NCLEX must knows pt.2
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
orange = CV, Teal = GI
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium
causes
infection
tumor
drugs
assessment findings
sharp chest pain
tachypnea
fever, chills
weakness
Tx - NSAIDs
Pericardial Effusion
collection of fluid in the pericardiacl sac
impairs cardiac function if severe
obstructive cardiogenic shock
assessment findings
chest pain
muffled heart sounds
Tx- pericardiocentesis
cardiac tamponade
blood, fluid, or exudate have leaked into pericardial sac
causes: MVC R ventricular biopsy, pericarditis, CABG
assessment
chest pain
SOB
decreased CO
muffled/distant heart sounds
JVD
narrowed pulse pressure (<40)
Tx- pericardiocentesis and surgery
note: Posisitve pressure ventilation (PPV) is detrimental to cardaic tamponade pts bc it increases intrathoracic pressure which decreases venous return to the heart
Endocarditis
infection and inflammation of the endocardium- valves
can lead to
valve abnormalities
stenosis
regurgitation
poor cardiac output
bacteremia
bacterial emboli
Tx- abx
Left-sided Heart Failure
left side of heart cannot move blood out to body
blood is backing up into the lungs
assessment
pulmonary congestion
wet lung sounds
dyspnea
cough
blood tinged sputum
S3
orthopnea
“FORCED”
Fatigue
Orthopnea
Rales/restlessness
Cyanosis/confusion
Extreme weakness
Dyspnea
#1 cause is HTN
Right sided Heart Failure
right side of heart cannot move blood to lungs
blood is backing up into the body
assessment
JVD
hepatomegaly
splenomegaly
ascites
weight gain
fatigue
anorexia
“BACONED”
Bloating
Anorexia
Cyanosis
Oliguria
Nausea
Edema
Distended neck veins (JVD)
caused by left sided heart failure
Heart Failure Tx
decrease the workload of the heart
primary strat is to decrease afterload
ACE inhibitors
increase stroke volume
ARBS
↑ CO
↑ contractility- Digoxin
Diuresis
↓ excess fluid
HF pt education
take diuretic meds in the AM
monitor electrolyte lvls while on diuretics
low sodium diet- helps ↓ fluid
elevate HOB- will help w diuresis
Daily weights!
same time, scale, clothes
report any increase of 2-3 lbs in one day
small intestines
receive digesting enzymes from the pancreas and liver
via pancreatic and common bile ducts
churn and mix ingested food, making it into chyme
absorb nutrients
move the food along its entire length, into the colon
gallbladder
stores bile (made by liver) and releases it into duodenum of small intestine
bile
emulsifies lipids so they can be absorbed
greenish, yellowish, brown substance
very alkaline
exocrine function of pancreas
produces and releases digestive enzymes
Trypsin: break down proteins
Amylase: breaks down carbohydrates
Lipase: breaks down fats
enzymes released into duodenum
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
aka hyperalimentation
contains
dextrose
amino acids
electrolytes
indications
enteral nutrition contraindicated
high risk for aspiration
GI tract obstruction
complications
infection
bag and tubing changed q24h
refrigerated until ready to hang
fluid overload
daily weights
check electrolytes
hypo/hyperglycemia
do not turn on or off suddenly
if you run out of TPN, give dextrose 10% at the SAME rate the TPN was running
titrate up when turning on and down when turning off
check BG q4-6h
embolism
Central line preferred!
ondansetron
class- antiemetic
indication- N/V
action- blocks effects of serotonin on vagal nerve and CNS
nursing considerations
administer slowly. Fast push can cause QT prolongation and VT
torsades de pointes vtach
Famotidine
class- H2 receptor antagonist- antihistamine
indication- short term Tx of gastric and duodenal ulcers, GERD, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, hypersecretion of stomach acid conditions, chronic NSAID/ASA use and GI distress
action- blocks release of histamine which means its blocking the secretion of gastric acid and pepsin
nursing considerations
monitor CBC and kidney function
can be given with meals
peak absorption of famotidine is within 2-3 hrs
available OTC in lower strengths. teach pts to only take as directed and for short durations
famotidine less likely to interact w other drugs so it is DOC when pts are on multiple drugs esp if the others have therapeutic/toxic level concerns
Omeprazole
class: proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) (-azole)
indication: GERD, ulcers
action: prevents the transport of H ions into the gastric lumen by binding to gastric parietal cells to decrease gastric acid production
nursing considerations
administer 30-60 minutes before meals
report black, tarry stools
indicates upper GI bleed
Sucralfate
class- disaccharide sulfates. it contains aluminum hydroxide and sucrose
indication- short-term Tx of duodenal or gastric ulcers, peptic esophagitis, NSAID/ASA induced GI damage
action- promotes healing of ulcers by providing a barrier over them. it creates a paste when exposed to hydrochloric acid and binds to proteins that are excreted by damaged cells in ulcerated tissue
nursing consideration
take on empty stomach 1 hr before meals or 2 hrs after meals and at bedtime.
