Genetics - FINAL - Unit 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe the three ways that DNA structure fulfills the requirements of a hereditary molecule
Replication
Information content
Ability to change
List the atoms that make up DNA
P, O, C, H, N
Draw the detailed chemical structure of a generic deoxyribonucleotide (base not specified)
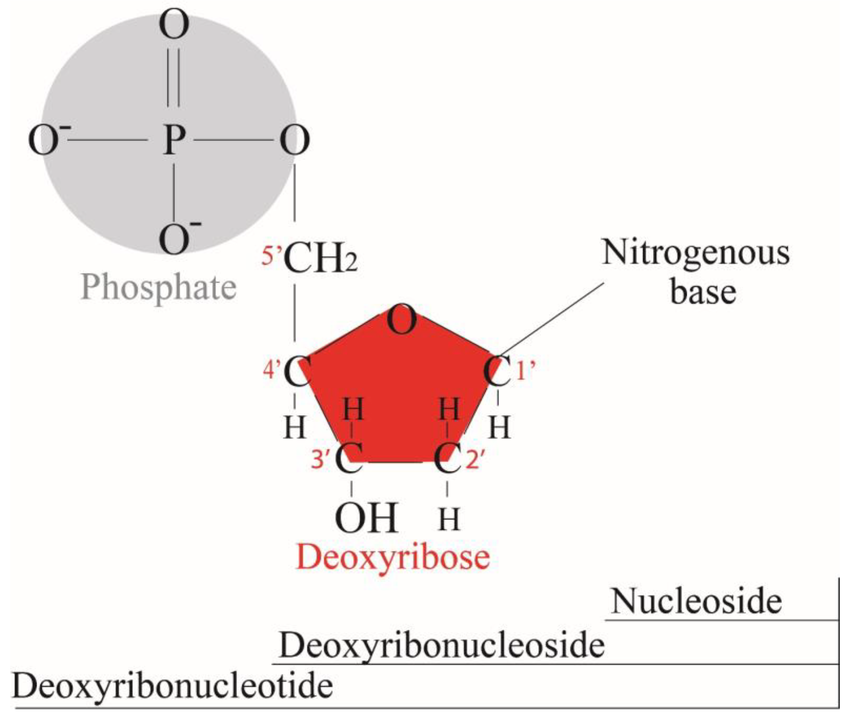
Describe the double-stranded nature of DNA, including base-pairing
2 anti-parallel strands
base pairing rules A w/ T, G w/ C
List the four DNA deoxyribonucleotides, categorize them as a purine or pyrimidine
Purines
Adenine & Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine & Thymine
Where does the base attach to the sugar?
At its 1’ carbon atom
Draw a short stretch of a DNA molecule, labeling hydrogen and covalent bonds, 5' and 3' ends, and the three components of each deoxyribonucleotide

Explain how the structure of DNA allows it to be faithfully replicated
One strand acts as a template strand
Describe the key elements of DNA & RNA function
Complementary base pairing
Recognition of specific sequences by proteins
Explain the relationship between DNA and chromosomes
DNA is the genetic material
chromosomes are tightly packed bundles of DNA that help it fit in the cell.
