Diagnostic Electrocardiogram - Mid term
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
The clinical situation known as pulseless electrical activity is defined as cardiac monitor electrical activity without palpable pulse present.
True or False
True
The direction of rapid transmission of the electrical impulses in the Purkinje fibers is:
Endocardium to the epicardium
Which one of the following is true about the relative refractory period?
Begins at the end of phase 3
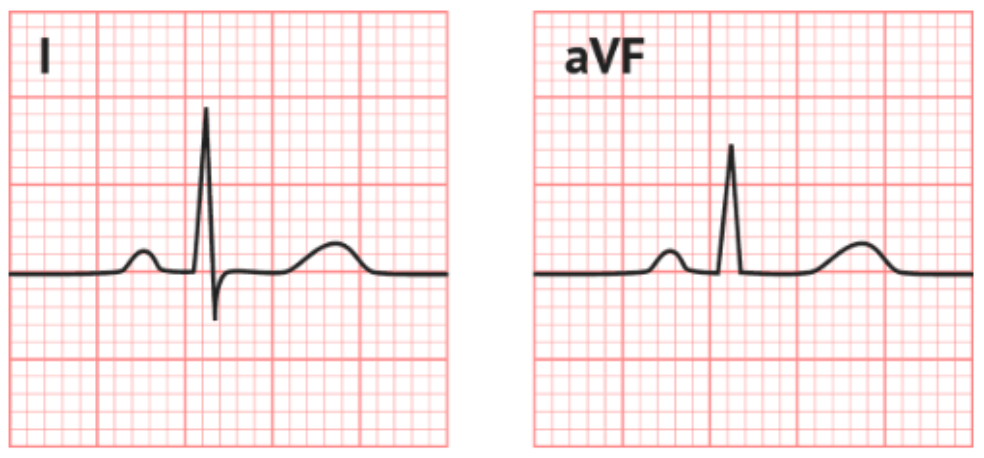
What is the axis of the following ECG?
-30 to + 90 degrees
What is the direction of lead II on the hexaxial reference system?
60 degrees
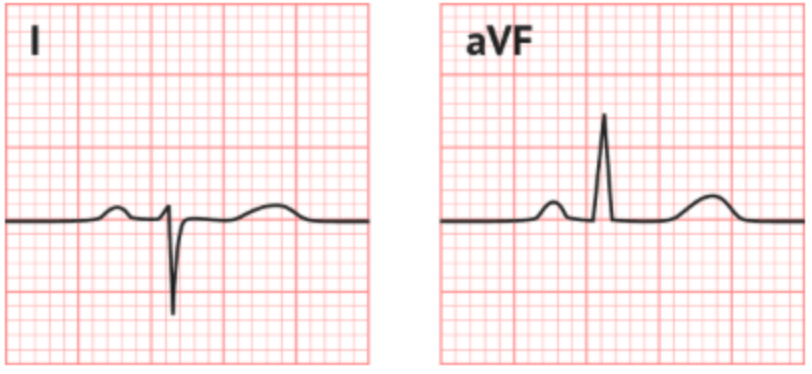
What is the axis on the following ECG?
RAD
Which one of the following statements about a positive, round peaked P-wave in lead II is correct?
It signals that the impulse originates in the SA node
Atrial fibrillation is caused by which one of the following mechanism?
altered automaticity
Atrial flutter is caused by which one of the following mechanisms?
reentrant rhythm
Couplet
2 premature beats in a row
Runs
3 or more beats in a row
Bigeminy
Every other beat is a premature beat
Trigeminy
Every third beat is a premature beat
Quadrigeminy
Every fourth beat is a premature beat
PACs have the following ECG characteristics, EXCEPT:
a. PACs are followed by a compensatory pause
b. PACs have abnormally shaped P-waves
c. PACs are followed by an incomplete pause
d. PACs have normal or prolonged P-R intervals
a. PACs are followed by a compensatory pause
An aberrantly conducted PAC can cause a QRS complex displaying the following pattern:
RBBB pattern
Which one of the following are typical ECG characteristics associated with multiform atrial rhythm?
Rhythm is usually irregular
What is the main difference between WAP and MAT?
Ventricular rate
All of the following are types of SVT, EXCEPT:
a. WAP
b. AVRT
c. AT
d. AVNRT
a, WAP
The most important ECG component in diagnosing tachycardia is
P-wave
A rapid, regular supraventricular tachycardia that starts and ends suddenly is called:
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
The most common type of SVT is:
AVNRT
In SVT, where the HR can be very high, it is very important to establish the type of rhythm before management and treatment of the symptomatic patients.
