Eye and Ear Abnormalities 321
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Ptosis
Drooping Upper Lid

Exophthalmos
Protruding Eyeballs
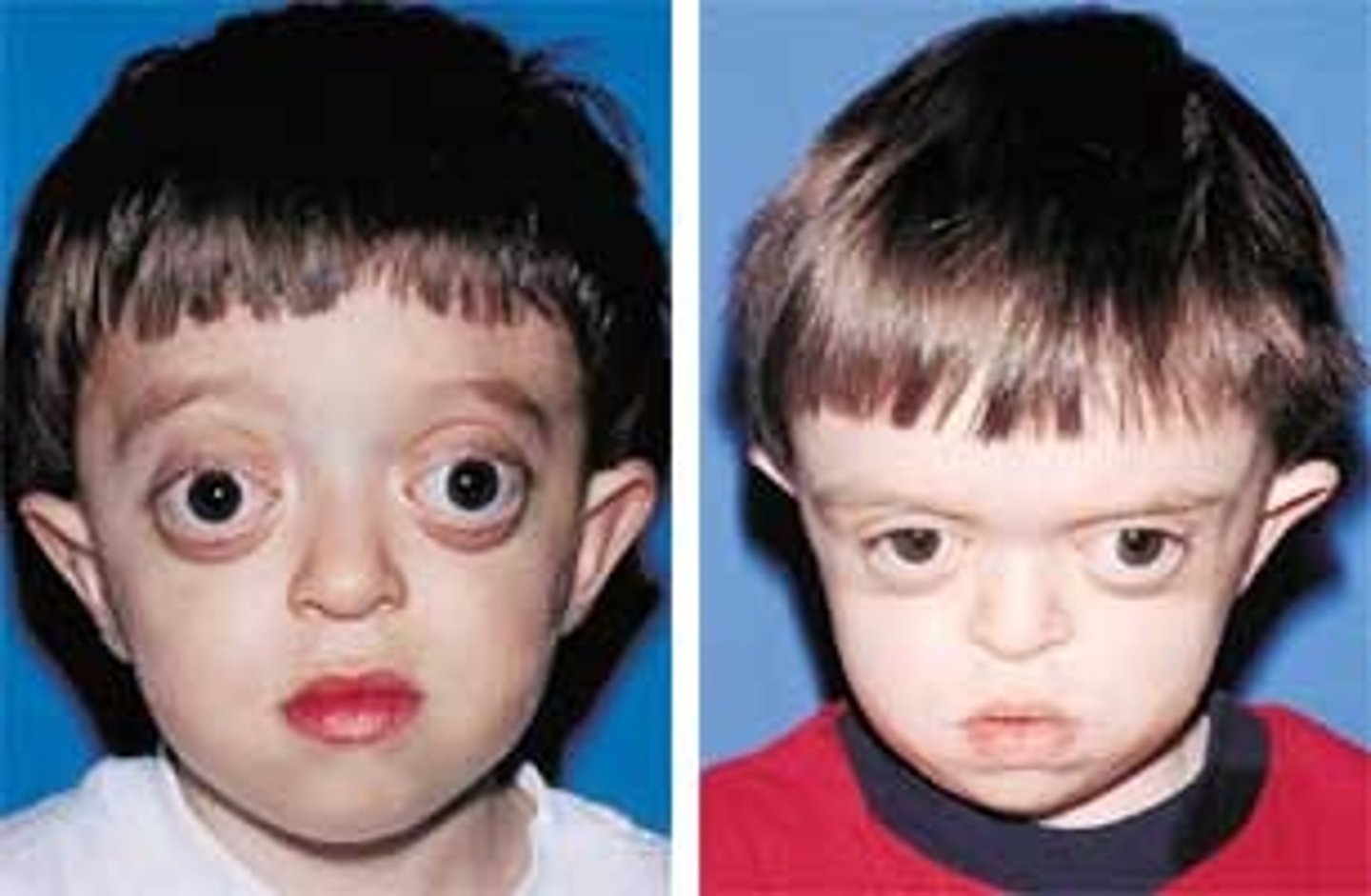
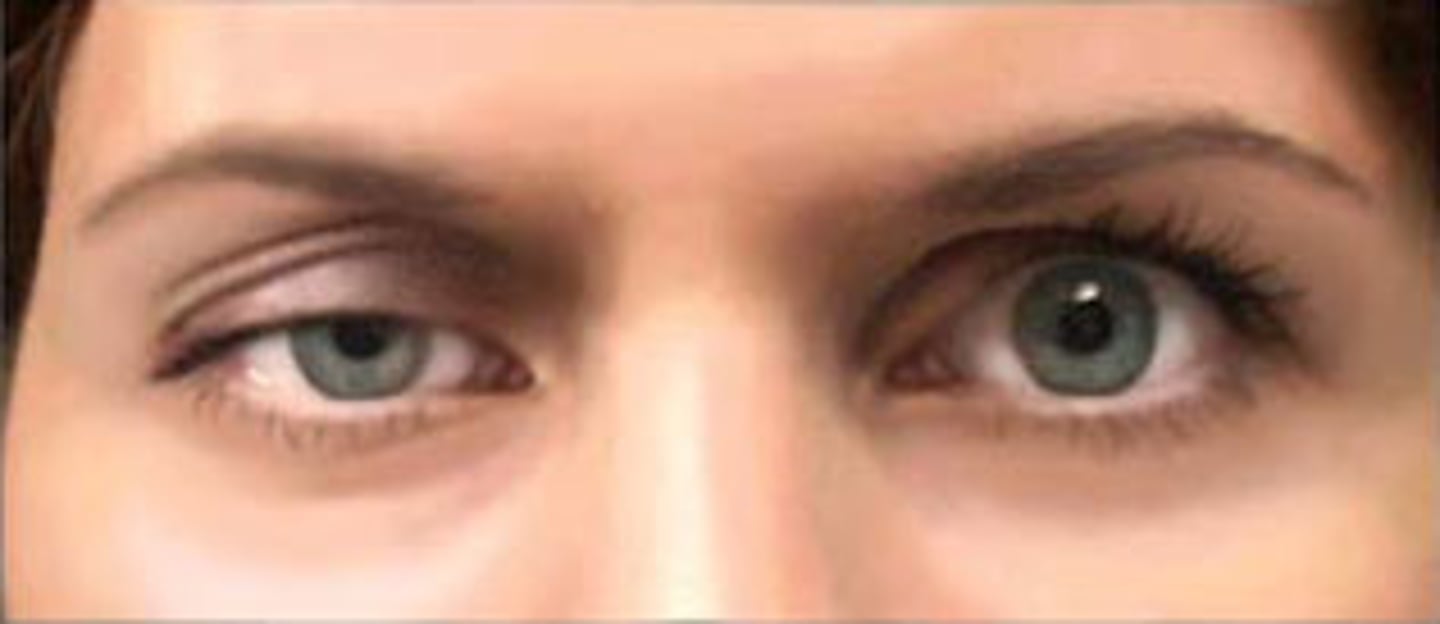
Entropion
Inverted Lower Lid
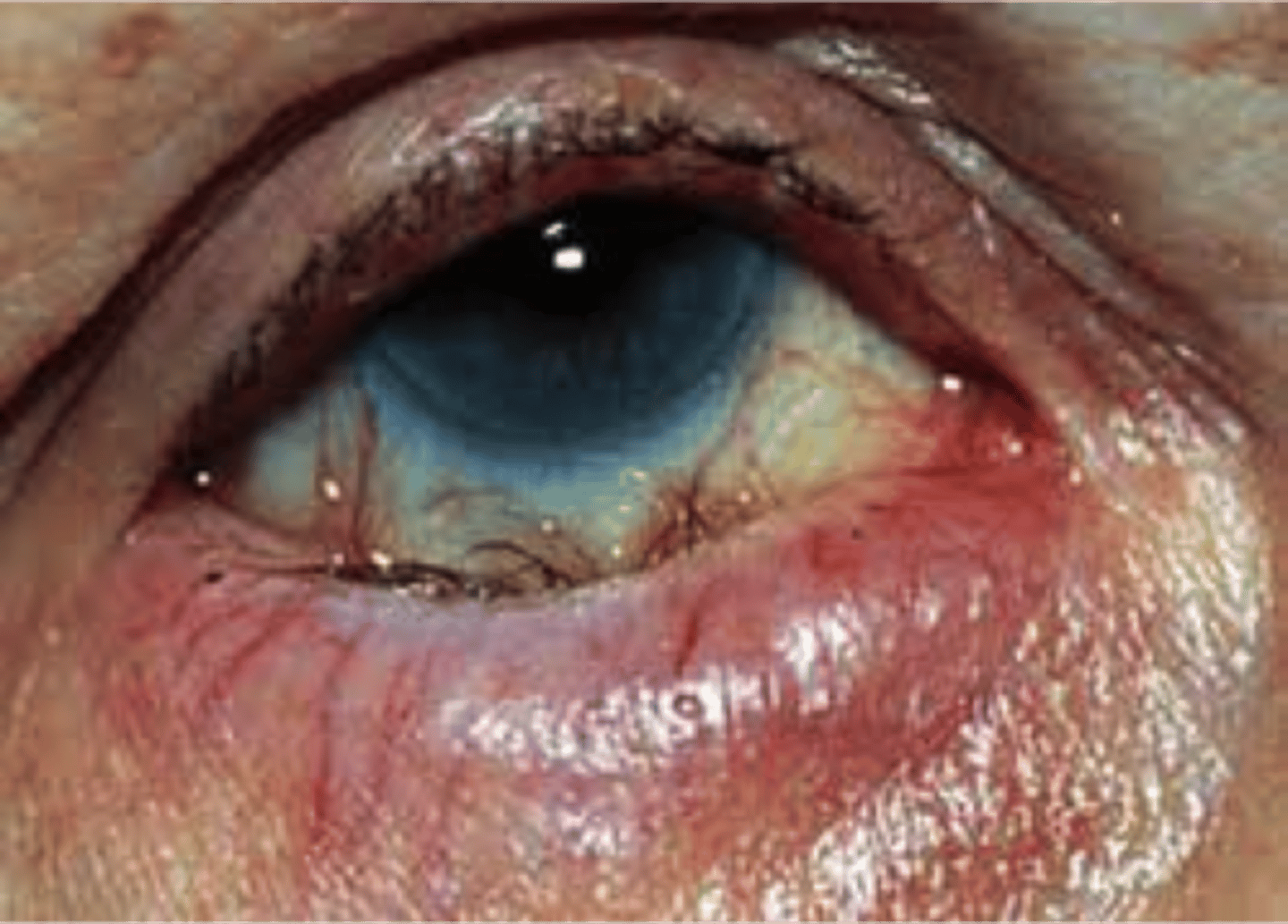
Ectropion
Everted Lower Lid
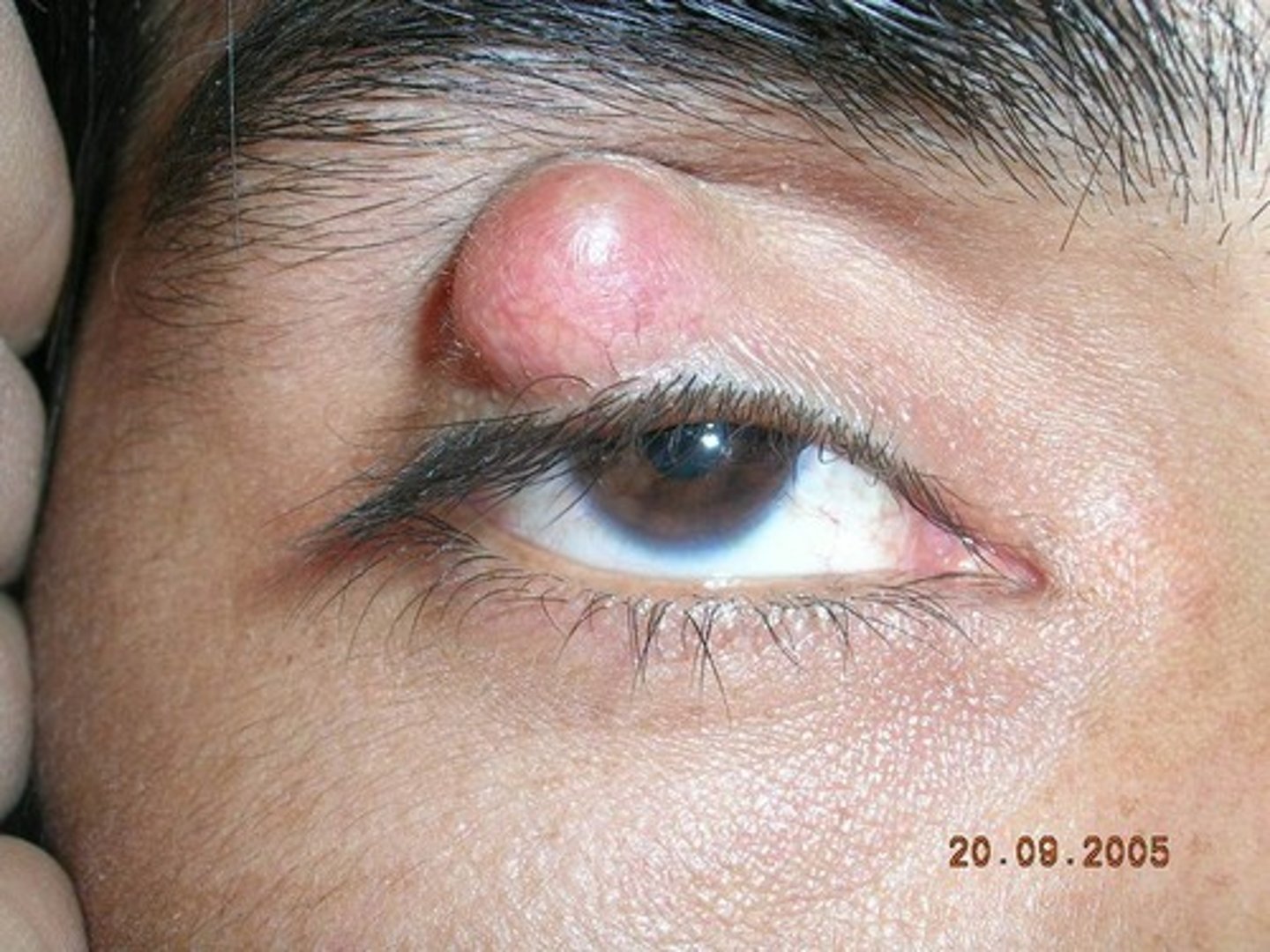
Chalazion
Infection Meibomian gland