often given up to 4x daily
don’t give within 30 min of antacids as they can ↓ effectiveness of sucralfate
take care giving antacids that contain aluminum to kidney failure pts bc aluminum toxicity
monitor BG in diabetics as sucralfate contains sucrose
can ↓ the bioavailability of warfarin, digoxin, and phenytoin, levothyroxine, and several classes of abx. separate these drugs from sucralfate for at least 2 hrs
other than nutrition, what can NG tubes be used for?
removal of stomach contents after overdose
With NG tubes, if you have a residual over ___ mL, you want to hold the feed and call PHCP.
500 mL
blakemore tube
tube inserted thru nose down esophagus and into the stomach w balloons that can be inflated to stop bleeding esophageal varices
aka Sengstaken-Blakemore or Minnesota tube
must keep a pair of scissors at the bedside in case of emergency!
if balloon becomes dislodged, it can compress trachea
cut the gastic balloon port to deflate it quickly so you can pull out tube
When administering Nitroprusside, which lab value should be monitored?
Thiocyanate levels
renal infarction
can manifest as a result of infective endocarditis
In a renal infarction, the septic emboli get lodged in the renal artery, creating significant pain and decreasing the blood flow to the affected kidney.
presents with flank pain or even microscopic/frank hematuria
Esophageal Varices
dilated mucosal veins in the esophagus
can burst and bleed
life-threatening emergency
causes
liver disease
alcoholism
Tx
blakemore tube
surgery
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
acid and refluxes from the stomach into the esophagus, causing esophagitis
conditions that increase abd pressure increase risk for GERD
vomiting, coughing, lifting, bending, obesity
Tx
sit upright after meals
small, frequent meals
H2 blockers
PPIs
Complication
Barrett’s esophagus- extended period of reflux changes esophagus and causes presence of precancerous or cancerous cells
Gastritis
inflammatory disorder of the gastric mucosa
acute gastritis
associated with Helicobacter pylori, NSAIDs, drugs, chemicals
clinical manifestations
vague abd discomfort, epigastric tenderness, and bleeding
Tx
Healing usually occurs spontaneously within a few days
D/C NSAIDs
H2 receptor blockers
PPIs
abx if due to H. pylori
gastric ulcer
cause
H. pylori
overuse of NSAIDs
Sx
pain 1-2 hrs after meal
abd pain aggravated by eating
vomiting
weight loss
hematemesis if hemorrhage occurs
Tx
treat H. pylori w abx
reduce stomach acid
H2- receptor blocker
PPI
Duodenal ulcer
cause
H. pylori
overuse of NSAIDs
Sx
pain 2-4 hrs after meals
food may relieve pain
weight gain
Melena if hemorrhage occurs
Tx
abs
H2 receptor blockers & PPIs
Crohn’s Disease
inflammation and erosion of the ileum and anywhere throughout the small and large intestines
idiopathic inflammatory disorder; affects any part of the digestive tract, from mouth to anus
Granulomatous colitis, ileocolitis, or regional enteritis
difficult to differentiate from ulcerative colitis
similar risk factors and theories of causation
Ulcerative Colitis
inflammation of the large intestines
chronic inflammatory disease that causes ulceration of the colonic mucosa
sigmoid colon and rectum
common in 20-40 y/o age range and ppl of jewish descent
suggested causes
infectious, immunologic (anticolon antibodies), dietary, genetics
pathophysiology
lesions are continuous with no skipped lesions, are limited to the mucosa, and are not transmural
Diverticular Disease
Diverticula- Herniation of mucosa through the muscle layers of the colon wall
Diverticulosis- asymptomatic diverticular disease
diverticulitis- inflammatory stage of diverticulosis
Possible causes
decreased dietary fiber
abnormal neuromuscular function
alterations in intestinal motility
>60 years of age
assessment
rebound tenderness
cramping
diarrhea
vomiting
dehydration
weight loss
rectal bleeding
bloody stools
anemia
fever
Tx
low fiber diet- food with casings can get stuck in pockets and cause inflammation
avoid cold or hot foods
no smoking
antidiarrheals
abx
steroids
in severe cases may end up surgically removing the affected portion of the intestines
ileostomy
colostomy
