lab 7: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, membranes and the integumentary system
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
Sacromere
Basic contracting unit of muscle cell consits of actin and myosin filaments
intercelated discs
special region where cells join end to end
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
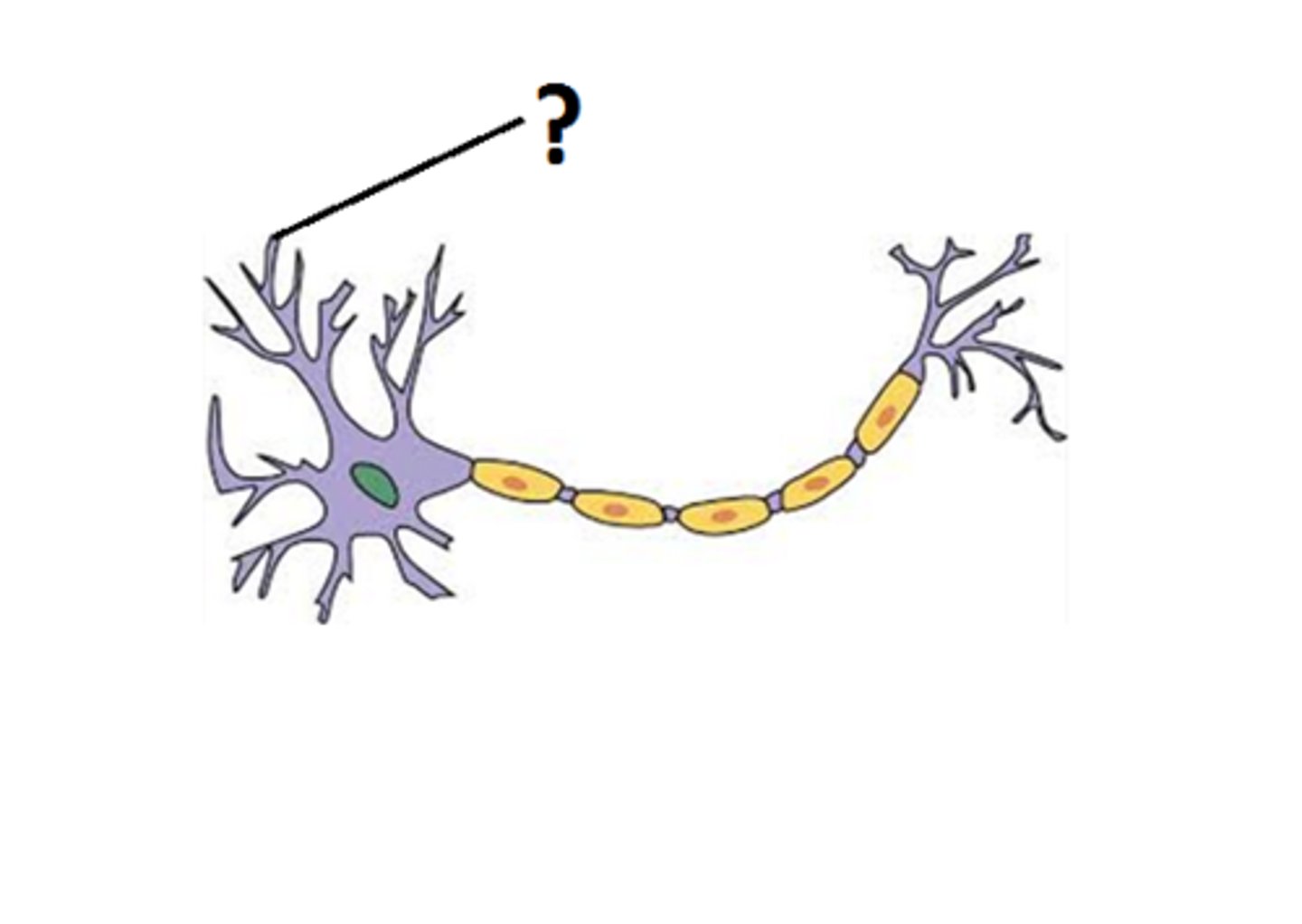
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
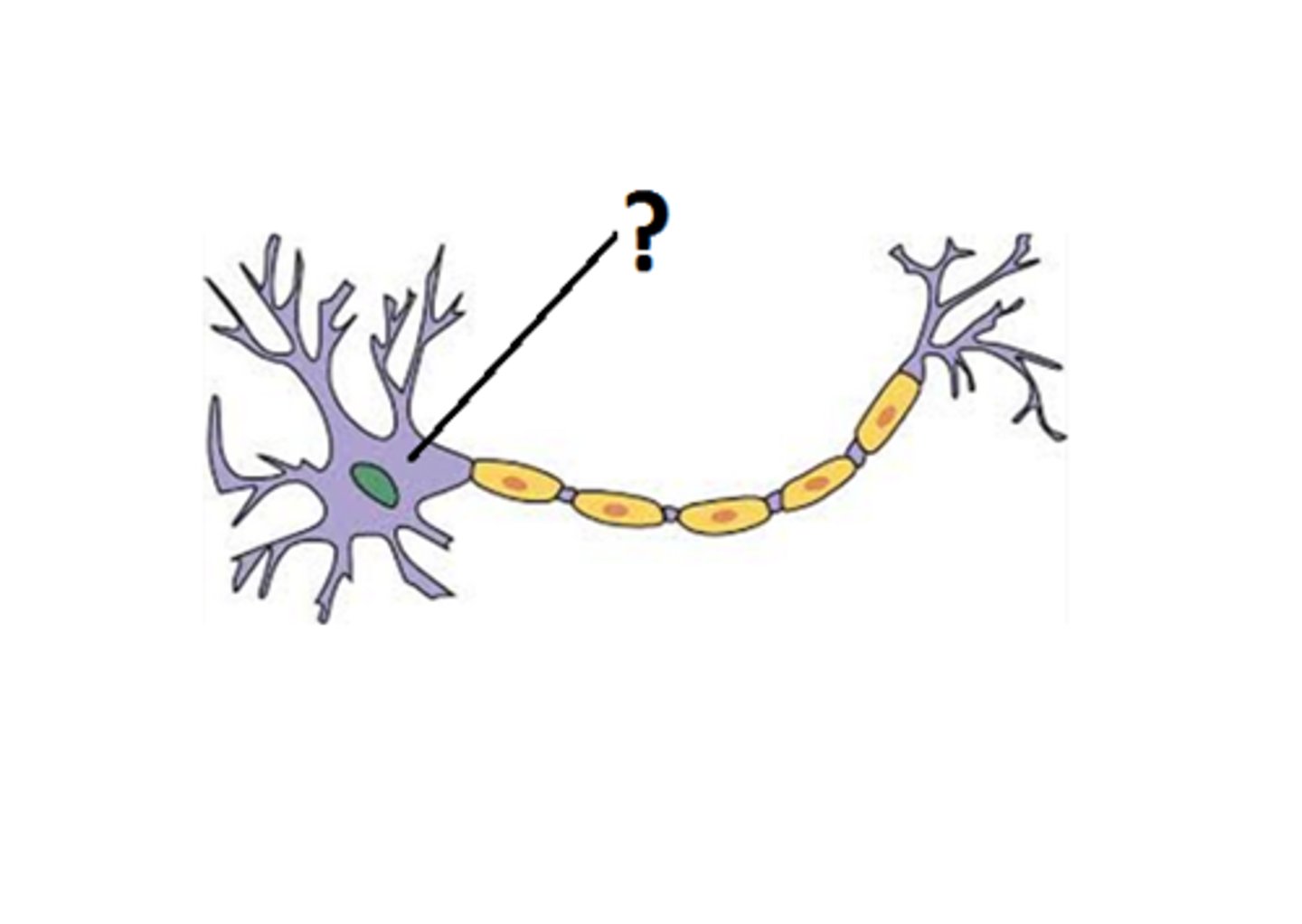
dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neuron
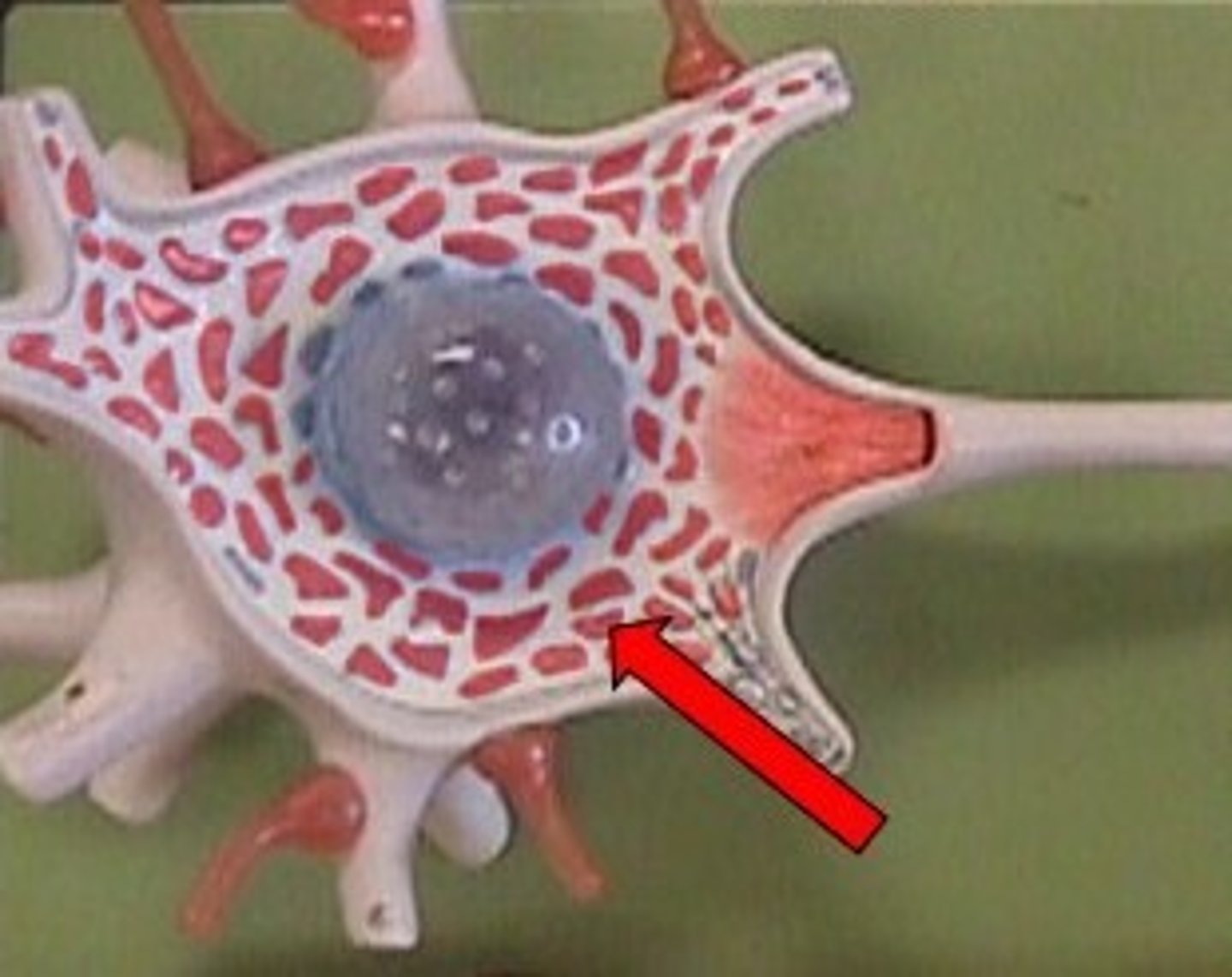