Blepharitis
Redness Lid Margins
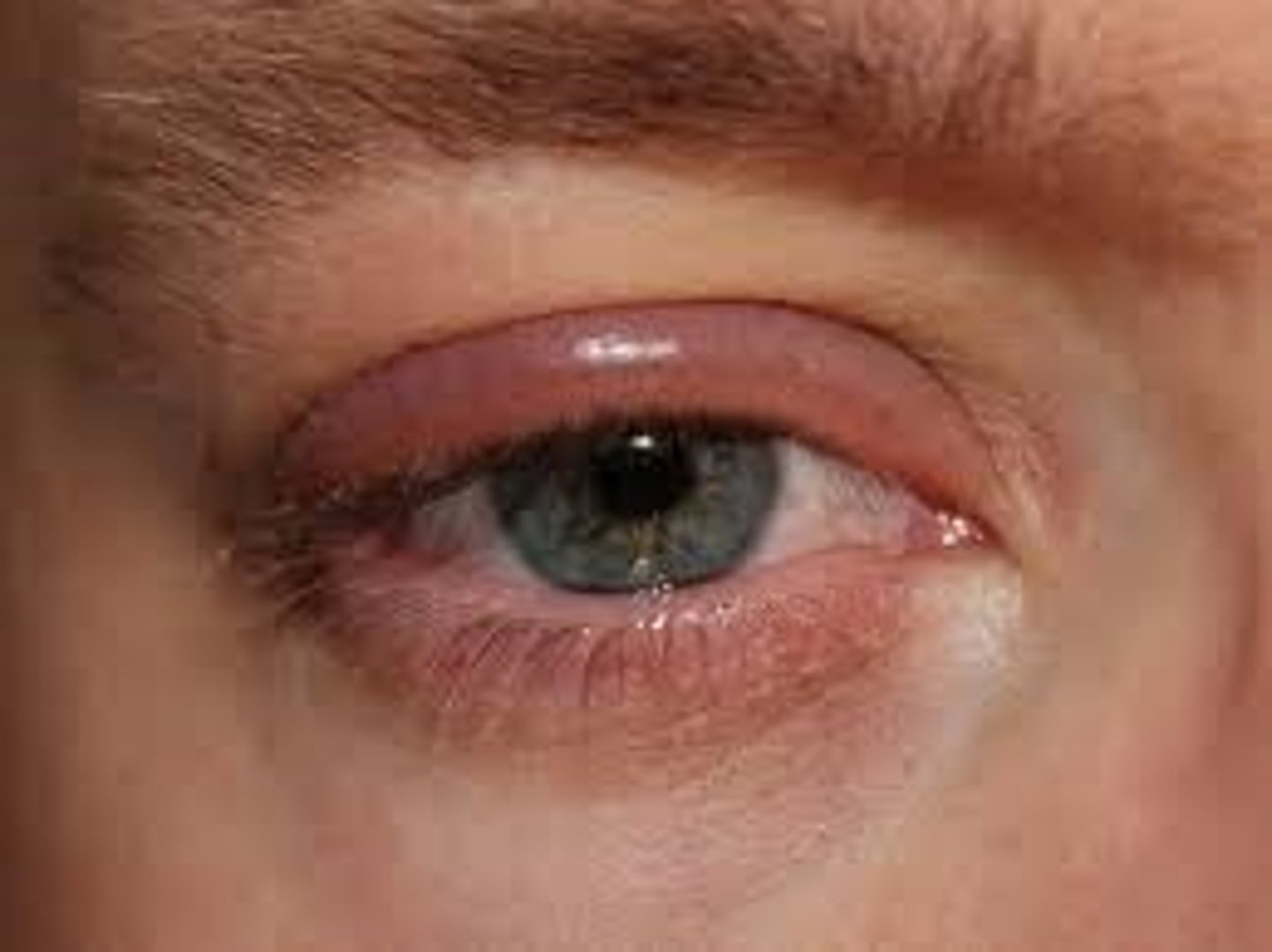
Conjunctivitis
Redness of Conjunctiva
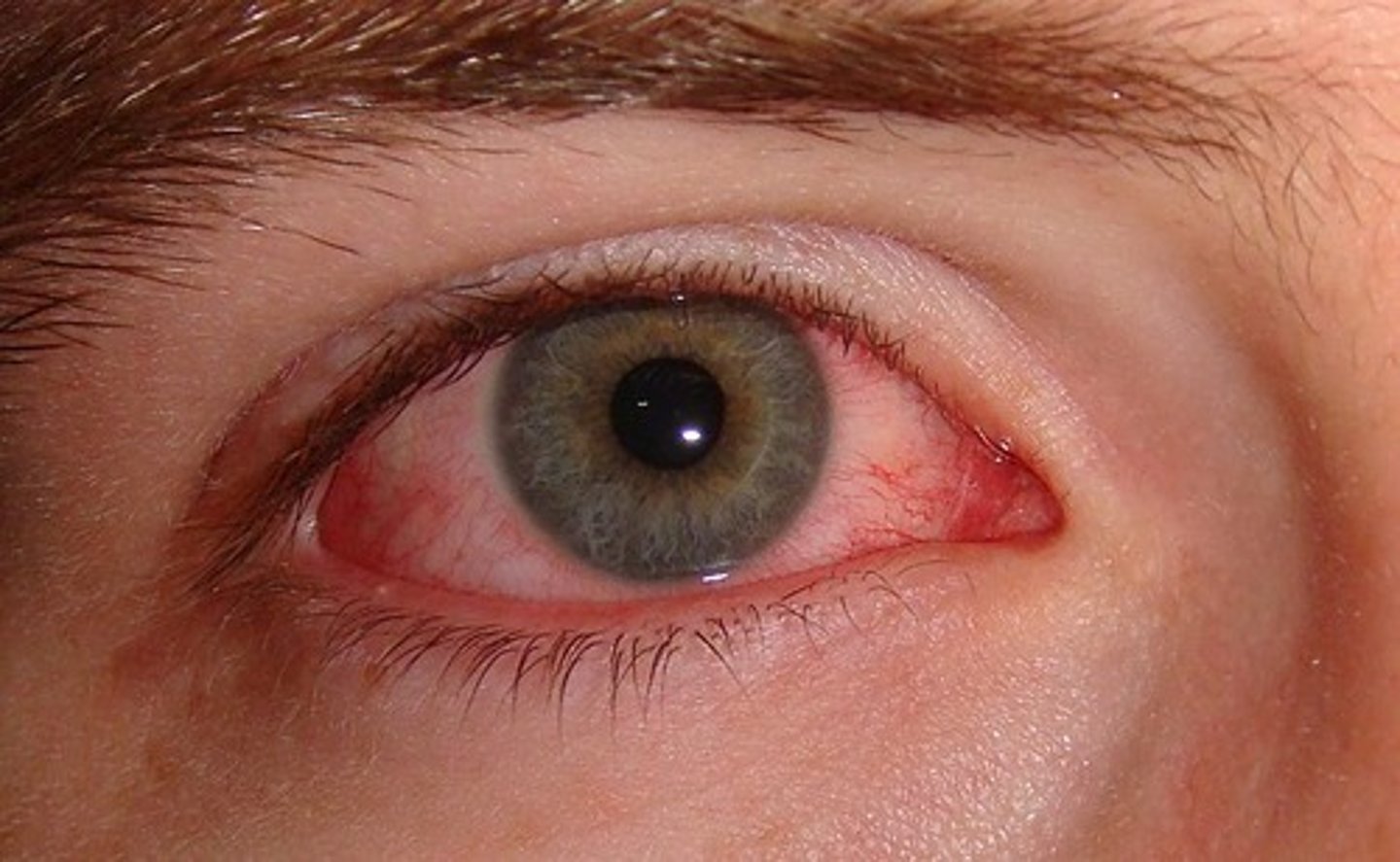
Hordeolum
Stye Hair Follicle Infection
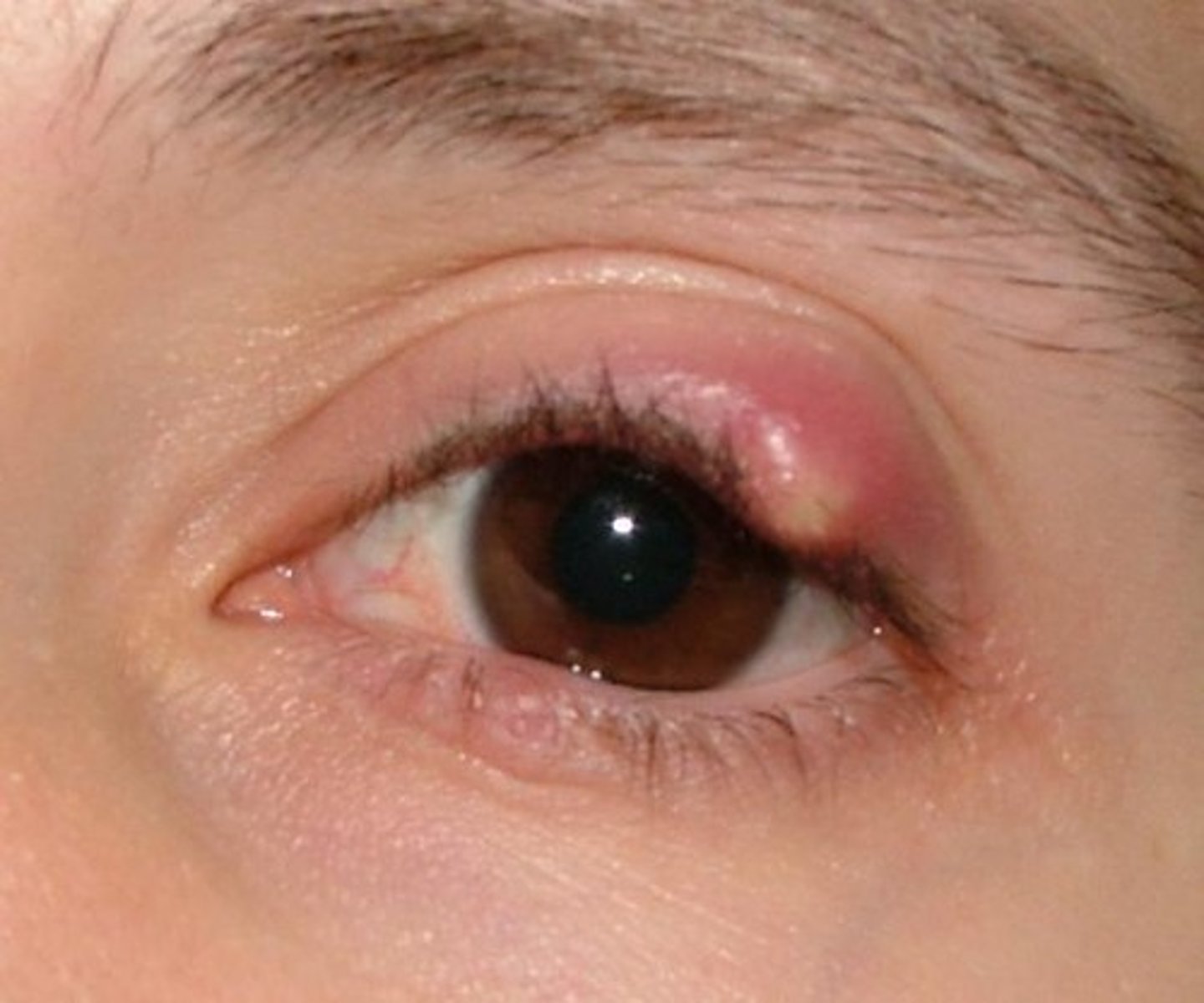
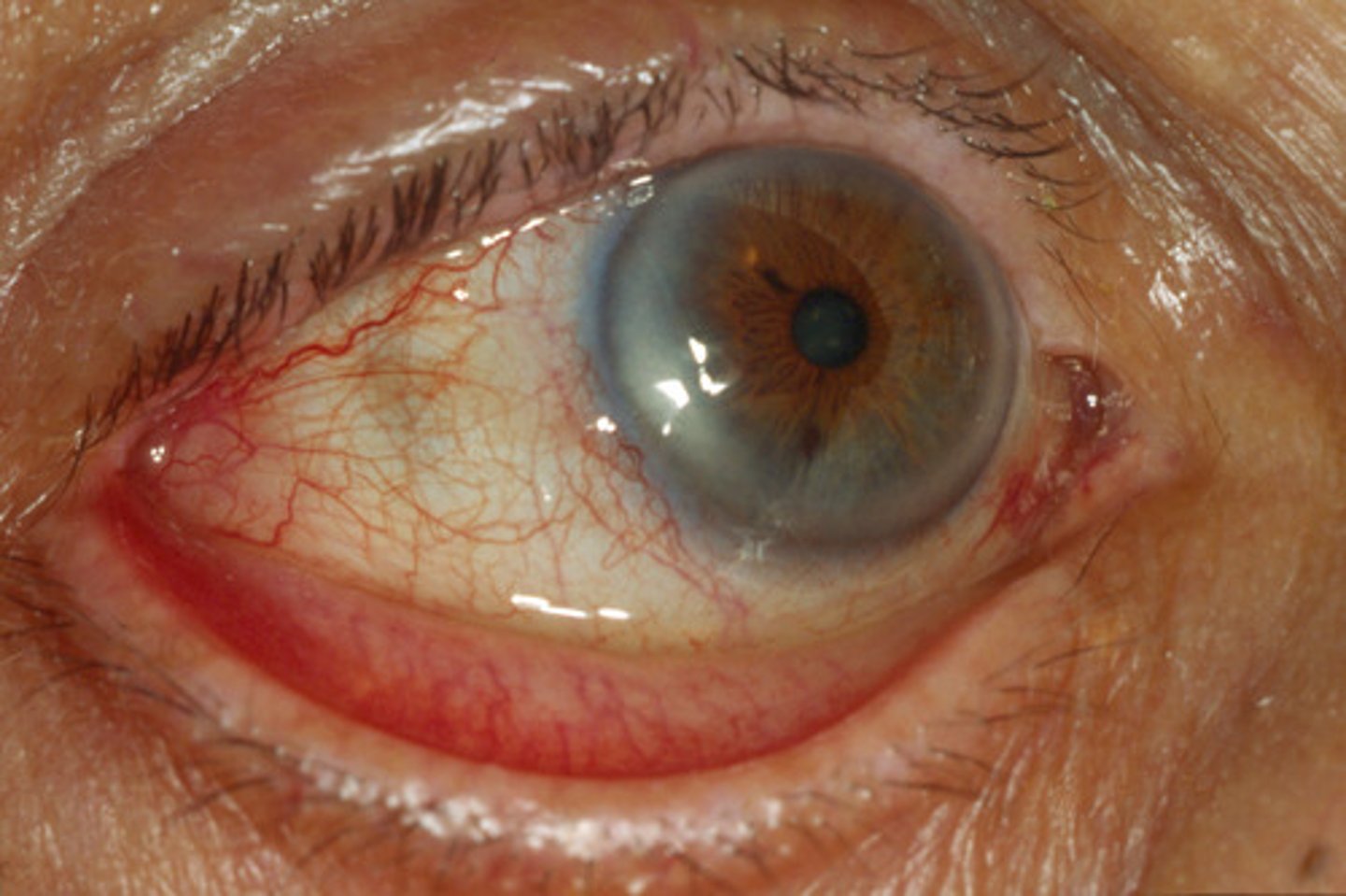
Diffuse Episcleritis
Inflammation Sclera
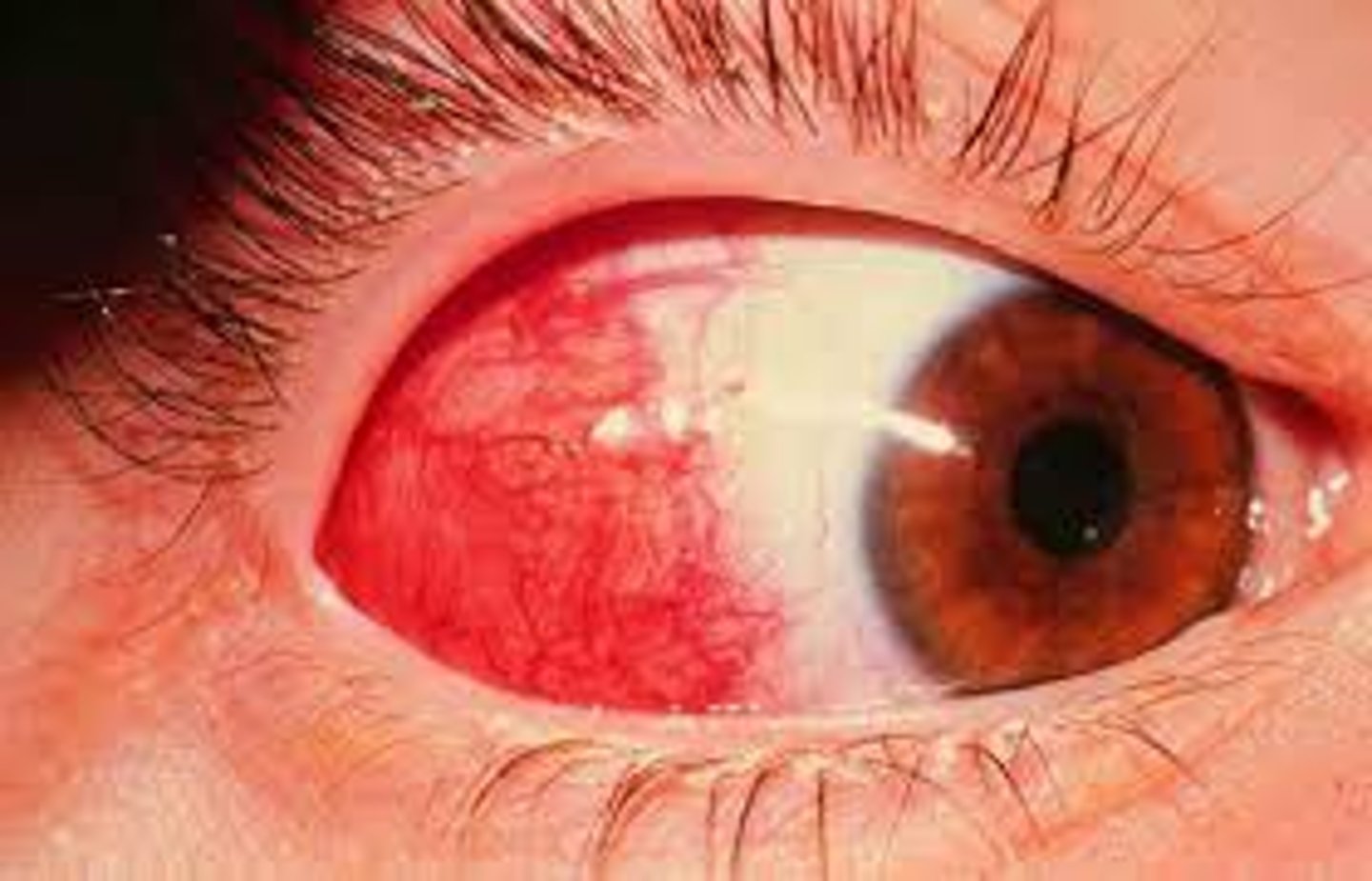
Miosis
Pinpoint pupils
