Arthropods
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Arthropods are what kind of protosomes?
Ecdysozoan protosome bilaterians
What group are they a part of?
Panarthropoda
What does Panarthropoda include? (subphyla)
Onychophorans (velvet worms)
Tardigrades
Arthropods
What are the living arthropod subphyla?
Chelicerata
Myriapoda
Crustacea
Hexapoda
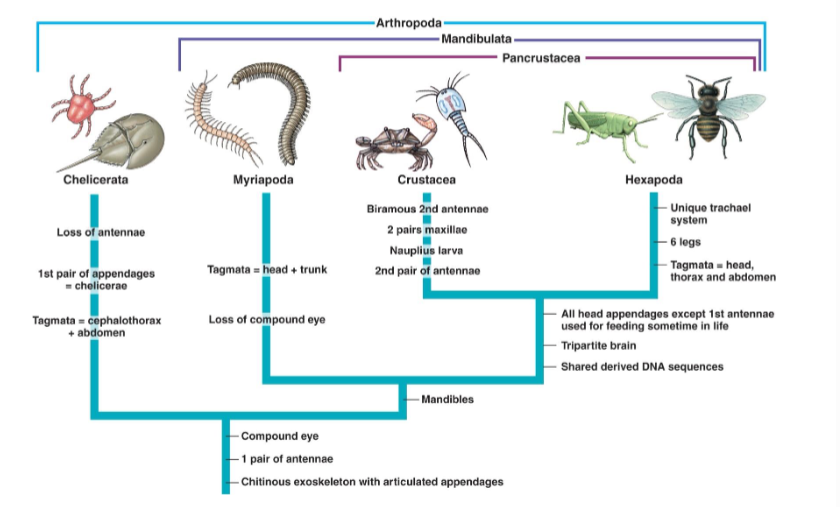
Arthropod Appendages and Mouthparts
Appendages:
Uniramous
Biramous
Mouthparts:
Chelicerae
Mandibles
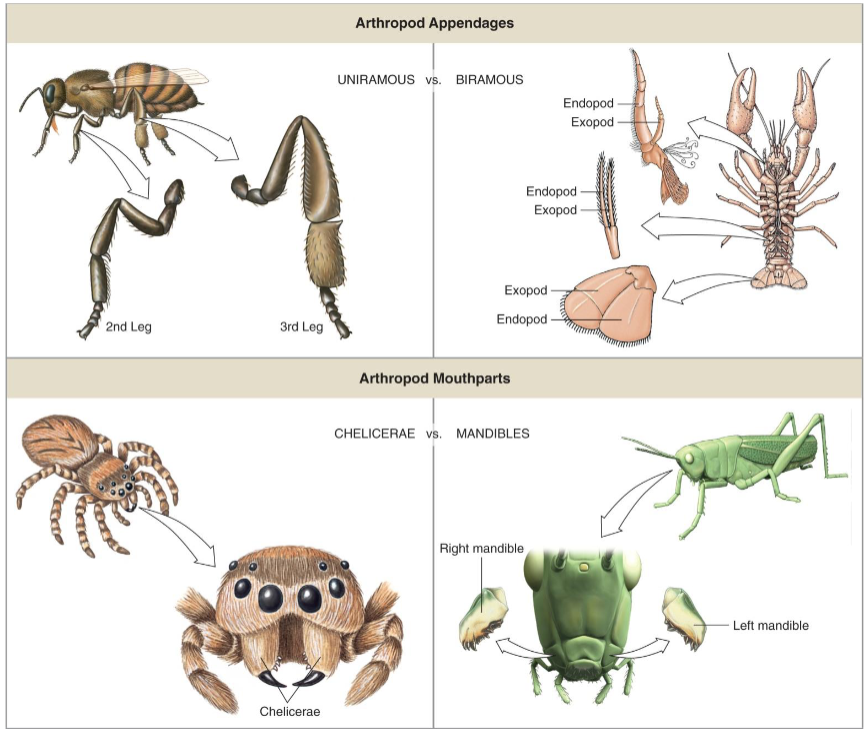
Homology of Chelicerae & Mandibles
Not the same thing
Expression of homeobox genes shows chelicerate arthropods retain their deutocerebral segment
Arthropod Features
Found in all habitats
Exoskeleton
Jointed appendages
Segmented Body
Tagmata (distinct regions of segments)
Triploblastic
Eucoelmate (hemocoel/reduced coelom)
Well dev Nervous sys and sense organs
Dioecious
Malpighian Tubes (terrestrial); excretory glands (aquatic)
