Knowt 5 - Classification and Macroevolution
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Science of Taxonomy and Speciation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Microevolution
Allele frequency; small scale; populations
Macroevolution (2 Ideas)
Significant changes accumulated over a long period of time
Includes speciation requires some form of separation/isolation
Systematics (2 Ideas)
The field of science concerned with studying the diversity of all life on earth, past and present
Concerned with taxonomy and phylogeny
Taxonomy (2 Ideas)
The science of naming and classifying organisms.
Standardized and universal.
Phylogeny (3 Ideas)
The study of evolutionary relationships between taxa (si. taxon)
Based on hypotheses and inference
Represented in phylograms
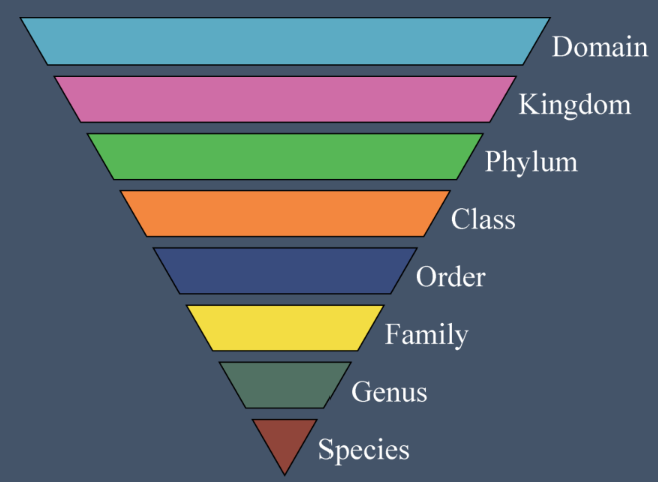
Classification (1. Top → 8. Bottom)
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Domain
Eucarya
Kingdom
Animalia
Phylum
Chordates
Class
Mammalia
Order
Primates
Family
Hominidae
Genus
Homo
Species
Homo Sapiens
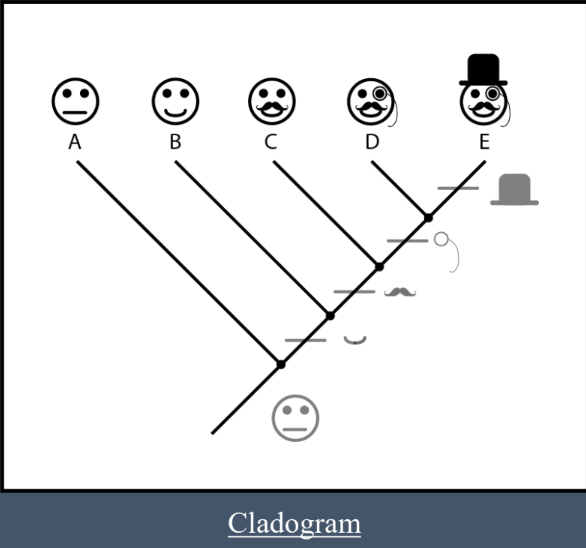
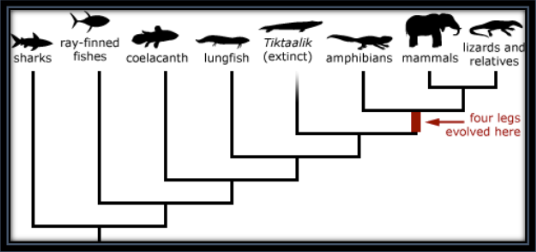
Basic Principles - Homologous Traits (4 Ideas)
A trait that is similar between organisms because they share a common ancestor
Can serve same or different function
Divergent evolution
Example: tetrapods
Tiktaalik
Homologous Traits - 2 Types
Ancestral Traits
Derived Traits
Ancestral Traits
Traits from a distant ancestor that are shared among multiple lineages; older
Derived Traits
A trait that is a modification of an ancestral form; can be shared or unique; newer.
Basic Principles - Analogous Characters (3 Ideas)
Characters that are similar between species that share a common function but were developed independently
Convergent evolution
Example: cetaceans, sirenians, pinnipeds

Biological Species Concept
Species a la John Ray (1627-1705)
Individuals who can breed together and produce fertile offspring
Paleospecies
Extinct species identified in fossil remains
Crucial to identify source of variation
Intraspecific?
Interspecific?
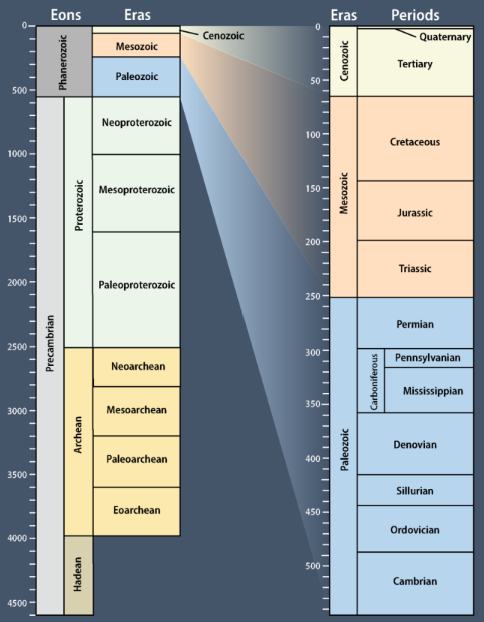
Geological Time Scale (2 Ideas)
Ordering of deep time into eons, eras, epochs, periods, and stages
4.5 Ga – present
Adaptive Radiation (3 Ideas)
Species rapidly expand into new ecological niches, diversify, and diverge
Followed by diversification and speciation
New niches exert new selective pressures
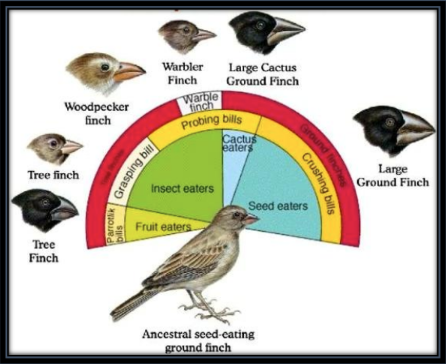
Adaptive Radiation - 3 Examples
Reptiles in Mesozoic
Mammals in Cenozoic
Darwin's finches
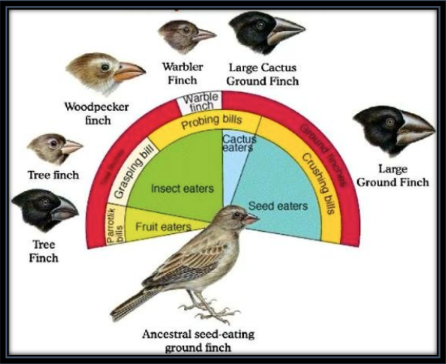
Generalized traits
Traits adapted to serve many functions
Good for adapting to new econiches
Specialized traits
Trait adapted for specific function
Restricted to original econiche
Basic Principles - Clade (3 Ideas)
All descendants of a single common ancestor
I.e., clades are monophyletic
Basis of cladistics