Cytology practical
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the three neoplastic different cell types?
-Epithelial
-Mesenchymal (eg, spindle cells)
-Round
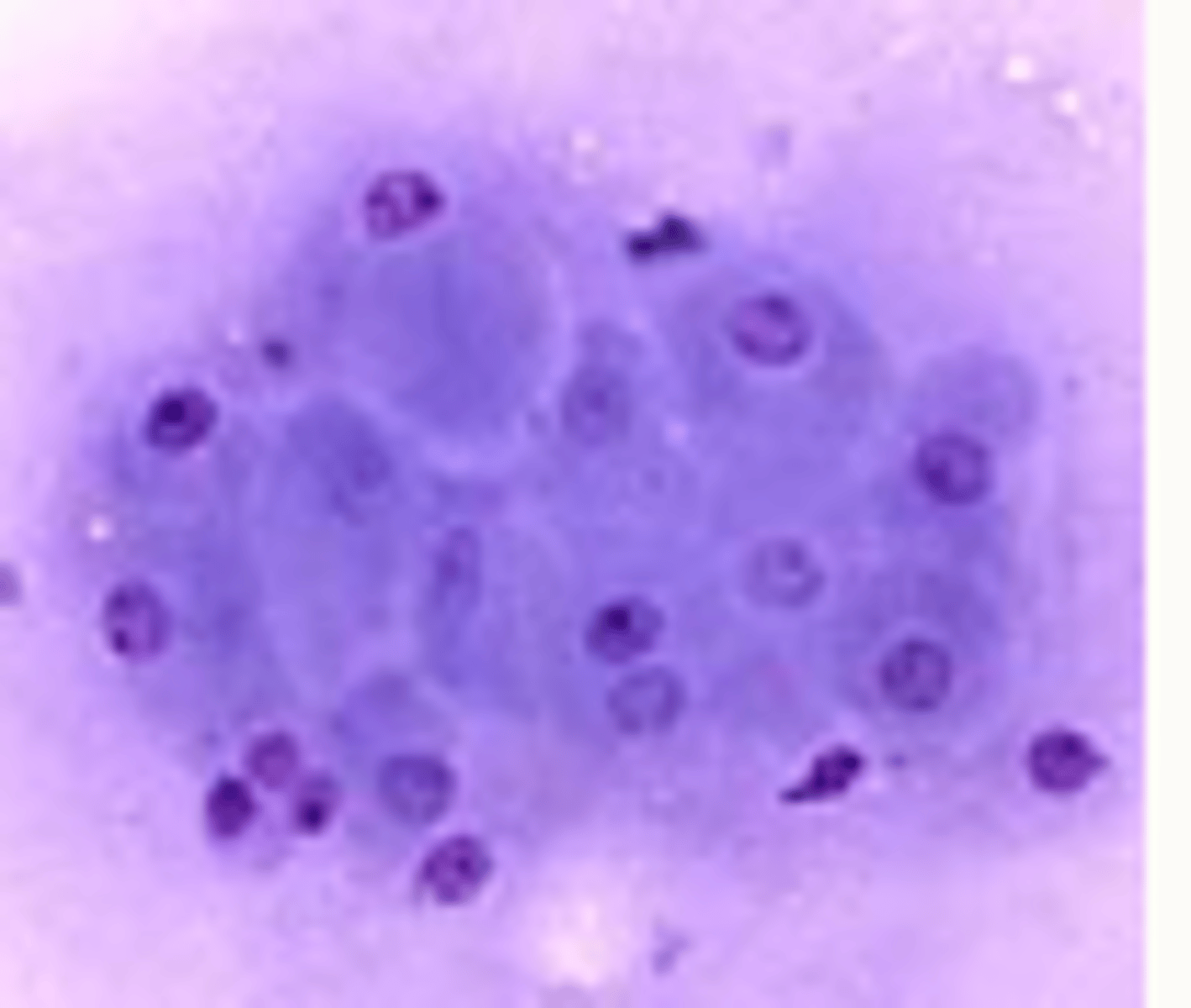
Epithelial
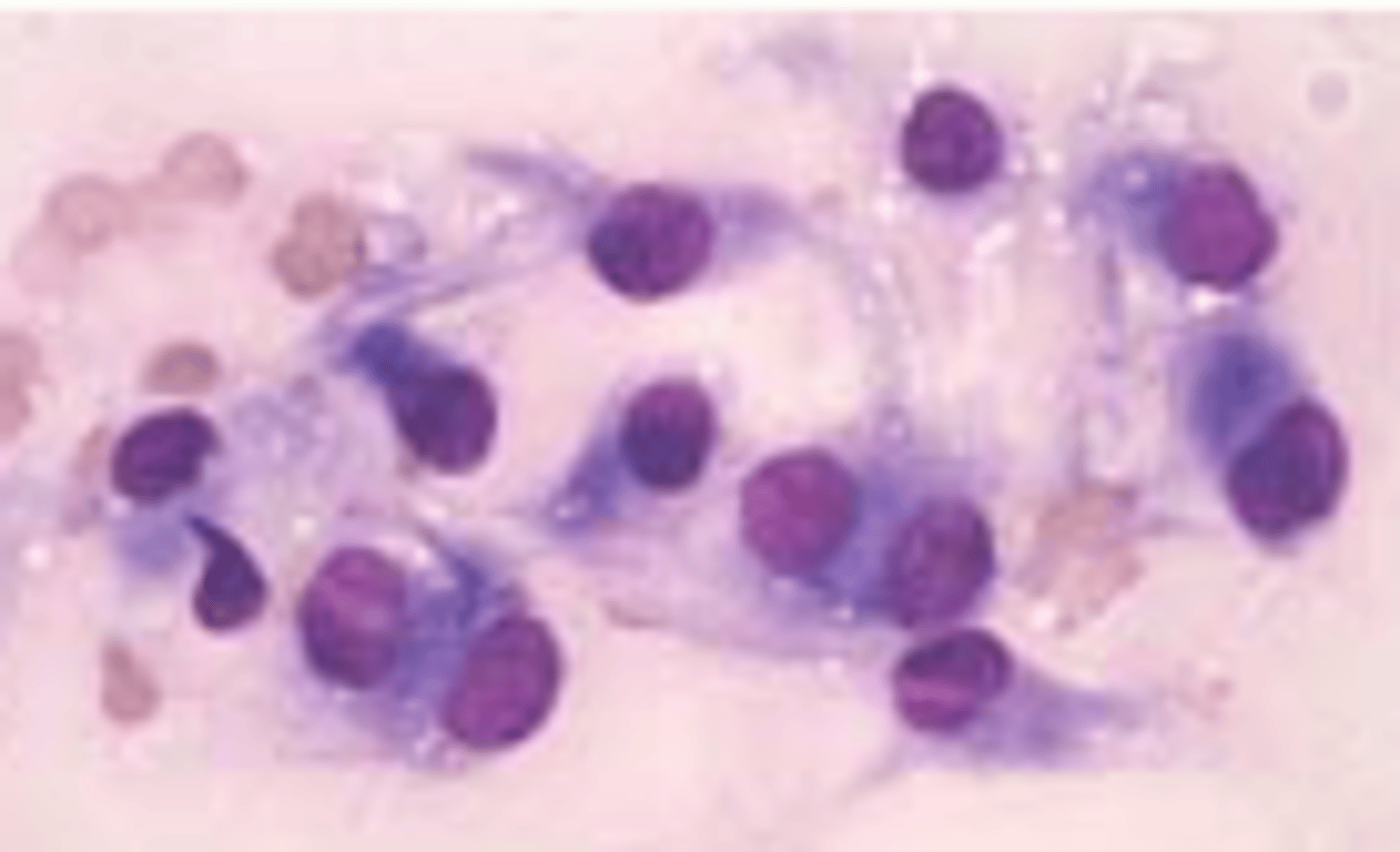
Mesenchymal (spindle)
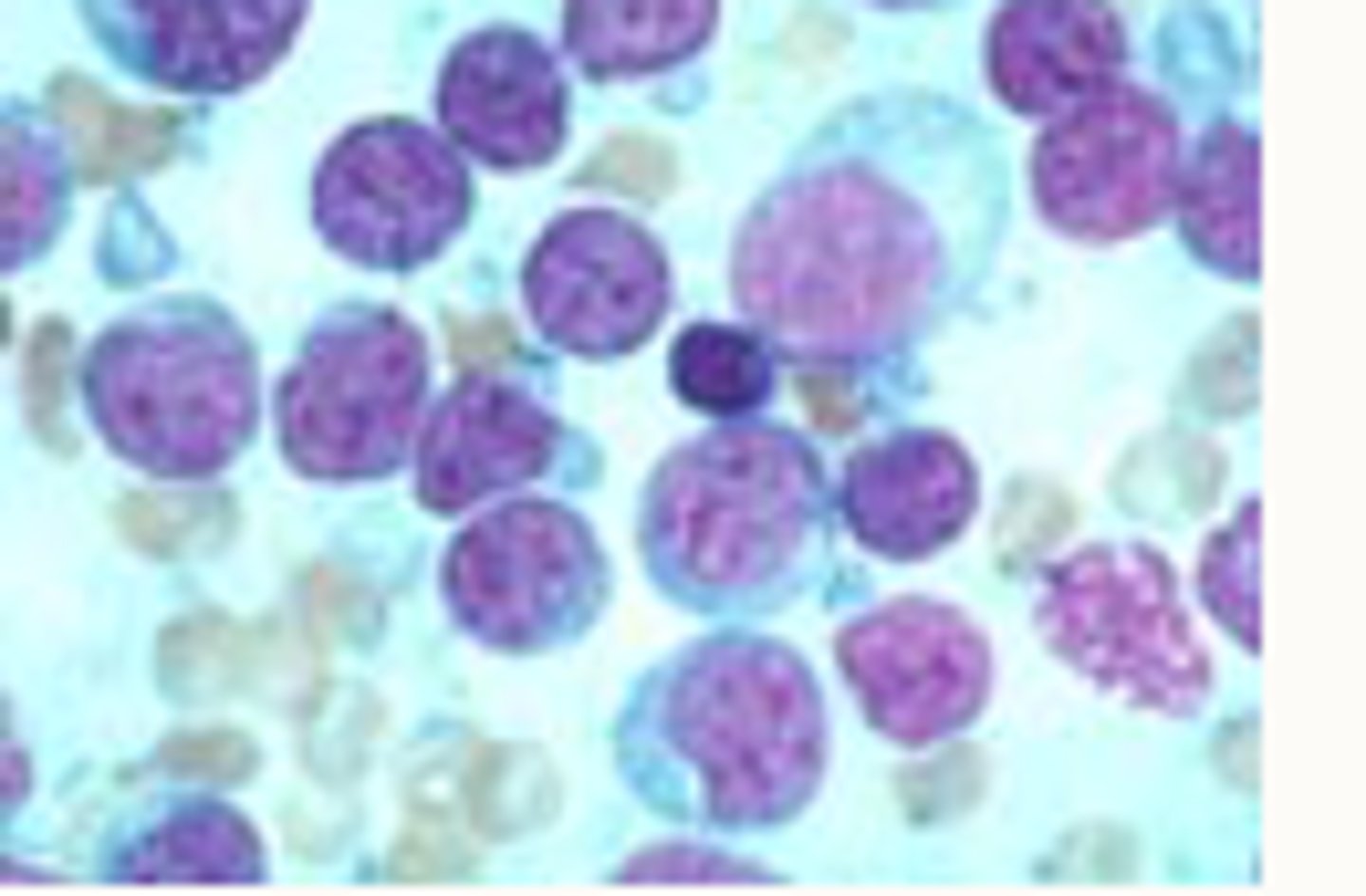
Round
how do we do a cytological examination
Low power review (x10 objective)
Good places to look at
Quality
Any/many cells?
Well/poorly preserved?
Background
Haemorrhage, granules, protein, matrix, debris, disrupted cells
Predominant cells
Neutrophils? Other cells?
Cells (x 40 or oil)
Individual or organised
