Low effort easy marks
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
5 chemicals required for life
Water
Carbon (food)
Nitrogen (DNA, RNA, amino acids/proteins)
Phosphorous (ATP)
Sulphur
Which nitrogenous bases are purines/pyrimidines and how many hydrogen bonds between them all?
Purines (double ring structure): Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines (single ring structure): Cytosine and Thymine/Uracil
3 hydrogen bonds: Guanine and Cytosine
2 hydrogen bonds: Adenine and Thymine/Uracil
What direction is DNA replicated/RNA synthesised?
5’ to 3’ with new nucleotides being added at the 3’ end
Examples of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
glucose
fructose
galactose
ribose
Disaccharides
maltose
sucrose
lactose
Polysaccharides
starch
cellulose
glycogen
Name the bonds between monomers of macromolecules
Nucleotides: Phosphodiester bond
Polysaccharides: Glycosidic bond
Triglyceride (3 fatty acid chains bound to glycerol): Ester bond
Polypeptides: Peptide bond
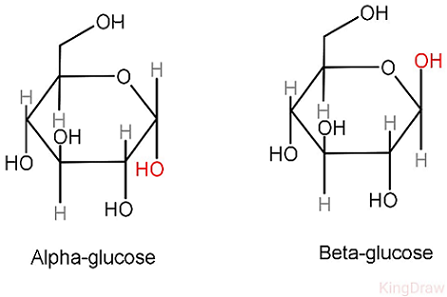
Compare and contrast the isomers of glucose
Alpha glucose: hydroxyl group below
Makes up glycogen, starch
