Basic Genetic Principles (Cram)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
The basic physical unit of inheritance consisting of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) at a specific location (locus) on a chromosome. These determine inherited characteristics
Gene
One of a number of long strands of DNA and associated proteins present in the nucleus of every cell. It is the storage unit of genes
Chromosome
Note: These come in pairs
The collection of genetic information
Genome
Nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions specifying the biological development of all cellular forms of life
DNA (deoxyribonucleuic acid)
Why are beefalos (bison x cattle) fertile and mules (donkey x horses) not fertile?
Bison and cattle have the same number of paired chromosomes (30 pairs), while donkeys (31 pairs) and horses (32 pairs) have a different number
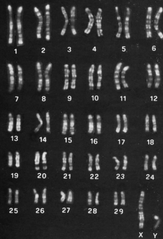
Refers to the chromosome complement of a cell or whole organism. It shows the number, size, and shape of the chromosome as seen in the metaphase of mitosis
Karyotype
What test can be preformed with a blood sample (WBC), fetal skin cells, or bone marrow to determine total number of chromosomes, the sex of the person being studied, and if there are any structural abnormalities with any of the individual chromosomes
Karyotype analysis
Fill in the blank: DNA found within cells is wound tightly around _____ in assemblies called _______. They resemble beads in a string along each chromosome.
proteins, nucleosomes
Normal number of complete chromosomes (2n)
Euploidy
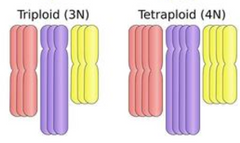
Increased number of complete chromosomes (3n or 4n)
Polyploidy
Whole chromosome missing or empty
Aneuploidy
Chromosome abnormality that is compatible with life (2n+1)
Trisomy
Note: Cause of down syndrome in humans
Autosomal chromosome abnormality that is incompatible with life (2n–1)
Monosomy
Which numerical abnormality causes spontaneous abortion?
Polyploidy
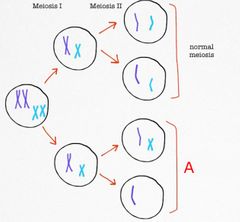
Label the condition indicated by A in this diagram
and Chromosone nondisjunction
What is this condition? It affects animals and humans, and results in a defect in the gene for the protein dystrophin, which has a structural role in muscle. Females carry the gene, but generally only males are affected
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Note: It is ultimately fatal
The specific location of a gene on a chromosome
Locus (plural: loci)
One pair of chromosomes having corresponding loci
Homolog
If the gene for hair colour is denoted by the letter "b", what does it mean when the letter is written in uppercase vs. lowercase?
There is a chemical and functional difference between them. Uppercase indicates a dominants gene, and lowercase indicates a recessive gene
Example: B denotes black hair colour, and b denotes red hair colour
An alternate form of a gene (ie. B is a different form of b, but they are both genes for hair colour)
Allele
Note: An animal inherits two alleles for every gene. For example a blue eye and a brown eye gene, though only one is expressed
True or false: There can be more than two possible alleles at a locus. If true, provide some possible examples.
True
Example: BB, Bb, or bb
The combination of genes at a single locus or a number of loci
Genotype
Example: BB is one genotype and Bb is another
A one-locus genotype containing functionally identical genes
Homozygote
Example: BB or bb
A one-locus genotype containing functionally different genes
Heterozygote
Example: Bb
Any observable or measurable characteristic of an individual
Trait
Example: Hair colour or weaning weight
An observed category or measured level of performance for a trait of an individual
Phenotype
Example: If the hair colour is red, red would be the phenotype
Fill in the blank: In the process of meiosis to form a sperm cell or an ovum, ___ [#] gene will be incorporated into each germ cell.
1
What is this law called: Genes assort independently during meiosis if all possible gametes are formed in equal proportions
Law of independent assortment
The random process which determines which ovum matures and which sperm succeeds infertilizing the ovum
Gamete selection
A two-dimensional grid used to determine the number of possible zygote genotypes from a mating
Punnett square
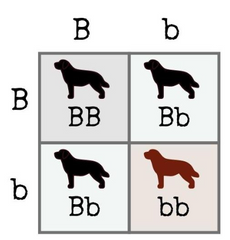
A form of dominance in which the expression of the heterozygote is identical to the expression of the homozygous dominant genotype
Complete dominance
Example: BB and Bb will both be expressed as black hair colour
A form of dominance in which the expression of the heterozygote is intermediate to the expressions of the homozygous genotypes
Partial dominance
Example: Short horn cattle come in red, roan, or white. RR = red, Rr = roan, and rr = white
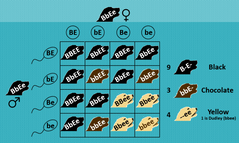
An interaction among genes at different loci such that the expression of genes at one locus depends on the alleles present at one or more other loci
Epistasis
Example: Labs come in yellow, brown, and black. The colour is determined by the genes at two loci, B and E.
The application of biological knowledge to practical needs. These include technologies for altering reproduction, and technologies for identifying, comparing, locating, or otherwise manipulating genes (“genetic engineering”)
Biotechnology
Name some examples of reproductive technologies
Artifical insemination, embryo transfer, estrus synchronization, superovulation, in vitro fertilization, cloning, embryo spitting, nuclear transplantation, and same sex mating
Name some examples of molecular technologies
DNA fingerprinting, marker assisted selection, gene map, gene transfer, transgenics, and chimerias
What is an exampe of a chimeria?
Sheep and goat, not a hybrid, but combining goat and sheep embryos in a lab. Some of its cells are sheep and some are goat

A reproductive technology for producing genetically identical individuals
Cloning
What is a technique for cloning that occurs when the zygote (embryo) divides into two by natural or artifical means?
Cloning by embryo splitting
When a zygote divides into two by natural means, what are the offspring called?
Identical twins
What is a technique for cloning that occurs whenova are matured in vitro, then the nuclei are removed surgically. Individual cells from a multi–cell embryo are then inserted into each egg, producing a number of identical embryos
Nuclear transplantation
Which technique of cloning can produce an unlimited number of identical offspring?
Nuclear transplantation
The science of manipulating genes that carryhereditary information
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering technology that involves taking a segment of DNA from a plant or animal cell, and transferring it to another cell to combine with the new cell’s DNA
Recombinant DNA
Note: Examples of uses include synthetic insulin, bacteria that can clean up oil spills, and genetically modified food
Fill in the blank: In recombinant DNA technology, ______ enzymes recognize a specific sequence in the DNA code and cut the strand of DNA at specific locations. The fragment of DNA cut out is said to have _____ _____ so that they can be inserted into the chromosome of another individual or species.
restriction, cut out
Which enzyme is part of the rejoining process in recombinant DNA technology?
Ligase