Topic 17 - Weathering and Mass Wasting
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Factors that influence weathering include …?
the agent (such as water or air), the composition of the material being weathered, the climate, and time
Weathering rates vary from one area to another due to..?
different surface conditions and climates
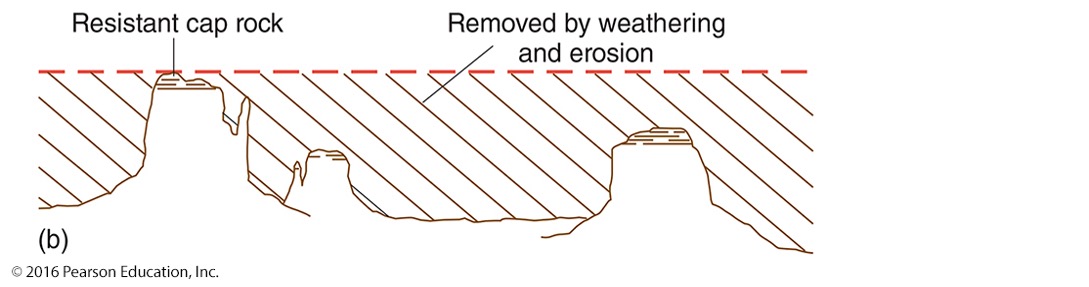
what is denudation?
implies a lowering of earths surface as material is removed
How does denudation occur?
Occurs as a result of three processes: weathering, mass wasting and erosion
what is weathering?
mechanical and chemical - breaking apart of rock material
what is mass wasting?
moving of this material downhill, by gravity
what is erosion?
movement of this broken material to a new location
what is mechanical weathering?
break rocks apart by force, end up with smaller pieces of the same material
what are the 4 types of mechanical weathering?
frost wedging, exploration/sheeting, thermal expansion and contraction, organisms
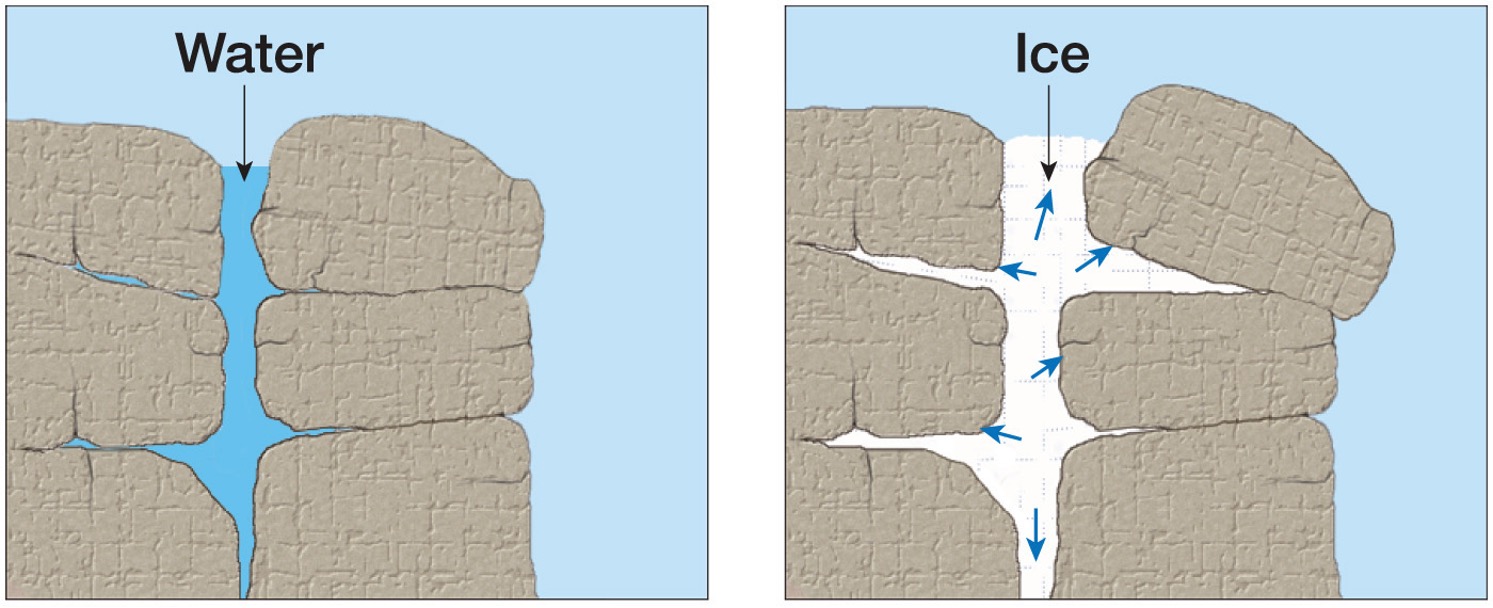
what is frost wedging?
when water freezes it expands, it increases in volume. This exerts enough pressure to split apart rocks
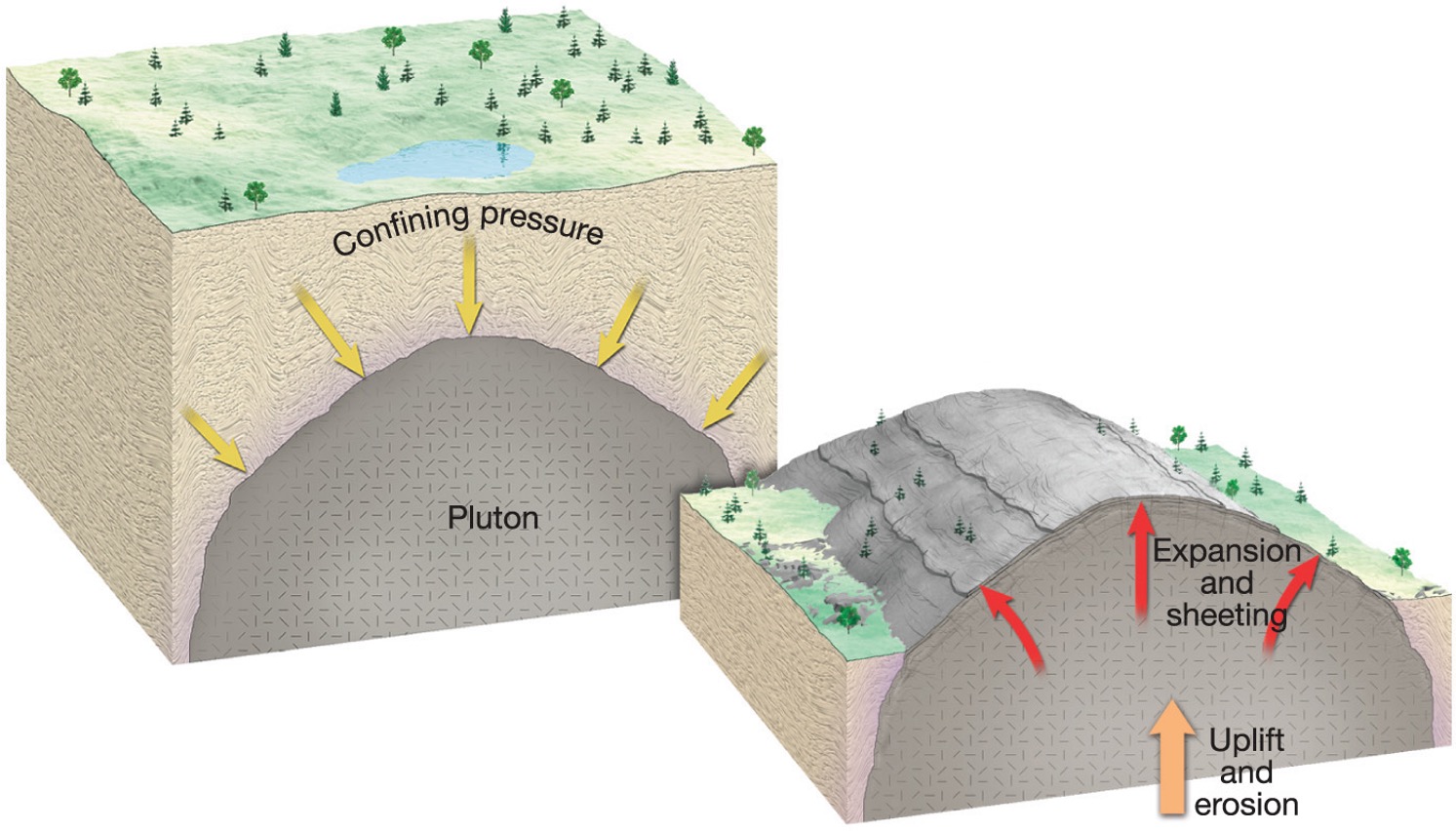
what is exfoliation/sheeting?
