CMPP -- Ischemic Heart Disease 1: Stable Angina
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
signs and symptoms indicating an active process of atherosclerotic plaque buildup or formation of a thrombus, or spasm within a coronary artery, causing a reduction or loss of blood flow to myocardial tissue; includes unstable angina and other pathological events leading to myocardial infarction (MI); early diagnosis and rapid treatment are critical to avoid or minimize damage to heart muscle
unstable angina; Non-ST segment elevation MI; ST segment elevation MI
clinical presentation ACS
Stable angina
predictable and consistent pain that occurs on exertion and is relieved by rest and/or nitroglycerine
ischemic heart disease/coronary artery disease
what is the most common cause of death?
decreased indigence in smoking, improved lipid management, better care of hypertension/diabetes, medical advances (PCI)
why have we had a drop in mortality form CAD over the past 30 years?
inadequate perfusion to meet myocardial demand
myocardial ischemia results from...
inspired level of oxygen, pulmonary function, hemoglobin concentration, adequate coronary blood flow
what determines myocardial oxygen supply?
heart rate, contractility, wall stress/tension
what determines myocardial oxygen demand?
restrict flow through the coronary vessels (atherosclerosis, vessel spasm, arterial thrombi, coronary emboli), reduce supply or amount of oxygenated blood available (aortic stenosis, anemia, presence of carboxyhemoglobin)
how can we "mess up" myocardial oxygen supply?
oxygen demand (coronary vasculature is able to vary resistance)
what dictates coronary circulation?
increased, decreased, increased
increased demand from myocardium leads to ____ dilation of vessels, which leads to _____ resistance, which leads to _____ perfusions to meet that demand.
diastole
the coronary arteries are perfused during...
large epicardial arteries (right and left coronaries), pre-arteriolar vessels, arteriolar and intramyocardial capillary vessels
3 types of coronary vessels
the left anterior descending artery and the left circumflex artery
left coronary circulation divides from the aortic root into...
the septum and anterior ventricular wall
the left anterior descending artery supplies...
LAD (left anterior descending artery)
what coronary artery supplies the septum and anterior ventricular wall?
the left ventricular wall
the left circumflex artery supplies...
left circumflex artery
what coronary artery supplies the left ventricular wall?
marginal branch, posterior descending
right coronary circulation divides from the aortic root into...
right ventricle
the marginal branch supplies the...
marginal branch
what coronary vessel supplies the right ventricle?
posterior and inferior left ventricle
the posterior descending branch supplies the...
posterior descending artery
what coronary vessel supplies the posterior and inferior left ventricle?
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
thickening and obstruction of coronary vessel from atherosclerotic plaques
Plaque
collection of fat, smooth muscles, and cells; diffusely distributed throughout the vasculature; not uniform in size, shape, or makeup
genetic factors, high fat diets, smoking, sedentary lifestyle
development of plaques is associated with...
obesity, type ii diabetes, insulin resistance
risk factors for development of plaques...
atherosclerosis
plaque built up in the vessels, which causes stenosis of the vessels; can affect coronary, cerebral, and peripheral circulation
coronary, cerebral, and peripheral circulation
atherosclerosis can affect...
elevated LDL, low HDL, smoking, HTN, DM (cause microvascular disease over time)
risk factors for atherosclerosis
disturb the normal function of the vascular endothelium, and this disruption leads to plaque formation
risk factors for atherosclerosis all...
20-75
the AHA says that all patients between ____ and ____ years should receive the 10 year CVD risk assessment
10-year Risk for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD)
assessment that helps predict your risk over 10 years of heart attack, stroke, or death from cardiovascular disease.
initiate statin therapy and consider aspirin therapy; encourage lifestyle modifications
if one has a 10-year ASCVD risk of 10% or greater
sub-intimal
a plaque is a _____ collection of lipids, smooth muscle, fibroblasts, and intracellular matrix
turbulent flow (branch points of vessels)
plaques tend to develop at points of...
no
are plaques a part of the circulation?
rupture/erosion into the bloodstream
plaques are at risk of...
small thin fibromuscular cap
plaques are covered by a...
there is inflammation and tissue factor release
if a plaque ruptures, what happens first?
platelets, clotting cascade
after the TF release caused by a plaque rupture, _____ aggregate at the site, which initiates the _____
a thrombus
after the activation of the clotting cascade following a plaque rupture, what forms in the BV?
platelets and fibrin join to trap RBCs from the bloodstream
a thrombus forms when...
ischemia/possibly infarction
thrombi further reduce blood flow in vessels, which leads to...
location of plaque, size of obstruction, and presence of collateral circulation
degree of ischemia is dependent upon...
collateral circulation
circulation formed by smaller blood vessels branching off from or near larger, occluded blood vessels
vasospasm (increased sympathetic firing leads to spasm and platelet aggregation; combined effect with thrombus will worsen ischemia)
occlusion of BVs can trigger the release of local mediators that cause...
