Module 7: Basin Analysis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Well Logs Versus Seismic Logs
Well Logs:
great vertical resolution
delimit bounding surfaces
establish lithology of penetrated
Seismic Logs:
great lateral continuity and resolution
define gross sediment geometry
What causes mudcake
Hydrostatic pressure of the mud column is usually greater than the pore pressure of the formations
This forces mud to filtrate into the permeable formations and a mud cake on the borehole wall
How does tool sensor relate to lithology?
Caliper sensor measures the size of the drilled borehole
electrical sensors: detect porewater amount, permeability, and ionic concentration of sediment and porewater
Gamma-ray sensors: measure the amount and type of radioactive elements (U, Th, K) in sediment
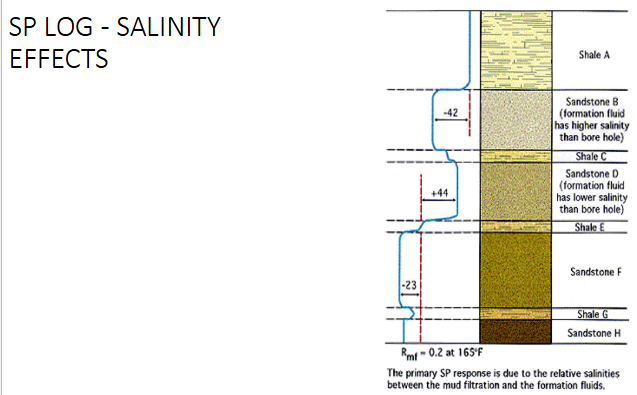
Spontaneous Potential (SP) Logs
Measures electrical current in well
Result of salinity differences between formation water and the borehole mud
Separates bed boundaries of permeable sands and impermeable shales
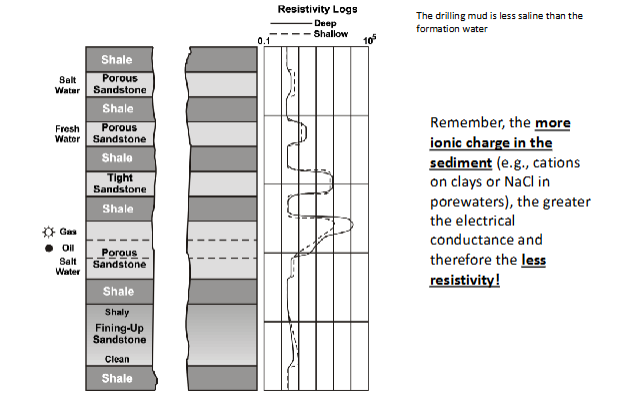
Resistivity Logs
Measures resistance of flow of electric current
Is function of permeability, porosity and pore salinity in rock
Frequently used to identify lithology that varies based on permeability
High Resistivity= little porewater
Low resistivity= more porewater
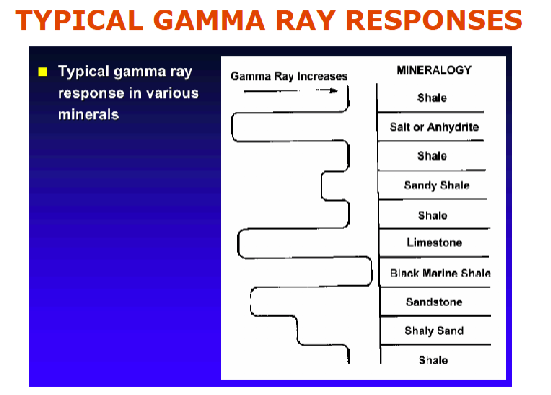
Gamma Ray Logs
records natural radioactivity of formation
shales have high gamma radioactive response
gamma ray logs infer grain size
gamma ray logs are more commonly used logs for sequence stratigraphic analysis
Acoustic Impedance
Seismic Wave Velocity x Density
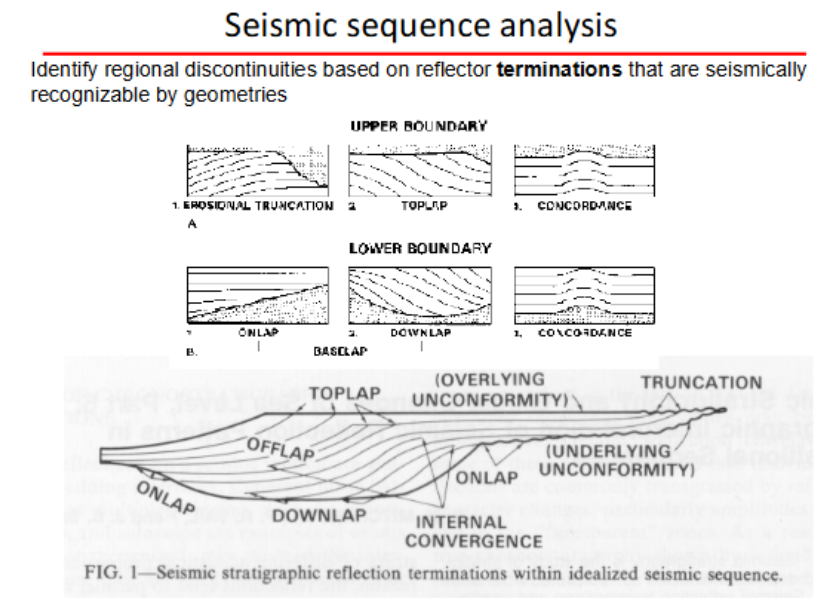
Seismic sequence analysis
Allostratigraphy
Bounding discontinuities including erosion surfaces, marine flooding surfaces, tuffs, tempestite, and/or turbidite boundaries as time markers
Sequence Stratigraphy
higher level allostratigraphic model which interprets depositional origin of sedimentary strata as products of “relatively sea level change”
Sequence Stratigraphy – Base Level
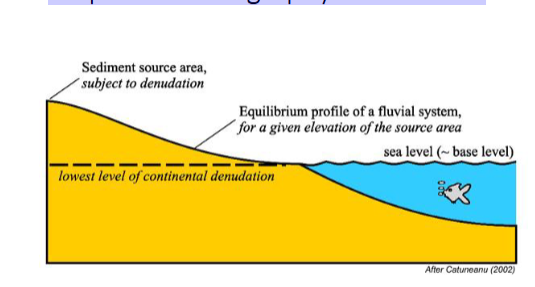
Boundary Types
Disconformity: unconformity separating parallel strata where there has been significant erosion
