Lab #4 | Reductive Amination
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Q1: What is a heterocycle
Cyclic molecules containing atoms other than carbon, like nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen
Amines
Nitrogen groups that are substituted by organic functional groups through single bonds
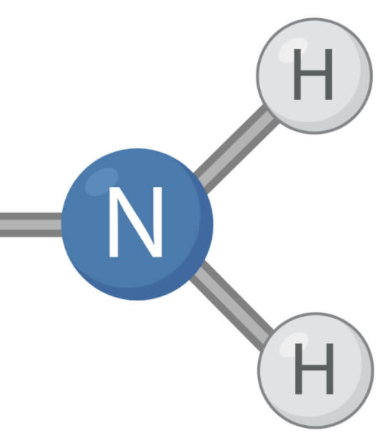
How to determine if an amine is an 1°, 2°, or 3°?
How many non-hydrogen substituents
ex: 1 non-hydrogen substituent = 1°
less nucleophilic (1)→ most nucleophilic (3)
Ammonium product
Quaternary (4 substituted with a plus charge on nitrogen) product
formed when an extremely nucleophilic 3° amine reaction with CH3I and nitrogen has no more lone pairs to react with
Reductive Amination
A more reliable way to synthesize substituted amines selectively, as amines are increasingly nucleophilic with substitution
Combine amine with an aldehyde or ketone, which are electrophilic
Forms a hemiaminal that is unstable and collapses to create an imine with a new C=N (electrophilic) bond with the loss of water
Amine is treated with a reducing agent like NaBH4, which will add hydrides to electrophiles
Q7: How to calculate yield for a multistep process?
ex: 1st step 80%, 2nd 80%
.8 x .8= 64%
Q10: What is the most important info gathered from IR?
The disappearance of C=O
Q11: Should p-toluidine or o-vanillin have a lower Rf?
Toluidine, as it is a polar molecule
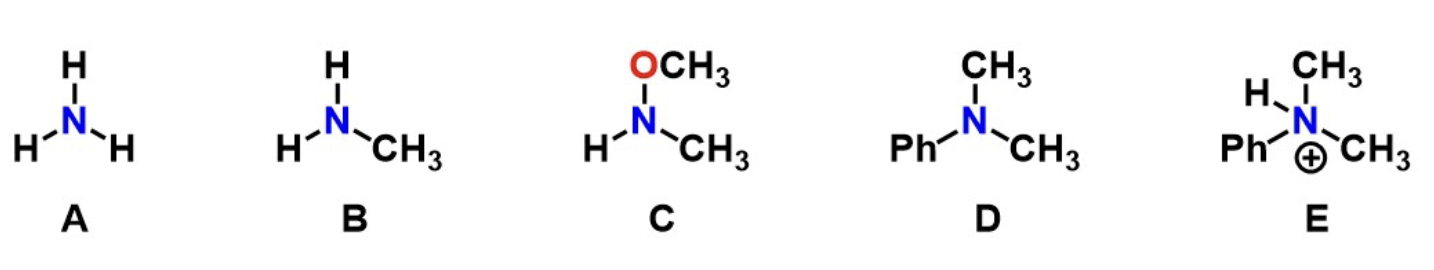
Q2: Which of the following is an unsubstituted amine?
A only
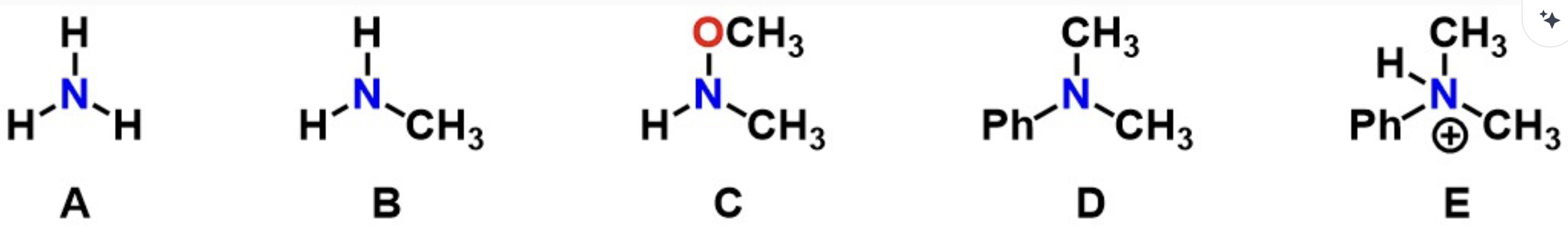
Q3: Which represents an ammonium product?
