Transportation and depositional processes
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
4 ways of moving beach materials
Suspension: fine material such as clay and sediment is carried by the sea
Solution: dissolved minerals are carried by the sea
Traction: large boulders and pebbles are rolled along the sea bed
Saltation: small stones, pebble and silt bounces along the sea bed
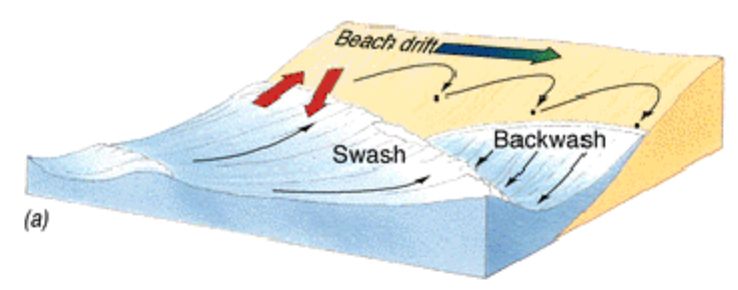
Beach drift
Sediment transported through the onshore and offshore movements by swash and backwash.
Sediment is moved onshore up the beach by swash obliquely (diagonally)
Sediment is moved down the beach by backwash perpendicular to the shoreline under the influence of gravity
Such zig-zag movement of sand, pebbles up and down the beach result in net lateral movement and transport of sediment along the shore.
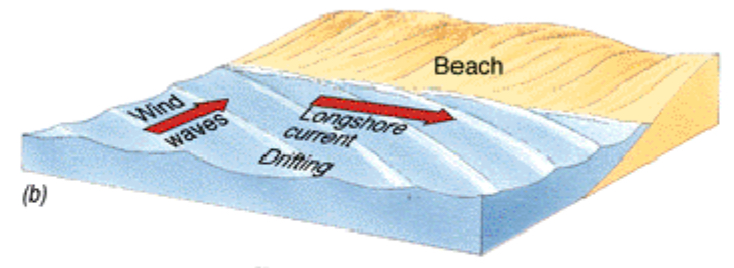
Longshore current
Ocean currents that flow parallel to the coast.
Sediment transport through movement along the coast.
It flows parallel to the shore in a direction away from the wind.
Sediments are hence transported in a direction parallel to the shore
Longshore drift
Both beach drift and longshore currents move sediments in the same direction and supplement each other.
The combined effect of sediment movement by longshore currents and beach drift is known as longshore drift
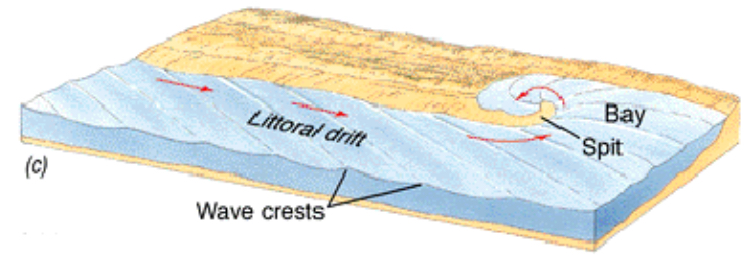
Spit
A narrow ridge of sand or shingle deposited by longshore drift at a sharp or abrupt turn to the coastline or across the mouth of a river.
One end of the spit is anchored to the mainland while the other end is free and projects into the sea.
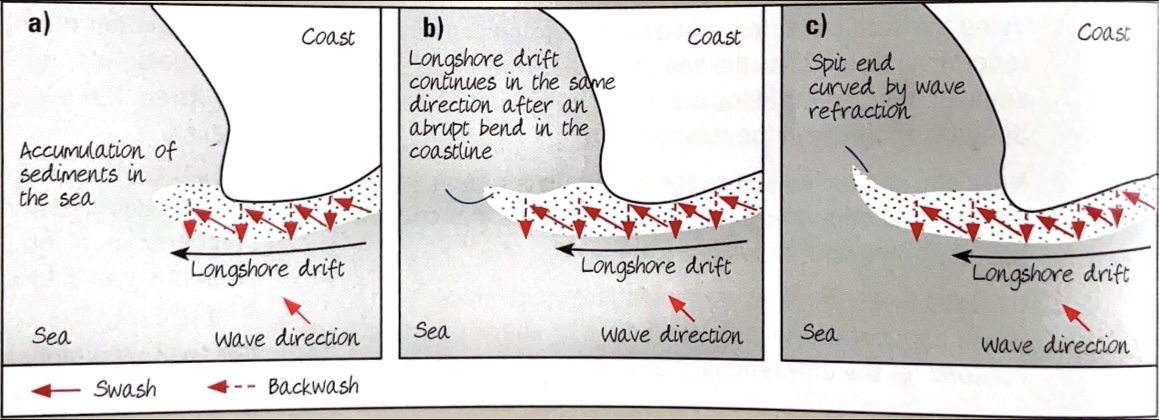
How are spits formed?
