EVST-101 Midterm
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Environmental Science
Study of humanity’s relationship with other organisms and the physical environment
Environmental Studies
•Interdisciplinary field combining information from many areas:
•Biology, chemistry, physics, geology, ecology, atmospheric sciences,
•Cultural Anthropology, sociology
•Natural resource management, Agriculture
•Engineering
•Law and Politics
•Humanities – ethics, theology, art, theatre, music, literature
Environmental Sustainability
Ability to meet humanity’s current needs without compromising the ability of future generations
Multidimensional Poverty
a person lives in a household deprived in a third or more of ten indicators, grouped into three dimensions of well-being
Three Dimensions of Multidimensional Poverty
health (using two indicators: nutrition, child mortality), education (using two indicators: years of schooling, school attendance), and living standards (using six indicators: cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, assets)
Highly Developed Countries
•Complex industrialized base
•Low rates of population growth
•High per person incomes
Moderately Developed Countries
•Medium levels of industrialization
•Per person incomes lower than highly developed countries
Less Developed Countries
•Low levels of industrialization
•High rates of population growth
•High infant mortality rates
•Very low per person incomes relative to highly developed countries
Ecological Footprint
Amount of productive land, fresh air and water, and ocean required on a continuous basis to supply that person with food, wood, energy, water, housing, clothing, transportation, and waste disposal
IPAT
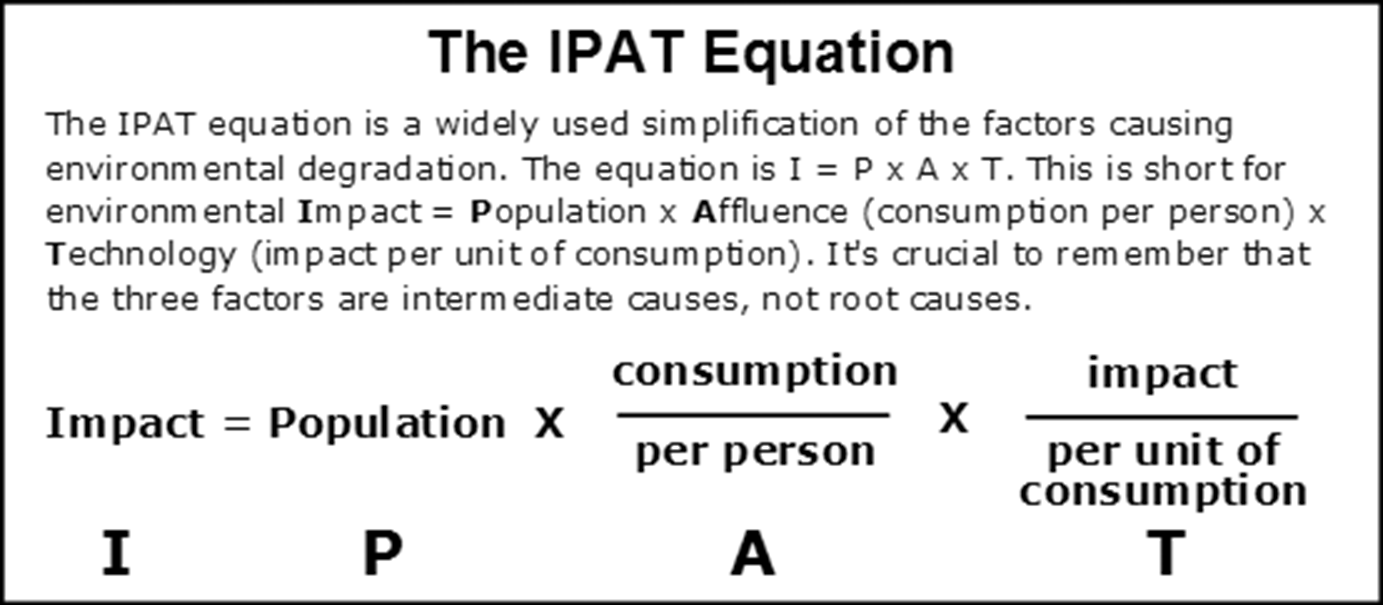
Theory
Integrated explanation of numerous hypotheses
Steps to Address Environmental Problems
1.Scientific Assessment
2.Risk Analysis -
3.Public Engagement
4.Political Considerations
5.Long-term environmental management
NIMBY
Not in my backyard
Ecology
The study of one’s house
Organism
A single individual
Population
Individuals of the same species in the same habitat
Community
Populations of several species in one habitat
Ecosystem
A habitat’s community and its abiotic factors
Landscape
The patchwork of ecosystems across a large area
Biosphere
All landscapes inhabited by living organisms on Earth
Producers
plants & photosynthetic organisms - use photosynthesis to absorb radiant energy à chemical energy
Consumers
“eat” other organisms; primary, secondary, and tertiary
Decomposers
break down dead organisms and waste products; e.g., bacteria and fungi
Transformation
•Potential energy è kinetic energy + heat
•Energy is linear, always a one way road…
•Usable energy (low entropy, organized) is decreasing over time
•While unusable energy (high entropy ex. low-temperature heat) is increasing
Remember energy itself is not decreasing, but usable energy
1st Law of Thermodynamics
A physical law which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, although it can change from one form to another.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