Single or mixed population?
Cell size, shape, variation?
Nuclear size, shape, variation, abnormal mitoses?
Describe epithelial
§High yield, cells associated with one another, rafts, sheets, acini, cuboidal, columnar
Describe mesenchymal
-Low yield, spindle shaped cells, usually single but may be in aggregates, there can be "matrix"
Describe round
§High yield, discrete round cells, not adherent
Examples of epithelial neoplasia
-Surface (squamous, transitional, hair follicles)
-Glandular (apocrine and exocrine)
-Benign (papilloma, adenoma)
-Malignant (Adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma)
Examples of round neoplasia
§Lymphocytes
§Mast Cells
§Histiocytes
§Plasma cells
-Benign (histiocytoma)
-Malignant (Mast cell tumour)
Examples of mesenchymal neoplasia
§Fibrocytes
§Muscle cells
§Osteoblasts
§Endothelial cells
-Benign (Fibroma, Leiomyoma)
-malignant (Haemangiosarcoma, Fibrosarcoma)
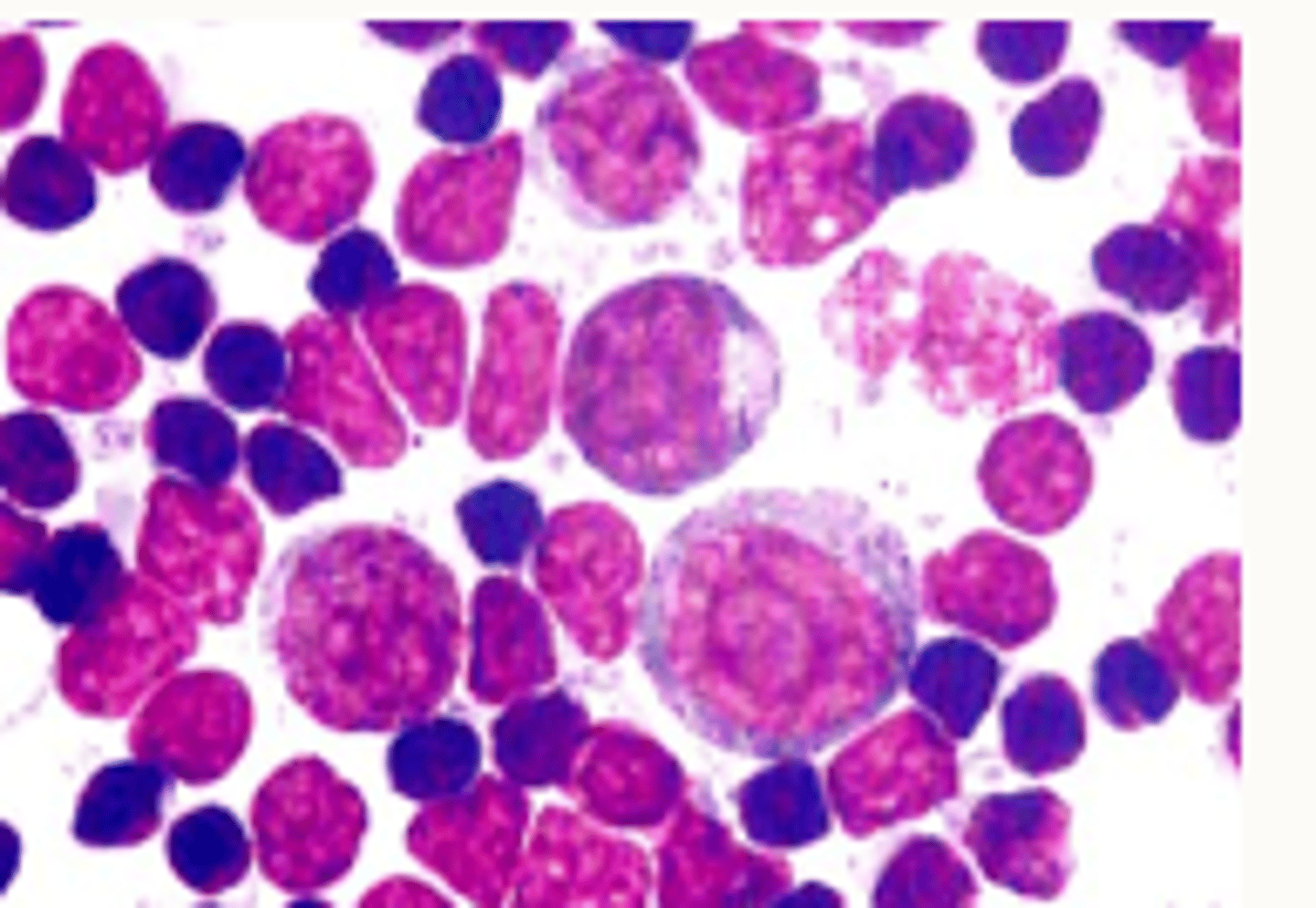
Lymph node- Reactive
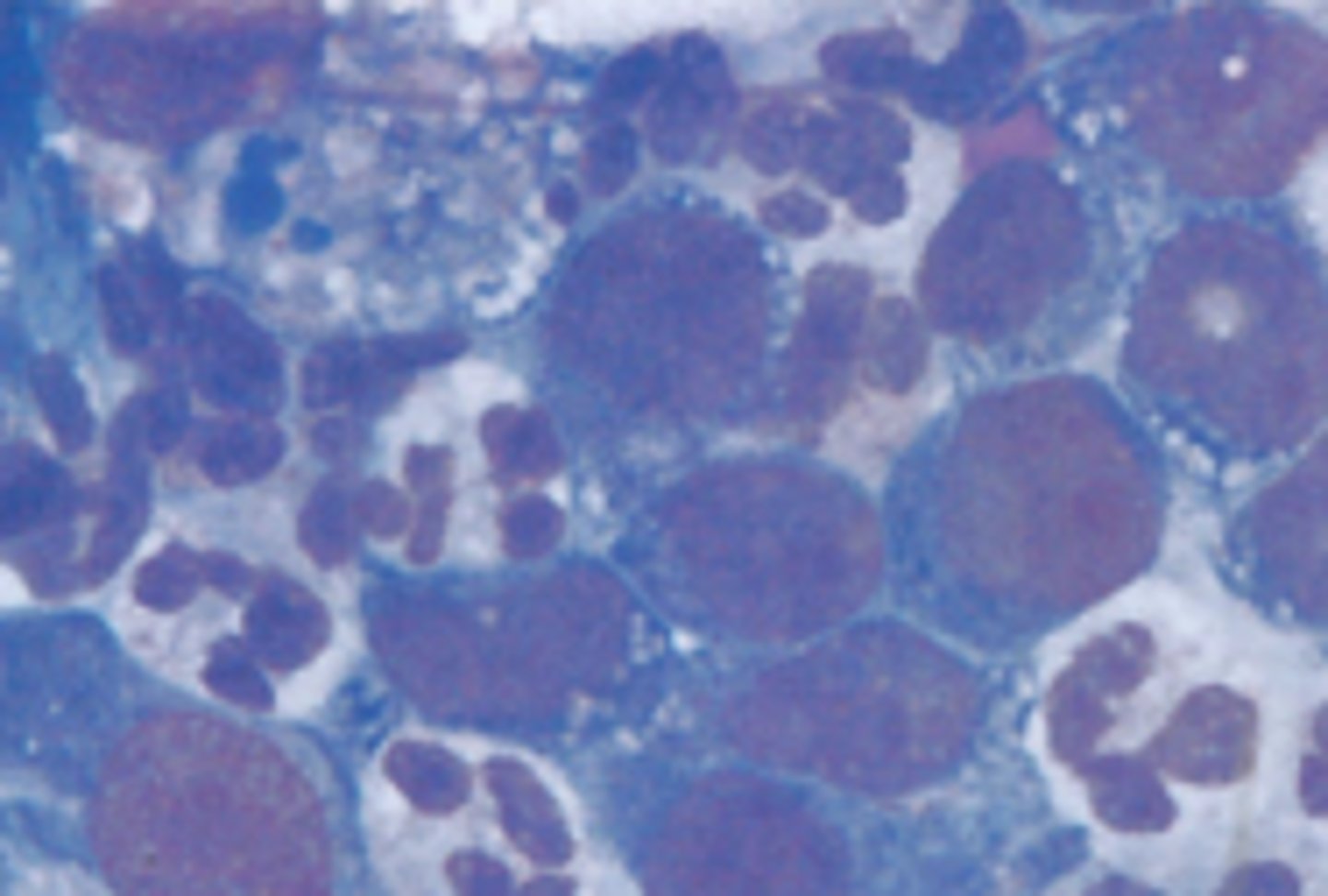
Lymph node- lymphadenitis
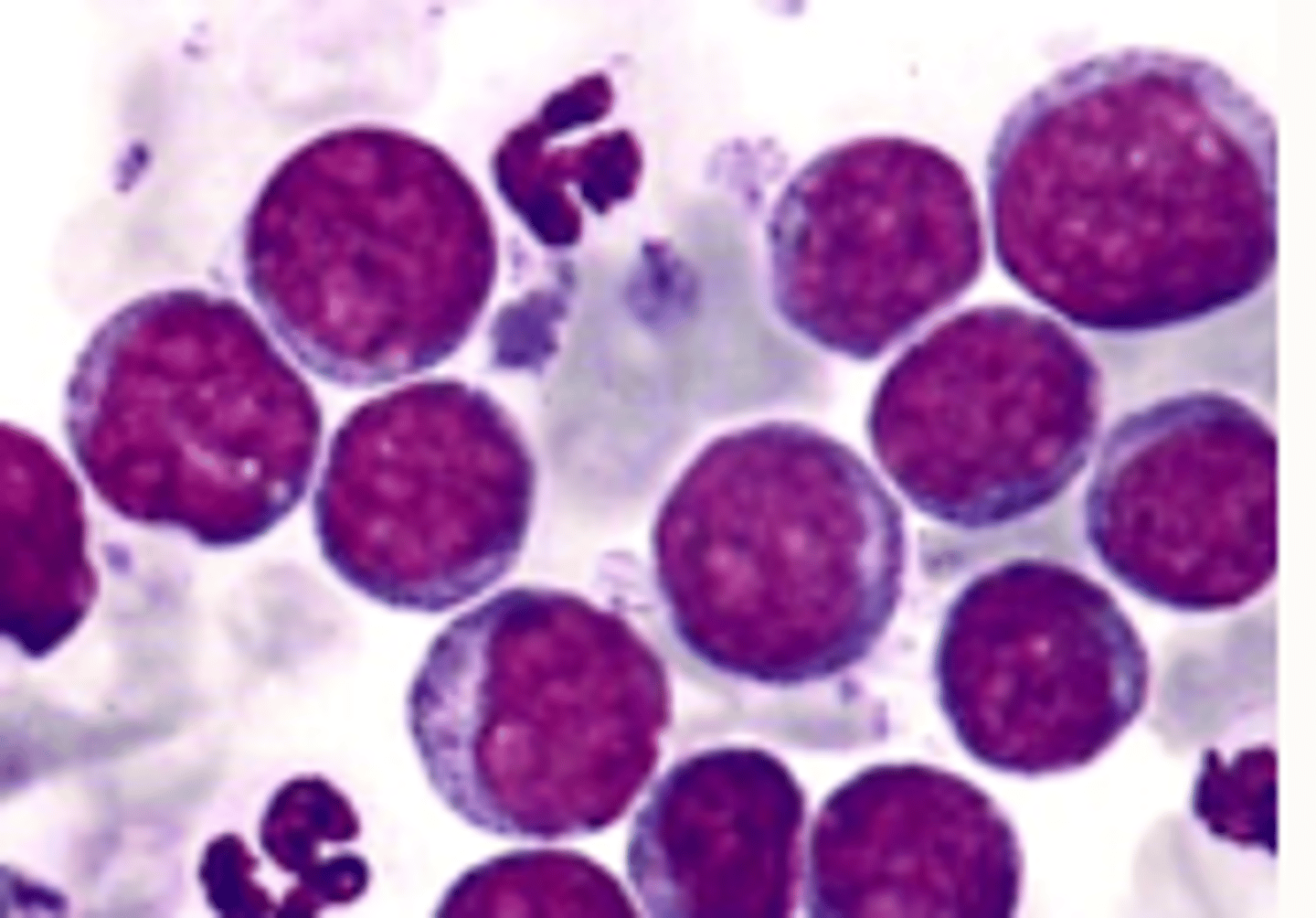
Lymph node- lymphoma
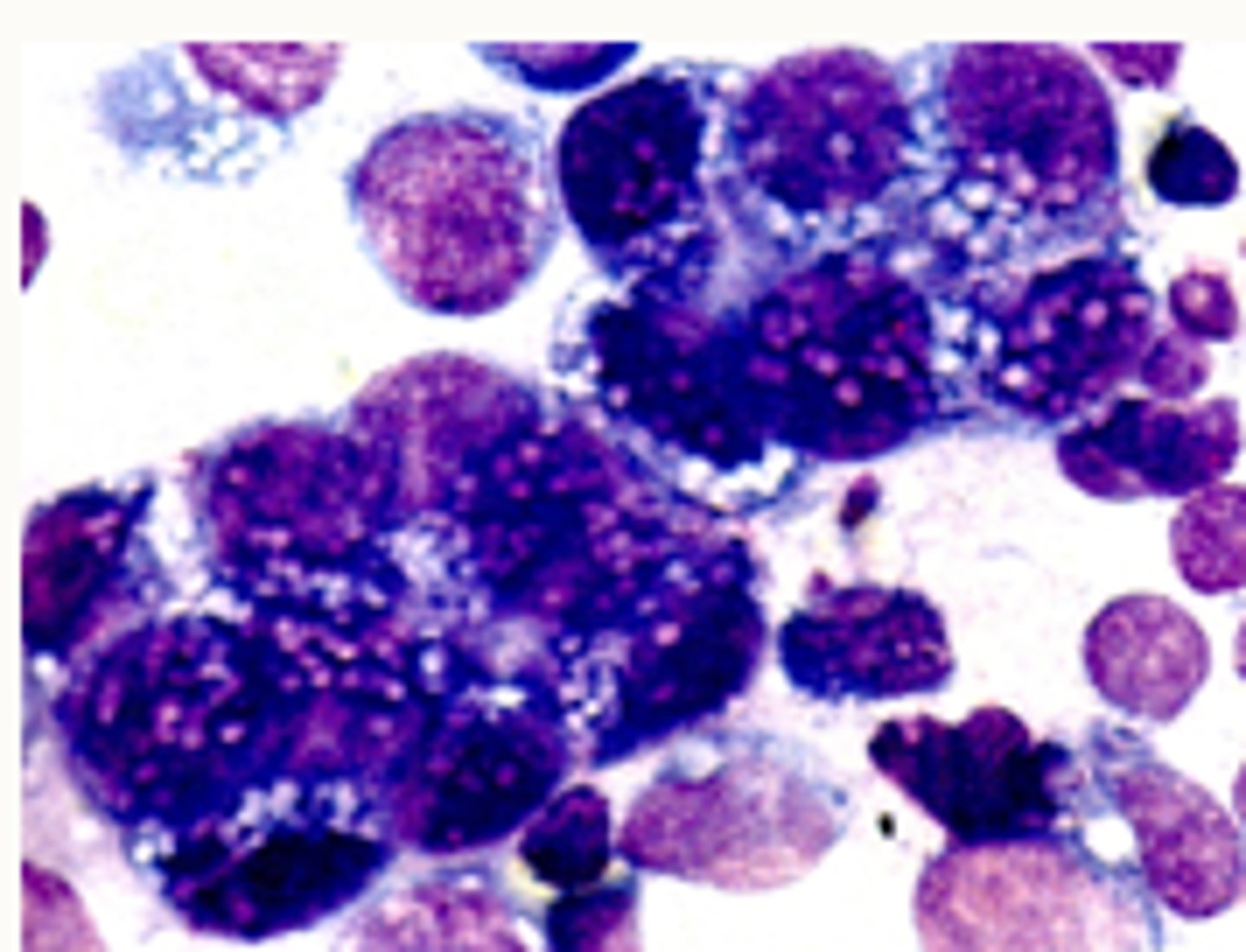
Lymph node- Metastatic
how can you approach an unknown mass
Is the sample sufficient for diagnosis
Inflammatory
What type?