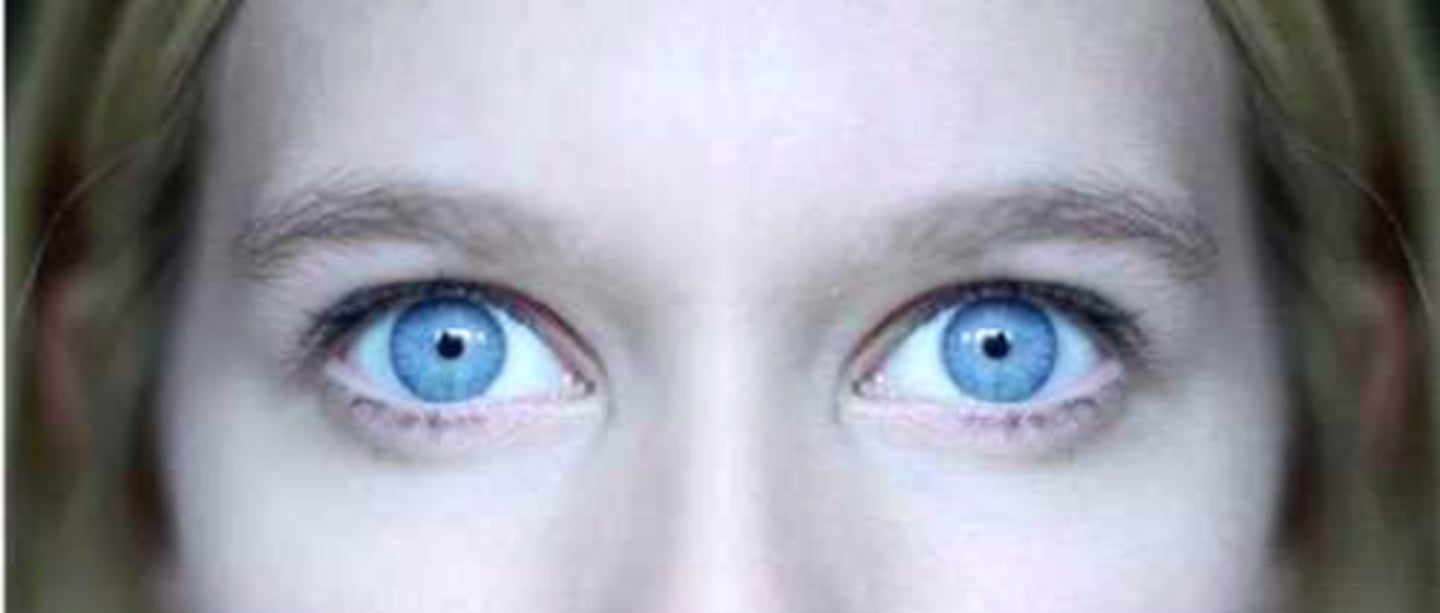

Anisocoria
Pupils Unequal
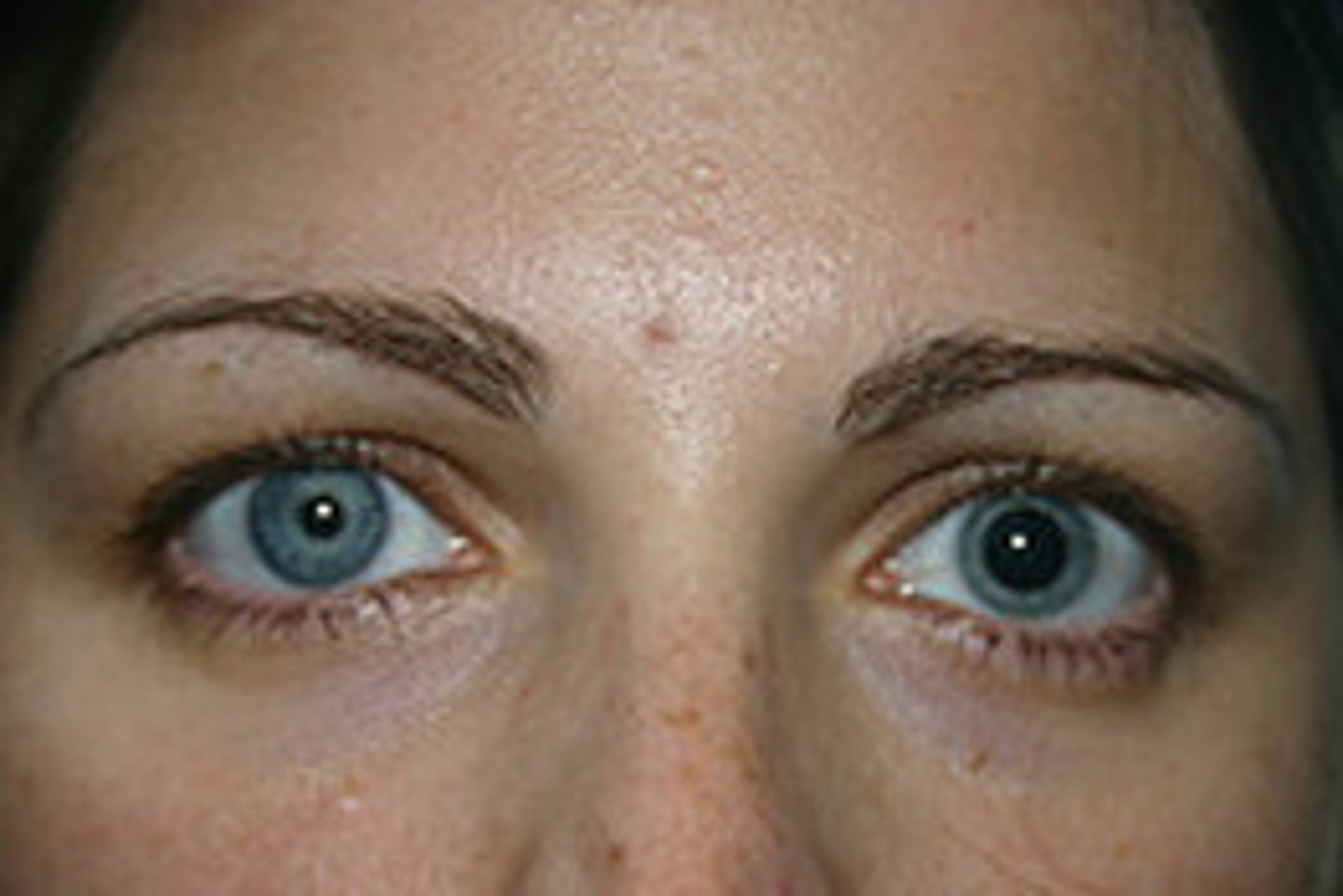
Mydriasis
dilated and fixed pup
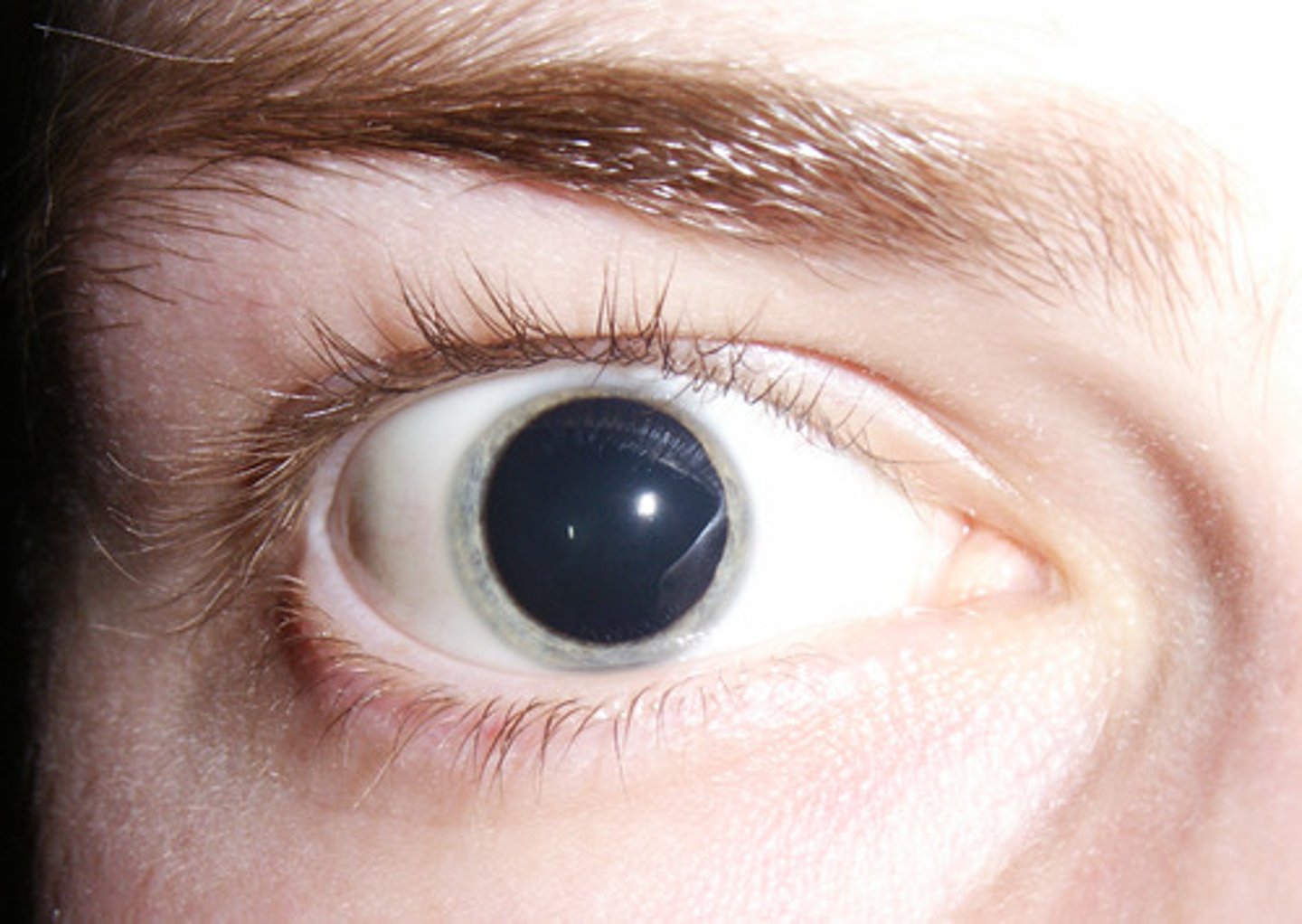
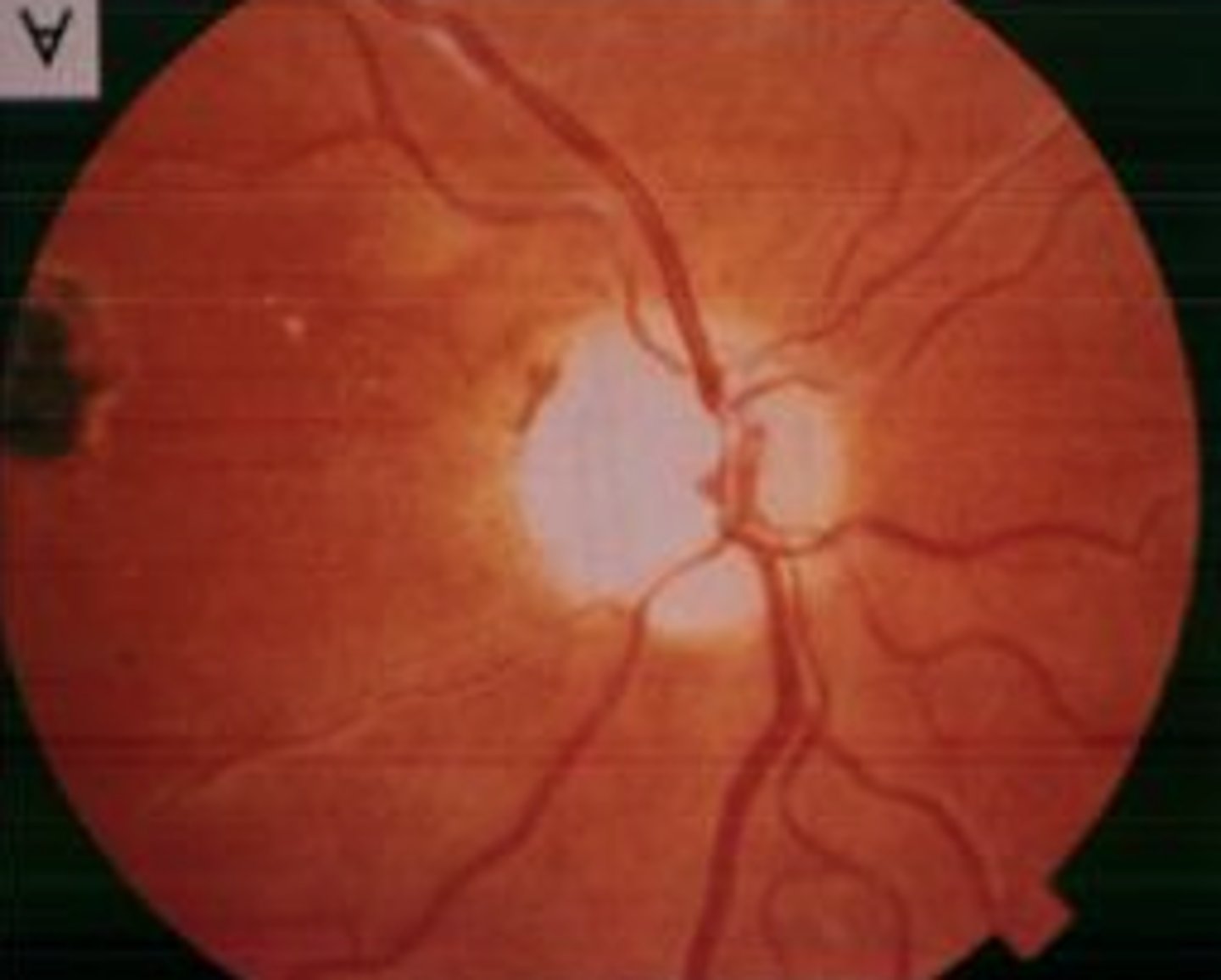
Papilledema
Swollen optic disc
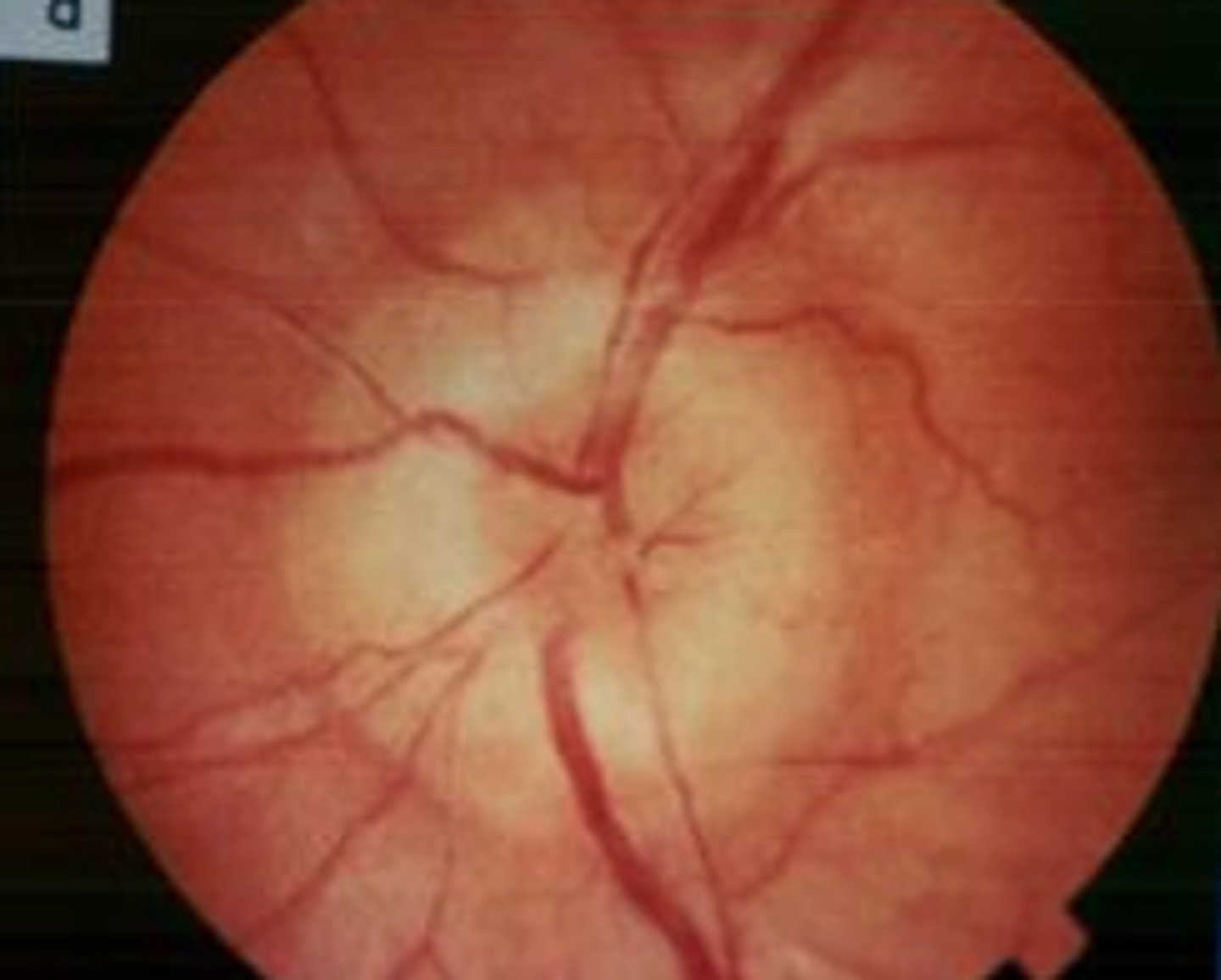
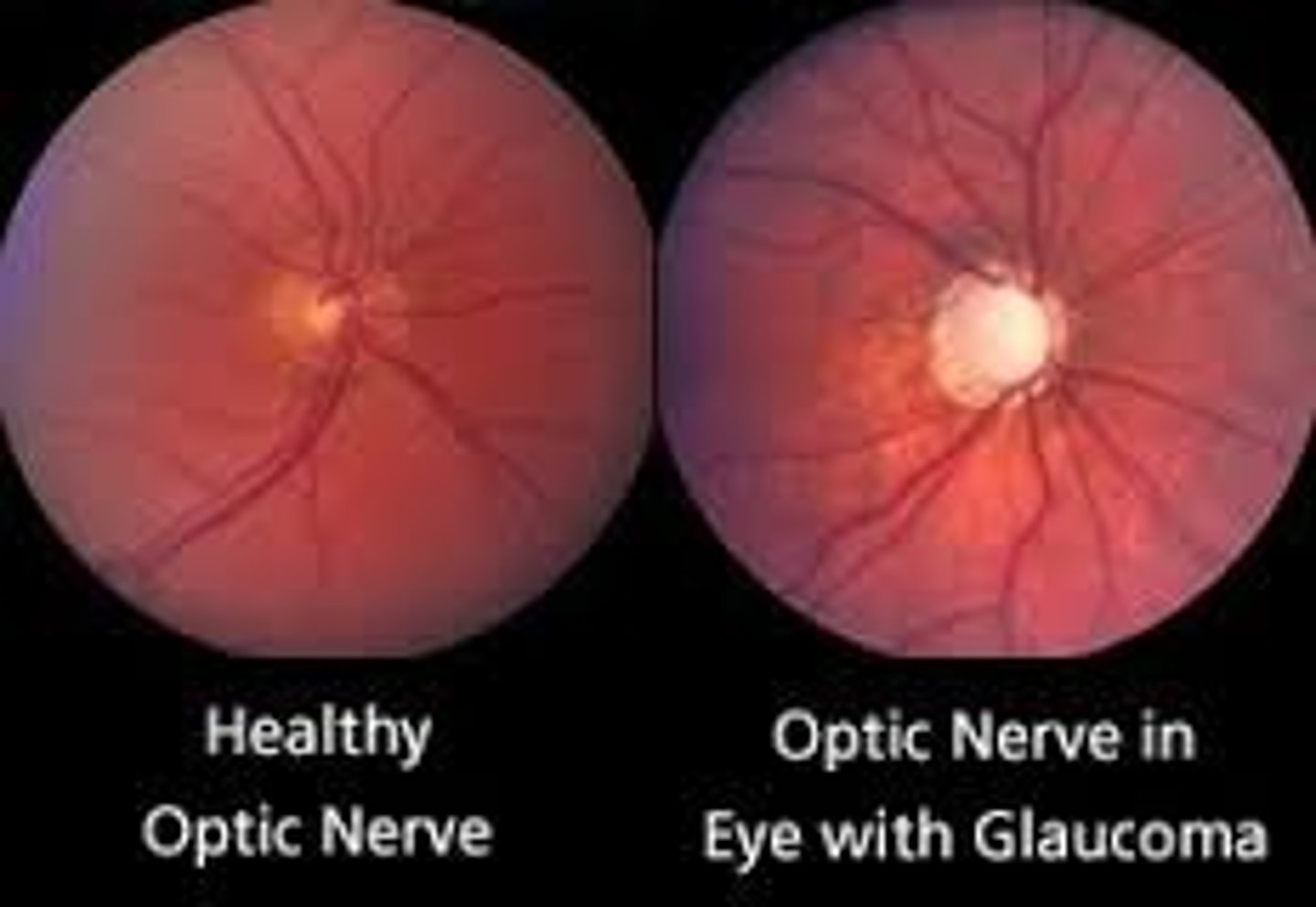
Glaucoma
Enlarged cup covers half the optic disc
Optic Atrophy
