Core science CAT Physics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Anode
attracts negative charges
Cathode
Attracts positive charges
Electrolyde
type of conducting fluid or paste where electric charges can flow.
electrode
is a electrical conductor used to make contact with a non metallic part of a circuit.
electricity
Electricity is a form of energy from charged particles.
static electricity
Electricity can be STATIC as charges collect and build up on an area
current
Current ( symbol I) is the flow of electric charge every second, past any point in a circuit. Measured in amps (A)
ampere (amp)
measure of the amount of electric charge in motion per unit time
what does electric charge do
causes matter to experience forces within electromagnetic fields, leading to attractions between opposite charges and repulsions between like charges (both positive or both negative)
what does a battery do in a circuit
a battery acts as a power source by converting stored chemical energy into electrical energy, creating a potential difference (voltage)
what does a resistor do in a circuit
introduces resistance into an electrical circuit to limit or reduce the flow of electric current and to control voltage levels
what does a globe do in a circuit
acts as an electrical load that converts electrical energy into light energy
what does a switch do in a circuit
acts as a controllable connection that allows you to turn the circuit on or off by opening or closing the path for electric current to flow
what is a magnet and what does it do
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field and exerts an invisible force, or magnetic field, that attracts or repels certain objects
what does a voltmeter do
measures the electrical potential difference (voltage) between two points in an electrical circuit
what does an ammeter do
measures the electric current in a circuit
what is a volt
a unit used to measure the electrical force that pushes electrons through a wire or circuit
Voltage ohm’s law formula
V = I x R
Current Ohm’s Law Formula
I = V/R
Resistance Ohm’s Law Formula
R = V/I
what is ohm’s law
the voltage drop of a resistor will always be the same to the current of the resistor. This means that current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points.
Difference between static and electricity
static electricity is a non-moving, accumulated electric charge, whereas electricity (or current electricity) is the continuous flow of electric charge
difference of parallel and series circuits
series circuits have a single path, meaning if one component fails, the entire circuit breaks, while parallel circuits offer multiple paths, so a failure in one branch doesn't affect the others
3 core metals you can use as a magnet
Magnetic materials include - Iron, Cobalt and Nickel
what a magnet creates around itself
invisible magnetic field
explain how a permanent and electro magnet works
Temporary magnets act like permanent magnets when they are in a strong magnetic field, but lose their magnetism when the magnetic field disappears.
A permanent magnet creates its own persistent magnetic field from materials such as nickel and iron requiring no external power source to function.
what is a solenoid
a type of electromagnet, that converts electrical energy into a linear mechanical force by using a coiled wire to generate a magnetic field that moves a magnetic plunger or armature
how does a solenoid work
by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion through magnetism

what is this
connecting wire
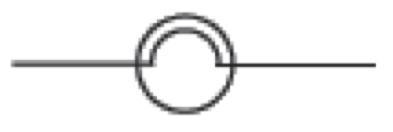
what is this
lamp (light globe)
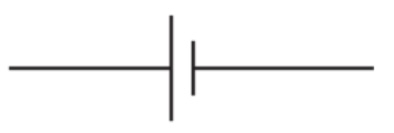
what is this
battery
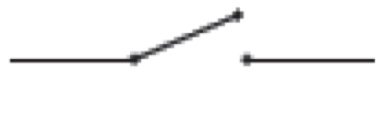
what is this
switch
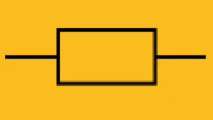
what is this
resistor
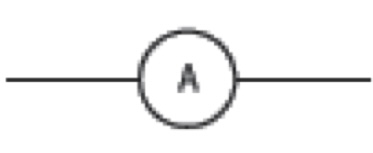
what is this
ammeter
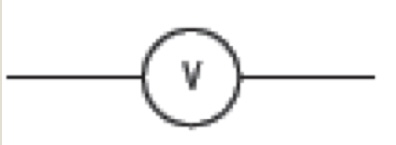
what is this
volt meter
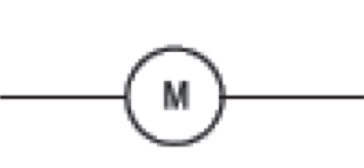
what is this
electric motor

what is this
closed switch

what is this
open switch