Urinalysis Module 3
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 3 Microexamination
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What materials are usually present in urine?
WBC, RBC, Epithelial cells, casts, crystals, Bacteria, yeast, parasites, spermatozoa, mucus, artifacts
What specific patient would most likely be tested?
what is most effective method to collect specimen?
pregnant women, diabetic, renal disease pt, geriatric, pediatric.
midstream clean-catch specimen
What can be suspected in an abnormal result?
color/clarity, blood, leukocytes, nitrite, glucose, protein
Microscopic analysis of urine include
specimen preparation, volume of specimen, centrifugation, Identification of formed elements
Macroscopic screening of urine specimen is used to:
Increase cost-effectiveness of urinalysis
What is the normal volume of urine in specimen?
10-15 ml
what can determine a false negative microscopic result?
Braking centrifuge, failing to mix specimen, diluting alkaline urine.
How do we adjust the microscope to examine urine sediment?
scan in reduced light
10 fields on low power (10x)
10 fields on high power (40x)
how can we identify casts on a cover slip? what provides a point of reference on a microscope?
casts are located on the perimeter/edges on a cover slip.
epithelial cells should be focused on first.
what organisms are detected on a low power field?
casts and squamous epithelial cells
what organisms can be detected on a high power field?
WBC, RBC, crystals, bacteria, yeast, parasites, RTE, Transitional epithelial cells, oval fat bodies
The sternheimer-Malbin stain is added to urine to:
increase visibility, change refractive index, delineate constituent structures
Which lipids are stained by Sudan III?
Neutral fats and Triglycerides
Which lipid is capable of polarizing?
Cholesterol
Red blood cells examination
normal range 0-3 hpf
can be seen using high power
average number are seen in 10 hpfs
Hypersthenuric urine shows what type of RBC's?
crenated RBC's due to loss of water
Hyposthenuric urine shows what kind of RBC's?
RBC's swell and lyse, leaving ghost cells
what cause Dysmorphic RBC's (acanthocyte) to show in urine
glomerular bleeding and strenuous excercise
RBCs in urine indicates
glomerular membrane damage and vascular injury to genitourinary tract
What can we indicate when a patient has severe back pain and increased RBC’s?
Renal Calculi
White blood cells examination
Normal value is 0-8 hpfs
larger than RBC's
contains granules and multi lobed nuclei
what is Pyuria?
what can be detected ?
increase in WBC's in urine
Bacteria is detected
Leukocytes that stain pale blue with Sternheimer-Malbin stain and have brownian movement are called:
glitter cells
due to absorption of water and swelling
Eosinophils are WBC's that require what kind of stain?
Hansel stain
mononuclear leukocytes are mistaken for:
Renal Tubular cells
WBC's in urine indicates what?
infections
usually found in females
report if pyuria is found
squamous epithelial cells
largest cells in urine
good reference in microscope
identify in low power field
non-pathological
what is a clinically significant Squamous epithelial cell?
Clue cell
Transitional epithelial cells
smaller than squamous cells
seen in high power field
originate from the bladder
increased Transitional cells are indicative of:
catheterization
Renal Tubular epithelial cells
smaller than transitional cells
proximal tubule- rectangular
distal tubule- small, round, oval
collecting duct- cuboid shape
What are renal fragments? and what does it mean if RTE are present?
RTE cells from collecting duct that appear in groups of 3.
indicates tubular injury and it is most clinically significant
affects the renal function.
what kind of pathologic substances can RTE cause?
bilirubin- cells appear deep yellow
Viral HEP
Liver disease
What are Oval Fat Bodies? and how can we confirm? Under what type of microscope?
lipid containing RTE cells
Staining with fat stain under Polarized microscopy
What can oval fat bodies indicate? what do bubble cells indicate?
glomerular damage
bubble cells= acute tubular necrosis
Bacteria in urine
Not normally present in urine
cocci/bacilli may be seen
associated with WBC's in UTI
specimens positive for increased bacteria should?
followed up with a culture
finding Yeast in urine is commonly associated with:
Diabetes mellitus
what is the most common parasite found in urine? where is it found?
Trichomonas vaginalis
STI that comes from vaginal/urethral contamination
what is the major constituent of Mucus?
uromodulin (glycoprotein from RTE)
has clinical significance
a person submitting urine after strenuous exercise should have___ in their urine:
hyaline casts, granular casts, RBC casts
What is the only formed element found in urine?