Which one of the following describes a sustained rhythm?
It can cause hemodynamic instability
Which one of the following pharmacological agents is NOT administered in supraventricular tachycardia?
Atropine
Vagal maneuvers are methods used to achieve which one of the following?
Slow conduction through the A-V node
Synchronized cardioversion as a treatment for SVT, refers to:
Electrical therapy with a shock delivered during the QRS complex
In the atypical AVRNT the P-wave is located in one of the following components of the ECG:
Before the QRS complex
Pre-excitation causes a widening of the QRS complex due to premature depolarization of the ventricles through an accessory pathway.
True or False
True
Secondary ST-T changes during pre-excitation occur due to early depolarization of the ventricles, in the same direction to the delta wave.
True or False
False
ECG characteristics of an orthodromic AVRT:
QRS < 0.11 sec
ECG characteristics of an antidromic AVRT:
Wide QRS with delta wave
The triad of WPW syndrome consists of:
Delta wave, wide QRS, short PRI
In atrial flutter, the P-waves are replaced by:
F-waves
Which one of the following phases of diastole are not represented on an ECG with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial systole
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation is characterized by episodes of AFib:
Under 7 days
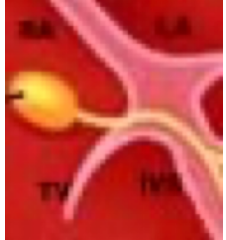
The following diagram represents which one of the following functional segments of the electrical conduction system of the heart?
AV junction
The pacemaker cells firing at a rate of 40-60 bpm are located in:
Common bundle
Junctional rhythms originating in the AV junction, pace the heart in all of the following circumstances, EXCEPT:
a. Sinus bradycardia
b. Sinus arrest
c. SA node impulse generated and conducted to the ventricles
d. SA block
c. SA node impulse generated and conducted to the ventricles
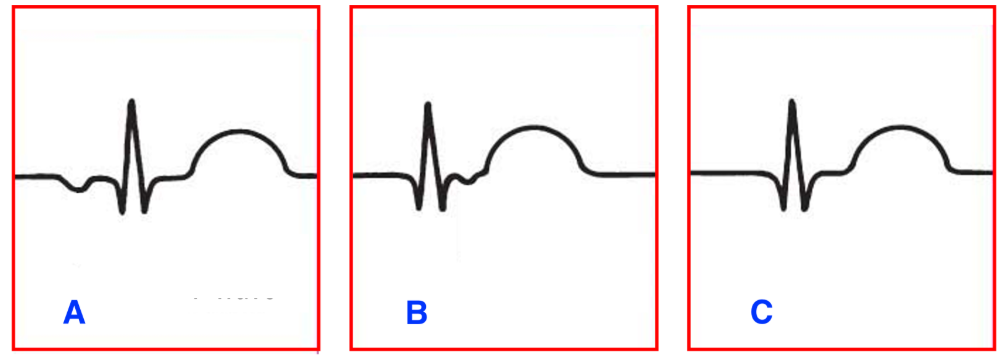
The following diagram represents the patterns of the P-wave displayed in junctional rhythms.
Match the letters representing each pattern to the correct description:
A. Atria depolarizes before ventricles
B. Atria depolarizes after ventricles
C. Atria depolarizes at the same time as ventricles
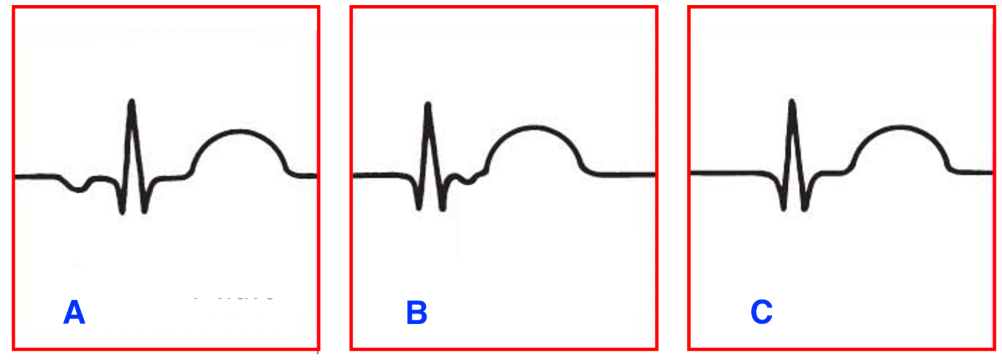
Premature junctional contractions are followed by which one of the following types of delay?
