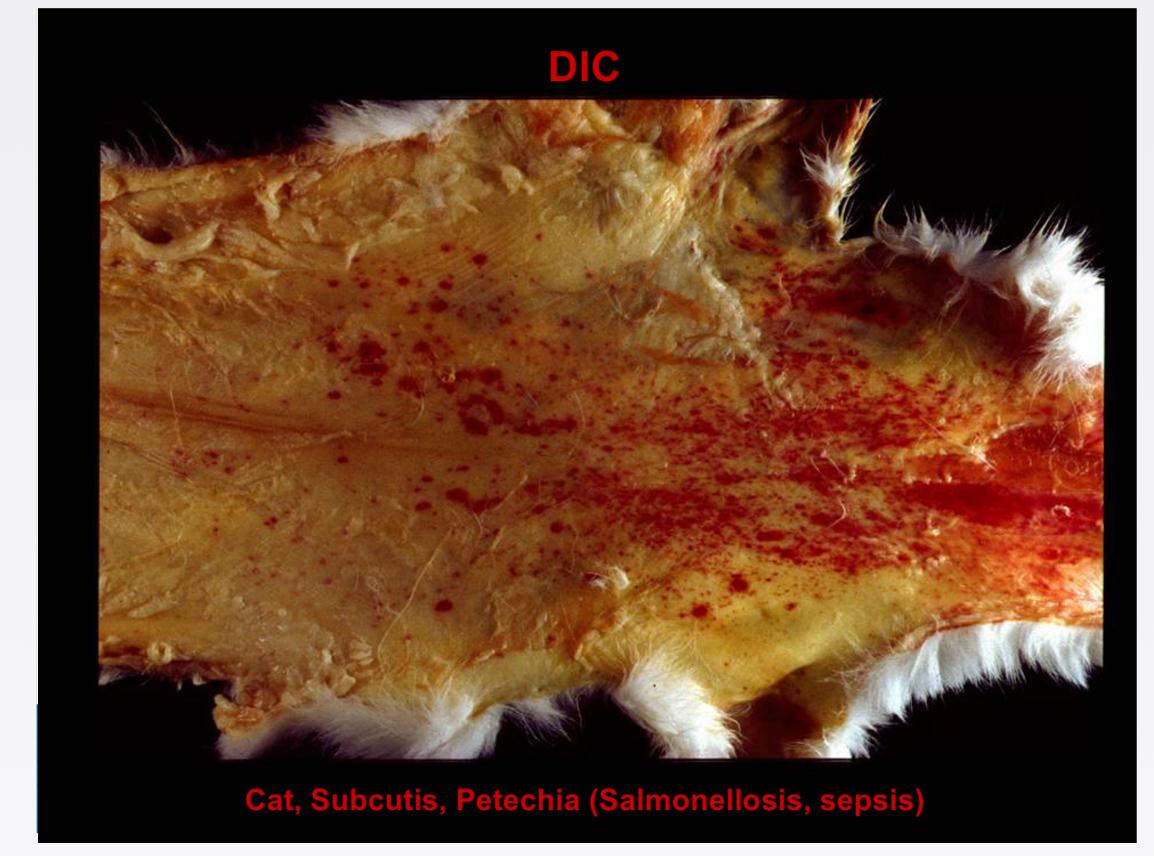
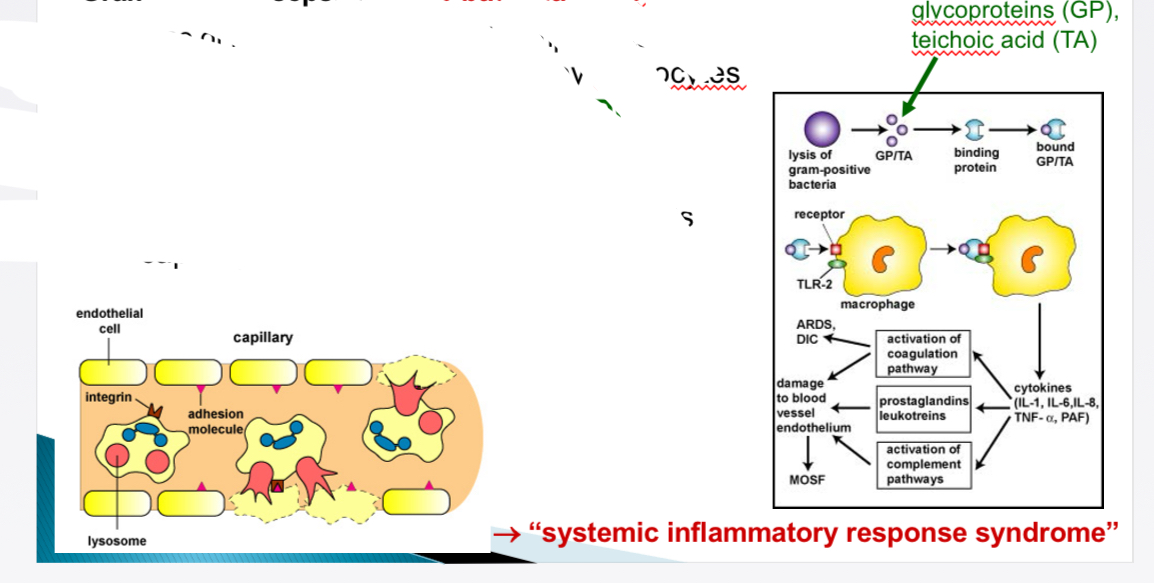
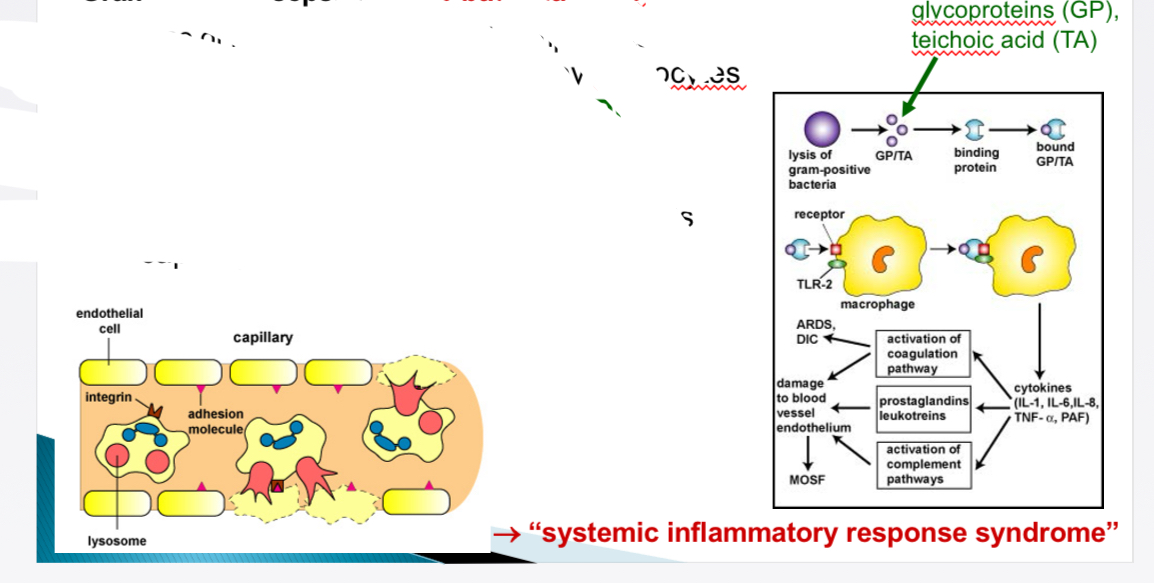
Pathogenesis of DIC- How does sepsis (gram +) leads to DIC
Bacterial lysis → release cell wall components → monocytes produce cytokines + SIRS + DIC
Neutrophils adhere to endothelium → release proteases + O radicals → capillary dmamage → haemorrhage → shock
