Theme 1, Modules 3 & 4 APPLIED Lecture
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Monogenic disease
Error in one gene
Most diseases are mistakes in multiple genes
Like cancer has more than one proteins with mistakes
What is cystic fibrosis?

It is a congenital diseases that means a person is born with it and it is inherited
Both parents are carriers for the mistake in the gene
ALL ducts are infected
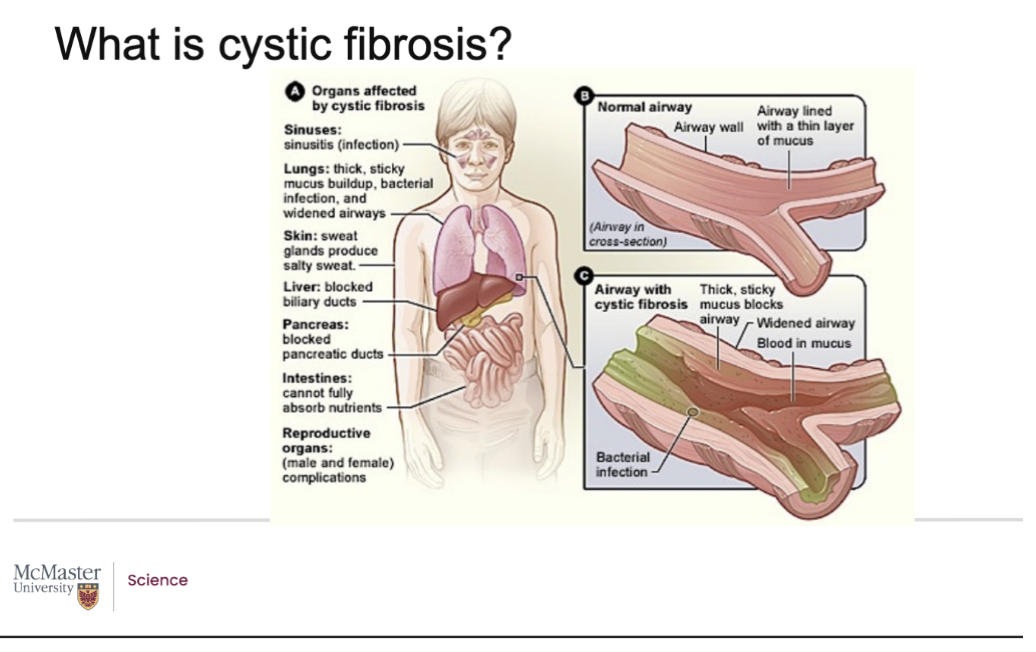
Air ways are greatly effected
People with CF cant pull up phlegm
So bacteria grow
Immune system will start attacking bacteria but because the immune system attach often with toxins and inflammatory factors it will also not just attack the bacteria but it will also cause inflammation of the tissue, it will also self-attack the body
So tissue starts getting bloated and filled with fluid, generally presenting characteristic of inflammation