Beta glucose: hydroxyl group above
Makes up cellulose
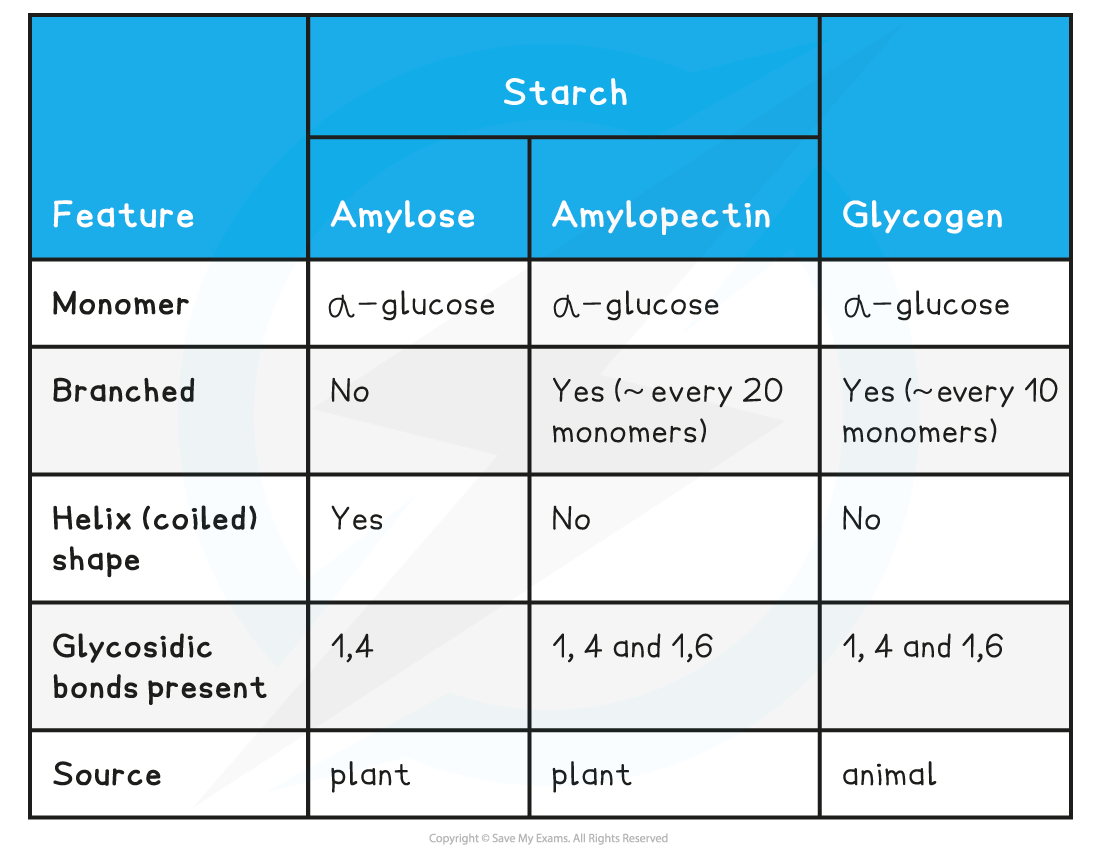
Compare and contrast the different types of starch
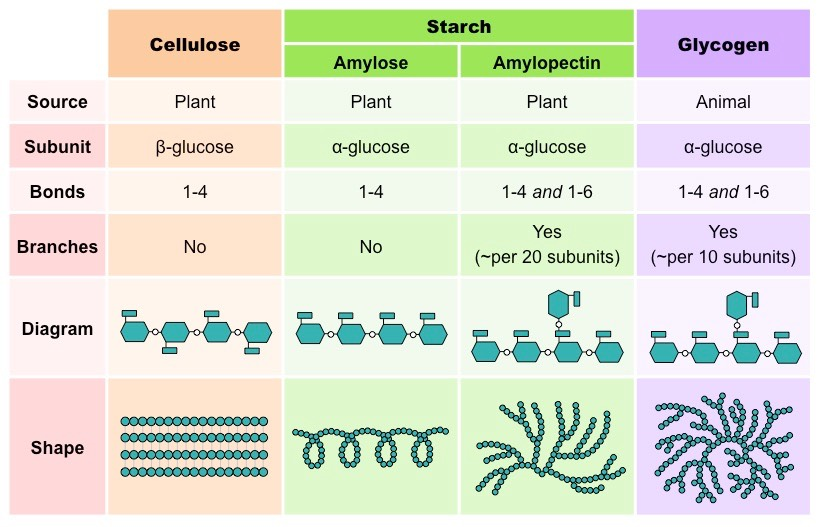
Describe cellulose
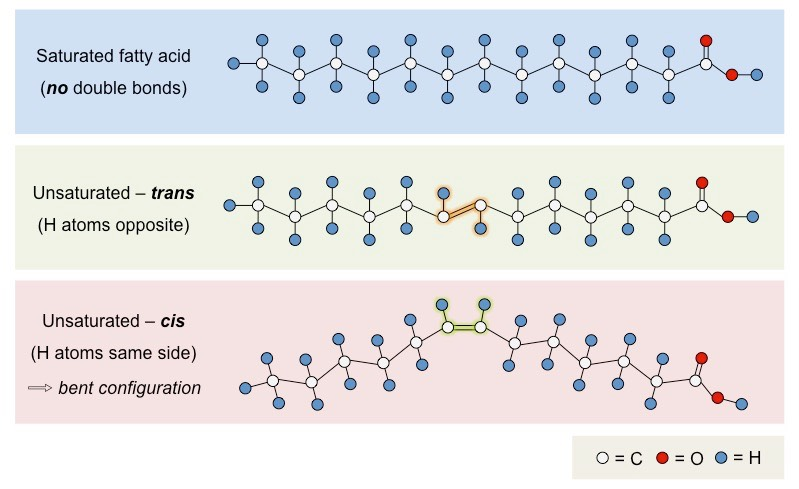
Compare different types of fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids (no double bonds)
Unsaturated fatty acids (double bonds in hydrocarbon chains)
Mono (one double bond) vs poly (multiple double bonds)
Cis (hydrogen on the same side) vs trans (hydrogens have opposing orientation)
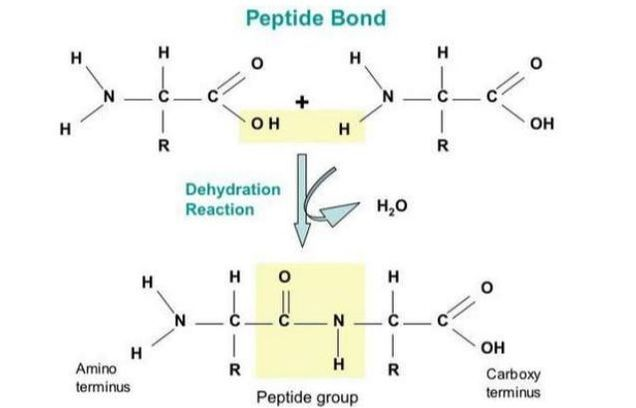
Draw and label a diagram of a peptide bond between two amino acids
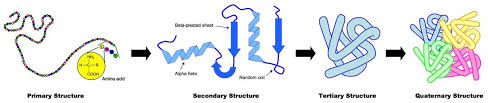
List the bonds in each structure of proteins
Primary: peptide bonds (polypeptides)
Secondary: hydrogen bonds (alpha helix vs beta pleated sheet)
Tertiary: disulfide bridges (covalent), hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions (between R groups to achieve 3D structure)
Quaternary: Bonds between multiple polypetide chains
Conjugated: combine with non amino acid material
Non conjugated: only made up of amino acids
What happens to proteins in different pH and temperatures?