Septic?
Is there cystic content?
What type
Mainly tissue cells - neoplasia
What type (epithelial, round, mesenchymal)
Benign or malignant
how can you approach known tissues
§E.g., lymph node, prostate, spleen, liver
§Is the sample sufficient for diagnosis?
§Think about the normal cell population in that tissue; does what you have on the slide match that? E.g., should it be epithelial, round or mesenchymal or a mixture, what functional cells should be present?
§Think about possible pathologies (e.g., what 4 things cause lymph nodes to enlarge, what 4 things cause prostatic enlargement); which does the cytology best fit with?
§Is there evidence of inflammation?
§Which of my narrowed list of possibilities fits best?
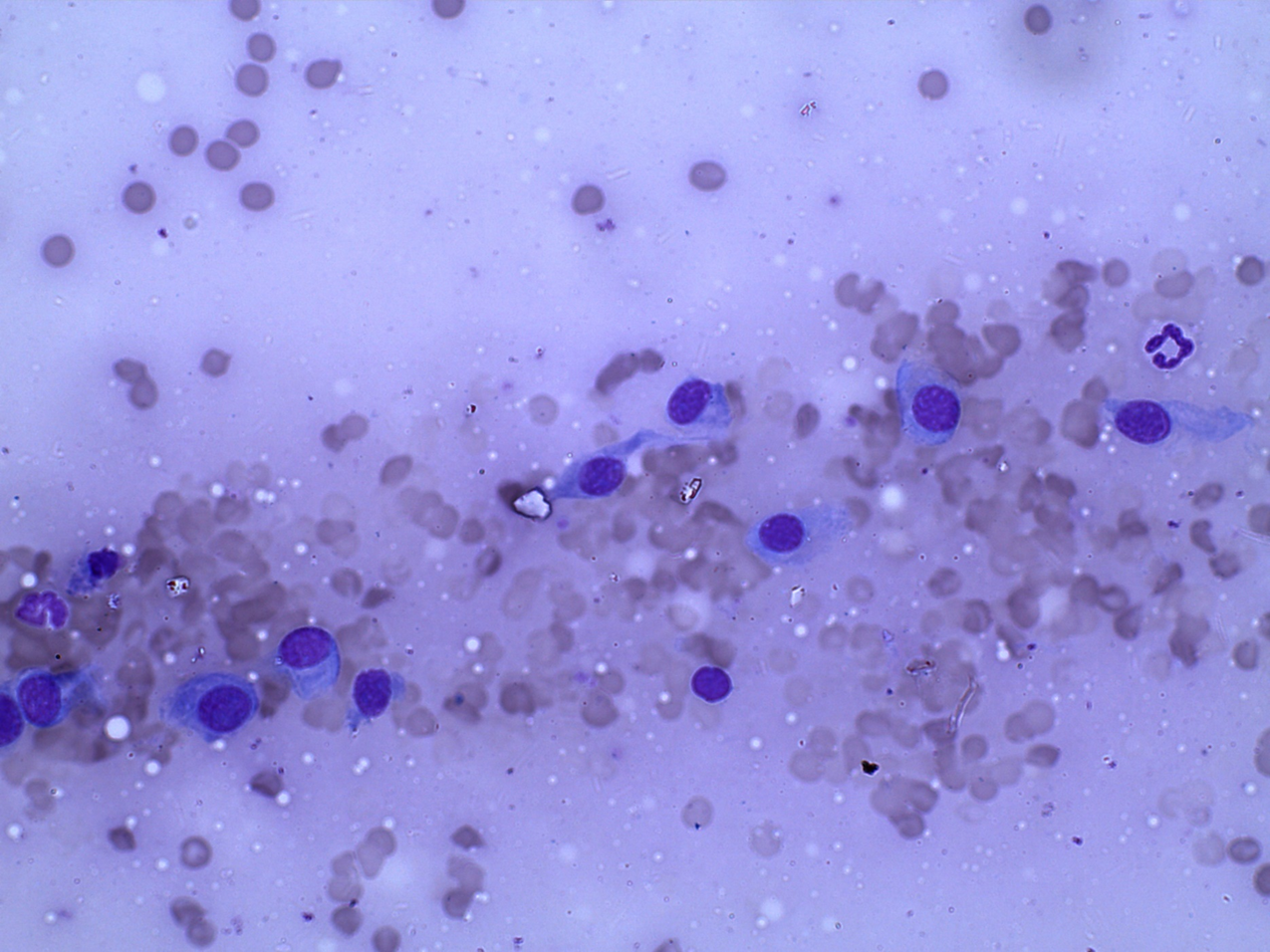
Dog: lump right thigh
Sarcoma
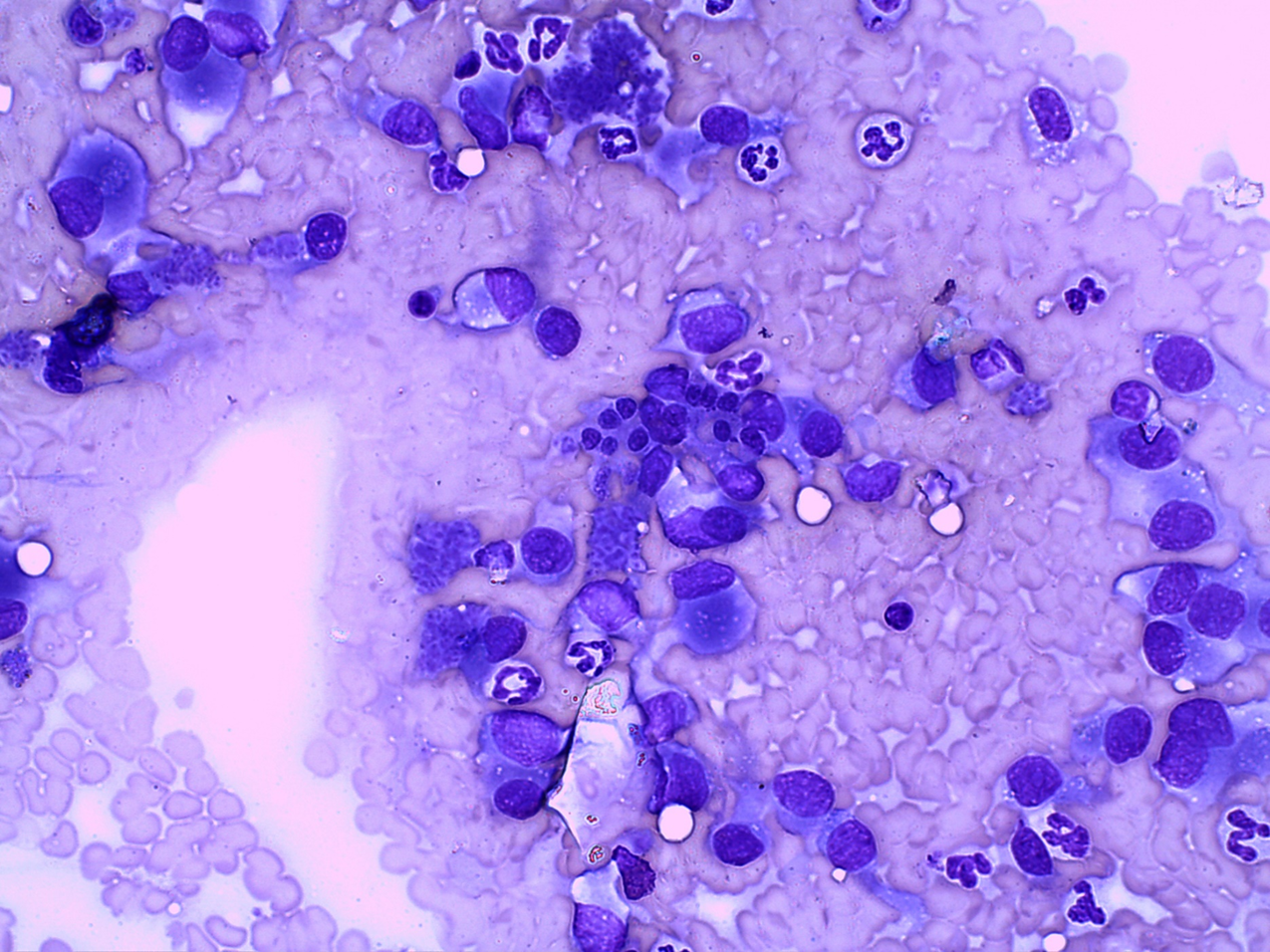
Dog: Submandibular lymphnode
Oral tumour metastasis
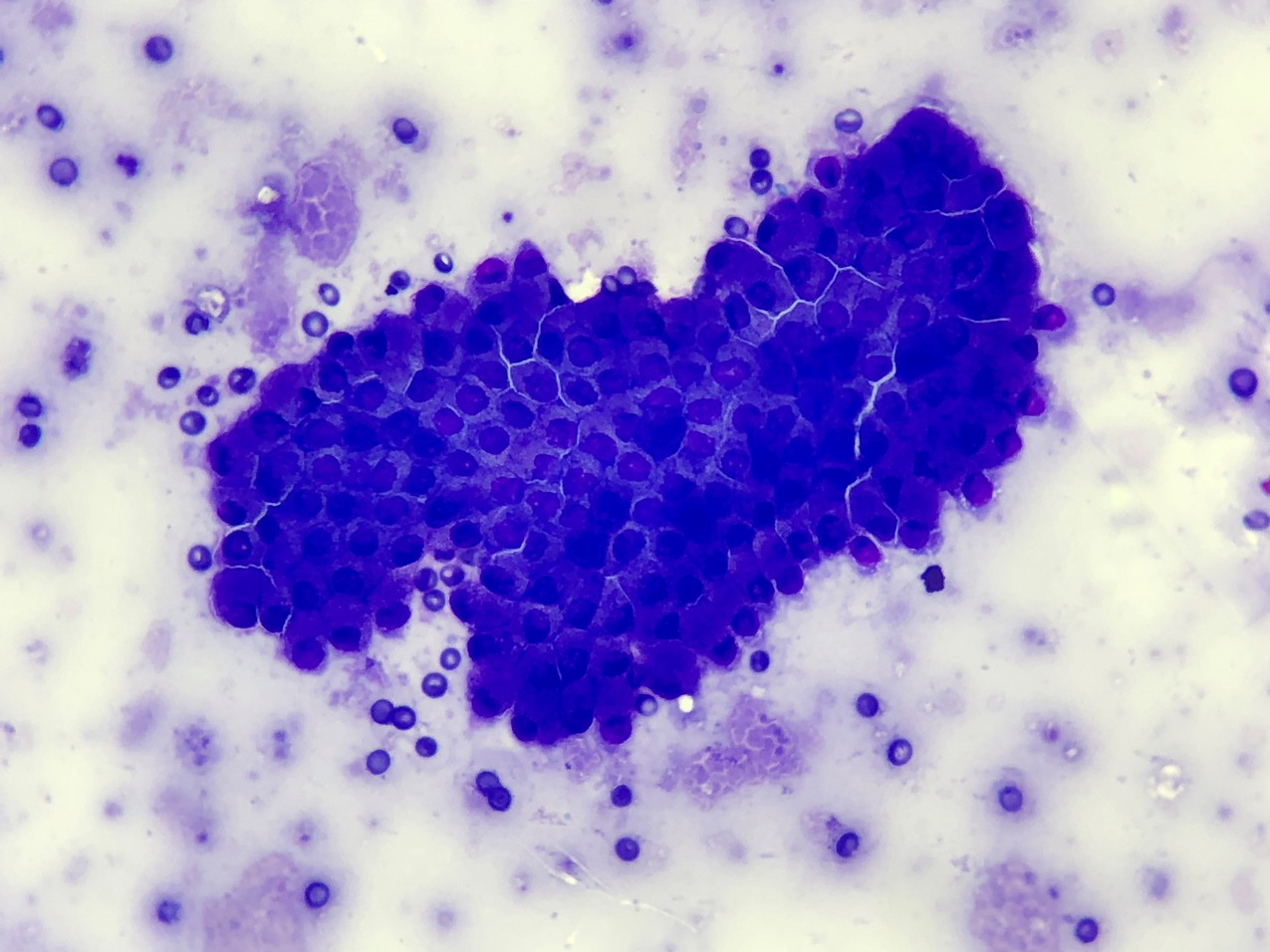
Dog: Prostate FNA
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