Intestinal obstruction
any condition that prevents the flow of chyme through the intestinal lumen or failure of normal intestinal motility in the absence of an obstructing lesion
clinical manifestations
small intestine obstruction
colicky pains caused by intestinal distention, followed by nausea and vomiting
large intestine obstruction
hypogastric pain and abd distention
Appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix
most common age = 10 yrs old
most common abd surgery in children
perforation more common in children
pain
begins as dull, steady periumbilical pain
over 4-6 hrs, pain progresses and localizes to RLQ
Sudden relief of pain may indicate appendix rupture
can lead to peritonitis
(+) McBurney’s sign: significant pain upon palpation
Tx
appendectomy
pre-op
no heat- can aggravate inflamed appendix and cause rupture
position R side, low fowlers for comfort
post-op
IVF, IV abx
pain management
NPO until return of bowel sounds
wound care
Pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas
# 1 cause = alcoholism
pathophysiology
digestive enzymes activate inside of the pancreas
this causes autodigestion of the pancreas
assessment
pain- increases with eating due to increased digestie enzymes
abd distention; possible ascites
abd mass- the hard pancreas
rigid abd
cullen’s sign- c shaped brusing above umbilicus
gray turner’s sign- bruising along the flank
fever
N/V
jaundice
hypotension- pt losing fluid into 3rd spaces
labs
increased WBC
increase serum lipase (pancreatic enzymes)
interventions- PANCREAS
Pain control
Antispasmodic rugs to reduce gut motility
NPO/NGT suction, TPN- pancreatic rest
Calcium replacement bc hypocalcemia
Replace fluids and electrolytes
Elevated enzymes (check amylase and lipase)
Antibiotics with fever
Steroids- corticosteroids for acute attacks
Cholelithiasis
aka gallstones
hardened deposits of bile in the gallbladder
can be the size of a grain of rice up to the size of a golf ball
causes
hyperlipidemia
hyperbilirubinemia
assessment
sudden, sharp RUQ pain
pain worsens continually
can radiate to back and between shoulder blades or R shoulder
gets worse at night or after a fatty meal
N/V
Tx
cholecystectomy
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
causes
cholelithiasis, infection, blocked bile duct
clinical manifestations
fever, leukocytosis, rebound tenderness, and abd muscle guarding
Tx
pain control
replacement of fluids and electrolytes
fasting
abx administration
perforated gallbladder: immediate cholecystectomy
Hepatitis
inflammation of the liver
can progress to cirrhosis
Types A, B, C, D, and E- caused by different viral infections
severe cases can lead to a hepatic coma (hepatic encephalopathy)
A- contaminated food or water; typ self-limiting; no risk chronic infection
B- contact w infected body fluids; acute supportive chronic antiviral therapy w or w/o interferon; yes risk for chronic infection
C- contact w infected body fluids; direct-acting antivirals (DAAs); yes risk for chronic infection
leading cause of end-stage liver disease worldwide
D- contact w infected body fluids; no specific tx, peglated interferon may help; yes risk for chronic infection
E- contaminated food or water; typ self-limiting; no risk chronic infection
lactulose
bacteria in the colon digests lactulose into chemicals that bind ammonia
used to decrease ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy
hepatic encephalopathy
assessment
fetor
changes in LOC
neuromuscular disturbances- asterixis, hyperreflexia
sleep, mood, and speech problems
Tx
decrease ammonia
lactulose
abx (neomycin or rifaximin)
reduces bacterial production of ammonia
decreased protein in diet
monitor serum ammonia
decrease fluid retention
potassium-sparing diuretics
avoid CNS depressants
Cirrhosis
chronic disease of the liver marked by degeneration of cells, inflammation, and fibrous thickening of tissue
liver cells destroyed and replaced with scar tissue
This impairs blood flow to liver, causing portal HTN
primary causes- “ABCD”
Alcohol
B hepatitis B
C hepatitis C
Diet
assessment
palpable, firm liver
ascites, edema
abd pain, bloating, dyspepsia, poor appetite
spider angiomas
jaundice
anemia!!