It our body has too much mucus in the airways our bodies will cough so CF people have persistent cough
How do we clinically evaluate airways?
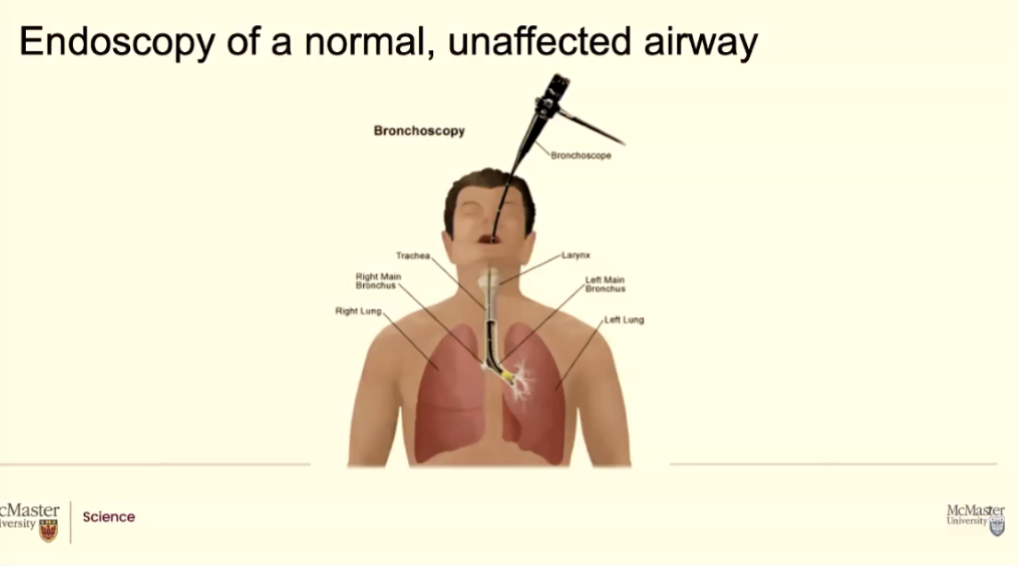
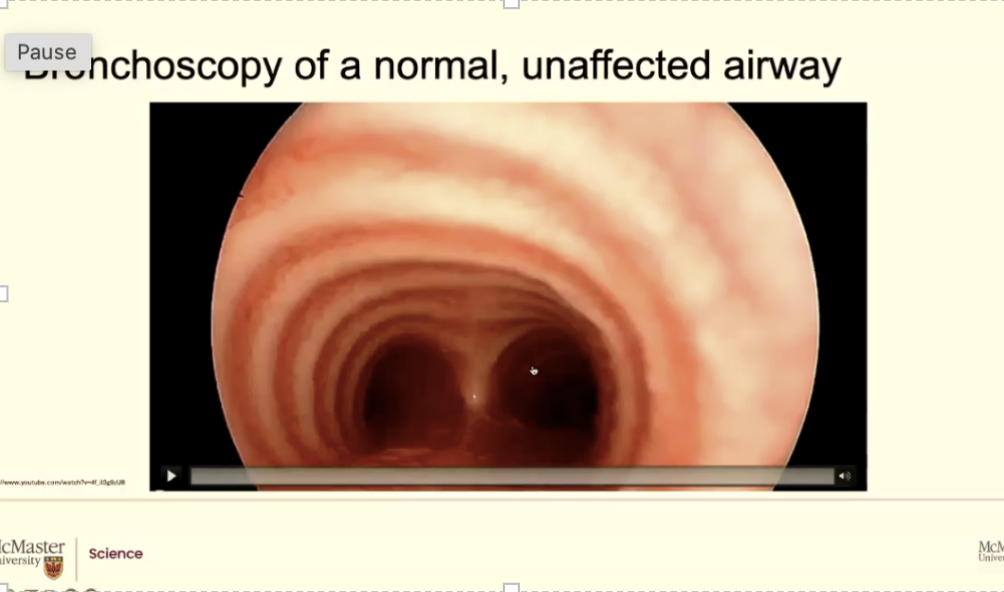
We use a type of endoscopy called bronchoscopy (same equipment as endoscope)
It goes down in the area in the airways, the trachea into the bronchi we call it a bronchoscopy technique
What you are doing is your able to go in as far as the thickest branch point of the lungs. So definitely through the voice box/larynx, through the trachea, down into the large left bronchus and then just where the bronchioles
start being visible (this is as far as you can go)
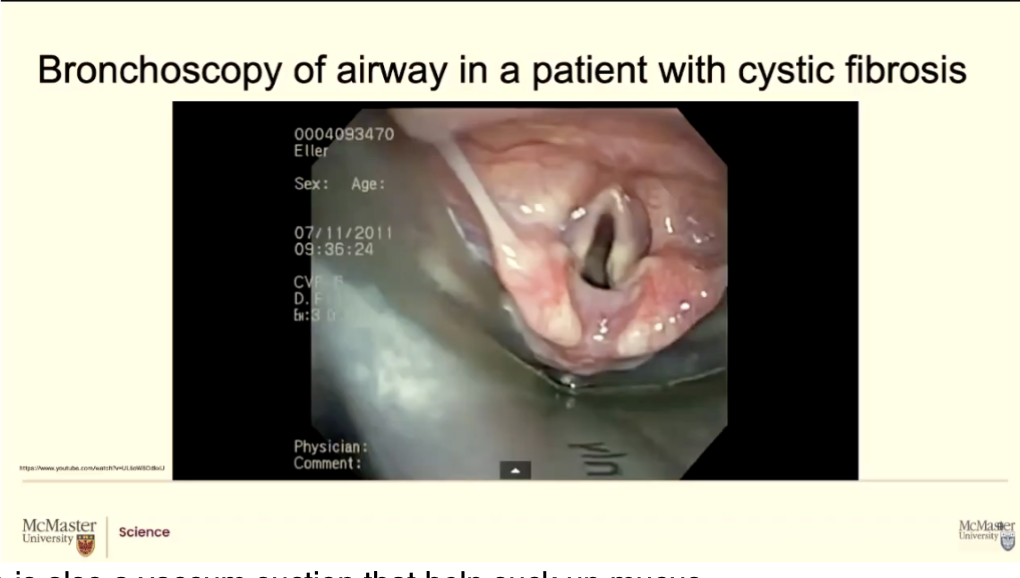
There is also a vaccum suction that help suck up mucus
What is our airways are made of?