Curved layers of rock break off when overlying weight is removed
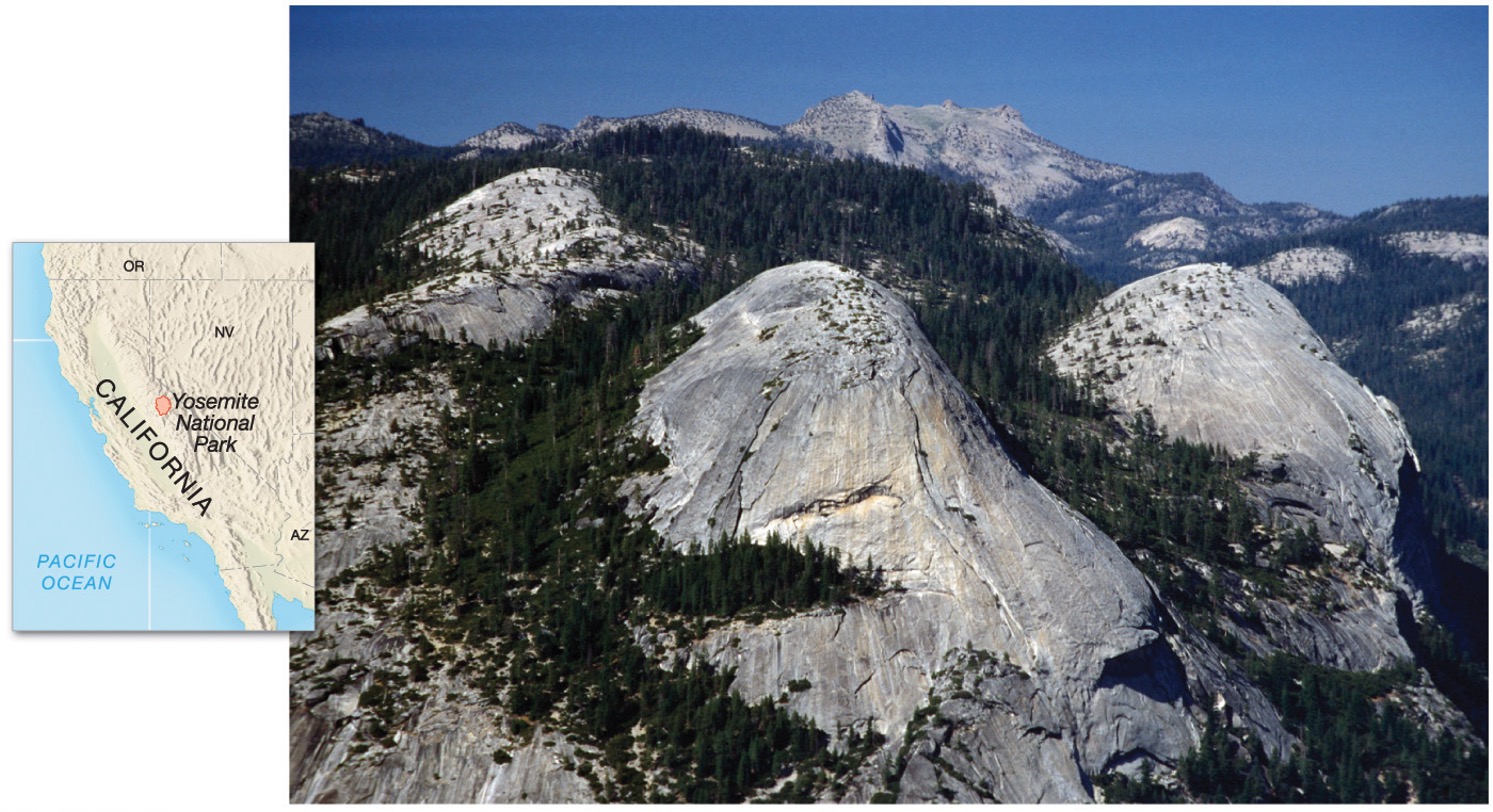

what does exfoliation/sheeting form?
Forms domes of rock such as in the Sierra Nevadas in California

what is thermal expansion and contraction?
Extreme changes in heat and cold cause rocks to expand and contract, they shatter in place

how do organisms take part in mechanical weathering?
tree roots and even smaller can break apart rocks as they grow into them
what is chemical weathering ?
minerals change into new minerals, or more stable elements or simply dissolve. The result is the breaking up or dissolving of the rock
what are the 2 types of chemical weathering?
acid (carbonation) and oxidation
what is the simple solution of chemical weathering?
Water and salt or acid will dissolve rock material
what is the chemical simple solution?
H2O + NaCl (sodium chloride) = H2O + Na(sodium) + Cl(chlorine)
what is sodium chloride ?
salt
what is acid?
