Caring for Clients with Sexually Transmitted Infections
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Infections spread through sexual activity with an infected person.
Chlamydia
Common STI easily cured with early treatment.
Gonorrhea
Bacterial STI treatable with appropriate medical care.
Syphilis
Bacterial infection with distinct stages, curable early.
Genital Herpes
Viral infection causing painful sores; no cure.
HPV
Human Papillomavirus; causes genital warts and cancers.
HIV/AIDS
Viral infection affecting immune system; lifelong management required.
Asymptomatic
Infected individuals show no symptoms of STIs.
High-risk partners
Individuals with behaviors increasing STI transmission risk.
Contraceptive techniques
Methods used to prevent pregnancy and reduce STIs.
5 P's of Sexual History
Framework for assessing sexual health: Partners, Practices, Prevention, Protection, Past.
Multiple concurrent partners
Engaging with more than one sexual partner simultaneously.
Nonadherence to treatment
Failure to follow prescribed STI treatment regimen.
Drug resistance
Microorganisms evolve to resist treatment medications.
Older adults and STIs
Misconception that older adults are sexually inactive.
Education on STIs
Providing information on prevention and treatment options.
Racial & ethnic minorities
Groups often face higher STI incidence due to disparities.
Limited healthcare access
Barriers preventing individuals from receiving necessary medical care.
Warm vaginal environment
Conditions favoring bacterial growth, increasing infection risk.
Receptive orifice
Body opening more susceptible to trauma during sex.
Sexual history assessment
Evaluating past sexual behavior to identify STI risk.
Chlamydia
Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria, common STI.
Gonorrhea
Infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria.
Syphilis
Curable STI caused by Treponema pallidum spirochete.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Highly contagious, controllable but not curable infection.
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Common virus linked to genital warts and cancers.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Complication from untreated STIs, affecting reproductive organs.
Asymptomatic
25% to 75% of Chlamydia cases show no symptoms.
Urethral Discharge
Common symptom of gonorrhea in men, purulent in nature.
Dysuria
Painful urination, symptom of both Chlamydia and Gonorrhea.
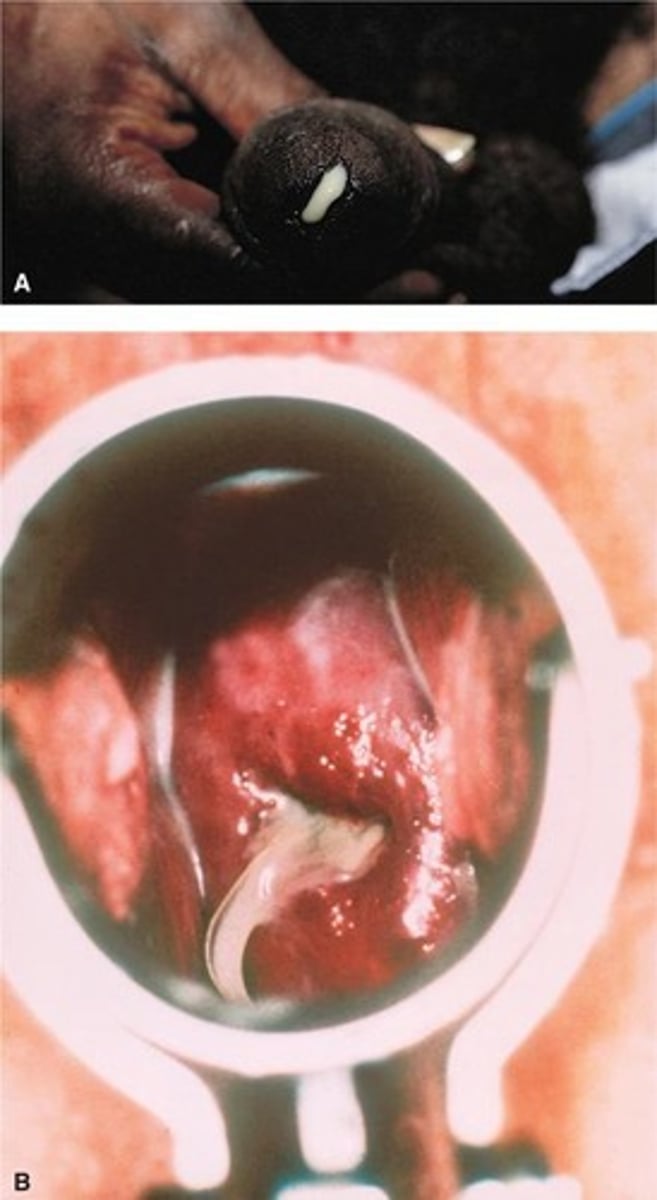
Chancre
Painless ulcer in primary syphilis stage.