Low pH: Denaturation
High pH: Denaturation
Low temp: Inactive
High temp: Denaturation
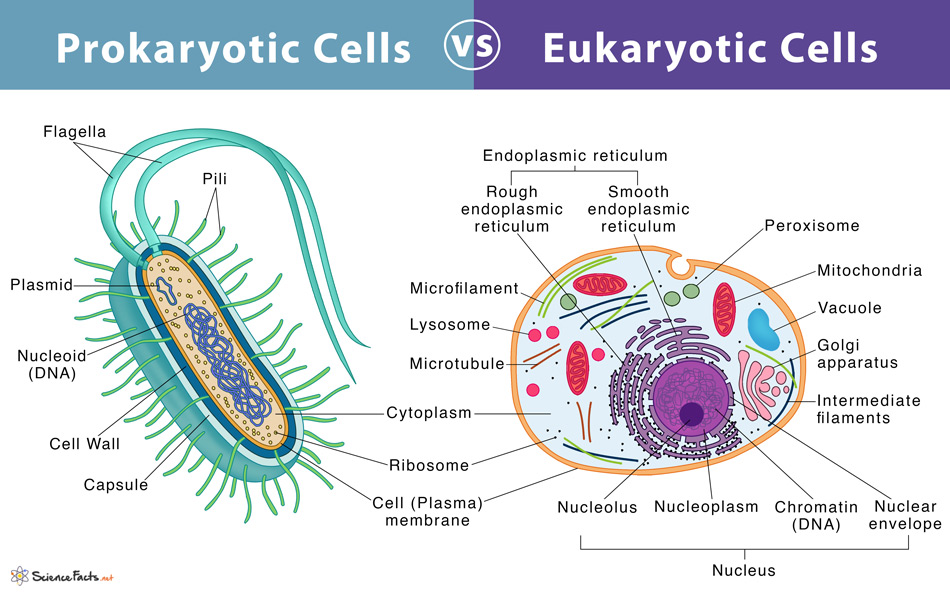
Identify organelles found in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
All living things have:
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Cytosol
DNA
Ribosomes
List different types of membrane proteins
Integral proteins: Embedded in lipid bilayer, ampiphatic, mostly transmembrane but some are only on one side
Channel proteins: Form channels/pores for membranes to pass through
Carrier proteins: Undergo conformational change to transport molecules
Aquaporins: hydrophilic inside channel to allow for transport of water molecules without need for osmosis
Peripheral proteins: Hydrophilic, membrane surface
Receptors: receive chemical signals and act as binding sites (for hormones or neurotransmitters)
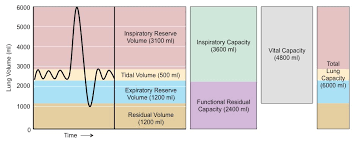
Define ventilation terms
Total lung capacity: Total volume of air in the lungs after taking the biggest breath
Forced vital capacity: After taking the biggest inhale, how much of that air you can exhale
Residual volume: The amount of air your lungs must have in them to avoid collapse
Tidal volume: Volume of air that moves in and out of lungs in a normal breath
Inspiratory reserve: Difference between tidal volume and total lung capacity
Expiratory reserve: Difference between tidal volume and residual volume
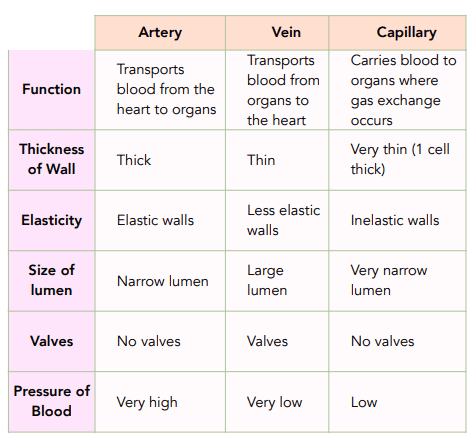
Compare arteries, veins and capillaries
Describe the two different types of speciation
Allopatric: speciation in different environments (geographical isolation)
Sympatric: speciation within the same environment (temporal isolation or behavioural isolation)
Describe adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiation: Common ancestor splitting into multiple species due to different variations exploiting different ecological niches.