Incomplete pause
A junctional escape rhythm comes early, before the next expected beat of the underlying rhythm.
True or False
False
Junctional escape beats are frequently caused by all of the following situations, EXCEPT:
a. After pauses of nonconducted PACs
b. Increased sympathetic tone
c. During episodes of sinus arrest
d. During sinus bradycardia
b. Increased sympathetic tone
Accelerated junctional rhythms are caused by altered automaticity of the bundle of His with an impulse firing rate of:
61-100 bpm
Irregular JT
Variable conduction to the atria
Nonparoxysmal JT
gradual rate increases <120 bpm
Automatic or focal JT
starts and ends suddenly >140 bpm
All of the following are standard management steps in hemodynamically unstable arrhythmias, EXCEPT:
a. Oxygen level check and administration
b. IV access
c. Vagal maneuvers
d. 12-lead ECG
c. Vagal maneuvers
The only difference between junctional rhythm and accelerated junctional rhythm is the increase in sinoatrial conduction.
True and false
False
Ventricular rhythms at a rate of 20-40 bpm are manifested in the following situations, EXCEPT:
a. The rate of firing of the SA node is faster than the ventricular originated rate
b. The impulse generated by the SA node is blocked as it exits the node
c. Irritable site in the ventricles produces an early beat or rapid rhythm
d. SA node fails to fire
a. The rate of firing of the SA node is faster than the ventricular originated rate
In ventricular arrhythmias, the T-wave is usually in a direction opposite to the QRS.
True or False
True
P-waves are always present in ventricular arrhythmias.
True or False
False
The QRS complexes of PVCs originating in the RV will have the following pattern in V1:
Wide, negative complex
The QRS complexes of PVCs originating in the LV will have the following pattern in V1:
Wide positive complex
Types of PVCs include all of the following, EXCEPT:
a. Aberrantly conducted PVCs
b. Multiform PVCs
c. Interpolated PVCs
d. R-on-T PVCs
a. Aberrantly conducted PVCs
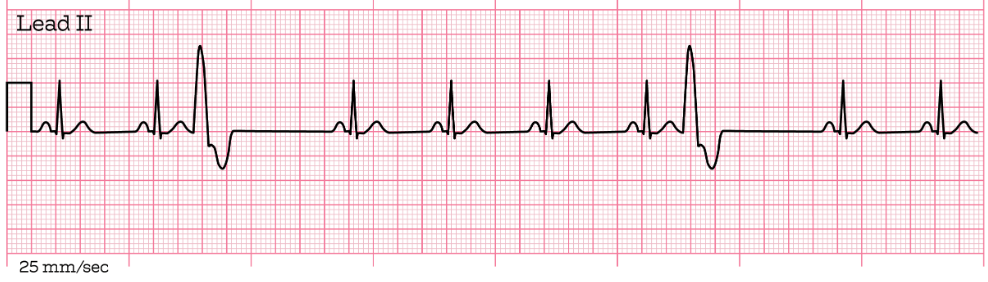
The PVCs seen in the following ECG strip are which of the following type?
Unifocal
PVCs occurring during the relative refractory period will coincide with which of the following components of an ECG?
Last half of the T-wave
PVCs occurring during the last half of the T-wave can trigger which type of arrhythmia?
Ventricular tachycardia
The difference between PVCs and ventricular escape beats are all of the following, EXCEPT:
a. PVCs have wide QRS and T deflects in the opposite direction of the QRS
b. Escape beats occur early
c. PVCs occur early
d. Escape beats occur after a pause in which supraventricular pacemaker failed to fire
b. Escape beats occur early
The rhythm of ventricular escape rhythm is regular
True or False
True
Which one of the following is a type of PVC that occurs between two normally conducted QRS complexes and does not disturb the next ventricular depolarization or SA node activity?
An interpolated PVC
The ECG characteristics of a monomorphic VT include all of the following, EXCEPT:
a. Ventricular rate of 101-250 bpm
b. QRS > 0.12 sec
c. Regular ventricular rhythm
d. PRI of 0.12-0.20 sec
d. PRI of 0.12-0.20 sec
The term for 3 or more PVCs occurring in a row at a rate > 100 bpm is:
A run of ventricular tachycardia
Select the shockable cardiac rhythms from the choices below
Pulseless VT
Which of the following statements are true about asystole?