E
Why is reductive amination needed?
Aniline (1° amine) can synthesize up to a quaternary ammonium product through SN2 and this cannot be limited, frequently resulting in over alkylation
Discuss the reactivity of amines?
As an amine gets more substituted, it becomes more nucleophilic and more reactive
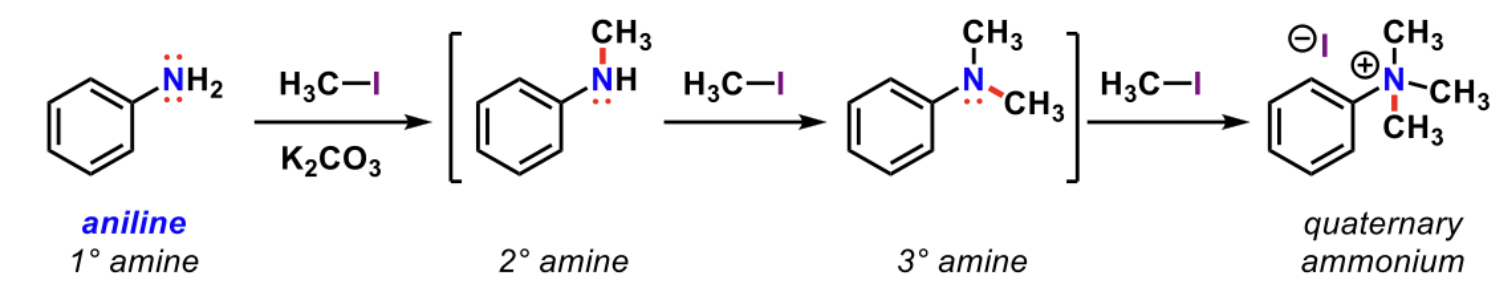
Q4: Referring to the picture, what is incorrect?
Primary amines are more reactive than secondary amines
What is the first step in reductive amination?
Combine the amine with an electrophilic C=O to form an unstable hemianimal, which collapses to form an imine
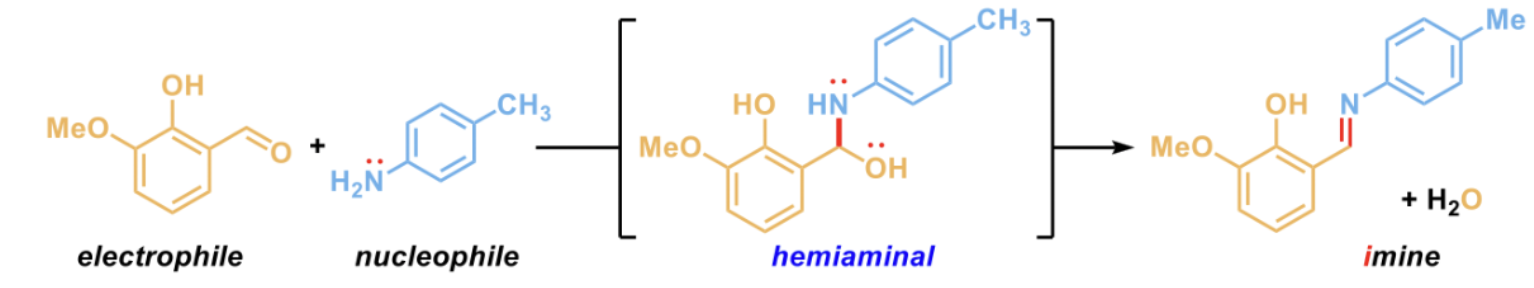
Discuss the stability of the produced imine?