Minimises competition
ex: Darwin’s finches developing different shaped beaks in line with the food source on their island
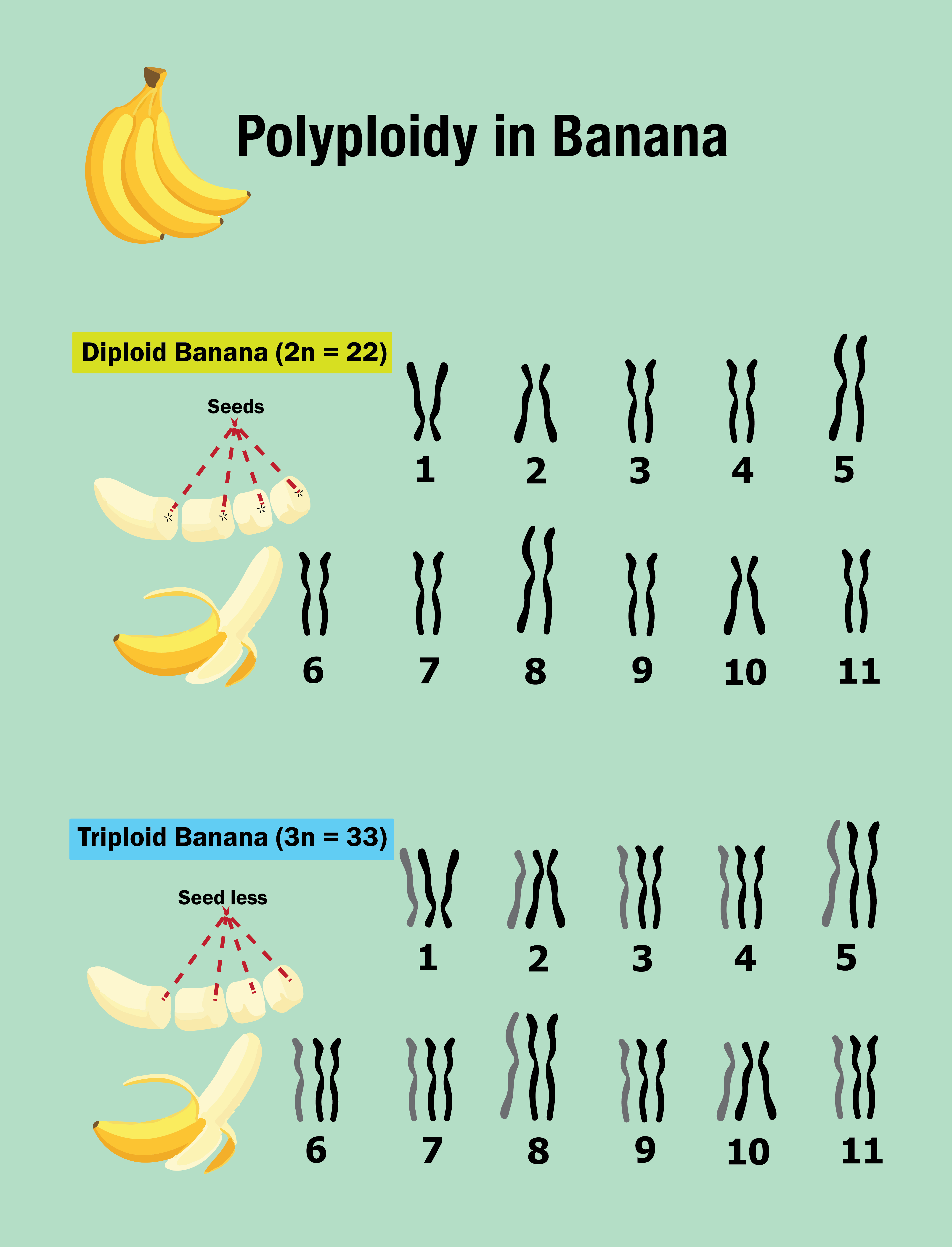
Describe polyploidy
Polyploidy: When homologous chromosome sets contain more than two (are not diploid)
Define anthropogenic
Anthropogenic: Caused by humans
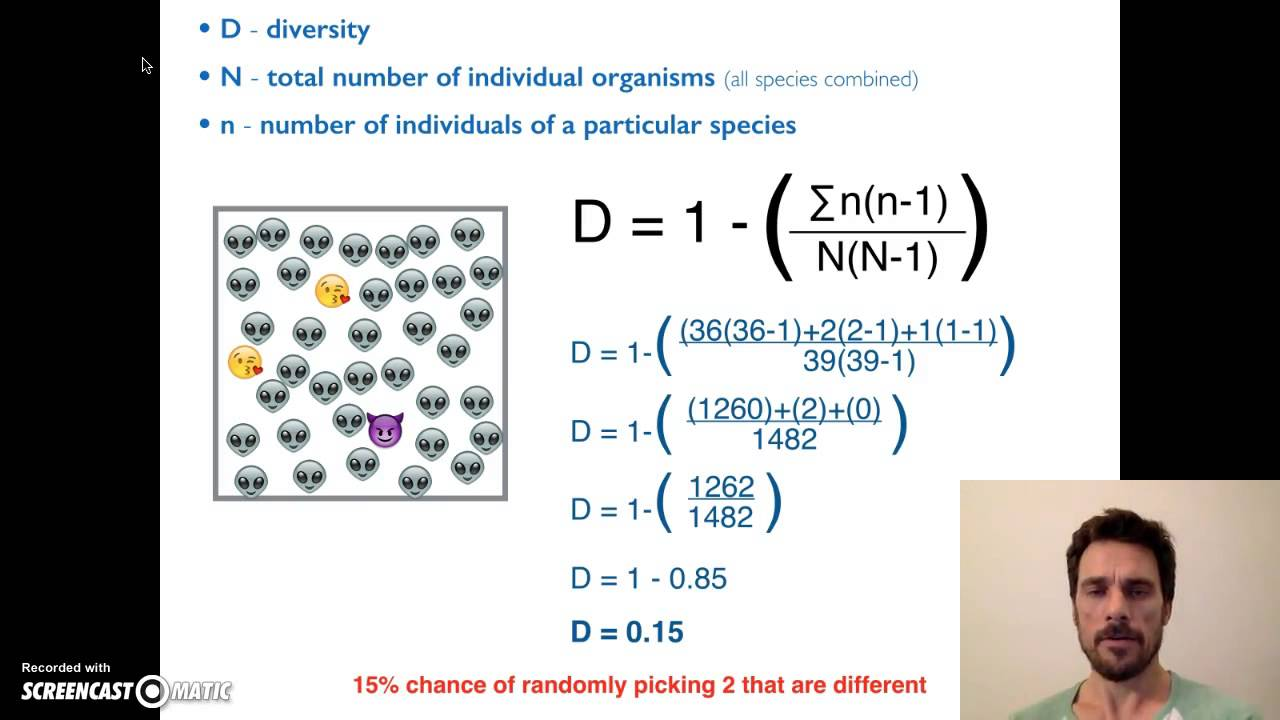
Describe formula for Simpson’s Diversity Index
High index when there is a high
Richness (lots of different species)
Evenness (not dominated by one species)
Direction of DNA processes
DNA sense/coding strand 5’ to 3’
DNA antisense/template strand 3’ to 5’