Use Hs and Ts when considering possible reversible causes of the rhythm
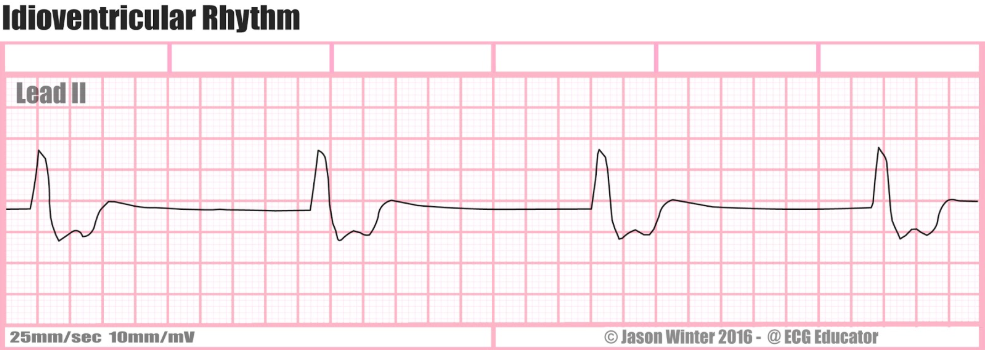
All of the following are characteristics of idioventricular rhythm, EXCEPT:
a. Rhythm: regular
b. Rate: 60-100 bpm
c. P-waves: absent
d. QRS duration: > 0.12 sec
b. Rate: 60-100 bpm
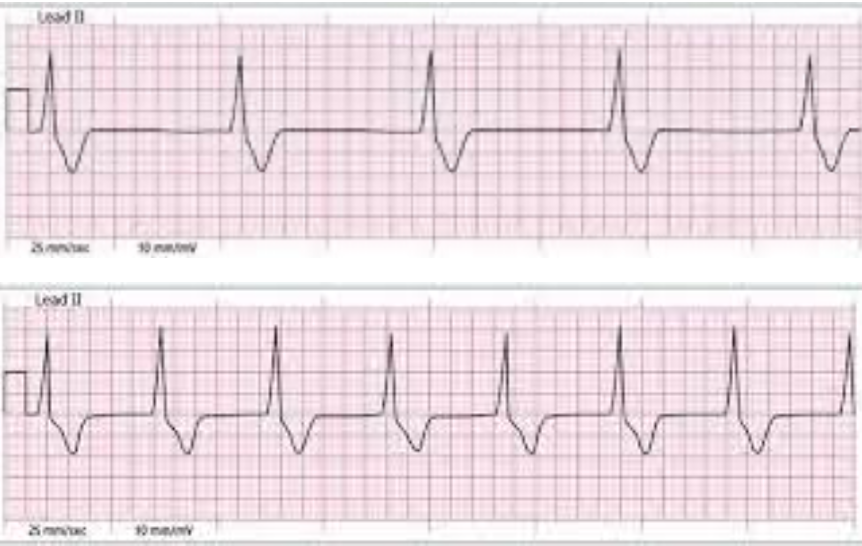
What is the rhythm in the following two ECG strips and what characteristic differentiates the 2 rhythms?