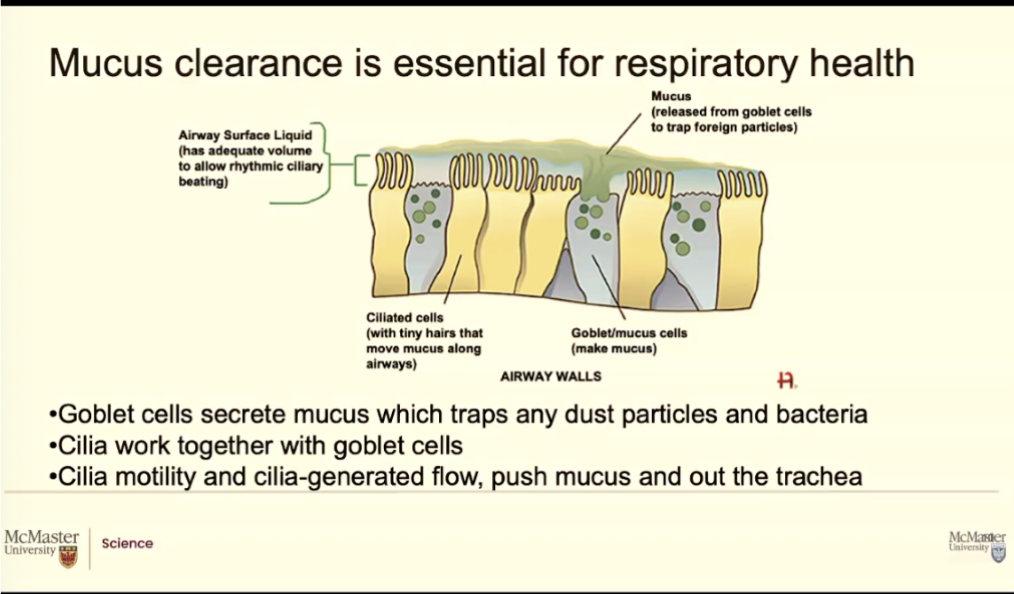
Our ariways are made of Epithelial cells and Goblet cells
What are Epithelial cells? What do they do?
Epithelial cells: Cells that stack up beside each other and make up the majority of the walls of ducts and goblet cells
They also have finger lie projections, that kinda move like microvilli of the intestine but they move in one direction (healthy people) they sweep fluid up, they help sweep mucus up
People with CF can't do this
Cillia can't beat in mucus
So between the ciliated cells and the mucus there is a layer called Airway surface liquid, which is just this liquidy region ( 7 microns in height) it's always going to be there to serve as a way for the cilia to beat in this very aqueous area
People with CF, this liquid is
compromised
What are Goblet cells? What do they do? What basement membrane?
Goblet cells: Mucus secreting cells
Their job is to make the musucs and secrete it out into the duct part, the open duct part
All of these cells are anchored at a membrane we call the basement membrane, like the basement of a house, its like the bottom floor
There is the partnership between globlet cells and epithelia
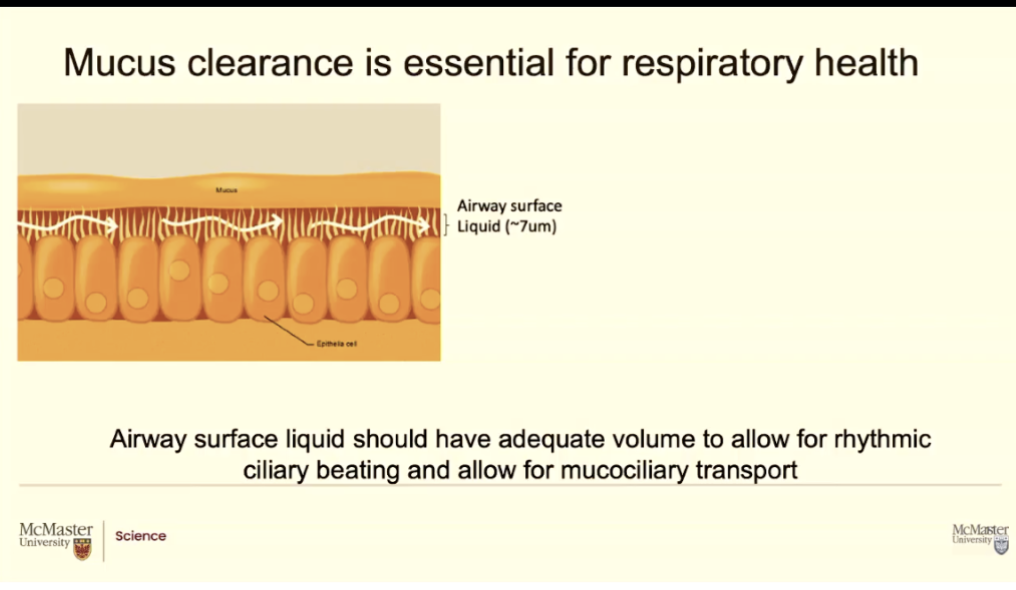
There is a partnership
Goblet cells release the mucus, mucus is sitting on top of this liquidy area, the aquesous area and the mususc is floating on top where the cillia produce and under current
The musuc rides the wave up into our upper airways then we spit it out
What caused CF?