most common is carbonic acid also called carbonation
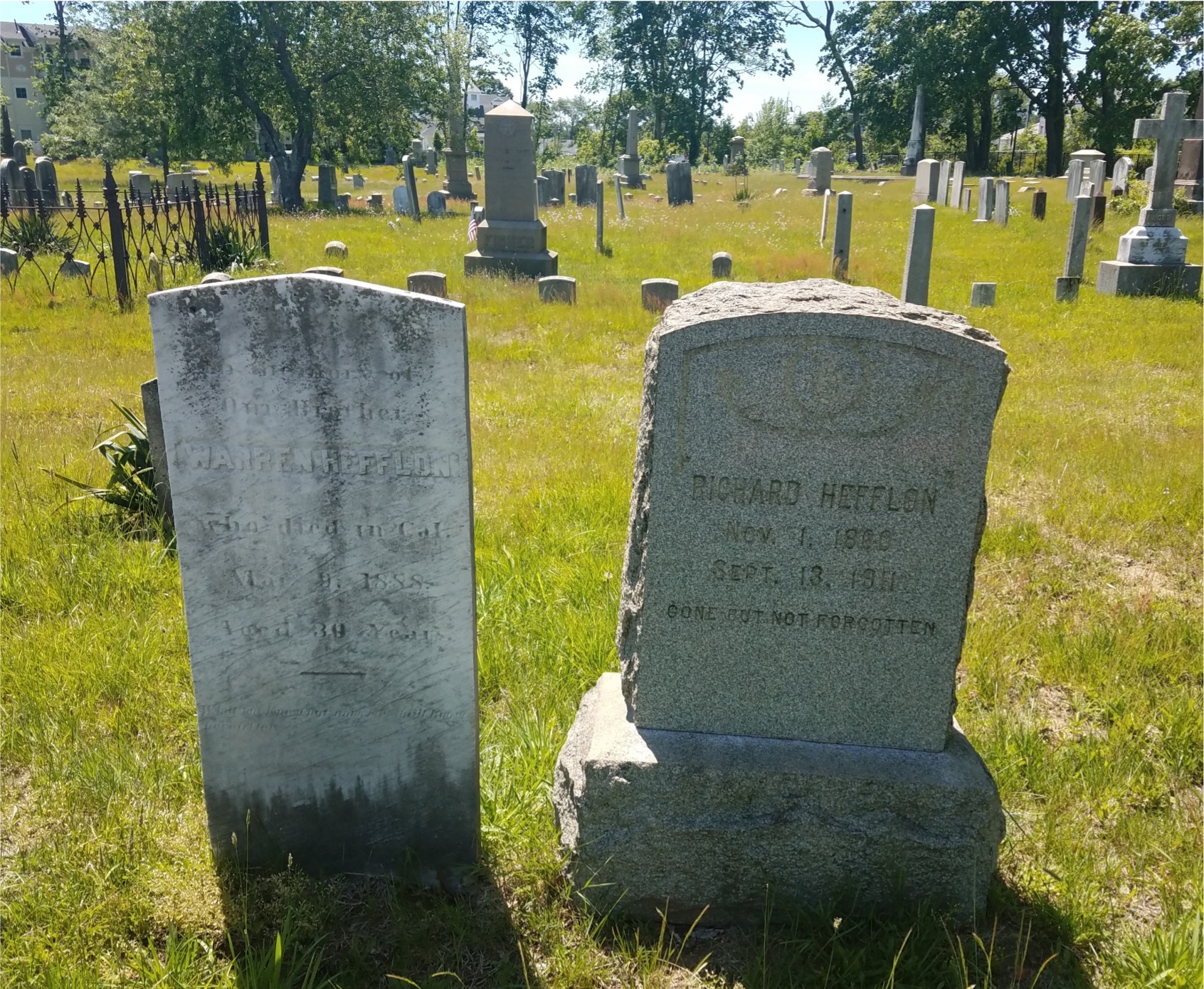

what does acid do?
This dissolves limestone rock and marble rock, we can see this in human activities - statues, building stone, gravestones

what is oxidation?
this occurs when a metal interacts with water and oxygen
what happens when iron, water and oxygen interact with each other ?
rust - iron oxide

what happens when Mg, water and oxygen interact with each other?
manganese oxide
what happens when Cu, water and oxygen interact with each other?
copper oxide - green color ex: Statue of Liberty
Climate has a direct affect on?
weathering
where is chemical weathering more common?
more common in tropical climates where it is warm and has lots of water
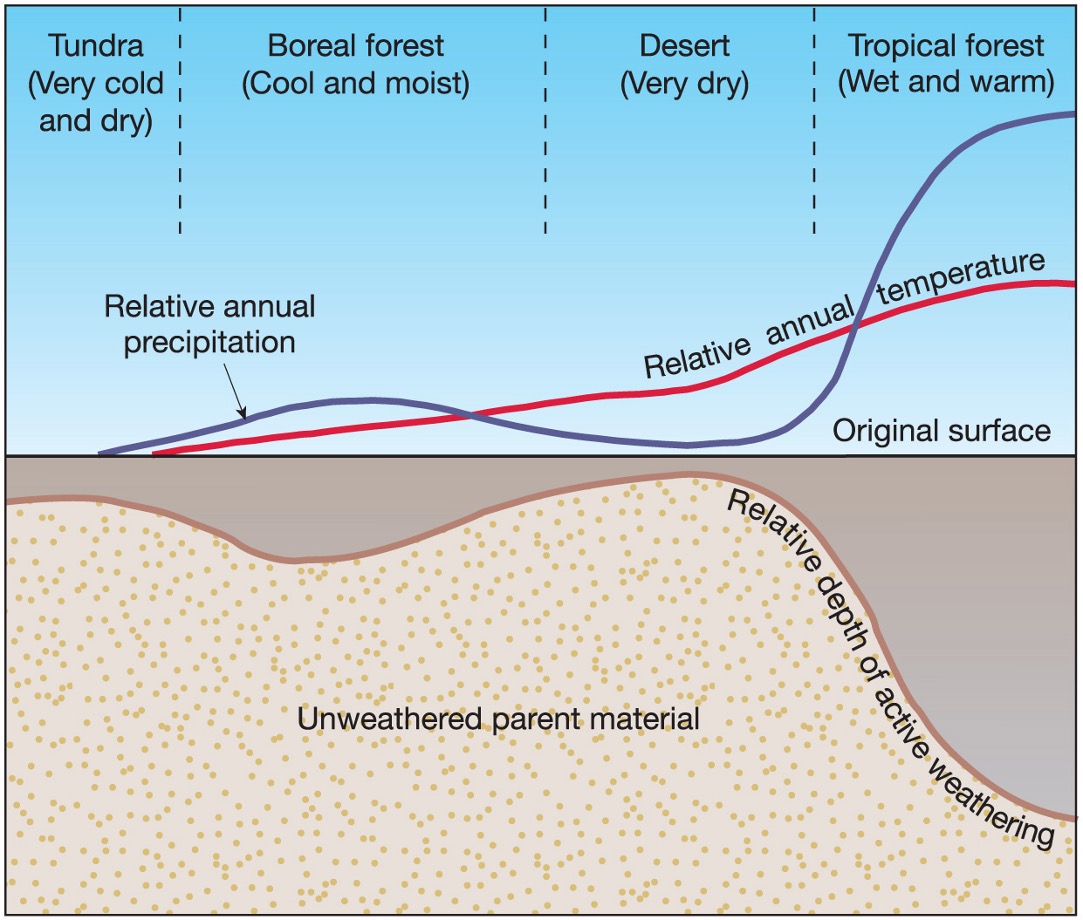
where is mechanical weathering more common?
