Dynamic Earth - Lecture 19: Gravity
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
History of gravity - Aristotle
Four basic elements - earth, water, air, and fire
Objects move toward their own elemental sphere - e.g., rocks fall to earth
“Proof”, he claimed, that heavier objects fall faster than lighter ones (not true)
History of gravity - Nicolaus Copernicus & Johannes Kepler
Nicolaus Copernicus proposed Earth orbits the Sun (as do the rest of the planets)
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion (based on gravity)
History of gravity - Galileo
All Masses Fall with the Same Acceleration due to Gravity
1589 Galileo dropped two balls of different masses from Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate : time of descent was independent of their mass
This experiment has been confirmed countless times including on the moon
History of gravity - Sir Isaac Newton
Legend says that Newton was struck on the head by a falling apple, prompting his ideas on gravity
This story is no doubt apocryphal, but he was the first person to realize that the force that caused objects to fall such as apples also held the planets in orbit
Based on Kepler’s laws, Newton formulated the Universal Law of Gravitation
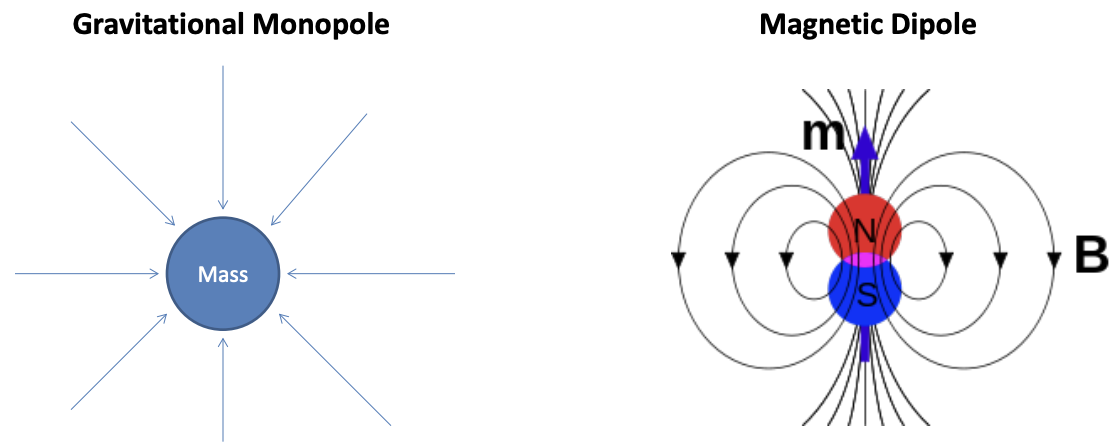
Gravitational monopole vs Magnetic dipole
Gravity is an attractive monopole
Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
Gravitational force of attraction between two objects is related to the mass of each object, and their distance apart
F = (GMm) / r²
F = fore of gravity
G = universal gravitational constant
M, m = masses of 2 objects
r = distance between the 2 objects
Newton’s 2nd law - Gravitational acceleration
Fgrav = mg
Gravitational acceleration, g: g = GM / r2
units = m/s2
g is approximately…
9.80 m/s2 at Earth’s surface
Why does a person feel the same force of gravity anywhere on earth?
Because of Earth’s spherical symmetry
Gravity variation with depth
If earth was the same density throughout, as you go deeper there is less mass beneath, so gravity would decrease
it would reach zero at the very centre
BUT thats not the case - the core is much denser so gravity doesn’t just decrease in a straight line
Apparent gravity
the gravitational acceleration, as measured by, say a bathroom weigh scale, is a result of Earth not being perfectly spherical, no spherically uniform density, and how it rotates
F = mg
weight = F = mg
What causes variation of gravitational acceleration with latitude?
The outward centrifugal force produced by Earth’s rotation
Earth’s equatorial bulge (causes objects at equator to be further from the planet
More mass located at the equator
centrifugal force (-0.0339 m/s2) + equatorial bulge (-0.0663 m/s2) + extra mass (+0.0485 m/s2)
= -0.0517 m/s2 lower acceleration at the equator than poles
Would you weigh more at the equator or at the poles?
You would weigh more at the poles than at the equator by ~0.5%