Lab 4: Life on the Cellular Level
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
3 domains of life
bacteria
archaea
eukarya
bacteria
single-celled organisms
archaea
prokaryotic single-celled organisms that usually are extremophiles
eukarya
organisms w/ eukaryotic cells
horizontal gene transfer (HGT)
genetic material is transferred between organisms without the need for reproduction
transformation
transduction
conjugation
gene transfer agents
transformation
naked DNA uptake by bacteria
transduction
genes transferred by virus
conjugation
genes transferred between two bacteria via pilus
gene transfer agents (GTA)
virus-like particles, transfer random genomic sequences from one prokaryote species to another
which of the 3 domains of life has a nucleus?
eukarya
which of the 3 domains of life has a mitochondria/chloroplast?
eukarya
which of the 3 domains of life has peptidoglycan?
bacteria
which of the 3 domains of life has branched membrane lipids?
archaea
which of the 3 domains of life commonly has introns in genes?
eukarya
how are chromosomes shaped in eukarya?
linear
how are chromosomes shaped in bacteria and archaea?
circular
theory of endosymbiosis
mitochondria resulted from the engulfment of aerobic bacteria
chloroplasts resulted from the engulfment of cyanobacteria
domain archaea
more closely related to eukarya
many but not all live in extreme environments
domain bacteria characteristics
most widespread and abundant organisms on Earth
many ways to classify
cell shape
oxygen requirements
cell wall structure
unique features and ability to transfer plasmids
domain bacteria cell shape
bacillus
coccus
spirillus
bacillus shape
rod-shaped
coccus shape
spherical or round shape
spirillus shape
spiral or helical
bacteria oxygen requirements
aerobic: require oxygen
anaerobic: cannot tolerate oxygen
facultative anaerobes: prefer oxygen, but can survive without it
bacteria cell wall structure
gram +
gram -
bacteria unique features
cell wall of peptidogylcan:
layer of polysaccharides crosslinked with peptides
thick in gram + bacteria
thin in gram - bacteria, often with a secondary outer membrane
bacteria ability to transfer plasmids
HGT
plasmids contain extra genetic material not found in the bacterial chromosomes
can give new capabilities to bacteria
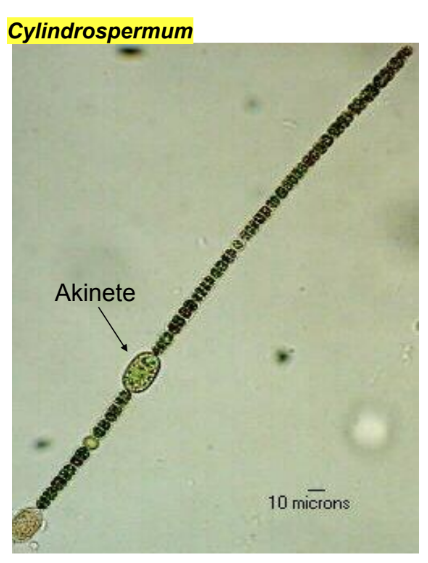

Cyanobacteria
performs photosynthesis
some have nitrogen-fixers cells called heterocysts
may survive harsh environments through the production of spore-like cells called akinetes
cylindrospermum
what are the nitrogen-fixer cells in cyanobacteria called?
heterocysts
what does akinetes (spore-like cells) aid cyanobacteria with?
surviving through harsh environments
what is the cyanobacteria we observed?
cylindrospermum
single-celled members of domain eukarya (protists) characteristics
have membrane bound organelles and DNA contained in a nucleus
most diverse group or organisms in terms of both structure and function
currently organized into 4 or 6 supergroups
Supergroup Excavata (eukarya)
some groups have an “excavated” feeding grove on their surfaces
generally, have 2 or more flagella
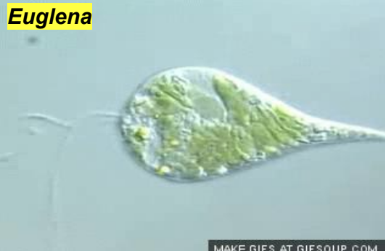
Euglenozoans (Excavata)
most are both photosynthetic and heterotrophic (mixotrophic)
2 flagella originating from within an infolded structure
stigma (eyespot): photosensitive organelle
flexible protein pellicle allows shape changes
Euglena
supergroup Archaeplastida (eukarya)
includes multicellular plants, red, and green algae
photosynthetic
fix CO2, store carbohydrates as starch, and have cellulose in their cell walls
Chlorophytes (Archaeplastida)
Chlamydomonas
Volvox
Spirogyra
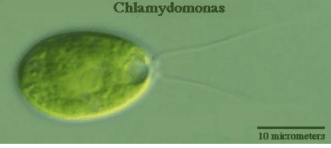
Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyte)
unicellular chlorophyte
pear-shaped morphology
2 anterior flagella
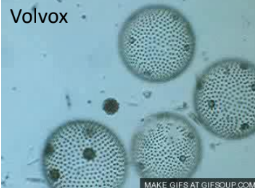
Volvox (Chlorophyte)
more complex and colonial