They got DNA from people who have and don’t have CF and looked at all the DNA and Chromosomes
There were missing nucleotides that led to nucleotides being missing
There were sometimes nucleotides that caused the coding for an hydrophilic amino acid instead of hydrophobic
There is an array of different muations
It all came down to this...
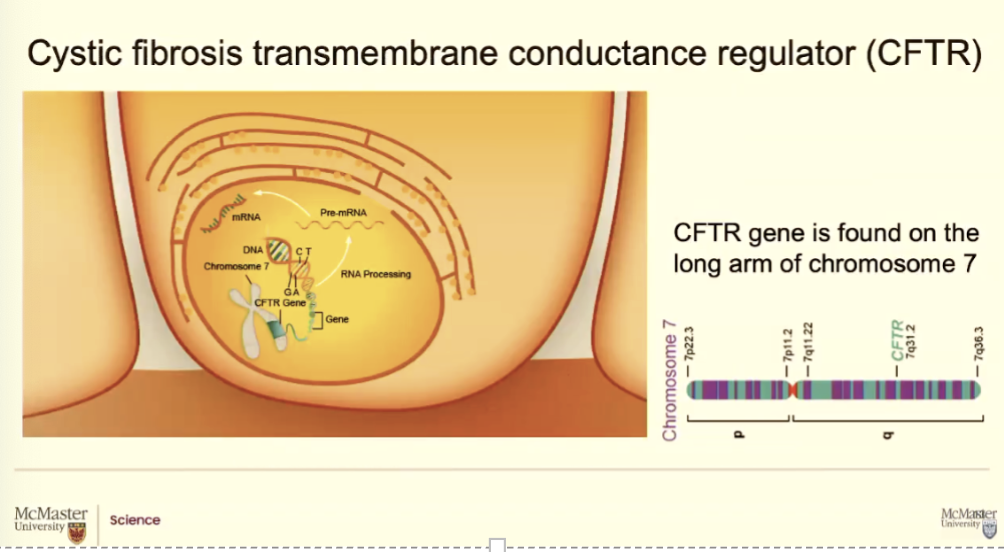
There is a mistake in patient with CF and you don’t see that in patients that don’t have CF and it sits on Chromosome 7
It is called Cystic Fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene (CFTR gene)
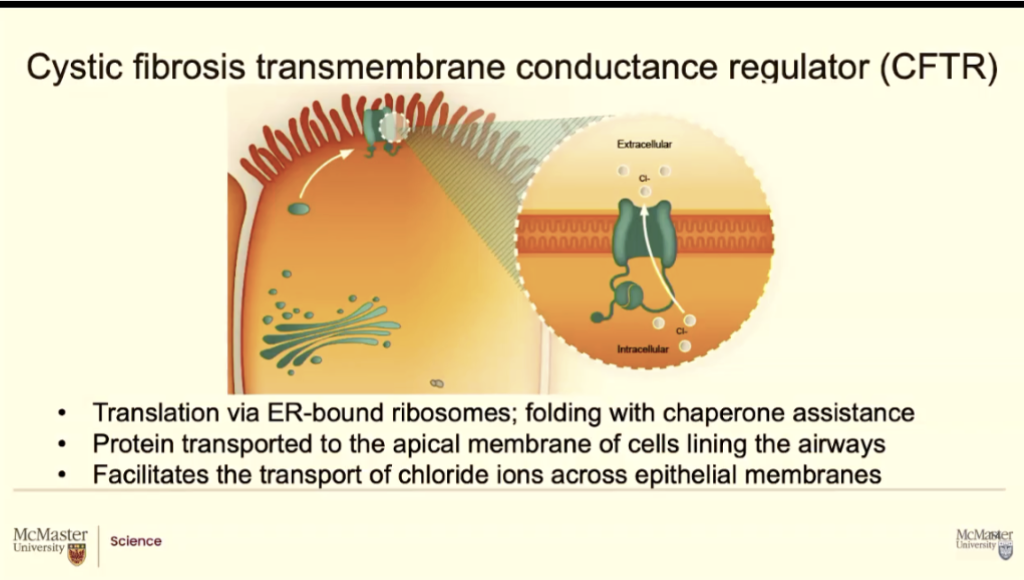
It codes for a protein and this gene gets transcribed and translation and becomes a importatn protein that goes through the endoplasmic reticulum and ends up at the top of those epithelial cells (like right beside those finger-like projections)
This protein that moves chloride ions form the inside of these cells to the outside they're like, how in the world does this?
