Session 5: Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defence Mechanisms
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Oxidation is the ___ of electrons and reduction is the ___ of electrons
Oxidation is the loss of electrons and reduction is the gain of electrons (OILRIG)
An oxidising agent (oxidant) ___ something else. A reducing agent (reductant) ___ something else
An oxidising agent (oxidant) oxidises something else. A reducing agent (reductant) reduces something else
What is oxidative stress
Condition in which the rate of generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) exceeds body’s ability to protect itself against them
What does oxidative stress result in?
Increase in oxidative damage to molecules (proteins, lipids and DNA)
Leading to cell/tissue damage
Oxygen can gain an electron to form ___
Oxygen can gain an electron to form superoxide
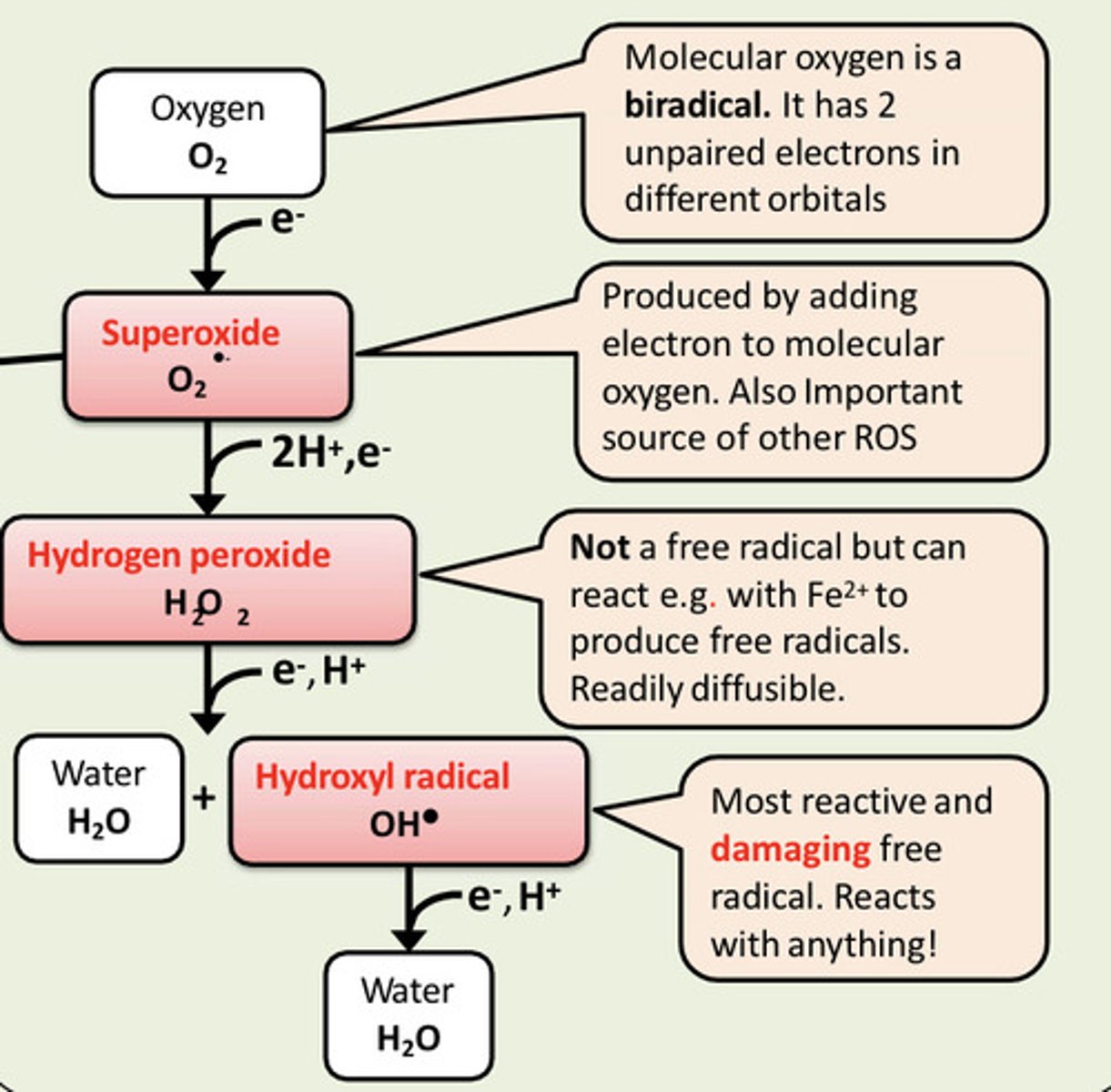
Superoxide can react with nitric oxide to form ___