Neurofibrils
bundles of neurofilaments that provide support for dendrites and axon
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
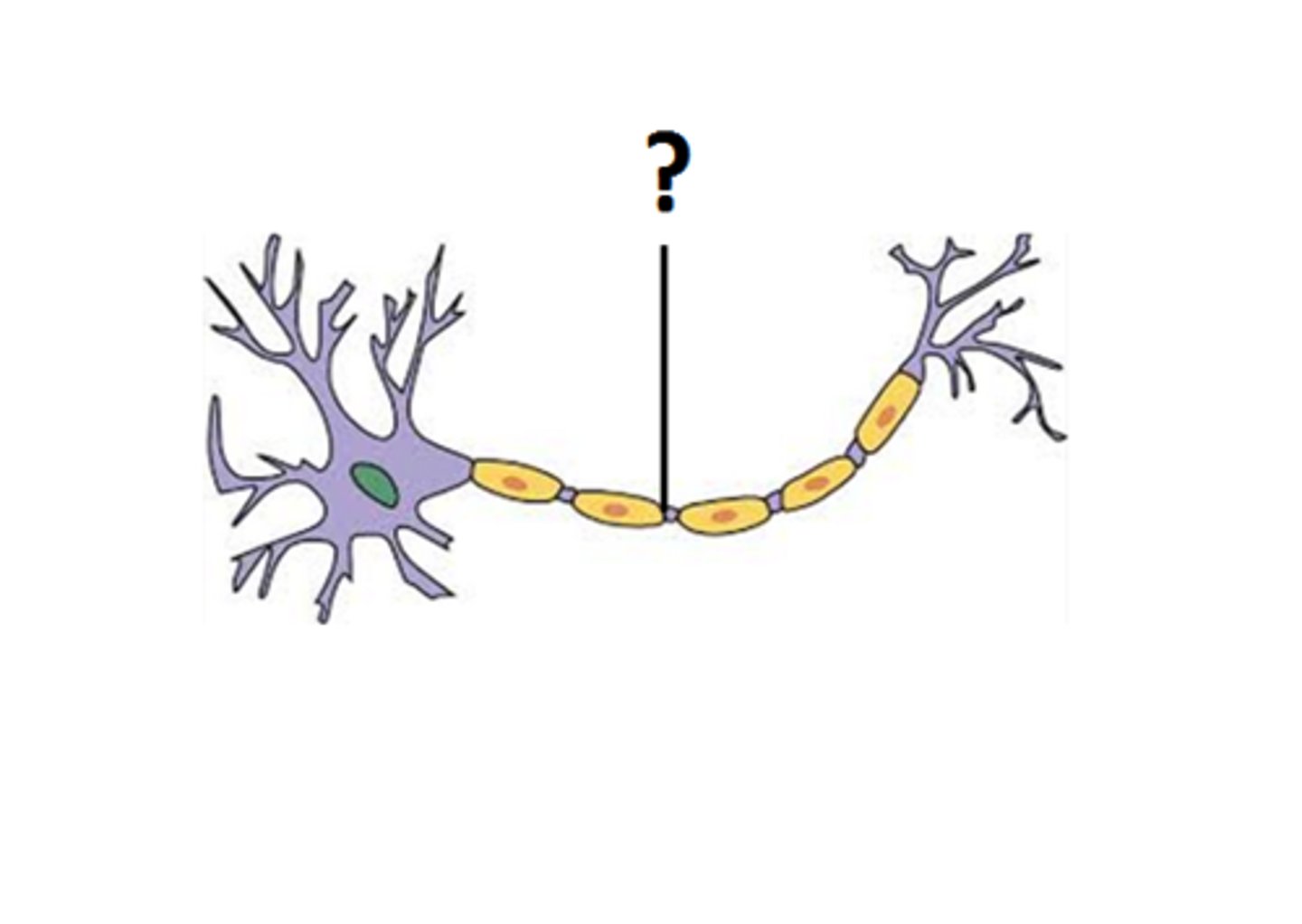
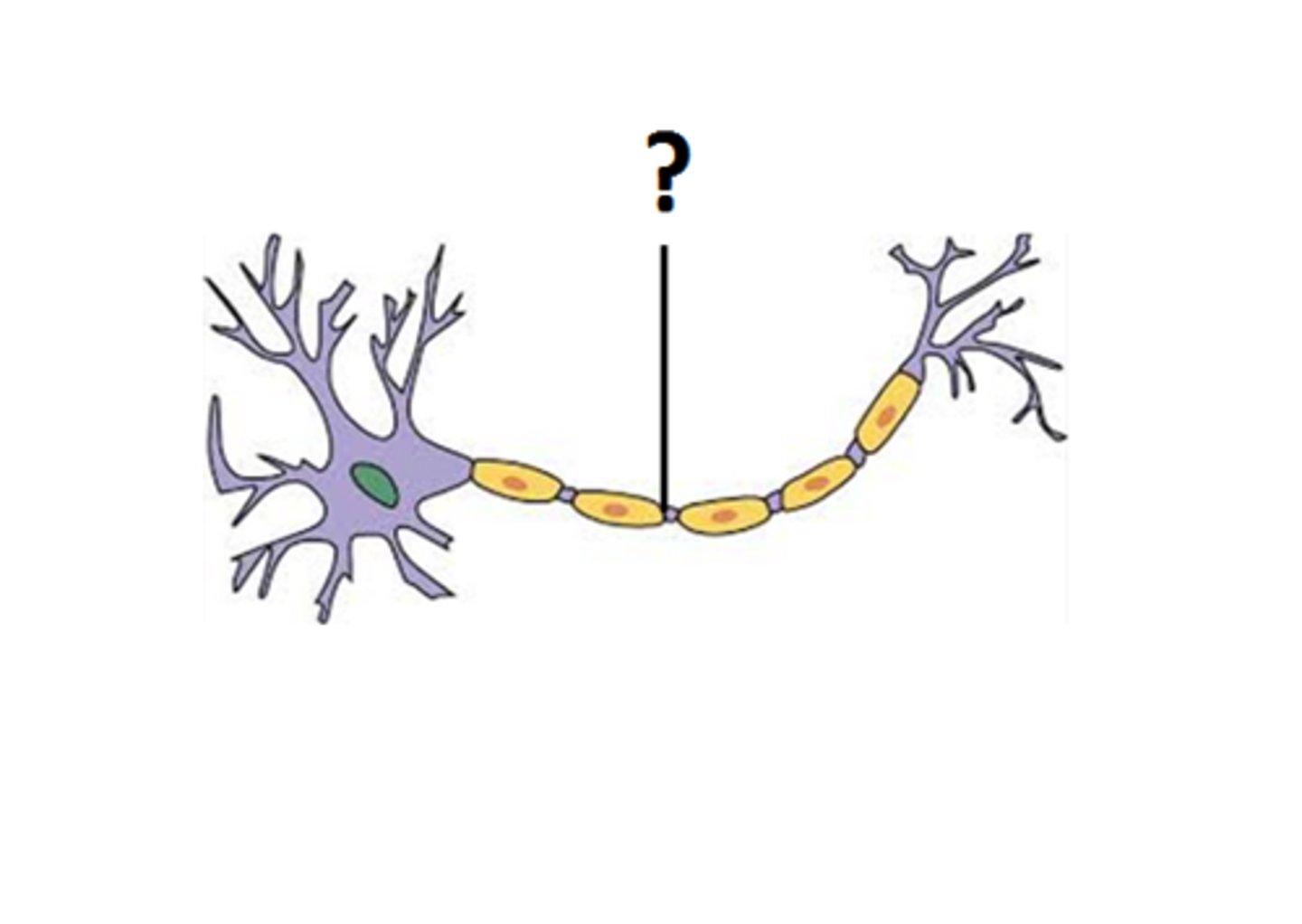
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
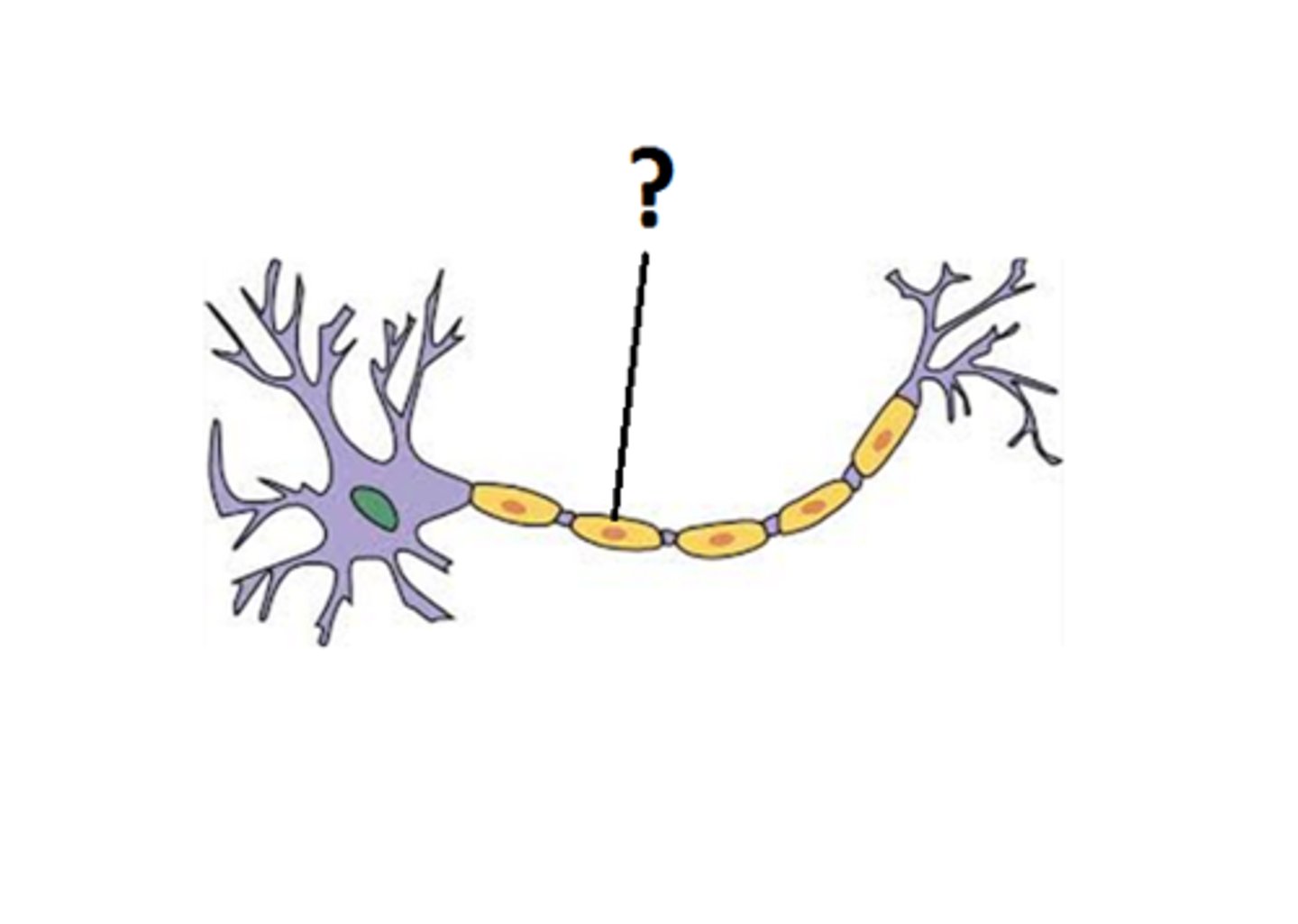
telodendrites
distant branches of the axon
ganglion
A cluster of nerve cell bodies, often of similar function, located in the PNS.
membrane
thin layer of tissue that covers a surface, lines a cavity, or divides a space or organ
mucus membrane