Charophytes (Archaeplastida)
closest living relatives to land plants and resemble them in morphology and reproductive strategies
Spirogyra
Supergroup “SAR”
3 groups
stramenopiles
alveolates
rhizarians
stramenopiles (SAR)
typically have 2 flagella: one “hairy” and the other “smooth” (include true kelp - multicellular brown algae)
Saprolegnia
Diatoms
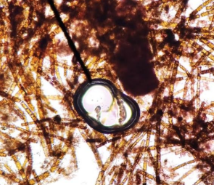
Saprolegnia (Stramenopiles)
parasitic
grows into hyphae similar to fungi
structure called an oogonium
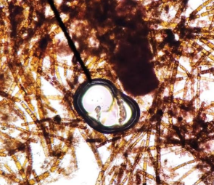
Diatoms (Stramenopiles)
cell wall composed of hydrated silica plates
carbohydrates stores as laminarin
Alveolata (SAR)
have membranous sacs underneath the cell membrane called alveoli
flagellum
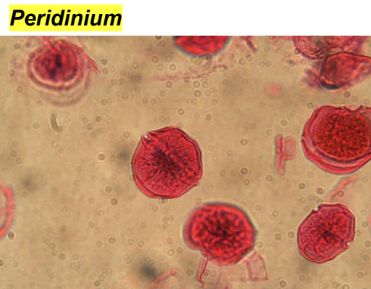
Dinoflagellate (Alveolata)
2 flagella in grooves, causes characteristics whirling motion
Peridinium
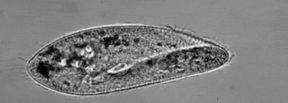
Ciliates (Alveolata)
uses many cilia to move
blepharisma
Rhizarians (SAR)
most members to employ psuedopoedia
mineralized test shell
composed by 2 subgroups
Foraminifera
Radiolaria

Foraminifera (Rhizarians)
possess a multi-chambered shell - still one cell
shell made of calcium carbonate

Radiolaria (Rhizarians)
spherically or radially symmetrical
shell made of silica
Supergroup Unikonta
generally have no set growth form
generally have a single flagellum
includes Nuclearids, Kingdom Fungi, Choanoflagellates, and Kingdom Animalia
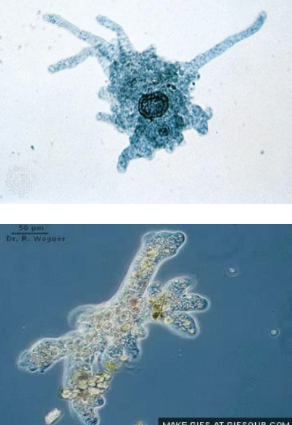
Amoebozoans (Unikonta)
very large single-celled organisms
no test/shell or cell wall present
lobe-shaped or tubular pseudopodia (mobility and food capture)
Opisthokonts (Unikonta)
characterized by a single, posterior flagellum on flagellated cells
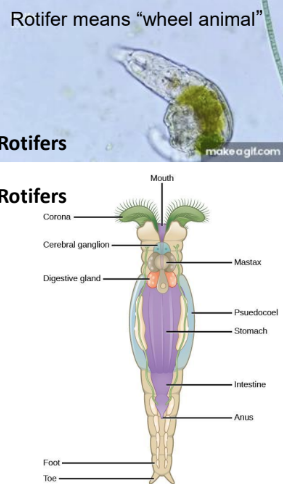
Rotifers (Opisthokonts)
Kingdom Animalia Phylum Syndermata:
Corona is a two-part ciliated structure around the mouth
advanced animal with a nervous system and other organ systems
smaller than some of the single-celled organisms we have seen today