The imine is stable but needs to be used ASAP because it can react with the water in the air to revert back to the starting material (not the hemianimal)
Q4: Which of the following are false regarding the mechanism of imine formation?
the hemiaminal is more stable than the imine
the hemiaminal cannot proceed to form an imine in the mechanism
What is the second step in reductive amination?
Imine is treated with a reducing agent like NaBH4

Q5: Predict the reaction
C, as this is not reductive amination based on the conditions, so the N will continue to be substituted
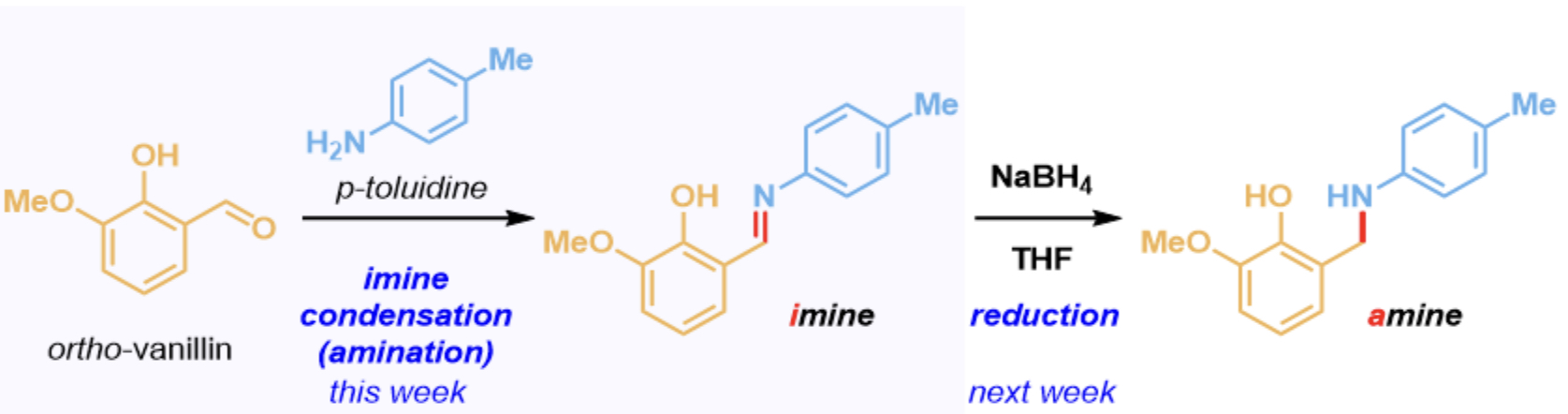
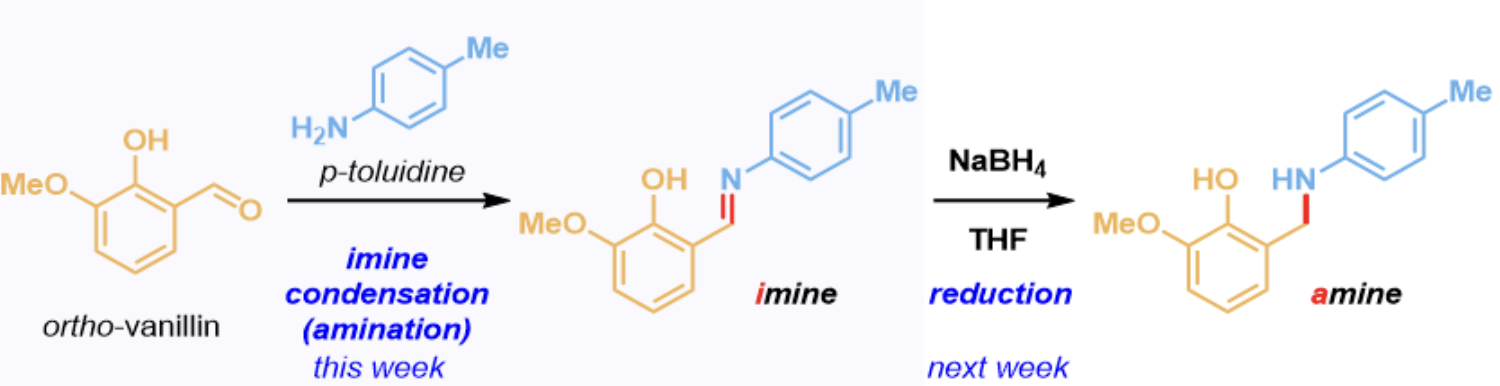
What is the basis of this reaction?