A physical law which states that when energy is converted from one form to another, some of it is degraded into heat, a less usable form that disperses into the environment.
Matter
matter, the material of which organisms are composed, moves in numerous cycles from one part of an ecosystem to another—from one organism to another and from living organisms to the abiotic environment and back again
5 Important Cycles
1.Carbon
2.Hydrologic
3.Nitrogen
4.Sulfur
5.Phosphorus
Parasitism
As an example of symbiosis, a parasite rarely kills its host, but rather lives with it and weakens it over time
Predation
A predator kills and then feeds on the dead organism. Therefore, over time, a predator will kill many organisms in order to feed itself and live
Ecology
Study of one’s house
Biome
large relatively distinct terrestrial region with similar climate, soil, plants, and animals
Tundra
the treeless biome in the far north that consists of boggy plains covered by lichens and small plants such as mosses; it has harsh, very cold winters and extremely short summers
Boreal Forest
a region of coniferous forest in the Northern Hemisphere, located just south of the tundra
Temperate Rainforest
a coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog, and high precipitation. Temperate deciduous forest is a forest biome that occurs in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation
Temperate Grassland
grassland with hot summers, cold winters, and less rainfall than is found in the temperate deciduous forest biome
Chaparral
a biome with mild, moist winters and hot, dry summers; vegetation is typically small-leafed evergreen shrubs and small trees
Desert
a biome in which the lack of precipitation limits plant growth; deserts are found in both temperate and tropical regions
Savanna
tropical grassland with widely scattered trees or clumps of trees
Tropical Rainforest
lush, species-rich forest biome that occurs where the climate is warm and moist throughout the year
Thermal Stratification
•Temperature changes with depth
•Fall and Spring turnovers for nutrient cycling; a function of the properties of water
•Cool, dense water
•Warm , less dense water
Eutrophication
•Natural process
•Exacerbated by human activities such as:
•Agricultural runoff
•Discharge of treated and untreated sewage
Flowing Water Ecosystem
•Highly Variable due to size
•Sunlight
•Strength of current
•Groundwater
•Inhabitants vary accordingly
•Human Threats
•Pollution
•Dam construction
Freshwater Wetlands
•Marshes (grasslike plants) and Swamps (woody trees or shrubs)
•Excellent wildlife habitat
•Soils waterlogged, anaerobic,
•Discourage decomposition
•Control flooding, groundwater recharge and purifier
•Major threats are pollution, development, agriculture, and dam construction
Brackish Ecosystem (Estuaries)
•Coastal freshwater river ecosystem with access to open ocean water
•Salt Marsh - temperate
•Mangrove Forest – tropical
•Fluctuating water levels and salinity (tidal, time of year, precipitation, and location in estuary)
•Major Human threat is coastal development
•Pollution – e.g., oil spills
•Unsustainable logging
Intrinsic Value
in contrast to instrumental value (extrinsic), it is the value of anything in and of itself rather than usefulness to humans