Superoxide can react with nitric oxide to form peroxynitrite
___ radicals are considered the most reactive and damaging free radical as it reacts with anything
Hydroxyl radicals are considered the most reactive and damaging free radical as it reacts with anything
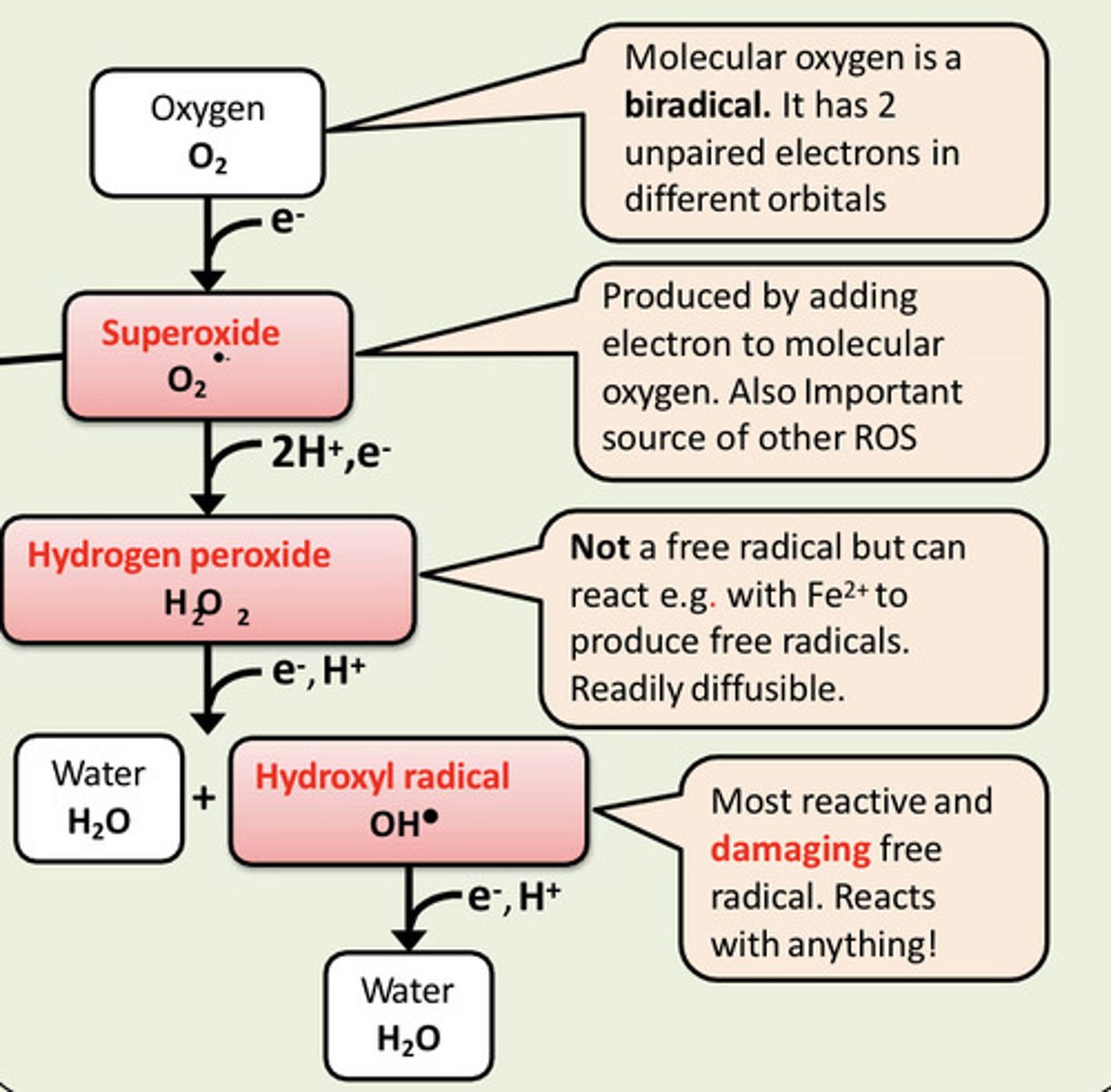
Hydrogen peroxide can react with ___ ions to produce free radicals
Hydrogen peroxide can react with Fe2+ ions to produce free radicals
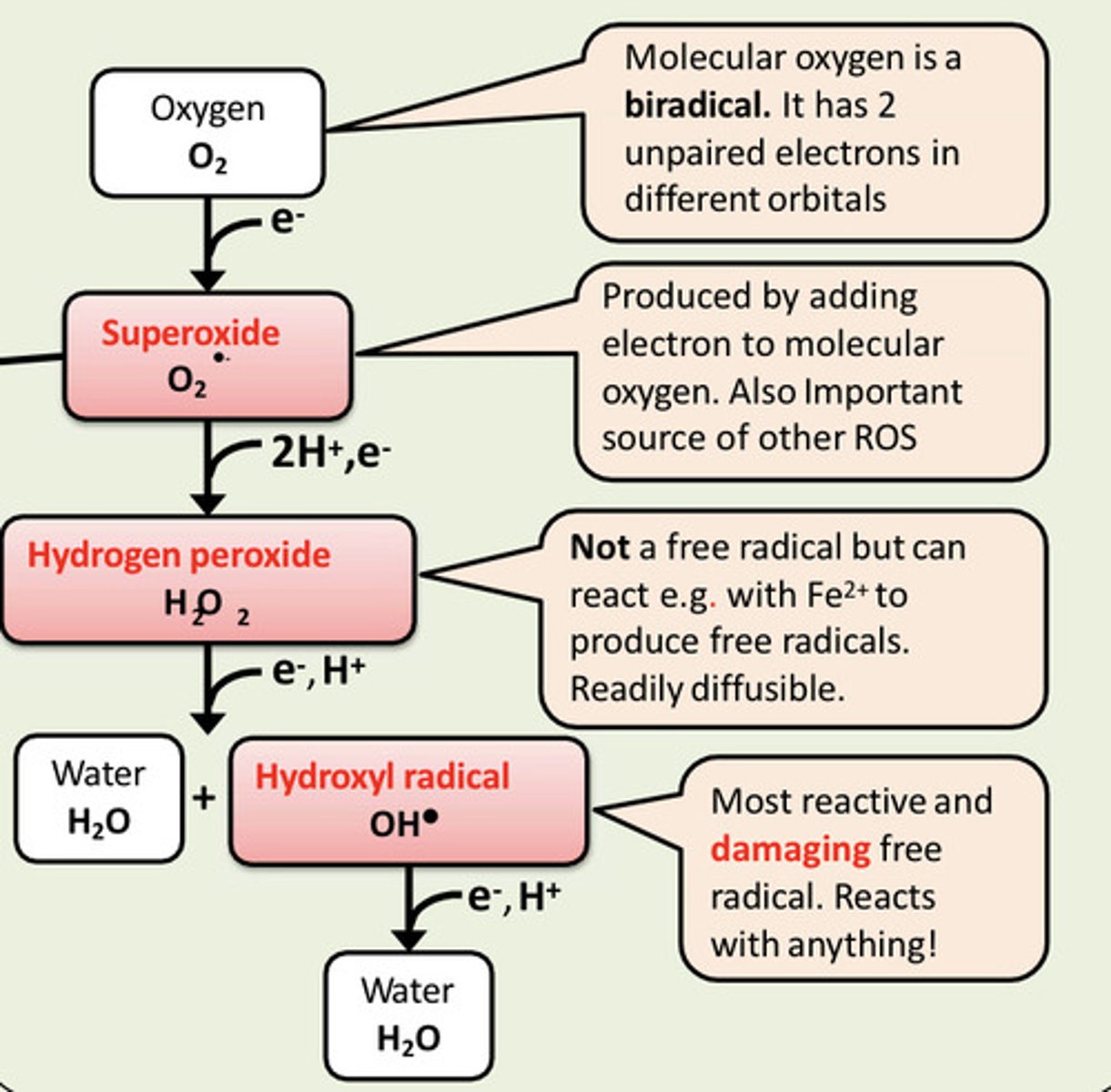
A free radical is an atom, molecule or ion that contains one or more ___ electrons, capable of independent existence
A free radical is an atom, molecule or ion that contains one or more unpaired electrons, capable of independent existence
What are some examples of endogenous sources of biological oxidants?
Electron transport chain, nitric oxide synthases, NADPH oxidases

What are some examples of exogenous sources of biological oxidants?
Radiation (cosmic rays, x-rays, UV light), pollutants, drugs (primaquine, paracetamol), toxins (paraquat herbicide, polonium-210)

What are the two main types of ROS damage to DNA?
1) ROS reacts with a base = modified base can lead to mis-pairing & mutation
2) ROS reacts with a sugar = ribose/deoxyribose causing strand break & mutation

When ROS reacts with DNA and causes DNA damage - failure of repair of this damage can lead to mutations which cause ___
When ROS reacts with DNA and causes DNA damage - failure of repair of this damage can lead to mutations which cause cancer
Reaction of unsaturated lipids with ROS is termed ___ ___.
Reaction of unsaturated lipids with ROS is termed lipid peroxidation.
What does lipid peroxides do to cell membranes?
Damage
ROS damage to lipids is thought to occur in the early stages of ___ disease
ROS damage to lipids is thought to occur in the early stages of cardiovascular disease
___ is produced by the body to protect against oxidative damage.
Glutathione is produced to synthesised by the body to protect against oxidative damage.