two-step reductive amination: imine condensation between o-vanillin and p-toluidine to form an imine product where the oxygen on the carbonyl fragment is substituted with the nitrogen from the amine
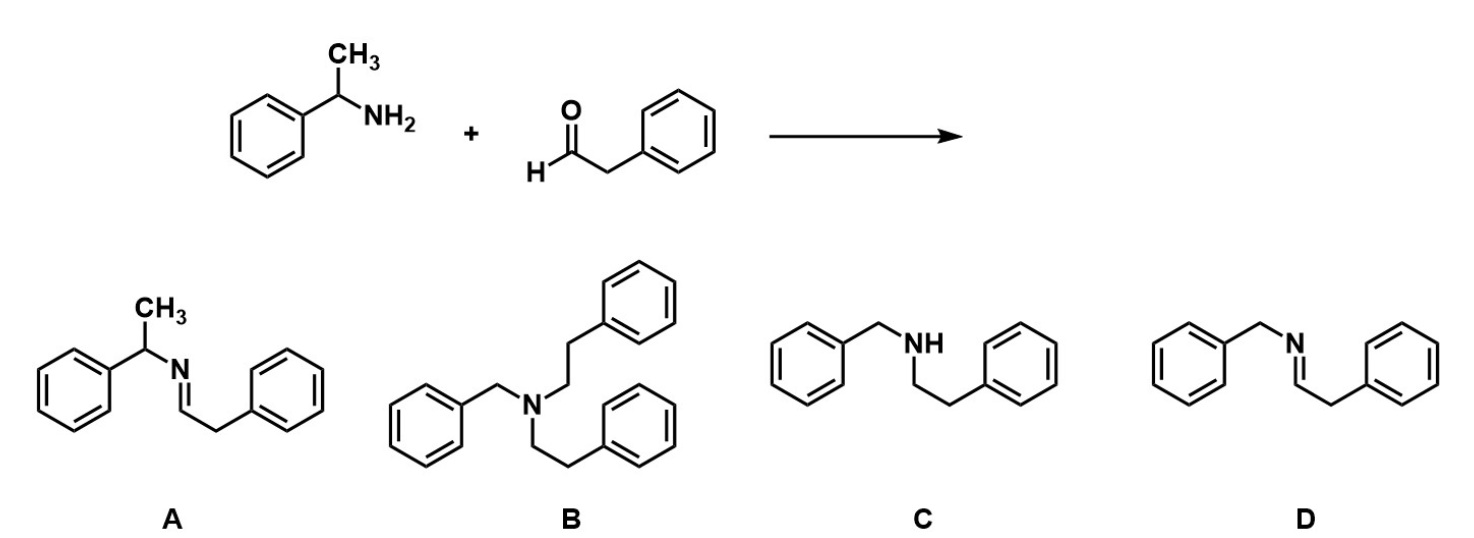
Q6: What is the product of this reaction?
A, as the C=N bond forms and there is not reducing agent like NaBH4
Q8: What has happened by the time both reagents form a homogeneous mixture?
The imine is formed
Q9: What can happen if too much hexanes is used in the recrystallization?
The yield will be significantly lower