Apical protein
See all the cells are anchored at the basement. The part of the cells that face the inside of the duct are called the apical part
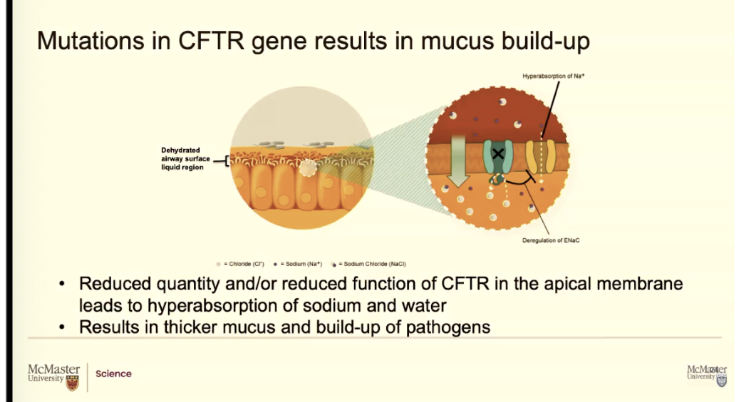
Why is CFTR important for airway clearance?
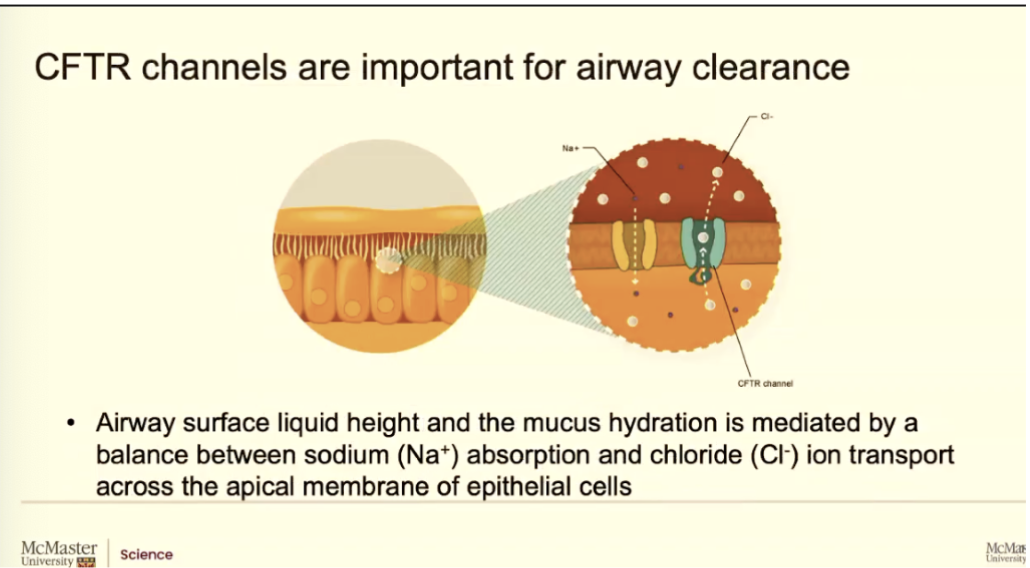
This chloride channel is super important because that’s its main role, but it also has a second role.
While it controls how much chloride it moves from the inside of the cell to the outside, like into the airway surface liquid aqueous region. It ALSO controls a special type of sodium channel and how much that sodium channel brings sodium into the cell
If it was not controlled by the chlorine channels (CFTR) they would take all the sodium form he airway surface liquid and just dump it into cells, nut that doesn’t happen
This protein normally controls how much chloride goes out by itself, how much sodium comes in by these nearby sodium channels, and because of that balance, there's enough water inside the cell. And that airway surface liquid height stays roughly 7 microns. So healthy airways, the CFTR protein has a really important role. It actually helps us maintain this aqueous height so our cilia can beat.