an epithelial tissue that secretes mucus and that lines many body cavities and tubular organs including the gut and respiratory passages.
serous membrane
thin layer of tissue that covers internal body cavities and secretes a fluid that keeps the membrane moist; also called serosa
cutaneous membrane
The skin; composed of epidermal and dermal layers
Epidermis
Outer layer of skin (stratified squamous epithelium)
Dermis
middle layer of skin
Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
3rd layer of the skin; Consists of connective tissue which binds the skin to the underlying muscle.
papillary layer
outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis
reticular layer
Deeper layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients
dermal papillae
Found in the upper layers of the dermis, they create your fingerprint pattern
Meissner's corpuscles
light touch receptors
Pacinian corpuscles
respond to deep pressure and vibration
sweat glands (sudoriferous glands)
tiny, coiled, tubular structures that emerge through pores on the skin's surface
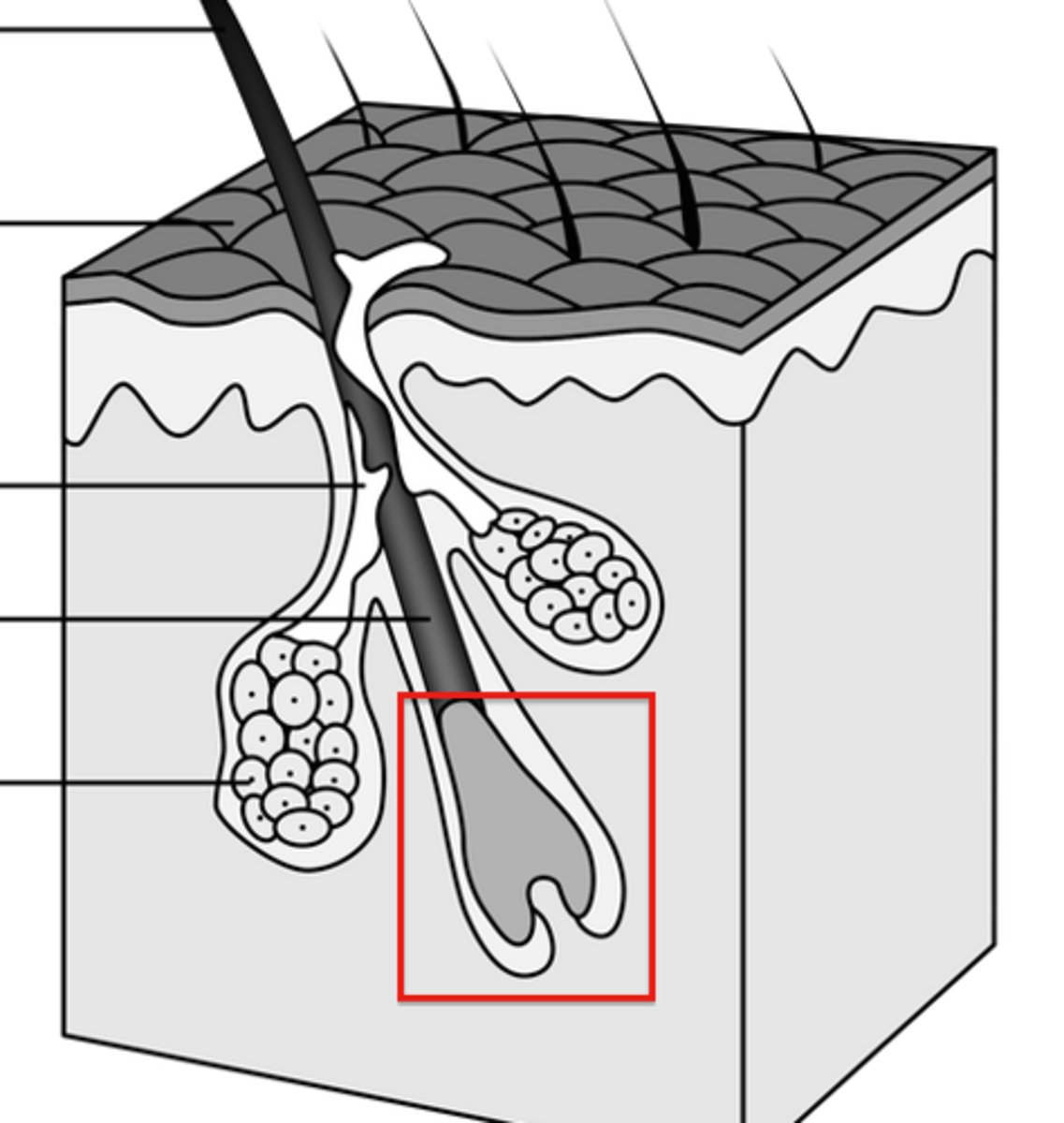
hair bulb
Lowest part of a hair strand; the thickened, club-shaped structure that forms the lower part of the hair root.