Gills; body surface; book lungs; trachea
Open circulatory system
Extinct Subphylum - Trilobita
paleozoic (545-245 mya)
Very diverse and abundant
Bottom feeders
3-lobed body
3 tagmata
head
thorac
pygidium
Compound eyes
Classes in Subphylum Chelicerata
Class Pycnogonida
Class Merostomata
Class Arachnida
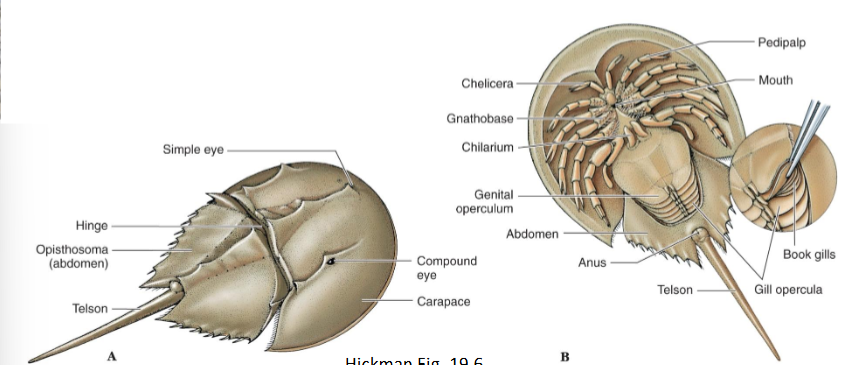
Subphylum Chelicerata Defining features:
6 pairs of free appendages
1 pair of chelicerae
1 pair of pedipalps
4 pairs of walking legs
Class Merostomata
Common name: Horseshoe Crabs
Living fossils
Feed on worms and Molluscs
Common in eastern US.
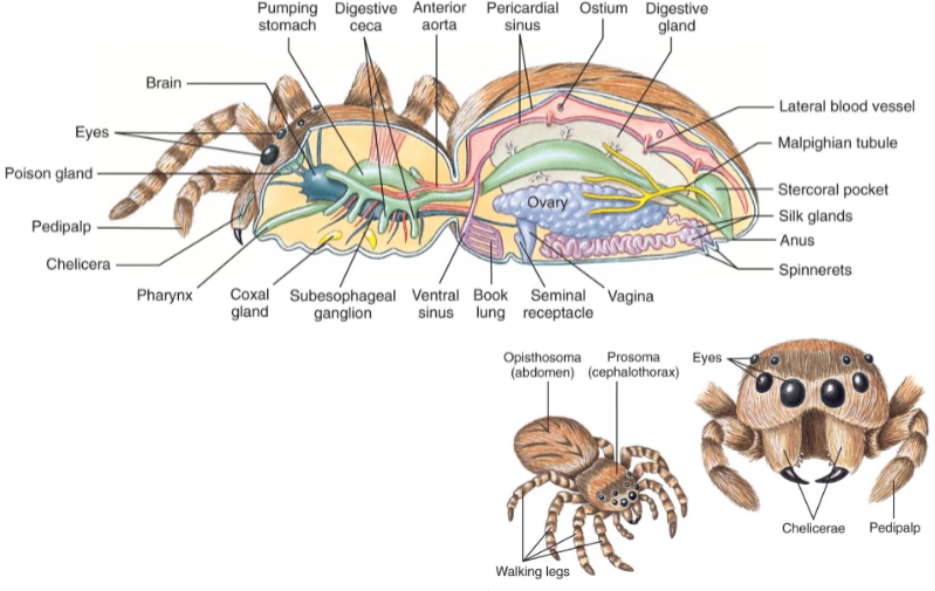
Class Arachnida: Spiders
Spiders (order Araneae)
Tagmata:
Prosoma (cephalothorax)
Opisthosoma (abdomen)
Chelicerae have fangs with poison
predaceous
most have silk glands
8 simple eyes
Class Arachnida: common names
Common names: Spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites
Class Arachnida: Scorpions