more common in polar and severe midlatitude climates where it is cold often freezing and has water
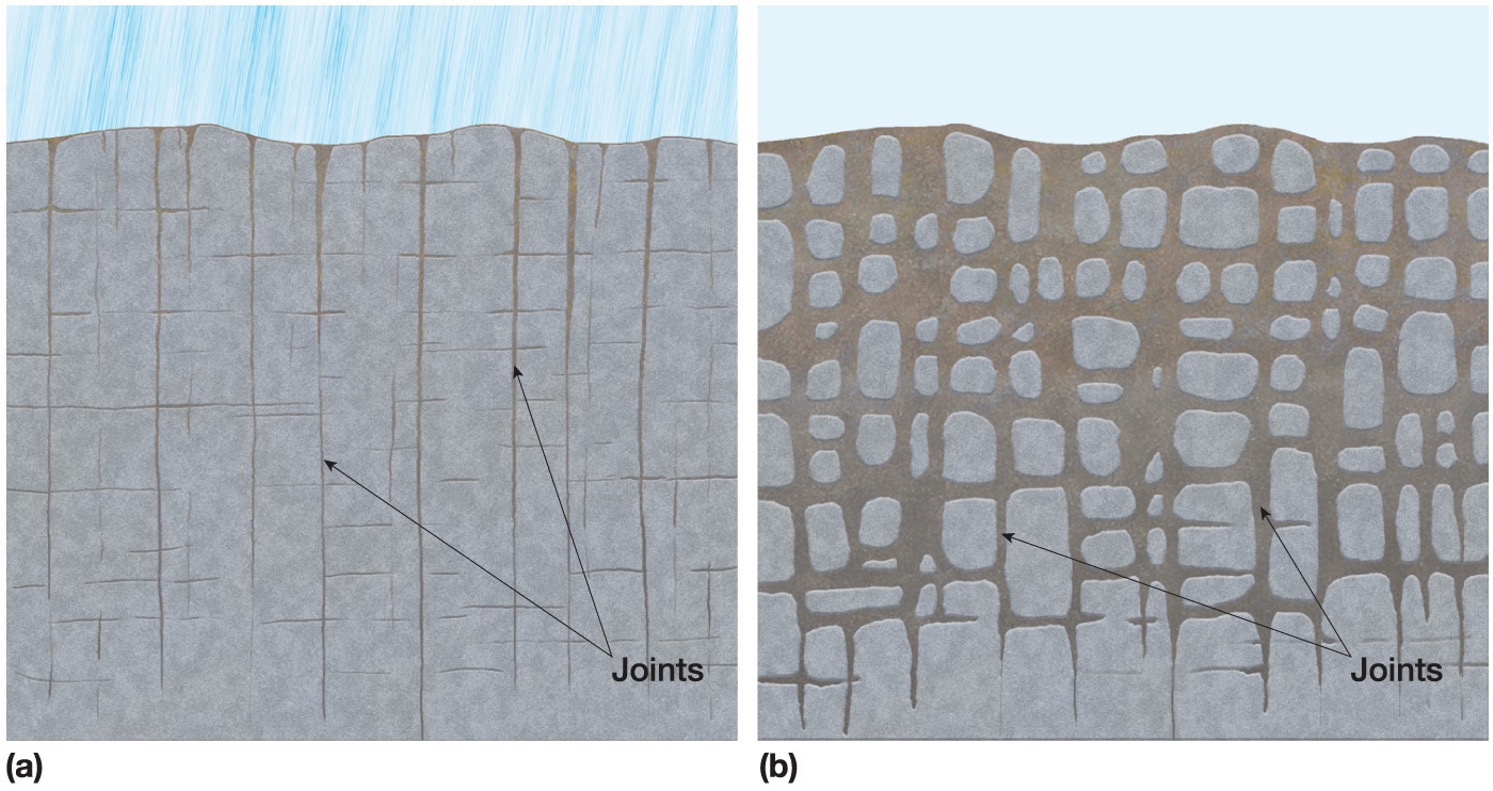
The more surface area …?
the faster and more efficient is the weathering
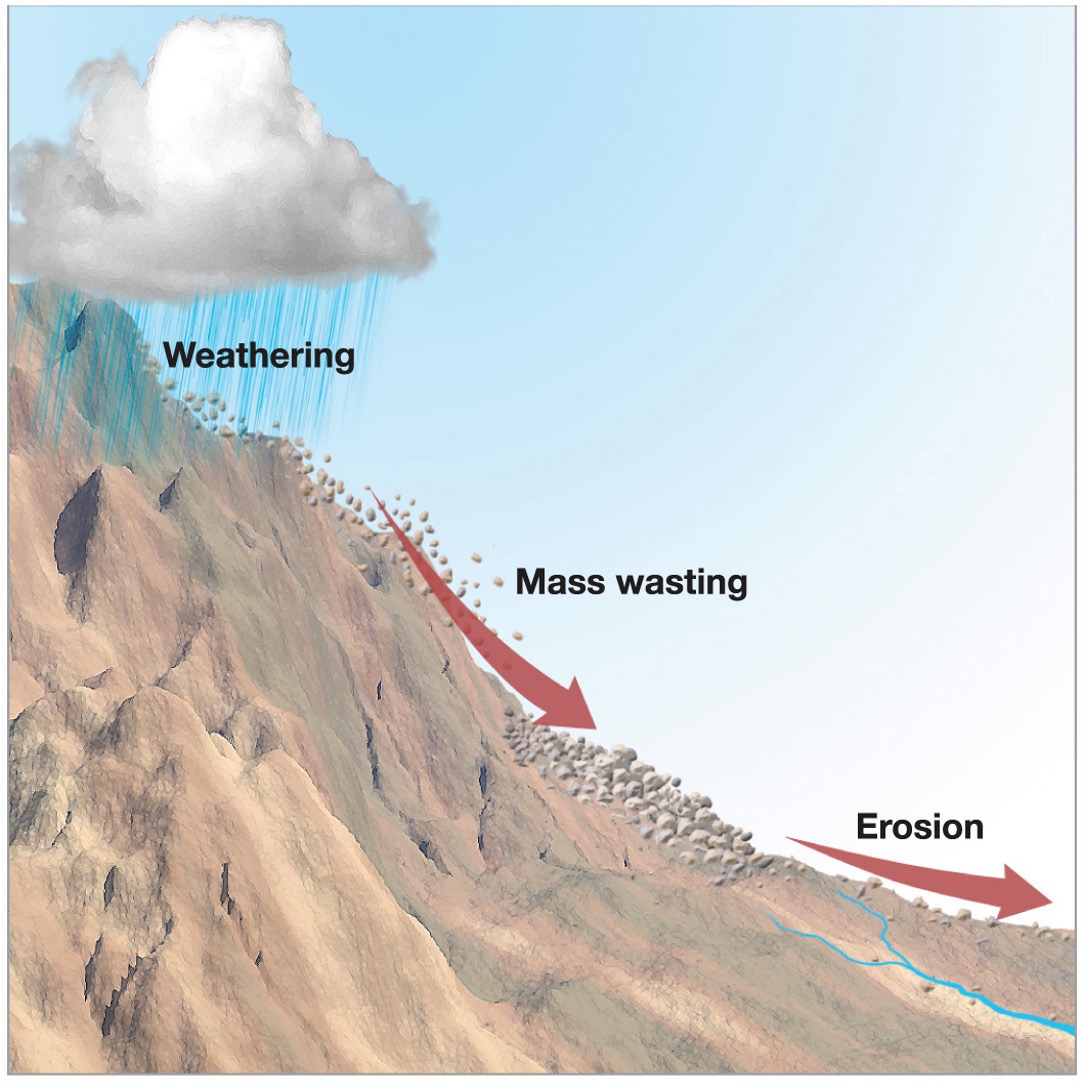
how does mass wasting occur?
with all of the weathering at Earth's surface and the pull of gravity on everything, a process called Mass Wasting occurs
Mass wasting does not need a transporting medium…?