IVR and rate
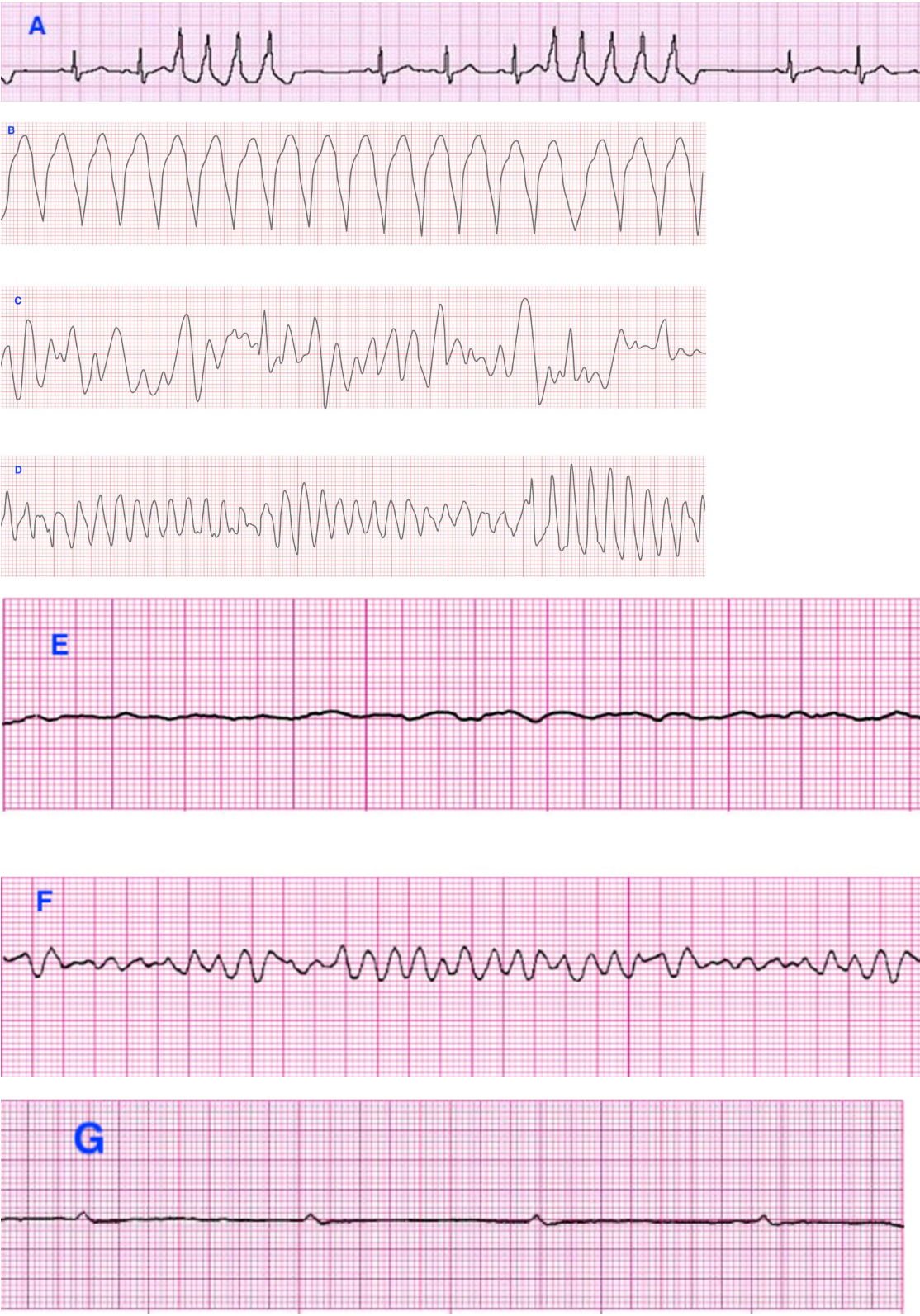
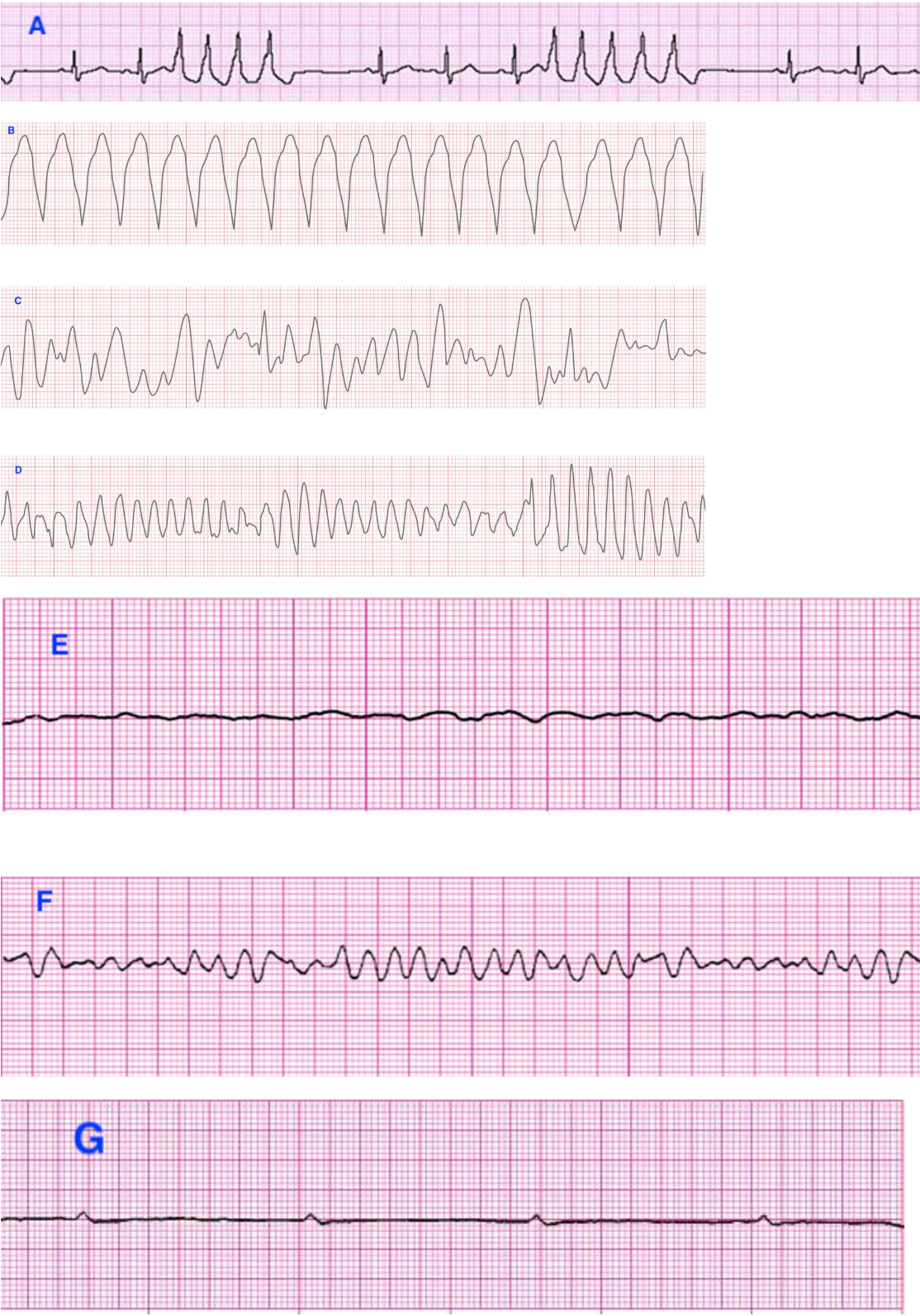
Match the following ECG strips to the correct ventricular rhythms:
A. Nonsustained monomorphic VT
B. Sustained monomorphic VT
C. Polymorphic VT
D. Torsades de pointes
E. Fine wave VF
F. Coarse wave VF
G. Ventricular standstill
Which of the following ECG components is used to detect AV conduction disturbances?
PR interval
Which of the following dysrhythmias may be a normal finding in individuals with no history of cardiac disease, especially athletes?
First degree AV block
The term second degree AV block type I is synonymous with
Wenckebach
Identify the characteristics of a 2:1 AV block
Every other P is not followed by a QRS
A key difference between type I and type II second degree AV block is one of the following:
In type II the PRIs before and after a blocked P-wave are constant
With third degree AV block, the PR interval
Is absent
AV interval
An artificial PRI
Oversensing
Inappropriate sensing of extraneous electrical signals
Dual chambers
Pacemaker type using an atrial and ventricular lead
Inhibition
Pacemaker response in which the output pulsed in surpassed
Demand
Type of pacemaker discharging when the HR drops below the preset rate for the pacemaker
Failure to capture
Pacemaker malfunction in which the artificial pacemaker stimulus fails to depolarize the myocardium
Failure to pace
Pacemaker malfunction in which the pacemaker fails to deliver an electrical stimulus at its programmed time
Rate modulation
The ability of a pacemaker to increase the pacing rate in response to physcial activity or metabolic demands
Undersensing
Pacemaker malfunction in which a pacemaker fails to recognize spontaneous myocardial depolarization
Fixed rate
Type of pacemaker continuously discharging at preset rate regardless of the intrinsic activity
Which one of the following are possible signs of hyperkalemia?
Tall, peaked T-waves
Which one of the following are signs of hypokalemia?