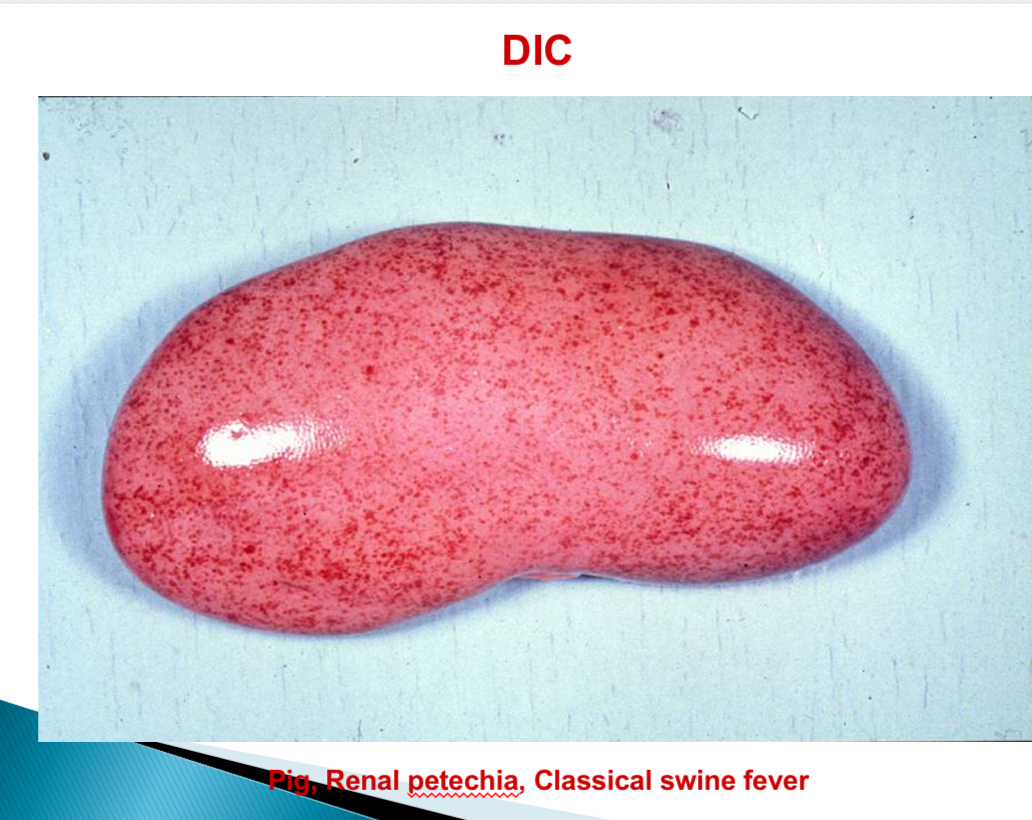
Viral diseases associated with DIC - pigs
Classical Swine fever
By endothelial alterations → petechia
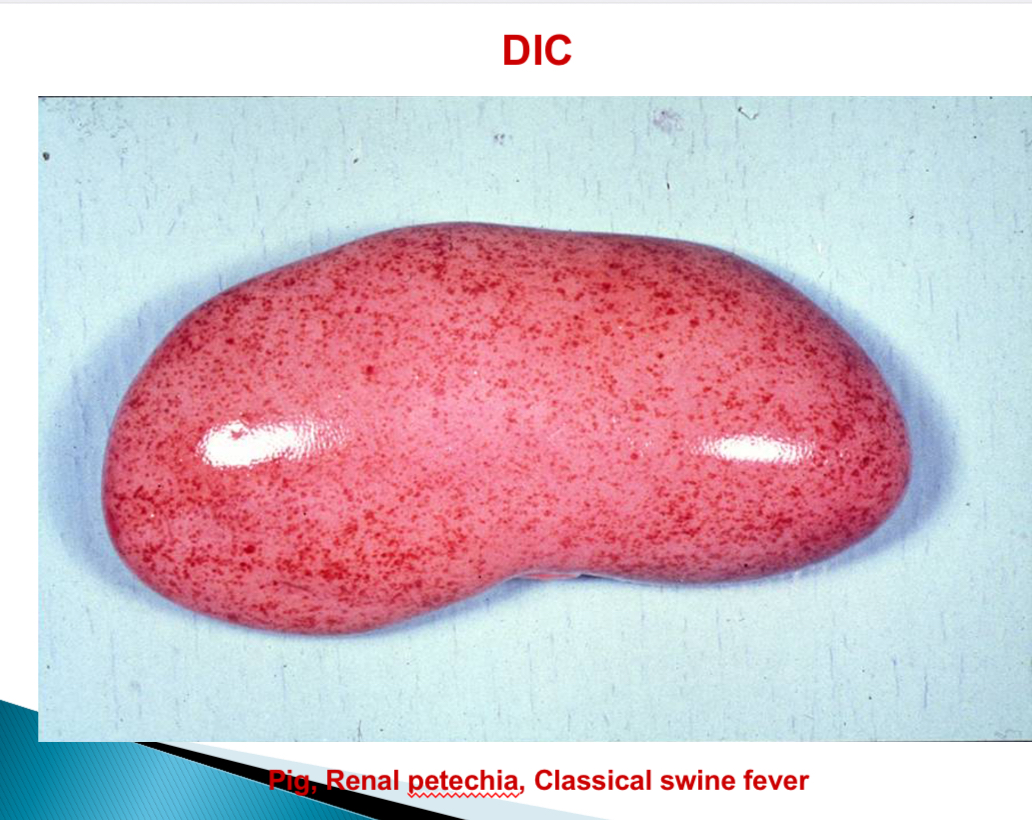
Viral diseases associated with DIC - Dog
Infectious canine hepatitis
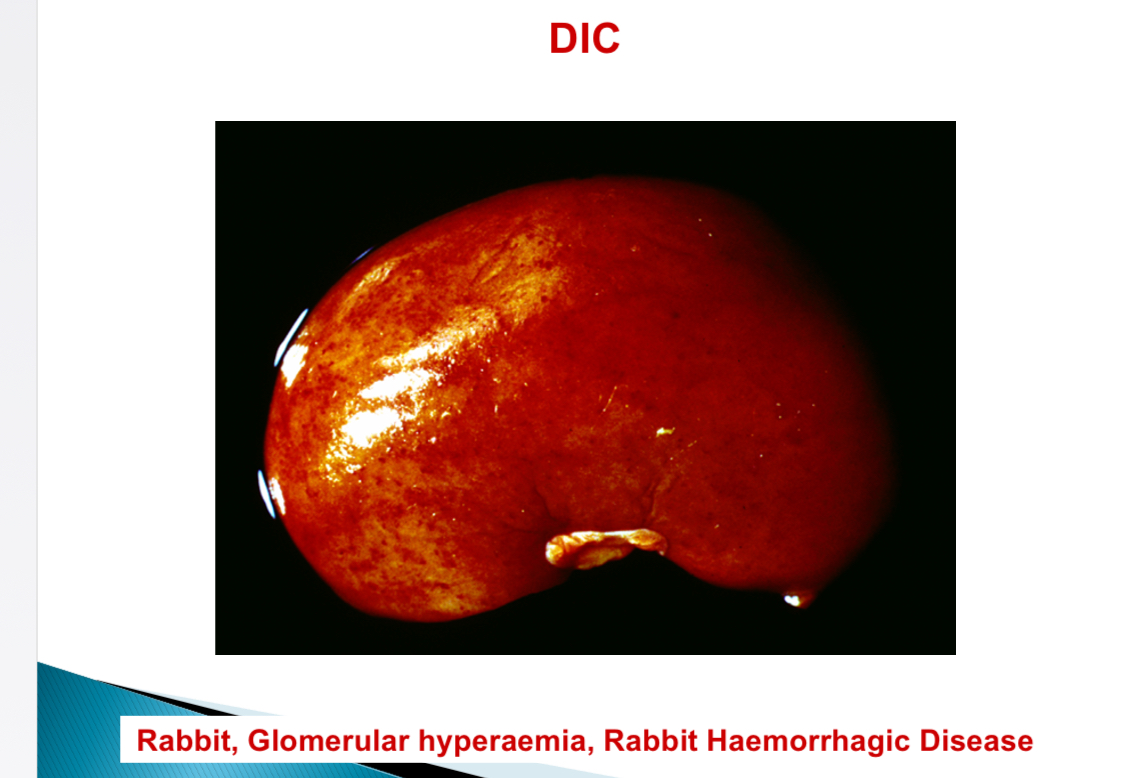