order Scorpiones
Nocturnal predators
Tagmata:
Cephalothorax
Preabdomen
Postabdomen
Pedipalps enlarged
String
Harvestmen (Order Opiliones)

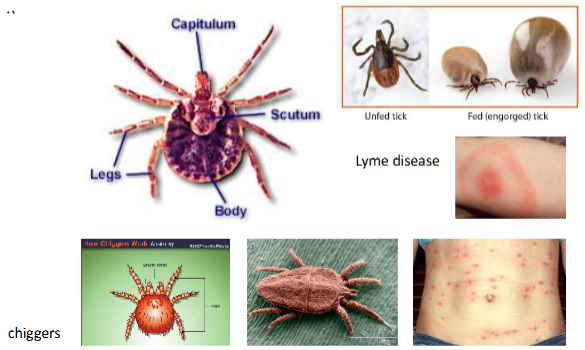
Class Arachnida: Ticks and Mites
Order Acari
Cephalothorax and abdomen fused
Mouthparts on capitulum
Free-living or parasitic on plants and animals
Important disease vectors in humans (Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever)
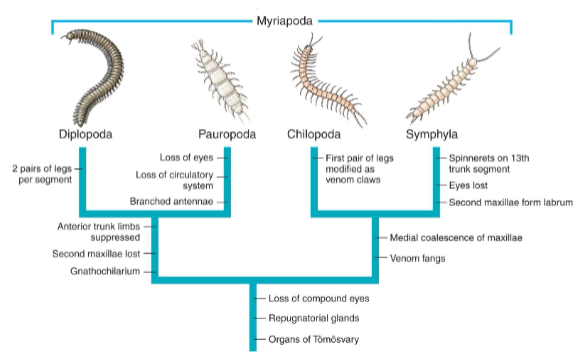
Subphylum Myriapoda: Classes
Class Diplopoda (millipedes)
Class Chilopoda (Centipedes)
Subphylum Myriapoda: Features
2 tagmata
Head
Trunk
Many legs
Trachea for respiration
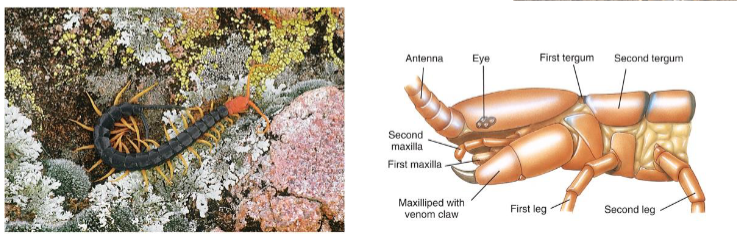
Myriapoda: Class Chilopoda
Centipedes
flattened body
One leg per segment
poisonous
predators
Myriapoda: Class Diplopoda
Millipedes
herbivorous
2 legs per segment
cylindrical body
repugnatorial glands

Subphylum Crustacea Basics
Diverse
marine, freshwater and terrestrial
