Pharm exam 4 question bank
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Which is correct
pd-1 is a cell surface protein present in T cells
pd-1 is a protein ligand for pd-l1
pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to pd-1 and activates t cells
pd-1 is a cell surface protein present in T cells
name one drug we mentioned earlier that helps prevent kidney damage caused by cytotoxic anticancer drugs
allopurinol
what is an antifungal drug related to 5-FU
flucytosine
exogenous mRNA is very immunogenic. incorporation of this nucleoside ____ into mRNA has solved this problem and made mRNA vaccine possible
n1-methylpseudouridine
what is the purpose of adding bicarbonate to LA in clinical practice
it will raise the effective concentration of the non-ionized form and thus shorten the onset time of a regional block
1. Both benzodiazepines and barbiturates are sedative-hypnotics. One main difference between these two types of drugs is
A) They act on different molecular targets
B) Benzodiazepines are relatively safer, as they have the so-called “ceiling” effect
C) Barbiturates are relatively safer, as they have very low affinity to the target
D) Their efficiencies in passing blood-brain barrier are drastically different
B) Benzodiazepines are relatively safer, as they have the so-called “ceiling” effect
Which of the following is true regarding GABAA?
A) Like many important drug targets, the GABAA receptor is a GPCR
B) The GABAA receptor is composed of 5 subunits, and it acts as an ion channel
C) Barbiturates and GABA compete for the same binding site on the GABAA receptor
D) Benzodiazepines and GABA compete for the same binding site on the GABAA receptor
B) The GABAA receptor is composed of 5 subunits, and it acts as an ion channel
Inhalational versus intravenous anesthetics:
A) Inhalational anesthetics are fast-acting, while intravenous anesthetics depress CNS more
B) Typically, intravenous one for induction and inhalational one for maintenance of anesthesia C) The very first demonstration of general anesthesia used intravenous anesthetics
D) All of the above statements are correct
B) Typically, intravenous one for induction and inhalational one for maintenance of anesthesia
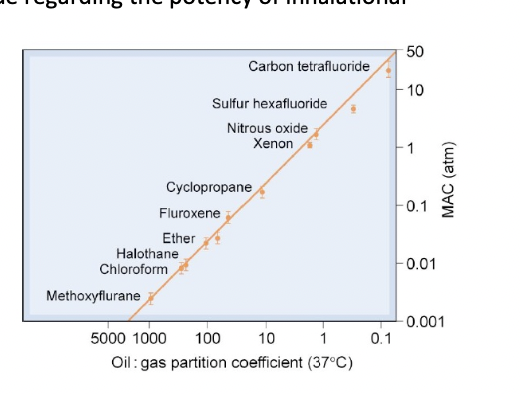
The graph on the right shows the relationship between anesthetic potency and lipid solubility of inhalational anesthetics. Which of the following is true regarding the potency of inhalational anesthetics?
A) The potency is indicated by the value of oil : gas
partition coefficient, and the higher the value, the higher the potency
B) The potency is indicated by the value of oil : gas
partition coefficient, and the higher the value, the lower the potency
C) The potency is indicated by the value of MAC, and the higher the value, the higher the potency
D) The potency is indicated by the value of MAC, and the higher the value, the lower the potency
D) The potency is indicated by the value of MAC, and the higher the value, the lower the potency
Thiopental versus propofol:
A) Both are intravenous anesthetics
B) Both are fast acting but thiopental has more “hangover” effectsC) Thiopental has been largely replaced by propofol
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
Which of the following is an important molecular target for lithium?
A) Enzymes required for inositol recycling
B) D2 dopamine receptor
C) D1 dopamine receptor
D) Serotonin receptor
A) Enzymes required for inositol recycling
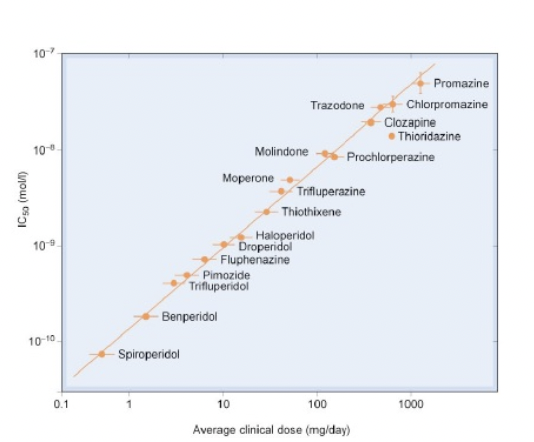
What does the graph on the right illustrate?
