PHSC 208, L26
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
. ox/phos
2 NADH —>
makes ~5 ATP
. ox/phos
(Citric Acid Cycle) 6 NADH —>
makes ~15 ATP
. ox/phos
(Citric Acid Cycle) 2 FADH2 —>
makes 3 ATP
Anaerobic glycolysis yields directly __ ATPs
2
Aerobic glycolysis to Krebs cycle yields directly __ ATPs
4
Mitochondria has __ membranes
2, inner and outer membrane
Outer mitochondrial membrane
porous to small metabolites
EX: lets water or ATP flow in and out
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Citric acid cycle occurs in MITOCHONDRIAL MATRIX
Oxidation is…
a series of removal of electrons from carbohydrates and intermediates
electrons pass through NADH and FADH2 to the electron transport system
then ATP synthesis occurs by oxidative phosphorylation
Ultimate proton acceptor in citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (aerobic respiration)
Oxygen
more positive E° value is
the more likely it steals electrons from something else
oxygen is very E° positive
NADH + H+ +1/2O2 —> NAD+ + H2O
A-reduced + B-oxidized <—> A-oxidized + B-reduced
losing electron= oxidized
gaining electron= reduced
Example of Redox Reaction
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ <—> Lactate + NAD+
Standard Reduction Potential
ΔG°’ = -nFE°’
electrons flow spontaneously from a substance with more negative reduction potential to a substance with a more positive reduction potential
-ΔG means it will spontaneously occur
A higher reduction potential =
it is more likely for the substance to be reduced
A lower reduction potential=
more likely to act as a reducing agent
Redox Coenzymes (high-energy electron carriers)
NADH, FADH2, NADPH
NADH and NADPH
co-substrates that bind to enzymes transiently
highly polar and water soluble
cannot cross mitochondrial membrane
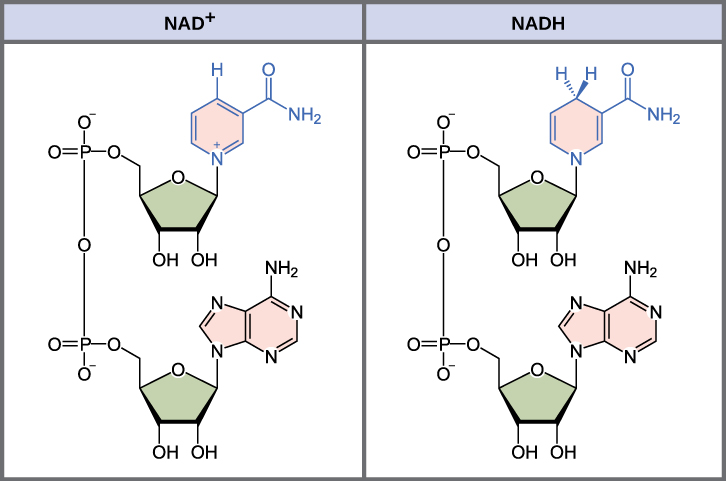
NADH specifics
made from glycolysis, TCA cycle, fatty acid oxidation
makes ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
NADPH
made from pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)
reducing agent in anabolic reaction
Where electrons are being accepted or donated from
the blue part i think
FAD (Flavin adenine nucleotide)
hydrophobic, don’t really move around
serves as “prosthetic groups”
Key Differences of NAD+/NADP+ vs FAD
NAD+/NADP+:
binds/releases 2 protons at a time
bind to enzymes transiently
highly polar and water soluble
FAD:
one and two-electron transfers
prosthetic group in enzymes
flavin ring system is hydrophobic
iClicker: In the production of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate, how many NADHs, CO2s, and acetyl-CoAs are made from 1 glucose molecule?
2 NADHs, 1 CO2, 1 acetyl-CoA