NAAT
Nucleic acid amplification testing for STI diagnosis.
Antibiotics for Chlamydia
Azithromycin or doxycycline used for treatment.
Ceftriaxone
Broad-spectrum antibiotic for gonorrhea treatment.
Gummas
Soft, rubbery growths in tertiary syphilis.
Tabes Dorsalis
Neurological symptoms from tertiary syphilis affecting CNS.
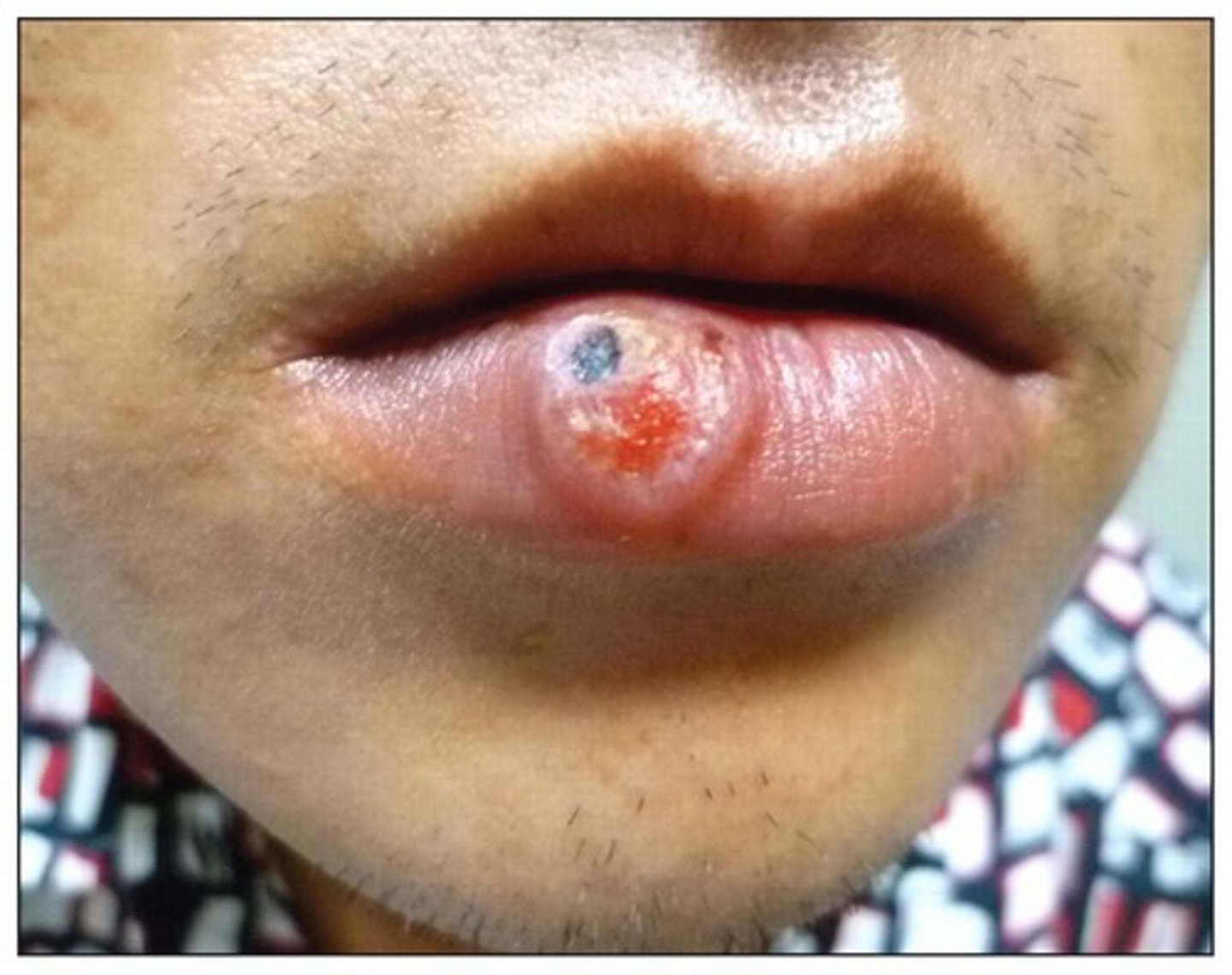
HSV-1
Herpes simplex virus type 1, causes oral lesions.