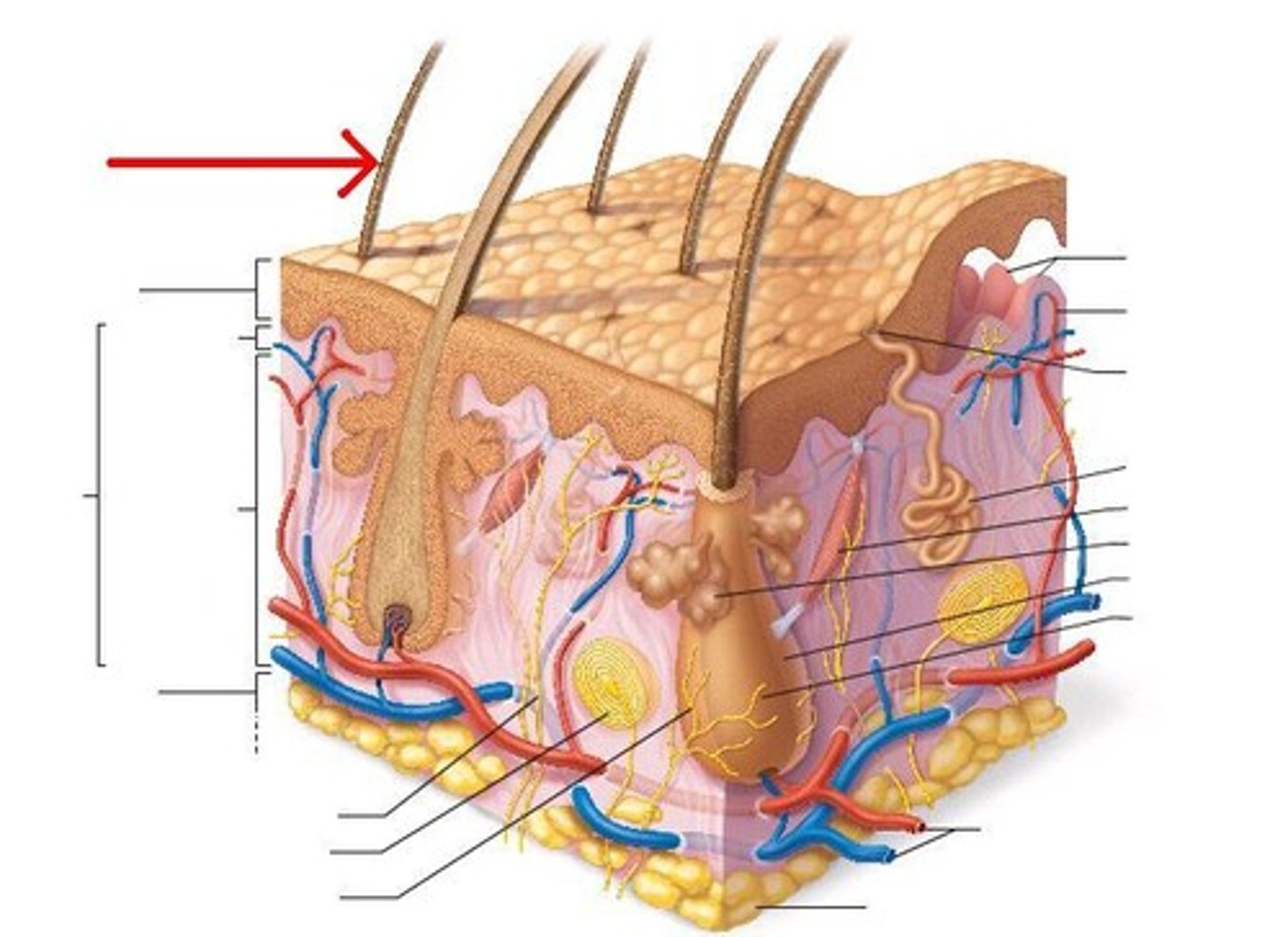
hair shaft
The portion of hair that projects above the epidermis
hair papilla
a peg of connective tissue containing capillaries and nerves
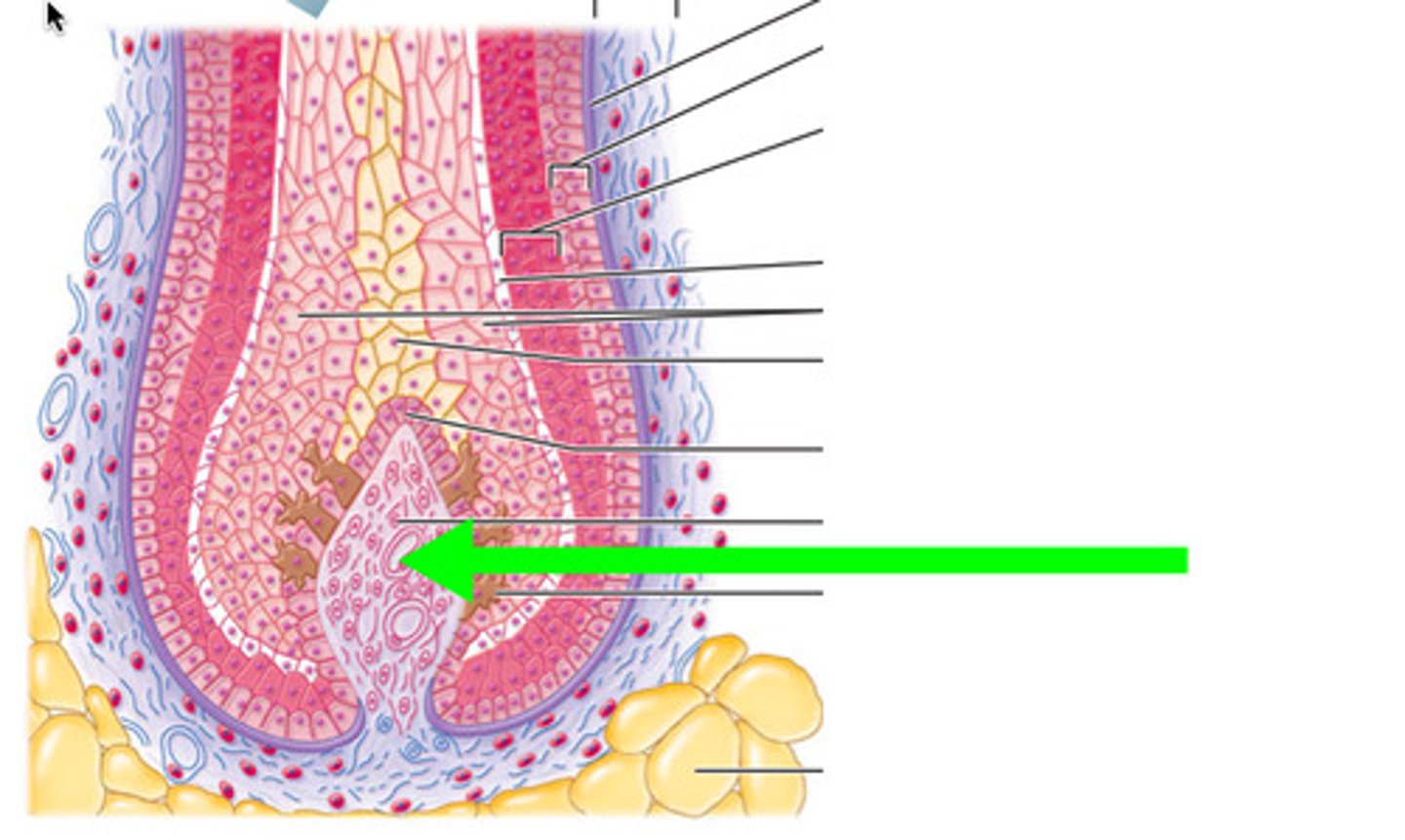
erector pili muscle
muscles that cause hair to stand up when it contracts
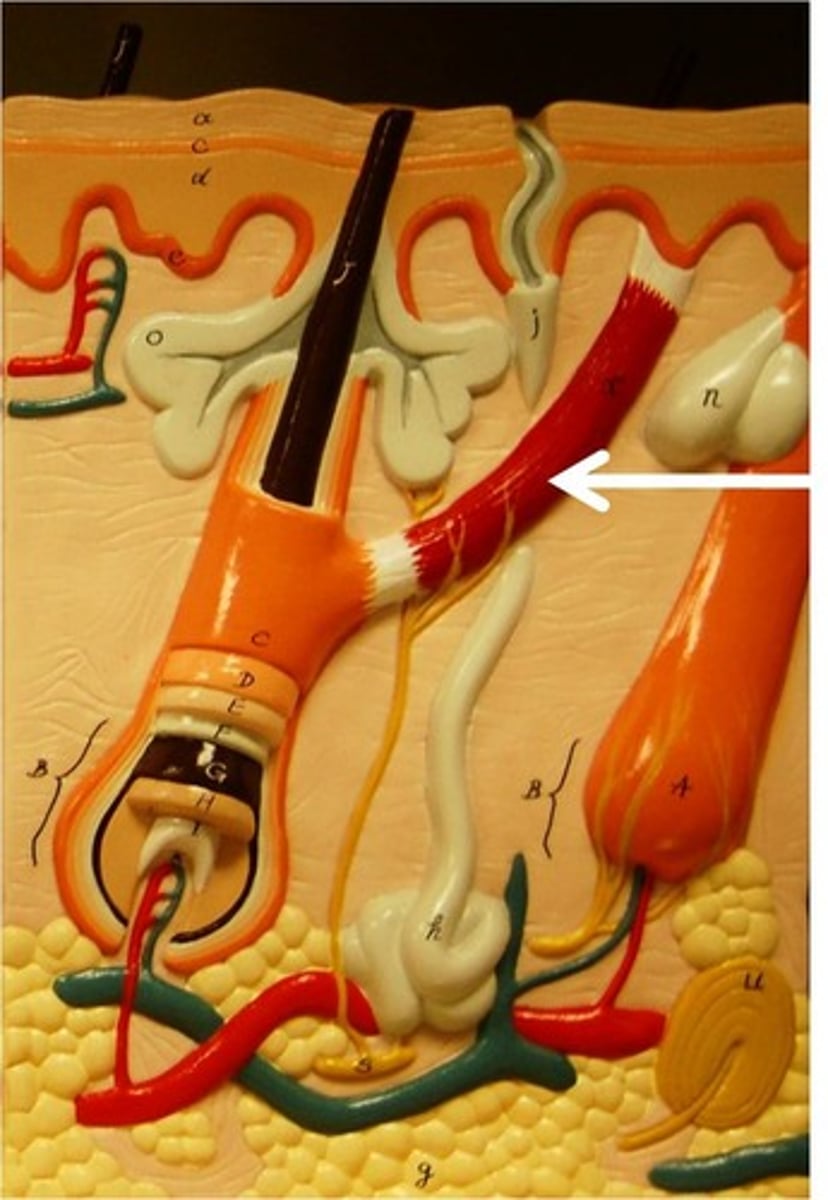
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