How can it be detected and identified in the microscope?
Casts
Detected in low power
Identified in high power
The majority of casts are formed in:
Distal Convoluted tubule
Cylindruria
presence of casts in urine
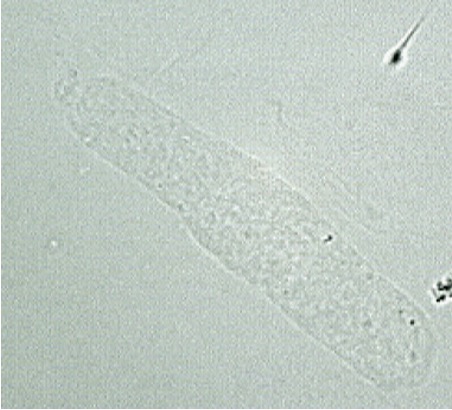
Hyaline casts examination
Most frequently seen
Normal range: 0-2 per lpf
an increase in hyaline casts indicate what kind of diseases?
Acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease, congestive heart failure
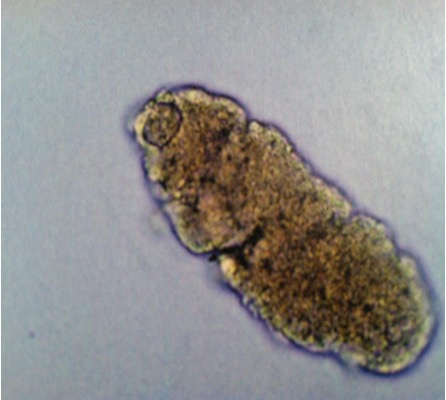
What do RBC casts contain and look like?
what does it indicate?
containing intact or deteriorated RBC’s.
Red-orange color; granular dirty-brown casts
indicates bleeding in nephron and glomerular damage. & proteinuria
What do WBC casts indicate?
indicates pyelonephritis
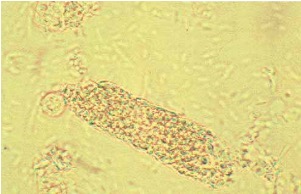
What do bacteria casts contain?
what does it indicate?
contain bacilli, bound to protein matrix, may be mixed with WBC’s
indicates pyelonephritis
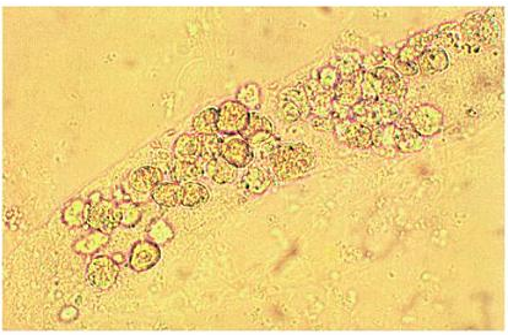
what do epithelial cells contain?
what does it indicate? what are they seen with?
contains RTE cells
indicated tubular destruction and seen with WBC casts in pyelonephritis
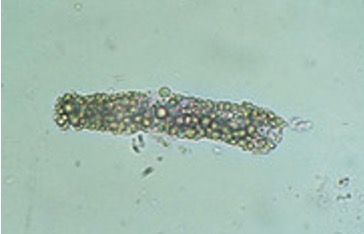
what are fatty casts seen with?
what does it indicate?
how can we confirm?
seen with oval fat bodies and free fat droplets
indicates Nephrotic syndrome
confirm with fat stain or polarized/phase microscope
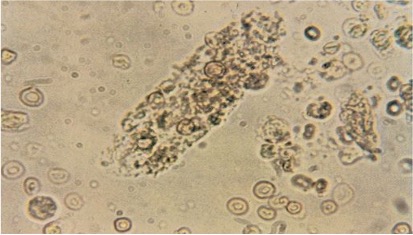
what are mixed cell casts
contain RBC& WBC=glomerulonephritis
WBC and RTE/WBC and bacteria= pyelonephritis
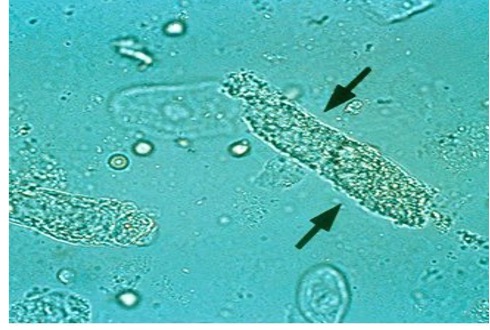
what are granular casts?