>95%
at rest, ischemia will develop with ___ stenosis
>60%
at exertion, ischemia will develop with ___ stenosis
quantity of ischemia (how MUCH of the heart is affected), severity and clinical manifestations (depending on where the heart is damaged, patients can present differently)
location of obstruction determines...
proximal
if obstruction in the heart is more ____, more tissue is affected
muscle won't contract properly due to lack of oxygen supply (cells cannot work correctly) which will lead to decreased CO
how does lack of oxygen lead to disturbances in mechanical functioning?
there will be abnormal labs due to lack of oxygen going to the tissues
how does lack of oxygen lead to disturbances in biochemical functioning?
cells are not getting enough oxygen, and then this will result in arrhythmias
how does lack of oxygen lead to disturbances in electrical functioning?
LV failure, angina, infarction and necrosis
ischemia of the LV leads to...
mitral regurgitation
ischemia of the papillary muscles of the LV leads to...
anaerobic, lactate, decreases
without oxygen, the tissues of the heart progress from aerobic to ______ metabolism, and glucose is covered to ______ and the pH ______
leaks out, is absorbed into
during the transition form aerobic to anaerobic metabolism when the heart is ischemic, potassium ______ of the cells, and sodium ______ the cells.
repolarization abnormalities
when the heart lacks oxygen, there are ________ seen on EKG
Subendocardial ischemia
there is ischemia within the endocardium itself; indicated on EKG by ST segment depression
St segment depression
what are the findings on EKG associated with subendocardial ischemia?
Transmural ischemia
occur when the whole thickness of the myocardium is schema; indicated on EKG by ST segment elevation
premature beats, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation
what are some ways in which ischemia can manifest as electrical instability?
unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI, sudden cardiac death
what conditions constitute acute coronary syndrome?
Angina