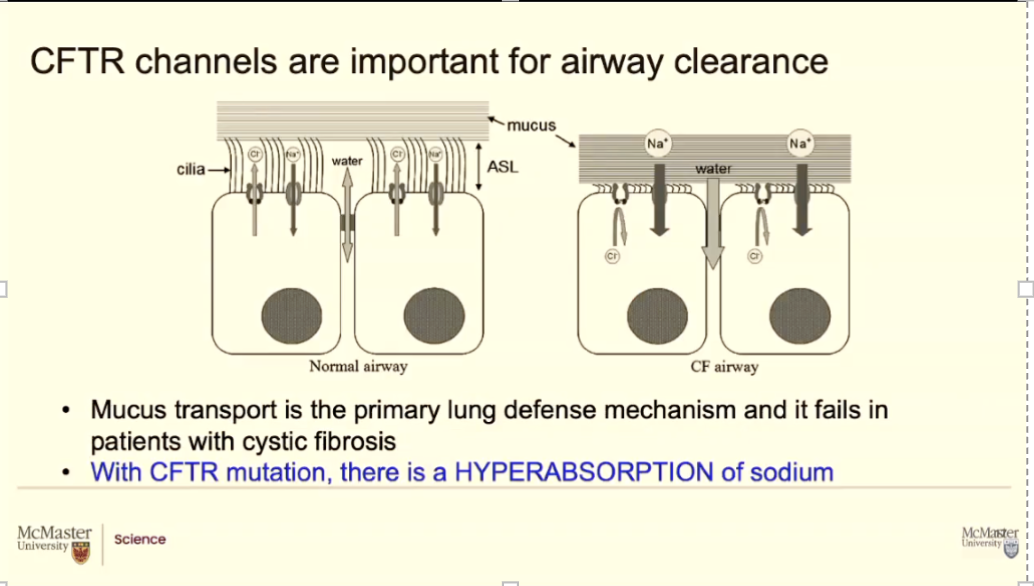
The CFTR channels, they're moving chloride out. That's their main job. Their second job is controlling these nearby sodium channels and how much sodium they bring in. With that, water is balanced. You got this nice 7 micron ASL airway surface liquid height region. The cilia are happy, they're beating, the mucus moves up.
Patients with cystic fibrosis, like I said, there's a mistake in the DNA code. That trickles down to the amino acid sequence that trickles down to how the protein folds. Soemtimes you don't get any CFTR proteins at all. If there is a mistake and the protein cant fold it, it may ever make it to the membrane OR if it does it isnt not working well.
It opens randomly or 25% of the time or 50% of the time (depends on how bad the mutation is)
If the CFTR protein isn't working, obviously chloride isn't moving, but the biggest problem for the airways and for all the symptoms we see is these sodium channels.
Remember I told you they're controlled by these CFTR proteins. So now there's no control. If CFTR protein isn't there or it's there but not really working. These sodium channels literally have a field day, just do this massive sodium dump from the ASL into the cell.
Now you suddenly have a high concentration of sodium inside that cell and water will follow
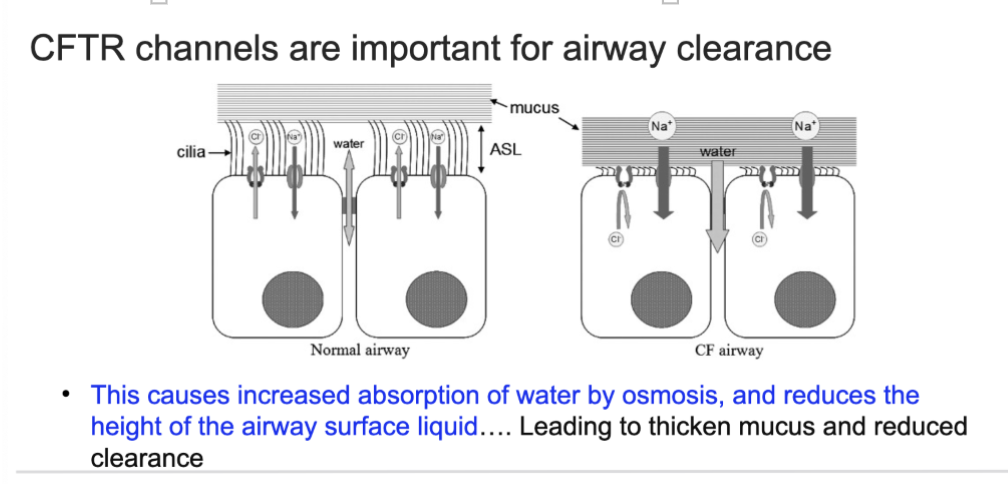
Why is that a problem?