White disc lack vessels
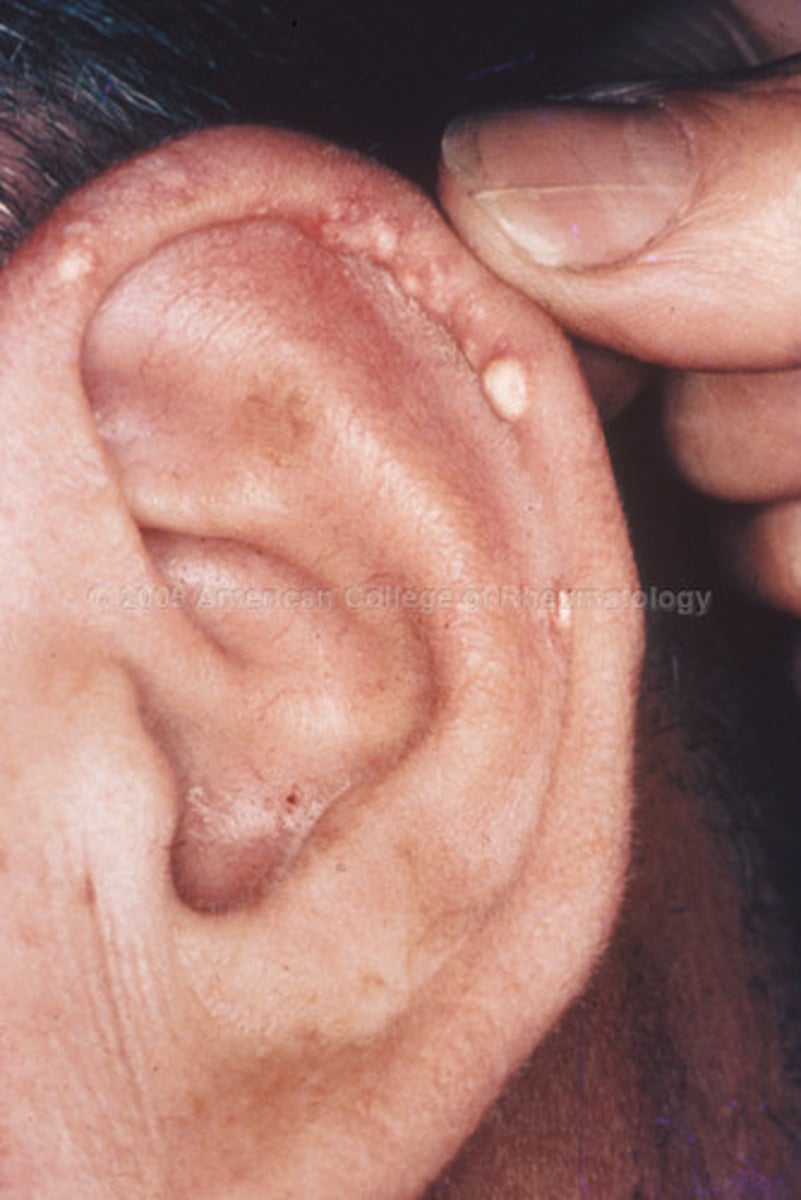
Tophi, Post auricular cyst
hard nodules
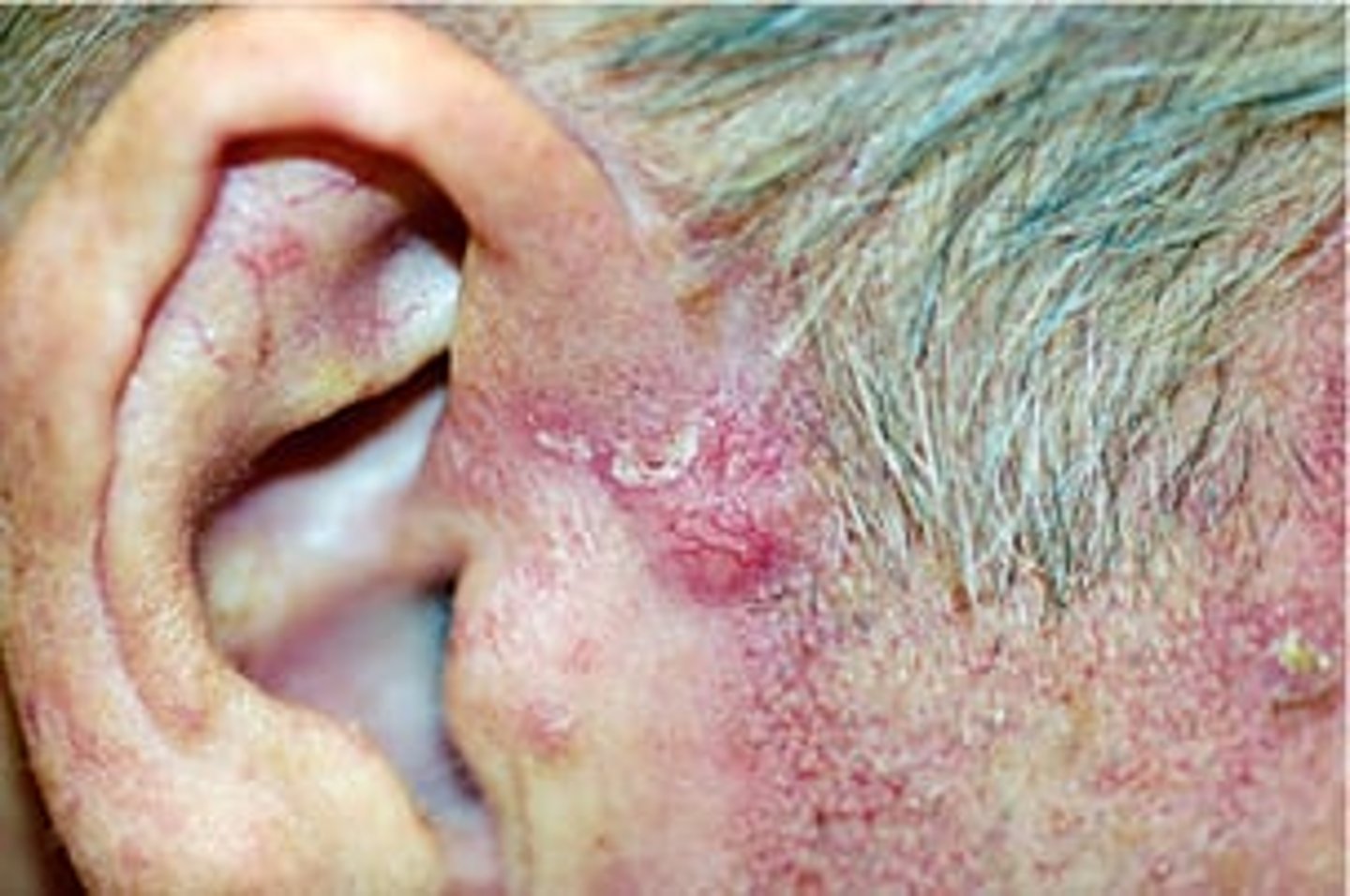
Malignant Lesion
Mass or Lump
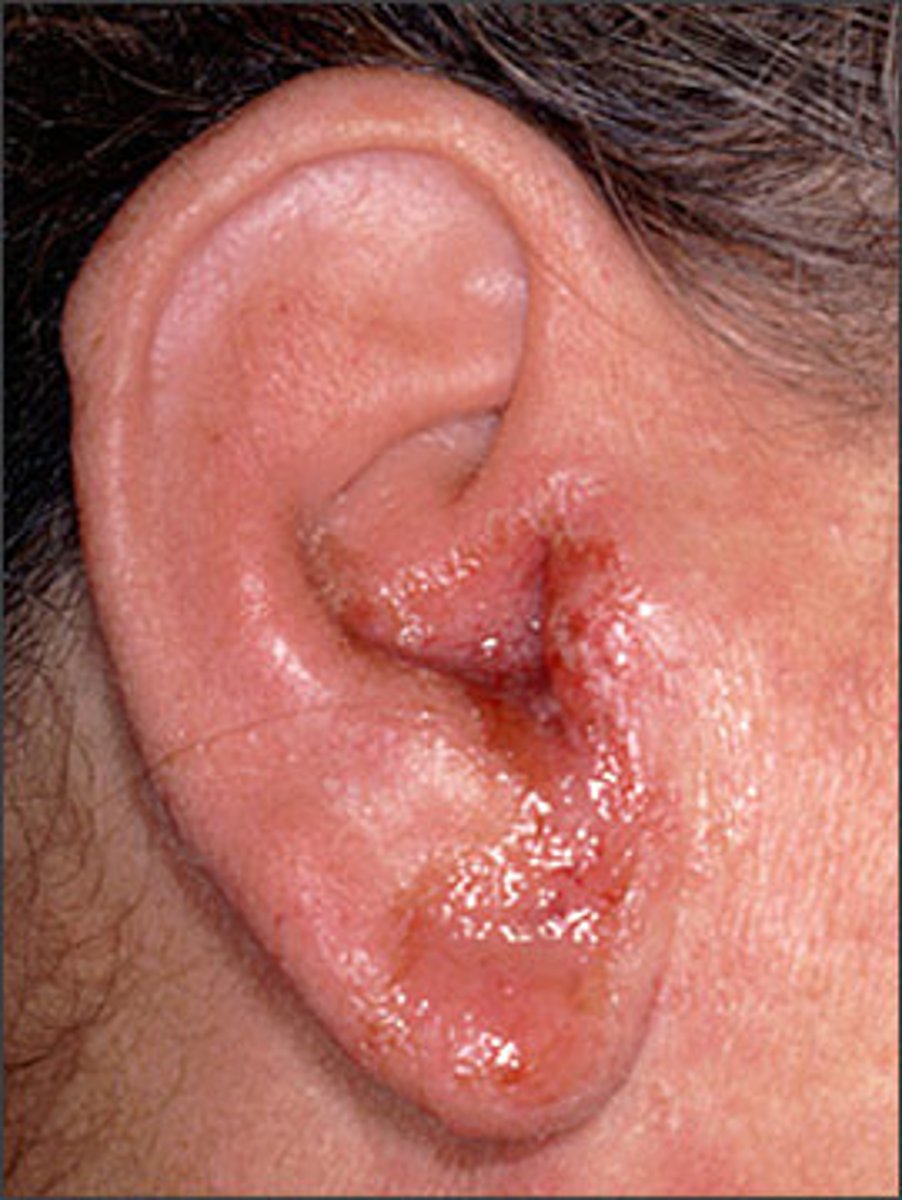
Otitis Externa
Infection out ear canal
Build-up of cerumen in ear canal
Block
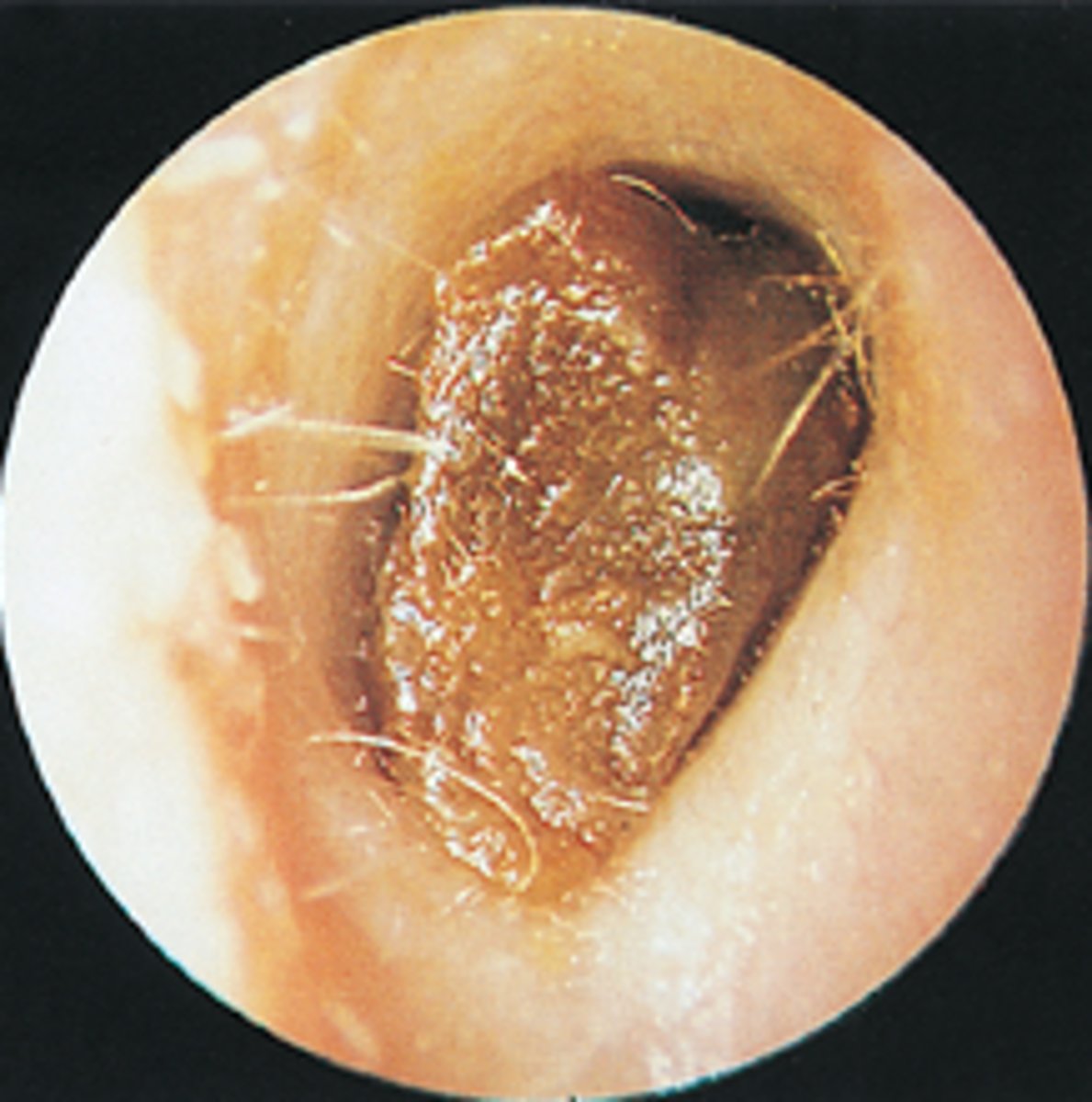
Polyp, Exostosis
Thickening and constriction
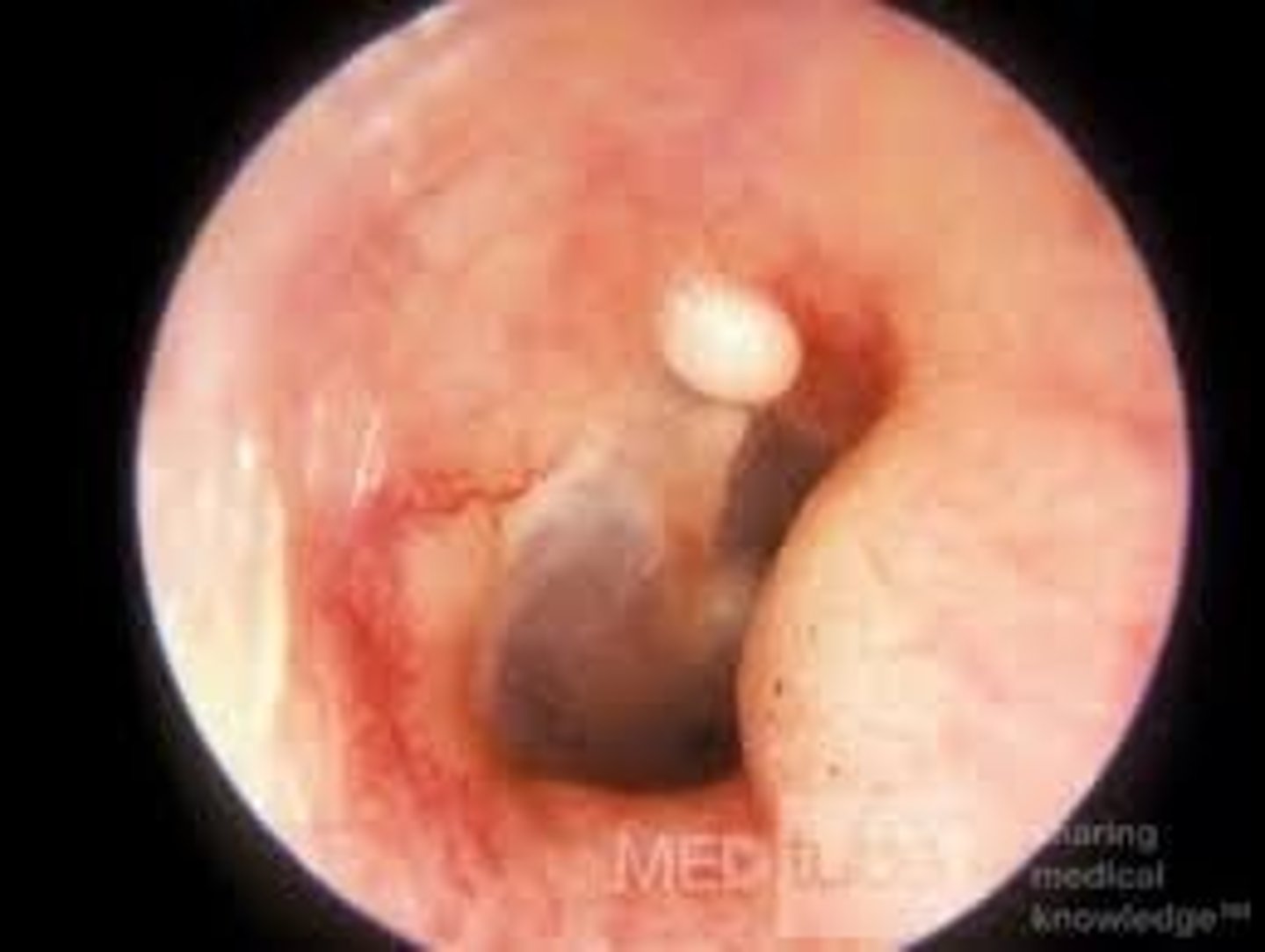