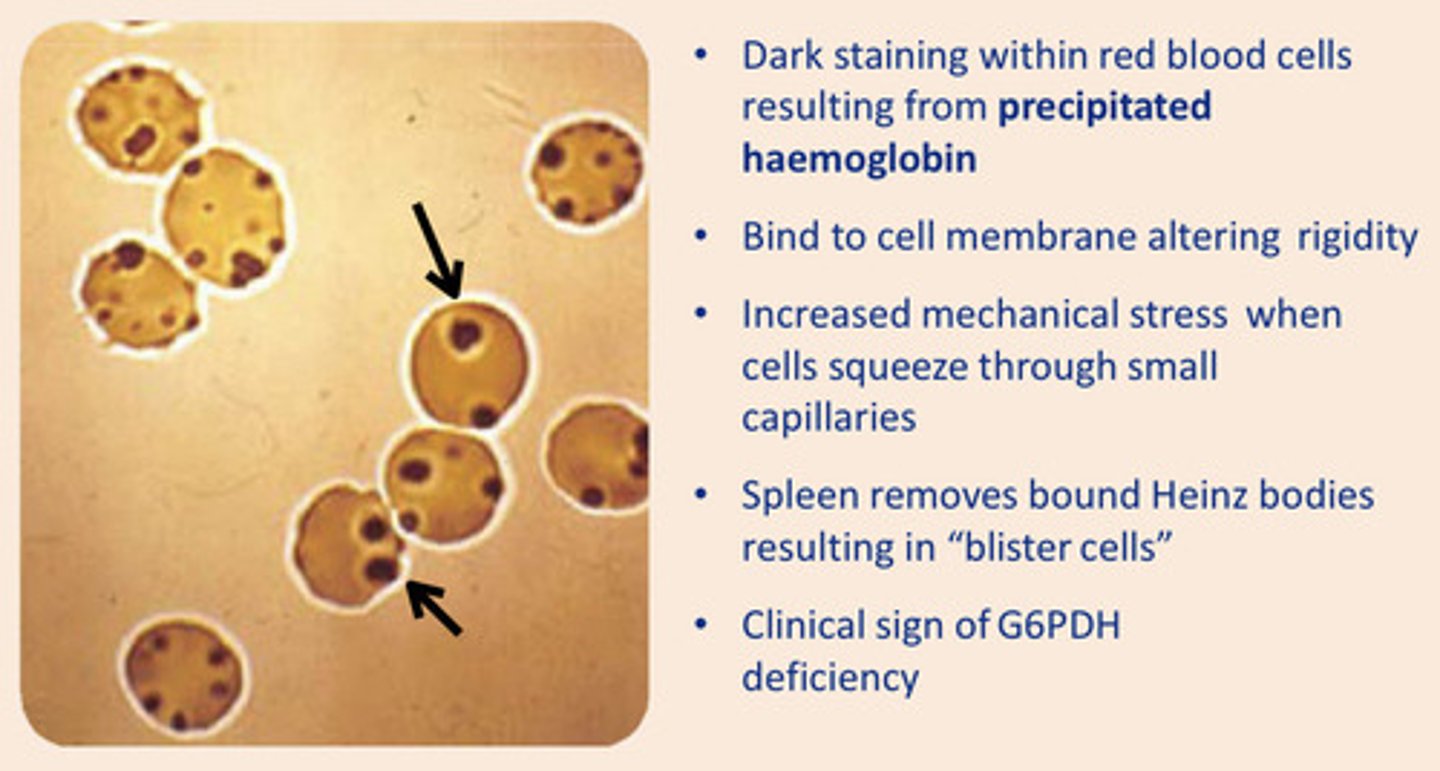
What are Heinz bodies a clinical sign of?
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PDH) deficiency
Describe the production of superoxide radicals in the mitochondria
The superoxide radical is produced by adding an electron to molecular oxygen
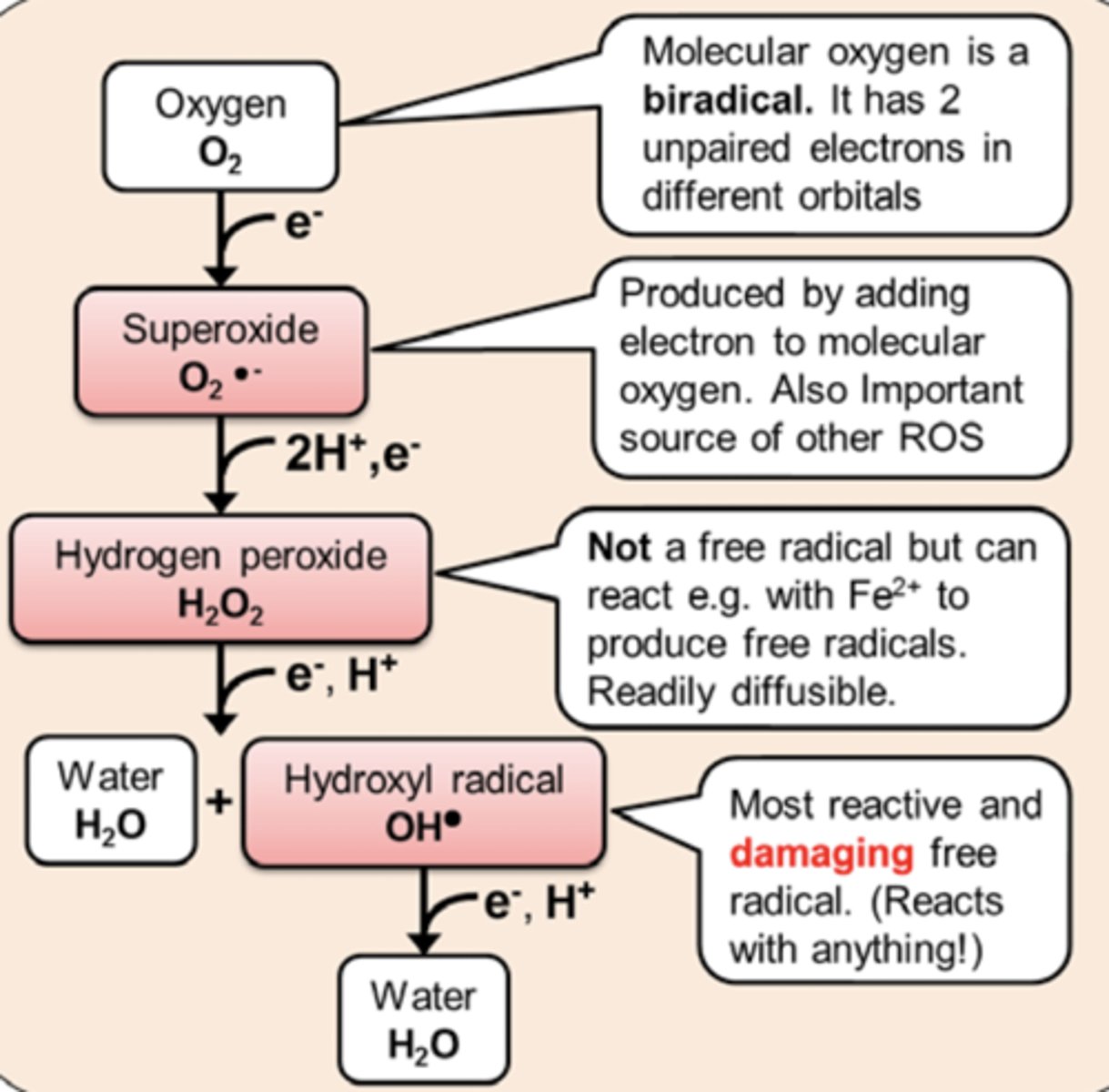
Is hydrogen peroxide a free radical? How is it produced? Why is it bad to accumulate hydrogen peroxide?