abnormal labs
decreased serum albumin
increased serum liver enzymes- ALT/AST
Tx
antacids
vitamins
diuretics
paracentesis
strict I&Os
daily weights
Be v careful w drug doses bc liver cant metabolize well. most doses need to be decreased. esp w
narcotics
acetaminophen
low protein, low sodium diet
bleeding precautions
skin care
Amphotericin b
potent IV antifungal
associated with several electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia
causes potassium to shift into the cells
it can have some effect on lipid metabolism, but the key lab value to monitor is potassium
Rivastigmine
indicated for use in dementia
increases acetylcholine in CNS through revrsible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase
comes in patch and tablet
adverse effects
N/V, weight loss, HTN, bradycardia
Phenelzine
MAOI
avoid foods high in tyramine like smoked bacon
can cause hypertensive crisis
post op tonsillectomy diet
foods that are soft, not hot, non-acidic, and do not have jagged edges
ice chips are okay cause they melt in the mouth ig??
Oxybutynin
anticholinergic used to treat urinary bladder urgency and incontinence
Metoclopramide
dopamine antagonist
effective for migraine-associated nausea and some HA relief
commonly used as adjunct Tx in emergency settings
Mechanical ventilation can cause stress ulcer. meds? complication?
PPI or H2 blocker
stress ulcer may lead to GI bleed
Before IV urography (pyelogram), what must pt do?
take a laxative the night before to clear the bowels
this is to ensure adequate visualization of urinary tract
during procedure, pt will empty bladder, IV contrast given, and series of x-ray and fluoroscopy used to observe passage of urine from renal pelvis to bladder
Rule of Nines for burns
head - 9%
chest - 18%
abdomen - 18%
each leg- 18%
each arm - 9%
genitals - 1%
Nicardipine
CCB
given during hypertensive emergency
administer with infusion pump while pt receives continuous cardiac monitoring
Restlessness indicates:
hypoxia!
Hydralazine
arteriolar vasodilator
intended for HTN
pt at risk for falls bc of orthostatic hypotension!!!
hydralazine toxicity s/s: hypotension, tachycardia, HA, and generalized skin flushing
reflex tachycardia may occur bc as BP declines, HR will increase to maintain CO
A patient with asthma exacerbation experiences a sudden absence of wheezing. What does this indicate?
Respiratory arrest
Before administering IV potassium, nurse should verify what in order to avoid hyperkalemia?
urinary output
note: peripheral IV potassium should be administered at 10 mEq/hr
maximum of 40 mEq/hr in central line
hypovolemic shock
not enough blood to enter heart (preload), which decreases CO
body will vasoconstrict to compensate
causes
hemorrhage
traumatic injury
dehydration
vomiting/diarrhea
burns
assessment
weak
pale, cool, clammy
tachycardic, hypotension
anxious
decreased LOC
decreased UOP
Tx
fix the cause
stop vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding (repair in OR)
replace volume
isotonic IVF (NS, LR)
blood products
support perfusion
vasopressors
cardiogenic shock
heart fails to pump sufficient blood out bc obstruction or weak heart muscle
causes
MI
cardiac tamponade
pulmonary embolism
assessment
decreased perfusion
hypotension
weak pulses
cool, pale, clammy
decreased UOP
decreased LOC
volume overload
JVD
crackles
SOB
muffled heart sounds
S3
Tx
treat the cause
MI- PCI, CABG
PE- thrombolytics
Tamponade- pericardiocentesis
improve contractility
dopamine
dobutamine
decrease afterload
diuretics
dobutamine
cardiac tamponade
too much fluid fills in the pericardial saac
leads to increased pressure in the heart
s/s muffled heart sounds, JVD, hypotension, and pleural friction rub
Tx- pericardiocentesis
distributive shock
immune or autonomic response that alters vascular tone and causes massive peripheral vasodilation
causes
anaphylactic- allergic reaction
neurogenic- SCI
septic- systemic infection
causes release of inflammatory cytokines
assessment
decreased oxygen
hypotension
tachycardia
tachypnea
warm, flushed skin
decreased LOC
Tx
anaphylactic
epinephrine
corticosteroids
bronchodilators
neurogenic
cooling
supportive care
septic
IV abx- get cultures
IVF
20 mL/kg up to 3 times
if still hypotensive, vasopressors!