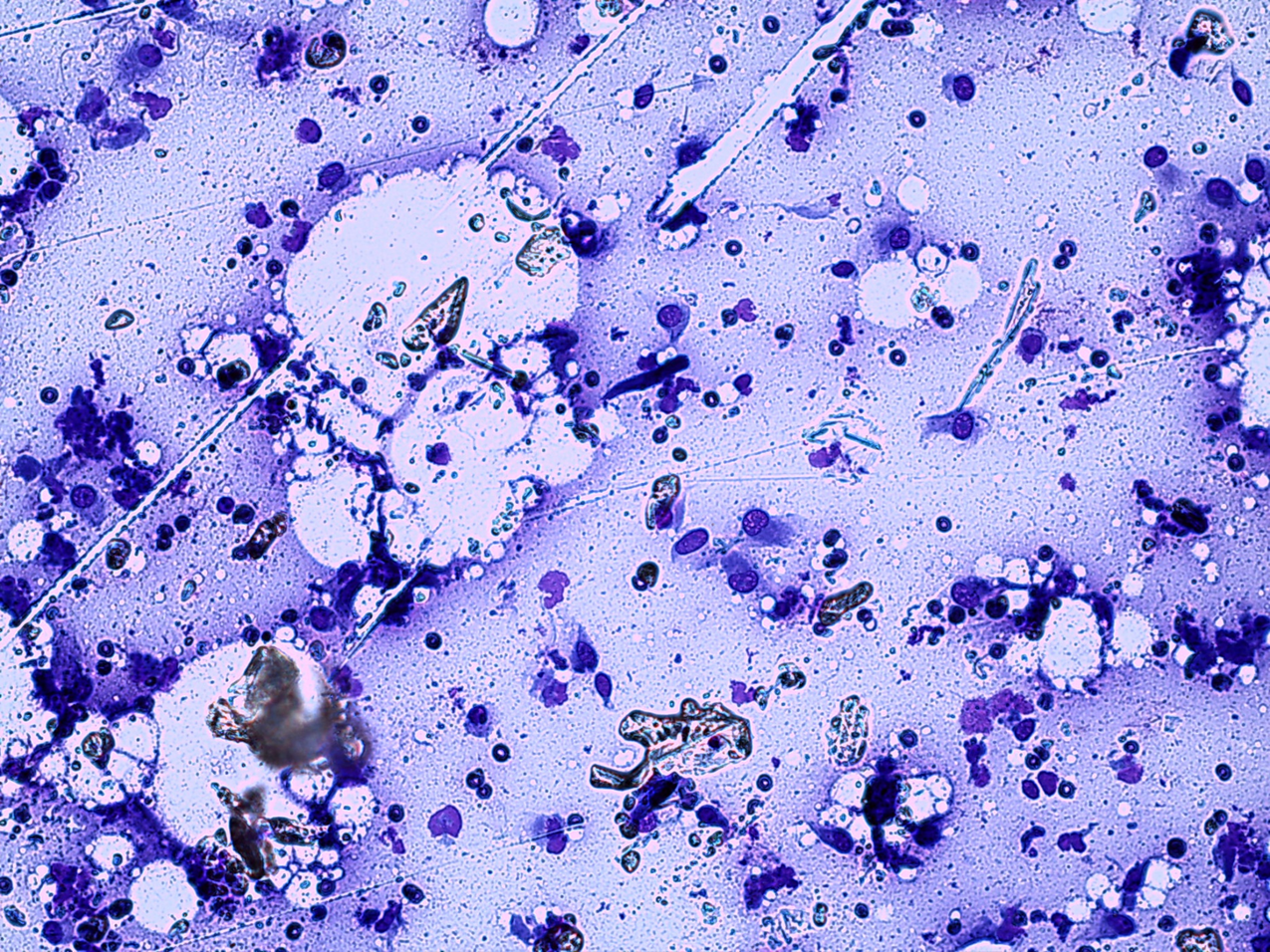
Dog: Skin distal right foreleg
Sarcoma
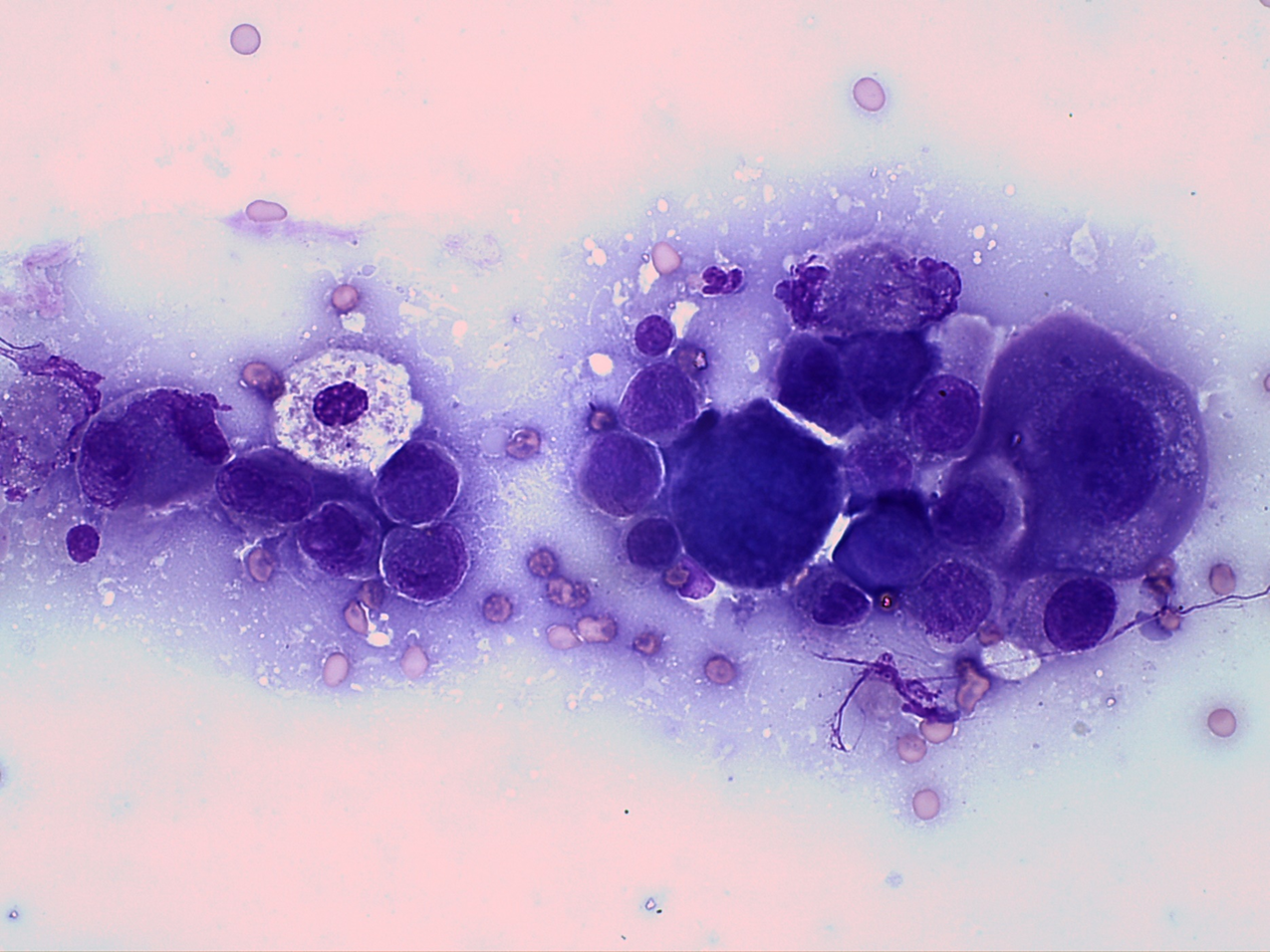
Dog: Thoracic fluid
Thoracic fluid: carcinoma
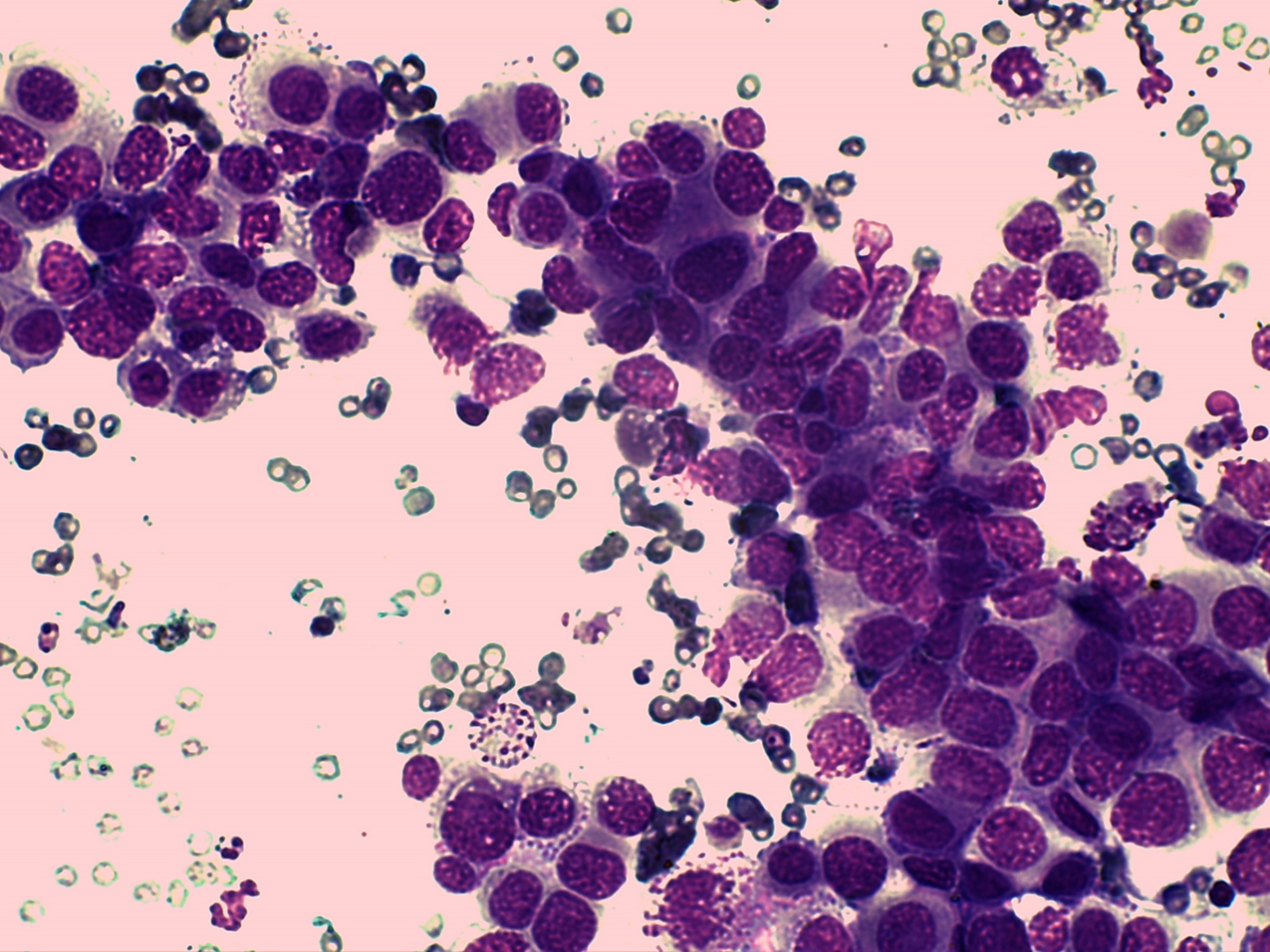
Dog: Mammary mass
Mammary Carcinoma
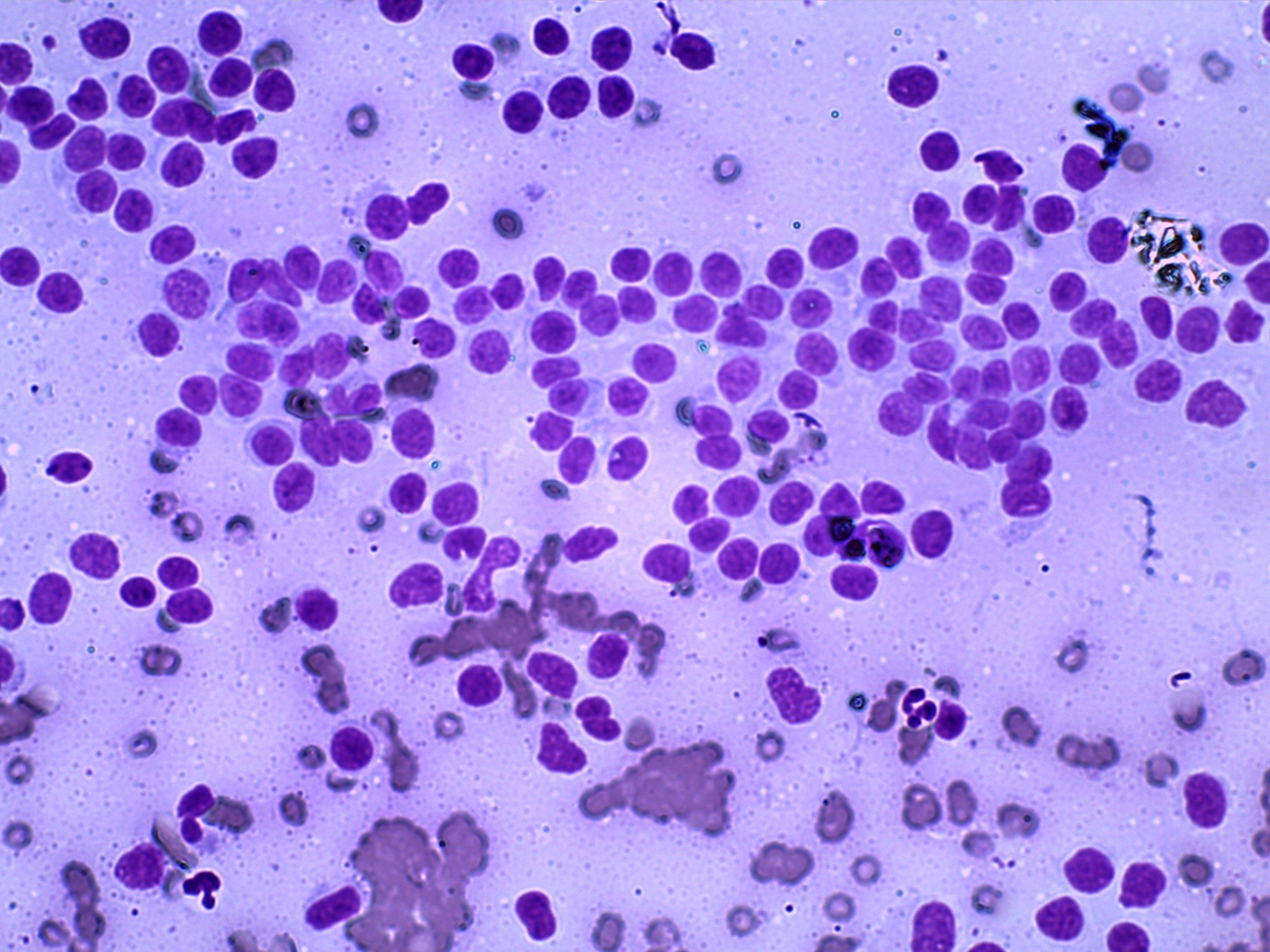
Dog: Skin mass ventral neck
Histiocytoma