DNA read in 3’ to 5’ direction for transcription (antiparallel to the mRNA being synthesised in a 5’ to 3’ direction)
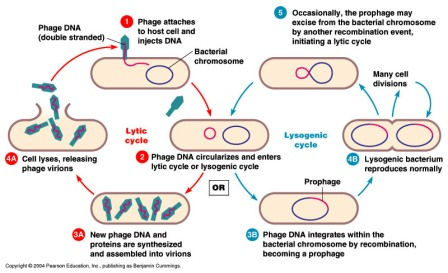
Lytic vs lysogenic cycle of the bacteriophage lambda
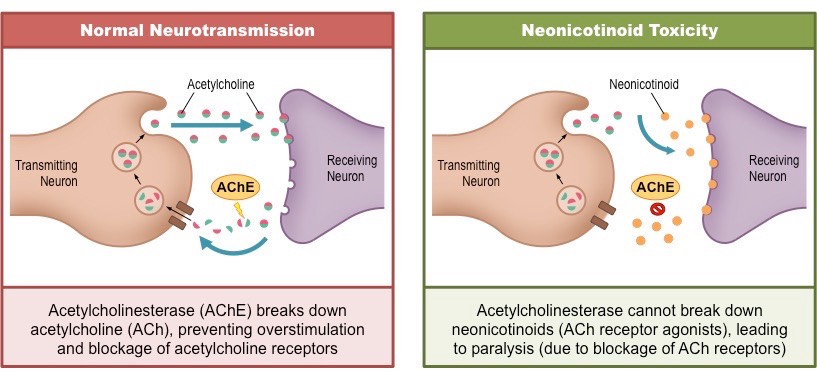
Neonicotinoid effect on neural signalling
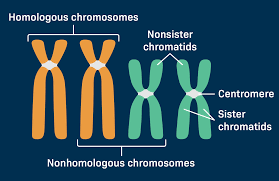
Sister chromatids vs homologous chromosomes
Sister chromatid: identical copies of a single chromosome
created during DNA replication, and are joined at the centromere
Homologous chromosomes: pair of chromosomes
one inherited from each parent
same size, shape, and genes
but may carry different versions (alleles) of those genes