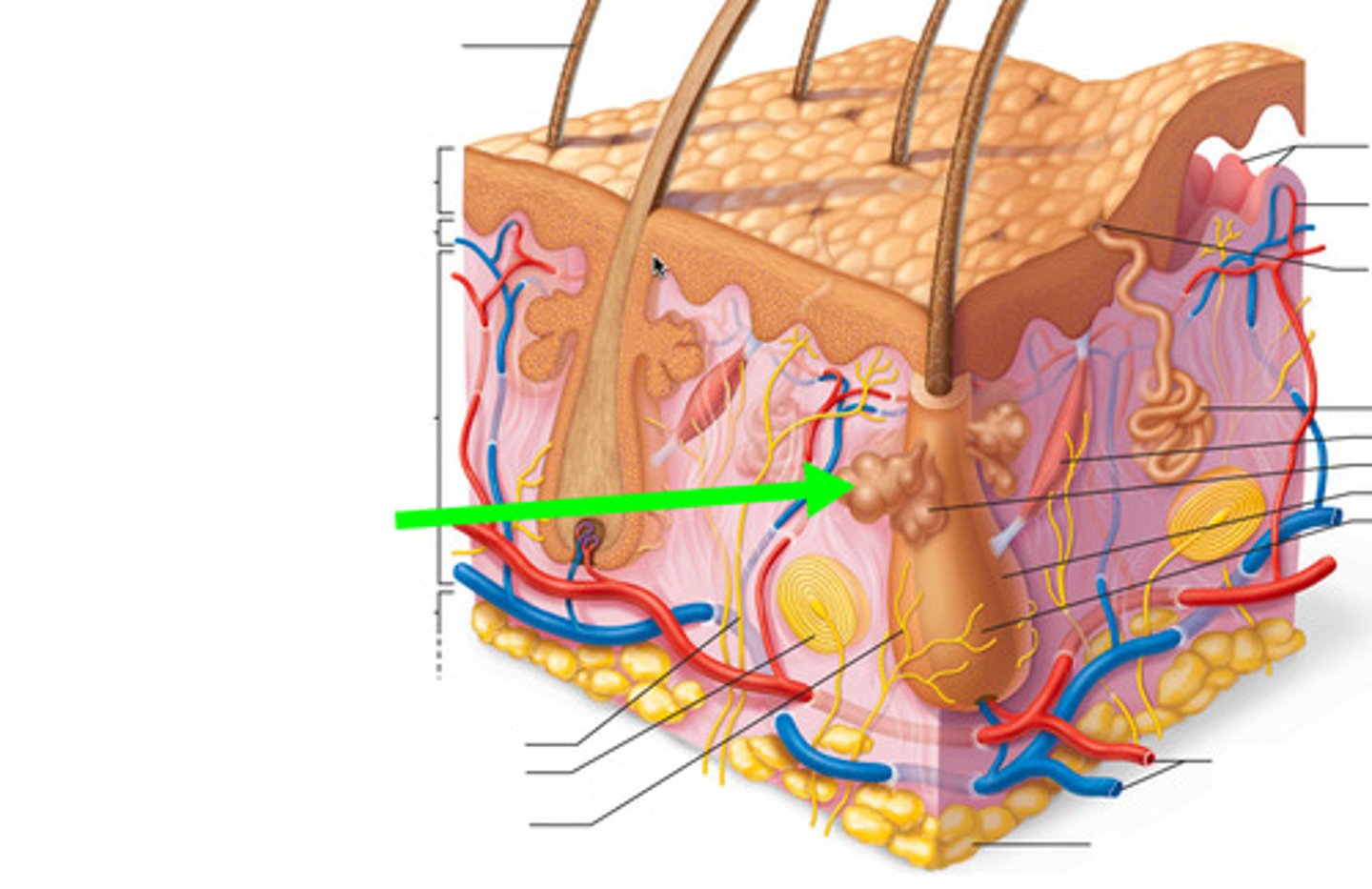
Melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color
Carotene
the yellow pigment of the skin
tactic discrimination of the skin (blue instrument)
sensitivity of the skin due to the difference in the density of touch receptors in different areas of the body
princess and the pea test
sensitivity to pressure