What do non pathogenic granular casts contain?
coarsely/fined granular
Cellular lysosomes
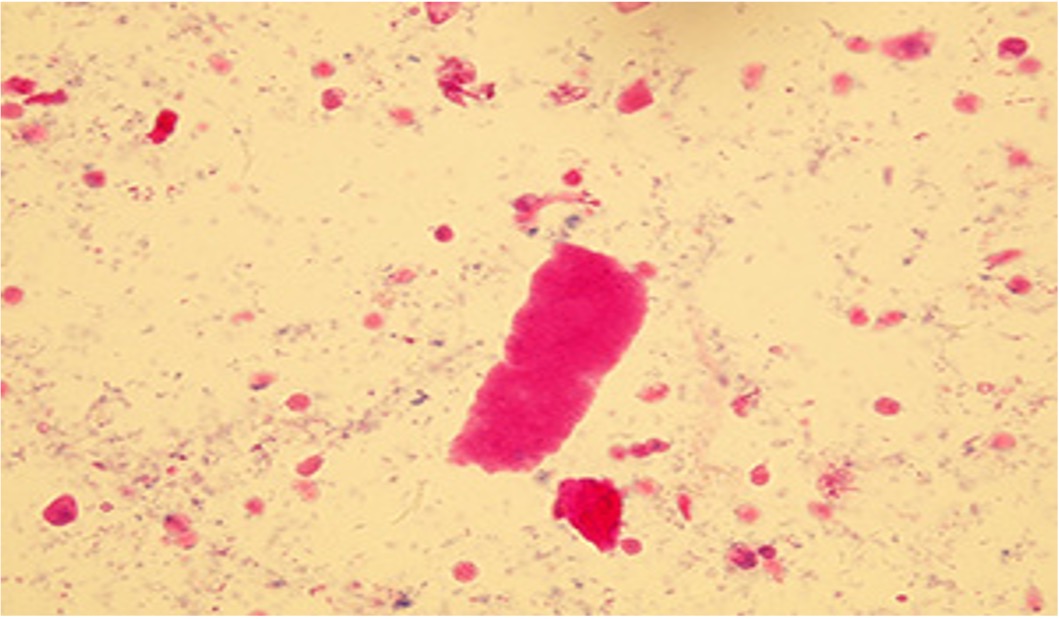
what do waxy casts represent?
how are they identified
represents extreme urine stasis, brittle consistency, and require staining to be visualized.
appear as fragmented with jagged ends and notched sides. Pink
Broad casts are also known as what?
what does it indicate?
are known as renal failure casts
indicates destruction of tubular walls
casts and fibers can be differentiated by using what kind of light?
polarized light
What 3 things enhance cast formation?
Urine stasis, pH, increased Sodium and Calcium
What affects solubility of crystal formation?
what is key to crystal identification?
where are all abnormal crystals found?