It occurs solely by for the force of gravity

The combined effects of weathering and mass wasting…?
creates the landscape
what influences the occurrence of mass wasting?
angle of repose, too much water, clay and permafrost
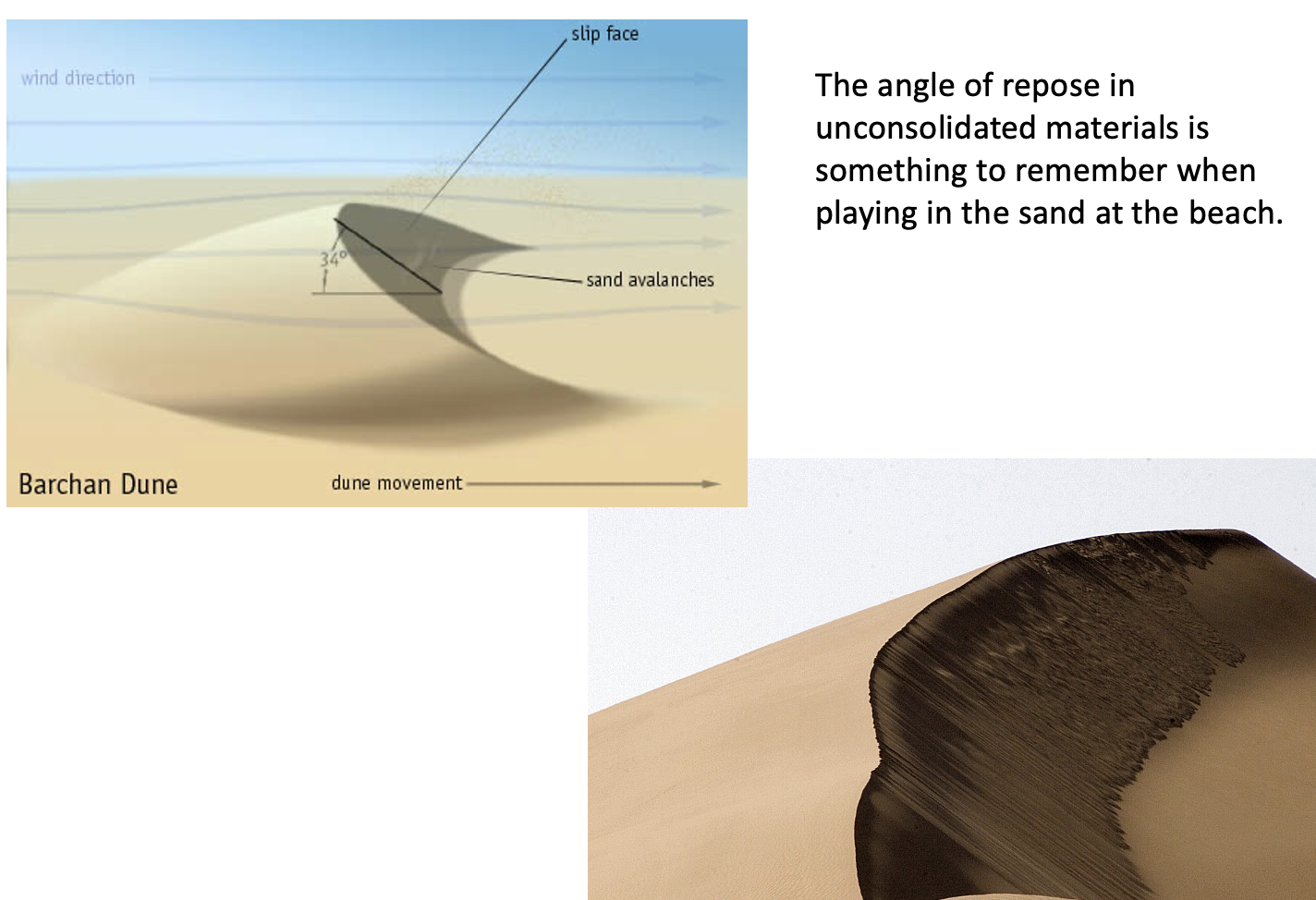
what is the angle of repose?
the largest angle that loose sediment can keep without collapsing
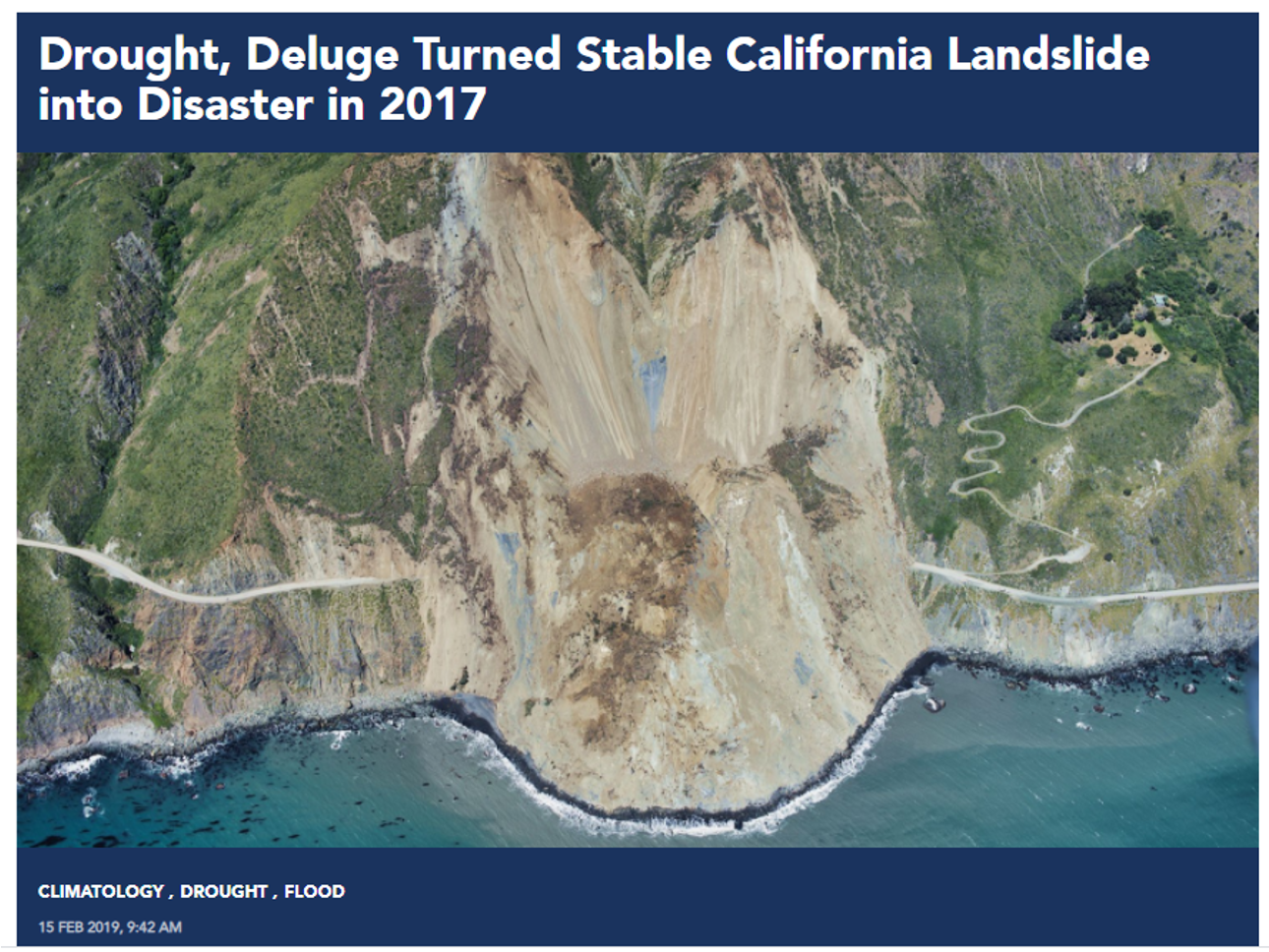
how does too much water influence the occurrence of mass wasting?
the sediment cannot stay together so it collapses
how does clay influence the occurrence of mass wasting?
water logged clay can cause layers of rock or ground to slide apart
what is permafrost?