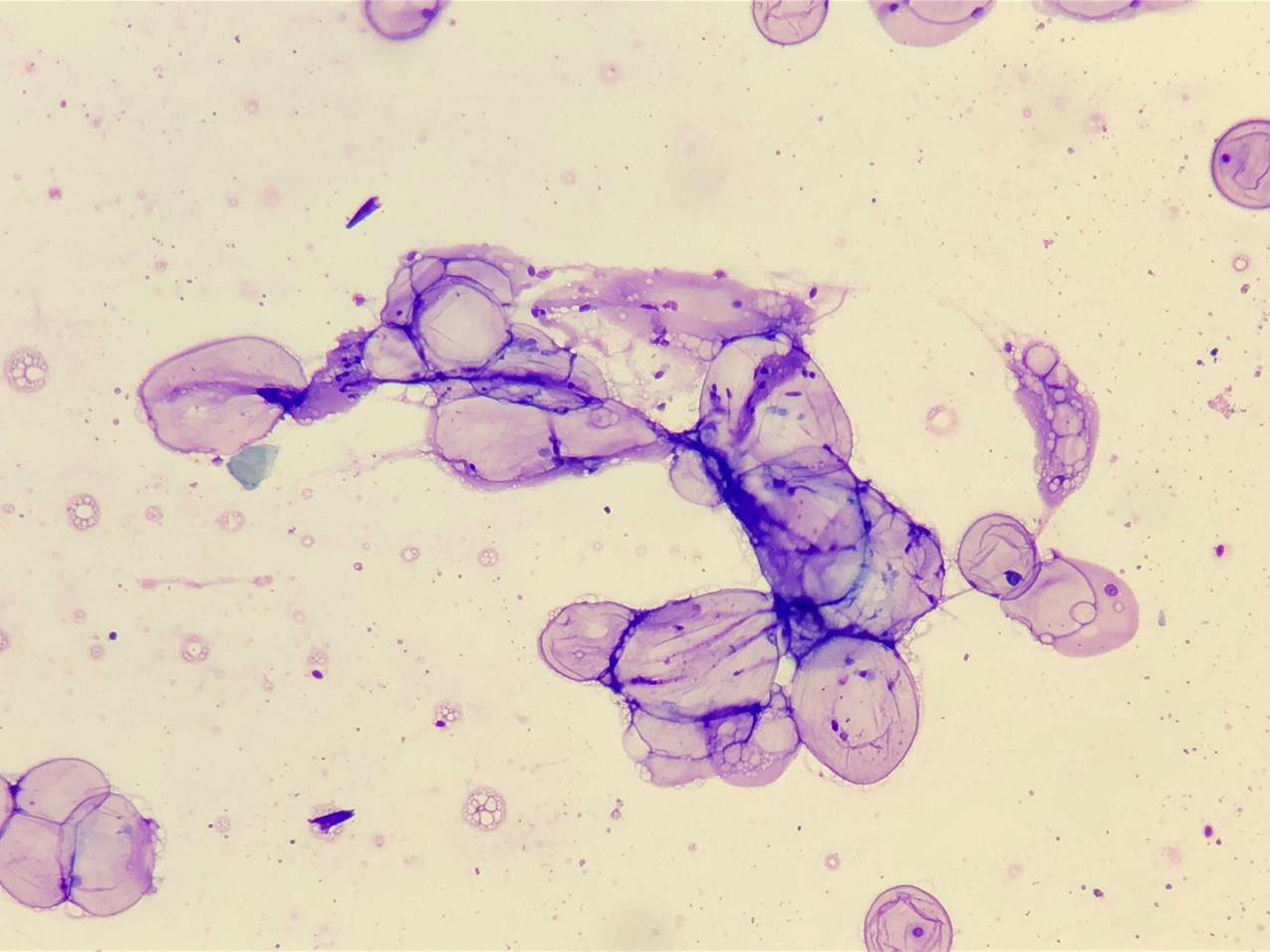
Dog: subcutaneous mass chest wall
Lipoma
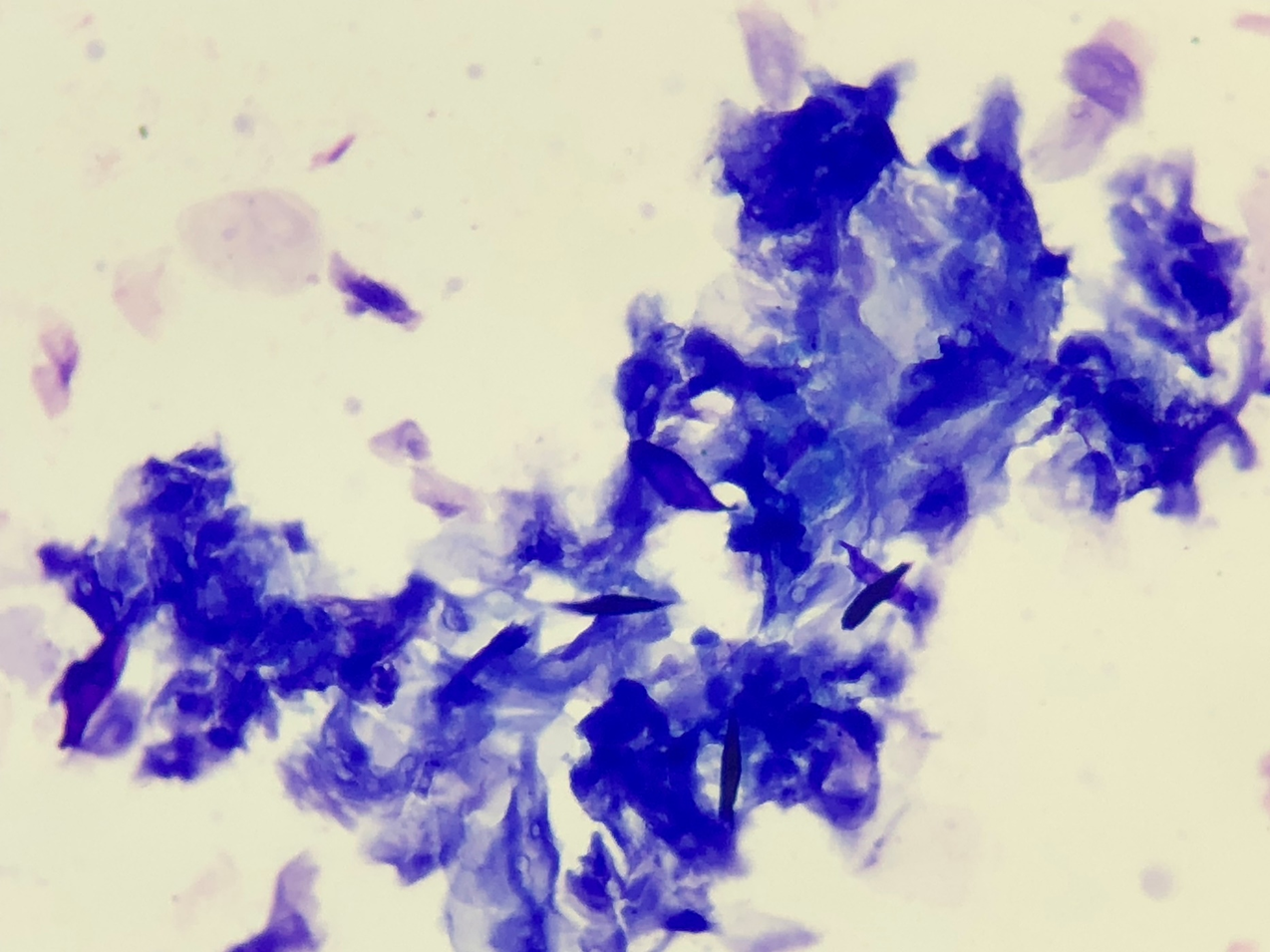
Dog: subcutaneous nodule head
Epidermal inclusion cyst
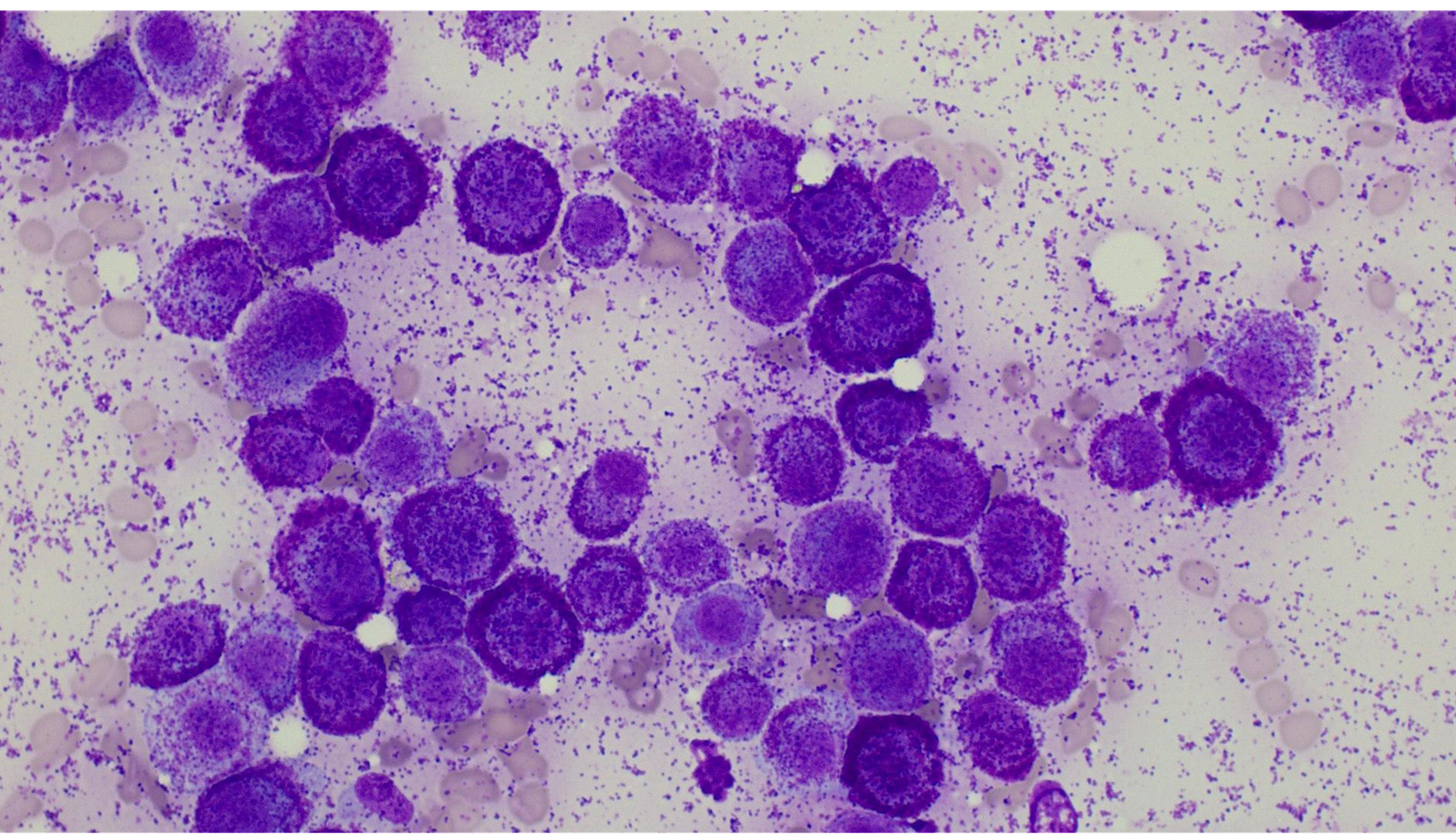
Dog: Skin mass on flank
Mast Cell Tumour
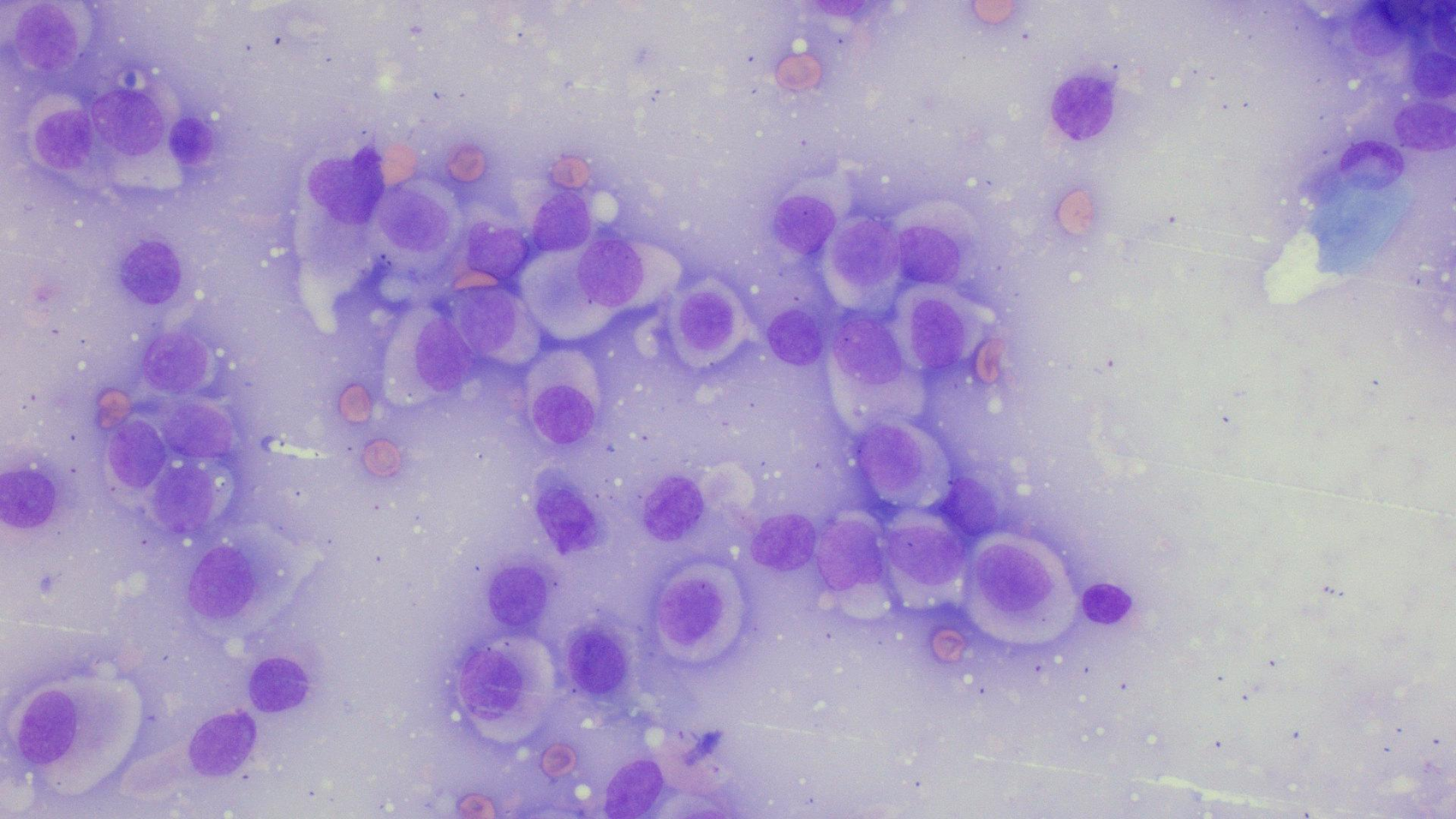
Dog: Skin mass dorsal neck
Histiocytoma