5.1.1 Reaction rates
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Zero order with respect to reactant
Changing conc. of reactant has no effect
on rate
on rate
2
New cards
First order with respect to reactant
Rate is directly proportional to conc. of reactant
3
New cards
Second order with respect to reactant
change in rate= change in conc. squared
4
New cards
How is overall order of reaction calculated?
Sum of individual orders
5
New cards
Units of k for a first order reaction
S-1
6
New cards
Units of k for a second order reaction
Mol-1 dm3 s-1
7
New cards
Units of k for a zero order reaction
Mol dm-3 s-1
8
New cards
How could you measure rate of reaction experimentally?
If there is a colour change: Use a colourimeter at suitable intervals
If gas is evolved: use a gas syringe to collect volume of gas
Measure change in mass of reaction mixture
If gas is evolved: use a gas syringe to collect volume of gas
Measure change in mass of reaction mixture
9
New cards
Half life
The time taken for concentration of a reactant to decrease by half (t1/2)
10
New cards
Relationship between first order reactions and half life
First order reactants have constant half lives
(Draw on the graph)
(Draw on the graph)
11
New cards
Equation to determine rate constant in a first order reaction (using half life)
k= ln2/ half life
12
New cards
Rate determining step
The slowest step in a reaction with multiple steps
13
New cards
What affects the value of the rate constant?
Temperature only
14
New cards
Arrhenius equation
ln k= -Ea/RT + ln A
k= rate constant for reaction
A= pre-exponential factor (number of collisions between reactant molecules)
R= gas constant (8.314)
T= temperature in Kelvin
Ea= activation energy for reaction (in Joules)
k= rate constant for reaction
A= pre-exponential factor (number of collisions between reactant molecules)
R= gas constant (8.314)
T= temperature in Kelvin
Ea= activation energy for reaction (in Joules)
15
New cards
The Arrhenius equation to plot a graph
Graph of lnk against 1/T is a straight line
Gradient= -Ea/R
Y intercept= lnA
Gradient= -Ea/R
Y intercept= lnA
16
New cards
Concentration time graph for a zero order reactant
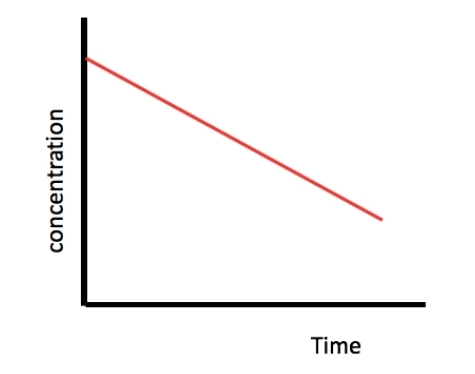
17
New cards
Concentration time graph for a first order reactant
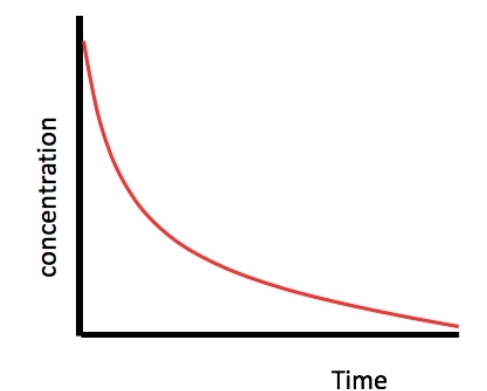
18
New cards
Rate concentration graph for a zero order reactant
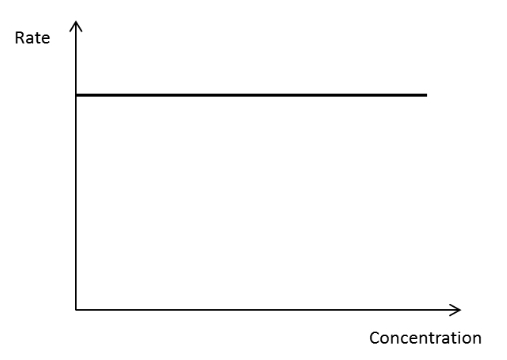
19
New cards
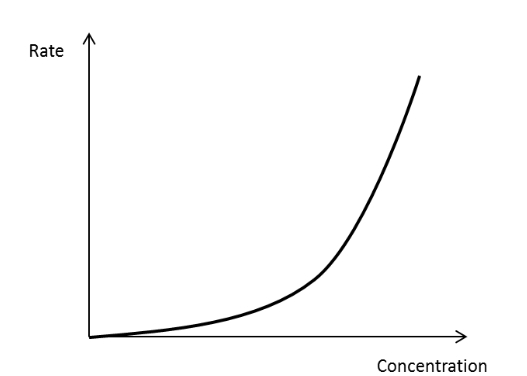
Rate concentration graph for a first order reactant
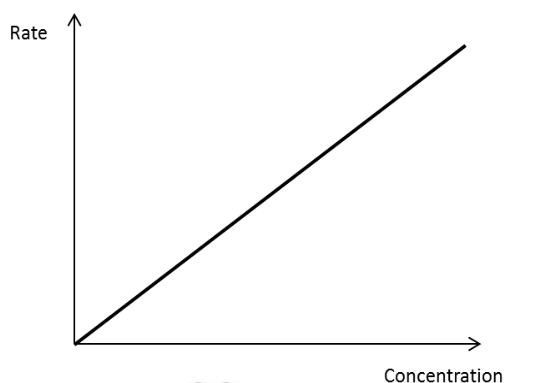
20
New cards
Rate concentration graph for a second order reactant