pressure or discomfort centrally located in the chest; choking, suffocating, heaviness
"tightening"
when people talk about angina, they are actually referring to...
Stable angina
transient episodic chest discomfort that is typically predictable and reproducible, frequency of attacks are consistent over time, resolves over a constant and predicable period of time with rest or meds (nitroglycerine)
physical stress (exertion, exercise, sexual intercourse), psychological stress, anemia, dysrhythmias,
stable angina triggers
men over 50 y/o and women over 60 y/o
stable angina is prominent in what populations?
episodes of sternal pain described classically as heaviness, pressure, squeezing, choking
common complaint of those with stable angina
2-5 minutes
stable angina episodes typically last...
crescendo-descrescendo
what is the pattern of stable angina pain?
within 1-5 minutes or slowed/decreased activity; sublingual nitroglycerin
stable angina is typically relieved with...
Levine's sign
the global position of heart attack; a fist clenched over the chest
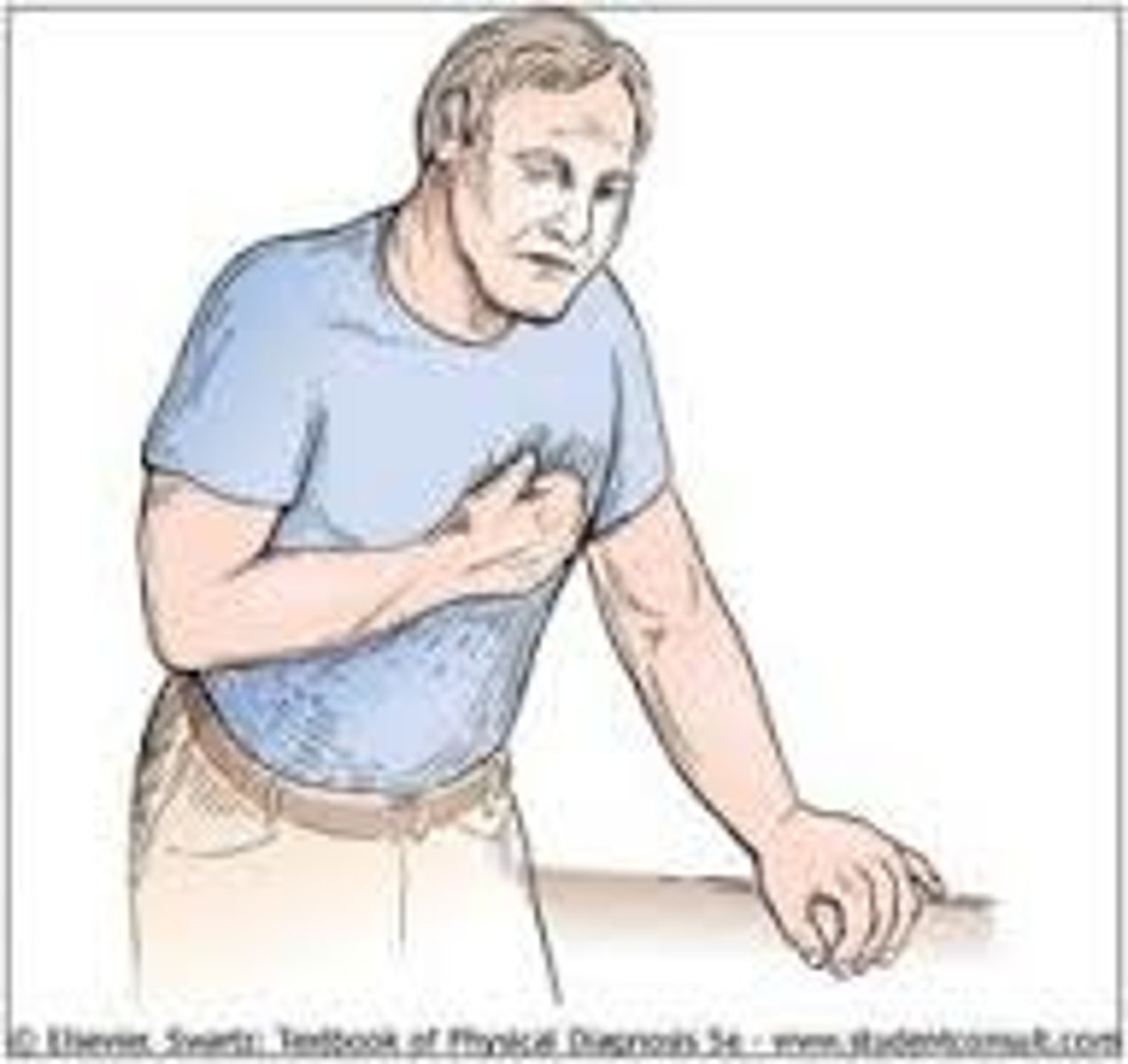
left shoulder, both arms, back, neck, jaw, teeth, epigastric area
in stable angina, pain can radiate to any of the following...
increased HR, dyspnea, elevated BP, diaphoresis, new/changed murmur, abnormal precordial pulsations
during a stable angina event, what are some signs for look for during physical exam?
obesity, nicotine stained fingers, AV nicking/cotton wool spots in the eyes, displacement of PMI, murmur, carotid/aortic bruits
what are some common findings on physical exam for one with stable angina and no active symptoms?
AAA pulsation, carotid bruits, decreed peripheral pulses
signs of atherosclerosis
xanthelasmas and xanthomas
what are some MAJOR signs of high cholesterol?
Xanthelasmas
cholesterol deposits in the eyelids
Xanthomas
yellow deposits of cholesterol in tendons and soft tissues
EKG (can be completely normal!!)
what is the first test you do on someone with a complaint of stable angina?
J point and ST segment depression (subendocardial ischemia)
what would the EKG of one with symptomatic stable angina look like?
