HNSC 2170: Unit 9
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What are some valid reasons for taking a vitamin/mineral supplement?
Those who fail to obtain recommended amounts from diet, those with special needs (e.g., pregnant, elderly)
What is the definition of Natural Health Products as part of the Canadian regulations?
Products that include vitamins, minerals, herbal remedies, homeopathic medicines, and traditional medicines
What is the regulatory process for Natural Health Products in Canada?
Products must be licensed, undergo safety and efficacy assessments, and have proper labeling and packaging
What is the difference between enteral and parenteral nutrition?
Enteral nutrition is through the digestive system, parenteral nutrition is through the bloodstream
How is the decision made for selecting an appropriate feeding method?
Consideration of patient's condition, ability to tolerate oral intake, and nutritional needs
What are some ways to improve intake of oral supplements?
Taking with meals, using flavored supplements, breaking tablets if needed
What are the advantages and disadvantages of different tube feeding routes?
Nasogastric: easy insertion, risk of aspiration; Gastrostomy: more secure, requires surgery

What are the four main types of enteral formulas?
Standard, elemental, specialized, modular
What are the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of administering enteral formulas?
Bolus: quick, potential for intolerance; Continuous: steady infusion, requires pump
What are some complications that can arise with tube feeding?
Aspiration, tube dislodgement, infection
What is the difference between peripheral parenteral nutrition and total parenteral nutrition?
Peripheral: short-term, through a peripheral vein; Total: long-term, through a central vein
How are nutrients delivered in PPN (Peripheral parenteral nutrition)?
nutrients are delivered using only the peripheral veins
What are the complications with PPN?
Phlebitis if damaged by overly concentrated solutions
How is nutrients delivered with CPN (central parenteral nutrition)?
which relies on the larger, central veins where blood volume is greater and nutrient concentrations do not need to be limited.
What are the different components and compositions of parenteral solutions?
Amino acids, glucose, lipids, electrolytes, vitamins, minerals
What are some complications that can arise with parenteral nutrition?
Infection, metabolic imbalances, liver dysfunction
How is parenteral nutrition administered and metabolic complications managed?
Through a central line, monitoring blood glucose and electrolyte levels
What health conditions are associated with dysphagia?
Stroke, Parkinson's disease, head and neck cancer
What are some complications that can arise with dysphagia?
Malnutrition, dehydration, aspiration pneumonia
What are the various texture modifications as per the WRHA Adult Diet Compendium?
Soft, minced and moist, pureed, liquidized
What are some ways to improve acceptance of mechanically altered food?
Enhancing flavor, using appealing presentation
What are the various viscosity modifications as per the WRHA Adult Diet Compendium?
Thin, nectar-like, honey-like, spoon-thick

What is the better practice regarding supplements?
Make changes to diet first and take supplements only when truly needed.
Why is it important to ask patients about their nutritional supplements?
Supplements can interact with medications, foods, and other supplements.
What is an example of a food product that can interact with many medications?
Grapefruit juice.
What percentage of Canadians regularly take vitamins and minerals?
71%.
What are vitamins, minerals, herbal products, and homeopathic medicines collectively known as?
Natural Health Products (NHPs).
When did the regulations for Natural Health Products in Canada come into effect?
Jan 1, 2004.
What was the purpose of the regulations for Natural Health Products in Canada?
To increase safety and efficacy of NHPs on the market.
Who was involved in the consultation process for the regulations?
Consumers, academics, practitioners, and industry stakeholders.
What are the provisions included in the regulations?
Product licensing, site licensing, good manufacturing practices, adverse reaction reporting, clinical trials, and labeling.
What is the purpose of the pre-market review for NHPs?
To ensure that the label matches the product.
What types of products do the regulations apply to?
Vitamins, minerals, herbal remedies, homeopathic medicines, Chinese traditional medicines, probiotics, amino acids, and essential fatty acids.
What indicates that an NHP has undergone a review?
Natural Product Number (NPN) or Drug Identification Number - Homeopathic Medicine (DIN-HM).
What does the NPN or DIN-HM signify?
The product is safe and has passed formulation, labeling, and instructions review.
Are products from other countries required to meet these regulations?
No.
Are products available on the Internet required to meet these regulations?
No.
What assurance for safety do products from other countries or the Internet have?
None.
What is the purpose of product licensing?
To ensure the safety and quality of NHPs.
What is the purpose of site licensing?
To ensure that NHPs are manufactured in a safe and controlled environment.
What is adverse reaction reporting?
The requirement to report any negative effects of NHPs.
What are tube feedings?
Nutrient intake through a tube when unable to eat orally.