permanently frozen ground
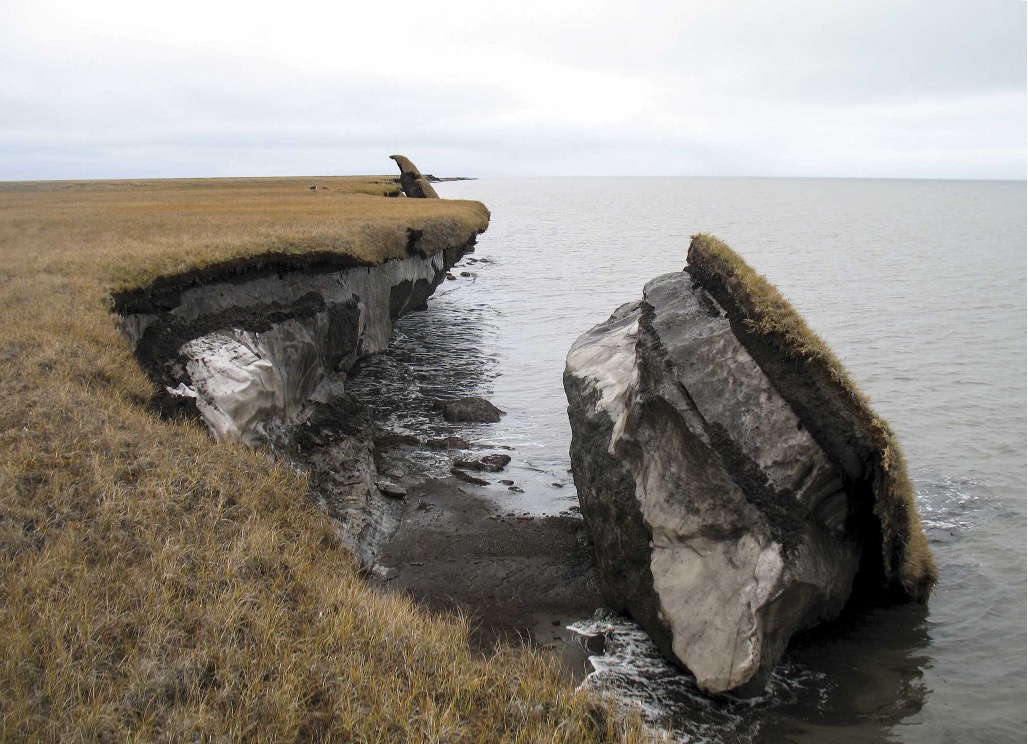

what is happening to permafrost?
this is melting and the layers of ground break apart releasing methane - melting permafrost
what are the 6 types of fast mass wasting?
rock fall, rock slide, landslide, slump, earthflow, mudflow

what is a rock fall?
a fall means the rock is “falling” through the air
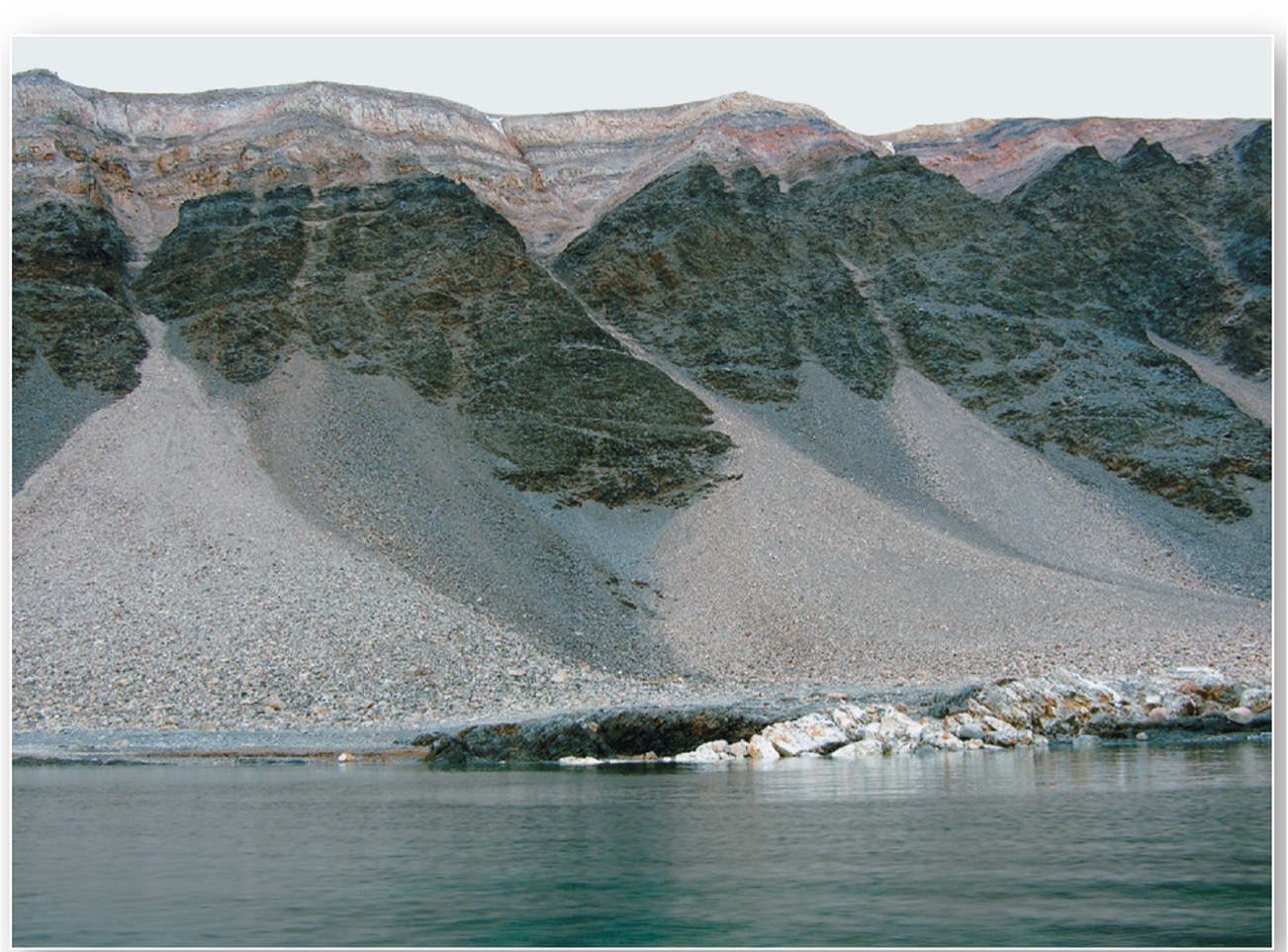

what is a rock slide?
the rocks are in contact with the ground, sliding
what does it mean when there is a slide?