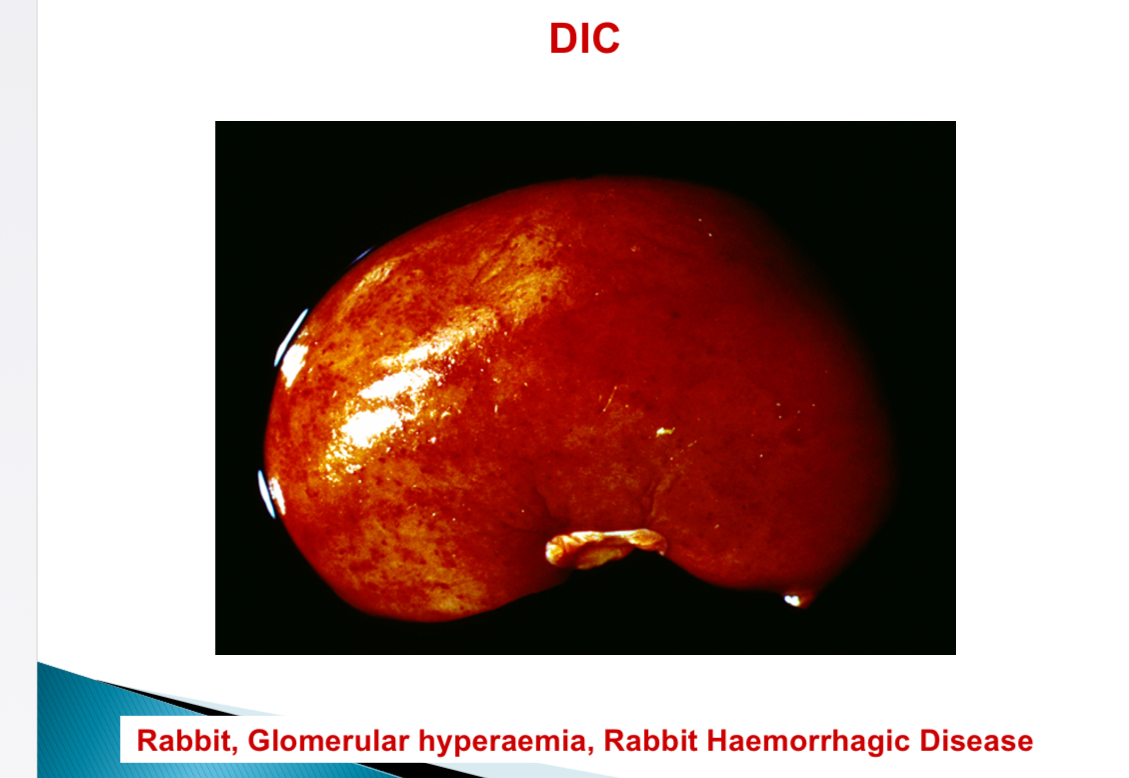
Viral diseases associated with DIC - Rabbit
Rabbit haemorrhagic diease
Hepatocyte necrosis
Viral diseases associated with DIC - Sheep
Blue tongue
Viral diseases associated with DIC - Mink
Aleutian disease
Immune complex deposition in BV wall → complement + coagulation cascade
Viral diseases associated with DIC - Deer