Traction Positioning
uses a pulling force to realign a bone
skeletal
uses screws/pins into the bone
15 - 30 lbs of pulling force
ex: halo traction
skin
decreases muscle spasms
5 - 10 lbs of pulling force
ex: buck traction
nursing actions
monitor circulation q1h for first 24 hrs and then q4h after that
pin site care
use of saline/vaseline dressings q8-12h
s/s of pin site infection
loose pins
purulent drainage from pins
clear drainage is expected finding
odor
fever
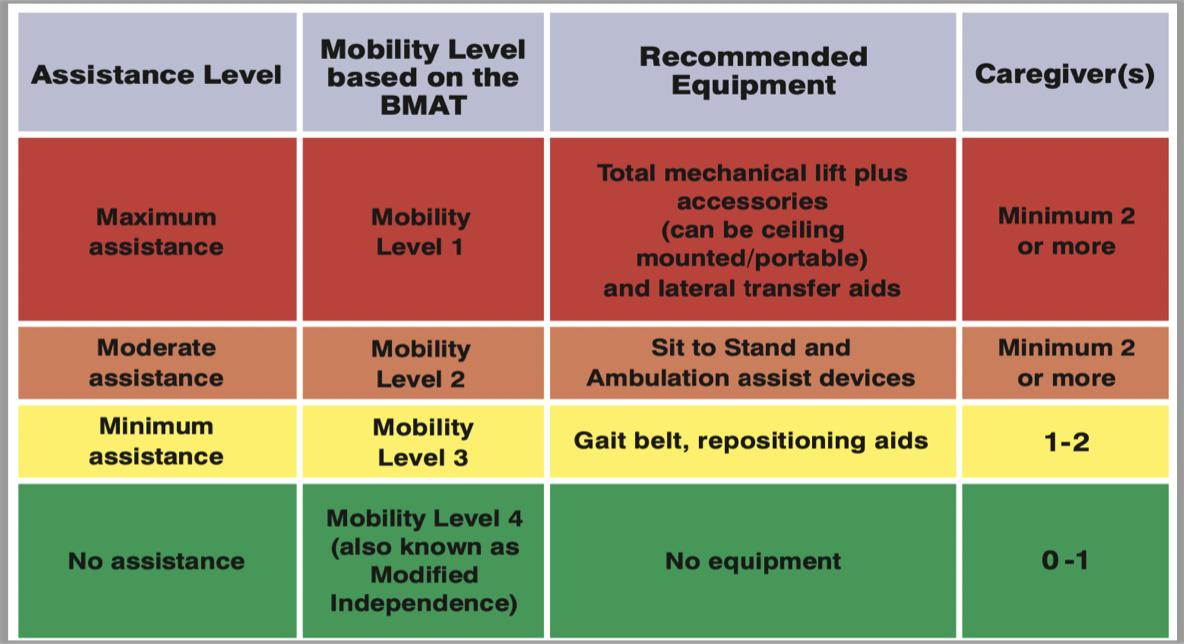
Bedside Mobility Assessment Tool (BMAT)
sit and shake
how is their trunk strength, seated balance, and cognition?
stretch and point
how is their lower extremity stability and strength?
stand
can they stand? strength from sitting to standing?
walk
how is their standing balance? assess their gait while walking
immobility complications
skin breakdown- pressure ulcers
contractures
muscular weakness
muscular atrophy
loss of calcium from the bones
osteoporosis
hypercalcemia
renal calculi
atelectasis- pneumonia
venous stasis- DVT
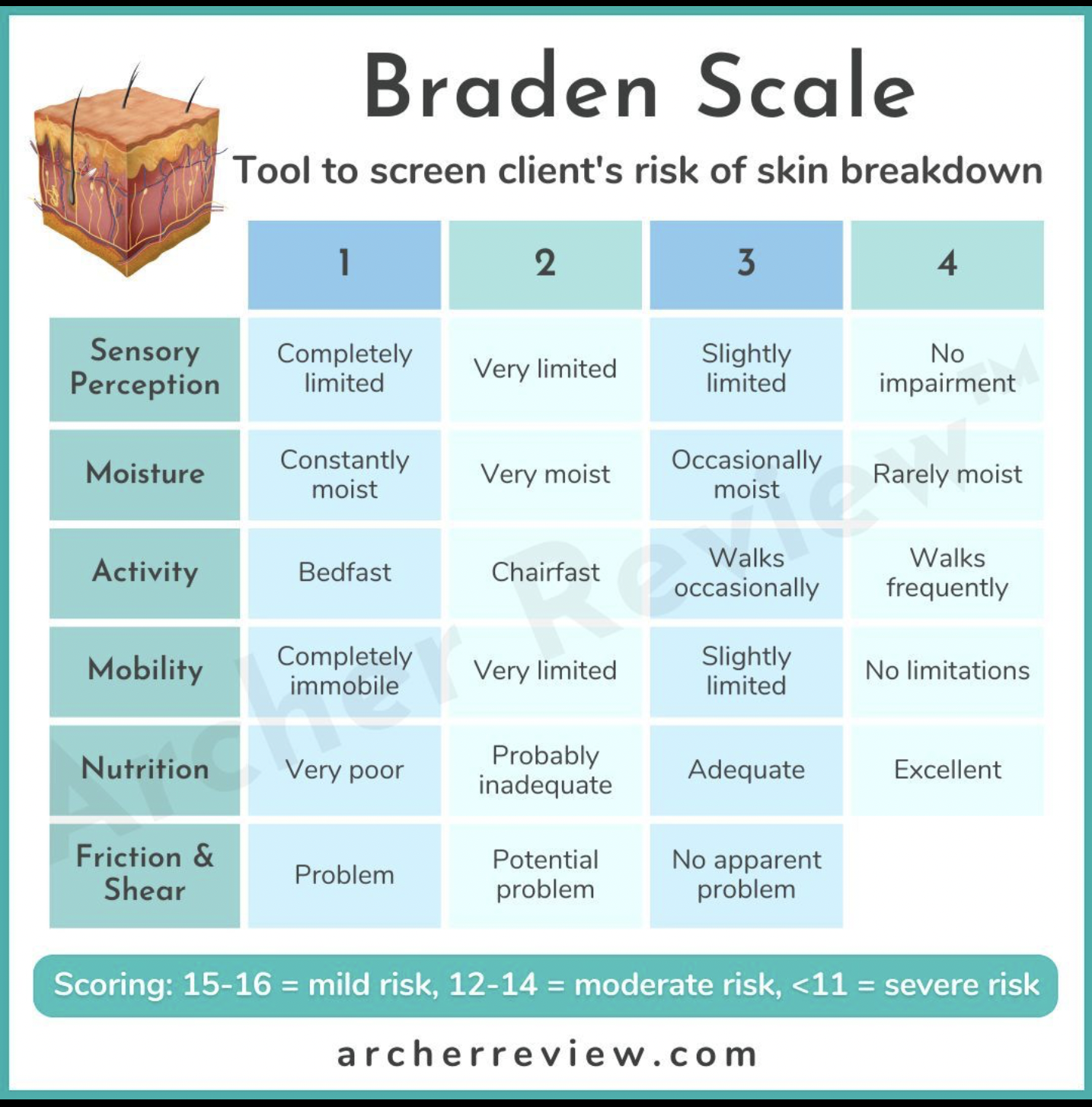
Braden Scale
scoring- 15-16 = mild risk, 12-14 = moderate risk, <11 = severe risk
open sores can lead to infection!
devices that promote venous return
TED hose
compression stockings
Sequential compression devices (SCDs)
BMI calculation
BMI = weight (kg) / height² (m²)
ex. 57 kg pt 1.52 m tall. = 57/2.3104 = 24.671
<18.5 = underweight
18.5 - 24.9 = normal weight
25.0 - 29.9 = overweight
> 30 = obese
TPN
IV nutrition
central line is preferred!!
made of proteins, dextrose, lipids, vitamins, minerals, electrolytes