Acute otitis media
Red, bulging, decreased light reflex
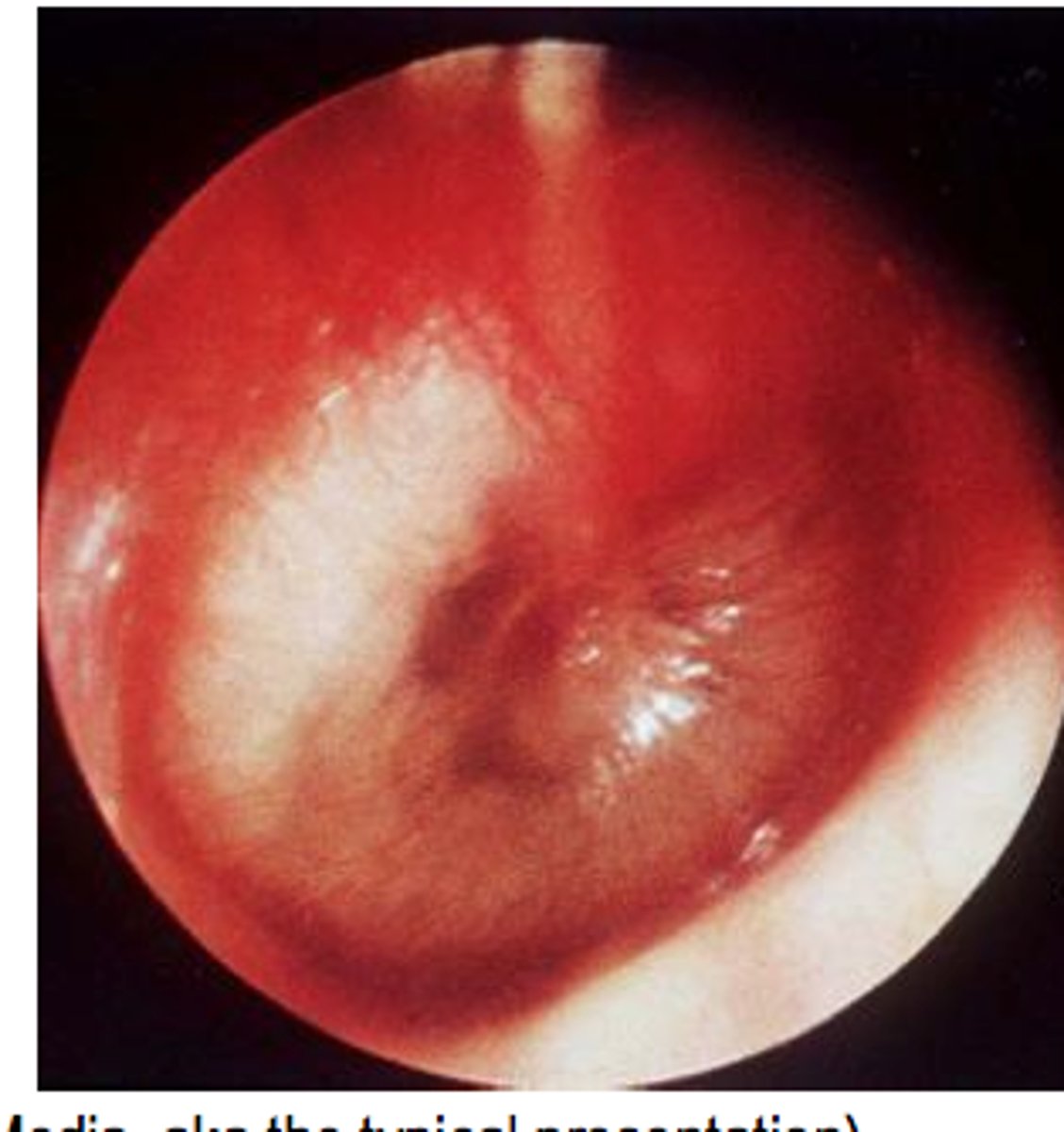
Serous otitis media
Yellowish bulging membrane
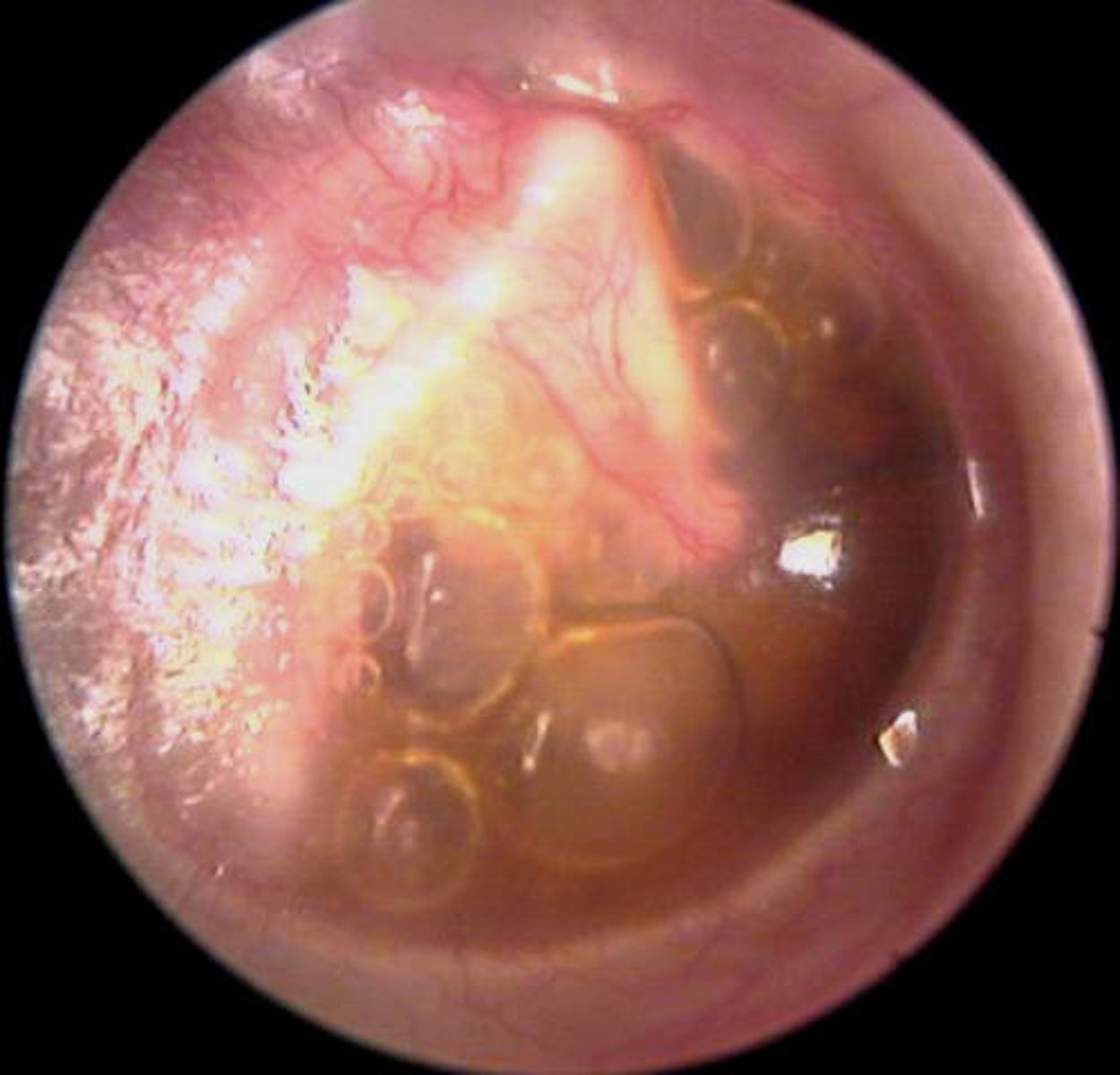
Blue/dark red tympanic membrane
Blood behind eardrum
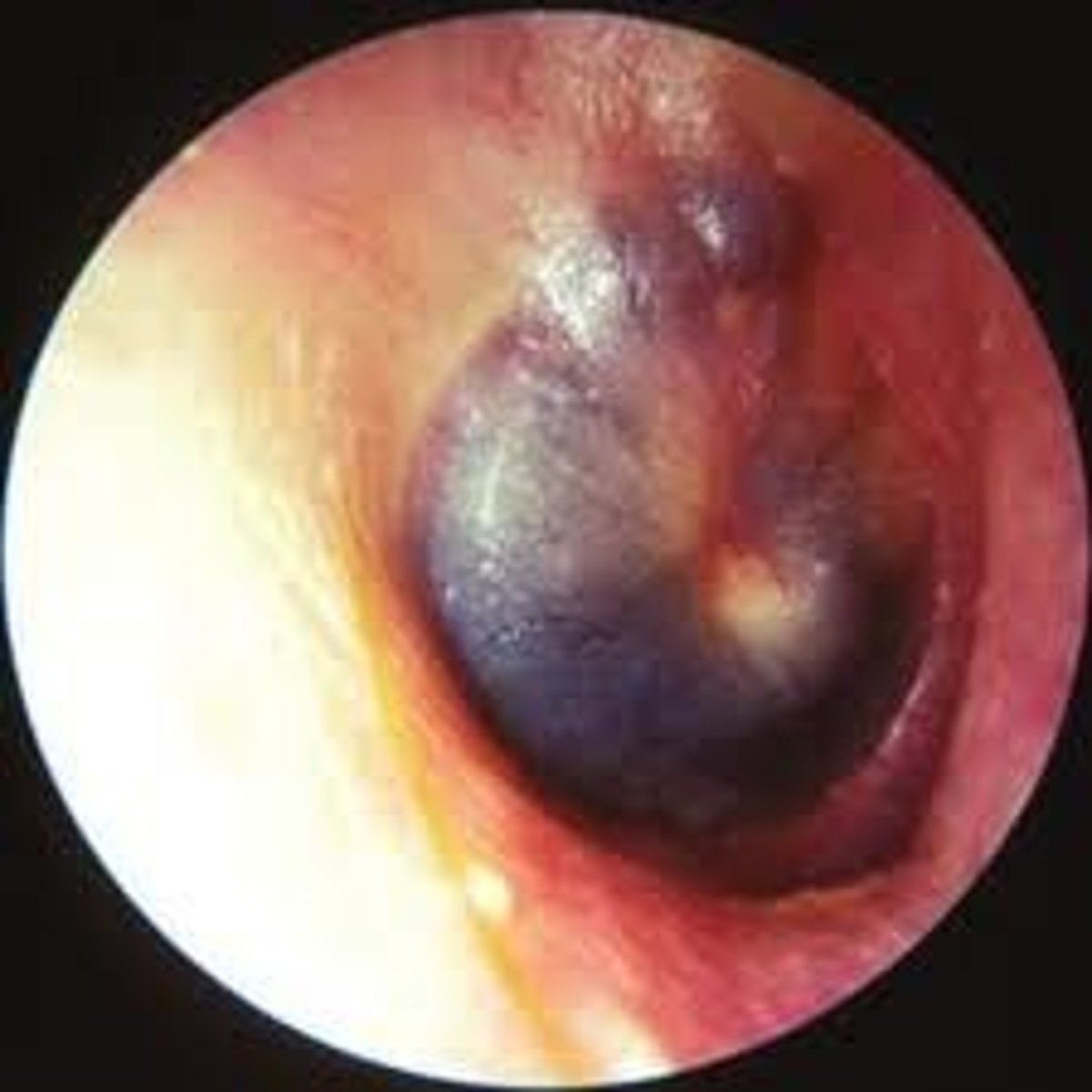
Scarred Tympanic Membrane
White spots and streaks
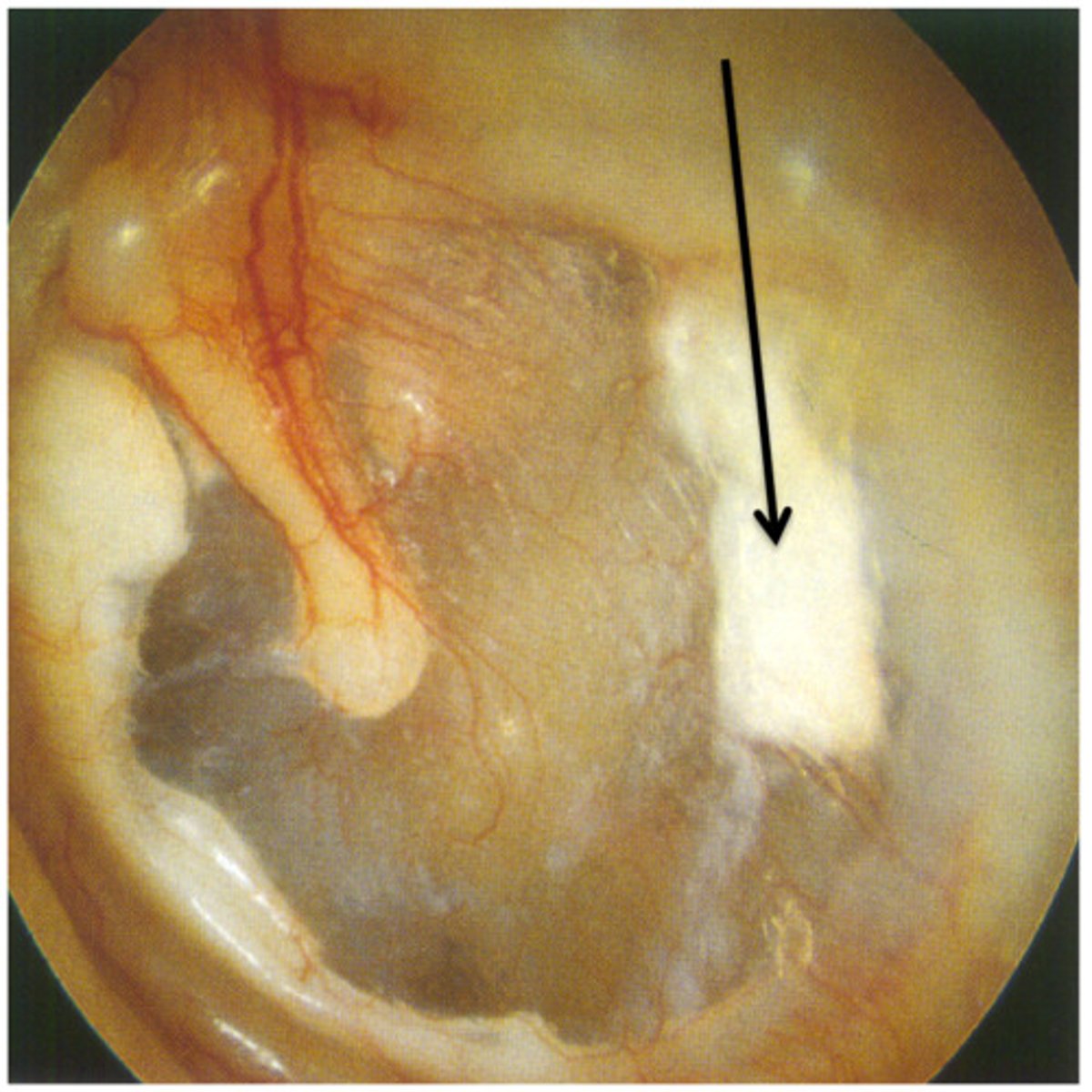