Who are candidates for tube feedings?
Individuals unable to meet nutrient needs orally.
- W/ GI bleeding, paralytic ileus or severe malnutrition
What are the main types of enteral formulas?
Standard, elemental, specialized, and modular formulas.
How is formula selection determined?
Based on medical condition, digestive capabilities, nutrient status, and tolerance.
What should be monitored during tube feeding?
Patient tolerance, nutrition, and metabolic parameters.
What are the types of feeding systems for tube feedings?
Open and closed feeding systems.
What should be ensured before starting tube feeding?
Correct placement and secure attachment of the tube.
What is the purpose of parenteral nutrition?
To provide nutrition intravenously.
What is parenteral nutrition?
Intravenous administration of nutrients.
When is parenteral nutrition indicated?
When gastrointestinal function is impaired.
What are the contraindications for parenteral nutrition?
GI tract functioning, short-term treatment, risks outweigh benefits, palliative care, patient instability, inability to obtain venous access.
What are the two methods of administering parenteral nutrition?
Peripheral and central.
How long is peripheral parenteral nutrition typically used for?
7-14 days.
Why are solutions for peripheral parenteral nutrition less concentrated?
To prevent damage to peripheral veins.
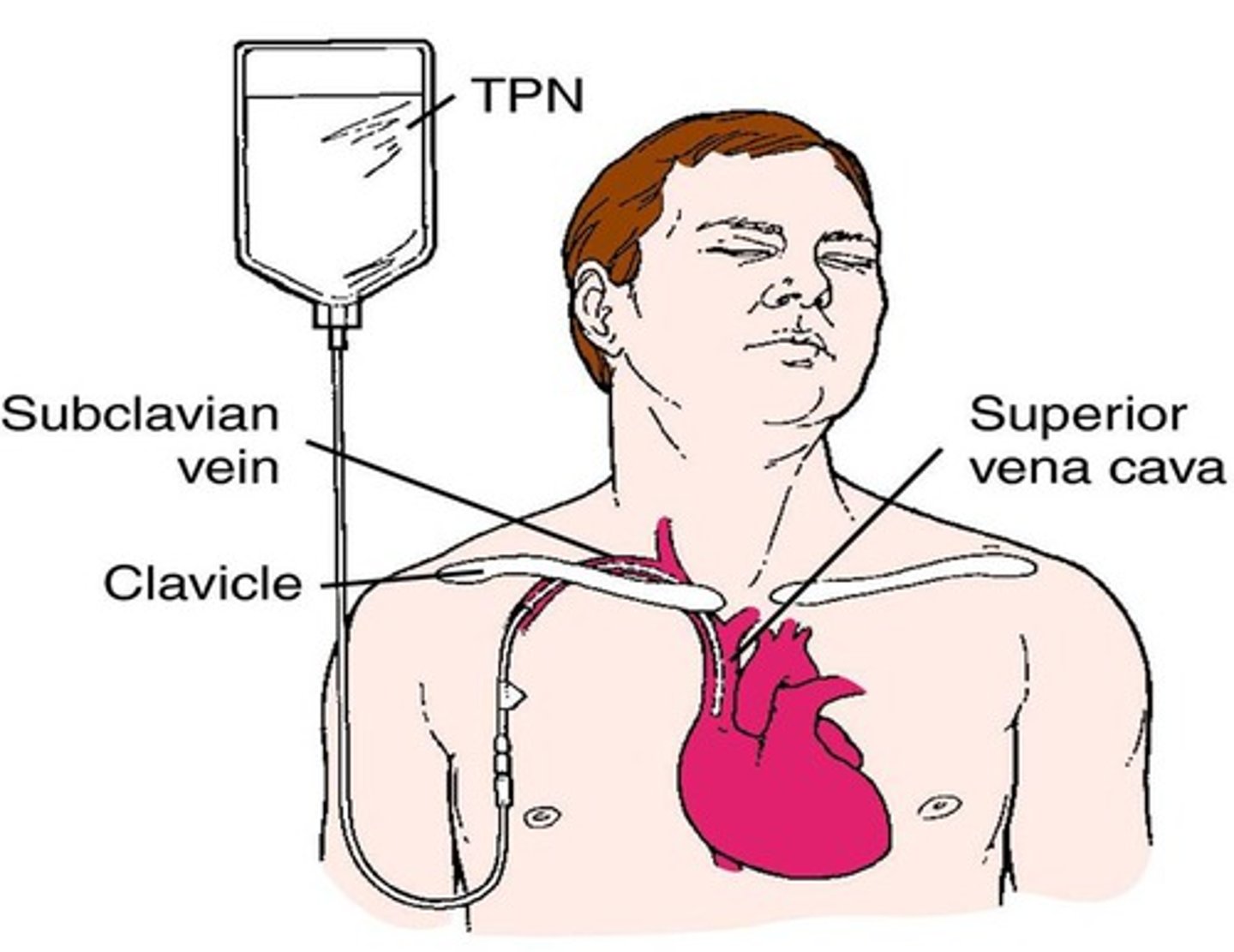
What is central parenteral nutrition also known as?