Evolution
Cumulative genetic changes in populations that occur during successive generations
Natural Selection
The tendency of better-adapted individuals—those with a combination of genetic traits best suited to environmental conditions—to survive and reproduce, increasing their proportion in the population
Succession
Community response to changing conditions
Primary Succession
•Previously uninhabited environment (e.g., glacial retreat)
•Lichens most important element in pioneer community
•Lichens → mosses → grasses → shrubs → trees
Secondary Succession
•Change in species composition following some destructive disturbance (i.e, soil present)
•Clearcut, wildfires, development, abandoned farmland,
crabgrass → horseweed, broomsedge, and other weeds → pine trees → hardwood tree
Population Ecology
r = (b - d) + (i - e)
Where growth rate (r) is the rate of change (increase or decrease) of a population’s size, expressed in percentage per year. On a global scale, growth rate is due to the birth rate (b) and the death rate (d): r = b – d. Emigration (e), the number of individuals leaving an area, and immigration (i), the number of individuals entering an area, also affect a local population’s growth rate
Biotic Potential
the maximum rate a population could increase under ideal conditions. (e.g.., larger organisms how lower BP)
Exponential Population Growth
the accelerating population growth that occurs when optimal conditions allow a constant reproductive rate for limited periods
Environmental Resistance
unfavorable environmental conditions that prevent organisms from reproducing indefinitely at their biotic potential, eventually, leads to a decrease in the growth rate to around zero or becomes negative
Carrying Capacity (K)
the largest population a particular environment can support sustainably (long term) if there are no changes in that environment
Demographic Transition
The process whereby a country moves from relatively high birth and death rates to relatively low birth and death rates
Infant Mortality Rate
the number of deaths of infants under age 1 per 1000 live births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
the average number of children born to each woman
Replacement-Level Fertility
the number of children a couple must produce to “replace” themselves
Age Structure
the number and proportion of people at each age in a population
•Helps predict future population growth.
•Highly Developed Countries – declining fertility rates, elderly pop. increases
•Developing Countries – younger age structure means higher-than-replacement-rate fertility rates
Culture and fertility
•Total fertility Rate correlation with infant/child mortality
Social and Economic Status of Women
•The single most important factor affecting high TFRs is the low status of women. The governments of many developing countries are trying to limit population growth.
•Education of women decreases the total fertility rate, in part by delaying the first childbirth. Education increases the likelihood that women will know how to control their fertility. Education also increases women’s career options, which provide ways of achieving status besides having babies.