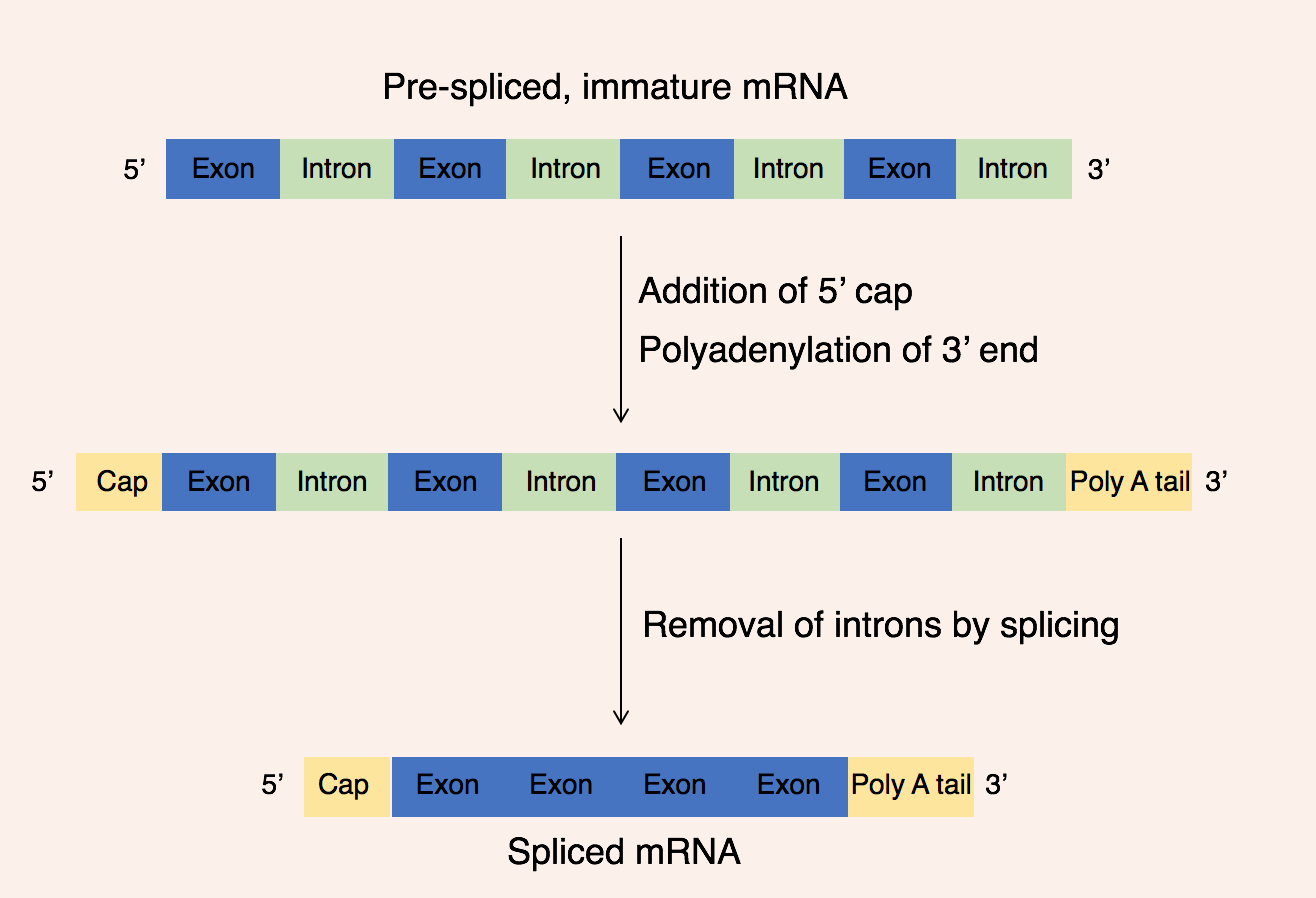
Describe mature mRNA
Mature mRNA is a product of post transcription modification in the nucleus
5’ cap and poly A tail added
exons spliced together
The poly A tail slows the rate of degradation
Describe epigenetic tags
Epigenetic tags: Chemical modifications that cause some genes to be activated and others to be silenced.
Doesn’t affect the gene itself, just the pattern of gene expression
Facilitates differentiation as all cells have the same genome but their function is dependent on their expression
Can be passed to offspring
Describe methylation
Methylation: A type of epigenetic tag that involves the addition of a methyl group