HSV-2
Herpes simplex virus type 2, causes genital lesions.
Autoinoculation
Self-transmission of infection to another body area.
Vesicles
Fluid-filled blisters from genital herpes outbreak.
PCR Testing
Identifies DNA of herpes virus from lesions.
Emotional Support
Important nursing care for patients with STIs.
Incidence
Rate of new cases in a specific population.
Sexual History
Assessment tool for STI risk and transmission.
Condom Use
Prevention method during sexual activity to reduce transmission.
Infant Transmission
STIs can be transmitted from mother to infant.
Follow-Up Care
Necessary after STI treatment to monitor effectiveness.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea
Includes fever, rash, and joint pain if systemic.
Treatment Adherence
Crucial to prevent complicated infections in STIs.
Lesion Care
Keep lesions dry using alcohol or peroxide.
Warm Baths
Consult physician about Epsom salts or baking soda.
Loose Clothing
Promotes air circulation around lesions.
Handwashing
Thoroughly wash hands after contact with lesions.
Personal Hygiene
Separate towels for lesions to prevent autoinoculation.
Papanicolaou Test
Annual test to detect cervical cancer.
Stress Management
Reducing stress decreases frequency of outbreaks.
HPV Prevalence
Affects 79 million people in the US.
HPV Strains
Over 100 strains; 13 cause cancer risk.
Genital Warts
Painless clusters of growths on genitals.
Vinegar Test
Warts turn white when vinegar is applied.
HPV Treatment
No antivirals available; vaccination is preventive.
Vaccination Timing
Administered before sexual activity, ideally at 11-12.
Podofilox Treatment
Apply BID for 3 days, then 4 days off.
Imiquimod Cream
Applied 3 times per week for 16 weeks.
Surgical Options
Includes excision, laser therapy, and cryotherapy.
Cancer Monitoring
Continued assessment for cancer development is essential.
Intimate Contact Advice
Avoid contact until warts are removed.
Condom Use
Use condoms even when lesions are absent.
Sexual Activity Precautions
Abstain from sex when infected; practice monogamy.
Condom Selection
Choose lubricated condoms; avoid natural membranes.
Condom Storage
Keep in cool, dry place; check expiration.
Condom Application
Pinch tip and unroll to base of penis.
Lubrication
Use water-based or silicone-based lubricants.
Condom Removal
Take off before penis becomes limp.
Condom Disposal
Dispose in a lined container.
New Condom Application
Use a fresh condom for each act.
Breakage Rates
Higher during anal sex compared to vaginal.
Dental Dam Origin
Developed for dental procedures to prevent contamination.
Dental Dam Usage
Used for oral sex since the 1990s.
Constructing Dental Dam
Cut condom or glove latex into rectangle.
Lubrication for Dental Dam
Apply water-soluble lubricant on contact surface.
Dental Dam Placement
Hold against vulva or anus during activity.
Single Use Dental Dam
Dispose after one-time use only.
Situational low self-esteem
Feeling inadequate in specific situations affecting behavior.
Acute pain
Severe, short-term pain requiring immediate attention.
Impaired skin integrity
Damage to skin affecting its protective function.
Risk for infection transmission
Increased likelihood of spreading infections to others.
Anxiety
State of excessive worry or fear affecting daily life.
Ineffective sexuality patterns
Unhealthy sexual behaviors impacting relationships and health.
Risk for ineffective health maintenance
Potential for failing to manage health effectively.
Emotional support
Providing empathy and understanding to those in distress.
Prescribed antimicrobials
Medications specifically ordered to treat infections.
Standard precautions
Basic infection control practices to prevent disease spread.
Role-play
Practicing communication skills in a simulated scenario.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Severe immune system disorder caused by HIV.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Virus that attacks the immune system, causing AIDS.
CD4 receptor
Cell surface protein targeted by HIV for infection.
HIV-1
Most common HIV subtype, prevalent in the US.
HIV-2
Less common HIV subtype, primarily in Western Africa.
Transmission routes of HIV
Methods include sexual contact, needles, and breast milk.