Hydrogen peroxide is NOT a free radical but it can react with iron ions (Fe2+) to produce free radicals...
H2O2 + Fe2+ --> Hydroxyl free radical
What is the most damaging free radical?
Hydroxyl free radical (OH*)
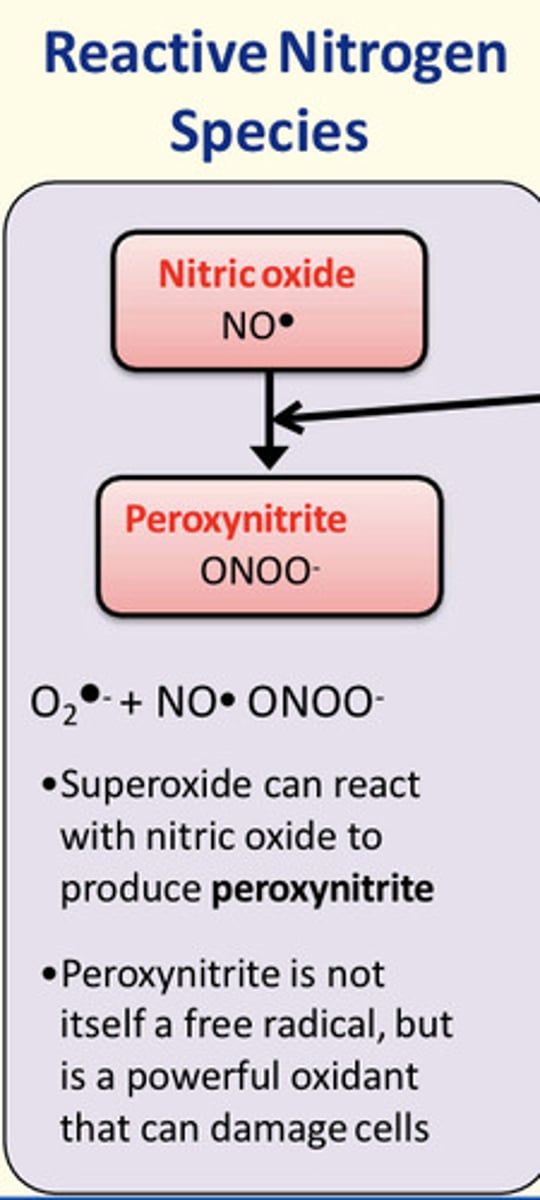
How is nitrogen oxygen species (NOS) produced?
Superoxide radicals can react with other free radicals such as nitric oxide (NO*) to produce peroxynitrite (ONOO-)
Peroxynitrite is not a free radical but it is a powerful oxidant that can damage cells
Oxidative stress
a condition in which the production of oxidants (ROS and RNS) and free radicals exceeds the body's ability to handle them and prevent damage
Oxidative stress can damage molecules such as...
Proteins, lipids, DNA
Cellular damage by ROS and RNS is indicated in multiple diseases including...
- CVD
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Crohn's disease
- COPD
- Ischaemia
- Cancer
- Pancreatitis
- Parkinson's disease (PD)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
What are some sources of endogenous biological oxidants?
Electron transport chain, nitric oxide synthases, NADPH oxidases
What are some sources of exogenous biological oxidants?
- Radiation (UV light, x-rays)
- Pollutants
- Drugs e.g., Primaquine (anti-malarial) and Paracetamol
- Toxins e.g., Paraquat (herbicide) and Polonium-210
What are the two forms of DNA damage by ROS and RNS?
1) Modified base (ROS + base) = leading to mispairing and mutation
2) Modified pentose sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) = leading to strand breakage and mutation as result of repair
How does protein damage occur via ROS and RNS?
- Side chains of amino acids or protein backbone can react with ROS
- Leads to modification of protein structure
- Loss of protein function
What is one of the most significant types of protein damage by ROS/RNS?