most familar animals belong to Class Malacostraca
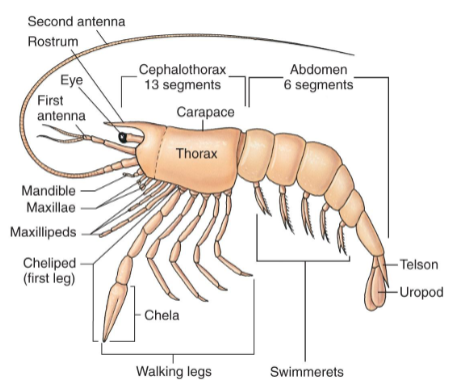
Crustacead Body Plan: External
biramous appendages
2 pairs of antennae
mandibles
2 pairs of maxillae
maxillipads
swimmerets
uropod
Rostrum
Telson
Tagmata:
Cephalothorax
Abdomen
Crustacead Body Plan: Internal
Open circ sys
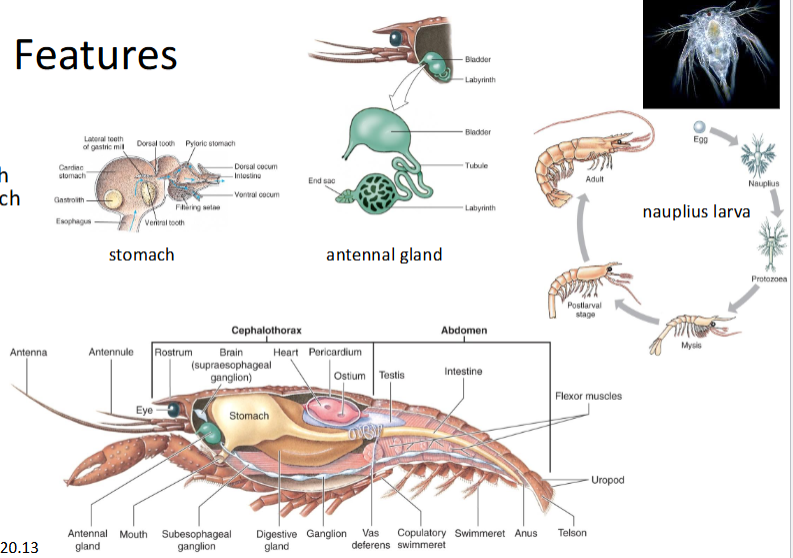
dig sys with gastric mill in stomach
excr org are antennal (green) glands
Crayfish have direct dev
Marine crustaceans have nauplius larval stage
Feeding is diverese
Crustacean Classes
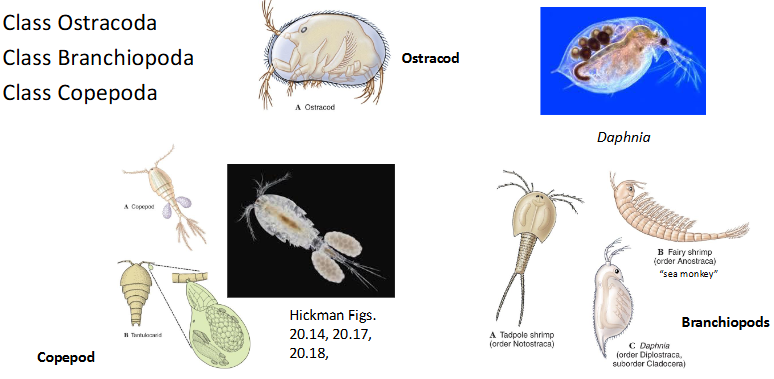
Class Ostracoda
Class Branchiopoda
Class Copepoda
Class Cirripedia (barnacles)
Class Malacostraca
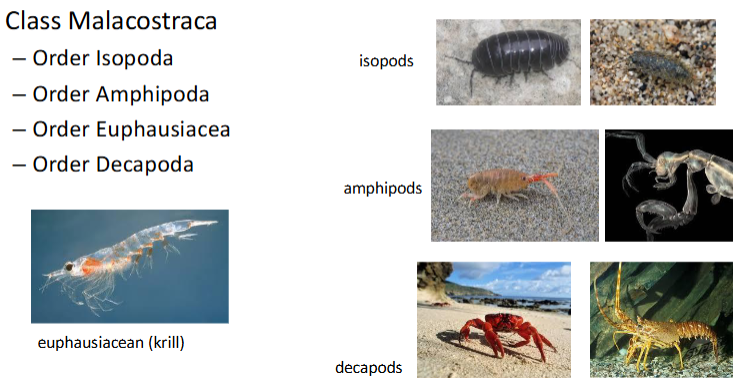
Class Malascostraca: orders
Order Isopoda
Order Amphipoda
Order Euphausia
Order Decapoda
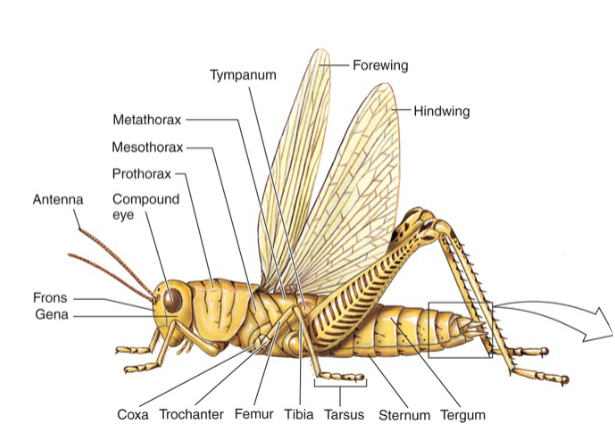
Hexapod Structure
Six Legs
3 tagmata:
Head
Thorax
Abdomen
1 pair of antennae
2 pairs of wings
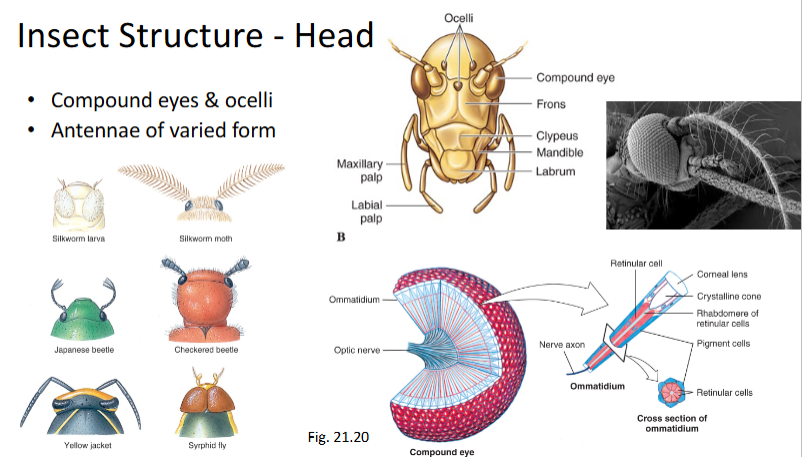