A) There is a good correlation between the
potency and efficacy among antipsychotic
drugs
B) There is an inverse relationship between the
clinical potency and efficacy among antipsychotic drugs
C) There is a good correlation between the
clinical potency and affinity for D2 receptor
D) There is an inverse correlation between the clinical potency and affinity for D2 receptor among antipsychotic drugs
C) There is a good correlation between the
clinical potency and affinity for D2 receptor
Beneficial gene transcription response that promotes neurogenesis and inhibits neural apoptosis can be stimulated by which of the following groups of molecules?
A) NA, 5-HT, and BDNF
B) Glutamate, Cortisol, and BDNFC) Glutamate, 5-HT, and BDNF
D) NA, Cortisol, and 5-HT
A) NA, 5-HT, and BDNF
Which of the following is a group of important anti-depressant drugs?
A) SSRI, SNRI, thiopental
B) SSRI, SNRI, TCA
C) MAOI, SNRI, barbiturateD) SSRI, cocaine, lidocaine
B) SSRI, SNRI, TCA
Which of the following is a correct grouping of terms?
A) Alzheimer’s disease (Ab); Parkinson’s disease (Tau); ALS (SOD)
B) Alzheimer’s disease (Ab); Parkinson’s disease (a-synuclein); ALS (Tau)
C) Alzheimer’s disease (Ab & Tau); Parkinson’s disease (a-synuclein); ALS (SOD)
D) Parkinson’s disease (SOD); Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (Tau); ALS (a-synuclein)
C) Alzheimer’s disease (Ab & Tau); Parkinson’s disease (a-synuclein); ALS (SOD)
These two enzymes: ______________, are responsible for generating Ab and are good drug targets.
A) Alpha- and beta-secretases
B) Alpha- and gamma-secretasesC) Beta- and gamma-secretases
D) Tau kinases
C) Beta- and gamma-secretases
Tacrine and donepezil are drugs that
A) Inhibit D2 dopamine receptor and boost up mood
B) Inhibit cholinesterase and improve cognitive function in AD patient
C) Activate dopamine receptor and improve the symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease
D) Stimulate opioid receptors and relief pain
B) Inhibit cholinesterase and improve cognitive function in AD patient
Which of the following is true regarding HERzyme?
A) HERzyme is a protein enzyme that utilizes Mg2+ as a cofactor to stop VEGF synthesis
B) HERzyme is a glycoprotein that binds to VEGF receptor
C) HERzyme is an engineered ribozyme that targets human epidermal growth factor 2
D) HERzyme is an anti-sense drug that prevents the formation of estrogen
C) HERzyme is an engineered ribozyme that targets human epidermal growth factor 2
Pegaptanib (aka Macugen) is the first aptamer drug for the treatment of ______________, via inhibiting ________________.
A) Breast cancer; Oncogenic Ras
B) Age related macular-degeneration; VEGF
C) Retinal degeneration; GAP
D) CML; Bcr-Abl
B) Age related macular-degeneration; VEGF
16. One advantage of the mRNA-based therapeutics is
A) Comparing to proteins, mRNA is much more stable
B) Comparing to viral vectors for gene therapy, mRNA does not pose the risk of insertional mutagenesis
C) Comparing to viral vectors, mRNA does not have the issue of immunoreactivity
D) Contrary to small molecules, mRNA is much easier to pass blood-brain barrier
B) Comparing to viral vectors for gene therapy, mRNA does not pose the risk of insertional mutagenesis
17. Which of the following is a component of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) for mRNA delivery?
A) Ionizable lipids
B) Cholesterol
C) PEG-lipid
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
Miravirsen is a drug that can potentially be used to control hepatitis C virus. The molecular target of miravirsen is
A) HCV envelop proteins
B) miR-122 in liver
C) HCV RNA
D) HCV DNA
B) miR-122 in liver
Administering local anesthetics such as lidocaine to infected tissues or tissues with acidosis often requires a higher dosage. This is because:
low pH will favor the charged form which is inefficient to pass the lipid bilayer
Spiegelmer refers to ___________, and
it has this advantage: ____
mirror image of D-oligonucleotides
high affinity and specificity for targets with sustained activity on chemokines. Resistance to enzymatic degradation and non-immunogenic nature
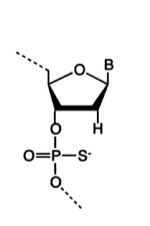
Backbone modification: The first is a phosphonothioate oligonucleotide. This replaces oxygen with a phosphate group (PMOs)
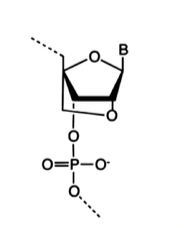
Sugar modification: the second is a locked nucleic acid (LNA) where the ribose ring is locked by methylene.