finger tips - knuckles - chin
adaption to pressure
your touch receptors do not send continuous signals; you get used to the clothes on your skin and cant feel them
relative temperature sense
free nerve endings are responsible for detection of hot and cold temperatures and also extremes of temperature. Temperature sensation is not very accurate
liquid crystal thermography
measures that amount of heat emitted by an area of the body by transforming the temperature into visible signals
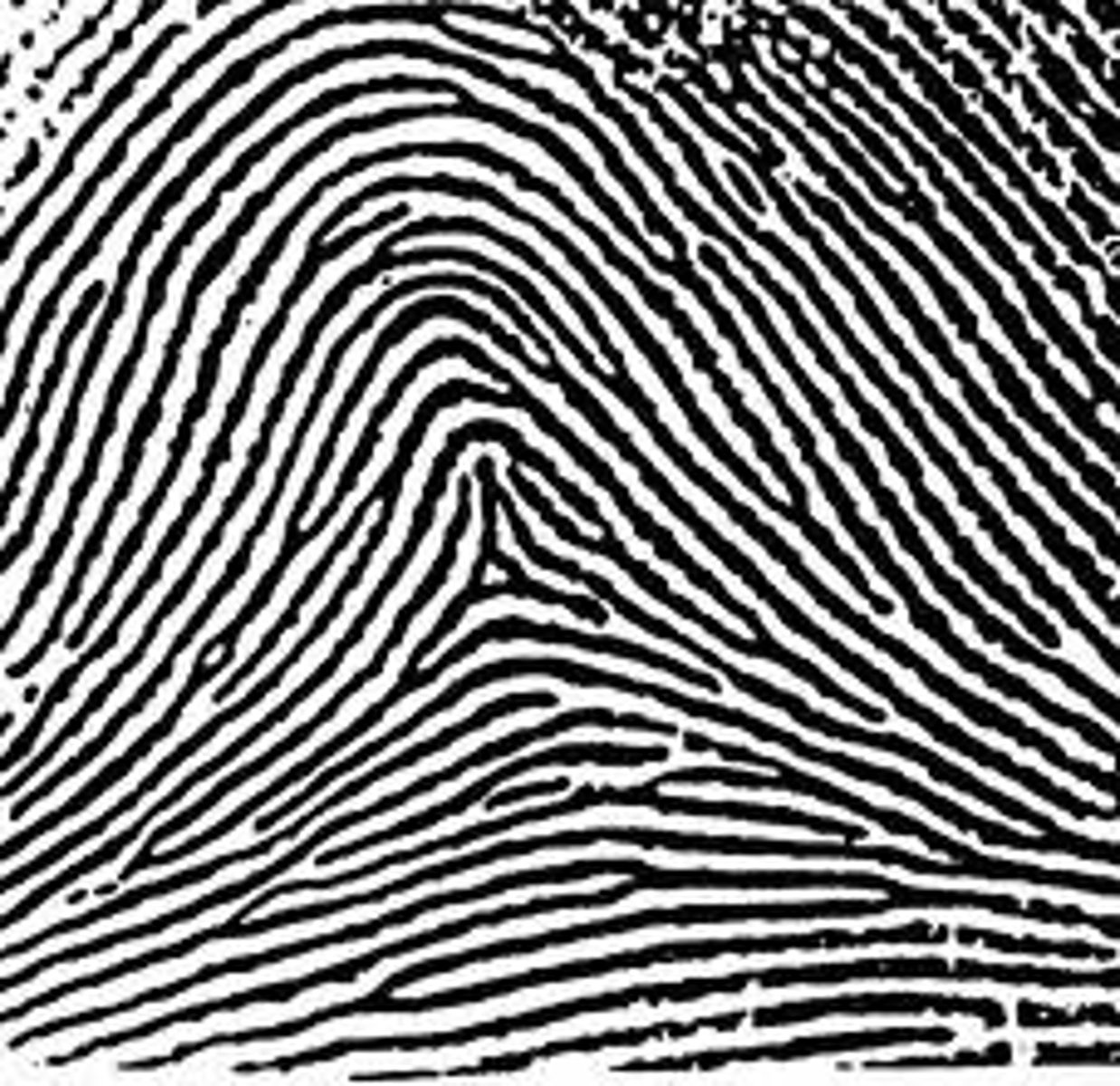
arch fingerprint

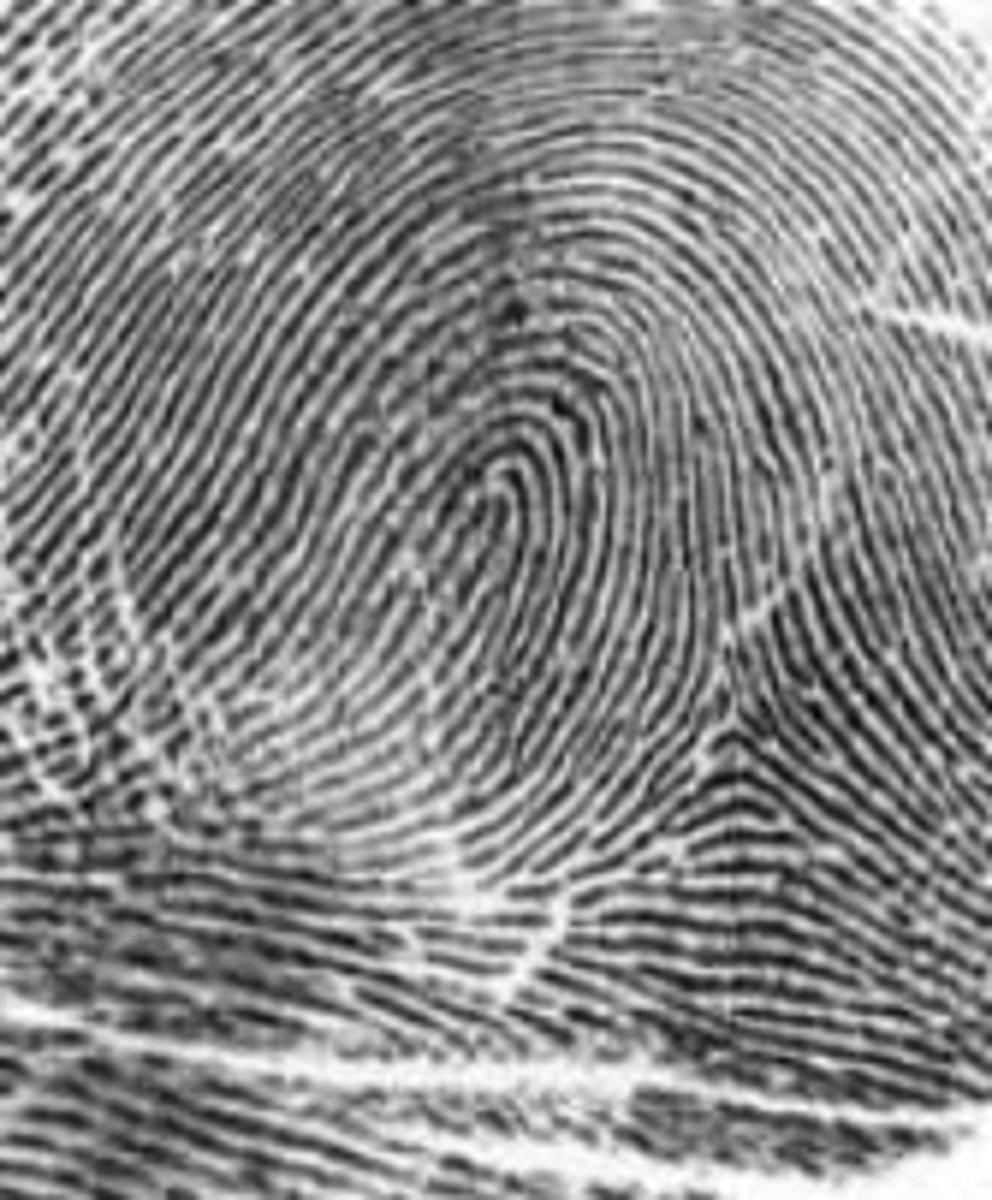
loop fingerprint

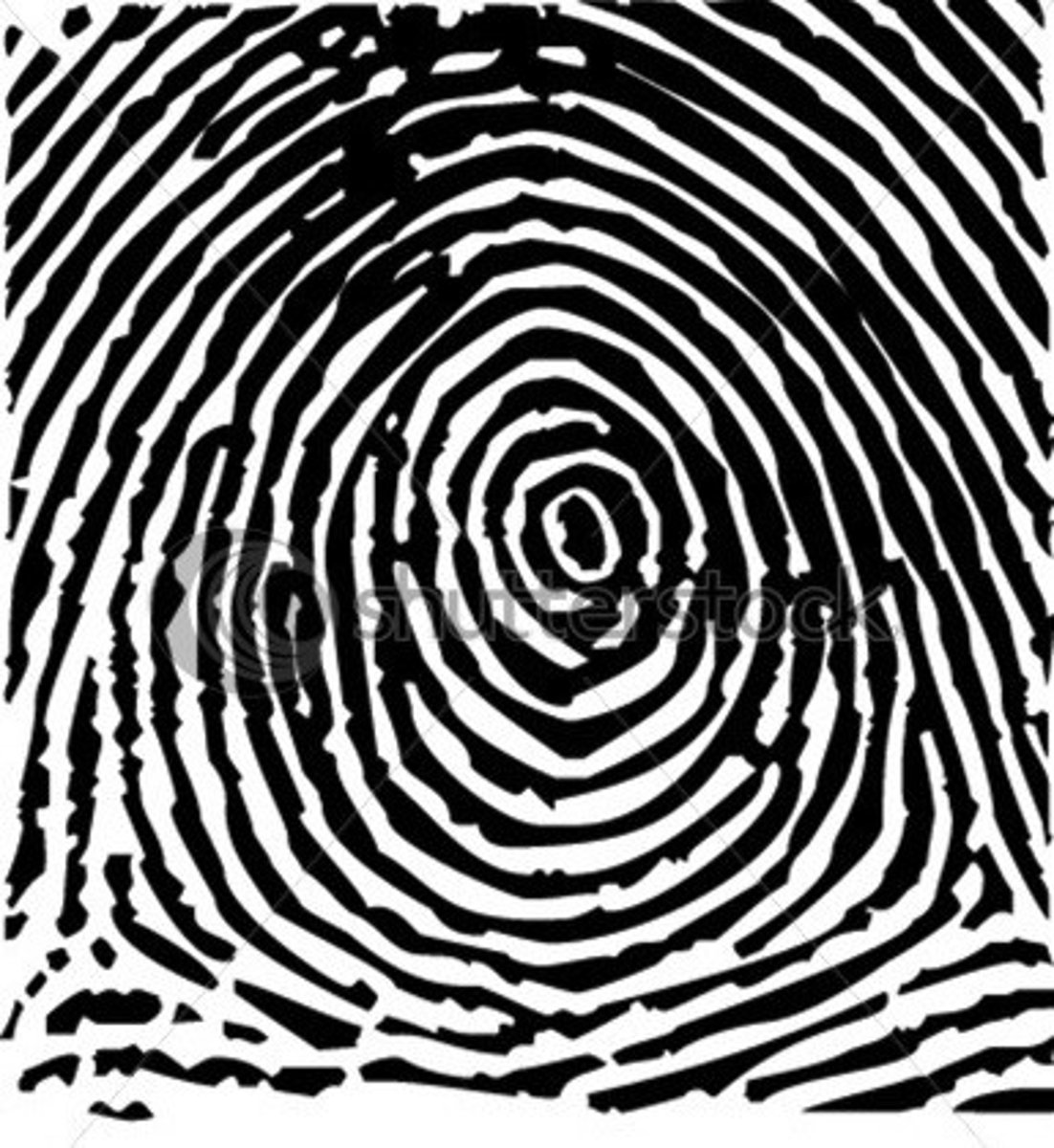
whorl fingerprint

fingerprint function
creates friction to increase the grip of the hand