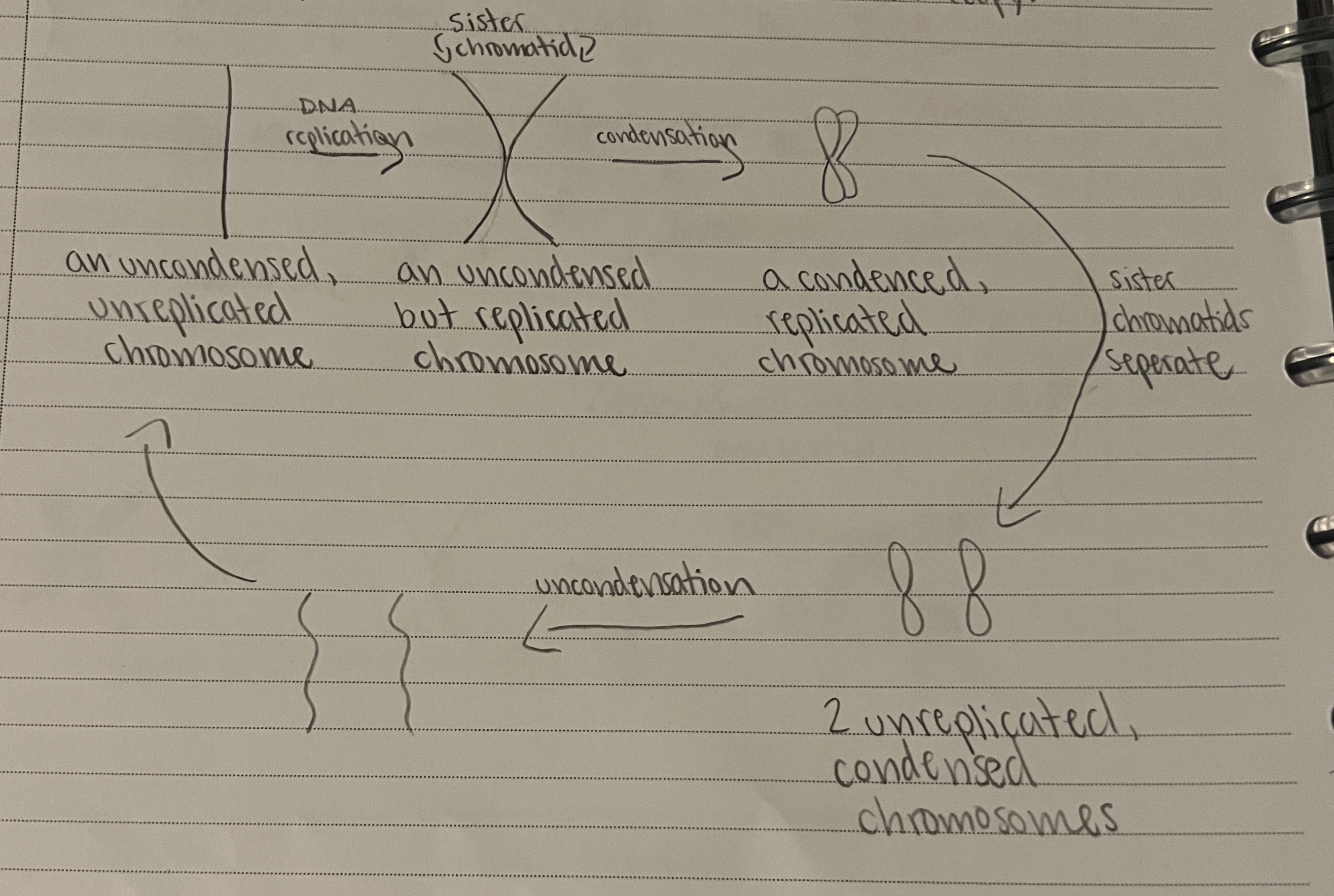
Distinguish between replicated and non-replicated chromosomes
Un-replicated Chromosome looks like I
Replicated chromosomes look like X
Describe the visible morphology and landmarks of a nuclear chromosome
two sister chromatids
a centromere that joins sister chromatids
telomeres at each end
Identify and draw chromosomes in various states (replicated/non-replicated, condensed/uncondensed)
Describe the relationship between homologous and non-homologous chromosomes
Homologous:
Same genes, same shape
Non-homologous:
Different genes, sometimes different shape
How does an individual acquire each member of a homologous pair or chromosomes?