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
When is TPN usually used?
When parenteral nutrition is required long-term.
Why are solutions for TPN more concentrated?
To reduce the volume needed.
What is the maximum duration for short-term parenteral nutrition?
Usually less than 7 days.
What is the maximum duration for long-term parenteral nutrition?
More than 7 days.
How often can the prescriptions of parenteral solutions change?
Daily, if the patient's condition is unstable.
What are the two types of parenteral solutions?
2-in-1 and 3-in-1.
What does a 2-in-1 solution contain?
Dextrose and amino acids.
How is the lipid emulsion administered in a 2-in-1 solution?
Separately.
What does a 3-in-1 solution contain?
Dextrose, amino acids, and lipids.
How can parenteral nutrition be administered?
Continuously or cyclically.
What is refeeding syndrome?
A complication of parenteral nutrition in severely malnourished individuals.
What are the symptoms of refeeding syndrome?
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances, hyperglycemia.
What are the symptoms of dysphagia?
Drooling, choking, coughing, pocketing food, absent gag reflex, inability to suck from straw, chronic upper respiratory infections, weight loss/anorexia, gurgly voice quality.
What is the goal of nutrition interventions for dysphagia?
To ensure a nutritionally adequate and palatable diet in a safe consistency.
What are common management strategies for dysphagia?
Altering food texture and altering the viscosity of fluids.
What is the role of a speech language pathologist in the management of dysphagia?
They are part of the multidisciplinary team and assess and treat swallowing difficulties.
What is the role of a dietitian in the management of dysphagia?
They are part of the multidisciplinary team and provide nutrition interventions and ensure dietary adequacy.
What is the role of an occupational therapist in the management of dysphagia?
They are part of the multidisciplinary team and help with adaptive strategies for eating and drinking.
What is the role of a pharmacist in the management of dysphagia?
They are part of the multidisciplinary team and help with medication management for patients with dysphagia.
What is the purpose of altering food texture in dysphagia management?
To make it easier for the patient to swallow and prevent choking or aspiration.
What is the purpose of altering the viscosity of fluids in dysphagia management?
To make it easier for the patient to swallow and prevent choking or aspiration.
What are some ways to modify the texture of foods?
Minced, pureed, blenderized
What types of foods are typically easier to swallow?
Naturally soft and cohesive bolus foods
How can sauces and gravies help with swallowing?
Make foods easier to swallow and add calories
What are the different levels of thickness for fluids?
Thin, nectar thick, honey thick
Which type of fluid is the easiest to swallow?
Thickened fluids
How can nectar thick fluids be consumed?
Dripped off a spoon or sipped through a straw
How do honey thick fluids differ from nectar thick fluids?
They are thicker and do not hold their shape on a spoon
What are some examples of naturally soft and cohesive bolus foods?
Macaroni casseroles, egg dishes, meat loaf
Why are mixed texture foods more difficult to manage?
Because of the different textures
What are alternative feeding techniques for dysphagia?
Exercises to strengthen the tongue, new methods of swallowing, or changing positioning.
Soft Standard diet
Soft to chew foods
Soft / Minced
Includes plain minced meats

Minced
Includes minced meats, whipped/mashed fruits and vegetables
Standard diet, modified with minced meat/poultry
Includes minced meats, soft casseroles
Standard diet, modified with minced, whipped or mashed fruits and cooked vegetables
Includes minced, whipped or mashed fruits and cooked vegetables
Standard diet, modified with soft breads and baked products
Includes soft breads and baked products
Standard diet, modified with sandwiches with minced consistency fillings or cheese
Includes sandwiches with minced consistency fillings or cheese
Standard diet, modified with cream/stock soups
Includes cream/stock soups with soft/minced meat and vegetables
Total Minced
Includes minced entrees, minced/whipped/mashed cooked vegetables and fruits
Total Minced, exclusion of whole breads and baked products, cheese portions, cold cereals
Excludes whole breads, baked products, cheese portions, cold cereals
Pureed
Only liquid or pureed foods of smooth texture
Blenderized
Foods blenderized to a liquid form
Are all eggs compliant with a soft diet?
Yes, all eggs are compliant.