If a slide, there is a trail of destruction
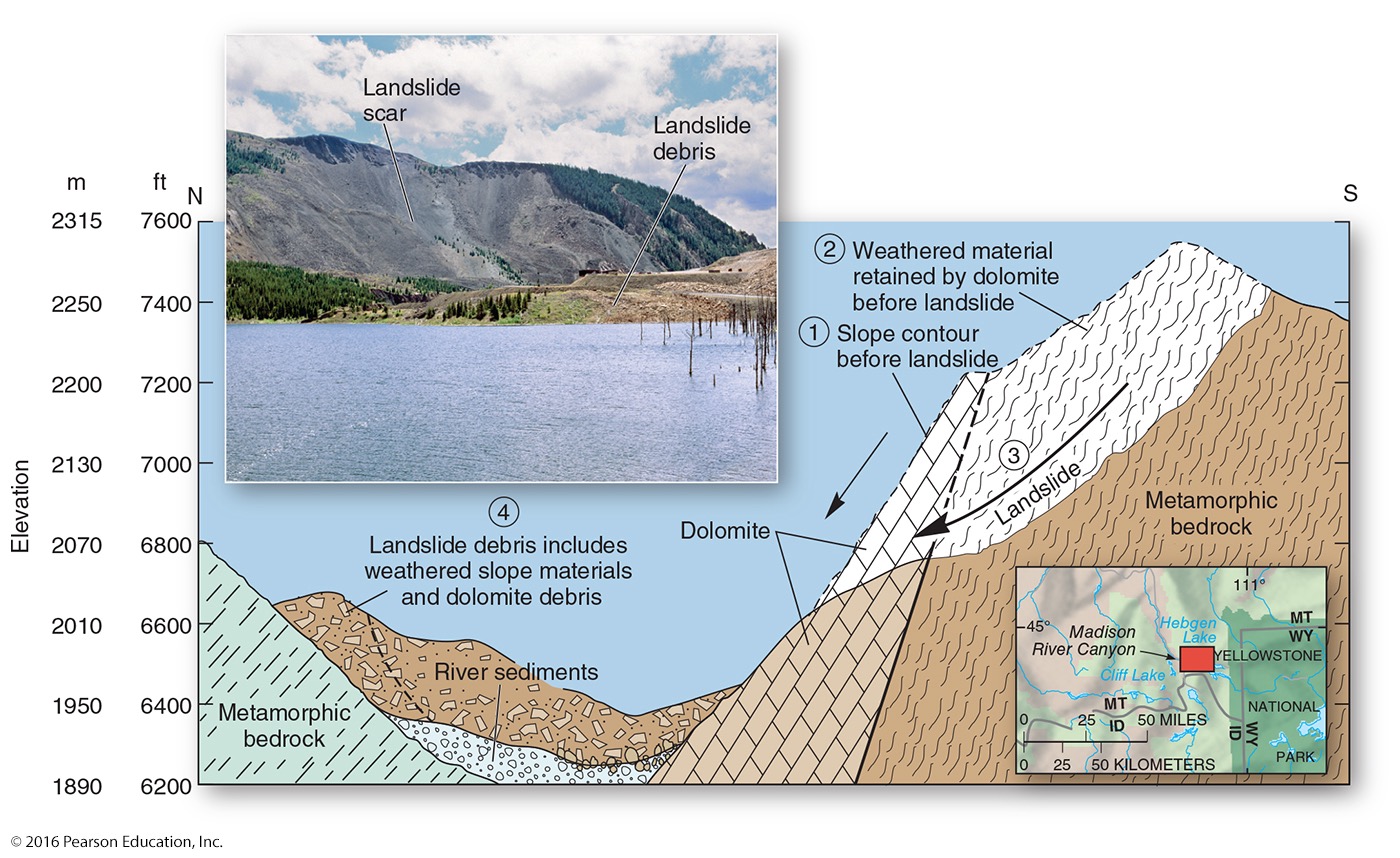
what is a landslide?
a mass of debris that slides down a steep slope
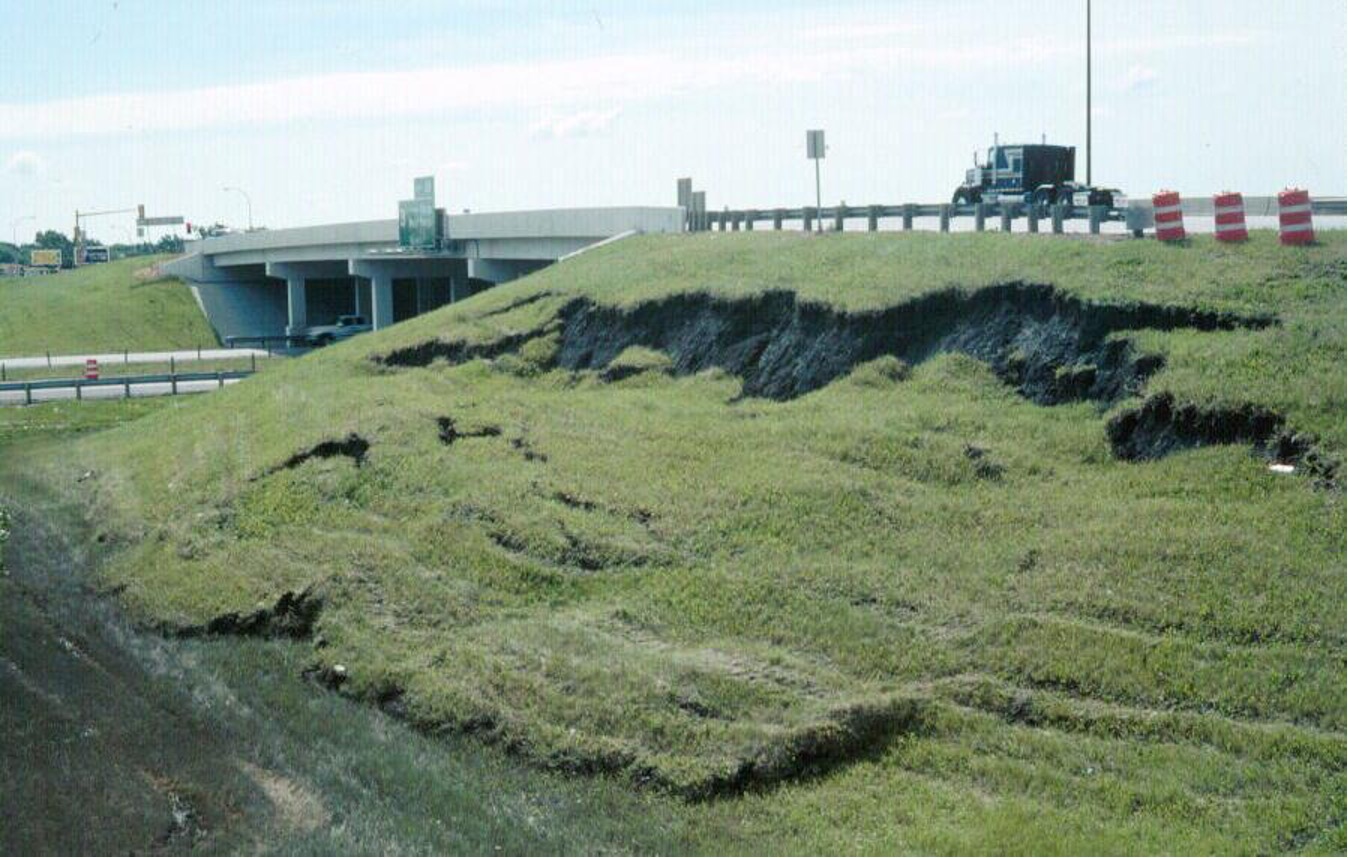

what is a slump?
a large chunk of rock, grass, soil etc. Tears away from the hillside

what is an earthflow?