Perforated Tympanic Membrane
Rupture from pressure
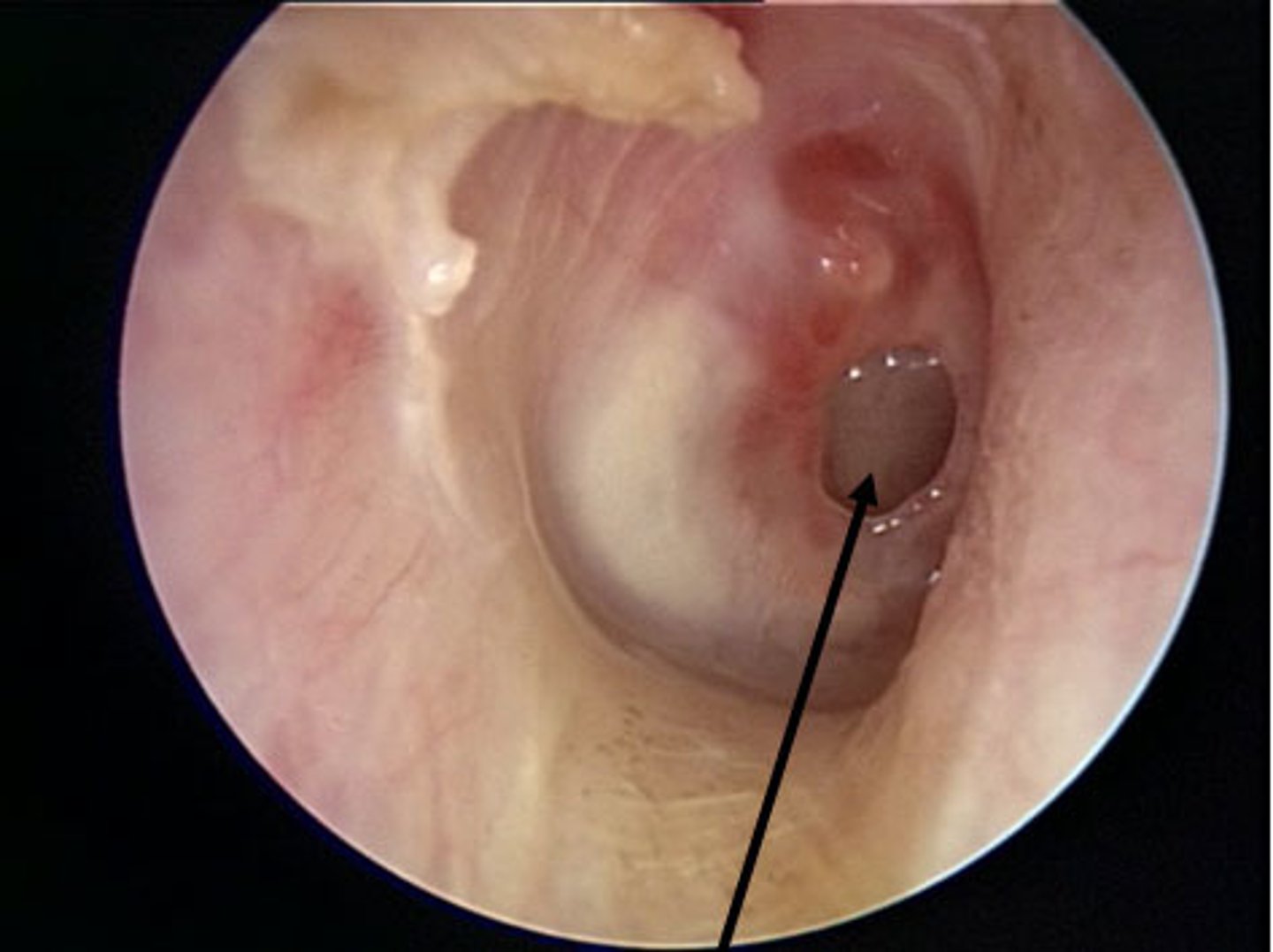
Retracted Tympanic Membrane
Prominent Landmarks
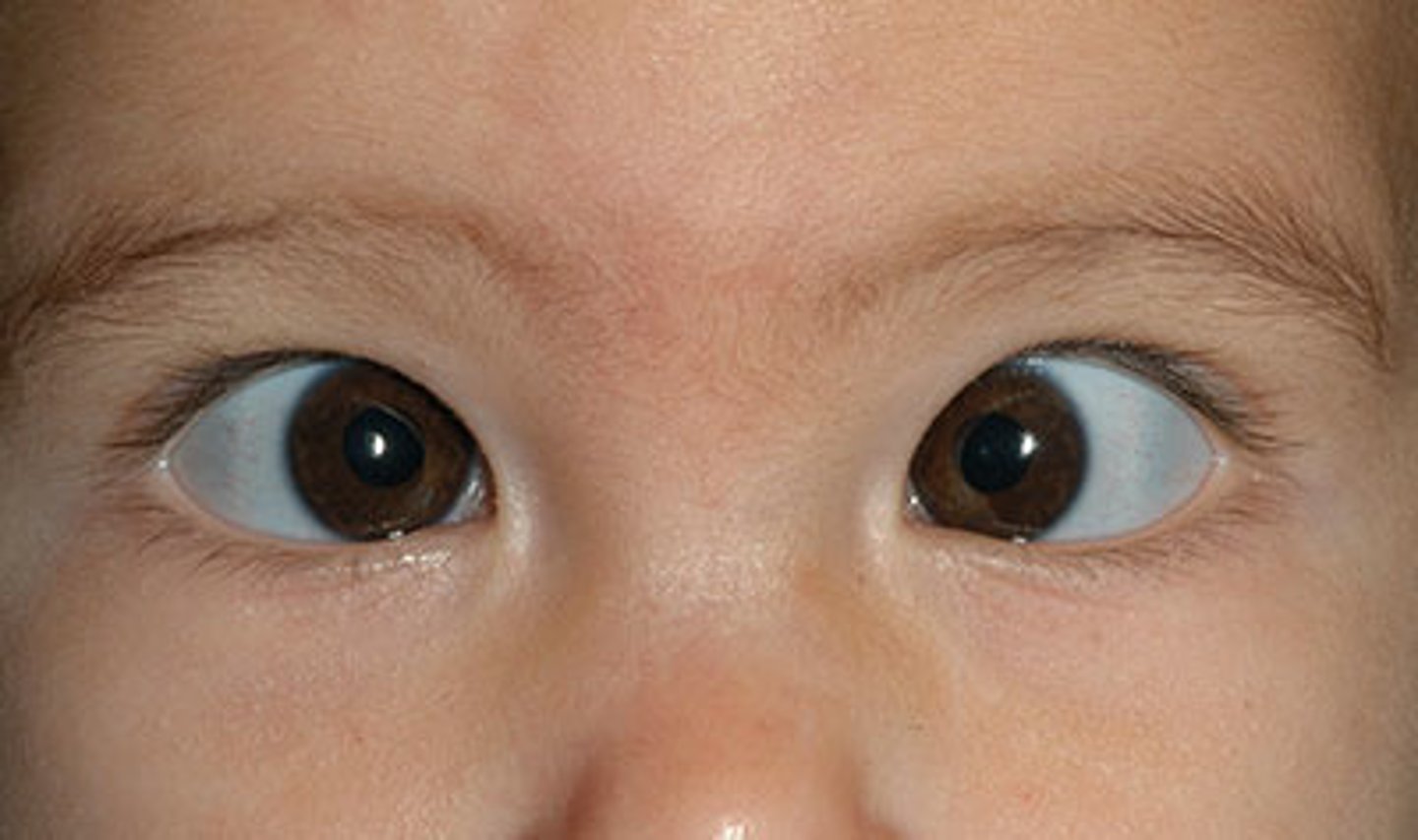
esotropia
sometimes called "crossed eyes". It is a condition where the eyes don't align properly and can be constant or intermittent
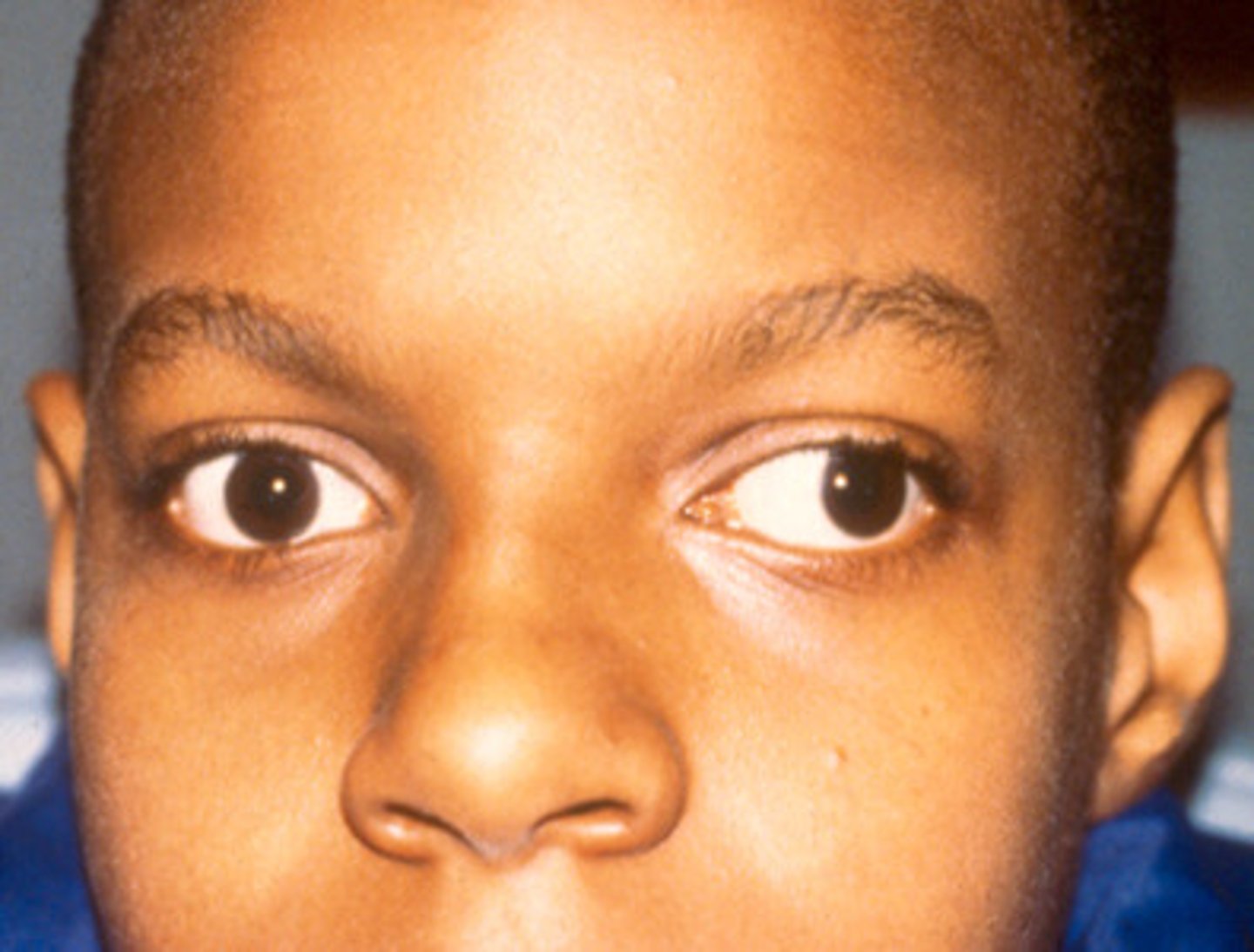
exotropia
