Secretory Pathways and Exocytosis
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
three ways to leave trans-golgi
endo-lysosomal pathway
regulated secretory pathway
constitutive secretory pathway
- proteins are sorted into the endo-lysosomal pathway
M6P-tagged
in the regulated secretory pathway, a small group or single type of small molecules or proteins - to form dense granules that are packaged into -
aggregate, secretory vesicles
proteins that lack - (two things) or fail to - default to the constitutive secretory,
M6P tag, ER retrieval signals, aggregate into secretory vesicles
secretory vesicles are destined for the - and -
plasma membrane, exocytosis
all cells use the constitutive secretory pathway to - or - the plasma membrane with new - and -
replenish, load, lipids, membrane proteins
constitutive secretory vesicles bud from the - and proceed to the -
trans-golgi, PM
specialized cells bud - carrying large amounts of - cargo
regulated secretory vesicles, concentrated
soluble cargo is only one or few types of small molecules or proteins which aggregate into - and segregate into regulated secretory vesicles
dense granules
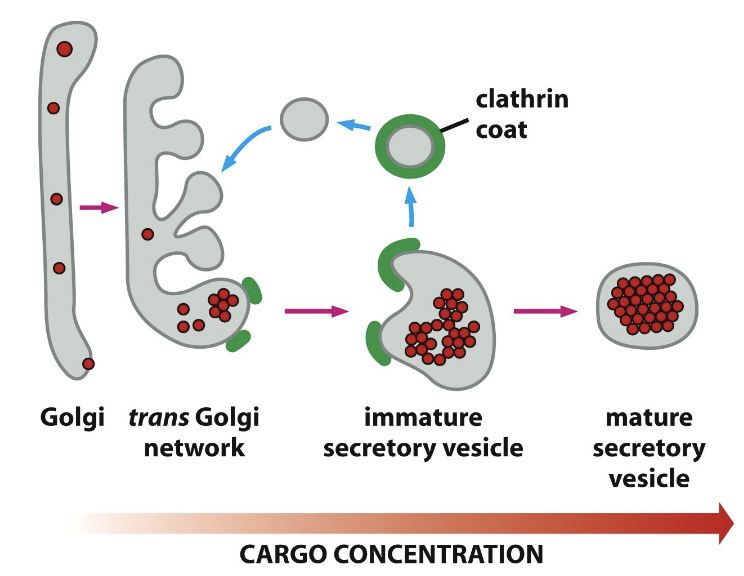
immature secretory vesicles bud-off - retrieval vesicles that recycle membrane proteins back to the -, reducing vesicle - and - cargo in the mature secretory vesicle
clathrin coated, trans golgi, size, concentrating
pancreatic beta cells form regulated secretory vesicles that are highly concentrated with - cargo
insulin
How are insulin secretory vesicles regulated by glucose concentration?
blood [glucose] rises → glucose transport - (into/out of) beta cells → increase in [-]
high [ATP] closes - channels → accumulation of - → membrane - (depolarization/repolarization)
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in PM - (open/close) → Ca2+ - (enter/exit) → Ca2+ primes -
secretory vesicles and PM fuse → -
into, ATP, ligand gated K+, K+, depolarization, open, enter, v-snares, insulin released
polarized cells direct exocytic vesicles to the - domain
appropriate plasma membrane
most epithelial cells in tissues are polarized and have two or more - or -
distinct membrane faces - domains
domains perform specialized functions and are thus composed of different types of - and -
membrane proteins, lipids