Insect Structure - Head
Compound eyes and ocelli
Antennae of varied form
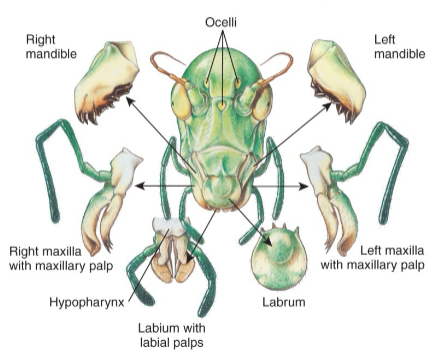
Insect - Mouthparts
labrum
mandibles
maxillae w/palps
labium w/ palps
hypopharynx
Insect Mouthpart - Diversity in function
Chewing
sucking
lapping
Insect: Internal Form and Function
gut tube w/ gastric ceca
open circulatory system with dorsal heart
respiration by tracheae
excretion by Malpighian tubules
ventral nervous system, well developed brain
sexual reproduction, sexes separate (dioecious)

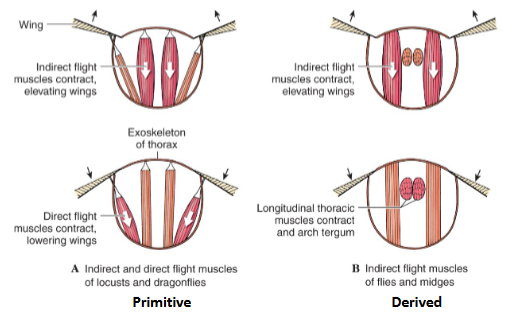
Insect Flight
Direct flight muscles vs Indirect flight muscles
Hexapod - reproduction and Life Cycle
Mating
spermatophores
copulation
Development
Ametabolous
egg > juvenile > adult
Hemimetabolous
egg> nymphs > adult
Holometabolous
egg > larva/grub/caterpillar > pupa (chrysalis) > adult (imago)
Each stage between molts is called an instar
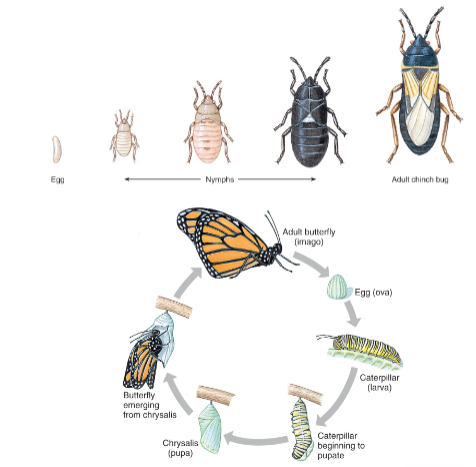

What is this?