Urbanization
the process whereby people move from rural areas to densely populated cities. In developing nations, most people live in rural settings, but their rates of urbanization are rapidly increasing
Rapid Urbanization
makes it difficult to provide city dwellers with basic services such as housing, water, sewage, and transportation systems
Compact Development
the design of cities so that tall, multiple-unit residential buildings are close to shopping and jobs, and all are connected by public transportation
Sustainable Consumption
The use of goods and services that satisfy basic human needs and improve the quality of life, but that also minimizes resource use
Sustainable Development
Economic growth that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
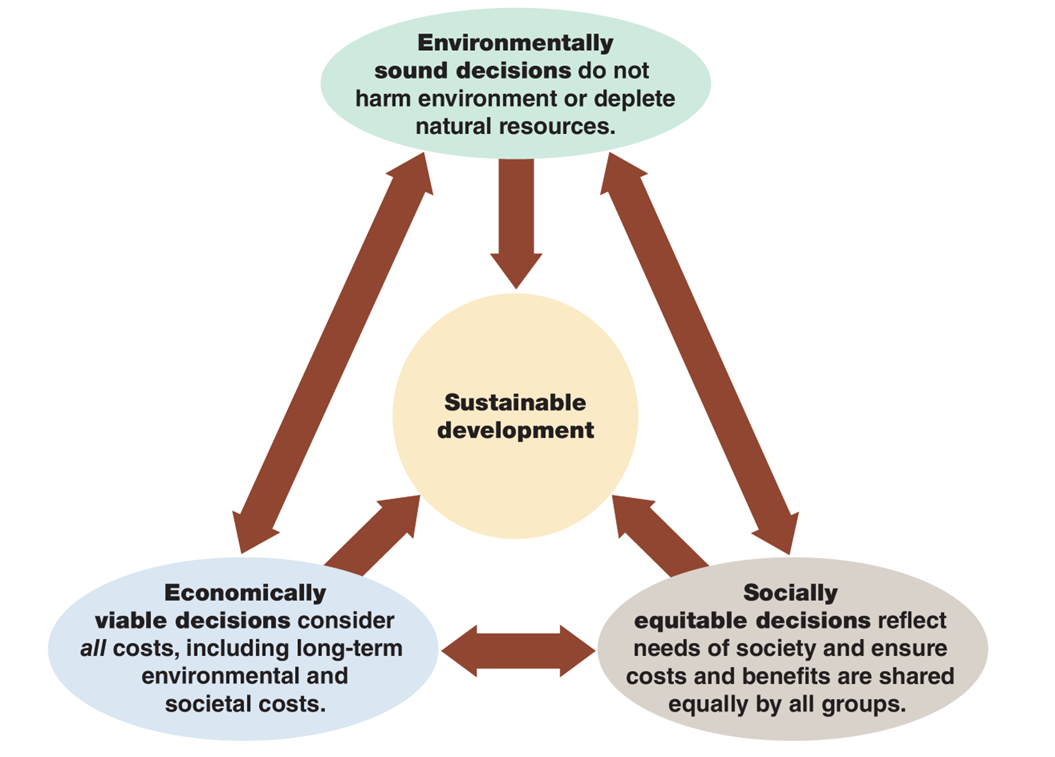
Environmental Ethics
Considers the moral basis of environmental responsibility; how humans should relate to the natural environment
Environmental Worldviews
A worldview based on how the environment works, our place in the environment, and right and wrong environmental behaviors
Western Worldview
A worldview based on human superiority over nature, the unrestricted use of natural resources, and economic growth to manage an expanding industrial base.; Human-centered and utilitarian; emphasizing instrumental value; As we will see in the Environmental History chapter, there are many examples of individuals and groups who are “Western,” but also have an environmental worldview.
Environmental Justice
The right of every citizen to adequate protection from environmental hazards
Overall Plan for Sustainable Living
•Eliminate poverty and stabilize the human population.
•Protect and restore Earth’s resources.
•Provide adequate food for all people.
•Mitigate climate change.
•Design sustainable cities.
Biodiversity
The number and variety of Earth’s organisms; consists of three components: genetic diversity, species richness, and ecosystem diversity
Genetic diversity
the genetic variety within all populations of that species
Species Richness
number of different species in a community
Determined by:
•Abundance of ecological niches - Closeness to the margins of adjacent communities - Geologic history
•Inversely related to Geographic isolation - Habitat stress - Dominance of one species over others
Ecosystem Diversity
variety of ecosystems found on Earth and the variety of interactions among organisms in natural communities
Ecosystem Services
important environmental benefits such as clean air, clean water, and fertile soil that the natural environment provides
Endangered and Extinct Species
•Current extinction rate is 100-1000 times the natural background rate
•Characteristics of Endangered species that make them vulnerable to extinction:
•Extremely small (localized) range
•Requiring large territory
•Living on islands, low reproductive success (small population size or low reproductive rate)
•Requiring specialized breeding areas
•Specialized feeding habits
The Red List Categories
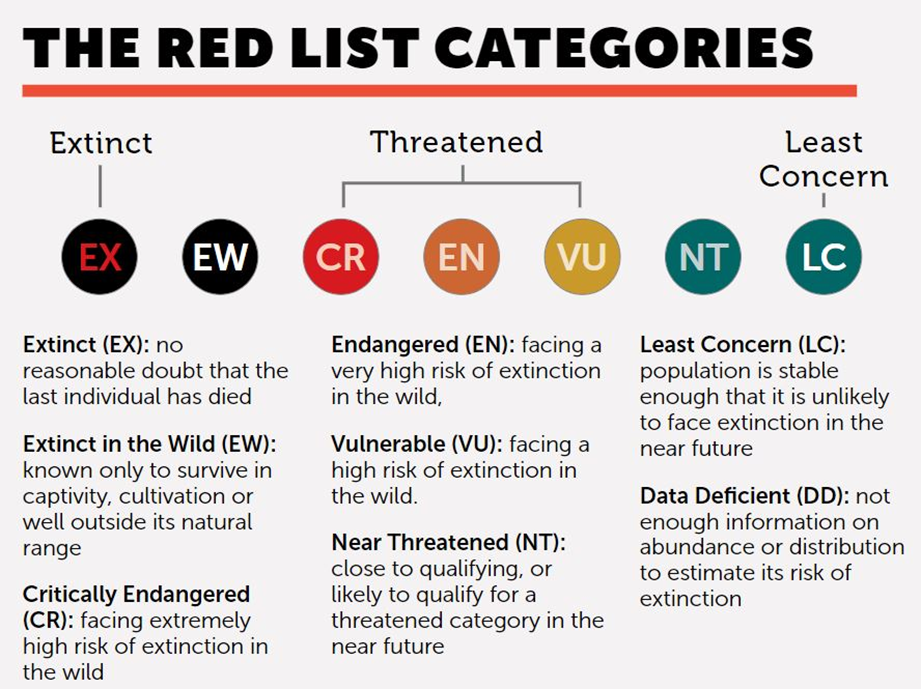
Biodiversity Hotspots