When ROS takes electron from a cysteine residue leading to formation of inappropriate DISULPHIDE bond
This leads to misfolding, cross-linking & disruption of protein function
An example of ROS damage to protein leading to inappropriate cross-linking and a clinical sign of G6PDH
Heinz bodies - precipitated haemoglobin within RBC altering their rigidity
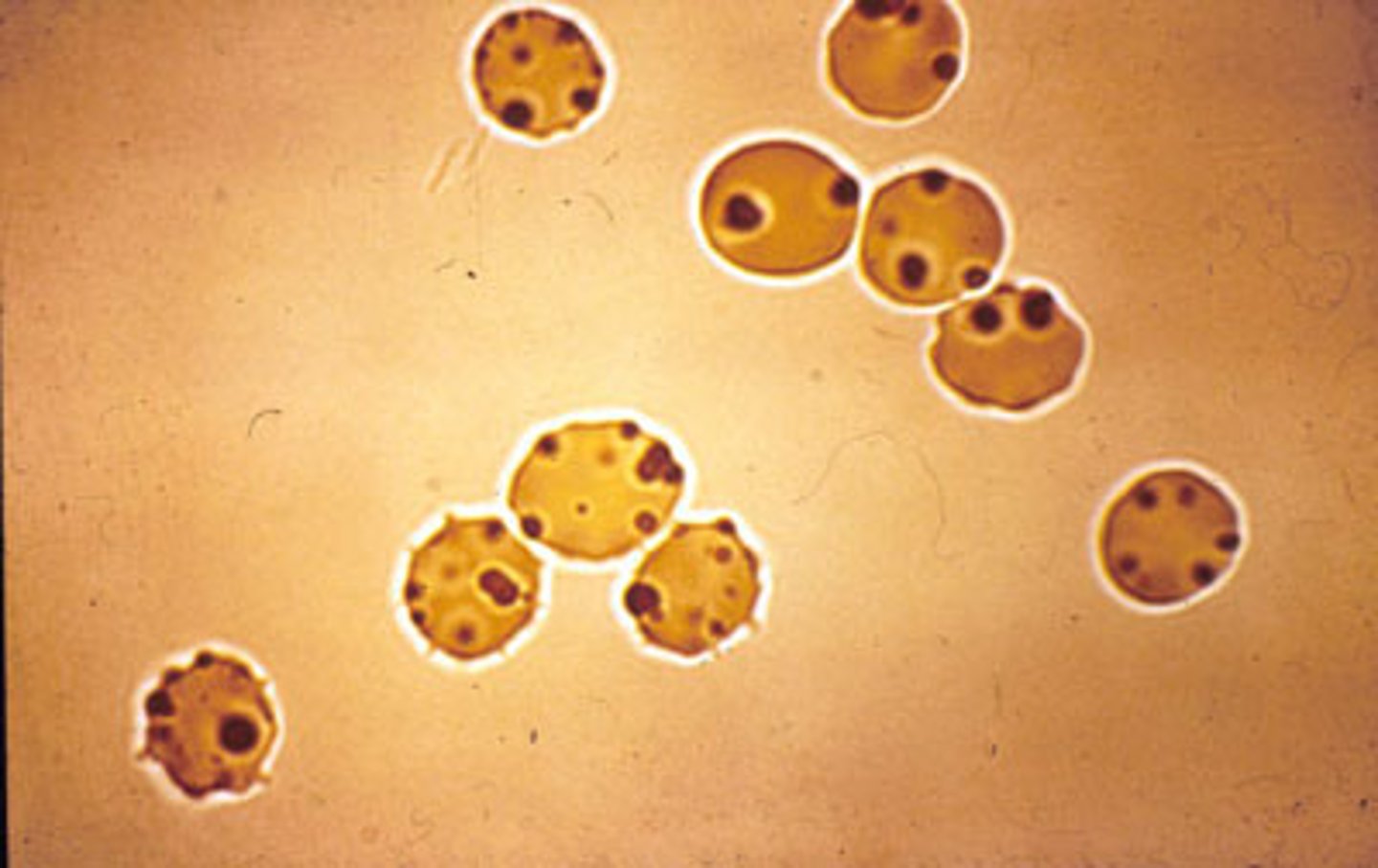
How does lipid damage occur by ROS and RNS?
- ROS reacts with lipids in lipid peroxidation
- Lipid peroxides (lipid peroxyl radicals) formed
- Lipid peroxyl radicals react with nearby fatty acids & hydrophobic environment of bilayer disrupting its integrity
- Damage to cell membrane integrity
What is the name of the process which describes oxidative damage by ROS in lipids specifically?
Lipid peroxidation
What process of oxidative damage is significant in the aetiology of atherosclerosis (early CVD)?
Lipid peroxidation is significant in the aetiology of atherosclerosis
Outline the two antioxidant defense systems
1) Enzymatic defense systems = superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (cGPx)
2) Non-enzymatic defense system = glutathione (GSH)
Enzymatic defense system
Superoxide radicals are converted to hydrogen peroxide by superoxide dismutase enzyme
O* -> H2O2 [superoxide dismutase, SOD]
Hydrogen peroxide is converted to water and molecular oxygen by catalase enzyme
H2O2 -> H2O + O2 [catalase, CAT]
![<p>Superoxide radicals are converted to hydrogen peroxide by superoxide dismutase enzyme</p><p>O* -> H2O2 [superoxide dismutase, SOD]</p><p>Hydrogen peroxide is converted to water and molecular oxygen by catalase enzyme</p><p>H2O2 -> H2O + O2 [catalase, CAT]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7649e259-97e2-4a1b-91b8-4dbfb03a6401.png)
Glutathione (GSH)
Helps to prevent damage by reactive oxygen species generated in the course of metabolism
Which vitamins are the 'free radical scavengers'?