The occurrence of longshore drift running parallel to a relatively straight coast, causes beach materials to be laterally transferred towards the wind direction, even at the coastline, due to strong prevailing wind. As slack water occurs at the turn, the waves lose energy and deposit the sand or shingle in the form of a ridge.
How are hooks formed?
A spit can grow and extend into deeper water, and wave refraction cases the free end to be curved towards the land.
Possibly enclosing a water body to form a lagoon
Tombolo
When a spit extends seawards and joins up an offshore island to another island or the mainland.

Bar
A narrow ridge of sand and/or gravel lying parallel to the coast.
It is deposited by waves across a shallow bay with gentle offshore slope and sheltered offshore waters.
Both ends are free ie not attached to the land.
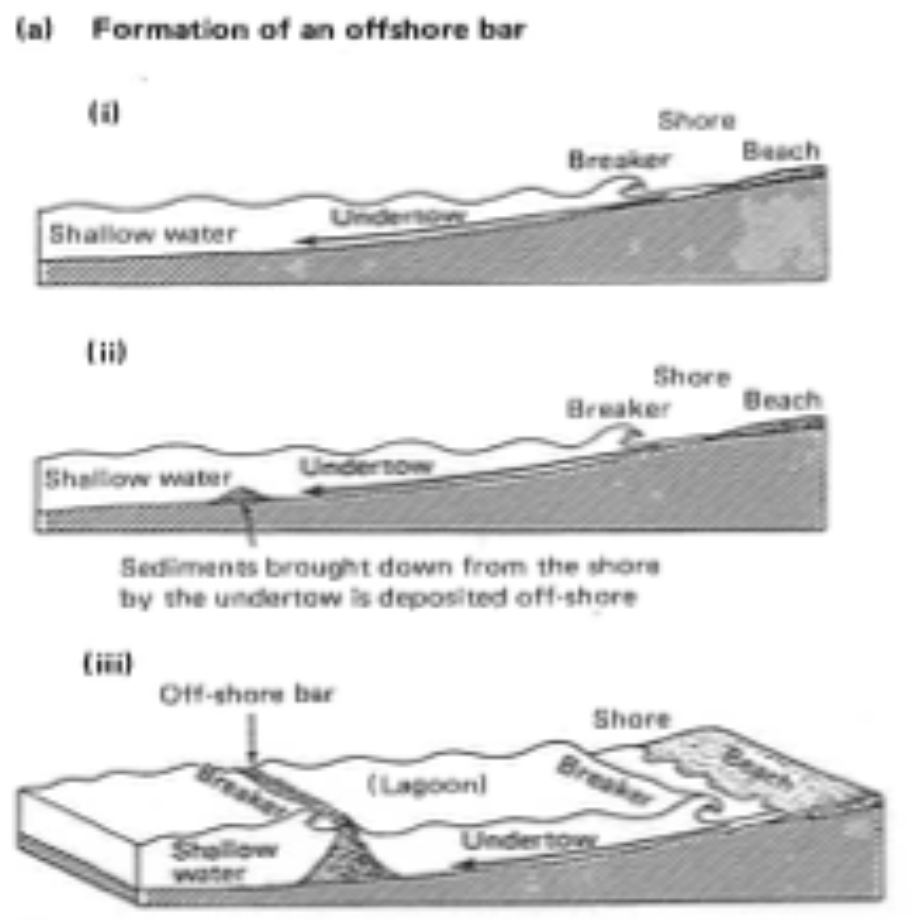
How are offshore bars formed?
Waves pick up and transport sediment from the shore and deposit it further out at sea.
As waves lose energy, they drop the sediment, forming a ridge of sand or shingle parallel to the coast.
Continued deposition may cause its ends to extend to join the land to form a lagoon