temperature, pH, solute concentration
pH is key to identification
abnormal crystals are found in acidic urine
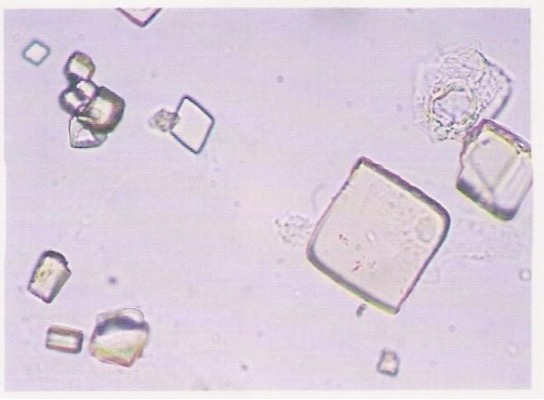

Amorphous Urates
pink sediment
acidic
Uric acid
yellow-brown to colorless
acidic
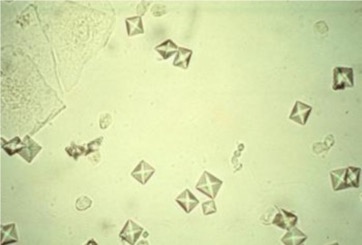
Calcium oxalate Dihydrate
envelope form
acidic
Calcium Oxalate monohydrate
ovoid shape
acidic
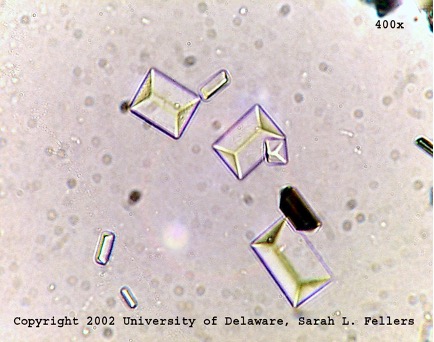
Triple phosphate
coffin lid shaped
alkaline

Calcium phosphate
rectangular thin prisms
alkaline
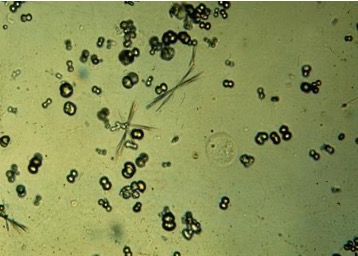
Calcium carbonate
spherical/ dumb-bell shaped
alkaline
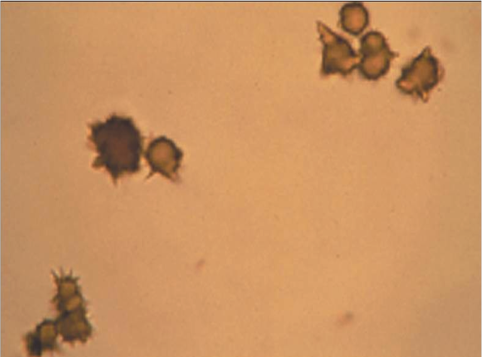
Ammonium biurate
thorny apple shaped in old specimens
alkaline
Amorphous phosphate
white precipitate
alkaline
Abnormal crystals are found in what type of urine?
found in acidic urine; rarely in neutral pH
what crystals are able to routinely polarize?
Uric acid, Cholesterol, Radiographic dye
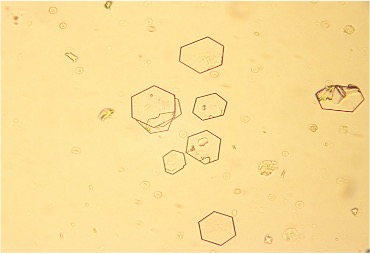
Abnormal crystals: Cystine
hexagonal plates that are thin or thick

Abnormal crystals: Cholesterol
rectangular plates with notch in one or more corners
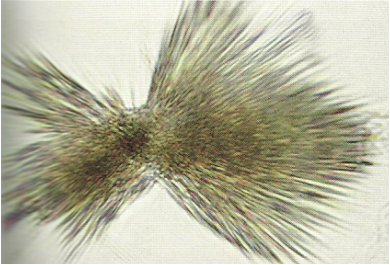
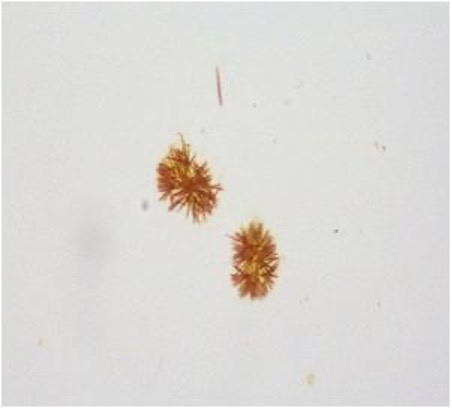
Abnormal crystals: Tyrosine
needles arranged in clumps
severe liver disorders
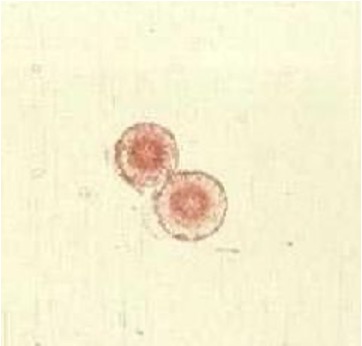
Abnormal crystals: Leucine
concentric circles, radial striations
Abnormal crystals: Bilirubin
bright yellow clumps