Vitamins A, C and E (ACE)
What trace elements are considered to be 'free radical scavengers'?
Melatonin, Selenium, Carotenoids, Polyphenols, Flavonoids
Free radical scavengers have a high ___ ___ absorbance capacity (ORAC)
Free radical scavengers have a high oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC)
Free radical scavengers like vitamins A, C and E are thought to reduce the risk of...
Chronic degenerative disorders
How do free radical scavengers protect the cell?
By donating a H+ atom and its electron to free radicals in a non-enzymatic reaction
Respiratory burst
Some phagocytic immune cells (neutrophils & monocytes) release ROS & RNS when stimulated. This is part of the antimicrobial defense system.
Which phagocytic immune cells carry out respiratory burst?
Neutrophils and monocytes
What membrane-bound enzyme is involved in respiratory burst process?
NADPH oxidase
Where is NADPH oxidase found
In the membrane of phagosomes of phagocytic immune cells (neutrophils & monocytes)
What disorder is caused by a genetic defect in the NADPH oxidase enzyme?
Chronic granulomatous disease
What occurs in chronic granulomatous disease?
Enhanced susceptibility to bacterial infections...
Atypical infections, pneumonia, abscesses, impetigo, cellulitis
Give an example of a disorder which arises from oxidative damage to proteins in the cell?
Aggregation of cross-linked haemoglobin producing Heinz bodies - this can lead to haemolysis and anaemia
Vitamin E
Lipid-soluble antioxidant
Protection against lipid peroxidation
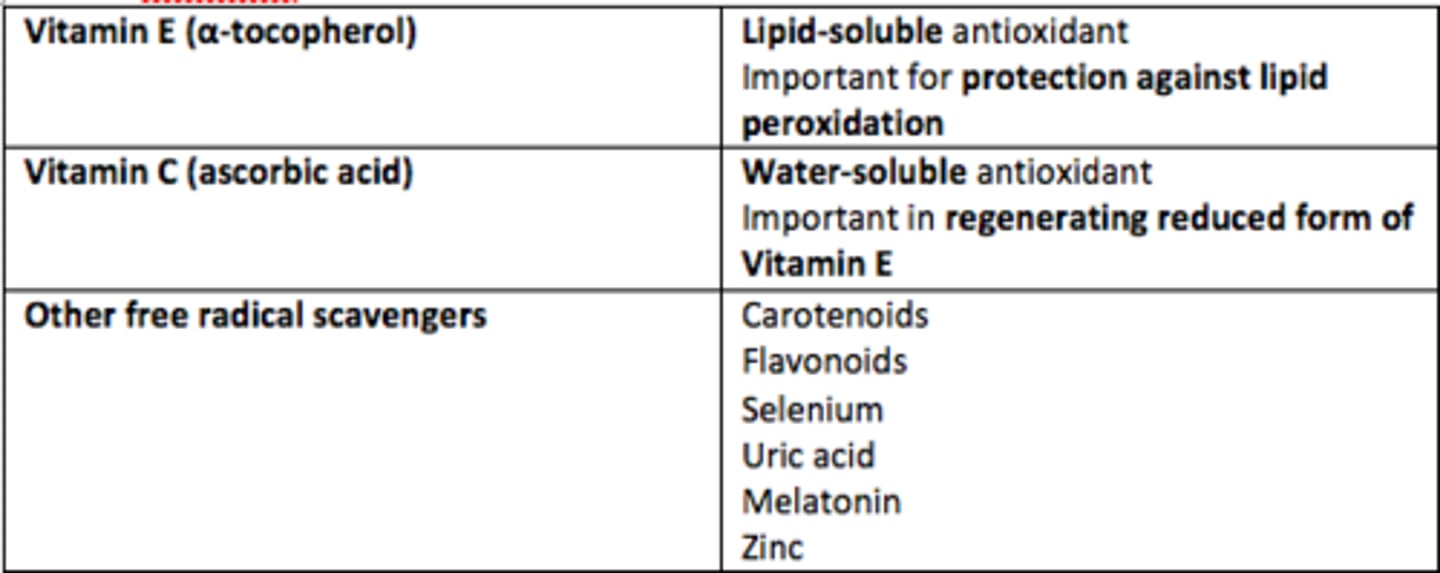
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
Water-soluble antioxidant
Important role in regenerating reduced form of Vitamin E
How is the Electron Transport Chain considered to be an endogenous source of ROS?
NADH and FADH2 donate electrons which pass through transport chain onto oxygen to form H2O.
Occasionally these electrons can escape the chain and react with dissolved oxygen to form superoxide radicals.
Superoxide radicals give rise to other ROS.
Free radical
Atom, molecule or ion that contains one or more unpaired electrons, capable of independent "free" existence
A ___ radical is any atom, molecule or ion that contains one or more unpaired ___. They are very reactive and they able to acquire ___ from other molecules causing cellular ___.