U-waves
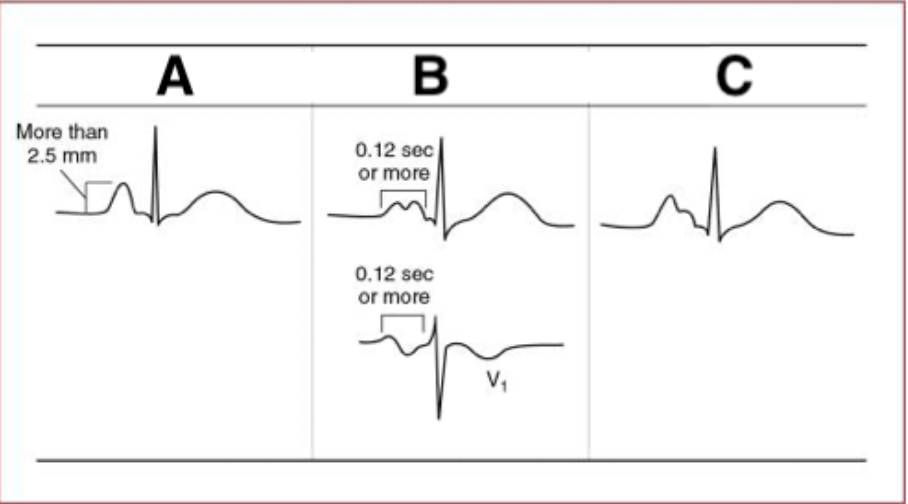
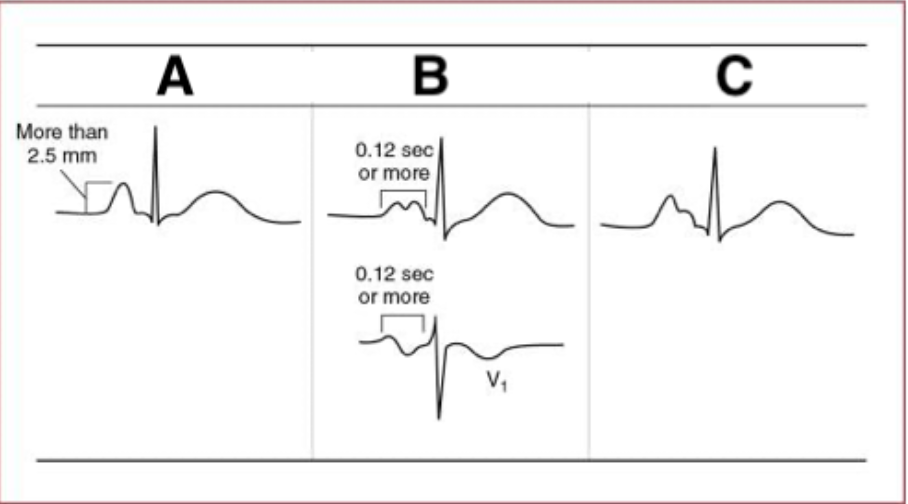
Match the letters with the correct description of ECG patterns of atrial abnormalities:
A. RAA
B. LAA
C. Combined atrial abnormality
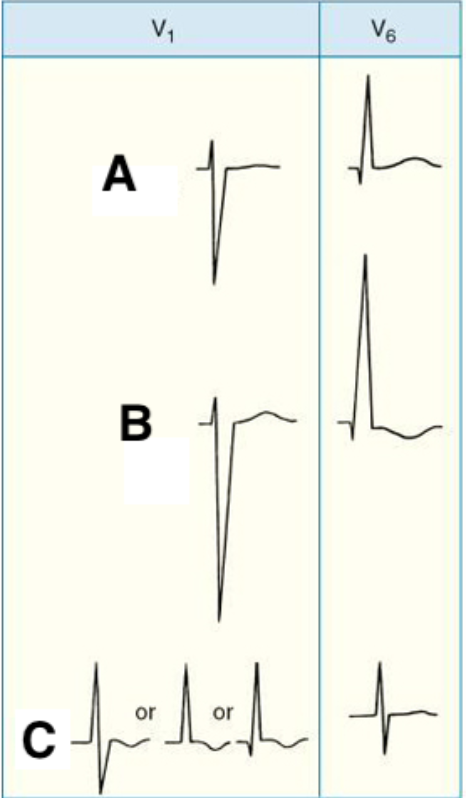
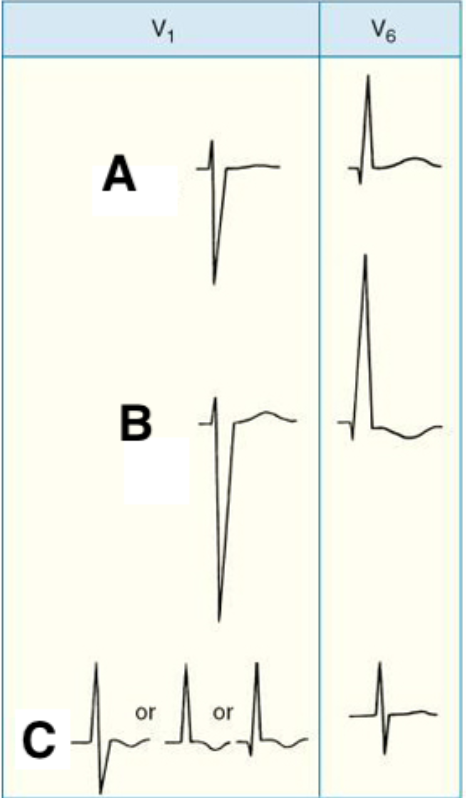
Match the following patterns of ventricular hypertrophy with the correspondent letters:
A, Normal
B. LVH
C. RVH
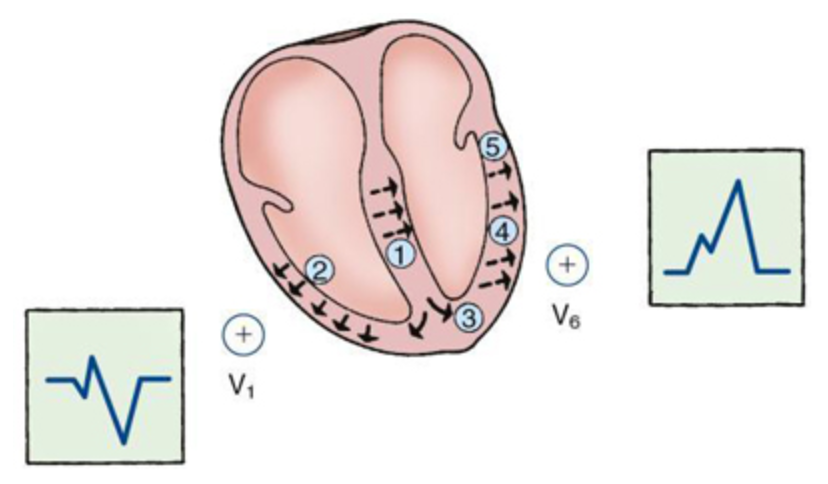