The only liquid in the airway it’s the airway surface liquid height. SO if too much sodium gets drawn in the liquid form the airway surface liquid height decreases
Now the muscus is sitting directly on those finger like projections and they can't beat in mucus
The build-up of mucus can lead to pneumodia
Difference between healthy people and people with CF?
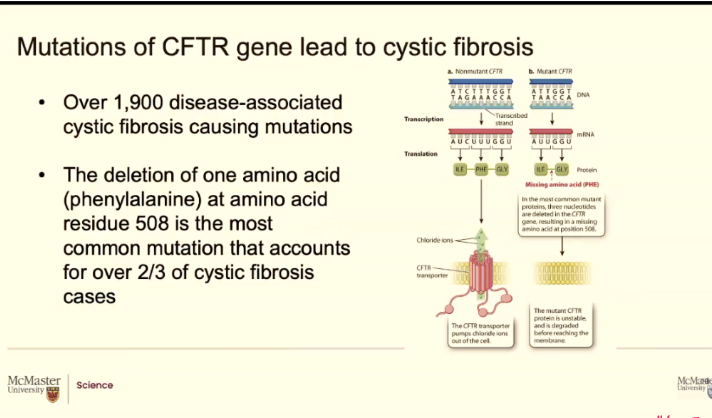
At the DNA level, we know at least 1900 different mutations that in the CFDR protein can cause cystic fibrosis.
Most common mutation is at amino acid 508 acids in the primary sequence (508 amino acids after methionine
Healthy people: 508 should be phenylalanine so 507 should be isoleucine and 509 should be glycine
CF: the patients don’t have phenylalanine is completely gone
So the 507 is still isoleucine but then 508 is glycine
So you're one amino acid short. This si going to hcange how protein fold. You now are missing completely one R group that influences how that protein folds
what is this image comparing? what does it mean?
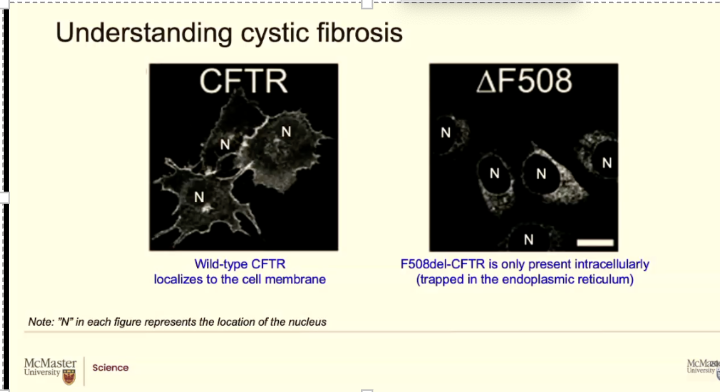
Triangle means change
F is the single letter abbreviation for phenylanine (PHE) the ginlge abbreviation is F
This is telling us that there is a change at phenylamine at the amino acid 508 and it had been deleted (there is nothing else after the 508)