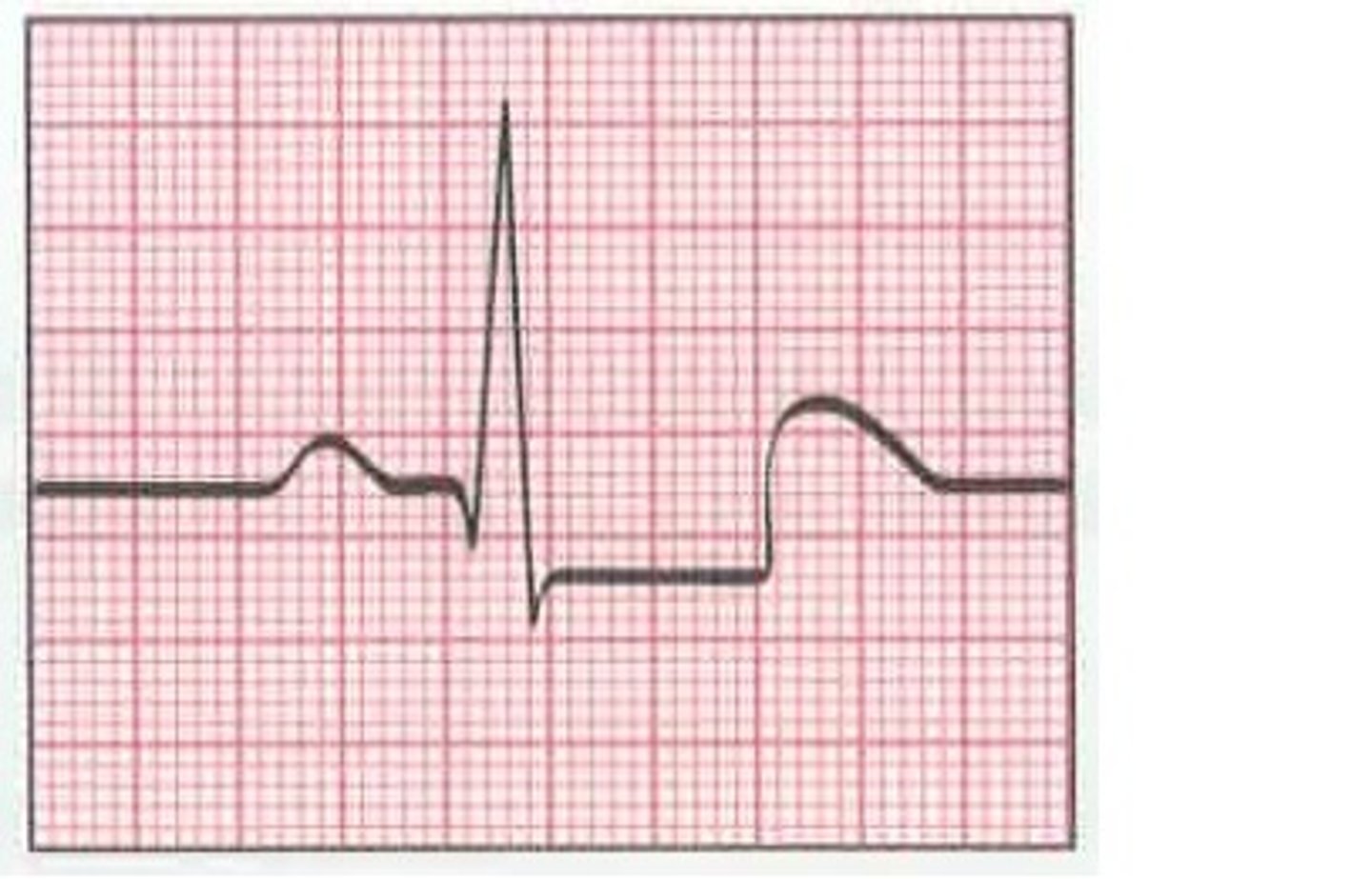
signs of a previous infarct, Q waves, non-specific ST segment, T wave changes, LVH
non-specific signs of stable angina on EKG
outpatient
bloodwork for stable angina is done in what setting?
CBC, CMP, HgbA1C, fasting cholesterol panel
what would a provider order on bloodwork for a pt with stable angina
assess for anemia which may be triggering angina
why would a provider order a CBC on a pt with stable angina?
to assess electrolyte, kidney, and liver function
why would a provider order a CMP on a pt with stable angina?
so we can get a longer view of blood sugar control
why would a provider order a HgbA1C on a pt with stable angina?
dyslipidemia
why would a provider order a fasting cholesterol panel on a pt with stable angina?
cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, widened mediastinum, pulmonary issue, pneumothorax, pneumonia
what can (potentially) be seen on a chest x-ray on one with stable angina?
Stress testing
method for evaluating cardiovascular fitness
to confirm the suspicion of ischemic heart disease and determine the extent of that ischemia; helps to est. the patient's relationship to chest discomfort
why do we perform stress tests?
8 hours
stress testing can be done in an acute setting for a patient pain free for at least...
treadmill/bike; dobutamine
how are stress tests administered?
injected with dobutamine to reproduce physical stress
what if a pt cannot go on a bike/treadmill for a stress test?
to compare EKG from rest to the EKG from stress
what is the end goal of the stress test?
Stress ECHO
stress test plus ECHO looking at structural changes in the heart secondary to stress
Nuclear stress test
stress test that uses a radioisotope to evaluate coronary blood flow; higher sensitivity than a regular stress test
Tc-99 Sestamibi
what is the radioactive tracer used in a nuclear stress test?