starts out as a slump, but with water ends up flowing
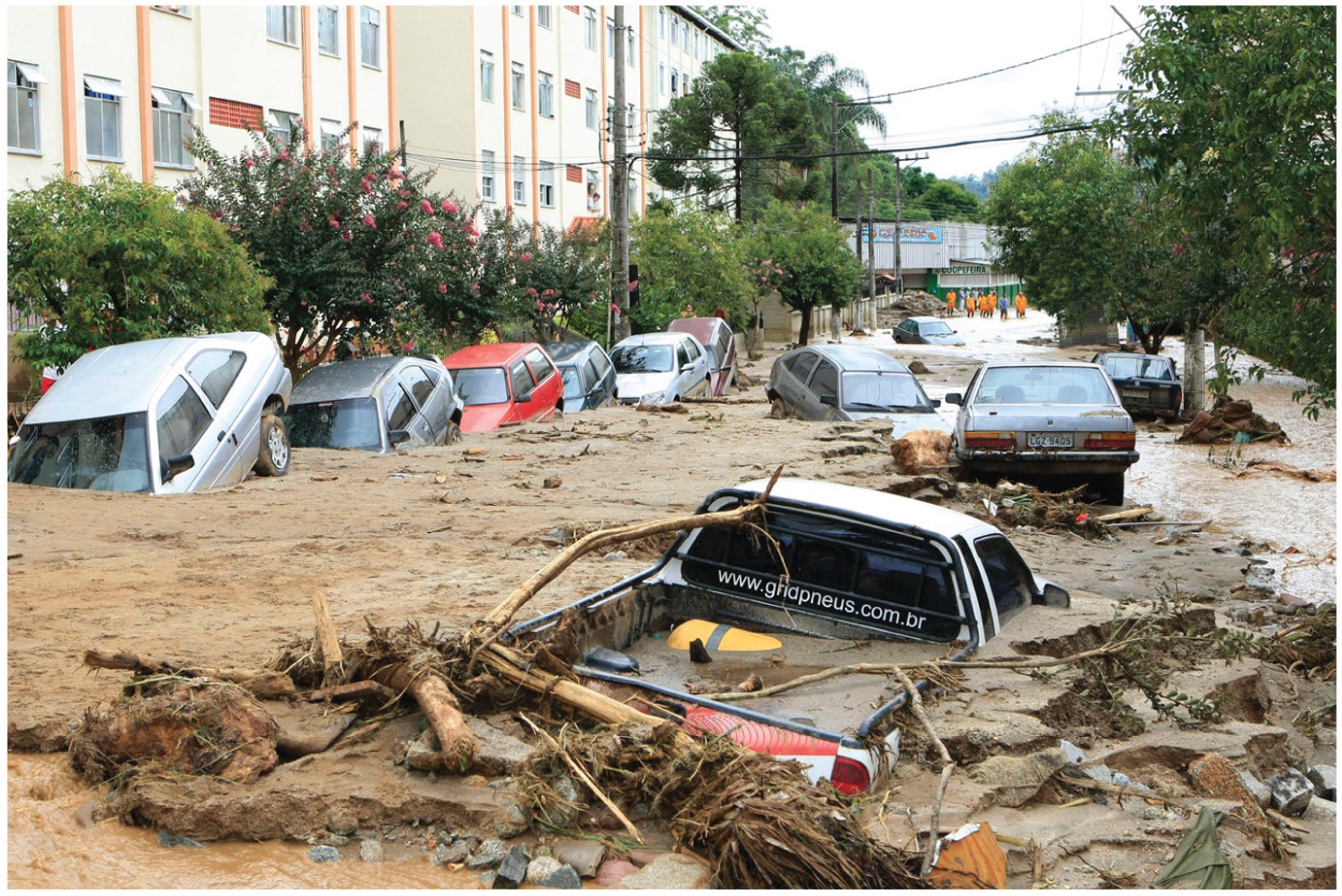

what is a mudflow?
water mixed with dirt, gets very thick!! Can be worse than a flood – mud doesn’t recede (go away) like water does. Makes it more difficult to clean up, to rescue
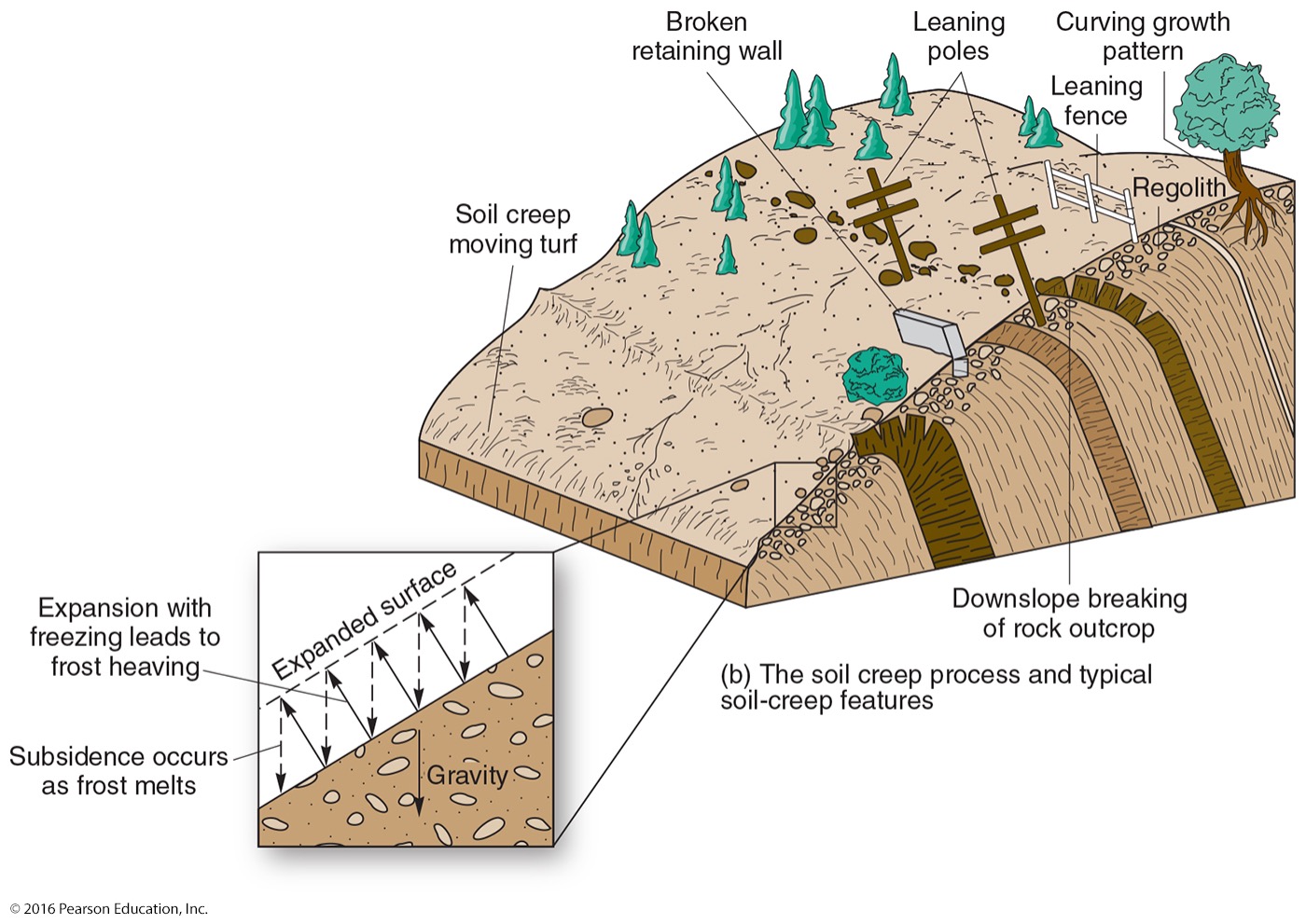
what is a type of slow mass wasting?
creep

what is a creep?
we don’t see this happening, but we see the results. ex: tilted phone poles, tilted fences, etc