Each member of the pair is obtained from mom and dad
Explain the concept of ploidy and different ploidy levels
Haploid: 1 set of chromosomes
Diploid: 2 sets of chromosomes
Polyploid: > 2 sets of chromosomes
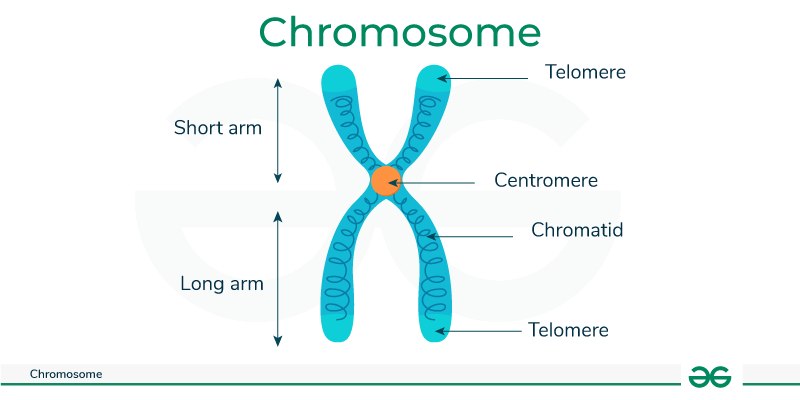
Chromosomes
Packaged DNA

Centromere
Constricted region of a condensed chromosome

Kinetochore
Proteins that can bind the centromere sequence
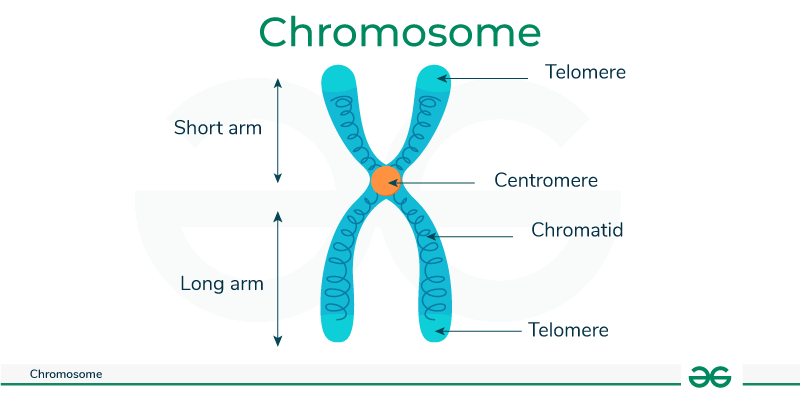
Telomere
Unique DNA sequence at the ends of chromosomes, which proteins bind to
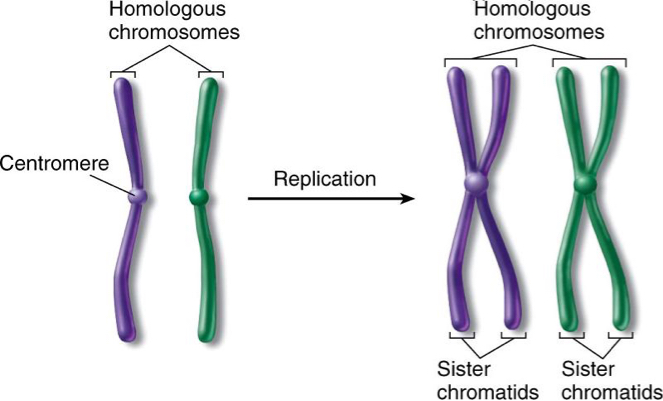
Homologous
Same genes, same shape
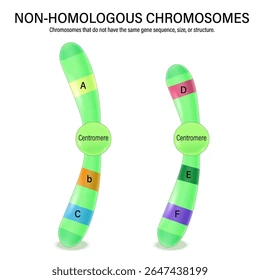
Non-homologous
Different genes, maybe different shape
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes
Sex chromosomes
X and Y in humans, chromosomes that look different between the sexes
Locus
Location on a chromsome
Allele
A version of a stretch of DNA that is mostly the same (DNA sequence)
Genotype
Combination of alleles
Homozygous
2 of the same (Ex: A/A)
Heterozygous
2 different (Ex: A/a)
Ploidy
Chromosome number
Haploid
1 set of chromosomes
Diploid
More than 1 set of chromosomes
Polyploid
More than 2 sets of chromosomes
Explain the origin of sister chromatids
Sister chromatids are created when a chromosome is copied
What created chromatids?
DNA replication