bacteria loves sugar!
high infection risk!!!
change TPN tubing q24h bc sugar sticky
if you run out of TPN, hang D10 at same rate as TPN was running
postmortem care
lines/tubes
autopsy- keep all lines/tubes in place
no autopsy- remove all lines/tubes
client care
place pillow under head
put in dentures
close eyes
assess for specific religious/cultural practices
assistive devices - walker
stand in center of walker
slide walker forward 6-8 inche
keep all 4 feet of walker on the ground
step forward with bad leg
keep weight on walker and unaffected leg
bring good leg up to walker
assistive devices- cane
cane goes on good side
slight bend at the elbow
cane moves forward 6-10 inches
bad leg moves forward with cane
good leg then moves past the cane
assistive devices- crutches
2-3 finger spaces b/w armpit and crutch
use shoulders and arms for strength
slight bend through the elbows
2-point gait
requires partial weight bearing on both feet
move R leg forward with left crutch at same time and vice versa
3-point gait
non-weight bearing and can progress to partial weight bearing
crutches advanced with affected leg
unaffected leg brought forward
swing-through gait
for non-weight bearing or partial weight bearing clients
required balance and coordination
stand on unaffected leg
move both crutches forward ab a foot
brace the hand grips for support
swing both legs through the crutches
4-point gait
only 1 point moving at a time
move R crutch forward
move L leg forward
move L crutch forward
move R leg forward
stairs with crutches
up with the good and down with the bad!