Relatively small areas of land that contain an exceptional number of endemic species and are at high risk from human activities
Habitat Loss – territorial and aquatic
•Destruction – human built environment, clear cut logging, mining, dams, draining water, outdoor recreation, agriculture
•Fragmentation – small isolated patches; islands
•Degradation
Pollution
•Acid precipitation and ozone depletion
•Industrial and Agricultural chemicals
•Organic pollutants from sewage
•Acid min drainage
Spread of Invasive Species
•Foreign species that spread rapidly in a new area if free of predators, parasites, or resource limitations that may have controlled their population in their native habitat.
•Brown Tree Snake in Guam – island vulnerability – birds, mammals, and reptiles either threatened or extinct in nature
Overexploitation
•Eradication or control of certain species
•Unregulated hunting/overhunting
•Illegal commercial hunting/poaching
•Commercial harvest and pet trade
Conservation Biology
study of how humans affect organisms and of the development of ways to protect biological diversity
In Situ Conservation
•Wildlife Refuges, Parks and Reserves, Conservation Land (nonprofits)
•Habitat Corridors
•Restoration ecology
Ex Situ Conservation
•Focused on saving threatened species
•Zoos
•Seed Storage of genetically diverse plant crops
US Endangered Species Act (ESA, 1973)
•Legal protection to listed species to reduce their danger of extinction
•Proposed changes
•Redefinition of “harm” to not include habitat modification and degradation.
•Streamlining emergency measures
Environmental Policy Making
requires attention to ethics, economics, culture, and politics
Economics
managing a household or environment; "the study of how people use their limited resources, given the assumption that each person strives to satisfy unlimited wants."
Natural Capital
Earth’s resources and processes that sustain living organisms, including humans; includes minerals, forests, soils, water, air, wildlife, and fisheries
National Income Amounts
measures the total income of a nation‘s goods and services for a given year; currently calculations do not include natural resource depletion or environmental degradation
External Cost (externalities)
harmful environmental and social cost that is borne by people not directly involved in selling or buying a product
Marginal Cost of Pollution
monetization (added cost) of additional units of pollution; injury, death, loss of species and other damages must be assigned dollar values
Marginal Cost of Pollution Abatement
added cost of reducing one unit of a given type of pollution
Optimum Amount of Pollution
amount of pollution that is economically most desirable
Command and Control Regulation
pollution control laws that work by setting limits on levels of pollution
Incentive-Based Regulation
an economic tool that forces producers to internalize external costs achieving optimum amount of pollution by establishing emission targets and providing incentives to reduce emissions
Environmental taxes
according to economic theory, when a company has to pay an amount equivalent to the damage they cause, it will find lower cost ways to reduce pollution instead.