Left is no mutation right is there is mutationN is the nuclus of 3 cells
CFTR is the membrane (fluorescently label a protein
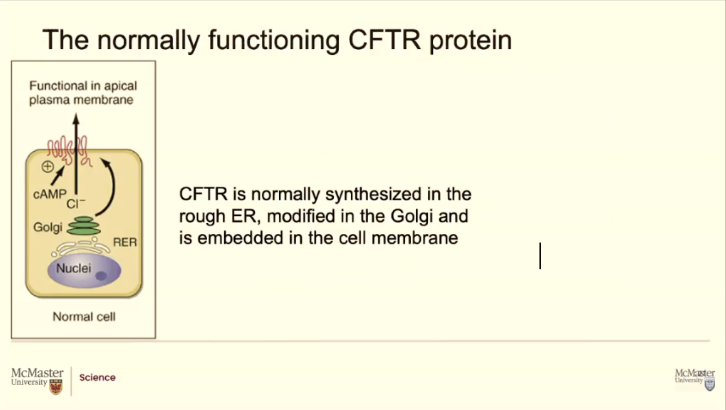
Normally its in the membrane doing its job
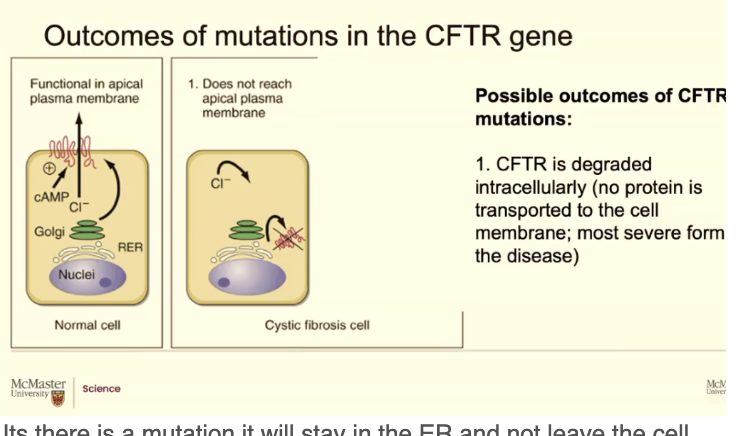
Its there is a mutation it will stay in the ER and not leave the cell
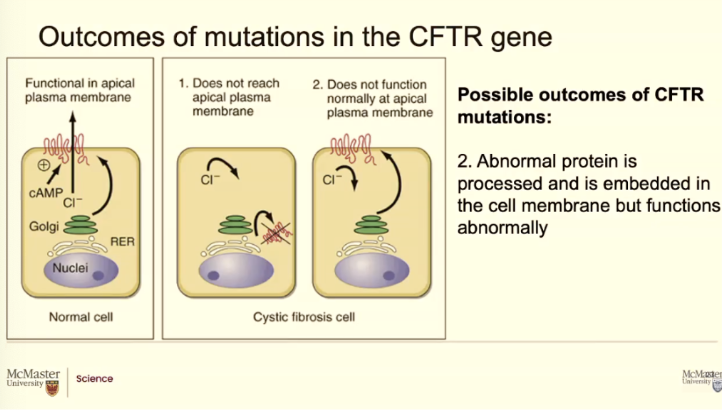
If the mutation isnt that bad it will let it go and it. Gets into the membrane put its not goin a good job
Opens randomly
what are possible therapeutics?
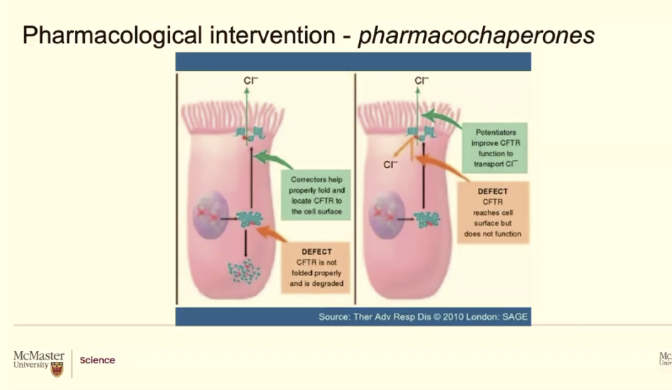
These are versions of chaperone proteins (called a)
Chaperone proteins are present in our cells
They are the ones that hold back proteins in the ER and try to fold these proteins or help the proteins fold
Organic chemists can make these in a labs that corrects the folidng
Medicinal chemists can make potentiators that target CFTR proteins that are at the membrane but are not working correclty
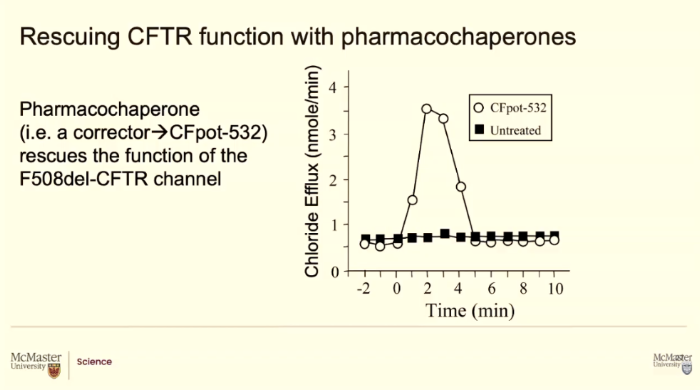
Test it on animals and cells
Use electrodes to measure chloride movment
Clear boxes shows moment

Lumacaftor
Acts like a wedge and keep the channel open. So even though they have a mutation that channel can go to the membrane and can function
Ivacaftor