Methylation of the promoter region of a gene inhibits transcription
Methylation of histone proteins can change how available DNA is to transcription factors
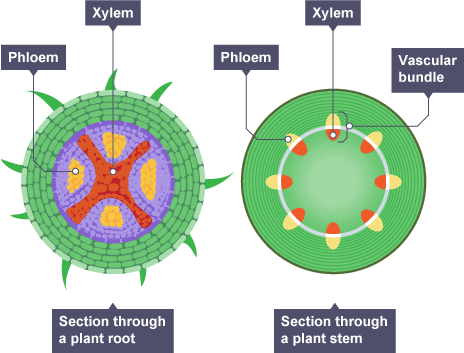
Xylem and phloem in plant root vs plant stem
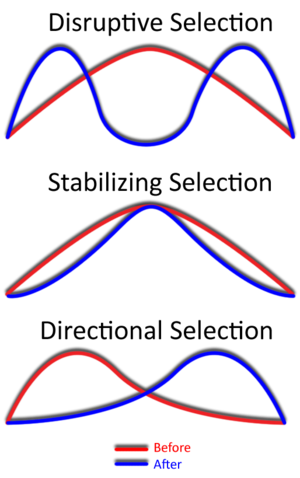
Describe disruptive, stabilising and directional selection
Disruptive: Both extreme phenotypes are favored over the intermediate one
Stabilising: The intermediate phenotype is favored, and extreme variations are selected against.
Directional: One extreme phenotype is favored, causing the population's average trait value to shift over time.