The following diagram represents the depolarization sequence and QRS pattern in which one of the following?
LBBB
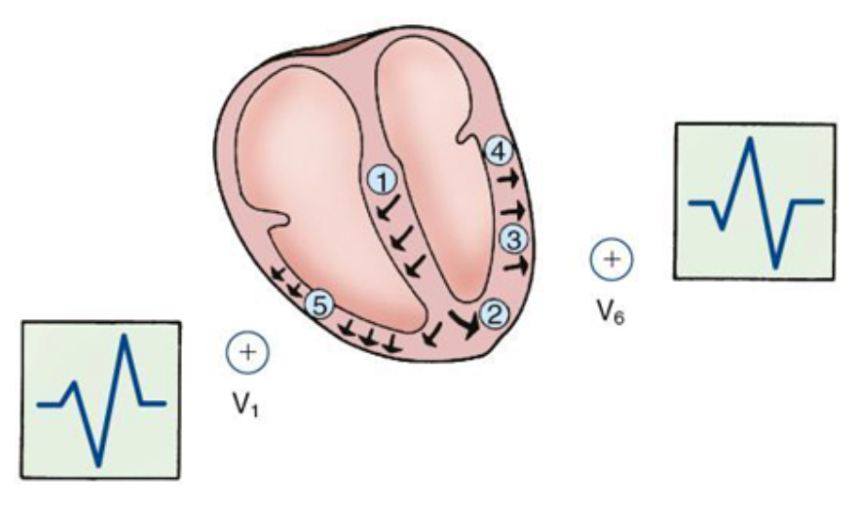
The following diagram represents the depolarization sequence and QRS pattern in which one of the following?
RBBB
All of the following steps are integral for the interpretation of RVH and LVH, EXCEPT:
a. T-waves in V1,V3, V5,V6
b. P-wave amplitude and length
c. QT interval
d. Axis determination
e. R and S waves in V1-V3 and lateral wall leads
c. QTI