one or both eyes turn outward. Symptoms include an outward eye turn, double vision, eye strain, and headaches, which may occur more frequently when the person is tired, sick, or stressed
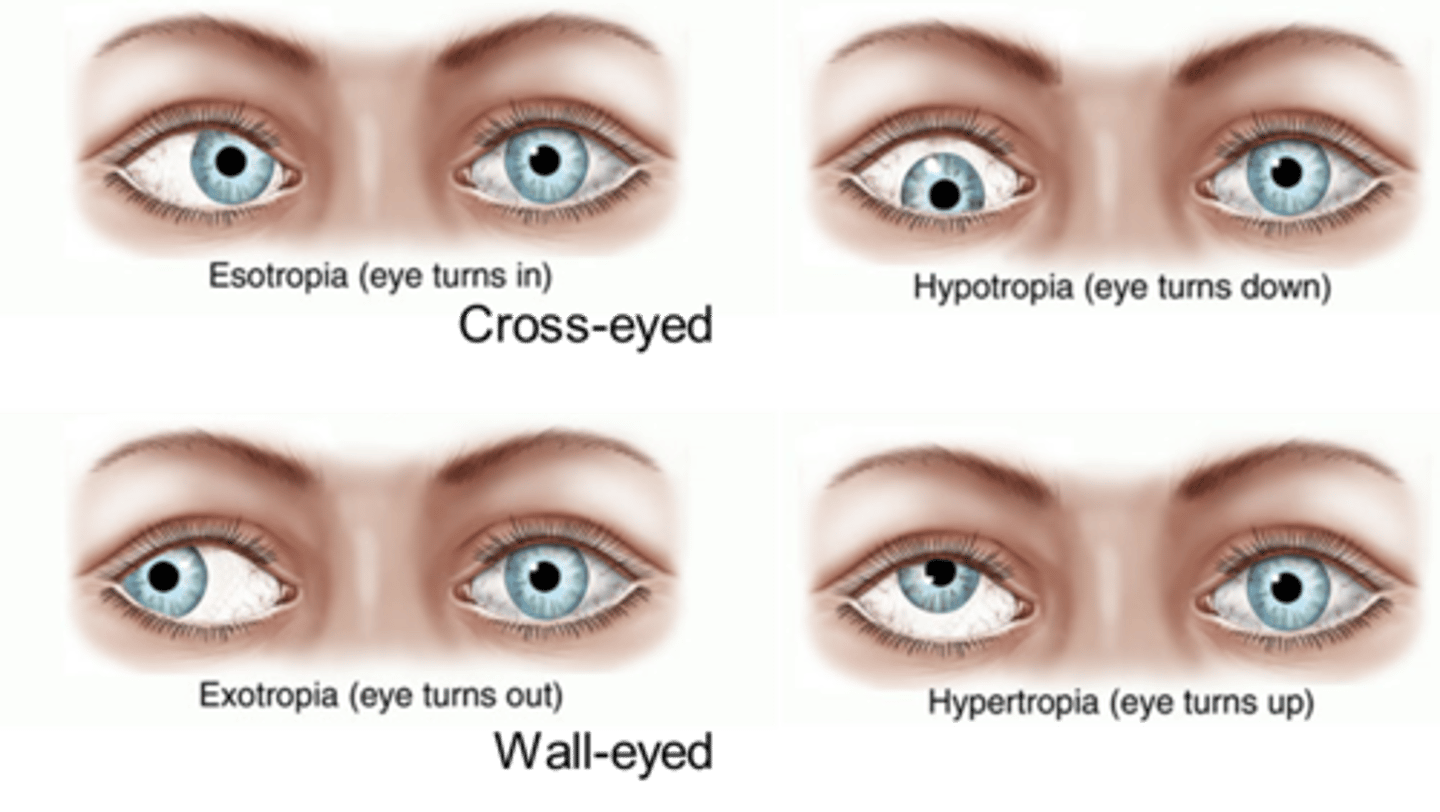
Strabismus
condition where the eyes are not aligned, causing them to look in different directions at the same time
exotropia and esotropia are included in this blanket term
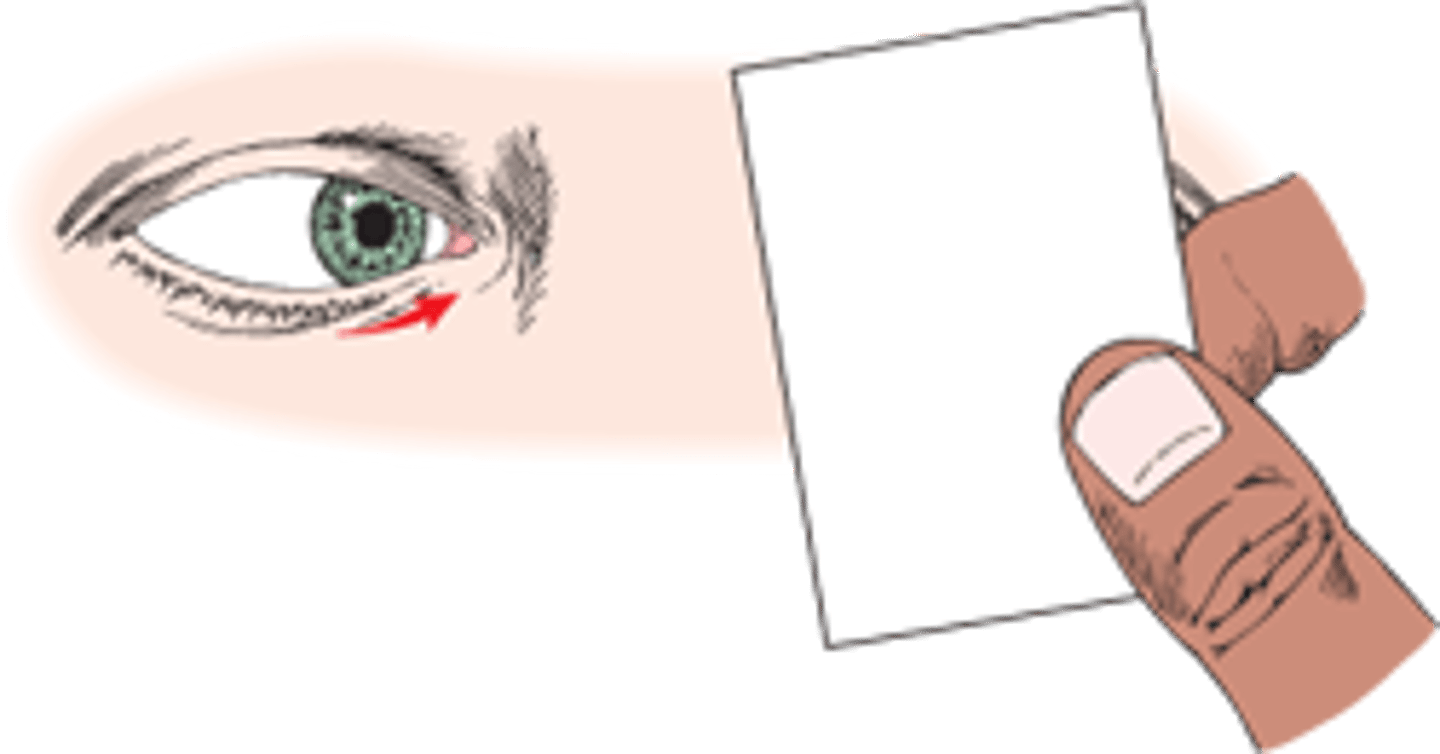
Phoria
latent tendency for the eyes to misalign, which is only revealed when an eye is covered. Unlike a tropia, which is a constant eye turn, a phoria is a temporary, hidden misalignment that the brain usually corrects to maintain single vision.

Nystagmus
apid, uncontrollable eye movements. If you have nystagmus, your eyes may move up and down, side to side or in a circular motion