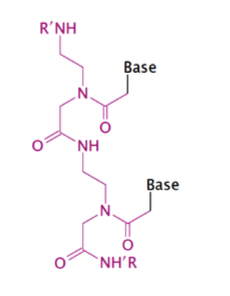
Base modification
On the following diagram, identifying the step that is affected by the following drugs, respectively:
levodopa, monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), SSRI, morphine, reserpine
a. Levodopa = step 2, synthesis
b. MAO = step 4, metabolism
c. SSRI = step 6, reuptake
d. Morphine = step 8, antagonist/agonist for receptors
e. Reserpine = step 3, storage
CTLA-4 and PD-1 are called ___________________, and their activation by cancer cells can lead to ____________________.
checkpoint; activation of T cell function
checkpoint; inhibition of T cell function
cell cycle proteins; activation of B cells
nuclear receptor proteins; inhibition of T cells
checkpoint; inhibition of T cell function
Lpilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab are
drugs that prevent heart attack
monoclonal antibodies that treat autoimmune diseases
monoclonal antibodies that act as checkpoint inhibitors to treat cancer
polyclonal antibodies that are used to treat cancer
monoclonal antibodies that act as checkpoint inhibitors to treat cancer
A solid tumor with a mass of 1 gram has this many cells:
1 billion
1 million
10 million
10 billion
1 billion
Nitrogen mustards are classified as this type of anticancer drugs:
antimetabolites
alkylating agents
cytotoxic antibiotics
microtubule inhibitors
alkylating agents
Methotrexate is a commonly used agent for chemotherapy. How does it work?
Methotrexate is a folate analog, which acts as an inhibitor for DHFR. Inhibiting DHFR can impair the conversion of dUMP to dTMP, as the methyl-donor for this reaction comes from tetrahydrofolate.
Methotrexate is a uracil analog, which competes with dUMP for thymidylate synthase.
Methotrexate is an analog of dUMP, and it acts as a competitive inhibitor for the enzyme that converts dUMP to dTMP
Methotrexate is a folate analog, which blocks the uptake of folate from the diet
Methotrexate is a folate analog, which acts as an inhibitor for DHFR. Inhibiting DHFR can impair the conversion of dUMP to dTMP, as the methyl-donor for this reaction comes from tetrahydrofolate.
The target for benzodiazepine and barbiturates is _____________; between these two drugs, this one _______ has a so-called "ceiling" effect and is relatively safer.
opioid receptor; benzodiazepine
GABAA receptor; benzodiazepine
opioid receptor; barbiturates
GABAA receptor; barbiturates
GABAA receptor; benzodiazepine
Matching the modifications.
PSP, phosphorothioates
PMOs
OMe and MOE
N1-methylpseudouridine
PSP, phosphorothioates = Backbone modification: O is replaced with S
PMOs = Backbone modification without S
OMe and MOE = Sugar modifications in RNA
N1-methylpseudouridine = enables mRNA drugs
What is RNase H?
An enzyme that recognizes double-stranded RNA and destroys it.
An enzyme that recognizes DNA:RNA duplex and destroys RNA.
An enzyme that recognizes DNA:RNA duplex and destroys DNA.
A unique type of ribozyme
An enzyme that recognizes DNA:RNA duplex and destroys RNA.
Which of the following is true regarding mipomersen, an orphan drug for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia? (check all that apply)
Mipomersen is an ASO drug
Mipomersen is an RNAi drug
Mipomersen is a single-strand DNA that targets the mRNA of apo B-100.
Mipomersen is the most expensive drug per injection.
Mipomersen is an ASO drug
Mipomersen is a single-strand DNA that targets the mRNA of apo B-100.
Which of the following is true regarding spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and its treatments? (check all that apply)
Nusinersen is an ASO drug for SMA.
Zolgensma is a gene therapy for SMMA.
Zolgensma is much more expensive than nusinersen.
SMA occurs 1 in one million new born.
Nusinersen is an ASO drug for SMA.
Zolgensma is a gene therapy for SMMA.
Zolgensma is much more expensive than nusinersen.
Which of the following is true regarding SELEX?
SELEX is a technique that allows efficient design of sgRNA for CRISPR.
SELEX is a technique that allows the selection of an aptamer.
SELEX is an ex vivo delivery for gene therapy.
SELEX is an in vivo delivery of gene therapy.
SELEX is a technique that allows the selection of an aptamer.