Hemimetabolous Nymphs

What are these?
Holometabolous Larvae
Eusociality

Honeybee Society
3 castes:
Queen
Drones
Workers
Males are haploid (haplodiploidy
“Royal Jelly” fed to larvae makes them queens
Waggle Dance
insect products:
Shellac and silk

Insect services:
Pollination
Insect Pests
Locusts, aphids, pine beetles
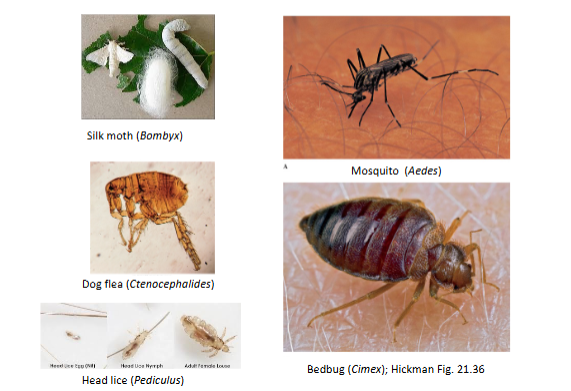
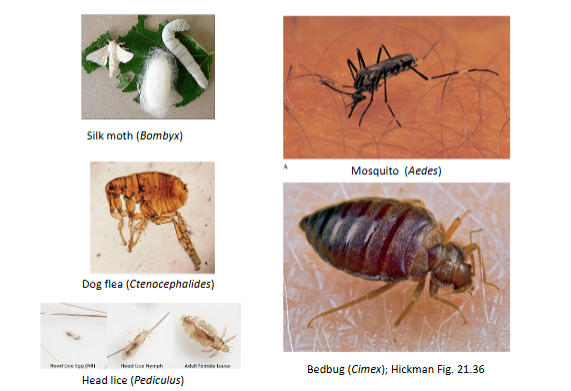
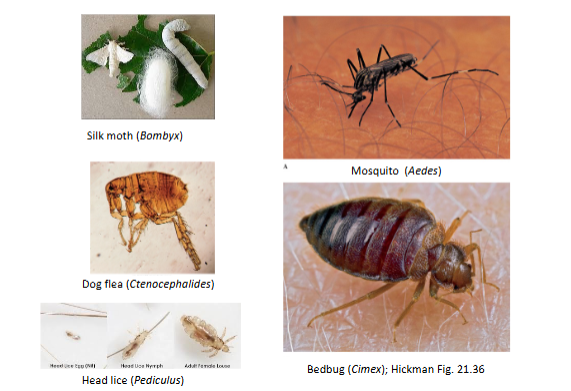
Insect Parasites:
Parasitoid Wasps
Lice
Fleas
Bedbugs
Mosquitos
Insect Subphylum
Hexapoda
Classes in Subph. Hexapoda
Cl. Entognatha
Cl. Insecta
Order in Cl. Entognatha
Order Collembola - springtails
Cl. Insecta - 10 Orders