Methotrexate
class- DMARD
indication- Rheumatoid arthritis
action- reduce joint destruction and slow disease progression by interfering in immune and inflammatory responses
nursing considerations
lifelong therapy; treats sx but disease continues to progress
must treat RA aggressively: start a DMARD early- within 3 months of RA
can be possible to delay or even prevent serious joint injury
Allopurinol
class- hypouricemic agent
indication- Gout
action- inhibits xanthine oxidase to prevent uric acid from forming
uric acid: byproduct of breakdown of purines
nursing considerations
monitor for side effects of leukopenia, fever & rash
dosage must be individualized
teach to avoid foods high in purine
beer, wine, cheeses, beans, anchovies, sardines, liver, kidneys, cream
Alendronate
class- biphosphonate
indication- osteoporosis
action- decreases bone resorption by osteoclasts
nursing considerations
SE- esophagitis
contraindicated in pts w pre-existing esophageal disorder
take with a full glass of water
remain upright for 30 min after taking ( do not take supine or lie down after taking)
if difficulty or pain with swallowing, or heartburn develops, pts should d/c med and contact PHCP
Baclofen
class- centrally acting muscle relaxer
indication- muscle spasticity: MS, CP, SCI
action- acts within the spinal cord to suppress hyperactive reflexes involved in the regulation of muscle movement
nursing considerations
monitor for CNS depression
do not discontinue abruptly- taper over 1-2 wks
can cause a seizure
spiral Fx
esp in peds or elderly, suspect abuse
caused by twisting force
traction nursing considerations- TRACTION
T- temperature
R- ropes (should be hanging freely)
A- alignment
C- circulation
T- tension (no tension on skin. high risk for skin breakdown!)
I- intake (monitor I&O)
O- overhead trapeze ( bar overhead to help w ROM)
N- no weights on floor
Rheumatoid Arthritis
chronic systemic inflammatory disease that leads to destruction of connective tissue and synovial membrane within the joints
weakens the joint, leading to dislocation and deformity of the joint
pannus forms at the junction of synovial tissue and articular cartilage and projects into the joint space which causes necrosis
RA exacerbations or “flares” occur during periods of fatigue and stress (emotional or physical)
assessment findings
inflammation, tenderness, stiffness of the joint
decreased ROM in joints
moderate to severe pain with morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 min
joint deformities
spongy, soft feeling in joints
might even feel warm reddened boggy
elevated ESR and positive rheumatoid factor
x-ray shows joint deterioration
synovial fluid shows inflammation
Tx- no cure
NSAIDs, DMARDs, glucocorticoids
preserve joint function
heat or cold therapy as prescribed
encourage consistent exercise program
avoid weight bearing on inflamed joints
surgical:synovectomy, arthrodesis, joint replaccement
Osteoarthritis S/S- “OSTEO”
O- outgrowths
bone spur formations
Heberden’s node: close to fingernail
Bouchard’s node: middle finger joint
S- stiffness
in the morning
lasting less than 30 min
T- tenderness
hard, bony, tender joints
E- exacerbated by exercise
crepitus w movement
pain w activity- goes away w rest
O- only in the joints
not systemic- no inflammation, redness, fever, fatigue, or other such sx
Gout
body cannot control uric acid production or exertion
high uric acid builds up in the body
uric acid crystallizes and deposits in connective tissue
causes inflammation and destruction of joints
most common location- big toe
complication- gouty arthritis
assessment
pain- gets worse as the day goes on
inflammation
redness
decreased mobility
very stiff
intense pain with pressure
Tophi
large clumps of uric acid crystals that have accumulated over time
white/yellow
can permanently damage joints
high uric acid level
nursing interventions
alternate cold and warm compresses
hydration
bed rest
NSAIDs
corticosteroids
allopurinol
prevents future attacks- does not tx current sx
decreases production of uric acids
low purine diet- avoid
red meat, organ meat, seafood, alcohol
Myopathy
primary muscle disorder causing weakness and atrophy
assessment findings:
decreased muscle strength and tone
causes
drugs
alcohol abuse
idiopathic
Rhabdomyolysis
injury to skeletal muscle
burns
trauma
compartment syndrome
muscles release intracellular contents into the blood
myoglobin- protein that helps form muscle
creatinine kinase- muscle byproduct
potassium
phosphorus
these substances become toxic in circulation
major kidney damage as nephrons try to filter toxins out
S/S
vomiting
bruising (ecchymosis)
fatigue
muscle weakness
dark urine (cola colored!)