Paraconformity: unconformity between parallel strata where there has been little erosion
Angular unconformity: unconformity where tilting and erosion of strata has been followed by deposition
Onlap
Onlap is baselap in which an initially sub-horizontal stratum laps out against an initially inclined surface
Both onlap and downlap are indicators of non-depositional breaks (hiatuses).
Downlap
Downlap is baselap in which an initially inclined stratum terminates down-dip against an initially sub-horizontal or inclines surface
Both onlap and downlap are indicators of non-depositional breaks (hiatuses).
Toplap
Toplap is lapout at the upper boundary of a depositional sequence and is a form of offlap
top lap is sometimes unrecognizable due to resolution limitations and the feature is mistakenly interpreted as truncation
indicators of non-depositional breaks (hiatuses).
Cedar Keys Formation
Cedar Keys Formation: dolostone and evaporites (gypsum and anhydrite) with minor limestone
Forms the base of the Floridian Cenozoic rocks over most of the state except NW Fl, where oldsmar formation forms the base
Middle Eocene Facies in FL
oldest unit exposed at surface is the Avon Park Limestone (Middle Eocene)
it occurs subsurface throughout the Florida peninsula and the eastern panhandle
Only locally exposed in sinks and quarries near the crest of the ocala platform in citrus and levy counties
The Avon Park Fm
composed of cream to light-brown or tan fossiliferous marine limestone (grainstone, packstone, and wackestone, with rare mudstone) interbedded with dolostone and gypsum
Ocala Formation
The Ocala Limestone typically consists of white or tan, homogeneous, porous and perme-
able, thickly bedded, foraminiferal limestone containing abundant granule to pebble sized
foraminifera, echinoids, mollusks, corals, and bryozoans. The Ocala Limestone characteristically consists of upper and lower lithozones (modified from Applin and Applin, 1944) which differ only slightly in average grain size and minor dolomite content
Suwannee Formation

Hawthorn Group –Coosawatchie Formation

Cypresshead Formation

Anastasia Formation

Undifferentiated Quaternary Sediments
Trail Ridge