A free radical is any atom, molecule or ion that contains one or more unpaired electrons. They are very reactive and they able to acquire electrons from other molecules causing cellular damage.
Oxidative stress refers to a cellular state at which cells do NOT have a sufficient antioxidant power to cope with ROS
True or false?
True
What is ROS
Reactive oxygen species
Name the inclusions of the red blood cells which form as a result of oxidative damage to haemoglobin
Heinz bodies
What are the three key antioxidant vitamins?
A,C,E
Which one of the following is ROS?
A) All of the above except hydrogen
B) Hydrogen
C) Hydroxyl radical
D) Hydrogen peroxide
E) All of the above
F) Superoxide radical
A) All of the above except hydrogen
Which one of these cellular components is MOST affected by ROS?
A) Nucleus
B) Golgi
C) Endoplasmic reticulum
D) Mitochondria
D) Mitochondria
Which key enzyme catalyses the conversion of superoxide to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen
Superoxide dismutase
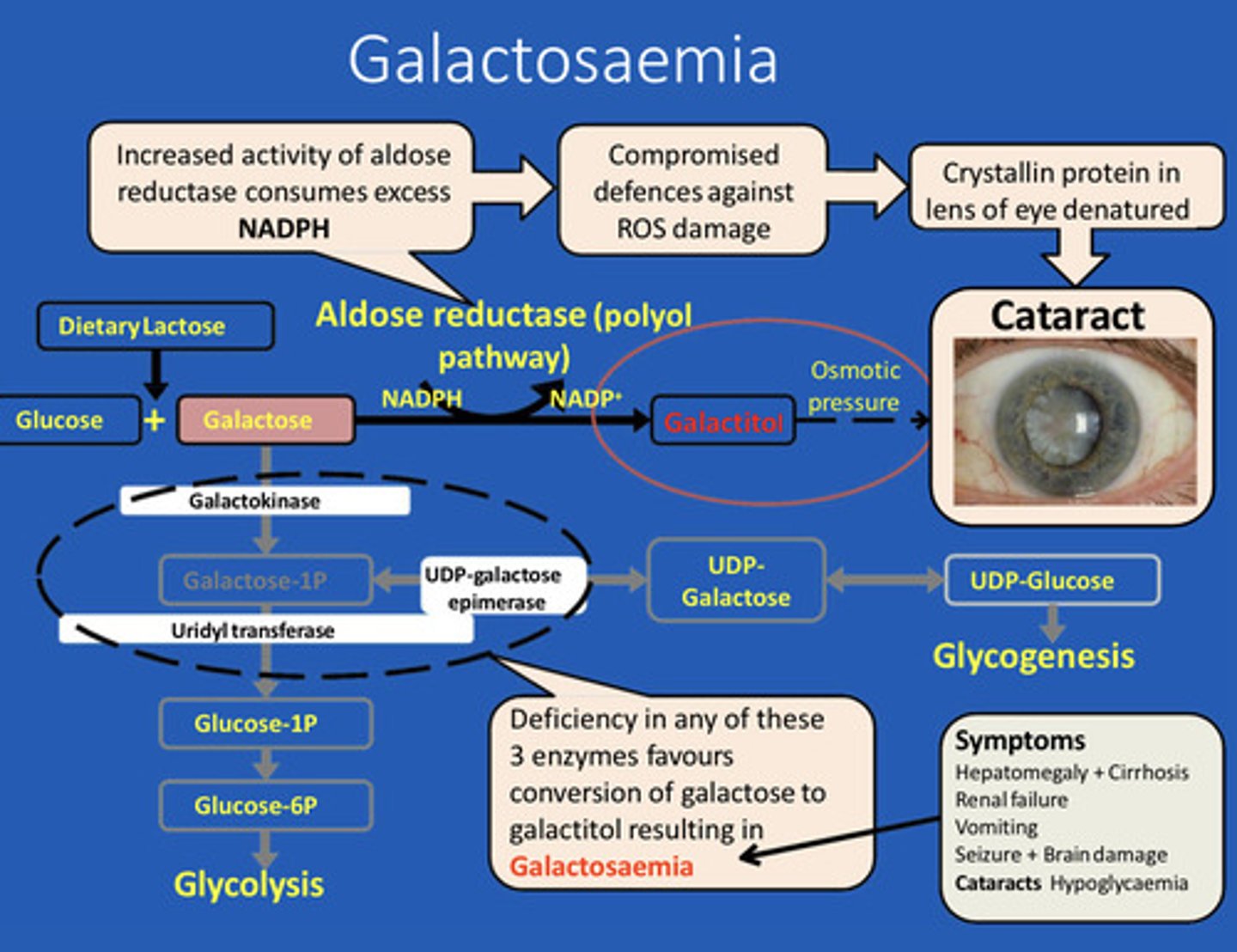
Oxidative stress is thought to be involved in many disease. Name one of them which is associated with deficiency of an enzyme. Involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates
Galactosaemia
People with G6PDH deficiency (reduced G6PDH activity) in the pentose phosphate pathway produce ___ GSH
Lower GSH
- This means less protection against oxidative damage from oxidative stress