epizootic haemorrhagic disease
Shock - def + causes
Culmination in systemic hypoperfusion due to reduced CO, reduced effective circulating blood vol
Causes of shock
Severe haemorrhage, microbial sepsis, extensive trauma/burns, large infarction, massive pulmonary embolism
Effects of shock
Hypotension → impaired perfusion → cellular hypoxia
Types of shock
Cardiogenic, hypovolaemic, septic, neurogenic, anaphylactic
Types of shock - cardiogenic
Failure of myocardial pump
Types of shock - hypovolaemic
Loss of blood/ plasma
Types of shock - septic
Systemic microbial infection
Types of shock - neurogenic
Depression of vasomotor centre
Types of shock - anaphylactic
Generalised IgE mediated hypersensitivity
Stages of shock
Non progressive, progressive, irreversible
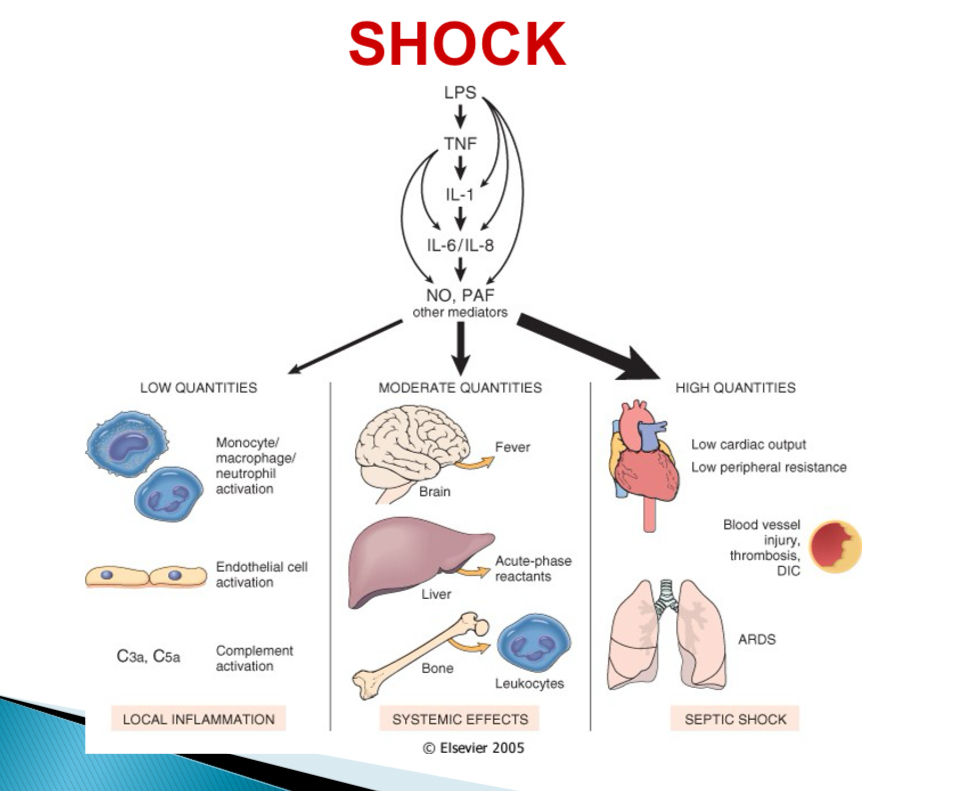
Pathogenesis of septic shock - type of bacteria
Endotoxin (LPS) producing gram -
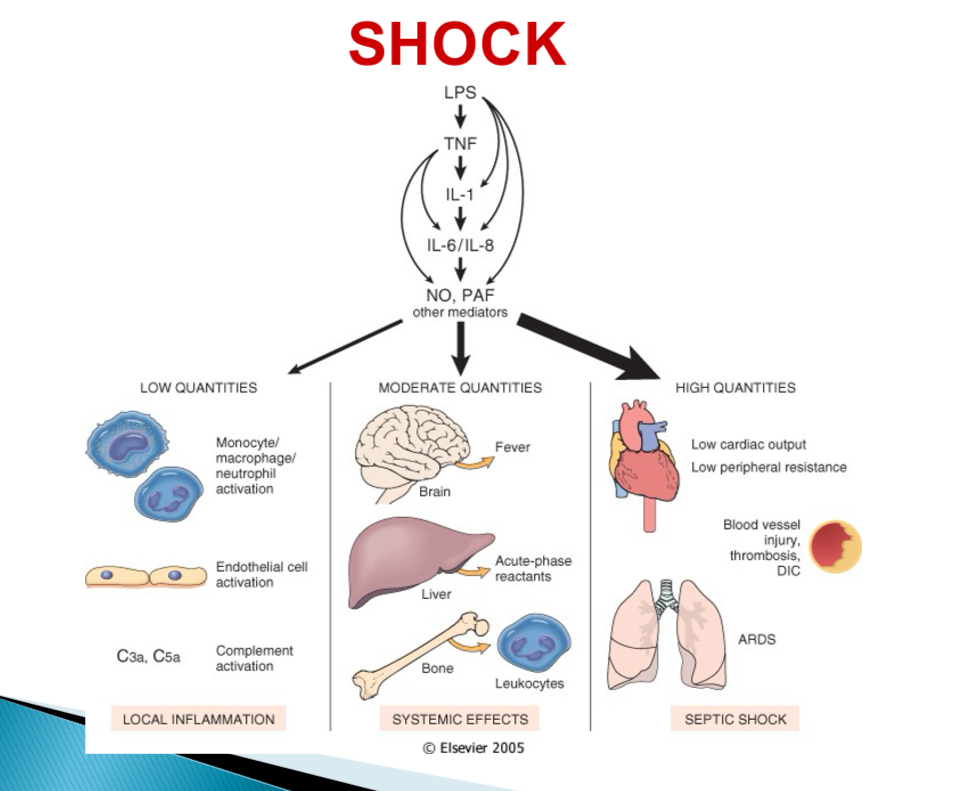
Pathogenesis of septic shock - With low LPS
Activation of monocytes, endothelial cells, complement → cascade → local acute inflammation + bacterial clearance
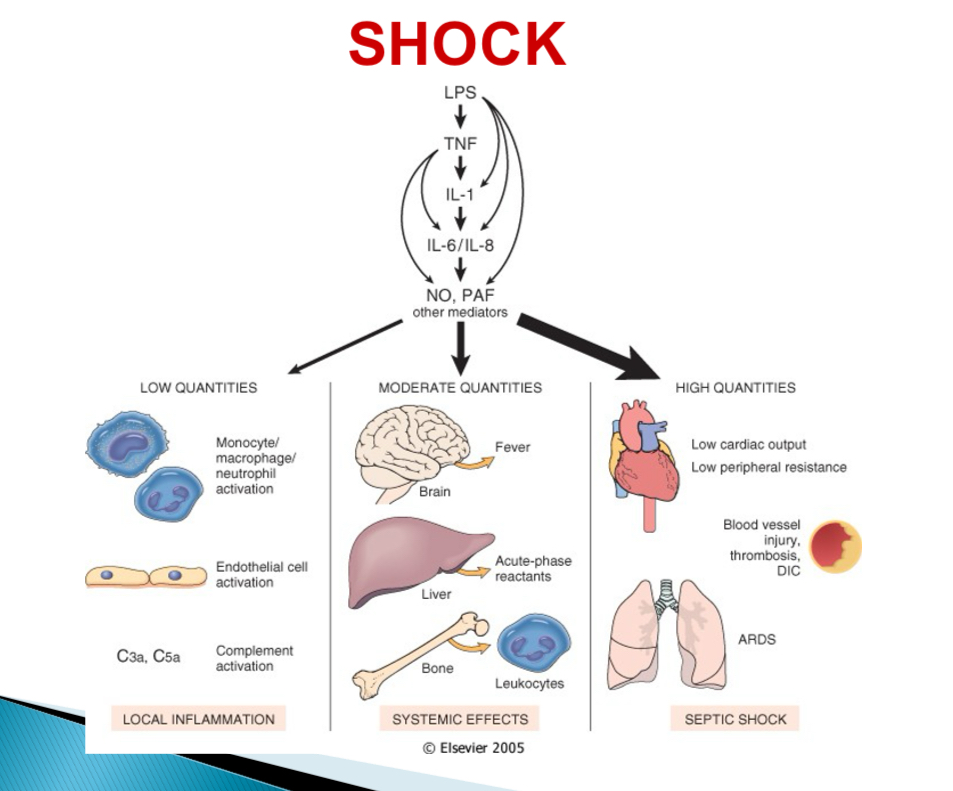
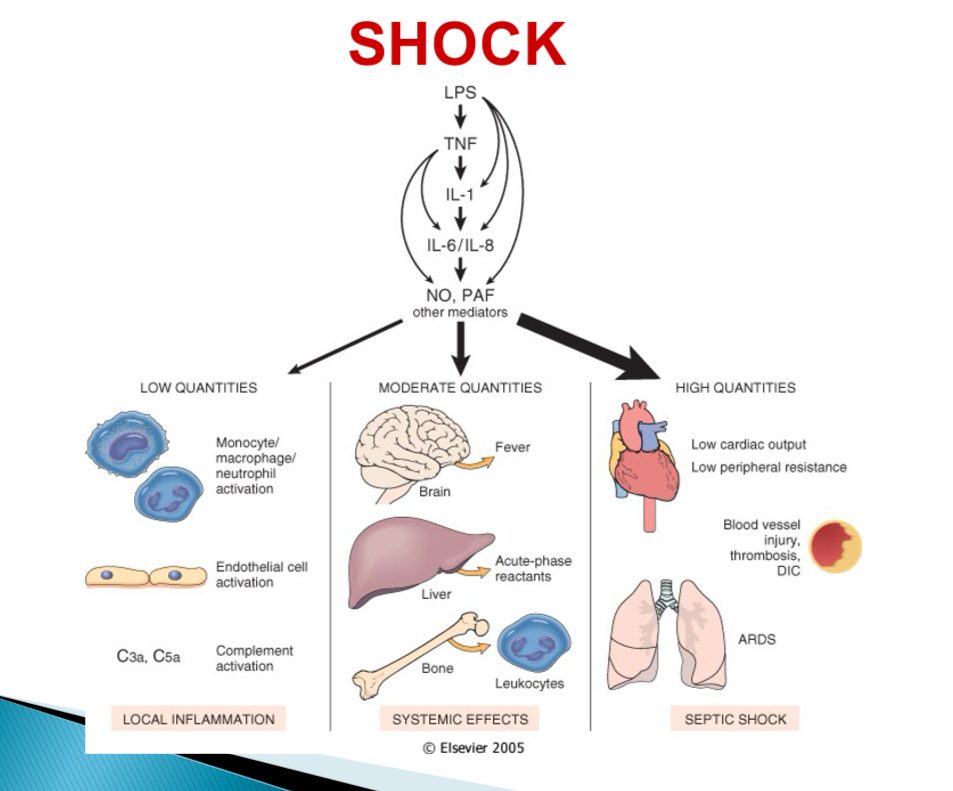
Pathogenesis of septic shock - With mod LPS
Cytokine induced effectors (NO + PAF) → fever, acute phase reactants, endothelial injury, DIC
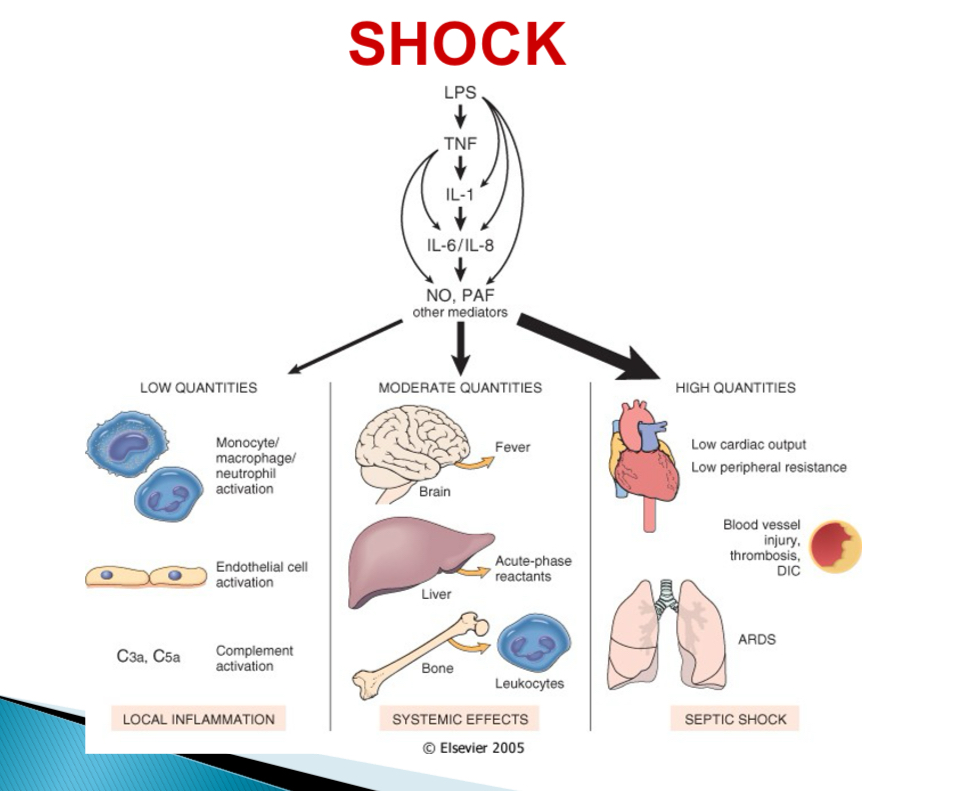
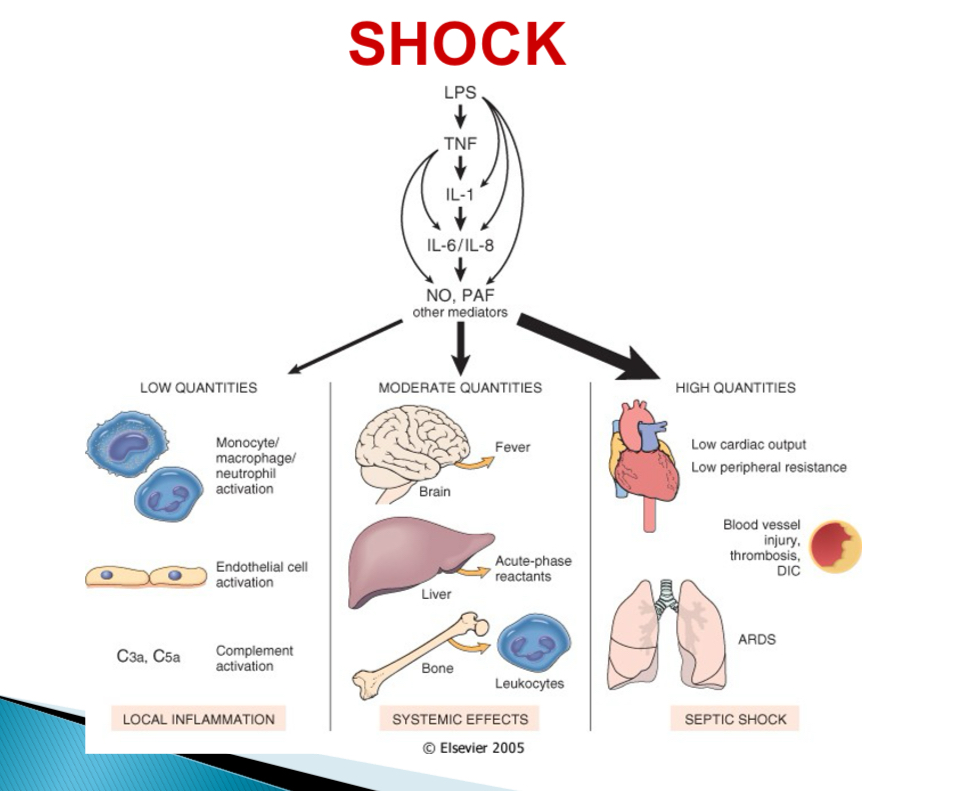
Pathogenesis of septic shock - With high LPS
Systemic vasodilation, reduced cardiac contractility, DIC → MOSF, SIRS
what does MOSF stand for
Multi organ system failure
Pathogenesis of septic shock in gram + bacteria
Cytokine production (monocytes), SIRS, DIC
Neutrophils adhering to endothelium, release of proteases, O radicals → shock