Tx
fluids- NS, flushes kidneys
diuretics
decreased swelling
increase UOP
flush out toxins
dialysis
if K too high or kidneys unable to clear the toxins on their own
bedrest
monitor electrolytes and CK
telemetry!!
Naegele’s rule
1st day of last menstrual period + 7 days - 3 months + 1 year = estimated due date (EDD)
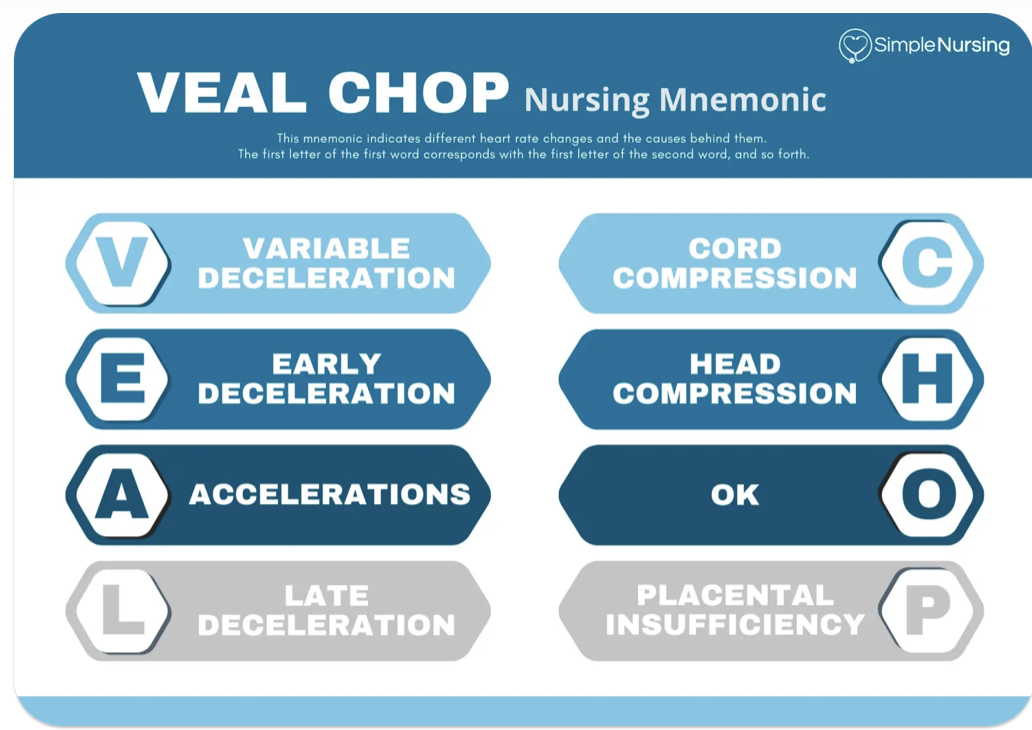
Early decelerations are caused by:
head compression
normal and no need to intervene
variable decelerations
we should see variability of 6-25 BPM.
indicates healthy nervous system
we want to see this moderate variability- reassuring
fetal bradycardia
HR <110 for 10 minutes or more sustained
due to prolonged cord compression, umbilical cord prolapse, anesthetic medications, fetal heart abnormalities
tx - side lying mom, IVF, O2, notify PHCP, stay at bedside w mommy
fetal tachycardia
HR >160 for 10 min or longer
due to maternal fever/infection, fetal hypoxia, maternal hyperthyroidism, cocaine use
tx underlying cause
fetal tachycardia + decreased variability = severe fetal distress!
late decelerations
decel happens after peak of contraction
prolonged return to baseline
cause is uteroplacental insufficiency (bc decreased BF to baby, fetal hypoxia)
LION PIT
s is also prep for surgery (C-sec)
variable decelerations
FHR tracing drops and comes back up rapidly
due to umbilical cord compression
increased fetal BP which leads to decreased FHR
tx
put mom in trendelenburg
knee-chest position
LION PIT
amnioinfusion PRN - for oligohydramnios
synthetic amniotic fluid
VEAL CHOP
Tumor lysis syndrome
Many cancer cells die in a short period
contents released into bloodstream
hyperkalemia
hyperuricemia
hyperphosphatemia
hypocalcemia